Showing 379 items
matching surgical equipment
-
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mouth opener, Heister, 1941
The advent of anaesthesia posed immediate problems for the oral surgeons and dentists who were used to operating on awake patients with intact airway reflexes. Early anaesthetics were very light and often created an uncooperative patient. Dentists were quick to complain they had trouble opening the mouth quickly enough and dental props soon made an appearance. Gags and tongue depressors proliferated, all initially devised to improve surgical and anaesthetic access, not to protect the airway. Other instruments for opening the jaws included the somewhat fearsome devices known as mouth openers. Heister's mouth opener was incorporated in anaesthetic practice but was not designed for this purpose. Lorenz Heister (1983 - 1758) used his device for mouth inspection and for operations on the palate, tonsils and teeth in the pre-anaesthesia era. He was not impressed with the way it was used by others in his life time and believed that it overstretched the jaw when used inappropriately. Despite its apparent brutality, the Heister mouth gag was still advertised for sale in 1983 and its useful mechanism has been incorporated into modern surgical retractors. This Heister heavy patterned mouth opener was acquired from an Italian Army medical unit at Tobruk in 1941 and donated to the museum in 1946.Scissor-like metal device with a screw mechanism at the top which allows for the open or closed position to be locked.heister, lorenz, mouth opener, gag, heavy patterned -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryInhaler, Bruck, 1908
The Bruck Inhaler is a modification of the Clover Inhaler, designed by Lambert Bruck. Bruck added a glass dome which enabled the level of ether to be monitored during administration. This was a revolutionary change as it removed guess work from the process.The Bruck Inhaler is a historically, aesthetically and scientifically significant piece. The basic design is based on the Clover Inhaler, but with a rounded bottom. The idea of a glass viewing window was possibly inspired by Wilson-Smith Inhaler. The Bruck Inhaler is historically significant as it is the first inhaler to be made with a completely clear lower glass section. This improved the usability for the ether administrator, and eliminated much of the guesswork associated with dosage and ether levels, which in turn improved the patient experience. This piece provides a strong local link to both anaesthetic and general medical practice at the turn of the century. The design is credited to Ludwig Bruck of Sydney, and was presumably manufactured in the same area. Bruck, as the attributed designer, holds much relevance to the significance of the object, as connected with him is much historical information about the social context of medical practice. Ludwig Bruck was a prominent figure in the medical industry. He started his medical career in Sydney as a Medical Transfer Agent, and later owned a shop at 16 Castlereagh Street, Sydney. This business is listed in the 1903 Register of Firms as a Medical Agent and Importer of Medical Instruments and Books. Bruck was vocal as a journalist and published analyses of medical statistics, as well as the well known Australasian Medical Dictionary and Handbook, which included the “List of Unregistered Medical Practitioners”. Ludwig Bruck was an immigrant. He was of German descent, which placed him in a precarious position within Sydney society during the turn of century. Bruck conducted several public conversations with prominent members of the Australian Natives Association through the Sunday News in regards to his disagreement of the employment of medical practitioners by the ANA specifically to corroborate their health insurance policies. He was also a stalwart supporter of the Australian arm of the British Medical Association, being the publisher of the first and subsequent editions of The Australian Medical Gazette. Bruck chose to end his life with a combination of poison and chloroform on 14 August 1915, after being accused of trading with the enemy during World War One. His suicide note stated his horror at leaving his business partner to deal with the tarring of his reputation as the reason for his decision. The Bruck Inhaler has aesthetic significance as it is a beautiful example of turn of the century surgical design and craftsmanship. Aseptic methods of surgery were well known by 1909, and the aesthetic design of the Bruck Inhaler conformed to these principles. The ability for the surgeon to unscrew, clean and sterilize each part of the Inhaler contributes to the streamlined design of the piece. The Buck Inhaler holds scientific significance. There is the capacity for further research to be undertaken on the object. Geoffrey Kaye often collected multiple examples of equipment, usually one for reverse engineering and another for teaching. There are currently two examples of the Bruck Inhaler in the collection, presenting an opportunity for further technical research on the object. The inhaler is oval shaped with one half made of glass to allow observation of the ether level. A vertical cross tube, 22mm in diameter passes between the face-piece and the bag [missing]. There is a stopcock for admission of oxygen or nitrous oxide opposite the bag attachment. There is a central tube, 28mm in diameter, with controllable ports on either side. There is also a tear-drop shaped fask mask.Hand engraved on side of base: L. Bruck / Sydneyclover, joseph, bruck, lambert, inhaler, rebreather, nitrous oxide, oxygen, williams, probyn -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryBook, Catalogue, Drug Houses of Australia Ltd, Surgical Instruments and Appliances, eighth edition
... with cloth covering produced as a trade catalogue for surgical ...Grey/brown hardcover book with cloth covering produced as a trade catalogue for surgical instruments and appliances, including anaesthetic equipment and apparatus -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Ramsay Surgical Limited
... the patient's face. Facemask Anaesthesia Ramsay Surgical Wire frame mask ...One of a range of metal face masks designed to have a cover which helps protect the patient's face.Wire frame mask designed to cover mouth and nose. There is a metal hook on the left hand side protuding from the base of the mask and wire mesh raised from the base with a circle in the middle.facemask, anaesthesia, ramsay surgical -
 Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and Archives
Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and ArchivesEquipment - Schimmelbusch anaesthetic mask, Mid 20th Century
The Schimmelbusch mask is an open breathing system for delivering an anesthetic. The device was invented by Curt Schimmelbusch in 1889, and was used until the 1950s (though it is still applied in some developing countries). The device consists of a wire frame which is covered with several beds of gauze and applied to the patient's face over the mouth and nose. Then high-volatility anesthetic (usually diethyl ether or halothane, and historically chloroform) is dripped on it, allowing the patient to inhale a mix of the evaporated anesthetic and air. The device is designed to prevent the anesthetic from coming in contact with the patient's skin, where it can cause irritation.This model differs from the others in that the mask's handle is attached to the mask, as opposed to the spring. The chloroform cloth was possibly held in place by the clamp, instead of a spring. Schimmelbusch anasthetic mask, made of Stainless steel. This mask was used with chloroform cloth. Missing spring. Martin and Co.surgery, anesthetic, chloroform, surgical instrument -
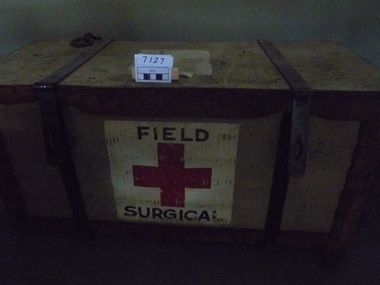 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Equipment - Equipment, Army, Field Surgical Pack
... of contents inside lid. Field Surgical Pack Equipment Equipment, Army ...Wicker trunk, canvas covered, plywood lid and base reinforced with leather on edges, rope carry handles, steel bindings with clasp and staple closures with 2 chains for transport. List of contents inside lid.IC on lid. FSP 1. FSP 1C. Filed surgical Red Cross on White background.field surgical pack, fsp -
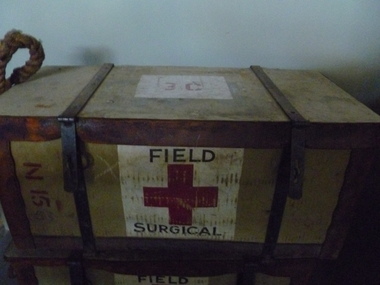 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Equipment - Field surgical pack
... surgical pack Red cross on white background with "field surgical ...Wicker trunk, canvas covered, plywood lid and base reinforced with leather on edges, ropes carry handles, steel bindings with clasp and staple closures with 2 chains for transport. Torn list of contents inside lid.Red cross on white background with "field surgical" on front FSP1 N15 53 30 3Cfsp, wicker trunk, field surgical pack -
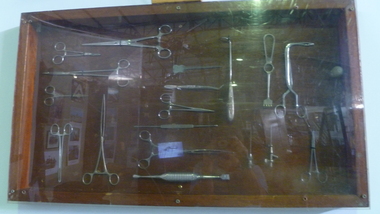 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Equipment - Equipment, Army, Medical cabinet
Eighteen Russian made surgical instruments in a timber and acrylic framed display case (left out the item on the far right)surgical instruments, display case -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumInstrument - HYPODERMIC NEEDLES, SOLE WHOLESALE DISTRIBUTORS : THE AMALGAMATED DENTAL (AUST) PTY LTD MELBOURNE - SYDNEY
BOX CONTAINING SURGICAL HYPODERMIC NEEDLES - 'SOLILA' BRANDlocal history, medicine, medical equipment, clunes hospital -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Darning Needles
Needles are part of a collection of sewing tools donated by Betty McPhee.Six darnng needles, self threading in paper envelope.The Darnet. The Stainless Surgical Needle Co Ltd, Alcesterhandcrafts, equipment -
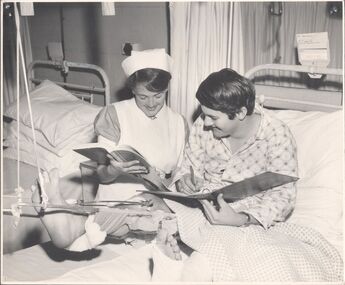 Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Northern District School of Nursing. Managed by Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Preliminary Training School 71
The Northern District School of Nursing opened in 1950 in to address the issues around nurse recruitment, training and education that had previously been hospital based. The residential school was to provide theoretical and in-house education and practical training over three years. The students would also receive practical hands-on training in the wards of associated hospitals. The Northern District School of Nursing operated from Lister House, Rowan Street, Bendigo. It was the first independent school of nursing in Victoria and continued until it closed in 1989.Nurse Jeanette Myers attending male patient.Bendigo Base Hospital Ward 5 Mens Surgical Ward Sr E Clergg Nurse Jeanette Myers School 71 PTS 12.2.68ndns, nursing training, nursing education equipment -
 Australian Army Museum of Western Australia
Australian Army Museum of Western AustraliaDiorama, 2015
This diorama is the focal point the Prisoner of War Gallery. It was originally designed and installed by a collaborative group of artists and craftsmen, all themselves former Prisoners of War in 1995. Bamboo for the display and replica prosthetics was sourced from Thailand. The mannequins are artistic interpretations of identified POW surgical staff and doctors. The original display was moved and reassembled during the Gallery redevelopment process in 2015. All items presented within the diorama are based on POW recorded drawings and diaries of experiences in the Thai Burma Railway POW camps.1:1 scale diorama showing operating theatre in POW camp on Burma Thai Railway together with reproductions of prothesis and improvised equipmentthai burma railway; -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Certificate - Photograph, colour, Melbourne District Nursing Society certificate of employment, 08.07.1913
This Certificate was presented to Trained nurse, known as 'Nurse' in those days, Nettie Osborne on completion of six months employment with Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS). This is the only example of a MDNS Nurses certificate in the RDNS collection. In 1913 the MDNS Nurses had their board and residence, uniforms, bicycles and laundry expenses provided. Newly employed Nurses were paid £50 a year for her first six months. At the end of a year her salary was increased by £5, and later she earned £60 a year. .Following the founding of the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) in February 1885 to care for the sick poor in Melbourne, subsequent meetings were held to form a Committee and to draw up a Code of Rules of the Society. It was decided that only nurses who had attended a Hospital Nurses Training School and were fully qualified would be employed by the Society. After interviewing several candidates, it was on the first of May 1885 when the first Trained nurse, known as 'Nurse' in those days, Mrs. Ferguson, was employed by MDNS with a salary of £100 per annum. She was employed for three months initially, but this was soon extended, "on the understanding she will make arrangements to live in the more immediate vicinity of her district". A Doctor agreed to assist the Nurse with advice at any time. In rotation, a member of the Superintendence Sub-Committee supervised the Nurse’s visits and could assist to alleviate some poor social conditions they found. A second Nurse, Mrs. Joanna Cannon was employed by MDNS six months later, with a trial period of six months which was extended. They were the stalwarts of the Society in the early years, Nurse Cannon remaining with the Society for four years and Nurse Ferguson for five years, though both had a short break due to illness through the heaviness of the work. Nurses salaries were reduced to account for the cost of uniforms, and then when establishments were rented by the Society and the Nurses could now live in the Nurses Home. The Nurses worked in the now CBD, ie from Spencer Street to Spring Street and from Victoria Parade to Flinders Street. From its inception the Society was at the forefront of health care. They liaised with Doctors and provided high quality trained nursing care; educated their patients in the curing and prevention of disease; teaching the importance of cleanliness, fresh air and good nutrition, both by verbal instruction and demonstration, even supplying soup and milk when needed. At that time they walked the streets and lane ways amid the slums of inner Melbourne carrying their nursing bag containing lotion, ointments, powders, liniment, bandages, dressings, a case of spirits, and the Nurse's own clean apron, soap and small towel. They supplied equipment on loan, such as earthenware hot water bottles, splints, urinals, bed pans, bed cradles, feeding mugs, and air-cushions as well as providing blankets and clean bed linen, and nightdresses as necessary. They provided nursing care to a range of people, often in destitute situations, some lying on rags on the floor as they had no bed, others with just a bed and maybe a thin blanket, a chair and nothing else. Their ages ranged from babes, children, adults to the elderly. The Nurses gave medications as ordered, dressed wounds e.g. to the injured, and surgical cases, and to those with leg ulcers; attended to patients with ‘surgical ailments’ such as ‘hip disease’; gave care to those with acute illnesses such as bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, measles, and scarlet fever, as well as those with chronic illnesses such as consumption (tuberculosis), heart disease, arthritis, cancer, debility, neuritis and paralysis. As the work increased a third Nurse was employed but this was arduous work, particularly in the heat of summer and many nurses only remained with the Society for several months. A Trained Midwife was employed in August 1893. The work was arduous, particularly in the heat of summer. Permission to use bicycles was given to the Nurses in 1898 and the Society decided to purchase their own in 1903. A business man offered ‘new free wheel’ bicycles at £13 each which included maintenance for one year. Bells and wooden frames were added, at a cost of £5 per frame, so the Nurses could carry extra equipment. Nurses’ bags were strapped to the handlebars. Soup was made for those in need 2-3 times a week and if patients could not arrange to have it collected the soup was delivered by the Nurses on their bicycles. The use of bicycles caused a change in uniform, with white pith helmets, and veils covering them and tied under their chin, now being used; straw hats were worn in summer. Over the years the Nurses complained that their veils became wet in the rain and asked for a change of uniform but this did not occur until 1921. Bicycles continued to be used in inner areas until 1945. Public transport was also used over the years, in conjunction with a Motor Auxiliary from 1929 to 1971. MDNS began with its own small fleet of vehicles in the early 1950s which gradually expanded into a full fleet.The coloured Certificate is made of white paper attached to a buff card forming a boarder. It is in gold print on the white background which has a thin gold border. In large bold script are the words "Melbourne District Nursing Society" In between the words "District" and "Nursing" is a red Maltese cross which extends above and below the writing. Underneath this, in smaller capital letters, are the words "For Nursing Sick Poor In Their Own Homes"/. Below this in bold script are the words "This is to Certify that"/. Under this, written in black handwriting, is "Nurse Nettie Osborne"/; below this in script is "has acted in the capacity of District Nurse", then in black handwriting the words "Six Months"/. The next two lines read "having fulfilled her Duties to the satisfaction of her Committee, /"and appreciation of her Patients". The Certificate is signed in black by Mary Leeper, Vice President; Kate Hood; Hon. Treasurer; C.M. Tatham Hon. Secretary, and has Date; 8th July 1913 in black handwriting. On paper attached with tape to the back of the Certificate, is a copy of a photograph of two unidentified people. [Possibly Nettie and her husband]. Some small marks, and in one area a small area of cracking is seen on the white background of the certificate.certificates, mdns, melbourne district nursing society, rdns, royal district nursing service, nurse nettie osborne -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, c.1890
This photograph shows a Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) Trained nurse, 'Nurse' in the 1890s who is giving care to a patient who has collapsed in the street. It depicts the type of conditions the Nurses faced in that era and the uniform she wore It shows the help the Nurses received from the Police in that era and also the style of uniform worn by the police. In 1885 it was recognized that nursing care was needed for the sick poor in inner Melbourne. The Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) was founded in February of that year, the first District Nursing Society in Australia, and it was decided only Nurses who had attended a Hospital Nurses Training School and were fully qualified would be employed by the Society. In those days even though they were trained they were called 'Nurse'. The Society began with one Nurse, and a second employed six months later, working in the now CBD, ie from Spencer Street to Spring Street and from Victoria Parade to Flinders Street. From its inception the Society was at the forefront of health care and liaised with Doctors. They provided high quality nursing care; educated their patients in the curing and prevention of disease; teaching the importance of cleanliness and good nutrition, both by verbal instruction and demonstration, even supplying soup and milk when needed. At that time they walked the streets and lane ways amid the slums of inner Melbourne carrying their nursing bag containing lotion, ointments, powders, liniment, bandages, dressings, a case of spirits, and the Nurse's own clean apron, soap and small towel. They supplied equipment on loan, such as earthenware hot water bottles, splints, urinals, bed pans, bed cradles, feeding mugs, and air-cushions as well as providing blankets and clean bed linen, and nightdresses as necessary. They provided nursing care to a range of people, often in destitute situations, some lying on rags on the floor as they had no bed, others with just a bed and maybe a thin blanket, a chair and nothing else. Their ages ranged from babes, children, adults to the elderly. The Nurses gave medications as ordered by a Doctor, dressed wounds e.g. to the injured, and surgical cases, and to those with leg ulcers; attended to patients with ‘surgical ailments’ such as ‘hip disease’; gave care to those with acute illnesses such as bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, measles, and scarlet fever, as well as those with chronic illnesses such as consumption (tuberculosis), heart disease, arthritis, cancer, debility, neuritis and paralysis. They educated their patients, and their Carers, in the curing and prevention of disease; teaching the importance of hygiene, cleanliness, ventilation and good nutrition. They taught them, by verbal instruction and demonstration, how to make poultices, to make and apply bandages, apply medical appliances such as splints; and the Nurses supplied milk, beef tea and cooked soup when needed. As the work increased a third Nurse was employed but this was arduous work, particularly in the heat of summer and many Nurses only remained with the Society for several months. Black and white photograph of a Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) Trained nurse, known as 'Nurse' in those days, wearing a white apron over her full length grey uniform with white collar seen; she is wearing a white cap. She is sitting on a step at the front of a weatherboard house attending to a man, who is dressed in dark clothing and is wearing a brimmed hat. He is lying on his side on the pavement with his head close to the Nurse and his face turned towards the road . A policeman, wearing his dark uniform and helmet, is kneeling beside the man. mdns, melbourne district nursing society, mdns uniforms, rdns, royal district nursing service, nursing care -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, 1907
This photograph was taken four years after bicycles were purchased by the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) and is a record of the first mode of transport used by their Trained nurses, and a record of the change of head ware needed now bicycles were in use. The uniforms were grey with white collar, belt and cuffs and a red Maltese cross was in the centre of the pith helmet. Prior to the use of bicycles the trained nurses walked to their patients and had become exhausted, particularly in summer. The bicycles were a solution to this problem, and now they could visit more patients and the Society's areas (districts) could be extended. In February 1885, 50 years after Melbourne was founded, it was recognized that nursing care was needed for the sick poor in inner Melbourne. The Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), the first such Society in Australia, was founded with one Trained nurse, called 'Nurse' in those days, and a second employed six months later. They worked in the now CBD, ie from Spencer Street to Spring Street and from Victoria Parade to Flinders Street. From its inception the Society was at the forefront of health care. They provided high quality nursing care; educated their patients in the curing and prevention of disease; teaching the importance of cleanliness and good nutrition, both by verbal instruction and demonstration, even supplying soup and milk when needed. At that time they walked the streets and lane ways amid the slums of inner Melbourne carrying their nursing bag containing lotion, ointments, powders, liniment, bandages, dressings, a case of spirits, and the Nurse's own clean apron, soap and small towel. They supplied equipment on loan, such as earthenware hot water bottles, splints, urinals, bed pans, bed cradles, feeding mugs, and air-cushions as well as providing blankets, clean bed linen, and nightdresses as necessary. Trained Midwives began home births in late 1893 taking midwifery bundles and providing clothes for the babe and mother as needed. This was arduous work, particularly in the heat of summer. Permission to use bicycles was given to the Nurses in 1898 and the Society decided to purchase their own in 1903. A business man offered ‘new free wheel’ bicycles at £13 each which included maintenance for one year. Bells and wooden frames were added, at a cost of £5 per frame, so the Nurses could carry extra equipment. Nurses’ bags were strapped to the handlebars. Soup was made for those in need 2-3 times a week and if patients could not arrange to have it collected the soup was delivered by the Nurses on their bicycles. The use of bicycles caused a change in uniform, with white pith helmets, and veils covering them and tied under their chin, now being used. The Nurses provided high quality nursing care to a range of people, often in destitute situations, some lying on rags on the floor as they had no bed, others with just a bed and maybe a thin blanket, a chair and nothing else. Their ages ranged from babes, children, adults to the elderly. The Nurses gave medications as ordered by a Doctor, dressed wounds e.g. to the injured, and surgical cases, and to those with leg ulcers; attended to patients with ‘surgical ailments’ such as ‘hip disease’; gave care to those with acute illnesses such as bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, measles, and scarlet fever, as well as those with chronic illnesses such as consumption (tuberculosis), heart disease, arthritis, cancer, debility, neuritis and paralysis. Over the years the Nurses complained that their veils became wet in the rain and asked for a change of uniform but this did not occur until 1921. Bicycles continued to be used in inner areas until 1945. Black and white photo of a group of ten (one partially hidden at rear) Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) trained nurses, with each standing with their bicycles in front of a spiked metal fence.The Nurses are wearing their MDNS uniform long grey frocks with white collar, cuffs and belt and white pith helmets with a central Maltese cross. Nursing bags are strapped to five of the bicycles. A large pedestal urn is seen to the left behind the fence between the 3rd and 4th nurse. Bushes and trees are seen in the background. melbourne district nursing society, mdns, nurses, uniforms, mdns transport, mdns equipment, rdns, royal district nursing service -
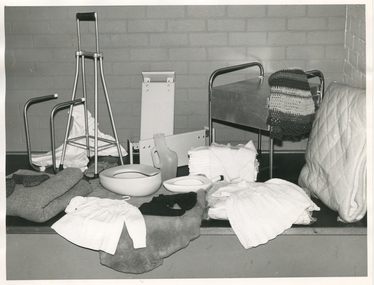 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, Barry Sutton, 1973
The equipment items in this photograph are loaned out to Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) patient's to use in their homes. They are returned to RDNS and sterilized, or cleaned with disinfectant, whichever is appropriate, once they are no longer required. The material items are given to patient's as required. Many of these items are made and donated by RDNS Auxiliary members. From its inception in 1885, the two Trained nurses (Nurses) of the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) worked in the now CBD, ie from Spencer Street to Spring Street and from Victoria Parade to Flinders Street. At that time they walked the streets and lane ways amid the slums of inner Melbourne carrying their nursing bags containing lotion, ointments, powders, liniment, bandages, dressings, a case of spirits, and the Nurse's own clean apron, soap and small towel. They supplied equipment on loan, such as earthenware hot water bottles, splints, urinals, bed pans, bed cradles, feeding mugs, and air-cushions as well as providing blankets and clean bed linen, and nightdresses and clothes as necessary. The Society was at the forefront of health care and continued to liaise with Doctors as the Society expanded. The Nurses provided high quality nursing care to a range of people, often in destitute situations, some lying on rags on the floor as they had no bed, others with just a bed and maybe a thin blanket, a chair and nothing else. Their ages ranged from babes, children, adults to the elderly. The Nurses gave medications as ordered, dressed wounds e.g. to the injured, and surgical cases, and to those with leg ulcers; attended to patients with ‘surgical ailments’ such as ‘hip disease’; gave care to those with acute illnesses such as bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, measles, and scarlet fever, as well as those with chronic illnesses such as consumption (tuberculosis), heart disease, arthritis, cancer, debility, neuritis and paralysis. They educated their patients, and their Carers, in the curing and prevention of disease; Over the years items were given and equipment was loaned and demonstrated to patients, and if appropriate, to their family members to enable them to care for their loved ones in their homes. The Trained nurses had the rehabilitation of their patients in the forefront of their minds to ensure they were able to live as independently as possible in their own homes. As the years passed the Trained nurses changed from being called 'Nurse' to 'Sister' and the Society changed its name. In the 1970s, now with Royal patronage, and known as Royal District Nursing Service ( RDNS), they contracted a Private and then employed, a Physiotherapist who taught RDNS Sisters the correct transferring techniques, including the use of a hoist when this became available. RDNS Sisters taught and used these techniques in patient’s homes to undertake safe transfer of the patient and to reduce physical strain on RDNS nursing staff and family members. Each RDNS Centre had a room or shed where equipment for loan was kept, and Headquarters also kept additional equipment which could be transported to Centres as required. This black and white photograph shows some of the equipment loaned, along with some to be given, to Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) patients as required. Rear L-R - a white long nightdress with dark embroidery and buttons on the front and embroidery on the edge of the short sleeves. Next are two wooden bath seats; a square metal commode with lid and with its round legs extended to form handles on the left and right sides. A folded dark and white striped crocheted rug hangs over one of the handles. In the centre L-R, is a metal bed cradle, a metal 4 prong walking stick, bed pans, male urinal, stack of nappies with a white child's knitted jumper hanging over them, and a doona. In the front, L-R is a grey blanket, dark coloured bed socks, a sheepskin with a white smocked baby dress sitting on it, and a white babies nightgown on a clear plastic covered white bundle. A black mat sits under these items and a cream brick wall is in the background. Barry Sutton LS 47royal district nursing service, rdns, rdns equipment, rdns auxiliaries -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Selection of surgical needles associated with Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson
... is engraved with the text '14G'. Equipment Selection of surgical ...This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Selection of five steel surgical needles. Four of the needles are 3" needles, and the fifth is a 3.5" needle. Each needle consists of a thin, hollow tube that is pointed at one end, attached to a circular fitting by which the needle can be attached to a syringe/vial. Between the circular fitting and the body of the needle is a section of metal with curved sides and squared edges to allow for grip. The grip section of the largest needle is engraved with the text '14G'.14Gsurgery -
 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing Archive
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing ArchiveEquipment - Portable electric suction machine, Clements Suction and Pressure Pump
This equipment was located in the outpatients department (Philip Block) until September 2021 when it was deemed obsolete by Infection Prevention. Hubert Ingham Clements (1886-1969) was an Australian engineer who established his own engineering business in NSW in 1908 manufacturing combustion engines. He became interested in anaesthesia equipment and from the 1920s Clements worked on improving ether apparatus and manufacturing portable suction machines for use in hospital operating theatres. The latter machines were to earn an unrivalled reputation for reliability; many remained in service over thirty years after their date of production. The business became H. I. Clements & Son when his son William joined the company. (https://adb.anu.edu.au/biography/clements-hubert-ingham-12846)Item is an example of equipment from its time period and is of historic significance.Portable Clements Suction & Pressure Pump built by H I Clements & Son Ltd Consists of motor with attached carry handle, attached pressure regulator, attached disposable drainage cannister with tubing and power cable mounted on a trolley with castors.H I Clements & Son Pty. Ltd. Metal Manufacturing label with: Serial Number 1725FS and SAA Certificate Number BCG/4S/60194 on motor (front side) Ward 11 engraved on motor handle AH Biomedical Engineering orange test due sticker and AH Biomedical blue test sticker (reverse side)suction, clements, portable suction, respiratory, pressure pump, surgical drainage -
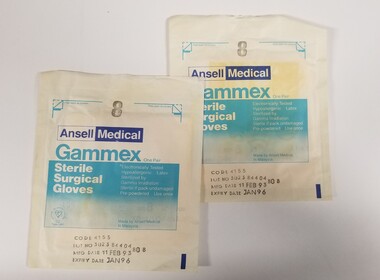 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Gammex surgical gloves associated with Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, 1984
... . Obstetrics Surgery Two sealed packs of Gammex surgical gloves, size 8 ...This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Two sealed packs of Gammex surgical gloves, size 8. Labelling on packaging indicates that the gloves were made by Ansell Medical, in Malaysia, and printing on the packaging indicates that the expiry date for both pairs of gloves is January 1996.obstetrics, surgery
