Showing 801 items
matching victoria architecture
-
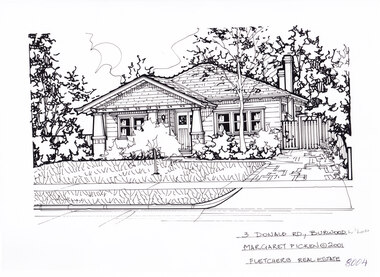
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Artwork, other - Ink Line Drawing, 10 Alfred St., Burwood, 1999
A property illustration by Margret Picken Commissioned by the real estate agency Woodards, Camberwell for the purpose of advertising 10 Alfred St., Burwood for sale in 1999. Made by using Rotring ‘Rapidigraph’ drafting pens with Rotring ink on Rapidigraph polyester drafting film, double matte. The suburb lines are believed to have been redrawn, making this property no longer in Burwood, but located in Glen iris. This property is listed as having sold for in 1999 for $380,000 Trained as a cartographic draftsman within the mining industry, Margaret Picken is an artist who worked producing property illustrations for real estate agencies in eastern suburbs of Victoria from 1983-2005. Retiring from the industry as technological changes favoured coloured photography over illustrations, and commissioning companies over sole contractors.This artwork is of Historical Significance as a record of local domestic architecture.A Black ink line drawing on drafters film by Maragret Picken, of 10 Alfred St., Burwood. Depicted is a one-story brick house situated back from a front lawn with a large tree, and a driveway on the right, leading to a connected carport. There to two hole punches just below the upper edge, and a approximately 1cmx1cm tape reside mark left of centre near the bottom edge 10 Alfred St., Burwood Maragret Picken - 99 Woodards - c'wellwhitehorse historical society, schwerkolt cottage, housing, architecture, margaret picken, burwood, glen iris, house, garden -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photgraph, Door at Carmel Welsh Church, Sebastopol, c2017
Carmel Welsh Church is located at 365 Albert Street, Sebastopol and is the only identified Welsh Presbyterian church surviving in Victoria,. It was built in 1865-6 to the design of Henry Richards Caselli, and of distinctive architectural character combining round arched windows of almost a Renaissance character, mediaevalising buttresses, and extremely chunky gable eaves of a domestic character, including square finials and raking brackets. It was established in 1861, the members and adherents were predominantly Welsh, the Welsh language was spoken freely and there were regular services in Welsh.Digital photograph of the door of the bluestone Welsh church, Sebastopol, Ballarat.carmel welsh church, sebastopol, bluestone, church, henry richards caselli, welsh -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesDigital photograph, Ballarat Railway Station
Ballarat Railway Station opened on 11 April 1862. Most of the 19th century architectural features of the railway station are intact. Its signal boxes and goods sheds are preserved, and it is one of only three stations in Victoria to have had a 19th-century train shed. This photo shows the facade of the south side of the station.Colour photograph of the Ballarat Railway Station.ballarat railway station -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photograph, Dorothy Wickham, Ballarat Railway Station Platform Stairs, c2017
Ballarat Railway Station opened on 11 April 1862. Most of the 19th century architectural features of the railway station are intact. Its signal boxes and goods sheds are preserved, and it is one of only three stations in Victoria to have had a 19th-century train shed. This photo shows the facade of the south side of the station.The stairway over the railway line at Ballarat Railway Station. ballarat railway station, stairs, railway platform -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Boroondara General Cemetery Springthorpe Memorial, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registerd by Heritage VictoriaFrom Heritage Victoria Statement of Significance Last updated on - December 15, 2005 What is significant? Boroondara Cemetery, established in 1858, is within an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. A brick cremation wall and a memorial rose garden were constructed near the entrance in the mid- twentieth century(c.1955-57) and a mausoleum completed in 2001.The maintenance shed/depot close to High Street was constructed in 1987. The original entrance was altered in 2000 and the original cast iron gates moved to the eastern entrance of the Mausoleum. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522) set at the entrance to the burial ground commemorates Annie Springthorpe, and was erected between 1897 and 1907 by her husband Dr John Springthorpe. It was the work of the sculptor Bertram Mackennal, architect Harold Desbrowe Annear, landscape designer and Director of the Melbourne Bortanic Gardens, W.R. Guilfoyle, with considerable input from Dr Springthorpe The memorial is in the form of a small temple in a primitive Doric style. It was designed by Harold Desbrowe Annear and includes Bertram Mackennal sculptures in Carrara marble. Twelve columns of deep green granite from Scotland support a Harcourt granite superstructure. The roof by Brooks Robinson is a coloured glass dome, which sits within the rectangular form and behind the pediments. The sculptural group raised on a dais, consists of the deceased woman lying on a sarcophagus with an attending angel and mourner. The figure of Grief crouches at the foot of the bier and an angel places a wreath over Annie's head, symbolising the triumph of immortal life over death. The body of the deceased was placed in a vault below. The bronze work is by Marriots of Melbourne. Professor Tucker of the University of Melbourne composed appropriate inscriptions in English and archaic Greek lettering.. The floor is a geometric mosaic and the glass dome roof is of Tiffany style lead lighting in hues of reds and pinks in a radiating pattern. The memorial originally stood in a landscape triangular garden of about one acre near the entrance to the cemetery. However, after Dr Springthorpe's death in 1933 it was found that transactions for the land had not been fully completed so most of it was regained by the cemetery. A sundial and seat remain. The building is almost completely intact. The only alteration has been the removal of a glass canopy over the statuary and missing chains between posts. The Argus (26 March 1933) considered the memorial to be the most beautiful work of its kind in Australia. No comparable buildings are known. The Syme Memorial (1908) is a memorial to David Syme, political economist and publisher of the Melbourne Age newspaper. The Egyptian memorial designed by architect Arthur Peck is one of the most finely designed and executed pieces of monumental design in Melbourne. It has a temple like form with each column having a different capital detail. These support a cornice that curves both inwards and outwards. The tomb also has balustradings set between granite piers which create porch spaces leading to the entrance ways. Two variegated Port Jackson Figs are planted at either end. The Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036) was constructed in 1912-13 by Sir Leo Cussen in memory of his young son Hubert. Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933), judge and member of the Victorian Supreme Court in 1906. was buried here. The family memorial is one of the larger and more impressive memorials in the cemetery and is an interesting example of the 1930s Gothic Revival style architecture. It takes the form of a small chapel with carvings, diamond shaped roof tiles and decorated ridge embellishing the exterior. By the 1890s, the Boroondara Cemetery was a popular destination for visitors and locals admiring the beauty of the grounds and the splendid monuments. The edge of suburban settlement had reached the cemetery in the previous decade. Its Victorian garden design with sweeping curved drives, hill top views and high maintenance made it attractive. In its Victorian Garden Cemetery design, Boroondara was following an international trend. The picturesque Romanticism of the Pere la Chaise garden cemetery established in Paris in 1804 provided a prototype for great metropolitan cemeteries such as Kensal Green (1883) and Highgate (1839) in London and the Glasgow Necropolis (1831). Boroondara Cemetery was important in establishing this trend in Australia. The cemetery's beauty peaked with the progressive completion of the spectacular Springthorpe Memorial between 1899 and 1907. From about the turn of the century, the trustees encroached on the original design, having repeatedly failed in attempts to gain more land. The wide plantations around road boundaries, grassy verges around clusters of graves in each denomination, and most of the landscaped surround to the Springthorpe memorial are now gone. Some of the original road and path space were resumed for burial purposes. The post war period saw an increased use of the Cemetery by newer migrant groups. The mid- to late- twentieth century monuments were often placed on the grassed edges of the various sections and encroached on the roadways as the cemetery had reached the potential foreseen by its design. These were well tended in comparison with Victorian monuments which have generally been left to fall into a state of neglect. The Boroondara Cemetery features many plants, mostly conifers and shrubs of funerary symbolism, which line the boundaries, road and pathways, and frame the cemetery monuments or are planted on graves. The major plantings include an impressive row of Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa), interplanted with Sweet Pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum), and a few Pittosporum crassifolium, along the High Street and Parkhill Street, where the planting is dominated by Sweet Pittosporum. Planting within the cemetery includes rows and specimen trees of Bhutan Cypress and Italian Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens), including a row with alternate plantings of both species. The planting includes an unusual "squat" form of an Italian Cypress. More of these trees probably lined the cemetery roads and paths. Also dominating the cemetery landscape near the Rotunda is a stand of 3 Canary Island Pines (Pinus canariensis), a Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii) and a Weeping Elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii') Amongst the planting are the following notable conifers: a towering Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), a rare Golden Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea'), two large Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris), and the only known Queensland Kauri (Agathis robusta) in a cemetery in Victoria. The Cemetery records, including historical plans of the cemetery from 1859, are held by the administration and their retention enhances the historical significance of the Cemetery. How is it significant? Boroondara Cemetery is of aesthetic, architectural, scientific (botanical) and historical significance to the State of Victoria. Why is it significant? The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical and aesthetic significance as an outstanding example of a Victorian garden cemetery. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance as a record of Victorian life from the 1850s, and the early settlement of Kew. It is also significant for its ability to demonstrate, through the design and location of the cemetery, attitudes towards burial, health concerns and the importance placed on religion, at the time of its establishment. The Boroondara Cemetery is of architectural significance for the design of the gatehouse or sexton's lodge and cemetery office (built in stages from 1860 to 1899), the ornamental brick perimeter fence and elegant cemetery shelter to the design of prominent Melbourne architects, Charles Vickers (for the original 1860 cottage) and Albert Purchas, cemetery architect and secretary from 1864 to his death in 1907. The Boroondara Cemetery has considerable aesthetic significance which is principally derived from its tranquil, picturesque setting; its impressive memorials and monuments; its landmark features such as the prominent clocktower of the sexton's lodge and office, the mature exotic plantings, the decorative brick fence and the entrance gates; its defined views; and its curving paths. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522), the Syme Memorial and the Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036), all contained within the Boroondara Cemetery, are of aesthetic and architectural significance for their creative and artistic achievement. The Boroondara Cemetery is of scientific (botanical) significance for its collection of rare mature exotic plantings. The Golden Funeral Cypress, (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea') is the only known example in Victoria. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance for the graves, monuments and epitaphs of a number of individuals whose activities have played a major part in Australia's history. They include the Henty family, artists Louis Buvelot and Charles Nuttall, businessmen John Halfey and publisher David Syme, artist and diarist Georgiana McCrae, actress Nellie Stewart and architect and designer of the Boroondara and Melbourne General Cemeteries, Albert Purchas.Digital image of the Springthorpe Memorial in the Boroondara General Cemeterycemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial, springthorpe memorial -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage Servicesphotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Syme Memorial Boroondara General Cemetery, c2010, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registered by Heritage VictoriaFrom Heritage Victoria Statement of Significance Last updated on - December 15, 2005 (undated change to citation made since 2005) What is significant? Boroondara Cemetery, established in 1858, is within an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery. Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. ... ... The Syme Memorial (1908) is a memorial to David Syme, political economist and publisher of the Melbourne Age newspaper. The Egyptian memorial designed by architect Walter Richmond Butler is one of the most finely designed and executed pieces of monumental design in Melbourne. It has a temple like form with each column having a different capital detail. These support a cornice that curves both inwards and outwards. The tomb also has balustradings set between granite piers which create porch spaces leading to the entrance ways. Two variegated Port Jackson Figs are planted at either end. ... How is it significant? Boroondara Cemetery is of aesthetic, architectural, scientific (botanical) and historical significance to the State of Victoria. ... ...Digital image of the Syme memorial in Boroondara Cemetery, Kew. cemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, Cussen Memorial in the Boroondara General Cemetery, Kew, Victoria, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registerd by Heritage VictoriaFrom Heritage Victoria Statement of Significance Last updated on - December 15, 2005 What is significant? Boroondara Cemetery, established in 1858, is within an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. A brick cremation wall and a memorial rose garden were constructed near the entrance in the mid- twentieth century(c.1955-57) and a mausoleum completed in 2001.The maintenance shed/depot close to High Street was constructed in 1987. The original entrance was altered in 2000 and the original cast iron gates moved to the eastern entrance of the Mausoleum. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522) set at the entrance to the burial ground commemorates Annie Springthorpe, and was erected between 1897 and 1907 by her husband Dr John Springthorpe. It was the work of the sculptor Bertram Mackennal, architect Harold Desbrowe Annear, landscape designer and Director of the Melbourne Bortanic Gardens, W.R. Guilfoyle, with considerable input from Dr Springthorpe The memorial is in the form of a small temple in a primitive Doric style. It was designed by Harold Desbrowe Annear and includes Bertram Mackennal sculptures in Carrara marble. Twelve columns of deep green granite from Scotland support a Harcourt granite superstructure. The roof by Brooks Robinson is a coloured glass dome, which sits within the rectangular form and behind the pediments. The sculptural group raised on a dais, consists of the deceased woman lying on a sarcophagus with an attending angel and mourner. The figure of Grief crouches at the foot of the bier and an angel places a wreath over Annie's head, symbolising the triumph of immortal life over death. The body of the deceased was placed in a vault below. The bronze work is by Marriots of Melbourne. Professor Tucker of the University of Melbourne composed appropriate inscriptions in English and archaic Greek lettering.. The floor is a geometric mosaic and the glass dome roof is of Tiffany style lead lighting in hues of reds and pinks in a radiating pattern. The memorial originally stood in a landscape triangular garden of about one acre near the entrance to the cemetery. However, after Dr Springthorpe's death in 1933 it was found that transactions for the land had not been fully completed so most of it was regained by the cemetery. A sundial and seat remain. The building is almost completely intact. The only alteration has been the removal of a glass canopy over the statuary and missing chains between posts. The Argus (26 March 1933) considered the memorial to be the most beautiful work of its kind in Australia. No comparable buildings are known. The Syme Memorial (1908) is a memorial to David Syme, political economist and publisher of the Melbourne Age newspaper. The Egyptian memorial designed by architect Arthur Peck is one of the most finely designed and executed pieces of monumental design in Melbourne. It has a temple like form with each column having a different capital detail. These support a cornice that curves both inwards and outwards. The tomb also has balustradings set between granite piers which create porch spaces leading to the entrance ways. Two variegated Port Jackson Figs are planted at either end. The Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036) was constructed in 1912-13 by Sir Leo Cussen in memory of his young son Hubert. Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933), judge and member of the Victorian Supreme Court in 1906. was buried here. The family memorial is one of the larger and more impressive memorials in the cemetery and is an interesting example of the 1930s Gothic Revival style architecture. It takes the form of a small chapel with carvings, diamond shaped roof tiles and decorated ridge embellishing the exterior. By the 1890s, the Boroondara Cemetery was a popular destination for visitors and locals admiring the beauty of the grounds and the splendid monuments. The edge of suburban settlement had reached the cemetery in the previous decade. Its Victorian garden design with sweeping curved drives, hill top views and high maintenance made it attractive. In its Victorian Garden Cemetery design, Boroondara was following an international trend. The picturesque Romanticism of the Pere la Chaise garden cemetery established in Paris in 1804 provided a prototype for great metropolitan cemeteries such as Kensal Green (1883) and Highgate (1839) in London and the Glasgow Necropolis (1831). Boroondara Cemetery was important in establishing this trend in Australia. The cemetery's beauty peaked with the progressive completion of the spectacular Springthorpe Memorial between 1899 and 1907. From about the turn of the century, the trustees encroached on the original design, having repeatedly failed in attempts to gain more land. The wide plantations around road boundaries, grassy verges around clusters of graves in each denomination, and most of the landscaped surround to the Springthorpe memorial are now gone. Some of the original road and path space were resumed for burial purposes. The post war period saw an increased use of the Cemetery by newer migrant groups. The mid- to late- twentieth century monuments were often placed on the grassed edges of the various sections and encroached on the roadways as the cemetery had reached the potential foreseen by its design. These were well tended in comparison with Victorian monuments which have generally been left to fall into a state of neglect. The Boroondara Cemetery features many plants, mostly conifers and shrubs of funerary symbolism, which line the boundaries, road and pathways, and frame the cemetery monuments or are planted on graves. The major plantings include an impressive row of Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa), interplanted with Sweet Pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum), and a few Pittosporum crassifolium, along the High Street and Parkhill Street, where the planting is dominated by Sweet Pittosporum. Planting within the cemetery includes rows and specimen trees of Bhutan Cypress and Italian Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens), including a row with alternate plantings of both species. The planting includes an unusual "squat" form of an Italian Cypress. More of these trees probably lined the cemetery roads and paths. Also dominating the cemetery landscape near the Rotunda is a stand of 3 Canary Island Pines (Pinus canariensis), a Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii) and a Weeping Elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii') Amongst the planting are the following notable conifers: a towering Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), a rare Golden Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea'), two large Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris), and the only known Queensland Kauri (Agathis robusta) in a cemetery in Victoria. The Cemetery records, including historical plans of the cemetery from 1859, are held by the administration and their retention enhances the historical significance of the Cemetery. How is it significant? Boroondara Cemetery is of aesthetic, architectural, scientific (botanical) and historical significance to the State of Victoria. Why is it significant? The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical and aesthetic significance as an outstanding example of a Victorian garden cemetery. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance as a record of Victorian life from the 1850s, and the early settlement of Kew. It is also significant for its ability to demonstrate, through the design and location of the cemetery, attitudes towards burial, health concerns and the importance placed on religion, at the time of its establishment. The Boroondara Cemetery is of architectural significance for the design of the gatehouse or sexton's lodge and cemetery office (built in stages from 1860 to 1899), the ornamental brick perimeter fence and elegant cemetery shelter to the design of prominent Melbourne architects, Charles Vickers (for the original 1860 cottage) and Albert Purchas, cemetery architect and secretary from 1864 to his death in 1907. The Boroondara Cemetery has considerable aesthetic significance which is principally derived from its tranquil, picturesque setting; its impressive memorials and monuments; its landmark features such as the prominent clocktower of the sexton's lodge and office, the mature exotic plantings, the decorative brick fence and the entrance gates; its defined views; and its curving paths. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522), the Syme Memorial and the Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036), all contained within the Boroondara Cemetery, are of aesthetic and architectural significance for their creative and artistic achievement. The Boroondara Cemetery is of scientific (botanical) significance for its collection of rare mature exotic plantings. The Golden Funeral Cypress, (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea') is the only known example in Victoria. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance for the graves, monuments and epitaphs of a number of individuals whose activities have played a major part in Australia's history. They include the Henty family, artists Louis Buvelot and Charles Nuttall, businessmen John Halfey and publisher David Syme, artist and diarist Georgiana McCrae, actress Nellie Stewart and architect and designer of the Boroondara and Melbourne General Cemeteries, Albert Purchas.Digital imagescemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial, cussen -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesDigital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, boroondara general cemetery Henty, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registered by Heritage VictoriaFrom Heritage Victoria Statement of Significance Last updated on - December 15, 2005 What is significant? Boroondara Cemetery, established in 1858, is within an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. A brick cremation wall and a memorial rose garden were constructed near the entrance in the mid- twentieth century(c.1955-57) and a mausoleum completed in 2001.The maintenance shed/depot close to High Street was constructed in 1987. The original entrance was altered in 2000 and the original cast iron gates moved to the eastern entrance of the Mausoleum. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522) set at the entrance to the burial ground commemorates Annie Springthorpe, and was erected between 1897 and 1907 by her husband Dr John Springthorpe. It was the work of the sculptor Bertram Mackennal, architect Harold Desbrowe Annear, landscape designer and Director of the Melbourne Bortanic Gardens, W.R. Guilfoyle, with considerable input from Dr Springthorpe The memorial is in the form of a small temple in a primitive Doric style. It was designed by Harold Desbrowe Annear and includes Bertram Mackennal sculptures in Carrara marble. Twelve columns of deep green granite from Scotland support a Harcourt granite superstructure. The roof by Brooks Robinson is a coloured glass dome, which sits within the rectangular form and behind the pediments. The sculptural group raised on a dais, consists of the deceased woman lying on a sarcophagus with an attending angel and mourner. The figure of Grief crouches at the foot of the bier and an angel places a wreath over Annie's head, symbolising the triumph of immortal life over death. The body of the deceased was placed in a vault below. The bronze work is by Marriots of Melbourne. Professor Tucker of the University of Melbourne composed appropriate inscriptions in English and archaic Greek lettering.. The floor is a geometric mosaic and the glass dome roof is of Tiffany style lead lighting in hues of reds and pinks in a radiating pattern. The memorial originally stood in a landscape triangular garden of about one acre near the entrance to the cemetery. However, after Dr Springthorpe's death in 1933 it was found that transactions for the land had not been fully completed so most of it was regained by the cemetery. A sundial and seat remain. The building is almost completely intact. The only alteration has been the removal of a glass canopy over the statuary and missing chains between posts. The Argus (26 March 1933) considered the memorial to be the most beautiful work of its kind in Australia. No comparable buildings are known. The Syme Memorial (1908) is a memorial to David Syme, political economist and publisher of the Melbourne Age newspaper. The Egyptian memorial designed by architect Arthur Peck is one of the most finely designed and executed pieces of monumental design in Melbourne. It has a temple like form with each column having a different capital detail. These support a cornice that curves both inwards and outwards. The tomb also has balustradings set between granite piers which create porch spaces leading to the entrance ways. Two variegated Port Jackson Figs are planted at either end. The Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036) was constructed in 1912-13 by Sir Leo Cussen in memory of his young son Hubert. Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933), judge and member of the Victorian Supreme Court in 1906. was buried here. The family memorial is one of the larger and more impressive memorials in the cemetery and is an interesting example of the 1930s Gothic Revival style architecture. It takes the form of a small chapel with carvings, diamond shaped roof tiles and decorated ridge embellishing the exterior. By the 1890s, the Boroondara Cemetery was a popular destination for visitors and locals admiring the beauty of the grounds and the splendid monuments. The edge of suburban settlement had reached the cemetery in the previous decade. Its Victorian garden design with sweeping curved drives, hill top views and high maintenance made it attractive. In its Victorian Garden Cemetery design, Boroondara was following an international trend. The picturesque Romanticism of the Pere la Chaise garden cemetery established in Paris in 1804 provided a prototype for great metropolitan cemeteries such as Kensal Green (1883) and Highgate (1839) in London and the Glasgow Necropolis (1831). Boroondara Cemetery was important in establishing this trend in Australia. The cemetery's beauty peaked with the progressive completion of the spectacular Springthorpe Memorial between 1899 and 1907. From about the turn of the century, the trustees encroached on the original design, having repeatedly failed in attempts to gain more land. The wide plantations around road boundaries, grassy verges around clusters of graves in each denomination, and most of the landscaped surround to the Springthorpe memorial are now gone. Some of the original road and path space were resumed for burial purposes. The post war period saw an increased use of the Cemetery by newer migrant groups. The mid- to late- twentieth century monuments were often placed on the grassed edges of the various sections and encroached on the roadways as the cemetery had reached the potential foreseen by its design. These were well tended in comparison with Victorian monuments which have generally been left to fall into a state of neglect. The Boroondara Cemetery features many plants, mostly conifers and shrubs of funerary symbolism, which line the boundaries, road and pathways, and frame the cemetery monuments or are planted on graves. The major plantings include an impressive row of Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa), interplanted with Sweet Pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum), and a few Pittosporum crassifolium, along the High Street and Parkhill Street, where the planting is dominated by Sweet Pittosporum. Planting within the cemetery includes rows and specimen trees of Bhutan Cypress and Italian Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens), including a row with alternate plantings of both species. The planting includes an unusual "squat" form of an Italian Cypress. More of these trees probably lined the cemetery roads and paths. Also dominating the cemetery landscape near the Rotunda is a stand of 3 Canary Island Pines (Pinus canariensis), a Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii) and a Weeping Elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii') Amongst the planting are the following notable conifers: a towering Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), a rare Golden Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea'), two large Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris), and the only known Queensland Kauri (Agathis robusta) in a cemetery in Victoria. The Cemetery records, including historical plans of the cemetery from 1859, are held by the administration and their retention enhances the historical significance of the Cemetery. How is it significant? Boroondara Cemetery is of aesthetic, architectural, scientific (botanical) and historical significance to the State of Victoria. Why is it significant? The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical and aesthetic significance as an outstanding example of a Victorian garden cemetery. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance as a record of Victorian life from the 1850s, and the early settlement of Kew. It is also significant for its ability to demonstrate, through the design and location of the cemetery, attitudes towards burial, health concerns and the importance placed on religion, at the time of its establishment. The Boroondara Cemetery is of architectural significance for the design of the gatehouse or sexton's lodge and cemetery office (built in stages from 1860 to 1899), the ornamental brick perimeter fence and elegant cemetery shelter to the design of prominent Melbourne architects, Charles Vickers (for the original 1860 cottage) and Albert Purchas, cemetery architect and secretary from 1864 to his death in 1907. The Boroondara Cemetery has considerable aesthetic significance which is principally derived from its tranquil, picturesque setting; its impressive memorials and monuments; its landmark features such as the prominent clocktower of the sexton's lodge and office, the mature exotic plantings, the decorative brick fence and the entrance gates; its defined views; and its curving paths. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522), the Syme Memorial and the Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036), all contained within the Boroondara Cemetery, are of aesthetic and architectural significance for their creative and artistic achievement. The Boroondara Cemetery is of scientific (botanical) significance for its collection of rare mature exotic plantings. The Golden Funeral Cypress, (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea') is the only known example in Victoria. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance for the graves, monuments and epitaphs of a number of individuals whose activities have played a major part in Australia's history. They include the Henty family, artists Louis Buvelot and Charles Nuttall, businessmen John Halfey and publisher David Syme, artist and diarist Georgiana McCrae, actress Nellie Stewart and architect and designer of the Boroondara and Melbourne General Cemeteries, Albert Purchas.Digital imagescemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial, henty -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Image - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Bishop's Palace Ballarat Featuring Chimneys and Roof Line, Ballarat, 2014, 23/02/2014
Bishops Palace was built in 1877 as the home for the first Catholic Bishop of Ballarat. Designed by Melbourne architect, Joseph Reed, of Reed and Barnes, it was built by George Broom at a cost of £6,000. Reed and Barnes also designed Melbourne’s State Library, Ripponlea Estate and the Melbourne Royal Exhibition Building. The original heritage-listed gold lead stencilled paintwork that can be seen in the front entry and on the staircase walls at Bishops Palace was replicated in the Royal Exhibition Building. The original property was 140 squares set on 11 acres of gardens and took up an entire block of Sturt Street. This was on scale with the importance of Ballarat as a gold-mining centre at the time. Bishop's Palace is of architectural, aesthetic and historical significance to the State of Victoria. The two-storey bluestone mansion is an impressive example of 19th-century Gothic architecture with an unusual design. It retains many of its original features, including lead stencilled paintwork, cornices, ceiling roses, fixtures and fittings. Since sold by the Catholic Church the Bishops Palace has undergone a number of transformations in its lifetime, from the home of the first Bishop to a private residence, and today, as a luxurious accommodation, wedding and events venue. The grounds were subdivided over the years, and the property is now surrounded by four of the original 11 acres of gardens. It opened its doors to the public in 2019.Colour image of the bluestone Bishop's Palace, and it's cast iron lace.architecture, garden, bishop's palace, cast iron lace, cast iron, catholic church -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Smeaton House, Smeaton, 2011, 09/04/2011
Captain Hepburn was a squatter who held the license for Smeaton Estate. Colour photographs of Smeaton House, Smeaton, built by squatters John and Elizabeth Hepburn. john hepburn, elizabeth hepburn, smeaton house, squatter, smeaton, architecture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Image, Melbourne Parliament House, c1951
... Office goldfields victoria melbourne Parliament house ...Photograph of Melbourne's Parliament House.victoria, melbourne, parliament house, architecture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph, Clare Gervasoni, Houses in LaTrobe St, Ballarat, 12/10/2020
Colour photographs of houses in LaTrobe St, Ballaratlatrobe street, ballarat, architecture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph, Lisa Gervasoni, Ballarat Arch of Victory, 15/08/2007
Four views of the Ballarat Arch of Victoria, the entrance to the Ballarat Avenue of Honour.architecture, world war one, ballarat arch of victory, ballarat avenue of honour -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photgraph, Carmel Welsh Church, Sebastopol, 05/10/2022
Carmel Welsh Church is located at 365 Albert Street, Sebastopol and is the only identified Welsh Presbyterian church surviving in Victoria,. It was built in 1865-6 to the design of Henry Richards Caselli, and of distinctive architectural character combining round arched windows of almost a Renaissance character, mediaevalising buttresses, and extremely chunky gable eaves of a domestic character, including square finials and raking brackets. It was established in 1861, the members and adherents were predominantly Welsh, the Welsh language was spoken freely and there were regular services in Welsh.Digital photograph of the interior of the bluestone Welsh church, Sebastopol, Ballarat.carmel welsh church, sebastopol, church, henry richards caselli, welsh -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photgraph, Clare Gervasoni, Stained Glass Window in Carmel Welsh Church, Sebastopol, 05/10/2022
Carmel Welsh Church is located at 365 Albert Street, Sebastopol and is the only identified Welsh Presbyterian church surviving in Victoria,. It was built in 1865-6 to the design of Henry Richards Caselli, and of distinctive architectural character combining round arched windows of almost a Renaissance character, mediaevalising buttresses, and extremely chunky gable eaves of a domestic character, including square finials and raking brackets. It was established in 1861, the members and adherents were predominantly Welsh, the Welsh language was spoken freely and there were regular services in Welsh.Digital photograph of ta stained glass window in the Carmel Welsh church, Sebastopol.Serve the Lord with gladness, come before his presence with singing. In loving memory of David William Davies Died Dec. 28th 1932 Choirmaster 1875 to 1885carmel welsh church, sebastopol, church, henry richards caselli, welsh, stained glass, david william davies, choirmaster -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photgraph, Clare Gervasoni, Stained Glass Window in Carmel Welsh Church, Sebastopol, 08/10/2022
Carmel Welsh Church is located at 365 Albert Street, Sebastopol and is the only identified Welsh Presbyterian church surviving in Victoria,. It was built in 1865-6 to the design of Henry Richards Caselli, and of distinctive architectural character combining round arched windows of almost a Renaissance character, mediaevalising buttresses, and extremely chunky gable eaves of a domestic character, including square finials and raking brackets. It was established in 1861, the members and adherents were predominantly Welsh, the Welsh language was spoken freely and there were regular services in Welsh.Digital photograph of ta stained glass window in the Carmel Welsh church, Sebastopol.In memory of the Welsh miners who from the darkness of the mines brought the light of Christ to Carmel.carmel welsh church, sebastopol, church, henry richards caselli, welsh, stained glass, welsh miners, poppet head -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Toilet at St Laurence O'Toole Catholic Church, Sandon, 2017, 08/04/2023
St Laurence O'Toole church and cemetery is located in a rural setting at 801/821 Creswick-Newstead Rd, Sandon. Originally a small wooden school (22’x14’) was erected in Sandon by Father Patrick Smyth (who was involved in the Eureka Stockade movement) in 1859. It was also used for Mass and became known as a chapel. In June 1882 tenders were called for the construction of a brick Church by the Castlemaine architect, T.F. Kibble, and it was built at a cost of 1000 pounds. The church was blessed by Archbishop Goold on 06 May 1883 and dedicated to St Laurence O'Toole. The brick building demonstrates original design qualities of a Victorian Rudimentary Gothic style, including the steeply pitched, parapet gable roof form, together with a central steeply pitched, gabled porch that projects slightly from the main gable end. Other intact qualities include the exposed brick wall construction, lapped galvanised corrugated iron roof cladding, minor gabled porch at the rear, small ventilation dormers nearby the roof ridgeline, series of stone steps that lead to the central porch with its double pointed door opening and vertical boarded doors, simple rose window in the main gable end, pointed windows, brick buttresses with double lower copings, and the light masonry detailing (the banding marking the floor level within, buttress copings, window and door surrounds and quoins, and the drip moulds).(Shire of Mount Alexander: Heritage Study of the former Shire of Newstead, 2000) The visually connected cemetery demonstrates important visual qualities formed by the regular rows of graves and cemetery architecture, and the grassed and treed rural landscape. It is a rare and substantially intact example of a Victorian Catholic Church with a cemetery in its churchyard. Many headstones and cemetery architecture, date from the 19th century and represent some fine examples of masonry craftsmanship. Some refurbisments occurred during the 1940s and in 2002 a major restoration project was undertaken from roof to footings, by a dedicated band of volunteers and trades people. Work was completed mid 2003 and in November 2003 St Laurence’s was re-dedicated with the celebration of Mass and a picnic tea. Colour photograph of a long drop toliet at the Catholic Church, Sandon, Victoria.sandon, sandon cemetery, st laurence o'toole catholic church, sandon -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Image, Maryborough Railway Station, c1951
Maryborough Railway Station was built in Victoria's heyday of railway planning. A black and white photograph of Maryborough Railway Stationmaryborough railway station, maryborough, architecture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Image, Lydiard Street Ballarat Looking North, C1890
Lydiard Street is a street in central Ballarat known for its Victorian architecture. The building with clock tower is the former Ballarat Post Office, the tower stage of the building dating from 1885. It sits on the corner of Sturt Street. Black and white photograph of Lydiard Street Ballarat.lydiard street ballarat, ballarat post office, tram, streetscape, architecture, vintage cars -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, L.J. Gervasoni, Avoca, 2011, 06/08/2011
Colour photograph of a double storey brick building in Avoca, Victoria.avoca, architecture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph, Clare Gervasoni, Toilet at St Paul's Church of England, Henty, 2015, 22/12/2015
This church is associated with the Henty family of Merino Downs.Colour photograph of a weatherboard toilet at Henty, Victoriahenty, st paul's church of england, henty, st paul's anglican church, henty, louisa henty, toilet, outhouse, out house, thunder box, drop box, architecture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Ballarat Synagogue, 2009, 07/01/2012
Colour photographs of the exterior of the Ballarat Synagogue.ballarat synagogue, jewish, star of david, architecture, religion -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesDigital photograph, Dorothy Wickham, Trajan's Columns, Victoria & Albert Museum, London, 2016, 09/2016
These original columns are marble, made in 113AD. They come from Rome, Italy and are held in the Cast Courts at the Victoria & Albert Museum, London. The collection of casts at the museum is one of the most important in the world. Their original purpose was educational when it was not easy to trail and see original works. they thus provided an opportunity for students to study. The Cast Courts opened in 1873 and allowed the display of large monuments. These galleries are currently divided by nationality. Photograph of a cast of Trajan's Column at the Victoria & Albert Museum, London. The column has been displayed in two parts. he massive cast is a tremendous feat of both engineering and casting. Displayed in the Architectural Courts from the time of their opening in 1873, it provided the opportunity for students (and others not able to travel to Rome) to see this iconic monument of the classical world. The cast of the column is made up of sections of plaster reliefs that are attached to an inner chimney built of brick. Each section was individually numbered so that the column could easily be assembled like a giant jigsaw puzzle. (http://www.vam.ac.uk/content/articles/t/trajans-column/)trajan's column, roman forum, plaster casts -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesDigital Photograph, Stairs from Salisbury Cathedral
These stairs are on display at Victoria and Albert Museum, London. Salisbury Cathedral is still in existence and houses the famous Magna Carta. Standing 123 metres high above the city that grew up around it Salisbury Cathedral is almost entirely Early English Gothic in architectural style. The Magna Carta housed at SAlisbury is the best preserved of the four originals dating from June 1215 and still in existence.It is written in Latin with a quill pen on treated animal skin (parchment). The sealed documents were sent throughout the country after the Charter was forced on King John barons who were unhappy with the way he was ruling England. Wooden stairsmagna carta salisbury cathedral king john stairs -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesDigital Photograph, Dorothy Wickham, The Cast Courts, 2016, 09/2016
This ornate cross sits at the right hand side of View of Trajan's column, Cast Courts, Room 46a, The West Court, Victoria and Albert Museum, London. Cast Courts: "When the Architectural Courts – or Cast Courts as they are now known – opened in 1873, The Builder magazine compared the experience of seeing them to a first glimpse of Mont Blanc, creating one of those 'impressions that can scarcely be effaced'. Since then, these two enormous rooms and the reproductions they contain have continued to impress and inspire visitors to the Museum. For centuries, antiquarian interest in world architecture and sculpture led to reproductions – or copies – being made of outstanding national monuments and notable sculptures. When the Museum was founded, it collected and displayed reproductions of great art and architecture from across the world in order to offer objects for study and tell a complete story of the history of art and design. Casts are made by placing several plaster moulds upon the surface of the original structure. Once hardened and removed, the moulds are then enclosed in an outer casing, the interior coated with a separating agent and the wet plaster poured in. When set, the pieces are then assembled and the joints and surfaces finished off, to make a complete reproduction of the original work. The finished product – as well as being a formidable technical achievement in its own right – enables admirers to study faithful reproductions of important monuments and works of art." Ref: https://www.vam.ac.uk/articles/history-of-the-cast-courtslondon, victoria and albert museum, cast courts -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photograph, Victoria and Albert Museum, London, 2016, 09/2016
The V&A is the world’s leading museum of art and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.3 million objects that span over 5,000 years of human creativity. The Museum holds many of the UK's national collections and houses some of the greatest resources for the study of architecture, furniture, fashion, textiles, photography, sculpture, painting, jewellery, glass, ceramics, book arts, Asian art and design, theatre and performance. https://www.vam.ac.uk/info/about-usDigital photographs of a stained glass window at the Victoria And Albert Museum, Londonvictoria and albert museum, window, interior, stained glass window -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Artwork, other - Ink Line Drawing, 11 Alfred St., Burwood, 1999
A property illustration by Margret Picken Commissioned by the real estate agency Woodards, Camberwell for the purpose of advertising 11 Alfred St., Burwood for sale in 1990. Made by using Rotring ‘Rapidigraph’ drafting pens with Rotring ink on Rapidigraph polyester drafting film, double matte. The suburb lines are believed to have been redrawn, making this property no longer in Burwood, but located in Glen iris. This property is listed as having sold for in 1990, Trained as a cartographic draftsman within the mining industry, Margaret Picken is an artist who worked producing property illustrations for real estate agencies in eastern suburbs of Victoria from 1983-2005. Retiring from the industry as technological changes favoured coloured photography over illustrations, and commissioning companies over sole contractors.This artwork is of Historical Significance as a record of local domestic architecture.A black ink line drawing on drafters film by Maragret Picken, of 11 Alfred St., Burwood. Depicted is a one-story weatherboard situated back from a front lawn with a large tree, and a brick driveway on the left. Bushes are planted in front of the porch, and greenery on the left and right of the image. There to two hole punches just below the upper edge. 11 Alfred St., Burwood Maragret Picken -'99 Woodards - Glen Iriswhitehorse historical society, schwerkolt cottage, housing, architecture, margaret picken, burwood, glen iris, house, garden -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Artwork, other - Ink Line Drawing, 1,2,3/16 Alfred St., Burwood, 1995
A property illustration by Margret Picken Commissioned by the real estate agency Woodards, Camberwell for the purpose of advertising 1,2,3/16 Alfred St., Burwood for sale in 1995. Made by using Rotring ‘Rapidigraph’ drafting pens with Rotring ink on Rapidigraph polyester drafting film, double matte. The suburb lines are believed to have been redrawn, making this property no longer in Burwood, but located in Glen iris. 1/16 Alfred St., Burwood is listed as having sold for in 1995 for $185,000 Trained as a cartographic draftsman within the mining industry, Margaret Picken is an artist who worked producing property illustrations for real estate agencies in eastern suburbs of Victoria from 1983-2005. Retiring from the industry as technological changes favoured coloured photography over illustrations, and commissioning companies over sole contractors.This artwork is of Historical Significance as a record of local domestic architecture.A black ink line drawing on drafters film by Maragret Picken, of 1,2,3/16 Alfred St., Burwood. Depicted are three one-story rendered houses on one block, one behind the other, situated back from a front lawn with a large tree on the right, and a driveway on the left leading to a garage There to two hole punches just below the upper edge An approximately 1.5cmx0.5 tape reside mark at the centre of the bottom edge A 1cm vertical line of dirty tape residue on the center of the upper edge. 1,2,3/16 Alfred St., Burwood Margaret Picken - 95 Woodards - c'wellwhitehorse historical society, schwerkolt cottage, housing, architecture, margaret picken, burwood, glen iris, house, garden -
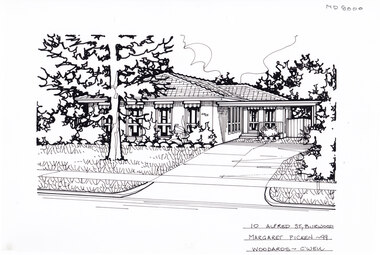
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Artwork, other - Ink Line Drawing, 26 Davis St., Burwood, 2003
A property illustration by Margret Picken Commissioned by the real estate agency Fletchers for the purpose of advertising 26 Davis St., Burwood for sale in 2003. Made by using Rotring ‘Rapidigraph’ drafting pens with Rotring ink on Rapidigraph polyester drafting film, double matte. This property is listed as having sold for in 2003 $373,000 Trained as a cartographic draftsman within the mining industry, Margaret Picken is an artist who worked producing property illustrations for real estate agencies in eastern suburbs of Victoria from 1983-2005. Retiring from the industry as technological changes favoured coloured photography over illustrations, and commissioning companies over sole contractors.This artwork is of Historical Significance as a record of local domestic architecture.A black ink line drawing on drafters film by Margaret Picken, of 26 Davis St., Burwood. Depicted is a two-story brick house situated back from a front lawn with a large tree, and a driveway on the right, leading to a garage26 Davis St., Burwood Picken © 2003 Fletcherswhitehorse historical society, schwerkolt cottage, housing, architecture, margaret picken, burwood, house, garden -
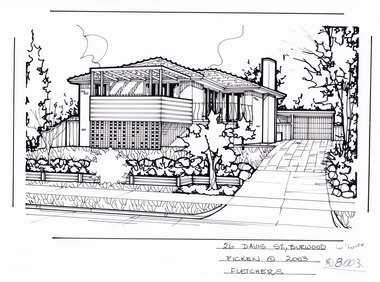
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Artwork, other - Ink Line Drawing, 3 Donald Rd., Burwood, 2003
A property illustration by Margret Picken Commissioned by the real estate agency Fletchers for the purpose of advertising 3 Donald Rd., Burwood in 2001. Made by using Rotring ‘Rapidigraph’ drafting pens with Rotring ink on Rapidigraph polyester drafting film, double matte. This property is listed as having sold for in 2001 $490,000 Trained as a cartographic draftsman within the mining industry, Margaret Picken is an artist who worked producing property illustrations for real estate agencies in eastern suburbs of Victoria from 1983-2005. Retiring from the industry as technological changes favored coloured photography over illustrations, and commissioning companies over sole contractors.This artwork is of Historical Significance as a record of local domestic architecture.A black ink line drawing on drafters film by Margaret Picken, of 3 Donald Rd., Burwood. A one story weatherboard bungalow, set back from a front lawn in foreground. There is a small tree in the center of the lawn, and a driveway on the right.3 Donald Rd., Burwood Margaret Picken © 2001 Fletchers Real Estatewhitehorse historical society, schwerkolt cottage, housing, architecture, margaret picken, burwood, house, garden
