Showing 454 items
matching valve
-
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, Public Transport Corporation (PTC), W class tramcar components:, 1992
Report - 4 A4 sheets - showing the monthly and annual usage of various W class tramcar components: Governor Linebreaker R/C Coil R/C Unit Relay Valve Governor tipshas in ink on top "found Feb. 1992"trams, tramways, w class, overhauls, preston workshops, equipment -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book - History of Alderdice Brassfounders Warrnambool, Bill Downing and Jane Downing, History of Alderdice Brassfounders Pty Ltd 1898-2015, 2016
History of Warrnambool Factory - Alderdice Brassfounders Pty LtdThis is a book of 108 pages. It has a brown cover with white printing and a black and white photograph on the front cover and printing and seven black and white photographs on the back cover. The pages contain printed material and black and white photographs. non-fictionHistory of Warrnambool Factory - Alderdice Brassfounders Pty Ltdalderdice brassfounders pty ltd, agriculture in warrnambool district, william & charles downing -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - BILL ASHMAN COLLECTION: SCALEBUOY
Black and white photo of a Scalebuoy being used with a gas Bath heater unit. Typed on the back: Scalebuoy Metropolitan Gas Bath Heater Unit. Fitted to the heater in conjunction with combination water cock and gas valve.sciences, instruments - general, scalebuoy, bill ashman collection - correspondence, scalebuoy unit, bath heater -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - IAN DYETT COLLECTION: AUCTION CATALOGUE - CARLTON AND UNITED BREWERIES LTD
White catalogue with blue printing for a sale on the 14th April, 1992 on account of Carlton and United Breweries Ltd, Abbotsford. For sale was pumps, valves, components and spares, New electrical fittings and parts, and general equipment and spares.business, auctioneers, j h curnow & son pty ltd, ian dyett collection - auction catalogue - carlton and united breweries ltd, malcolm mackinnon, j h curnow & son p/l, occupational health and safety act 1985, noel dyett, fred dyett, ian dyett, bolton bros p/l -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncTool - Realia, Glass working bench torch burner, 1960's
Can be operated on Natrua Gas, Town Gas, and Bottled Gas, Needle valves for gas and Air Supplies allows fine flame adjustment. Burner Nozzle canTripod shaped base with ball joint nozzle and two gass inletsscience, education -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Instruction, "Jelbart Road Roller"
Instruction of starting, adjustments, fuel, speed, operation, maintenance, air valve timing, and lubrication of the SEC Jelbart Road Roller. This item is now at the Bylands Tramway Museum.Yields information about the operation of the SECV Ballarat Road roller supplied by Jelbart.Four quarto sheets, stapled in top left hand corner.secv, ballarat, jelbart, instructions, road roller -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Spring Scale
The first spring balance in Britain was made around 1770 by Richard Salter of Bilston, near Wolverhampton. He and his nephews John & George, founded the firm of George Salter & Co., still notable makers of scales and balances, who in 1838 patented the spring balance. They also applied the same spring balance principle to steam locomotive safety valves, replacing the earlier deadweight valves. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spring_scale Today, spring scales are very popular with recreational fishers. The ability to weigh things reasonably accurately with a small inexpensive apparatus allowed for the exact weight of items to be ascertained. However, it was not accurate enough to weigh small amounts in ounces or grams.Scale. Has ring for hanging, spring and hook device for weighing. Measures in lbs.Scale of pounds weight.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Black and White, Aerial Photograph of the Ballarat School of Mines and Ballarat East, Pre 1967
Black and white aerial photograph of the Ballarat School of Mines, White Flat Oval, Ballarat Gaol, Ballarat Brewery, Ballarat Club, Uniting Church, John Valves (Lydiard Street), Ballarat Girls' Technical School and Ballarat ballarat gaol, white flat, ballarat uniting church, ballarat girls' technical school, armstrong street south, lydiard street south, yarrowee channel, humffray street south, m.b. john, john valves, former ballarat gaol, ballarat brewery, dana street, grant street, lydiards street south, white flat oval, aerial photograph -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - WESTINGHOUSE M3 FEED VALVE
Two page brochure, with two drawings attached, for Westinghouse M3 Feed Valve and pipe brackets. On bottom of front page The Westinghouse Brake co. of Australasia Ltd., Head Office and Works: Concore West, N.S.W. 1931.The Westinghouse Brake Co. Of Australasia Ltd. Concord West, N.S.W.organisation, commerce, westinghouse -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumBook, Westinghouse Brake & Saxby Signal Co. Ltd, "The Westinghouse Brake - Reference Book", 1904
One Hundred page book with nine fold out plates tipped in, green card titled "The Westinghouse Brake - Reference Book", published by Westinghouse Brake Co. in 1904. Text has been sewn into sections and then bound into the book. Plate inside front cover, has been printed in colour showing the extent of the use of the Westinghouse brake system that had been adopted on the various railways. Plat 110E (page 43) has an orange plastic component acting as a brake handle and showing how the various ports and parts interrelated in the valve. Inside the back cover are two loose folded sheets, plate 209 and 209A, Improved triple valve and the "Graduating Release Valve", dated August 1905. Covers compressed air brake systems on railway trains, showing how they are designed, operated, parts listing and has a number of pasted in erratum in the book. "Colin Rutledge" stamped on top of page 1 and inside front cover. On cover written in black ink "Melbourne Office, WB Co. of A, Jan '11"trams, tramways, westinghouse, railway brakes, equipment, compressors, carriages -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: FLOWING
The Laanecoorie Weir on the Loddon River supplies both irrigation and domestic water. It was the second Victorian irrigation scheme after the Goulbourn. It was constructed 1889-1892 with the outlet valves installed in 1891.Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from 2003. Flowing: this photograph was taken at the Laanecoorie Weir in the mid 1980s. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBand Instrument and case
Brass Band Instrument - Cornet "Clear Bore" Class a Light Valve. Boosey & Co makers, 295 Regent Street London. No 80772 (64988) Imported by Allan & Co Pty Ltd Melbourne. Horn 4�" Length 12�"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, Lecture Notes, 1945 and 1946
.1) A set of handwritten and printed notes. .2) Serveral sets of handwritten notes on blue-lined foolscap loose-leaf sheets about thermodynamics. .3) A set of fordigraphed foolscap sheets tites 'Volume s and Valve Gear .e.j. barker, jack barker, lecture notes, univesity of melbourne, engineering -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Pressure Gauge, Barclay Curle & Co shipbuilders, Circa 1873
The Loch Ard got its name from "Loch Ard" a loch that lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curle & Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen, and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead, and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold their position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Lochard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy that had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost families in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce, and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Lochard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Lochard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Lochard Gorge. Cargo and artifacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register.The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artifacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artifacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck of which the subject items are a small part. The collection's objects give us a snapshot of how we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. Through is associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Pressure gauge; round brass instrument with brass fittings: gate valve and handle. The two separate parts include a small bracket. Encrustations are on the surface. The flat side has been lacquered. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, pressure gauge, mechanical instrument -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePressure Gauge
Pressure Gauge section, circular section of gauge with glass missing attached to a gate-valve. H 205mm x W 130mm x D 30mm. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. Previous number PWO 0349.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, pressure gauge, loch ard -
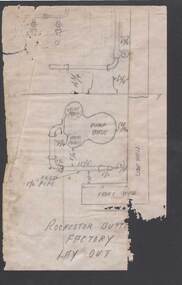 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BILL ASHMAN COLLECTION: SCALEBUOY DIAGRAM
Lay Out of Scalebuoy at the Rochester Butter Factory drawn in pencil on a piece of paper with the bottom right corner missing. Lay Out includes measurements, pump base, 2 valve houses, front and side walls and pipe layout.sciences, instruments - general, scalebuoy, bill ashman collection - correspondence, rochester butter factory lay out -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - AAP 7271.048-3 727.149 Part Model or Type No B99-26-203 and B99-26-204 Valve, Fuel Cut Out Type 16
Released around 1970 by the Royal Australian Air Force. A manual for part model or type no B99-26-203 and B99-26-204 valve, fuel cut out type 16.royal australian air force, valve and fuel cut out type 16, australian air publication -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - AAP 7276.019-3MB1 to B2 Single Barrel Servo Control Jack Amendment List 12
Released around 1970 by the Royal Australian Air Force. A manual for part model or type no B99-26-203 and B99-26-204 valve, fuel cut out type 16.royal australian air force, valve and fuel cut out type 16, australian air publication -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - AAP 7276.019-3 Single Barrel Servo Control Jack Type 103-35-1 Amendment List 6
Released around 1970 by the Royal Australian Air Force. A manual for part model or type no B99-26-203 and B99-26-204 valve, fuel cut out type 16.royal australian air force, valve and fuel cut out type 16, australian air publication -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyradio, C1950's
Old radios recall a time when society was very different. The 1950s were the heyday of radios in Australia. Families often had more than one in the home. When transistor radios arrived instead of listening on the valve mantel, people were able to grab a tiny radio, taking music and news anywhere they wanted. This item reflects the time before portable radio communication. A 240V valve radio in a wooden cabinet. It is a mantel radio with four knobs at the front - two on each side - for volume, tuning, tone/on/off and band. There is a lead with a plug attached and earth at the back. Under each corner is a small wooden foot. "S.T.C. Made in Aust."radio communication entertainment -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPugh's inhaler - replica
Replica of original glass ether inhaler used by Dr William Russ Pugh in Launceston in 1847. William Russ Pugh is credited with being the first person in Australia to administer ether as anaesthesia. Pugh created his own ether inhaler based on a report in the London Illustrated News, dated January 1847. The paper reached Pugh in May and by June he had already designed, made and used the ether inhaler. On 7 June 1847 he performed two surgeries using anaesthesia. He also had a journalist present to record the event.The main container comprises an inverted funnel shaped glass jar that is connected to the top glass globe via an etched glass valve. Sea sponges are located within the glass vessel and the woven cloth tube is connected to the base of the glass container. inhaler, anaesthesia, william russ pugh, replica, glass, sea sponge, ether, launceston, illustrated london news, lady howden, dr john belisario, dr gwen wilson -
 Trafalgar Holden Museum
Trafalgar Holden MuseumVehicle - Buick Sedan, 1938
The Special Sport Sedan is a rear wheel drive saloon (sedan) motor car with a front located engine, manufactured by Buick. The Special Sport Sedan is part of Buick's Series 40 family of cars. It is powered by a naturally aspirated engine of 4.1 litre capacity. This unit features overhead valve valve gear, in line 8 cylinder layout, and 2 valves per cylinder. It has an output of 107 bhp (108 PS/80 kW) of power at 3400 rpm, and maximum torque of 275 N·m (203 lb·ft/28 kgm) at 2000 rpm. A 3 speed manual transmission transmits the power. Buick scored another first in 1939 when it became the first company to introduce turn signals, which did not appear on other car brands until almost a decade later.[ All 1939 models also had a steering column mounted shift lever1938 Buick Sedan . Bodied in Australia by GMHBurgundy 4 door rear wheel drive sedan automobile, bodied, car -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPhotograph
The Lidwill machine was designed by Mark Lidwill in 1913, for the purpose of mechanical or insufflation anaesthesia. It was manufactured by Elliott Bros. of Sydney. Shortly afterwards, the Anaesthetic and Portable Machine Company of Sydney devised a machine that was functionally the same but also contained an electric lamp heater.Colour photograph of a modified Lidwill anaesthetic machine sitting on carpet, taken from above. The vaporiser is metal and circular, and has metal valves and controls and two orange tubes. The machine has an electric cord and power plug which is coiled on the floor.anaesthetic equipment, lidwill anaesthetic machine, mark lidwill, ether vaporiser, anaesthetic and portable machine company of sydney, vaporiser -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Technical pamphlet/s, Westinghouse Brake Company of Australasia Limited and The Westinghouse Brake & Saxby Signal Co. Ltd. of 82 York Road and Kings Cross London, "The Westinghouse Brake with Electro-Pneumatic Control", Dec. 1926
2285.1 - 12 page technical pamphlet (2 sheets of paper - pages 5 -10 formed as a concertina folded centre sheet) titled "Interlocked electo-pneumatic brake", published by Westinghouse Brake Company of Australasia Limited, December 1926. Manual D.P. 9. Stapled with two steel staples along fold. Describes in detail the electro-pneumatic brake system as used on Sydney Suburban trains, complete with diagrams, brake valve operation, magnet valve and isolating cock switch. 2285.2 - Six page technical pamphlet, titled "The Westinghouse Brake with electro-pneumatic control", published by Westinghouse Brake and Saxby Signal Co. 1915. Pages 3 and 4 have been tipped in the cover sheet. Describes standard brake equipment for use with electric trains and electro pneumatic control over the brakes. Gives details of house the brake valve (No. 18 EP) operates. Scanned to the COTMA Website 4-10-2015."Colin Rutledge" stamped on top of page 1.trams, tramways, westinghouse, electric trains, electro - pneumatic brakes, sydney suburban trains -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Steam locomotives J-547 and J-512 in the locomotive shed, Bendigo Railway Station, 1962
"J547 undergoes maintenance that required removal of its motion gear, axle box and wheel set. The dome cover has also been removed to facilitate a boiler inspection and/or work on the regularor valve. November 1962" - NewsrailDigital TIFF file Scan of 35mm Ilford FP3 black and white negative transparencybendigo, bendigo railway station, george coop collection, j-512, j-547, j-class steam locomotive (vulcan foundry), railway turntable, railway workshop -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumDocument - DOCUMENTS/MAP, 1874-5
COLLECTION OF LETTERS - 1 X JANUARY 5,1874 1 X MAY 23, 1874 1 X JANUARY 8, 1874 1 X SEPTEMBER 4, 1874 1 X JANUARY 10, 1874 1 X APRIL 5, 1875 1 X JANUARY 15, 1874 1 X MAY 10, 1875 1 X JANUARY 22, 1874 1 X MAY 13, 1875 (3 PAGES) 1 X JUNE 7, 1875 1 X JANUARY 28, 1874 1 X JUNE 29, 1875 1 X JANUARY 29, 1874 1 X DECEMBER 23, 1875 DONATED TO MUSEUM BY JEFF MACKCOLLECTION OF LETTERS(3) FROM MR. JESSUP (SOLICITOR) OF CLUNES WATER SUPPLY FROM 1870. PRIVATE LETTER FROM JEFF MACKAY. MAP - CLUNES RETICULATION CIRCA 1874. DETAILS OF PIPES LAID AND PROPOSED PIPE LINES, FIRE PLUGS, VALVES.CORRESPONDENCE FROM SOLICITOR (MR. JESSUP) 1874-5document, letters, map, water supply, mr. jessup -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c1930
Taken on 25 October 1930, various houses with the Hume Dam under construction are depicted in the background. The construction of the Hume Dam took place from 1919 to 1936. At the time of construction, it was the second largest dam in the world. It was also one of the earliest civil projects developed after the Federation. Some of the Dam workers consisted of World War I veterans. Dam workers often settled their families in Mitta Junction Village and Wodonga. Archaeological surveys were completed by Austral Archaeology, which was done when the Department of Land & Water Conservation was doing work to improve Hume Dam. The archaeological report that came out of the survey recommended three sites of interest where archaeological excavation should be done: Camp Ganger’s Quarters, Stableman’s Quarters, and the Industrial Dump. The excavation uncovered artefacts. Mitta Mitta: Mitta Mitta is situated between Mount Welcome and Mount Misery. It is named after the river that explorers Hume and Hovell discovered in 1824. The town would eventually become a huge gold mining town. Mitta Mitta is called Midamodunga by the local Indigenous peoples Wodonga: Wodonga is situated on the Murray River and is part of North East Victoria. Hume and Hovell: Hamilton Hume (1979-1873) and William Hilton Hovell (1786-1875). W. H. Hovell was born in Norfolk England and Hume was born in Parramatta, New South Wales Hovell and Hume undertook an exploration journey in 1824 and thought they discovered a river, which turned out to be the Murray River. They returned home in 1825, but returned to the area in 1826 and discovered coal in the area.This photo is historically significant as it shows the Hume Dam under construction in 1930. The Dam was named after Hamilton Hume, who is an important historical figure for this area as he helped discover the area where resources were found.Sepia rectangular photograph printed unmountedReverse: 84-19-2/ 1997.3188/ These are the four / release valves they are / not always open (illegible) this / when closed the water flows / over the spillway. [featuring trademark: kodak print] photograph number: 354construction, houses, veterans, mitta junction village, hume dam, world war i, federation, wodonga, archaeological survey, excavation, austral archaeology, department of land & water conservation, camp ganger's quarter's, stableman's quarters, industrial dump, artefacts, mitta mitta, mount welcome, mount misery, murray river, hamilton hume, william hilton hovell, hume and hovell expedition -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomInstrument - Trumpet, Cavalry, Couesnon Cie, 1901 (exact)
The 2nd Light Horse Regiment was raised at Enoggera in Queensland on 18 August 1914. Its recruits came mainly from Queensland but some hailed from the northern rivers district of New South Wales. The 2nd was one of three regiments of the 1st Light Horse Brigade – the first Australian mounted formation raised by Australia during the First World War. The regiment sailed from Brisbane on 25 September and disembarked in Egypt on 9 December. The 2nd Light Horse Regiment deployed to Gallipoli without its horses and landed there on 12 May 1915, joining the New Zealand and Australian Division. It played a defensive role for most of the campaign but did attack the Turkish trenches opposite Quinn’s Post, one of the most contested positions along the ANZAC Line. The first assault wave was mown down and fortunately the officer commanding the attack had the wisdom and courage to call it off. The 2nd was withdrawn from the front line in September and left the peninsula on 18 December. Back in Egypt, the 2nd Light Horse joined the ANZAC Mounted Division. Between January and May 1916, the regiment was deployed to protect the Nile valley from bands of pro-Turkish Senussi Arabs. On 18 May, as part of its parent brigade, it joined the forces defending the Suez Canal. The 1st Light Horse Brigade played a significant role in turning back the Turkish advance on the canal at the battle of Romani on 4 August. In ensuing days the regiments of the brigade participated in the immediate follow-up of the defeated Turks, but were soon withdrawn to rest. The 2nd Light Horse Regiment rejoined the Allied advance across the Sinai in November and was subsequently involved in the fighting to secure the Turkish outposts on the Palestine frontier – Maghdaba on 23 December 1916 and Rafa on 9 January 1917. A stint of protective duty along the line of communications through the Sinai followed. The 2nd’s next major engagement was the abortive second battle of Gaza on 19 April. Gaza finally fell on 7 November, after a wide outflanking move via Beersheba, in which the 1st Light Horse Brigade played a part. With the capture of Gaza, the Turkish position in southern Palestine collapsed. The 2nd Light Horse Regiment participated in the advance to Jaffa that followed, and was then committed to operations to clear and occupy the west bank of the Jordan River. It was involved in the Amman (24–27 February) and Es Salt (30 April–4 May) raids and the repulse of a major German and Turkish attack on 14 July 1918. The final British offensive of the campaign was launched along the Mediterranean coast on 19 September 1918, with the ANZAC Mounted Division taking part in a subsidiary effort east of the Jordan aimed at Amman. Turkey surrendered on 30 October 1918. The 2nd Light Horse Regiment sailed for Australia on 13 March 1919 without their horses, which were either shot or transferred to Indian cavalry units. Events in the daily routine of the soldier were signalled by bugle and trumpet calls. This trumpet is signicant because historically, it was issued to the 2nd Australian Light Horse Regiment in 1912. This Regiment served with distinction in Gallipoli and Palestine in World War 1. It is probable, but not confirmed, that tthe trumpet was used by the Regiment during these operations. Each light horse regiment was divided into four squadrons. Each squadron had a trumpeter sergeant, equipped with a cavalry trumpet, who was employed at the Squadron Headquarters Technically called a cavalry trumpet, this brass instrument can be described as a "simple trumpet" ie. the direct forerunner of the modern valve trumpet. It is in E flat not B flat as is the bugle. Both were carried slung over the player's body by means of green tasselled cords.Crest with inscription: "Exposition Universelle De Paris" with circular logo with inscribed "1900". "Hors Concours Membre De Jury". Logo formed of initials (not deciphered). "Couesnon Cie 94 Rue Dangouleme Paris". Bomb burst type logo with "01" in centre. "W H Paling & Co Ltd Sydney NSW Brisbane" On bell: "Mounted Rifles (2nd ALH)" trumpet, cavalry, musical instrument, 2nd light horse, mounted rifles -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryBronchial Blocker, Macintosh Leatherdale Left Bronchial Blocker, 1955
This tube is designed for left pneumonectomy (surgical removal of a lung or part of a lung). The left stem bronchus may be completely blocked off, while the right lung is inflated. There is provision for aspiration of the left bronchus.Rubber tubing with curved and tapered end for insertion into lung. Three smaller tubes come off the larger end, two of which have small rubber valves attached. The tube appears with a banded effect however, the banding is represents the now disintegrated rubber cuff.Blue sticker with white writing on side of tube: S.I.6.bronchus, bronchial, blocker, pneumonectomy, macintosh, leatherdale -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPhotograph
Black and white photograph of a drawing of a portable drawover apparatus. There are two vaporisers with metal valves, one made of glass, connected to the ends of two corrugated tubes which are connected to a face mask at the other ends. A small rebreathing bag is connected to the underside of one of the vaporisers.Handwritten in black ink on surface of photograph the letters A - H, J, labelling each part of the apparatus.drawover apparatus, vaporiser, anaesthetic apparatus
