Showing 2209 items
matching 1920s
-
 8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental Collection
8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental CollectionTrophy, McClure Cup
Battery Quartermaster Sergeant Harold Bauerle served with the Albury Battery in the 1920s and 1030s. Shortly following Federation the military unit in Albury was redesignated No 4 New South Wales Battery Australian Field Artillery (AFA). It was under the command of Major John Wilkinson, an Albury solicitor and comprised about 100 citizen soldiers, 4 guns and about 40 horses. Training centred on the Albury Drill Hall located in Victoria Street. A reorganisation in 1912 resulted in the Battery being named No 17 Battery AFA. When war broke out in 1914 the Battery then under the command of Major Joseph Shellshear, and Albury doctor, offered its services as a trained artillery battery to the Australian Imperial Force (AIF). The Battery cooled its heels and continued to train till July 1915 when a second division was raised in the AIF and trained artillery was needed. When the call came 150 officers and men of the 17th Battery went into the AIF, many to the 13th Battery with Major Shellshear in command and others to other AIF batteries of the 4th and 5th Artillery Brigades. The 13th Battery was adopted immediately by the townsfolk of Albury as the Albury Battery. The Battery served in France and Belgium and was involved in all the major battles fought by the Australians perhaps most notably at Noreuil where the Battery found itself surrounded but continued to fight till eventually the enemy was driven back. Following the war members of the Battery nominated this battle as their most significant achievement and consequently a newly developed recreational reserve on the Murray River foreshore was named Noreuil Park. In 1919 the Battery resumed training as part of the Citizen Military Forces or Militia. Changes of title were frequent, first 27th Battery, then 60th Battery and finally 40th Battery AFA. Battery commanders included Captain Leslie Colquhoun, an Albury real estate agent, Captain Roy Collings, Albury town clerk and Captain Clifton Mott a newspaper editor. The Depression of the early 1930s almost brought about the closure of the Albury Battery but it survived through the intervention of the mayor, Alderman Alfred Waugh, who made direct representation to the Minister for Defence. When the Second World War erupted in 1939, the Battery was at full strength and a rich source of officers and trained men for the second AIF. Militia training of the few remaining officers and Albury adopted the 2/23rd Infantry Battalion which had been raised at the Showground. Following WWII, CMF soldiering recommenced in the form of an armoured regiment, the 8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles. After nearly a half a century of service in war and peace the Albury Battery has faded and exists now in this collection of objects and images. This trophy is representative of community support for a Citizen Military Forces unit drawn from a regional NSW Town in the period between the World Wars.Silver cup with two handles mounted on Bakelite base being the McClure Cup for most efficient NCO in Albury Battery 1935-36 . inscription on side of cup."McClure Cup / for / Most efficient NCO / 1935-36 / won by / BQMS H.C. Bauerle"bauerle h c bqms, albury battery, mcclure cup -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncDomestic object - Haeusler Collection Lactogen baby formula measuring spoon c.1920s
The Wodonga Historical Society Haeusler Collection provides invaluable insight into life in late nineteenth and early twentieth century north east Victoria. The collection comprises manuscripts, personal artefacts used by the Haeusler family on their farm in Wodonga, and a set of glass negatives which offer a unique visual snapshot of the domestic and social lives of the Haeusler family and local Wodonga community. The Haeusler family migrated from Prussia (Germany) to South Australia in the 1840s and 1850s, before purchasing 100 acres of Crown Land made available under the Victorian Lands Act 1862 (also known as ‘Duffy’s Land Act’) in 1866 in what is now Wodonga West. The Haeusler family were one of several German families to migrate from South Australia to Wodonga in the 1860s. This item is a Nestlé Lactogen baby formula measuring scoop used in the preparation of formula for bottle feeding. It was used by Ilma Margaret Ernestine Haeusler (née Tasker, b.1900 in Tallangatta) to feed her son Alfred who was born in 1922. Ilma died in childbirth in 1928. This measuring spoon is one of several objects in the Haeusler Collection concerning early childhood that provide insight into family and home life in early twentieth century Wodonga. The first fully artificial infant milk formula, Farine Lactee, was developed in the 1860s. Companies continued to attempt to develop synthetic formulas which nutritionally replicated human breast milk in the decades that followed. Nestlé began producing Lactogen in 1921. It was marketed to women as a nutritionally superior substitute for breast milk, and as a nutritional supplement for breast feeding mothers. From the 1920s, when the Haeusler Collection measure was produced and used, Nestlé employed nurses in major Australian cities to promote Lactogen and its supposed health benefits to new mothers. They also used print advertisements to offer free product samples and instruction booklets advising on pregnancy and infant care for the same purpose. Nestlé was formed in 1905 by the merger of the Anglo-Swiss Milk Company, established in 1866 by brothers George and Charles Page, and Farine Lactée Henri Nestlé, founded in 1866 by Henri Nestlé. The company grew significantly during the First World War and again following the Second World War, expanding its offerings beyond its early condensed milk and infant formula products. In the twenty-first century, Nestlé has faced criticism and boycotts over its decision to market baby formula as an alternative to breastfeeding in developing countries. The adoption of bottle feeding in countries without access to clean water and sanitation infrastructure has contributed to high infant mortality rates. This item has well documented provenance and a known owner. It forms part of a significant and representative historical collection which reflects the local history of Wodonga. It contributes to our understanding of domestic and family life in early twentieth century Wodonga, as well as providing interpretative capacity for themes including local history, social history, and women’s history.Silver toned alloy measuring spoon for Lactogen infant formula, produced by food and drink manufacturing company Nestlé. Embossed with the Lactogen brand name, and teaspoon and tablespoon measurements. "LACTOGEN MEASURE" on central handle/"TABLESPOON" on large inner scoop/"TEASPOON" on small inner scoopchildren, babies, household, domestic, motherhood, family, kitchen -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Panton Hill Primary School, 27 March 2008
The Panton Hill Primary School building, which has served the community since 1889, was not the area's first. Kingston School (an early name for Panton Hill) opened in May 1865. This was replaced in 1871 when the Panton Hill School number 1134 opened and in 1874 the school moved to its current location [September 2023] where many additions and renovations have taken place to meet the needs of local children in the 21st century. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p63 The Panton Hill Primary School building, which has served the community since 1889, was not the area’s first. In 1871 Henry Edelman opened a Common School in a paling-clad hut, replacing the Kingstown No 786 school. The two-acre (0.8ha) site of crown land had previously been held under Miners Right. In 1875 the Education Department bought a building on the main road for State School No 1134, for £200 and remodelled it as a school.4 Panton Hill had as one of its teachers, Frank Tate, who was to become one of Victoria’s most influential educational reformers. It was his first school, when he began teaching on January 22, 1884, as a 20 year old.5 The following month Robert J Harris was appointed to the school and remained as head teacher until his death in 1887. His son R C Harris was apprenticed to Mr Rossiter, editor of the first local paper. The Evelyn Observer, first published in 1873. Harris later bought the newspaper which remained a family business until the 1920s. J Hughes of Cherry Tree Road succeeded Harris as teacher at Panton Hill and sold his land for the school site. Though now unrecognisable, the school building includes the classroom of the last Smiths Gully State School No 1737, which was built in 1882, and moved to Panton Hill in 1894. From 1922 each school day began with the ringing of the bell, which is still in its stand, and is an unusually old memorial of this kind. To accommodate the growing population, the building was remodelled, with additions in 1923 and classrooms were added in 1955, 1963 and 1970. The former teacher’s residence is the only surviving 19th century dwelling in the centre of Panton Hill, and is now used as part of the school. The residence was originally rectangular but is now L-shaped. Similar weatherboard State School buildings in the shire from this period are the Kangaroo Ground and the St Andrews Primary Schools. All were standard Education Department/Public Works Department designs.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, panton hill primary school -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Dr Roy Phillips, 8th October 2000 (exact date unclear)
Roy Phillips was born in 1907 in Yackandandah and moved with his family to Beechworth when he was five years old. His father was involved in dredging operations at Lake Sambell but his parents also had other family living in Beechworth, with whom they lived. Dr Phillips tells vivid stories about life in Beechworth in the first half of the Twentieth Century, from the daily lives of young children of the time to the town's relationship to the local Chinese community. He discusses features of the landscape such as 'The Rock' at which community concerts were held and 'The Echo' (an echo-sounding point over a nearby gully) which he states are no longer used in the same way. He also discusses changing community attitudes to various issues, for example, 'not being coddled' as a child but living in a town with very strict rules about people of different religions mingling. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Dr Roy Phillips' account of his life in Beechworth in the early part of the 20th Century is historically and socially significant to the cultural heritage of the region. He describes town life from a child's point of view during a time of transition to life after the Gold Rush era, including social tensions existing between cultural groups such as the Chinese community and European-heritage townspeople and between people of different religious groups in Beechworth. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Dr Roy Phillips /beechworth, yackandandah, wangaratta, mining, dredging, 1910s, 1920s, 1930s, chinese community, typhoid, lake kerferd, reminiscences, memories, childhood, lake sambell, alcoholism, new year celebrations, transport, horses, foresters lodge, oddfellows lodge, funeral practices, child-rearing practices, star hotel, the rock, racism, chinese dragon, benevolent society, star lane coach building factory, outdoor concerts, gold, jimmy ingram, kelly gang, kelly family, churches, catholic, methodist, protestant, anglican, confuscionist, buddhism, women's christian temperance association, hotels, twentieth century, coronation of king george iv, echo point, the echo, tippany cat, marbles, children's games, cornish, cornwall, listen to what they say, oral history -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Peter Pidgeon, Graves of George and Janet Bird and family, Eltham Cemetery, Victoria, 5 April 2021
George Bird was born in England in 1845 and arrived in Australia in 1856 as a child of assisted migrants. Soon afterwards he came out to Eltham to live with his uncle George Stebbings, working for him as bricklayer's assistant in building, amongst others, Shillinglaw Cottage and the Anglican and Methodist Churches in Eltham. He later purchased 72 acres at the eastern end of Pitt Street (bounded by Eucalyptus Road, Mount Pleasant Road and present-day Rockliffe Street) and established the property ‘View Hill’, which was worked as a mixed farm and orchard (including berries). In 1878 he married Janet Kilpatrick, who had emigrated from Scotland. They had ten children, three of whom died in infancy. The wedding in 1904 of their eldest surviving daughter Sarah (‘Sis’) to Edward Pepper appears to have been quite a society event. George was a staunch Methodist and was a Church Steward and a Sunday School Superintendent in about 1890. Janet died in 1915 and George died in 1920 (though his gravestone says 1921). George's will stated that his property was to be divided between all his children in equal shares. This necessitated subdivision of the View Hill property, which took place progressively between 1922 and 1926. One son, George Hugh Bird, operated a drapery store in Main Road (near Bridge Street) in around 1915. Later, in the 1920s, he ran a greengrocer's shop (also selling confectionery) in Main Road opposite Eltham Station. It was the first shop in Eltham to have plate glass windows. At the same time, his brother Reg had a grocery store on the station side of Main Road. George and Janet are buried together in a family plot in Eltham Cemetery. Several descendants are also buried in the cemetery. In Loving Memory Of George Bird Died 5 December 1921 aged 76 years And his beloved wife Janet Bird Died 5 Sept 1915 aged 57 years Also their children William James Bird Died 25 Feb 1888 aged 8 years Mary Jane Bird Died 8 Oct 1891 aged 7 years Pte Edwin John Bird Killed in action in the Great War 11 Aug 1918 aged 30 years Buried in France And on the base stone George Hugh Bird Died 26 Feb. 1965. Aged 79 years Arthur Andrew Bird Died 25 Mar. 1970 Aged 75 years To the left In Loving Memory of Dr. J. R. (Roger) Bird 1927 2001 Son of Arthur & Helen (nee Lyon) Bird Husband of Betty Father of Janet & Alison Grandpa of Evan & Helen Scientist & Gentleman To the right In Loving Memory of Harold Edwin Bird OAM 1922 - 2015 Son of Arthur & Helen (nee Lyon) Bird Husband of Yvonne Father of Estell & Russell In our hearts Forever moreBorn Digitaleltham cemetery, gravestones, arthur andrew bird, arthur bird, edwin john bird, george bird, george hugh bird, harold edwin bird, helen bird (nee lyon), j. r. (roger) bird, janet bird (nee kilpatrick), william james bird, yvonne bird -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncNegative - Photograph, Harry Gilham, Grave of Christopher Watson, Eltham Cemetery, Victoria, 1 Aug 2007
George Bird was born in England in 1845 and arrived in Australia in 1856 as a child of assisted migrants. Soon afterwards he came out to Eltham to live with his uncle George Stebbings, working for him as bricklayer's assistant in building, amongst others, Shillinglaw Cottage and the Anglican and Methodist Churches in Eltham. He later purchased 72 acres at the eastern end of Pitt Street (bounded by Eucalyptus Road, Mount Pleasant Road and present-day Rockliffe Street) and established the property ‘View Hill’, which was worked as a mixed farm and orchard (including berries). In 1878 he married Janet Kilpatrick, who had emigrated from Scotland. They had ten children, three of whom died in infancy. The wedding in 1904 of their eldest surviving daughter Sarah (‘Sis’) to Edward Pepper appears to have been quite a society event. George was a staunch Methodist and was a Church Steward and a Sunday School Superintendent in about 1890. Janet died in 1915 and George died in 1920 (though his gravestone says 1921). George's will stated that his property was to be divided between all his children in equal shares. This necessitated subdivision of the View Hill property, which took place progressively between 1922 and 1926. One son, George Hugh Bird, operated a drapery store in Main Road (near Bridge Street) in around 1915. Later, in the 1920s, he ran a greengrocer's shop (also selling confectionery) in Main Road opposite Eltham Station. It was the first shop in Eltham to have plate glass windows. At the same time, his brother Reg had a grocery store on the station side of Main Road. George and Janet are buried together in a family plot in Eltham Cemetery. Several descendants are also buried in the cemetery. In Loving Memory Of George Bird Died 5 December 1921 aged 76 years And his beloved wife Janet Bird Died 5 Sept 1915 aged 57 years Also their children William James Bird Died 25 Feb 1888 aged 8 years Mary Jane Bird Died 8 Oct 1891 aged 7 years Pte Edwin John Bird Killed in action in the Great War 11 Aug 1918 aged 30 years Buried in France And on the base stone George Hugh Bird Died 26 Feb. 1965. Aged 79 years Arthur Andrew Bird Died 25 Mar. 1970 Aged 75 years To the left In Loving Memory of Dr. J. R. (Roger) Bird 1927 2001 Son of Arthur & Helen (nee Lyon) Bird Husband of Betty Father of Janet & Alison Grandpa of Evan & Helen Scientist & Gentleman To the right In Loving Memory of Harold Edwin Bird OAM 1922 - 2015 Son of Arthur & Helen (nee Lyon) Bird Husband of Yvonne Father of Estell & Russell In our hearts Forever moreeltham cemetery, gravestones, memorials, arthur andrew bird, arthur bird, edwin john bird, george bird, george hugh bird, harold edwin bird, helen bird (nee lyon), j. r. (roger) bird, j.r. (roger) bird, janet bird, janet bird (nee kilpatrick), william james bird, yvonne bird -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Peter Pidgeon, Main Road, Eltham, 2 Aug. 2022
Comparison photo: SEPP_0610 - Main Road near Railway Station, c.1911 Shows Luther and Ada Haley’s General Store, Bakery and Tea Rooms opened September 1902 directly opposite present day Arthur Street. This was the first building in what is now Eltham’s present shopping town centre. Haley previously ran the General Store and Bakery on the corner of Main Road and York Street until his lease expired and the premises were bought by Mrs Sarah Burgoyne in 1902. Haley sold the store to Hannah Lloyd in 1917 who operated it until 1920. It then went through a succession of owners until Eric Staff purchased it in 1939. Ray Staff succeeded his father in 1954 and eventually demolished the store in 1965 opening up a new supermarket, the Eltham Big Star Food Centre. That building still stands at 929 Main Road and is the Nongkhai Thai Restaurant. On the eastern (right) side of Main Street is Haley’s Paddock, which was used on occasions for community picnics. Capable of holding 10,000 people, with ample shade and hilly surroundings it was an ideal place for any community gathering such as the State Schools’ Picnic in 1904. It was not until the early 1920s that stores started to appear between Luck and Dudley Streets. Part of a presentation by Peter Pidgeon to the Society, 13 August 2022 showcasing a series of photographs taken by John Henry Clark over the period 1895 to 1930. John Henry Clark was the youngest of three boys born to William Henry Clark (1823-1877) and Maria White (1843-1914). He and his brothers, William Charles Clark (1872-1945), Clement Kent Clark (1874-1912) operated a photography business (Clark Bros.) from 25 Thomas Street, Windsor near Prahran during the period c.1894 to 1914. Following death of Clement in September 1912 and their mother in 1914, the Clark Bros business appears to have dissolved, the premises demolished, and a new house was under construction in 1915. John set up business independently in 1914 operating out of 29 Moor Street, Fitzroy where he is registered in the 1914 and 1915 Electoral Rolls. By 1916 John had relocated to Eltham where he continued his practice as a photographer and took many of the early images around the district of Little Eltham. Around 1930 John changed professions and opened a small cobbler's shop in 1931 near the pond opposite Dalton Street adjacent to the Jarrold family cottage. He never married and continued his profession as a bootmaker from this little shop, maintaining a close relationship with Mrs Jarrold for the rest of their lives. His bootmaker shop remains today beside the Whitecloud cottage and is one of only three remaining shops in the area from the early 20th century.Comparative photo taken 2022 with one taken from same location over 100 years earlier by noted local photographer J.H. ClarkBorn Digitaleltham, j.h. clark photo (2022), main road -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph (item), J.H. Clark, View of Eltham from Main Road, c.1907
An F-class 2-4-0 steam locomotive and tender hauls a train of two open wagons, a guards van and a single Tait passenger car over the Eltham Railway Trestle Bridge, heading for Melbourne. This type of steam locomotive was replaced by the F-Class 2-4-2. The house on the right, originally known as 'Derril' was purchased in the early 1920s by Walter Ernest and Alice Miriam Gahan. On the western side of Main Road near the present-day site of Shillinglaw Cottage, they remained till about 1960 when Walter died. The house was demolished in 1968 during the widening of Main Road. In the distance beyond the trestle bridge on what would become Central Park appears to be an orchard of fruit trees. A young man with waist coat, jacket and hat stands beside an older man wearing suspenders without jacket and bare headed, sitting on the post fence. Photographer: J.H. Clark John Henry Clark was the youngest of three boys born to William Henry Clark (1823-1877) and Maria White (1843-1914). He and his brothers, William Charles Clark (1872-1945), Clement Kent Clark (1874-1912) operated a photography business (Clark Bros.) from 25 Thomas Street, Windsor near Prahran during the period c.1894 to 1914. Following death of Clement in September 1912 and their mother in 1914, the Clark Bros business appears to have dissolved, the premises demolished, and a new house was under construction in 1915. John set up business independently in 1914 operating out of 29 Moor Street, Fitzroy where he is registered in the 1914 and 1915 Electoral Rolls. By 1916 John had relocated to Eltham where he continued his practice as a photographer and took many of the early images around the district of Little Eltham. Around 1930 John changed professions and opened a small cobbler's shop in 1931 near the pond opposite Dalton Street adjacent to the Jarrold family cottage. He never married and continued his profession as a bootmaker from this little shop, maintaining a close relationship with Mrs Jarrold for the rest of their lives. His bootmaker shop remains today beside the Whitecloud cottage and is one of only three remaining shops in the area from the early 20th century. There are a couple of images of Eltham taken by Clark Bros. in the Eltham District Historical Society collection, one such example being Hunniford’s Post Office with Miss Anne Hunniford out front (EDHS_00140 - marked on the back of the print, Clark Bros., 25 Thomas St. Windsor), which would date this image between c.1894 and 1914. Other early images of Eltham taken by John Henry Clark are marked on the face “J. H. Clark Photo” and it is assumed these are dated between 1914 and 1930. It is noted that the Grant of Probate for John H Clark of Eltham South dated 5 April !957 (513/387) records his occupation as "X Photographer".derril, eltham railway trestle bridge, f-class 2-4-0 steam locomotive, gahan house, j.h. clark photo, main road, orchards, postcards, steam train, tait train, victorian railways -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Chair, 1897-1921
These cane chairs are one of many 19th century items of furniture, linen and crockery donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by, Vera and Aurelin Giles. The items are associated with Warrnambool and the Giles Family history. Items donated by the family have come to be known as the “Giles Collection”. Many items in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage were donated by Vera and Aurelin Giles and mostly came from the home of Vera’s parents-in-law, Henry Giles and his wife Mary Jane (nee Freckleton) who married in 1880 and whose photos are on display in the parlour. Henry was born at Tower Hill in 1858, and was a labourer on the construction of the Warrnambool Breakwater before leaving in 1895 for around seven years to build bridges in NSW. Mary Jane was born in 1860 at Cooramook and she attended Mailor’s Flat State School and where she eventually was to become a student teacher. After which she became a governess at “Injemiara” where her grandfather, Francis Freckleton, had once owned land. Henry and Mary’s family consisted of six, some of the children were born at Mailor’s Flat and later some children at Wangoom. They lived with their parents at Wangoom and Purnim west, and this is where Henry died in 1933 and Mary Jane in 1940. Heywood & Wakefield Furniture Co: The Heywood-Wakefield Company is an American furniture manufacturer established in 1897. It went on to become a major presence in the US. Its older products are considered collectibles and have been featured on television antique programs. The Heywood brothers established themselves in 1826, as furniture makers and the Wakefield Company began in 1855 as a separate company. Both firms produced wicker and rattan furniture, and as these products became increasingly popular towards the end of the century, they became serious rivals. In 1897 the companies merged as Heywood Brothers & Wakefield Company (this name was changed to Heywood-Wakefield Company in 1921), purchasing Washburn-Heywood Chair Company in 1916, Oregon Chair Company in 1920, and Lloyd Manufacturing Company in 1921. While its wooden furniture plant in Gardner, Massachusetts closed in 1979, a branch in Menominee, Michigan continued to manufacture metal outdoor seats, auditorium seats, and school furniture. The Heywood-Wakefield Company Complex in Gardner was added to the National Historic Register in 1983. The South Beach Furniture Company acquired the rights to the name in 1994 and reproduces its wooden furniture. Both founding companies produced wicker and rattan furniture in the late 19th century. The wicker styles drew on the Aesthetic Movement and Japanese influences simpler designs arose in the wake of the Arts and Crafts Movement. The merged entity stayed abreast of wicker furniture trends by hiring designers such as Paul Frankl and Donald Deskey during the 1920s. Its furniture was exhibited at the 1933 Century of Progress exhibition and the 1964 New York World's Fair. During the 1930s and 1940s, Heywood-Wakefield began producing furniture using sleek designs based on French Art Deco.The Giles family collection has social significance at a local level, because it illustrates the level of material support the Warrnambool community gave to Flagstaff Hill when the village and Museum was established. The wicker furniture is a fine example of late 19th and early 20th century light weight domestic furniture that are today very collectible items and quite rare and valuable.Pair of wicker armchairs, painted dark brown. The open wicker weave pattern extends from the seat up to the armrests and completely over the backrest, plus across the front of the chair below the seat. The seat is very firmly woven and fitted into a timber frame. A reinforcing pattern of wicker work covers the top edges of the armrests and backrest in one piece and folds around to the underside, referred to as ‘rolled serpentine arms and back’. The hollow ends of the armrests are filled with a circular knob of wicker work. The back legs are also completed with decorative wicker knobs. One chair base (3788.01) has been strengthened with metal bracing. The other chair (3788.02) has the remnants of an orange manufacture’s tag fixed to the base. The chairs were made 1897-1921 by Heywood Brothers & Wakefield Company, USA. These chairs are part of the Giles Collection.Printed in black on an orange tag “MANUFA - Heywood B – GARDNE”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, giles collection, giles family, henry and mary jane giles, tower hill, cooramook, warrnambool breakwater, mailor’s flat, wangoom, 19th century furniture, wicker armchairs, rolled serpentine wicker work, cane armchair, classic wicker furniture, victorian style furniture, domestic furniture late 19th century, heywood-wakefield company -
 Ruyton Girls' School
Ruyton Girls' SchoolPhotograph, Ruyton Girls' School, 1952
Depicted are 14 students comprising the the 1952 Ruyton Girls' School hockey team. The photograph is an official school portrait taken outdoors on a patch of grass with a leafy bush visible in the background. The students are all dressed in light coloured shorts with a collared, buttoned blouse, wool blazers, white socks and white sneakers. Six girls are kneeling in the front row, and eight are standing up in the back row. All of the students are holding their own hockey stick. The idea of field hockey for female players was brought to Victoria by two sisters, Lillian and Margaret Irving, who had first seen girls playing it during their travels in England in 1902. By 1903, the Irving sisters were joint headmistresses of Lauriston, a school they had founded two years earlier. Both had deep connections to Ruyton Girls' School through their time as teachers at the older school during the 1880s-1890s. For Lilian Irving, this had included seven years as Ruyton's co-Principal with Miss Eliza Bromby from 1888-1895. With these links it was only natural that Ruyton students would join Lauriston to try out the new game. On a vacant block on the corner of Mercer and Malvern Roads, students from Ruyton and Lauriston Girls' Schools had assembled to play Victoria’s first ever inter-school hockey match for girls. Some students from Melbourne Girls' Grammar School came along to watch the spectacle and assess the new game's potential. Hockey quickly caught on, and friendly games were soon being played amongst a number of Melbourne's girls' schools. An Association was formed in 1905, and the rules formalised. These included arrangements around the competition fixture and the length of games (35 minutes for each half). In celebration of their joint role in bringing field hockey to Victorian school girls, Ruyton and Lauriston have met for friendly re-enactment matches in 2003 and 2018. The photograph also illustrates the shift in hockey uniform and apparatus. In the early 1920s, Ruyton established instructions for playing attire: "skirts must be eight inches off the ground. No white petticoats...", and importantly, least any team get an unfair advantage, "hard-rimmed hats and hatpins must not be worn during play." Ruyton appears to have taken the latter instruction to heart, and adopted the soft tam o’shanter hat as seen in surviving photographs of early teams. The tam o’shanter may have been removed for play, but the blouse and long skirt had to be put up with. According to Lilian Irving they had "a horrid habit of parting company", and she was delighted to see the transition to a more comfortable tunic in later years. Another change she observed was the hockey stick itself, which originally were all of "uniform thickness from handle to head, about the thickness of a stout walking stick" and so very different from the hockey sticks that are used today.The record has strong historic significance as it depicts a former notable student, Helen Gordon (maiden name Cole), pictured third from the right in the front row. Helen started at Little Ruyton in Prep 1940 and finished Year 12 in 1952 as School Captain, Bromby Captain, Form Captain for Matric, Tennis Captain, Hockey Captain, Swimming Vice Captain, and an award for Best All-Round Girl. She also played baseball for Victoria. After finishing school, Helen went on to graduate from the University of Melbourne as a physiotherapist in 1956. Her first position at age 19 involved setting up clinics with the Victorian Health Department Poliomyelitis Rural division. Helen’s strong ties to Ruyton continued when she held the position of President of the Old Ruytonians’ Association from the start of 1966 to the end of 1967. In 2019, Helen received an Order of Australia Medal for service to community health as a physiotherapist. She was also the recipient of the 2022 Victorian Senior Achiever Award at Parliament House. Helen passed away in July 2023 at age 88. The record's significance is further enhanced by its strong provenance, having been produced by Ruyton Girls' School and donated to the Archives by a familial connection.Black and white rectangular photographs printed on matte photographic paper.Reverse: gton / Margaret Hanesho (?) / Helen Gordon / 1952 / Mary Macpherson-Smith /ruyton girls' school, kew, victoria, tennis, sport, women's sport, students, school, 1950s, uniform, lauriston, hockey, field hockey, hockey stick -
 Ruyton Girls' School
Ruyton Girls' SchoolPhotograph, Ruyton Girls' School, 1950
Depicted are 13 students comprising the the 1950 Ruyton Girls' School hockey team. The photograph is an official school portrait taken outdoors on a patch of grass with a leafy bush visible in the background. The students are all dressed in light coloured shorts with a collared, buttoned blouse, wool blazers, white socks and white sneakers. Five girls are kneeling in the front row, and seven are standing up in the back row. All of the students are holding their own hockey stick. The idea of field hockey for female players was brought to Victoria by two sisters, Lillian and Margaret Irving, who had first seen girls playing it during their travels in England in 1902. By 1903, the Irving sisters were joint headmistresses of Lauriston, a school they had founded two years earlier. Both had deep connections to Ruyton Girls' School through their time as teachers at the older school during the 1880s-1890s. For Lilian Irving, this had included seven years as Ruyton's co-Principal with Miss Eliza Bromby from 1888-1895. With these links it was only natural that Ruyton students would join Lauriston to try out the new game. On a vacant block on the corner of Mercer and Malvern Roads, students from Ruyton and Lauriston Girls' Schools had assembled to play Victoria’s first ever inter-school hockey match for girls. Some students from Melbourne Girls' Grammar School came along to watch the spectacle and assess the new game's potential. Hockey quickly caught on, and friendly games were soon being played amongst a number of Melbourne's girls' schools. An Association was formed in 1905, and the rules formalised. These included arrangements around the competition fixture and the length of games (35 minutes for each half). In celebration of their joint role in bringing field hockey to Victorian school girls, Ruyton and Lauriston have met for friendly re-enactment matches in 2003 and 2018. The photograph also illustrates the shift in hockey uniform and apparatus. In the early 1920s, Ruyton established instructions for playing attire: "skirts must be eight inches off the ground. No white petticoats...", and importantly, least any team get an unfair advantage, "hard-rimmed hats and hatpins must not be worn during play." Ruyton appears to have taken the latter instruction to heart, and adopted the soft tam o’shanter hat as seen in surviving photographs of early teams. The tam o’shanter may have been removed for play, but the blouse and long skirt had to be put up with. According to Lilian Irving they had "a horrid habit of parting company", and she was delighted to see the transition to a more comfortable tunic in later years. Another change she observed was the hockey stick itself, which originally were all of "uniform thickness from handle to head, about the thickness of a stout walking stick" and so very different from the hockey sticks that are used today.The record has strong historic significance as it depicts a former notable student, Helen Gordon (maiden name Cole), pictured third from the right in the front row. Helen started at Little Ruyton in Prep 1940 and finished Year 12 in 1952 as School Captain, Bromby Captain, Form Captain for Matric, Tennis Captain, Hockey Captain, Swimming Vice Captain, and an award for Best All-Round Girl. She also played baseball for Victoria. After finishing school, Helen went on to graduate from the University of Melbourne as a physiotherapist in 1956. Her first position at age 19 involved setting up clinics with the Victorian Health Department Poliomyelitis Rural division. Helen’s strong ties to Ruyton continued when she held the position of President of the Old Ruytonians’ Association from the start of 1966 to the end of 1967. In 2019, Helen received an Order of Australia Medal for service to community health as a physiotherapist. She was also the recipient of the 2022 Victorian Senior Achiever Award at Parliament House. Helen passed away in July 2023 at age 88. The record's significance is further enhanced by its strong provenance, having been produced by Ruyton Girls' School and donated to the Archives by a familial connection.Black and white rectangular photographs printed on matte photographic paper.Reverse: Ruyton Hockey Team 1950. / 17 Cole / From left to right standing. / Helen Cole. / Left to right kneeling. /ruyton girls' school, kew, victoria, tennis, sport, women's sport, students, school, 1950s, uniform, lauriston, hockey, field hockey, hockey stick -
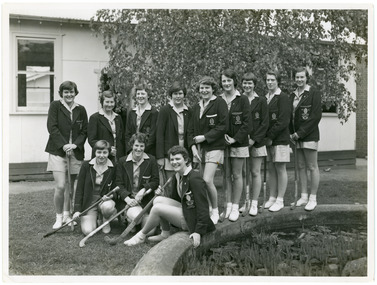 Ruyton Girls' School
Ruyton Girls' SchoolPhotograph, Ruyton Girls' School, 1951
The photograph depicts 12 young women students who were part of the 1951 Ruyton Girls' School hockey team. The students are all dressed in light coloured shorts with a collared, buttoned blouse, wool blazers, white socks and white sneakers. Three girls are kneeling in the front row, and nine are standing up in the back row. All of the students are holding their own hockey stick. The photograph was taken on School grounds, next to a pond which is no longer in existence at Ruyton. The idea of field hockey for female players was brought to Victoria by two sisters, Lillian and Margaret Irving, who had first seen girls playing it during their travels in England in 1902. By 1903, the Irving sisters were joint headmistresses of Lauriston, a school they had founded two years earlier. Both had deep connections to Ruyton Girls' School through their time as teachers at the older school during the 1880s-1890s. For Lilian Irving, this had included seven years as Ruyton's co-Principal with Miss Eliza Bromby from 1888-1895. With these links it was only natural that Ruyton students would join Lauriston to try out the new game. On a vacant block on the corner of Mercer and Malvern Roads, students from Ruyton and Lauriston Girls' Schools had assembled to play Victoria’s first ever inter-school hockey match for girls. Some students from Melbourne Girls' Grammar School came along to watch the spectacle and assess the new game's potential. Hockey quickly caught on, and friendly games were soon being played amongst a number of Melbourne's girls' schools. An Association was formed in 1905, and the rules formalised. These included arrangements around the competition fixture and the length of games (35 minutes for each half). In celebration of their joint role in bringing field hockey to Victorian school girls, Ruyton and Lauriston have met for friendly re-enactment matches in 2003 and 2018. The photograph also illustrates the shift in hockey uniform and apparatus. In the early 1920s, Ruyton established instructions for playing attire: "skirts must be eight inches off the ground. No white petticoats...", and importantly, least any team get an unfair advantage, "hard-rimmed hats and hatpins must not be worn during play." Ruyton appears to have taken the latter instruction to heart, and adopted the soft tam o’shanter hat as seen in surviving photographs of early teams. The tam o’shanter may have been removed for play, but the blouse and long skirt had to be put up with. According to Lilian Irving they had "a horrid habit of parting company", and she was delighted to see the transition to a more comfortable tunic in later years. Another change she observed was the hockey stick itself, which originally were all of "uniform thickness from handle to head, about the thickness of a stout walking stick" and so very different from the hockey sticks that are used today.The record has strong historic significance as it depicts a former notable student, Helen Gordon (maiden name Cole), pictured third from the right in the front row. Helen started at Little Ruyton in Prep 1940 and finished Year 12 in 1952 as School Captain, Bromby Captain, Form Captain for Matric, Tennis Captain, Hockey Captain, Swimming Vice Captain, and an award for Best All-Round Girl. She also played baseball for Victoria. After finishing school, Helen went on to graduate from the University of Melbourne as a physiotherapist in 1956. Her first position at age 19 involved setting up clinics with the Victorian Health Department Poliomyelitis Rural division. Helen’s strong ties to Ruyton continued when she held the position of President of the Old Ruytonians’ Association from the start of 1966 to the end of 1967. In 2019, Helen received an Order of Australia Medal for service to community health as a physiotherapist. She was also the recipient of the 2022 Victorian Senior Achiever Award at Parliament House. Helen passed away in July 2023 at age 88. The record's significance is further enhanced by its strong provenance, having been produced by Ruyton Girls' School and donated to the Archives by a familial connection.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper.Reverse: Felicity Jacobs / Ann Dickinson / RGS011/1951/0002 /ruyton girls' school, ruyton, hockey, sport, school sport, field hockey, kew, melbourne, girls school, students, school uniform -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph, Norma Bull portrait
Norma Bull in a window of 'Medlow', 1920s Her brother (Ronald) Richard was a keen photographer and is believed to have taken the photographs of the family and in the grounds of 'Medlow'. Norma Catherine Bull (7 September 1906 – September 1980) was an Australian painter, printmaker and etcher best known for the paintings and sketches she made in Britain during World War II. Norma was the daughter of Richard Joseph Bull (1874-1927) and Catherine Grace Perrier (1884-1972). Her father was the Director of Bacteriology at Melbourne University. Richard and Catherine had 2 children. Norma was born in Hawthorn in 1906 and her brother Ronald Richard was born in Surrey Hills in 1912, where in 1911 Richard bought a property at 42 Warrigal Road, Surrey Hills developed by Colonel William Cairncross, known as ‘Willcyrus’ and renamed ‘Medlow’ by the Bulls. As a child, Norma was a high achiever both intellectually and artistically. She was educated at Fintona, where she matriculated as Dux of the School and winner of an exhibition in French. She won a scholarship to attend the University of Melbourne where she studied French, Zoology, Philosophy, English and History, leading to a Bachelor of Arts in 1929. Following this she studied painting and drawing at the National Gallery Art School for seven years. Whilst most of the students of the 1930s were inspired by Modernism, Norma followed more traditional styles and became known for her etchings and realistic depiction of urban scenes. Her work was strongly influenced by the conservative nature of the National Gallery Art School under Bernard Hall, and she remained a traditionalist all her life. In 1938, she was awarded the Sir John Longstaff Scholarship in Fine Art. This enabled her to travel to England to study at the Royal Academy in London. She arrived in April 1939 and after the outbreak of war, she worked as a volunteer at a First Aid Clearing Station and applied to become a war artist. In 1941, she was given a sketching permit by the War Artists Advisory Committee to record bomb damage in the Bristol area. In 1947, an exhibition of her 205 wartime works entitled “Two Hemispheres”, opened at Australia House in London. Many were acquired for major collections in England including the Victoria and Albert Museum, the Imperial War Museum and the Royal Collection. The “Two Hemispheres” exhibition toured Australia in 1948 and for over twelve months she followed Wirth’s Circus around the country, painting aspects of circus life. From then on she lived at Medlow’, From 1960 she was secretary of the Fellowship of Australian Artists. She was a finalist in the Archibald Prize on 2 occasions and is remembered through a biennial Art Prize, ‘The Norma Bull Portraiture Scholarship’ which is administered by The Victorian Artist’s Society. She continued to paint landscapes and seascapes in her traditionalist style. She had holiday homes at Anglesea and Bright. After she died in September 1980, 31 of her works were bequeathed to Bright Art Gallery. A black and white photograph of a lady holding a sun umbrella and sitting in a window frame.miss norma bull, medlow, house names, warrigal road, surrey hills, mr ronald richard bull -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAudio - Gramophone Cylinder, National Phonograph Co, Poor old England, 1908
Edison Records was one of the early record labels that pioneered sound recording and reproduction, and was an important player in the early recording industry. The first phonograph cylinders were manufactured in 1888, followed by Edison's foundation of the Edison Phonograph Company in the same year. The recorded wax cylinders, later replaced by Blue Amberol cylinders, and vertical-cut Diamond Discs, were manufactured by Edison's National Phonograph Company from 1896 on, reorganized as Thomas A. Edison, Inc. in 1911. Until 1910 the recordings did not carry the names of the artists. The company began to lag behind its rivals in the 1920s, both technically and in the popularity of its artists, and halted production of recordings in 1929. Thomas A. Edison invented the phonograph, the first device for recording and playing back sound, in 1877. After patenting the invention and benefiting from the publicity and acclaim it received, Edison and his laboratory turned their attention to the commercial development of electric lighting, playing no further role in the development of the phonograph for nearly a decade. Start of the Recording Industry: In 1887, Edison turned his attention back to improving the phonograph and the phonograph cylinder. The following year, the Edison company introduced the ”Perfected Phonograph”. Edison introduced wax cylinders approximately 4+1⁄4 inches (11 cm) long and 2+1⁄4 inches (5.7 cm) in external diameter, which became the industry standard. They had a maximum playing time of about 3 minutes at 120 RPM, but around the turn of the century the standard speed was increased to (first 144) and then 160 RPM to improve clarity and volume, reducing the maximum to about 2 minutes and 15 seconds. Several experimental wax cylinder recordings of music and speech made in 1888 still exist. The wax entertainment cylinder made its commercial debut in 1889 at first, the only customers were entrepreneurs who installed nickel-in-the-slot phonographs in amusement arcades, saloons and other public places. At that time, a phonograph cost the equivalent of several months' wages for the average worker and was driven by an electric motor powered by hazardous, high-maintenance wet cell batteries. After more affordable spring-motor-driven phonographs designed for home use were introduced in 1895, the industry of producing recorded entertainment cylinders for sale to the general public began in earnest. Blank records were an important part of the business early on. Most phonographs had or could be fitted with attachments for the users to make their own recordings. One important early use, in line with the original term for a phonograph as a "talking machine", was in business for recording dictation. Attachments were added to facilitate starting, stopping, and skipping back the recording for dictation and playback by stenographers. The business phonograph eventually evolved into a separate device from the home entertainment phonograph. Edison's brand of business phonograph was called the Ediphone. The collection of three phonograph cylinders are an example of early recorded music use for domestic entertainment. They are significant as they represent the beginnings of the modern recording industry.Cardboard tube-shaped gramophone cylinder box with lid. The printed label on the outside of the box advertises the maker and patent details. The Catalogue Number and Title are either printed or hand written on the cylinder’s lid. This cylinder contained Record no. 13619, the recording “Poor old England” published by Castling and Godfrey, sung by Billy Williams. Made by National Phonograph Company USA. C.1907On lid “Edison Record” and “This record should turn at 160 revolutions per minute, no faster” Written on lid in blue pen “Trumpet”, “EDISON AMBEROL RECORD / FOUR MINUTE”warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, gramophone record, gramophone cylinder, edison cylinder, edison record, home entertainment, music recording, edison laboratory orange nj, usa, national phonograph company of australia ltd sydney, thomas a. edison -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAudio - Gramophone Cylinder, Sandy McNab, 1908
Edison Records was one of the early record labels that pioneered sound recording and reproduction, and was an important player in the early recording industry. The first phonograph cylinders were manufactured in 1888, followed by Edison's foundation of the Edison Phonograph Company in the same year. The recorded wax cylinders, later replaced by Blue Amberol cylinders, and vertical-cut Diamond Discs, were manufactured by Edison's National Phonograph Company from 1896 on, reorganized as Thomas A. Edison, Inc. in 1911. Until 1910 the recordings did not carry the names of the artists. The company began to lag behind its rivals in the 1920s, both technically and in the popularity of its artists, and halted production of recordings in 1929. Thomas A. Edison invented the phonograph, the first device for recording and playing back sound, in 1877. After patenting the invention and benefiting from the publicity and acclaim it received, Edison and his laboratory turned their attention to the commercial development of electric lighting, playing no further role in the development of the phonograph for nearly a decade. Start of the Recording Industry: In 1887, Edison turned his attention back to improving the phonograph and the phonograph cylinder. The following year, the Edison company introduced the ”Perfected Phonograph”. Edison introduced wax cylinders approximately 4+1⁄4 inches (11 cm) long and 2+1⁄4 inches (5.7 cm) in external diameter, which became the industry standard. They had a maximum playing time of about 3 minutes at 120 RPM, but around the turn of the century the standard speed was increased to (first 144) and then 160 RPM to improve clarity and volume, reducing the maximum to about 2 minutes and 15 seconds. Several experimental wax cylinder recordings of music and speech made in 1888 still exist. The wax entertainment cylinder made its commercial debut in 1889 at first, the only customers were entrepreneurs who installed nickel-in-the-slot phonographs in amusement arcades, saloons and other public places. At that time, a phonograph cost the equivalent of several months' wages for the average worker and was driven by an electric motor powered by hazardous, high-maintenance wet cell batteries. After more affordable spring-motor-driven phonographs designed for home use were introduced in 1895, the industry of producing recorded entertainment cylinders for sale to the general public began in earnest. Blank records were an important part of the business early on. Most phonographs had or could be fitted with attachments for the users to make their own recordings. One important early use, in line with the original term for a phonograph as a "talking machine", was in business for recording dictation. Attachments were added to facilitate starting, stopping, and skipping back the recording for dictation and playback by stenographers. The business phonograph eventually evolved into a separate device from the home entertainment phonograph. Edison's brand of business phonograph was called the Ediphone. The collection of three phonograph cylinders are an example of early recorded music use for domestic entertainment. They are significant as they represent the beginnings of the modern recording industry.Cardboard tube-shaped gramophone cylinder box with lid. The printed label on the outside of the box advertises the maker and patent details. The Catalogue Number and Title are either printed or hand written on the cylinder’s lid. This cylinder was made by Edison 1908 and contains Record number 53 by Sandy McNab. c. 1908On label “Edison Record No. 53, Sandy McNab" and "Form no. 1130, April 1908. Patented December 6 1904, No. 2109, and December 6 1904 No. 2110. “This record is sold by the National Phonograph Company of Australia Ltd, at Sydney Australia.” Trade Mark Thomas A. Edison warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, gramophone record, gramophone cylinder, edison cylinder, edison record, home entertainment, music recording, edison laboratory orange nj, usa, national phonograph company of australia ltd sydney, thomas a. edison -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAudio - Gramophone Cylinder, B & H Jack, 1907
Edison Records was one of the early record labels that pioneered sound recording and reproduction, and was an important player in the early recording industry. The first phonograph cylinders were manufactured in 1888, followed by Edison's foundation of the Edison Phonograph Company in the same year. The recorded wax cylinders, later replaced by Blue Amberol cylinders, and vertical-cut Diamond Discs, were manufactured by Edison's National Phonograph Company from 1896 on, reorganized as Thomas A. Edison, Inc. in 1911. Until 1910 the recordings did not carry the names of the artists. The company began to lag behind its rivals in the 1920s, both technically and in the popularity of its artists, and halted production of recordings in 1929. Thomas A. Edison invented the phonograph, the first device for recording and playing back sound, in 1877. After patenting the invention and benefiting from the publicity and acclaim it received, Edison and his laboratory turned their attention to the commercial development of electric lighting, playing no further role in the development of the phonograph for nearly a decade. Start of the Recording Industry: In 1887, Edison turned his attention back to improving the phonograph and the phonograph cylinder. The following year, the Edison company introduced the ”Perfected Phonograph”. Edison introduced wax cylinders approximately 4+1⁄4 inches (11 cm) long and 2+1⁄4 inches (5.7 cm) in external diameter, which became the industry standard. They had a maximum playing time of about 3 minutes at 120 RPM, but around the turn of the century the standard speed was increased to (first 144) and then 160 RPM to improve clarity and volume, reducing the maximum to about 2 minutes and 15 seconds. Several experimental wax cylinder recordings of music and speech made in 1888 still exist. The wax entertainment cylinder made its commercial debut in 1889 at first, the only customers were entrepreneurs who installed nickel-in-the-slot phonographs in amusement arcades, saloons and other public places. At that time, a phonograph cost the equivalent of several months' wages for the average worker and was driven by an electric motor powered by hazardous, high-maintenance wet cell batteries. After more affordable spring-motor-driven phonographs designed for home use were introduced in 1895, the industry of producing recorded entertainment cylinders for sale to the general public began in earnest. Blank records were an important part of the business early on. Most phonographs had or could be fitted with attachments for the users to make their own recordings. One important early use, in line with the original term for a phonograph as a "talking machine", was in business for recording dictation. Attachments were added to facilitate starting, stopping, and skipping back the recording for dictation and playback by stenographers. The business phonograph eventually evolved into a separate device from the home entertainment phonograph. Edison's brand of business phonograph was called the Ediphone. The collection of three phonograph cylinders are an example of early recorded music use for domestic entertainment. They are significant as they represent the beginnings of the modern recording industry.Cardboard tube-shaped gramophone cylinder box with lid. The printed label on the outside of the box advertises the maker and patent details. The Catalogue Number and Title are either printed or hand written on the cylinder’s lid. This cylinder contained Record no. 49, “B & H Jack” and was made at the Edison Laboratory USA. C. 1905On lid “Edison Record No. 49”, written in pencil “B & H Jack” (it looks like this) On cylinder “EDISON GOLD MOULDED RECORDS ECHO ALL OVER THE WORLD” Patents listed for 1904 & 1905warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, gramophone record, gramophone cylinder, edison cylinder, edison record, home entertainment, music recording, edison laboratory orange nj, usa, national phonograph company of australia ltd sydney, thomas a. edison -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPostcard, George Rose, c.1945
The Rose Stereograph Company first began producing postcards, identified as the 'P' series (like this particular example) in 1913 and continued in this business until 1967 after which they switched to machine manufactured colour postcards printed by an external company. These were produced by Victorian-era photographer George Rose (1861-1942) often reputed as one of the best photographers in Australia during the later 19th Century and early 20th Century. Rose was born in 1861 in Clunes and began his photography business in 1880 when he founded the Rose Stereograph Company. He later switched to producing postcards after stereographs lost popularity in the early 1920s. The Mayday Hills Hospital was one of these locations photographed by George Rose and published as a postcard. Beechworth's Mayday Hills was chosen as the site of Victoria's newest asylum, at the time, due to the landscape and altitude. The hilltop atmosphere and the native fauna, it was argued, would assist in the cure of the patients kept at the hospital (Wood 1985, 122). The positioning of the hospital had a beneficial effect on the rural town. A pamphlet published by James Ingram and Son (1849) reveal that famous landmarks in Beechworth which included the Post Office, Gaol, Courthouse and Asylum "demonstrate the appreciation of Beechworth by the Government not only as as important district center, but also as a site unrivaled as a sanitarium". There were other locations in contention at the time, but ultimately Beechworth was chosen (Craig 2000,33). Prior to the creation of the Asylum in Beechworth, those charged with having mental illnesses or, as it was termed, "insanity" were unable to be properly cared for in the Gaol (which is where they were often sent). John Buckley Castieau wrote, in 1861 for the Ovens and Murray Advertiser, that the Gaol was unable to properly care for those classified then as "insane" but that they would endeavor to treat them above the other inmates (which he notes is not always the case in other establishments). Castieau wrote this in favour of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth. It was stated that at the time the Mayday Hills Hospital was built, there were 83 prisoners kept in the Gaol who were to be rehoused to the Hospital on the grounds of "insanity". The classification as someone as "insane", in this period of time is a reflection on the inability to cure and understand illnesses of the mind during the mid to late 1800s. Opening on the 24th of October 1867, the Mayday Hills Hospital was originally named the "Ovens Lunatic Asylum", a title which is very much a product of its time. Whilst controversial, changes to the name is part of the history of the Hospital and can provide much insight into the understanding of mental illness throughout history and the use/disuse of this term provides information into the reception/changing opinions of mental illness in society. The Hospital would later become known as the "Mayday Hills Asylum" and/or "Mayday Hills Hospital" with the latter being the most commonly used title. An article in the Ovens and Murray Advertiser notes that on the 7th of March 1865, the foundation stone of the Hospital was laid (it would officially open in 1867) and that it was such a moment of accomplishment and joy for Beechworth that a letter to the editor even suggested that there should be a holiday dedicated to the day the foundation stone as laid. This reveals an extent to which the townspeople of early Beechworth valued the construction of the Hospital in their town. It provided the town with a sense of prestige and honour. At first glance, the remains of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth, Victoria, inspire tragedy, trauma and beauty. The buildings themselves, with their Italianate style Renaissance architecture designed by J.J. Clark (Craig 2000, 49 & Smith 2016, 203) reflect a bygone period of European and Australian history. The gardens provide a sense of tranquility and beauty. The experience of those within these walls remains a valuable area of study to provide a more complete understanding. This particular hospital is considered the fourth of its like and one of three identified as the largest of their kind. The Mayday Hills Hospital is a sister to the Kew and Ararat Asylums in Melbourne which are both located in relative proximity. Understanding the role of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth history is integral to understanding the development of the goldfields town, but also for providing important information as to the history of caring for, and the reception of, mental illnesses in Australian and wider European history. Mayday Hills provides a case study which can be researched through oral history, an analysis of the grounds/buildings and through images like this postcard which portray the structure in a highly deliberate manner. Images like this depict the strong façade of the Hospital and provide a glimpse into the tranquility of the gardens. This has been done deliberately to provide a sense of comfort and healing about the building to those looking from the outside. Further research into the importance of the Hospital in Beechworth and it's connection to the town will be supported through images like these kept in the Mayday Hills photo album in the collection of the Burke Museum.Pale sepia toned rectangular postcard printed on matte card.Obverse: THE ROSE SERIES P. 4689 / COPYRIGHT / ADMINISTRATIVE OFFICES, MENTAL HOSPITAL, BEECHWORTH, VIC / Reverse: Published by the Rose Stereograph Co. / Armadale, Victoria / POST CARD / THE "ROSE" SERIES / DE LUXE / A REAL PHOTOGRAPH / PRODUCED IN AUSTRALIA /mayday hills, asylum, mental hospital, hospital, beechworth -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Peter Pidgeon, Grave of Beulah Alice Rutter and children, June and Samuel, Eltham Cemetery, Victoria, 5 April 2021
Hubert and Beulah Alice (Simpson) Rutter had five children: Hubert Jnr. (Joe) in 1913, David in 1915, June in 1917, Donald in 1922 and Samuel in 1926. Samuel died as an infant aged 17 days. Hubert was a notable figure in Eltham and beyond, with a career as a mining manager in Australia and Malaya. He served in the AIF in the First World War. While the children were growing up at ‘Yarra Braes’, Eltham, their father was an Eltham Shire Councillor in the 1920s, shire president in 1928 and a leading figure in establishing the Shire of Eltham War Memorial League, which was responsible for building the Shire of Eltham War Memorial tower at Kangaroo Ground, near where the Shire Offices were located until the 1930s. The Rutter name was commemorated after the war at Eltham High School with one of the schoolhouses named ‘Rutter House’ and at Geelong Grammar School until the 1960s where a ‘Rutter Badge’ was awarded to junior boys for leadership. The family home, ‘Yarra Braes’ was destroyed in the devasting Black Friday bushfire, 13 January 1939 and Beulah relocated to Toorak, Hubert working in Western Australia. Tragedy struck the family again December 19, 1940 when daughter June was killed after falling from the Heidelberg train on to an adjacent track into the path of a Reservoir train at Victoria Park station. Sons David and Donald both served in the R.A.A.F. during the Second World War and were killed in action, David in Libya in 1941 and Donald in Germany in 1945. The wreck of his plane and his body were not recovered at the time and Hubert never ceased to chase down leads as to his whereabouts. Beulah never gave up hope that Donald was still alive. Hubert had received several reports shortly after the war that his son was still alive but these were ultimately accepted as misidentification. Such was the anguish of the grieving parents, their son’s plane not found to confirm the fact for certain. Hubert wrote to the Air Force in frustration, failing to understand how the plane could disappear when it crashed in a relatively populated area. Unfortunately the answers came too late for Beulah who died in 1946 and was buried in Eltham Cemetery along with her daughter June and baby Samuel. Donald’s plane was eventually located and his body recovered in 1949. He is buried in the Hanover War Cemetery, Germany. David is commemorated on Column 245, Alamein Memorial, Egypt. Both David and Donald are commemorated on Eltham’s Roll of Honour Board, commissioned by the Eltham War Memorial Trust to be hung in the Baby Health Centre, part of the Eltham War Memorial building precinct. Hubert Senior and Hubert Junior both continued to work in the mining industry in Western Australia. Hubert senior died 1957 at Plantagenet Western Australia and Hubert junior in 1979 at Gascoyne, Western Australia. Sacred to the memory of Beulah AliceBeloved wife of Hubert Rutter Died August 21st 1946 also June Beloved daughter of Beulah and Hubert Rutter Died 19th December 1940 aged 23 years Also her baby brother Samuel Died 7th October 1926, aged 17 daysBorn Digitaleltham cemetery, gravestones, beulah alice rutter, hubert rutter, june rutter, samuel rutter -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPostcard - Photograph postcard, Panorama at Eltham, Vic, c.1923
The Rose Series P. 4284 post card Taken from near what would be present day CLC car park looking southwest across Diamond Street, present-day Andrew Park to the railway station and developing Eltham shopping precinct. Arthur Street visible, Pryor and Luck Street not evident. Sunnybrook, the Taylor home is visible at the top of the hill in Bible Street. Only three residences visible in Arthur Street on the southern side, two of these are the David Harbison Rest Home at 10 and 12 Arthur Street (built and opened in November 1919), present day site of Eltham Mall. There are none on the north side of the street. Based on 1945 aerial view there are 8 buildings on the northern side between Main Road and Bible Street which and given the extent of commercial development on Main Road, it is estimated this image is circa 1925. Luther Haley was the first to build an open a baker and General Store in this location next to the railway station in 1902. However, it took nearly twenty years until the early to mid-1920s when a period of significant growth in the Eltham shopping centre happened with many businesses relocating their operations from the original town centre of Maria Street in Little Eltham as well as new businesses opening. Other stores/buildings noted (L-R) are: Stationmaster's House built circa 1910 Eltham Hardware Store opposite the railway station first opened on Main Road opposite the Railway Station around late 1922. An advertisement placed in the Hurstbridge Advertiser advised that the Hardware Store had just opened with a varied stock of Saws, Hammers, Nails, Shovels, Screw Drivers, and every article required in a house or on a farm. People were also encouraged to try their Jams, Pickles, Sauces, Cups and Saucers, etc. Newsagency with 'Leader' advertising on awning - E. J. Andrew opened his newsagency shop opposite the station in March 1923, advertising for sale stationery, school requisites and periodicals. Bird Brothers Cash Grocer & Fruiterer opposite the railway station offering summer drinks and confectionery a specialty with a full Stock of groceries of the best quality always on hand at city prices opened December 1921 William Capewell's Butcher shop at the corner of Dudley Street. Capewell previously had a small shop in front of the station opposite Luck Street. He enlisted in the AIF during WW1 and returned home in 1919. He re-applied for a slaughtering license in February 1920 and was advertising by October 1922 supplying all districts. Not visible (or not yet identified) but in business by October 1922 were: J.H. Fraser, Carpenter and Builder at Luck Street opposite the station George A. Danslow, Hairdresser and Tobacconist opposite the railway station Miss Barber's 'Blue Gum' Soda Fountain opened October 1922 opposite the railway station (hidden behind Stationmaster's House). It was so named due to its proximity to a tall Blue Gum tree G.H. McDonald Boot Repairer opposite the railway station In December 1923 the first portion of the main street to be formed from Dudley to Arthur streets was almost completed. This is the section in front of Capewell's Butcher shop though it is difficult to fully make out from the photoDigital file only Postcards scanned from the collection of Michael Aitken on loan to EDHS, 2 Sep. 2022michael aitken collection, eltham, postcards, arthur street, david harbison rest home, electrine candles, eltham railway station, eltham shopping centre, lloyd's general store, red rattler, rose series postcard, rose stereograph company, tait train, velvet soap, andrew park, bible street, bird brothers cash grocer & fruiterer, bird brothers cash grocer and fruiterer, butcher, diamond street, dudley street, eltham hardware and timber, eltham hardware store, eltham mall, main road, station masters house, stationmaster's house, sunnybrook, w.j. capewell, w.j. capewell butcher shop -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Containers, matchbox 'Redhead' with matches, 20thC
On 15th December 1909, Bryant & May, Australia’s first match factory at Church Street, Richmond, Victoria. was opened by The Honourable Alfred Deakin, Prime Minister of Australia, and Mrs. Deakin. It was heralded by the first Commonwealth Government of newly-federated Australia because the government of the day was anxious to encourage secondary industry and pledged tariff protection of local manufacturers. The building was constructed in 1909 as the Empire Works to a design by prolific Melbourne architect William Pitt and was purchased soon after by British safety match manufacturer Bryant and May, who significantly expanded the building, adding another level and the landmark clock tower. Bryant and May were unique in that they operated as a model factory, providing workers with conditions and amenities that even today seem generous. These included a dining hall and sports facilities such as a tennis court and bowling green which were constructed in the 1920s. Bryant and May ceased Australian match manufacture in the early 1980s as a result of import competition. Their iconic Redheads matches are now imported from Sweden. The complex has since been converted for use as offices and showrooms but is extremely well preserved. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. Bryant and May was a United Kingdom (UK) company created in the mid-nineteenth century specifically to make matches. Their original Bryant and May Factory was located in Bow, London. They later opened other match factories in the United Kingdom and Australia, such as the Bryant and May Factory, Melbourne; and owned match factories in other parts of the world. Bryant and May survived as an independent company for over seventy years, but went through a series of mergers with other match companies and later with consumer products companies. To protect its position Bryant and May merged with or took over its rivals. In 1971 the Northern Ireland factory, Maguire & Patterson closed down following a terrorist attack.. In the 1980s, factories in Gloucester and Glasgow closed too leaving Liverpool as the last match factory in the UK, until December 1994. . The registered trade name Bryant and May still exists and it is owned by Swedish Match, as are many of the other registered trade names of the other, formerly independent, companies within the Bryant and May group. Two French chemists, Henri Savene and Emile David Cahen, proved in 1898 that the addition of phosphorus sesquisulfide meant that the substance was not poisonous, that it could be used in a "strike-anywhere" match, and that the match heads were not explosive. British company Albright and Wilson, was the first company to produce phosphorus sesquisulfide ( Red Phosphorous) matches commercially. The company developed a safe means of making commercial quantities of phosphorus sesquisulfide in 1899 and started selling it to match manufacturers. Matches were first produced by Bryant & May in Australia in 1909. The Redhead name applies to the red striking heads of the matches which were introduced to Australia in 1946. The logo on the matchbox depicted the head and shoulder of a redheaded woman and has had four major updates since that time with a number of special issues depicting birds, animals and notable persons also produced.The Bryant & May Ltd factory in Church St Richmond is a listed building and has been converted to apartments following the closure of the Company 1980. Bryant & May's Ltd were influential in fighting against the dreadful disease known as Phossy jaw which was caused by white phosphorus used in the manufacture of the early matches. They were also the object of the 'Match Girls Strike' in London 1888, which won important improvements in working conditions and pay for the mostly female workforce working with the dangerous white phosphorus. The public were slow to purchase these safety matches because of the higher price .A box of safety matches with unused matches made by Bryant & May Pty Ltd , Richmond Victoria Australia. The tray containing the matches slides inside the open ended cover.. The striking patch is on both sides of the cover. Av. CONTENTS 50 MADE IN AUSTRALIA / Brymay / 1/3 / Safety Matches / Redheads / a colour picture of a Kookaburra / Laughing KOOKABURRAsafety matches, bryant & may pty ltd, phossy jaw disease, early settlers, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, lights, lamps, tobacco, white phosphorous, phosphorus sesquisulfide, swedish match pty ltd, pitt william, savens henri, cahen emile david , richmond victoria, -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Slab hut, Warrandyte, Warrandyte Mystery Tour, 29 May 1994, 29/05/1994
[article by Bettina Woodburn in EDHS Newsletter No. 97, July 1994:] THE WARRANDYTE MYSTERY TOUR MAY 29TH 1994 - Members of the Eltham Historical Society met at the Old Post Office, now converted into the Warrandyte Historical Museum, for a picnic lunch on the sunny back verandah overlooking the shimmering Yarra River. Interesting photographs and artefacts filled various rooms outlining the history of this area, and told tales of Aboriginal and more recent neighbours of the Eltham Shire. The weather was calm, cloudy mostly with only occasional sunny patches, but it wasn't cold, although the autumnal leaf colours had changed to wintry brown. "All Aboard" and we set off in the Warrandyte Community Bus (with the School Bus sign displayed at the rear) to learn about local places of "Pride and Joy” from Bruce our guide and Tom the driver. Almost directly opposite we entered Whipstick Gully to explore the first of the district's hidden treasures - the Victory, one of the largest of the six or so major mines, past the old quarry now used for abseiling practice. By torchlight we entered the rocky hillside and saw the seams of quartz the miners had followed in their search for gold. Stamping batteries, and there was one in this gully, converted discarded rock into 'road metal'. Warrandyte is proud to be the first declared Goldfield in 1851, and one of the longest surviving, into the 1920s. A pleasant drive across the Bridge and along Bradley's Lane to Norman's Reserve brought us to see another Tunnel at Pound Bend through which the Yarra was diverted to allow about three miles of river-bed to be used for prospecting for alluvial gold. Still on this side of the river we visited the Old Slab Hut in Castles Road. This remnant of miners' housing is preserved because it had been incorporated into a weatherboard house, and saved from the bulldozers - a last minute reprieve, for preservation, by the National Trust. Devastating bush fires have destroyed other old cottages built of wattle and daub, with bark roofs and stone fire-places. The Cairn commemorating the disclosure of Gold Discovery at Warrandyte on June 30th 1851 beside Anderson's Creek Road was our next point of historical interest. We drove on to South Warrandyte and circled back to above the ford on Anderson's Creek to the entrance of the 4th Hill Mine. Again we crept along with our torches, careful of the low roof-rock, and side shafts. At a junction in a large cavity we were able to stand, look up a long air-vent which some 'cavers' climb down, and marvel at, and experience an aspect of a miner's life. Outside we heard the same bird songs, the trills and bell-pealing, saw the same straggly eucalypts, and a silver leafed wattle in flower, native grasses and ferns, and the neat present day houses, often of Warrandyte stone, perhaps veneered only. The day ended pleasantly, seeing more of the Yarra from Everard Drive, and the water rushing out of the Tunnel at Pound Bend, before returning to afternoon tea or coffee at the Museum. A great day for all concerned - many thanks to the Organisers.Colour photographslab hut, warrandyte, "warrandyte miner's cottage" -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Pound Bend tunnel, Warrandyte, Warrandyte Mystery Tour, 29 May 1994, 29/05/1994
[article by Bettina Woodburn in EDHS Newsletter No. 97, July 1994:] THE WARRANDYTE MYSTERY TOUR MAY 29TH 1994 - Members of the Eltham Historical Society met at the Old Post Office, now converted into the Warrandyte Historical Museum, for a picnic lunch on the sunny back verandah overlooking the shimmering Yarra River. Interesting photographs and artefacts filled various rooms outlining the history of this area, and told tales of Aboriginal and more recent neighbours of the Eltham Shire. The weather was calm, cloudy mostly with only occasional sunny patches, but it wasn't cold, although the autumnal leaf colours had changed to wintry brown. "All Aboard" and we set off in the Warrandyte Community Bus (with the School Bus sign displayed at the rear) to learn about local places of "Pride and Joy” from Bruce our guide and Tom the driver. Almost directly opposite we entered Whipstick Gully to explore the first of the district's hidden treasures - the Victory, one of the largest of the six or so major mines, past the old quarry now used for abseiling practice. By torchlight we entered the rocky hillside and saw the seams of quartz the miners had followed in their search for gold. Stamping batteries, and there was one in this gully, converted discarded rock into 'road metal'. Warrandyte is proud to be the first declared Goldfield in 1851, and one of the longest surviving, into the 1920s. A pleasant drive across the Bridge and along Bradley's Lane to Norman's Reserve brought us to see another Tunnel at Pound Bend through which the Yarra was diverted to allow about three miles of river-bed to be used for prospecting for alluvial gold. Still on this side of the river we visited the Old Slab Hut in Castles Road. This remnant of miners' housing is preserved because it had been incorporated into a weatherboard house, and saved from the bulldozers - a last minute reprieve, for preservation, by the National Trust. Devastating bush fires have destroyed other old cottages built of wattle and daub, with bark roofs and stone fire-places. The Cairn commemorating the disclosure of Gold Discovery at Warrandyte on June 30th 1851 beside Anderson's Creek Road was our next point of historical interest. We drove on to South Warrandyte and circled back to above the ford on Anderson's Creek to the entrance of the 4th Hill Mine. Again we crept along with our torches, careful of the low roof-rock, and side shafts. At a junction in a large cavity we were able to stand, look up a long air-vent which some 'cavers' climb down, and marvel at, and experience an aspect of a miner's life. Outside we heard the same bird songs, the trills and bell-pealing, saw the same straggly eucalypts, and a silver leafed wattle in flower, native grasses and ferns, and the neat present day houses, often of Warrandyte stone, perhaps veneered only. The day ended pleasantly, seeing more of the Yarra from Everard Drive, and the water rushing out of the Tunnel at Pound Bend, before returning to afternoon tea or coffee at the Museum. A great day for all concerned - many thanks to the Organisers.Two colour photographswarrandyte, activities, pound bend -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBadge - World Council of Churches, OIKUMENE, 1940s
This small label badge carries the symbol of the World Council of Churches (WCC), which was established in 1948. The WCC states on its website "The World Council of Churches (WCC) is the broadest and most inclusive among the many organized expressions of the modern ecumenical movement, a movement whose goal is Christian unity. " The 'V' on the back of the badge possibly stands for Victoria. The word on the logo of this badge has the spelling "OIKUMENE" but in many other WCC logos, the Greek word "Oikoumene" is used. The term is translated as "inhabited earth" and is used fifteen times in the original Greek New Testament, including in Matthew 24:14, which says "And the gospel of the kingdom shall be preached in all the world for a witness unto all nations and then shall the end come." The WCC explains that the logo uses early Christian symbols to portray its message, with the church portrayed as a boat afloat on the sea of the world with the mast in the form of a cross. This badge is part of a set of eleven badges collected from the 1920s to the 1940s by Dr W. R. Angus. The set represents various organisations that he had interests in. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. The set of badges is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” which includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at the University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was a house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was a physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as the new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1927 at Ballarat, the nearest big city to Nhill where he began as a Medical Assistant. He was also Acting House surgeon at the Nhill hospital where their two daughters were born. During World War II He served as a Military Doctor in the Australian Defence Forces. Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool in 1939, where Dr Angus operated his own medical practice. He later added the part-time Port Medical Officer responsibility and was the last person appointed to that position. Both Dr Angus and his wife were very involved in the local community, including the planning stages of the new Flagstaff Hill and the layout of the gardens there. Dr Angus passed away in March 1970.This religious lapel badge of the World Council of Churches represents one of the organisations in which Dr Angus had an interest. The set of badges is significant for connecting Doctor Angus with Australian organisations of the early-to-mid 20th century, including those relating to military service support. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The Collection includes historical medical objects that date back to the late 1800s.Lapel badge; a small round blue enamel badge with gold image and text. The image contains the symbol of a cross above a small boat on waves. The image is the logo of the World Council of Churches.This badge is part of a set of badges collected by Dr W R Angus. the set represents organisations that he was involved in, and is part of the W.R. Angus Collection.Test above Logo: “OIKUMENE” Logo; [cross] above [small boat] above [waves] Text under clip; “V” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, oikumene, w.r. angus, metal badge, enamel badge, organisation badges, religious badge, lapel badge, oikoumene, world council of churches, wcc, christian unity -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured Objects, safety matches 'Redheads' 2015, c2015
This is a current example of the 'Redhead' logo used by Bryant & May Ltd Richmond,Victoria, Australia c 1946 - 1980 On 15th December 1909, Bryant & May, Australia’s first match factory at Church Street, Richmond, Victoria. was opened by The Honourable Alfred Deakin, Prime Minister of Australia, and Mrs. Deakin. It was heralded by the first Commonwealth Government of newly-federated Australia because the government of the day was anxious to encourage secondary industry and pledged tariff protection of local manufacturers. The building was constructed in 1909 as the Empire Works to a design by prolific Melbourne architect William Pitt and was purchased soon after by British safety match manufacturer Bryant and May, who significantly expanded the building, adding another level and the landmark clock tower. Bryant and May were unique in that they operated as a model factory, providing workers with conditions and amenities that even today seem generous. These included a dining hall and sports facilities such as a tennis court and bowling green which were constructed in the 1920s. Bryant and May ceased Australian match manufacture in the early 1980s as a result of import competition. Their iconic Redheads matches are now imported from Sweden. The complex has since been converted for use as offices and showrooms but is extremely well preserved. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. Bryant and May was a United Kingdom (UK) company created in the mid-nineteenth century specifically to make matches. Their original Bryant and May Factory was located in Bow, London. They later opened other match factories in the United Kingdom and Australia, such as the Bryant and May Factory, Melbourne; and owned match factories in other parts of the world. Bryant and May survived as an independent company for over seventy years, but went through a series of mergers with other match companies and later with consumer products companies. To protect its position Bryant and May merged with or took over its rivals. In 1971 the Northern Ireland factory, Maguire & Patterson closed down following a terrorist attack.. In the 1980s, factories in Gloucester and Glasgow closed too leaving Liverpool as the last match factory in the UK, until December 1994. . The registered trade name Bryant and May still exists and it is owned by Swedish Match Industries as are many of the other registered trade names of the other, formerly independent, companies within the Bryant and May group. Two French chemists, Henri Savene and Emile David Cahen, proved in 1898 that the addition of phosphorus sesquisulfide meant that the substance was not poisonous, that it could be used in a "strike-anywhere" match, and that the match heads were not explosive. British company Albright and Wilson, was the first company to produce phosphorus sesquisulfide ( Red Phosphorous) matches commercially. The company developed a safe means of making commercial quantities of phosphorus sesquisulfide in 1899 and started selling it to match manufacturers. Matches were first produced by Bryant & May in Australia in 1909. The Redhead name applies to the red striking heads of the matches which were introduced to Australia in 1946. The logo on the matchbox depicted the head and shoulder of a redheaded woman and has had four major updates since that time with a number of special issues depicting animals, birds and notable persons also producedThe Bryant & May Ltd factory in Church St Richmond is a listed building and has been converted to apartments following the closure of the Company 1980. Bryant & May's Ltd were influential in fighting against the dreadful disease known as Phossy jaw which was caused by white phosphorus used in the manufacture of the early matches. They were also the object of the 'Match Girls Strike' in London 1888, which won important improvements in working conditions and pay for the mostly female workforce working with the dangerous white phosphorus. The public were slow to purchase these safety matches because of the higher price An empty box of 'Redheads' safety matches made in Sweden for ST-Group, Springvale, Victoria, Australia c2015. The tray for the matches slides inside the open ended cover. The striking patch is on both sides of the cover. The matches have been removed. Matches were first produced by Bryant & May in Australia in 1909. The Redhead name applies to the red striking heads of the matches which were introduced to Australia in 1946. The logo on the matchbox depicted the head and shoulder of a redheaded woman and has had four major updates since that time with a number of special issues depicting animals, birds and notable persons also produced. Bryant and May ceased Australian match manufacture in the early 1980s.Top of cover ; Redheads / 45 safety / matches . Logo ; head & shoulders of a female with red hair Base of coverMade in Sweden / Redheads (R) is proudly marketed / by ST- Group Australia. / 718 Princes Highway Springvale Vic. 3171 / .............../ Readheads is a registered trademark / of Swedish Match Industries AB. / Complies ith European / Match Standard EN 1783-1997-SAF/ WARNING; / KEEP OUT OF REACH / OF CHILDREN. STRIKE / GENTLY AWAY FROM BODY . / barcode.redheads safety matches, safety matches, bryant & may pty ltd, phossy jaw disease, early settlers, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, lights, lamps, tobacco, white phosphorous, phosphorus sesquisulfide, swedish match pty ltd, pitt william, savens henri, cahen emile david , richmond victoria, match girls strike 1888, -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwaySectioned Tangye Steam Operated Water Pump, 1900s
Sectioned steam pump so that the pump workings can be seen. Inscriptions & Markings: Tangye Birmingham, This steam pump was presented by the colonial gas Assn Ltd (brass plaque) The Colonial Gas Association was originally formed in London on 2 February 1888, as The Australasian Gas Association Limited. The primary objective of the company was to provide investment capital to help finance the construction and management of gasworks being established by the London engineering firm John Coates & Co in metropolitan cities and regional towns throughout Australia and New Zealand. By 1890, the Australasian Gas Association had acquired gasworks at Benalla, Shepparton, Wangaratta, Warragul, Maldon and Seymour, and had constructed a large gasworks at Box Hill to supply the eastern suburbs of Melbourne. In 1893, the company's name was changed to the Colonial Gas Association Limited. During the 1890s, the company acquired regional gasworks in Queensland, Western Australia and South Australia, followed by its first gasworks in New South Wales, in 1911. In 1914, the company consolidated its metropolitan supply area by purchasing the Oakleigh and Footscray gasworks. Further expansion occurred in the 1920s with the purchase of established gasworks at Williamstown, Frankston and Dandenong and the acquisition of ten further gas undertakings in Queensland and New South Wales, making the firm the fifth largest gas producer in Australia. info from The Colonial Gas Association Limited, circa 1893 https://collections.museumvictoria.com.au/items/1553322 Originally formed by the five Tangye brothers from Cornwall as James Tangye & Brothers in 1857, this Birmingham engineering firm grew to become one of the largest suppliers of jacks, pumps, steam and oil engines, hydraulic presses, gas producers and machine tools in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The successful sideways launching of I.K. Brunel's 'Great Eastern' from the mud of the Thames in 1857 using Tangyes hydraulic jacks gave the firm much needed publicity and new orders flowed in. To finance expansion, George Price provided additional capital and the company name became Tangye Brothers & Price in 1859. A new factory known as the 'Cornwall Works' was built in Clement Street, Birmingham. In 1872, the firm became Tangye Brothers and in about 1879- 1880 began production of internal combustion stationary engines based on Horace Robinson's patents, later using the Otto four-stroke design for its Soho range of gas engines. Examples of the Soho engine were exhibited by the firm at the 1880 Melbourne International Exhibition. Petrol and oil engines were made from the 1890s onward, and by 1910 had developed into the Model B, BR and AA series engines. Tangyes supplied custom-built pumps and presses for particular applications, becoming a major exporter of engineering equipment. In 1884, Tangye Brothers opened a custom-built branch office, showroom and warehouse in Melbourne at Cornwall House in Collins Street West, advertising the full range of engineering products. These lantern slides images are taken from Tangyes product catalogues from the 1910-1925 period and are believed to have been used as sales promotional aids in Australia by the Tangye Brothers. info from https://collections.museumvictoria.com.au/articles/4670 Historic - Industrial Steam Operated Water Pump built by Tangye Bros and used by the Colonial Gas Company - Melbourne, Victoria, AustraliaSectioned steam pump so that the pump workings can be seen. Tangye Birmingham, This steam pump was presented by the colonial gas Assn Ltd (brass plaque)puffing billy, steam pump, sectioned, tangye bros -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBadge - ACF Australian Comforts Fund badge, P J King Pty Ltd, 1940
This Australian Comforts Fund badge is part of a set of eleven badges collected from the 1920s to the 1940s by Dr W. R. Angus. The badge was sold by the ACF in 1940 to raise funds for gifts to send to the Australian troops serving overseas. The badge is one of a set of badges that represents various organisations that he had interests in. The Australian Comforts Fund was a mostly female, volunteer-run organisation officially recognised by the Government. It began in 1916 as an amalgamation of groups of people who wanted to support the Australian troops abroad with Items of comfort to supplement the essential items provided by the Australian Military Forces. The ACF raised funds to purchase goods, pack them and send them overseas. One of their fund-raising activities was 'button days' where buttons such as this one were given to those who gave donations. The ACF closed down after World War I but was re-formed at the start of World War II. Items that the ACF sent to the troops included personal toiletry items such as toothbrushes and toothpaste, magazines, pyjamas, singlets and socks. They also provided sporting equipment, recreational music, writing materials and postcards. Special hampers were sent to the troops at Christmas time. The maker, P J King, (Percy John King), originally established his engraving and ie casting business in Russell Street, Melbourne in 1893 in partnership with Charles Walder Bridgland, continuing on his own from 1899. Percy and his son John Howard King set up a new business P J King Pty Ltd in 1928 making uniform buttons. In the late 1980s, it merged with two other companies that then became J J Cash, now known as Cash's Australia. The set of badges was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” which includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) and Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. The W.R. Angus Collection: - The W.R. Angus Collection includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) and Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. It includes historical medical and surgical equipment and instruments from the doctors Edward and Thomas Ryan of Nhill, Victoria. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1927 at Ballarat, the nearest big city to Nhill where he began as a Medical Assistant. He was also Acting House surgeon at the Nhill hospital where their two daughters were born. During World War II He served as a Military Doctor in the Australian Defence Force. Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool in 1939, where Dr Angus operated his own medical practice. He later added the part-time Port Medical Officer responsibility and was the last person appointed to that position. Dr Angus and his wife were very involved in the local community, including the planning stages of the new Flagstaff Hill and the layout of the gardens there. Dr Angus passed away in March 1970.This badge represents the efforts of the women volunteers in Australia to support the Australian troops overseas in WWI and WWII. This badge is one of a set of significant badges that connects Doctor Angus with Australian organisations of the early-to-mid 20th century, including those relating to military service support. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The Collection includes historical medical objects that date back to the late 1800s.The ACF Badge is a star-shaped, gold, glittered red enamel and metal badge. The star has six points. The enamel surface is textured. The border and front inscription of the badge is gold. It is the badge of the Australian Comfort Fund, made by P.J. King and dated 1940. This badge is part of a set of badges collected by Dr W R Angus. the set represents organisations that he was involved in, and is part of the W.R. Angus Collection.Front: “ACF / 1940” Reverse embossed “P.J. KING”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, metal badges, enamel badges, organisation badges, acf, presbyterian brotherhood, oikumene, w.r. angus, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, australian comforts fund, button day, volunteer, australian military forces, christmas hamper, 1940 acf badge, fund-raising, p j king pty ltd, percy john king, donor's badge, world war ii, 1939-1945, australians at war, voluntary work, volunteers, home front, w.r. angus collection -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayG42, Garratt Steam Locomotive, 1926
G42 Garratt Steam Locomotive Traffic and train loadings on Victoria's narrow gauge railways reached their peak during the 1920s. To assist in handling the longer, heavier trains, the Victorian Railways ordered two larger, more powerful Beyer Garratt locomotives. These were delivered in 1926 and were numbered G41 and G42. They were sent to work on the Colac–Beech Forest–Crowes line and the Moe–Walhalla line respectively. After the line from Moe closed in 1954, G42 was sent to Colac, where it worked with its mate, G41, until closure of that line in mid-1962. G41 had been in poor condition and was scrapped, whereas a brighter future awaited G42. The Victorian Railways offered G42 to the Puffing Billy Preservation Society, for display as a static exhibit in the Menzies Creek Museum. Over time, a plan evolved to restore G42 to operation, a goal that was eventually achieved by the launch of G42 back into traffic in April 2004. G42 now continues to operate as a restored member of the Puffing Billy Railway's locomotive fleet. No. originally constructed: 2 No. in service: 1 (No. 42) Boiler pressure: (lb/sq. in) 180 Boiler heating surface: 1268 sq ft (117.8 m2) Tractive effort: (85%) 26,860 lbs (12.18 t) Driving wheel diameter: 36" (91.44 cm) Max axle load: 9t 5cwt Length Overall: 51' 7" (15.72m) Height Overall: 10' 8" (3.28m) Date of manufacture: 1926 Manufacturer: Beyer Peacock Place of manufacture: Manchester UK Locomotive Type: Garratt Coal capacity: 70 cwt Cylinder diameter: 13" (33.02 cm) Cylinder stroke: 18" (45.72 cm) Wheel arrangement: 2-6-0+0-6-2 Roadworthy weight: 69t Water capacity: 1680 gal (7,637.43 l) Beyer Peacock - Garratt Locomotives Register Works Number - 6268 / 1926 Gauge/Railway/Class - 2'6"/Victorian Government Rlys/G Type - 2-6-0+0-6-2 No. G42 Notes - Australia G42 Built in 1926 and painted all-over black, this Garratt locomotive was issued to the Moe to Walhalla line where it remained—other than for overhauls—until the line closed in 1954. After an overhaul at Newport Workshops, it was issued to the Colac to Crowes line and remained there until that line closed in 1962 when it was returned to Newport Workshops for storage. In 1964 it was sold to the Puffing Billy Preservation Society and removed from the V.R. register 3 months later. It arrived at Belgrave in 1968 and was hauled to Menzies Creek for static display in the museum. 1986 saw the commencement of restoration the Belgrave workshops and has been restored to its 1946 to 1954 condition with raised cab roof, raised marker lamps, steel cow-catchers and all-over black livery. It was returned to service on April 18, 2004. Service History : Jun 1926 - Moe - initial allocation of a new locomotive Jun 1926 - Oct 1954 Moe Oct 1954 - Jan 1955 Workshops Jun 1955 - May 1962 Colac Jul 1962 - Dec 1965 Workshops - Stored Jan 1968 - Feb 1968 Belgrave - Stored Feb 1968 - 1982 - Menzies Creek Steam Museum 1982 - 2004 - Under restoration Apr 2004 - Belgrave - In active service at Puffing Billy Railway BelgraveHistoric - Victorian Railways - Narrow Gauge - Garratt Steam Locomotive - G42 Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) Number H2187 G42 Garratt Steam Locomotive made of steel, iron and wrought iron with brass fittings - the Locomotive is in Active Service - Belgrave Station G42puffing billy, narrow gauge, garratt, g42, steam locomotive, beyer peacock, victorian railways -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Historical, Warrnambool, C. 1854-1871
This is an image of the Warrnambool Lighthouse Complex on Middle Island in 1854. The Store, Lighthouse Keeper's Quarters, Lighthouse and Flagstaff are in the background. The foreground shows a covered buggy drawn by two horses and a person in attendance, and another wheeled vehicle behind it with a figure nearby. There is a saddled horse to the right with two males in conversation nearby. The ground is soft, perhaps the riverbed or sandy shore. THE LIGHTHOUSE KEEPERS Lighthouse Keepers were responsible for keeping their Lighthouse’s lights shining at night. They kept a lookout for passing vessels and changes in weather. They were expected to clean, polish and maintain the equipment and buildings. They kept regular and detailed records of who was on watch, and the time the light was lit, trimmed and extinguished. They kept a journal about other events that occurred. They keep regular, accurate Meteorological Logs. It was expected that they were competent in Morse code signalling. They would be called to help in times of disasters and shipwrecks and to give official statements about these events. Many Lighthouse Keepers also volunteered as members of the lifeboat crew. The Lady Bay lighthouses were officially classified as small, so the Keepers had the official titles of Senior Assistant Lighthouse Keeper and Assistant Lighthouse Keeper. They were employed by the Public Service and paid rent to live in the Lighthouse Quarters. They were compulsorily retired at the age of 60, with most receiving a superannuation payment. Despite their time-consuming duties, there was time to follow hobbies and crafts such as growing vegetables, playing musical instruments, making models of buildings including lighthouses, and crafting furniture pieces. An example of a keeper’s skills is the carved fire screen made by /assistant Keeper Thomas Hope in the late 19th century and displayed in the Lighthouse Keeper’s cottage at Flagstaff Hill. Both Alexander and Farncombe had served under Senior Keeper Robert Deverell, who was the first and only Senior Lighthouse Keeper at the Middle Island Complex. John Alexander was the Assistant Keeper in the 1850s. Andrew Farncombe was the last Assistant Keeper at Middle Island, serving there with his family from 1864 to 1871. During 1871 and 1872 the Lighthouse Complex was moved to Flagstaff Hill on Merri Street. Farncombe and Deverell then became the first Keepers and occupants of the Lady Bay Lighthouse Complex at Flagstaff Hill. They continued their service together; overall, Deverell served from 1859 to 1885 and Farncombe from 1864 to 1974. WARRNAMBOOL'S LADY BAY LIGHTHOUSE COMPLEX - The original Lighthouse Complex was built on Middle Island in 1858-1859 then transferred stone-by-stone to Flagstaff Hill in 1871. The Complex comprised the Lighthouse, the Lighthouse Keepers’ Quarters and a Privy. The bluestone Keeper’s Quarters was a cottage divided into two compartments, one for the Senior Keeper and his family, the other for the Assistant Keeper and his family. The bluestone Store was divided into three; a store, a workshop, and an oil store (or office). The Privy comprised a small building also divided into two separate, back-to-back toilets, one for each Keeper and his family. In the 1970s the Flagstaff Hill Planning Board was set up under the chairmanship of John Lindsay. The Board was to make recommendations to the Warrnambool City Council regarding the use of the buildings and the rest of the Crown Land on the site. The Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village opened in 1975 and began renovating the Cottage in stages, during which time evidence of a 1920s fire was found in the eastern section of the cottage. Additions of a porch on the west and a washroom on the east were made in the 1980s. The western part of the building is now a Shipwreck Museum and the east has returned to a late 19th-century Lighthouse Keeper’s cottage and includes the screen made by Assistant Lighthouse Keeper Thomas Hope in the late 19th century. Hope served two periods of time at the Lighthouse. This photograph is significant as a visual record of the original Warrnambool Lighthouse Complex on Middle Island, the origin of what is now the Lady Bay Lighthouse Complex. The photograph is significant for its connection to the Complex, which is now listed on the Victorian Heritage Register, H1520, for being of historical, scientific (technological) and architectural significance to the State of Victoria. The Complex is significant as an example of early colonial development. The photograph is significant for its connection with the important navigational function of the Lighthouses, a function still being performed to this day. The photograph is also significant as it shows an example of buildings organised by the Public Works Department in Victoria in the mid-to-late 19th century. The structures tare still stand strong. Photograph of horses, a buggy and three gentlemen in the foreground and the background shows a lighthouse and accompanying buildings. Printed in black and white. (Another two horse-drawn vehicles are partially visible). The subject is the Lighthouse Complex on Middle Island, Warrnambool, dated between 1854 and 1871.An inscription is handwritten in black pen on the back of the mounting board."The lighthouse and accompanying buildings were / established on Middle Island in 1854, as this / picture shows. In 1871 they were moved to their / present site on Flagstaff Hill."flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, warrnambool, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, lighthouse keeper's cottage, lighthouse residence, lighthouse, chart room, quarters, privy, middle island, beach lighthouse, obelisk, lighthouse complex, lady bay complex, warrnambool port, warrnambool harbour, lady bay, keepers, lighthouse keeper, upper lighthouse, lower lighthouse, assistant keeper, ports and harbours, cottage, meteorological record, 1854, 1871 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle and Pen, Caldwell’s Ink Factory, Early 20th century
This shaped ink bottle made by Caldwell's is called a 'boat ink bottle'. It was shaped especially to hold a nib pen when the pen was not in use. The design of the bottle is sometimes called a ‘cottage’ or ‘boat’ shape. The Caldwell’s handmade glass ink bottle was mouth-blown into a two-piece mould, a method often used in the mid-to-late 19th century. The glass blower burst the bottle off the end of his blowpipe with a tool, leaving an uneven mouth and sharp edge on the bottle, which was usually filed. The bottle was then filled with ink and sealed with a cork. More expensive bottles would have a lip added, which was more time-consuming and costly to produce. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. Pen and ink have been in use for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used up until around the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. The nis only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. Caldwell’s Ink Co. – F.R. Caldwell established Caldwell’s Ink Company in Australia around 1902. In Victoria, he operated from a factory at Victoria Avenue, Albert Park, until about 1911, then from Yarra Bank Road in South Melbourne. Newspaper offices were appointed as agencies to sell his inks, for example, in 1904 the New Zealand Evening Star sold Caldwell’s Flo-Eesi blue black ink in various bottle sizes, and Murchison Advocate (Victoria) stocked Caldwell’s ink in crimson, green, blue black, violet, and blue. Caldwell’s ink was stated to be “non-corrosive and unaffected by steel pens”. A motto used in advertising in 1904-1908 reads ‘Makes Writing a Pleasure’. Stationers stocked Caldwell’s products and hawkers sold Caldwell’s ink stands from door to door in Sydney in the 1910s and 1920s. In 1911 Caldwell promised cash for returned ink bottles and warned of prosecution for anyone found refilling his bottles. Caldwell’s Ink Stands were given as gifts. The company encouraged all forms of writing with their Australian-made Flo-Eesi writing inks and bottles at their impressive booth in the ‘All Australian Exhibition’ in 1913. It advertised its other products, which included Caldwell’s Gum, Caldwell’s Stencil Ink (copy ink) and Caldwell’s Quicksticker as well as Caldwell’s ‘Zac’ Cough Mixture. Caldwell stated in a 1920 article that his inks were made from a formula that was over a century old, and were scientifically tested and quality controlled. The formula included gallic and tannic acids and high-quality dyes to ensure that they did not fade. They were “free from all injurious chemicals”. The permanent quality of the ink was important for legal reasons, particularly to banks, accountants, commerce, municipal councils and lawyers. The Caldwell’s Ink Company also exported crates of its ink bottles and ink stands overseas. Newspaper advertisements can be found for Caldwell’s Ink Company up until 1934 when the company said they were the Best in the business for 40 years.This pen and ink bottle set is of significance as the bottle has its original cork and retains remnants of ink, which was made from a recipe that at the time was over 100 years old, according to Caldwell.. The handmade, mould blown method of manufacture is representative of a 19th-century handcraft industry that is now been largely replaced by mass production. The bottle and its contents are of state significance for being produced by an early Melbourne industry and exported overseas. The pen and ink set is historically significant as it represents methods of handwritten communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and typewriters were becoming part of standard office equipment.Victorian boat ink bottle; small rectangular clear glass ink bottle with horizontal grooves made in the glass for resting and holding the pen. The set includes one pen and nib with the bottle and cork. The bottle is made by Caldwell's and contains its Flo-Eesi Blue Black Ink brand."Caldwell's Flo-Eesi Blue Black Ink."flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, flo-eesi, blue black ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, two-part mould, sheer-lip bottle, burst-lip, cork seal, f r caldwell, caldwell’s ink company, albert park, south melbourne, inkstands, stencil ink, copy ink, quicksticker, zac cough mixture -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottles, Caldwell’s Ink Factory, Early 20th century
This crate of bottles may have come from a wholesaler, business, stationer or school. The design of the bottles is sometimes called a ‘cottage’ or ‘boat’ shape. Each of the 70 Caldwell’s handmade glass ink bottles was mouth-blown into a two-piece mould, a method often used in the mid-to-late 19th century. The glass blower burst the bottle off the end of his blowpipe with a tool, leaving an uneven mouth and sharp edge on the bottle, which was usually filed. The bottle was then filled with ink and sealed with a cork. More expensive bottles would have a lip added, which was more time-consuming and costly to produce. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. Pen and ink have been in use for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used up until around the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. The nis only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. Caldwell’s Ink Co. – F.R. Caldwell established Caldwell’s Ink Company in Australia around 1902. In Victoria, he operated from a factory at Victoria Avenue, Albert Park, until about 1911, then from Yarra Bank Road in South Melbourne. Newspaper offices were appointed as agencies to sell his inks, for example, in 1904 the New Zealand Evening Star sold Caldwell’s Flo-Eesi blue black ink in various bottle sizes, and Murchison Advocate (Victoria) stocked Caldwell’s ink in crimson, green, blue black, violet, and blue. Caldwell’s ink was stated to be “non-corrosive and unaffected by steel pens”. A motto used in advertising in 1904-1908 reads ‘Makes Writing a Pleasure’. Stationers stocked Caldwell’s products and hawkers sold Caldwell’s ink stands from door to door in Sydney in the 1910s and 1920s. In 1911 Caldwell promised cash for returned ink bottles and warned of prosecution for anyone found refilling his bottles. Caldwell’s Ink Stands were given as gifts. The company encouraged all forms of writing with their Australian-made Flo-Eesi writing inks and bottles at their impressive booth in the ‘All Australian Exhibition’ in 1913. It advertised its other products, which included Caldwell’s Gum, Caldwell’s Stencil Ink (copy ink) and Caldwell’s Quicksticker as well as Caldwell’s ‘Zac’ Cough Mixture. Caldwell stated in a 1920 article that his inks were made from a formula that was over a century old, and were scientifically tested and quality controlled. The formula included gallic and tannic acids and high-quality dyes to ensure that they did not fade. They were “free from all injurious chemicals”. The permanent quality of the ink was important for legal reasons, particularly to banks, accountants, commerce, municipal councils and lawyers. The Caldwell’s Ink Company also exported crates of its ink bottles and ink stands overseas. Newspaper advertisements can be found for Caldwell’s Ink Company up until 1934 when the company said they were the Best in the business for 40 years.This large collection of similar ink bottles is of particular significance as the bottles have come from the same source, most have their original corks and some retain their original labels, which is rare. The method of manufacture of these bottles is also representative of a 19th-century handcraft industry that is now been largely replaced by mass production. The bottles and their contents are of state significance for being produced by an early Melbourne industry and exported overseas. This case of ink bottles is historically significant as it represents methods of handwritten communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and typewriters were becoming part of standard office equipment.Ink bottles in a wooden crate; 70 rectangular, hand-blown clear glass ink bottles. They have side seams, uneven thickness, especially at the bases, and rough, burst-off mouths. The shoulders on the long sides have horizontal grooves used for pen rests. The bottles vary; some have labels, some contain remnants of blue-black ink, and many have their original corks. The glass has bubbles and imperfections. The remnants of printed labels are on white paper with a swirly border and black text. The bottles contained Caldwell’s blend of blue black ‘Flo-Eesi’ ink.Printed on label; “CALDWELL FLO-EESI BLUE BLACK INK” “ - - - - “ Printed script signature “F.R. Caldwell”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, flo-eesi, blue black ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, two-part mould, sheer-lip bottle, burst-lip, cork seal, f r caldwell, caldwell’s ink company, albert park, south melbourne, inkstands, stencil ink, copy ink, quicksticker, zac cough mixture
