Showing 2643 items
matching beauty
-
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyMould Candle Making, Circa mid 1900's
Candle stick manufacturing moulds were extensively used throughout the Kiewa Valley and its regions to provide rural homes and businesses with illumination during times of limited light e.g. night time. These candles were used before the Kiewa Valley was placed of the electrical grid. The candles were made from parrafin wax. Before the 1920"s electricity was in limited supply due to the inability of the private electricity suppliers to service isolated rural regions. It was not until the Victorian State Government passed legislation (1920) to improve electricity supplies by forming the State Electricity Commission of Victoria (S.E.C.V.) Isolated rural communities could not meet the higher costs to have electricity supplies connected and therefore it was not until the 1950's that adequate domestic electrical power could be supplied.The isolation that the Kiewa Valley provided was of a greater hindrance to any utility (power,roads & telephone) where the cost per instillation was beyond the rural population's ability to pay either directly or indirectly. One of the benefits that the "closed" community of Mount Beauty had, when it was administered by the SECV was that some utility costs were a lot lower than that of the other settlements in the Kiewa Valley. This disparity led to a conference in 1928 of the rural and regional councils to demand from the Government an equality of electricity tariffs. This equality did not take place until 1965. The demand and usage of cheaper and affordable lighting that wax candles provided was for some rural families a way of life until the mid 1900's.This candle making mould is made from mild rolled sheet steel(tin). The top basin is rectangular in shape with beveled edges(facing in on all sides. There are six holes in the top basin for vertical hollow tubes to feed off. The six tapered cyclindrical tubes running from the top basin to the bottom raised platform base. All connections are welded together. The bottom of each cylinder has an opening for the candle wick. The wick is positioned in place before the molten wax is poured into the cylinders. A positioning ring has been welded to one bottom ring for stability.parrafin wax, candles, domestic household ighting -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyMould Butter, unknown, post 1967
This butter mould/pat may have been manufactured post 1967(year post codes appeared in Australia) however the post code was only stamped on after it was machined. This type of butter mould was used by rural families to fashion home/farm made butter. This period was in most rural regions a time of self sufficiency where any domestic type implement which could be fashioned by the family would be crafted with skill. Shopping for goods required catalogues from stores located in major rural towns and cities and involved lengthy waiting times. Travelling to and from these specialised stores was not pleasant due to the relatively poor quality of the roads and the lengthy times taken. The small general stores in the Kiewa Valley could not cater for all the needs of the valley. The 1960's was a time when facilities especially goods and services started to improve drastically. The S.E.C. of Victoria with its Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme provided not only an improvement of facilities in the valley but also a increase in the population. This increase resulted in a greater demand for local produce. This item is one of many domestic food processing implements used by Kiewa Valley households in the mid 1900s, whether on the farm or in the small towns and hamlets. Self sufficiency was the key to survival during these early times. Where ever possible supplies from within the valley were preferred to that brought in by travelling salesmen or traders. This butter mould and butter pat was commonly used to fashion "home" made butter throughout the valley and in some cases supplied to "outside" regional towns. Although this method of production was phased out by better access to goods from nearby cities the revival of the good organic home grown produce in the 1980s saw a greater demand of this type of farm based produce.This well crafted circular wooden butter mould could also be used as a butter pat.The handle in the middle of the mould was not added after the crafting but has been fashioned from the initial block of wood when the bowl was crafted. The bowl structure has a rim around the edge.The top of the handle has an ink stamp "T. & W. Dav" on the top line and "Tawonga 3697" underneath.domestic food preparation, wooden butter pat, butter mould circular, dairy industry -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPat Butter Profiler, Circa 1950s
This butter pat profiler may have been manufactured post 1967(year post codes appeared in Australia) however the post code was only stamped on after it was machined. This type of butter mould was used by rural families to fashion home/farm made butter. This period was in most rural regions a time of self sufficiency where any domestic type implement which could be fashioned by the family would be crafted with skill. Shopping for goods required catalogues from stores located in major rural towns and cities and involved lengthy waiting times. Travelling to and from these specialised stores was not pleasant due to the relatively poor quality of the roads and the lengthy times taken. The small general stores in the Kiewa Valley could not cater for all the needs of the valley. The 1960's was a time when facilities especially goods and services started to improve drastically. The S.E.C. of Victoria with its Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme provided not only an improvement of facilities in the valley but also a increase in the population. This increase resulted in a greater demand for local produce.This item is one of many domestic food processing implements used by Kiewa Valley households in the mid 1900s, whether on the farm or in the small towns and hamlets. Self sufficiency was the key to survival during these early times. Where ever possible supplies from within the valley were preferred to that brought in by travelling salesmen or traders. This butter mould and butter pat was commonly used to fashion "home" made butter throughout the valley and in some cases supplied to "outside" regional towns. Although this method of production was phased out by better access to goods from nearby cities the revival of the good organic home grown produce in the 1980s saw a greater demand of this type of farm based produce.This butter Pat/Profiler has on its base two patterns. On each end it has horizontal grooves cut into the wood which produce distinct lines onto the surface of the butter. between these grooves there is a section of two double lines crossing in the middle and separated by eleven horizontal lines The base has an elongated rectangular shape. The upper body has been sanded into a smooth convex shaped form where a wooden circular hand grip has been fashioned.On the top of the hand grip is stamped in black print"T. & W. Davies" and under this"TAWONGA 3697"domestic food preparation, wooden butter pat, butter mould circular, dairy industry -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPat Butter, Circa 1950
This butter pat profiler may have been manufactured post 1967 (year post codes appeared in Australia) however the post code was only stamped on after it was machined. This type of butter mould was used by rural families to fashion home/farm made butter. This period was in most rural regions a time of self sufficiency where any domestic type implement which could be fashioned by the family would be crafted with skill. Shopping for goods required catalogues from stores located in major rural towns and cities and involved lengthy waiting times. Travelling to and from these specialised stores was not pleasant due to the relatively poor quality of the roads and the lengthy times taken. The small general stores in the Kiewa Valley could not cater for all the needs of the valley. The 1960's was a time when facilities especially goods and services started to improve drastically. The S.E.C. of Victoria with its Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme provided not only an improvement of facilities in the valley but also a increase in the population. This increase resulted in a greater demand for local produce.This item is one of many domestic food processing implements used by Kiewa Valley households in the mid 1900s, whether on the farm or in the small towns and hamlets. Self sufficiency was the key to survival during these early times. Where ever possible supplies from within the valley were preferred to that brought in by travelling salesmen or traders. This butter mould and butter pat was commonly used to fashion "home" made butter throughout the valley and in some cases supplied to "outside" regional towns. Although this method of production was phased out by better access to goods from nearby cities the revival of the good organic home grown produce in the 1980s saw a greater demand of this type of farm based produce.This butter pat is one of two,see KVHS 0071 (B). It has been crafted from wood. One side has grooves running from the handle to the square shaped bottom. These grooves would stop the wet butter from clinging to the pat. The top side of the pat has been bevelled on both sides and the bottom edge. The hand grip is flat and curved to allow for a comfortable hold.domestic food preparation, wooden butter pat, butter mould circular, dairy industry, butter -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPat Butter Profiler, Circa 1950
This butter pat profiler may have been manufactured post 1967(year post codes appeared in Australia) however the post code was only stamped on after it was machined. This type of butter mould was used by rural families to fashion home/farm made butter. This period was in most rural regions a time of self sufficiency where any domestic type implement which could be fashioned by the family would be crafted with skill. Shopping for goods required catalogues from stores located in major rural towns and cities and involved lengthy waiting times. Travelling to and from these specialised stores was not pleasant due to the relatively poor quality of the roads and the lengthy times taken. The small general stores in the Kiewa Valley could not cater for all the needs of the valley. The 1960's was a time when facilities especially goods and services started to improve drastically. The S.E.C. of Victoria with its Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme provided not only an improvement of facilities in the valley but also a increase in the population. This increase resulted in a greater demand for local produce.This item is one of many domestic food processing implements used by Kiewa Valley households in the mid 1900s, whether on the farm or in the small towns and hamlets. Self sufficiency was the key to survival during these early times. Where ever possible supplies from within the valley were preferred to that brought in by travelling salesmen or traders. This butter mould and butter pat was commonly used to fashion "home" made butter throughout the valley and in some cases supplied to "outside" regional towns. Although this method of production was phased out by better access to goods from nearby cities the revival of the good organic home grown produce in the 1980s saw a greater demand of this type of farm based produce.This butter pat is one of two,see KVHS 0071 (A). It has been crafted from wood. One side has grooves running from the handle to the square shaped bottom. These grooves would stop the wet butter from clinging to the pat. The top side of the pat has been bevelled on both sides and the bottom edge. The hand grip is flat and curved to allow for a comfortable hold.domestic food preparation, wooden butter pat, butter mould circular, dairy industry -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyShaker Spices, after 1895
This item was used at a time when there was a limited range of spices available and sought after by domestic and commercial kitchens. The taste buds of the average Australian diner were limited to the basic English style dishes which had been delivered by the early colonial days. Rural areas where slower in experimenting with Asian and European cuisine. The influx of European cuisine from refugees fleeing both World War I and world War II brought a different appreciation of gourmet food. The increase in Asian spices was brought about by Australians becoming more aware of the Asian "scene" through the conflicts of Korean and Vietnam military action. The "standard" type spices such as Cinnamon, nutmeg and similar spices offered by Robert Harper and later other Food and Spices whole sellers and processors where a direct result of a greater influx of migrants from spices rich societies and resulted in a greater range of "Asian" spices This became more visible after demise of the "White Australian Policy" on immigration and the great media revolution of Televised cooking shows from the 1950s on. The sustainability of containers such as this re-useable tin and cardboard spice holder, which could be replenished and not thrown away after it was empty was it a time period well before the "throw away" society had crept into the Valley.This spice container was used mainly in domestic kitchen within the Kiewa Valley. Those European construction workers of the SEC Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme had brought their continental cuisine into the valley and that was the beginning of a new era in highlighting different tastes. This rural valley had a greater interaction with people from other nation's cuisines and by association became more infused with a broader range of spices and food preparations.This item (spice shaker) is constructed by using a thick cardboard cylinder with both ends closed by tin plated light steel lids. The bottom lid is not removable however the top lid is removable to allow the contents (Cinnamon Spice) to be refilled. The lid has thirteen small holes which allow the contents to be shaken out. The outer side of the cylinder has been covered (glued on) by a printed black and yellow label detailing contents , weight, and supplier.On the front side of the printed label outside of the label boundary is "To make a shaker of this tin - take the lid off and remove the paper from inside the lid" Within the marked horse shoe shaped boundary is" HARPER'S ground spices star brand" underneath "CINNAMON" underneath this is printed "1 oz. NET WEIGHT" and under this, within its own frame " ROBERT HARPER COMPANY LIMITED (incorporated in Victoria) AUSTRALIA." On the back within its own box is "HARPER'S star brand GROUND SPICES" and underneath "These Pure Spices are packed in the following Varieties". Below this is a list (going down) "CINNAMON CARRAWAYS CAYENNE MIXED CLOVES CASSIA CORIANDER GINGER MACE TURMERIC NUTMEGS PIMENTO"kitchen spices, spice shakers, food preparation -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySaucer Ceramic, circa 1940's to 1950's
This item was used by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria in their mess rooms for their workers during the construction of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme. The imprint of the year "1921" was to identify the year that the SECV was formed and relieved the private VHEC (Victorian Hydro-Electric Company). As the scheme was of such a huge, isolated and time consuming nature the feeding of its workers was quite demanding of cutlery and crockery. The use of sturdy English cups and saucers was essential. The period of construction and the isolation of the Kiewa Valley area placed heavy demand for "solid" crockery that could wear abusive handling. This period in time was one when crockery, whether for domestic or commercial use, was imported from "mother" England. This scenario was more so for governmental bodies such as rail, jails and electricity providers than domestic users. The influx of cheaper Asian crockery had not yet begun.This type of crockery item was used by the thousands of SEC Victorian staff and construction workers involved in the building of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme, over the extensive period (1938 to 1961). This was a period when Government bodies and other semi- government organisations were still tied to the "establishments" of "mother" England. It was a period in Australia's development when the Asian influence was very weak and the established ties to England and Europe was still very strong. The majority of heavy equipment and machinery was either made in England or Europe. Local/European expertise in dam construction and water management in alpine terrain came from migrants or specially recruited English and Europe specialists. The quality of workmanship from big steel manufacturing plants in England and Europe could not be matched from anywhere else in the developed world.This item is a white ceramic State Electricity Commission Of Victoria saucer (tea /coffee). It is made in England and is of strong and durable ceramic. The bottom cup indent is for either tea or coffee cups of a similar ceramic structure. The 5mm thickness of the ceramic suggests this saucer belongs to a commercial kitchen environment and not domestic. The indent bottom of the saucer is 5mm deep with a side curvature ratio of 2:5. The ceramic is glazed to a commercial standard (worker's mess). See also KVHS 0128 (B to D)The seal of the State Electricity Commission Of Victoria is imprinted on the top inside rim within a curved scroll. Snuggled within the borders of the scroll is a banner with the five stars of the southern cross and an arm with a closed fist projecting from the top with five lightning bolts projecting outwards. On the underside "Vitrified sold by Cafe & Hotel Supplies Pty Ltd Dunn Bennett & Co. Ltd. Burslem Made in England"saucer, plate, secv, state electricity commission of victoria, crockery, mt beauty chalet, bogong mess hall -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySaucer Ceramic, from 1921 to 1961
This item was used by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria in their mess rooms for their workers during the construction of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme. The imprint of the year "1921" was to identify the year that the SECV was formed and relieved the private VHEC(Victorian Hydro-Electric Company). As the scheme was of such a huge, isolated and time consuming nature the feeding of its workers was quite demanding of cutlery and crockery. The use of sturdy English cups and saucers was essential. The period of construction and the isolation of the Kiewa Valley area placed heavy demand for "solid" crockery that could wear abusive handling. This period in time was one when crockery, whether for domestic or commercial use, was imported from "mother" England. This scenario was more so for governmental bodies such as rail, jails and electricity providers than domestic users. The influx of cheaper Asian crockery had not yet begun.This type of crockery item was used by the thousands of SEC Victorian staff and construction workers involved in the building of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme, over the extensive period (1938 to 1961). This was a period when Government bodies and other semi- government organisations were still tied to the "establishments" of "mother" England. It was a period in Australia's development when the Asian influence was very weak and the established ties to England and Europe was still very strong. The majority of heavy equipment and machinery was either made in England or Europe. Local/European expertise in dam construction and water management in alpine terrain came from migrants or English and European specialist. The quality of workmanship from big steel manufacturing plants in England and Europe could not be matched from anywhere else in the developed world.This item is a white ceramic saucer (tea /coffee). It is made in England and is of strong and durable ceramic. The bottom cup indent is for either tea or coffee cups of a similar ceramic structure. The 5mm thickness of the ceramic suggests this saucer belongs to a commercial kitchen environment and not domestic. The indent bottom of the saucer is 5mm deep with a side curvature ratio of 2:5. The ceramic is glazed to a commercial standard (worker's mess). See also KVHS 0128 (A,C and D) The seal of the State Electricity Commission Of Victoria is imprinted on the top inside rim within a curved scroll. Snuggled within the borders of the scroll is a banner with the five stars of the southern cross and an arm with a closed fist projecting from the top with five lightning bolts projecting outwards. On the underside "Vitrified sold by Cafe & Hotel Supplies Pty Ltd Dunn Bennett & Co. Ltd. Burslem Made in England"saucer, plate, secv, state electricity commission of victoria, crockery, mt beauty chalet, bogong mess hall -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySaucer Ceramic, from 1921 to 1961
This item was used by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria in their mess rooms for their workers during the construction of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme. The imprint of the year "1921" was to identify the year that the SECV was formed and relieved the private VHEC (Victorian Hydro-Electric Company). As the scheme was of such a huge, isolated and time consuming nature the feeding of its workers was quite demanding of cutlery and crockery. The use of sturdy English cups and saucers was essential. The period of construction and the isolation of the Kiewa Valley area placed heavy demand for "solid" crockery that could wear abusive handling. This period in time was one when crockery, whether for domestic or commercial use, was imported from "mother" England. This scenario was more so for governmental bodies such as rail, jails and electricity providers than domestic users. The influx of cheaper Asian crockery had not yet begun.This type of crockery item was used by the thousands of SEC Victorian staff and construction workers involved in the building of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme, over the extensive period (1938 to 1961). This was a period when Government bodies and other semi- government organisations were still tied to the "establishments" of "mother" England. It was a period in Australia's development when the Asian influence was very weak and the established ties to England and Europe was still very strong. The majority of heavy equipment and machinery was either made in England or Europe. Local/European expertise in dam construction and water management in alpine terrain came from migrants and specialist recruited from England and Europe. The quality of workmanship from big steel manufacturing plants in England and Europe could not be matched from anywhere else in the developed world.This item is a white ceramic saucer (tea /coffee). It is made in England and is of strong and durable ceramic. The bottom cup indent is for either tea or coffee cups of a similar ceramic structure. The 5mm thickness of the ceramic suggests this saucer belongs to a commercial kitchen environment and not domestic. The indent bottom of the saucer is 5mm deep with a side curvature ratio of 2:5. The ceramic is glazed to a commercial standard (worker's mess). See also KVHS 0128 ( A,B&D)The seal of the State Electricity Commission Of Victoria is imprinted on the top inside rim within a curved scroll. Snuggled within the borders of the scroll is a banner with the five stars of the southern cross and an arm with a closed fist projecting from the top with five lightning bolts projecting outwards. On the underside "Vitrified sold by Cafe & Hotel Supplies Pty Ltd Dunn Bennett & Co. Ltd. Burslem Made in England"saucer, plate, secv, state electricity commission of victoria, crockery, mt beauty chalet, bogong mess hall -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySaucer Ceramic, Circa 1921
This item was used by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria in their mess huts/rooms for their workers during the construction of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme. The imprint of the year "1921" was to identify the year that the SECV was formed and relieved the private VHEC (Victorian Hydro-Electric Company). As the scheme was of such a huge, isolated and time consuming nature the feeding of its workers was quite demanding of cutlery and crockery. The use of sturdy English cups and saucers was essential. The period of construction and the isolation of the Kiewa Valley area placed heavy demand for "solid" crockery that could wear abusive handling. This period in time was one when crockery, whether for domestic or commercial use, was imported from "mother" England. This scenario was more so for governmental bodies such as rail, jails and electricity providers than domestic users. The influx of cheaper Asian crockery had not yet begun.This type of crockery item was used by the thousands of SEC Victorian staff and construction workers involved in the building of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme, over the extensive period (1938 to 1961). This was a period when Government bodies and other semi- government organisations were still tied to the "establishments" of "mother" England. It was a period in Australia's development when the Asian influence was very weak and the established ties to England and Europe was still very strong. The majority of heavy equipment and machinery was either made in England or Europe. Local and European expertise in dam construction and water management in alpine terrain came from migrants for England and Europe. The quality of workmanship from big steel manufacturing plants in England and Europe could not be matched from anywhere else in the developed world. These saucers were used in the mess huts including later in the Bogong mess hall and the Mount Beauty Chalet.This item is a white ceramic saucer (tea /coffee). It is made in England and is of strong and durable ceramic. The bottom cup indent is for either tea or coffee cups of a similar ceramic structure. The 5mm thickness of the ceramic suggests this saucer belongs to a commercial kitchen environment and not domestic. The indent bottom of the saucer is 5mm deep with a side curvature ratio of 2:5. The ceramic is glazed to a commercial standard (worker's mess). See also KVHS 0128 (A to C)The seal of the State Electricity Commission Of Victoria is imprinted on the top inside rim within a curved scroll. Snuggled within the borders of the scroll is a banner with the five stars of the southern cross and an arm with a closed fist projecting from the top with five lightning bolts projecting outwards. On the underside "Vitrified sold by Cafe & Hotel Supplies Pty Ltd Dunn Bennett & Co. Ltd. Burslem Made in England"saucer, plate, secv, state electricity commission of victoria, crockery, mt beauty chalet, bogong mess hall -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPlate Bread & Butter, Circa 1921
This item was used by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria in their mess rooms for their workers during the construction of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme. The imprint of the year "1921" was to identify the year that the SECV was formed and relieved the private VHEC (Victorian Hydro-Electric Company). As the scheme was of such a huge, isolated and time consuming nature the feeding of its workers was quite demanding of cutlery and crockery. The use of sturdy English cups and saucers was essential. The period of construction and the isolation of the Kiewa Valley area placed heavy demand for "solid" crockery that could wear abusive handling. This period in time was one when crockery, whether for domestic or commercial use, was imported from "mother" England. This scenario was more so for governmental bodies such as rail, jails and electricity providers than domestic users. The influx of cheaper Asian crockery had not yet begun.This type of crockery item was used by the thousands of SEC Victorian staff and construction workers involved in the building of the Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme, over the extensive period (1938 to 1961). This was a period when Government bodies and other semi- government organisations were still tide to the "establishments" of "mother" England. It was a period in Australia's development when the Asian influence was very weak and the established ties to England and Europe was still very strong. The majority of heavy equipment and machinery was either made in England or Europe. Local expertise in dam construction and water management in alpine terrain came from migrants for England and Europe. The quality of workmanship from big steel manufacturing plants in England and Europe could not be matched from anywhere else in the developed world.This item is a white ceramic plate (bread & butter). It is made in England and is of strong and durable ceramic. The bottom of the plate is flat with edges sloping out (to position the bread) and the extended rim is to catch any spillages. The 5mm thickness of the ceramic suggests this plate belongs to a commercial kitchen/eating establishment (mess) and not a domestic dining room. The indent bottom of the plate is 5mm deep with a side curvature ratio of 2:5. The ceramic is glazed to a commercial standard (see KVHS 0128 for its saucer part of a dinner set.The seal of the State Electricity Commission Of Victoria is imprinted on the top inside rim within a curved scroll. Snuggled within the borders of the scroll is a banner with the five stars of the southern cross and an arm with a closed fist projecting from the top with five lightning bolts projecting outwards. On the underside "Vitrified sold by Cafe & Hotel Supplies Pty Ltd Dunn Bennett & Co. Ltd. Burslem Made in England"saucer, plate, secv, state electricity commission of victoria, crockery -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBook - A History of the Kiewa Valley, Kiewa Valley Historical Society, A History of the Kiewa Valley by Esther Temple and David Lloyd, Circa 1991
This book was compiled by Esther Temple and David Lloyd with illustrations by Betty Barberis and additional material provided by Clare Roper, Joan Macdonald, Wilma Davies and Nell Bateman. The book was first penned in 1971. It briefly covers the period from the indigenous tribes(broken down into family groupings) known as the "first Australians" who lived in the valley well before English settlers arrived. first white settlement (graziers, miners, stockmen) to smaller settlements.The development or transformation from a pristine(hunter/gatherer) valley environment to one that has been gradually changing to a more commercial rural/industrial landscaped valley. This transformation was made within a time span of two hundred years. The book details the first pioneers and their descendants, along with the changes to their environments both domestic and commercial. The book highlights dates and events that shaped the "feel" of the valley. The extreme hardships faced by pioneer families during the extremely isolated times away from "civilisation".This publication provides an insight to the struggles and victories against the harsh Australian bushland by people who had not been raised in such a sometimes inhospitable environment. It was this transformation which instilled into the Australian psyche of self sufficiency and the ability to grasp onto ideas or "bush" remedies to overcome enormous difficulties. It is is ability that has produced the many inventions useful in the 20th and 21st centuries.This book has a 250 g/m cream coloured cover with print and drawings of rural aspects of historical significance ( Aboriginal and early white settlers). The book contains 124 pages of black and white photographs(139), black and white sketches(75), two pages of sketches and freehand drawings, two freehand maps one county lease /subdivision plan and black and white printing. See KVHS 0237 (B) for the official invitation to the launch of the book.The front top cover heading(in shaded print and enclosed in a banner form) "A HISTORY OF THE KIEWA VALLEY" The bottom printing "BY ESTHER TEMPLE & DAVID LLOYD ILLUSTRATIONS BY BETTY BARBERIS" and at the very bottom "KIEWA VALLEY HISTORICAL SOCIETY" oN THE BOOK SPINE "A HISTORY OF THE KIEWA VALLEY.....BY ESTHER TEMPLE & DAVID LLOYD"early settlers, dederang, tawonga, mount beauty, sec vic hydro electricity, falls creek early settlers, bonegilla -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyJar Stone Earthenware, circa early 1900s
This type of "stone" jar drinking container was used before glass and later plastic material made it "out of date" as a drink container. The qualities of the glazed pottery (stone) drinking containers made from this natural thermal insulation material was to contain the liquid to a prescribed temperature either hot or cold, as required. This was particularly important in rural environments that lacked adequate refrigeration means. The rural regions where the last areas in Australia where this type of drinking container remained in use. The late 1960's saw a revival of the basic rural ethos by the "hippie" culture of going to basic survival non "commercial" living.This particular stone jar drinking container was also a method of advertising for a Wodonga Stone masonry manufacturer. It is both relevant and significant to the Kiewa Valley because it highlights the type of industry that has breached the evolutionary trend for cheaper "throw away" drinking containers. Although this particular type of container is limited to quality liquids and it is still available in most rural sectors of the Australian "bush" environment.This stone/earthenware jar has a lip 250mm in length and 150mm thick. This lip will allow the thumb and forefinger to be used to grip the container for either pouring its contents out or securing it for any movement. The external glazed surface may become slippery when wet. The jar is heavy even when empty and would be too heavy for small children to carry. By using a cork seal the jar can be reused and therefore become more economical for the longer term. The thickness of the vessel provides a good insulation for the liquid contained. Most of this type of container would have contained ginger beer.Within two elliptical circles are painted (in freehand) "S. MASON" in the top half and "WODONGA" in the bottom half.These are separated by an asterisk on both sides. A large "S" overlaid by a similarly large "M" is within the inner circle. Stamped into the jar when still wet during manufacture is "PINNACLE BRAND" in 5mm lettering.drinking container, stone jar, ginger beer container, s. mason, wodonga earthen ware -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyScoop metal, no makers identification, circa mid to late 1900's
This scoop was professionally made and well before plastics and aluminium scoops were manufactured. It was in a period when mass production and cheap imports where not common. This item would have been produced well after World War II and before the cheap Asian imports. It was a period in time(the last years) when items such as this scoop were made to last and consumerism was not at the "throw away" mass consumption time of the late 1900's. The rural sector in the Kiewa Valley used this type of "made to last" domestic implement when home made cakes and pastries were commonly made in the household kitchen. Because of the relatively isolation of the valley, bulk supplies of flour, sugar and other cooking ingredients were the required quantity for both domestic household and farm use. Local general stores also had these scoops to provide clients with their required flour, sugar and other bulk loose grains (processed or unprocessed) This lite galvanised rolled steel flour/sugar scoop has a tapered handle extruding from a small cone shaped base. It has a half circle scoop extending from a full circular base which has a small containment ridge which acts as a collection rim. The collection scoop has its front shovel end tapered and rolled edge (outwards) presenting a barrier and air relief when thrust into the flour/sugar. All the edges are rolled and connection links have been soldered. The handle is not of solid steel which accounts for the light weight. The base of the "shovel" is slightly concave to allow gravitational forces to keep the flour centre of mass. The handle has a ridge pressed in the sheet metal at about two thirds up the shaft All metal to metal joins have been pressed and soldered together.loose grains, sugar, millet, nus, nails, loose grocery items. -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPot Coffee, Circa 1950
This coffee pot was made for flat heating surfaces and not the open fire. The enamel coating was used as a thermal barrier to keep the contents hot. This could have been used as an all day coffee source for busy farm workers or breakfast and lunch times. When this pot was used at dinner time, it was a time period when dinner was more formal, with the whole family sitting at the dinner table. The white enamel would have been sufficient for the majority of households. When this pot was in use the dinner period was when the whole family was together and communication within the family was considered very important as a cohesive force. This was a time before television intruded into the atmosphere of relaying the day's activities to the whole family.In small rural communities within the Kiewa Valley a good cup of tea or coffee was a time for relaxation from the hard work of the day. This relaxation period was beneficial for not only the mind but also the body. This was particularly for the house bound mother with domestic chores that had, at this time in history not many "time saving" pieces of domestic equipment. A good pot of tea or coffee at "smoko" was a god sent. Although regarded by well groomed city folk that a coffee pot was for coffee only the less social etiquette standards of country folk permitted its use for tea. Versatility even within the household was of great benefit to the folk in the Kiewa Valley. This was even so for the immigrants that joined in and were warmly welcomed within this rural sector of Australia.This coffee pot is in the French style with a goose neck. It is fully coated in white enamel and has a concave bottom. It has a hinged lid and the main body has been rolled fastened to the bottom plate. The sandwiched steel body is approximately 1mm thick. The two piece neck has been welded together similarly the hinged lid and handle. Rivets are installed to the both bases of the handle. country kitchens, well heated coffee, coffee break in rural regions -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, early 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons) and produced. In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "clear" glass. There are other milk bottles that have a "green" tint in them.Around the bottom side of the bottle and blown into the glass "ONE PINT" and on the opposite side "MILK". Below these markings is "This BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLES RECOVERY LTD" below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION. On the base of the bottle is molded a big "M". An identification mark of "90" over "9" is beneath the "M". glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles, milk, dairy, farms, kiewa valley -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid 1800's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the large volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36"This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against sunlight penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it 6/33 and next to this "ONE PINT" and under this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "4"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, circa mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt Beauty.This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head was manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle which contained milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it "6/18" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "3"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
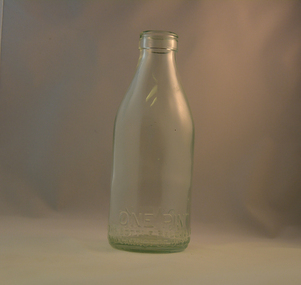 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) until the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt Beauty.This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottle along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it "6/36" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "15" glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up until the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under the house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt BeautyThis heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it "6/18" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "4"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded), until the time that cheaper containers were invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under the house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt BeautyThis heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle, to contain milk, required its thickness because of the extensive handling (man and machine) before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle is a circle within it "6/35" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "20"milk, dairy, glass bottle -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up until the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under the house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt BeautyThis heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottle along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a half pint capacity and is made from "clear" glass. There are other milk bottles that have a "green" tint in them and this tint was to protect the contents from sun damage. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the top half of this bottle is "MILK" and opposite "HALF PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base is "2 M" underneath this "8/11" and underneath is "ISM -169"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle - Ginger Beer, early to late 1900's
This glass ginger beer bottle was manufactured and used early to late 1900's, until the time that cheaper containers were invented(plastic bottles). This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the ginger beer processing plants from the brewing vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1990s the bottle slowly became phased out of production however boutique suppliers still preferred thick glass to contain any explosive action. Two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. were the main suppliers for the Victorian State. In the period when this bottle was manufactured and used the major ginger beer brewing plants for the whole of Victoria were located in Melbourne because this was where its greatest consumer base was there and most rural areas were supplied by domestic sources (mother brewing ginger beer for the children). The Kiewa Valley and its region was one rural area which until road invrastructure was enhance covered the ginger beer thirst by local family production. As the population expanded considerably in the late 1940's (SECV Hydro Scheme) with a greater demand for "soft" drinks" being established supplies from larger towns and cities were call for. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents were from a reputable supplier (H Taylor) and where it originated from. These bottles were recyled by the manufacturer as a way to cut production costs. This method of recycling the bottles back to the specific manufacturer has (except for South Australia)been overtaken by a no cost recycling collection by councils (funded by their communities). This method by passes the user cost principle as the bottles are processed as non generic. The uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic containers however did not provide the keen domestic brewer of the "beer" with a reusable bottle. This heavy gauged glass ginger beer bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the filling production line. The method of pouring ginger beer into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one and a half pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). This thick glass bottle, to contain ginger beer, required its thickness because of the extensive handling (man and machine) before final consumption. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck. Ginger beer was a "soft drink" of great demand. On the middle portion of this bottle is a large elongated circle within it and following the spherical line is "H. TAYLOR" ans a star separates this from "MELBOURNE" rounding out the bottom curviture. Within these words are the large initials "T H" . The "T" superimposed onto the "H". On the base and covering the whole bottom is the letter "T". At the opposite side to the manufacturers logo is "THIS BOTTLE CANNOT BE SOLD OR USED BY ANY OTHER PERSON & IS NOT COMPLETE WITHOUT STOPPER" glass bottle, non alcoholic drink, taylor ginger beer bottle, reuseable bottles -
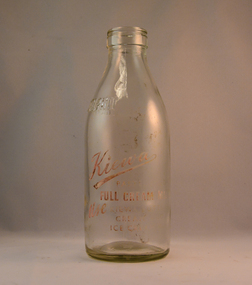 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, Circa mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons) and produced. In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" This particular one has "7/14".This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one Imperial pint capacity and is made from "clear" glass. There are other milk bottles that have a "green" tint in them. Around the bottom side of the bottle and blown into the glass "ONE IMPERIAL PINT". Below these markings and stenciled is "KIEWA" (in freehand style and underlined) underneath is "PASTEURISED FULL CREAM MILK" underneath this ,in freehand stiyle is "USE" next to this in block style "KIEWA BUTTER, CREAM, AND ICE CREAM MIX" to the left of this ,and barely readable is stenciled "THIS BOTTLE ALWAYS REMAINS/ THE PROPERTY OF/ NORTH EASTERN DAIRY Co. Ltd". On the base of the bottle is molded a big "2". with a smaller "m". An identification mark of "7" over "14" is within a circled boundary. Below this is moulded "RM - 15". glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Ginger Beer, circa mid to late 1900's
This glass ginger beer bottle was manufactured and used early to late 1900's, until the time that cheaper containers were invented(plastic bottles). This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the ginger beer processing plants from the brewing vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1990s the bottle slowly became phased out of production however boutique suppliers still preferred thick glass to contain any explosive action. Two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Australian Glass Manufacturers and the Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. were the main suppliers for the Victorian State.In the period when this bottle was manufactured and used the major ginger beer brewing plants for the whole of Victoria were located in Melbourne because this was where its greatest consumer base was there and most rural areas were supplied by domestic sources (mother brewing ginger beer for the children). The Kiewa Valley and its region was one rural area which until road invrastructure was enhance covered the ginger beer thirst by local family production. As the population expanded considerably in the late 1940's (SECV Hydro Scheme) with a greater demand for "soft" drinks" being established supplies from larger towns and cities were call for. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents were from a reputable supplier (PHIBBS Bros) and where it originated from. These bottles were recycled by the manufacturer as a way to cut production costs. This method of recycling the bottles back to the specific manufacturer has (except for South Australia)been overtaken by a no cost recycling collection by councils (funded by their communities). This method by passes the user cost principle as the bottles are processed as non generic. The uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic containers however did not provide the keen domestic brewer of the "beer" with a reusable bottle.This heavy gauged glass bottle (Ginger Beer) has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the production line. The method of pouring ginger beer into the bottle has been part of the "production line" process of automation. This bottle has a capacity to hold 250ml of ginger beer and is made from "clear" glass. The marority of ginger beer bottles produced in this time frame where made with a "green" tint in them.This tinting helped reduce the sunlight effecting the contentsAround the bottom side of the bottle and blown into the glass is "THIS BOTTLE IS THE PROPERTY OF PHIBBS BROS, ALBURY" above this, in "running script" and sloping up from left to right is "Phibbs Bros" and underneath parallel to it "ALBURY". On the base of the bottle is molded a big "L 289" underneath this "M" and below this "AGM".ginger beer bottle, soft drink bottles, cordial bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBadge Girl Guides, circa mid to late 1900's
This commemorative badge identifying the wearer as a Girl Guide and was used in the 1970's and later. The Girl Guides "World Camps" was founded in 1924 and each subsequent "camp" was in other global countries. The Camp Baree was held in 1947/1948 in Pennsylvania in the USA. In Victoria, Australia, a Barree Regional location for Girl guides, encompasses the Kiewa Valley and its regions. Girl guides in rural areas covered the same developmental programs as in the city areas but the bush settings of annual camps did not have the same impact as for city based guides. The comradeship however, bringing together girls from a widely diverse background, was still a very important objective of the Girl Guide movementThe significance of this badge is that the Girl Guides held a World Camp in the Barree region which included the Kiewa Valley.This world wide attention(Girl Guides) to this region paid special attention to the "home side" girls and highlighted in particular those girls in the Kiewa Valley who participated in the Girl Guide movement. The ability to have such a personal contact with so many girls from so many world regions helped to break the somewhat isolated regional life. The fundamental lessons of the girl guides was and still is to enrich young girls knowledge of skills which provides self esteem, pride in achievements and the togetherness with like minded girls. Social barriers are left behind and good friendships are formed. Some of these friendships continued as life long links.This round badge made from brass and has coloured enamel sections outlining various "Barree Region" scenery. In the far distant horizon are snow capped mountains. These are coloured brown with white tipped summits.The central focus is a blue stream with a dark blue "gum" tree to the left and a brass etched tent pegged onto green grass. These pictures are framed within a house structure. A red coloured boomerang lies under the "house" frame with the name of the region on it,"BARREE REGION" The badge is fastened onto a lapel or other clothing by two "L" shaped hooks extending from the back of the badge.On the front of the badge (on the sketched boomerang "BARREE REGION". On the back in raised lettering is"BERTRAM BROS MELB."societies, girl guides, barree region, metal identity badges -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBadge Boy Scout, circa mid to late 1900's
This badge, which was used in the mid to late 1900's (Scouts started in Australia in 1909) clearly demonstrates that the families in the Kiewa Valley although slightly remote were still able to participate in one of the prime "boy" only social groups. The Boy Scouting movement brought together boys from all the socio-economic areas in the Australian population. The scouting group applied the concept of self sufficiency and friendship to all its membership. It was an avenue to cross the boundaries of distance and regional mores. Many of the boys in the Kiewa Valley and its regions would have been more "in tune" with the core principles of the scouting movement because being in a rural environment and "living on the land" was a day to day part of their life. What was an important aspect to they was the "mateship" and the belonging to a very large, and international, group of "like minded" boys. This avenue of interacting with a larger group of boys cut through the "small population" mores of a rural and at times isolated environment. This Boy Scouting activity was both mentally and physically significant to growing boys within the Kiewa Valley as it opened up the world to them.This brass badge has a front formed in a half circle base supporting a "Fleur de Leis" in a spear shape with "cut outs" at the appropriate places to provide the emphasis needed to project the form. Attached to the badge is a crescent moon shaped pronged frame for attaching the badge to lapels or collars or button eyelets. On the bottom scroll "BOY SCOUTS" and on the back type fastener "STOKES & SONS" below this "Melb".societies, boy scouts, apparel badges, numismatics badges -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBadge Red Cross, circa 1968
When this winter appeal badge was produced the Australian economy was in recession (financial down turn) and the ability of some of the unemployed sectors of the community required but could not purchase warm clothes. The Australian recessions of 1945 and 1961 left their mark on the economy and accounted for a long and slow recovery in the 1960's and 1970's. The Red Cross was one of a few benevolent agencies/organisations that provided those more affluent in society to donate money to these types of appeals for financial donations. the money collected was used in obtaining warm close for those in need.In the Kiewa Valley the lingering recessional consequences (high interest rates, slowdown in Australian manufacturing) had an effect upon those whose produce was consumed by large towns and cities. The manufacturing industries including textile and clothing industries were feeling the start of the invasion of cheaper imports. Unemployment was beginning to be an ongoing major political and social issue. The need for support for the financial strapped city and country towns was on the increase and this Red Cross Badge (Winter Appeal) was one of several appeals to help those financially disenfranchised families to overcome the severe clothing shortages in both country and city environments.This badge has an enamel front with red and blue lettering and the circumference is marked to represent a 'life ring, life buoy, life belt' which has all of the red lettering with in its boundary. The fastening mechanism is a "stick" pin made from mild steel (fashioned as a semi circular spring contained within the back rim of the badge. The "stick" protrudes beyond the badge allowing it to be fastened onto clothing.At the top of the badge and in red print "RED CROSS" and at the bottom "WINTER APPEAL" with a"1/-" (one shilling coin - modern equivalent to 10 cents). In the middle of the badge is printed a red cross and above that "HELP"societies, red cross appeals, apparel badges, numismatics badges -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyContainer Postage Stamps, circa early 1900's
This unique postage stamp container, fashioned as a postal letter is from an era 1800 to early 1900, when items with no real bravado of wealth, were produced to satisfy the basic needs of their owners. A small yet "simple" postage stamp container made from silver would stand out but yet not that "vulgar". This was a period that flouting wealth was not done. This attitude changed when "old" wealth of property and titles moved to industrial and merchant "new" wealth merged.This item was introduced to the Kiewa Valley by a "genteel" woman who had come from "old" wealth in the "mother" country. In rural Australia such flashing of wealth or even "one up man ship" is frowned upon. The Kiewa Valley residents, in this time frame, would have reacted in a "true blue" manner. The significance of this item is that it highlights a time when the "Australian" heart was closely aligned to "mother Great Britain". These national bindings and self identity were only to last until World War II. The realisation of untying the national umbilical chord between Great Britain and Australia came when the United States of America provided its support and a closer bond developed. This container for postal stamps is fashioned as a letter. The lid(flap) is hinged to the main letter frame, allowing access to the contents (stamps). It is made of thin silver (sterling) with the silver markings on the inside of the flap. The folds on the opening flap side mirror the early dated letter envelope (glued on two sides, folded and glued on the third). The markings on the inside, clearly visible when the flap is open has the Assay Office Birmingham "anchor" stamped before the sterling silver "lion" mark. Stamped on inside flap "92" and "M" .Inside the letter facing the opener is the "Anchor" symbol and next to that the "Lion" symbolpostal stamp container, stamps, envelopes -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyScales Weighing, early 1900's
Although these scales cannot be identified against a historical period of Australian development they are therefore placed in a time frame when commercial markings from manufacurers were not important enough to have domestic kitchen items labeled. These cast iron scales were made for domestic and possibly rural areas and not for cities where demand for known branded utensils was more an issue. These scales are very "basic" and not to the level of weighing detail that commercial scales had to be at. These scales do not show any visible markers for accurate measurement. The "near enough is good enough" principle can be related to these scales.These scales are significant as they identify one of the basic preparation items for the weighing of foodstuff before the televising of "cooking" shows (1960s onward). The meals for which quantity measurements are required for domestic cooking is not exact however the use of cup measurements for large dishes is tedious and these scales offer the capacity for a larger mixture and an easier method for the "cook". As the need for accurate measurements of ingrediants for rural domestic meals has in the past been not been critical the requirement of accuracy that these scales do not provide is of no consequence. Domestic kitchens in the Kiewa Valley and the type of meals produced would not have required the accuracy of ingrediants that "modern " international cuisines of the later 1900's require. These kitchen scale were used whenrecipes had the terms "pinch, dollop, squidge and smidgen" were about as accurate as most recipes needed to be.Black cast iron, medium weighing scales, with a two arm cradle. On one side of the cradle is a two half circle holding frame for the retention of the metal container scoop. This light weight steel scoop/dish allows for the weighing of loose grain or similar type material to be contained and held in place for establish its saleable contents. On the other side of the weighing cradle is a flat circular platform to hold various metal disc. All the disks used on this platform have their weight stamped on them. When the produced filled in the scoop balances with the metal weight on the opposite end of the balance match (visual horizontal appraisal) the appropriate quantity required is obtained. This scale does not have any visual markings on the arms to identify a true balance. It is therefore reasonable to assume that these scales were for domestic use only and not for commercial transactions. There are two weights that are useable with these scales, one is stamped "1 lB"(pound) and one stamped "1" and both are made as a solid round piece of cast metal.The smaller disc has a "1 lb" moulded and pressed form within a marked inner circle and a mouled ridge outer circle enclosure. The other weight is slightly larger and has a moulded "1" located on the top within a raised circular edge.domestic kitchen scales, weighing scales, metal scales
