Showing 12003 items
matching tools-and-equipment
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Chamber Pot, Possibly 1820-1830
A rare standard design pewter chamber pot possibly made during George the IV reign (1820-1830)A significant early domestic item of interest mainly due to its social history connection.Chamber pot pewter possibly made during the reign of George IV9" on baseflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chamber pot, chamber pot pewter, pewter pot -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Container - TOFFEE TIN
Mackintosh's old fashioned treacle toffee tin, green tin with red, gold & green print & showing a street scene with people in period costume.Manufactured by John Mackintosh limited the toffee mills Halifax Yorkshiredomestic equipment, containers, tin -
 Australian Commando Association - Victoria
Australian Commando Association - VictoriaWeapon - Dyak sword
-
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Container - WATKINS SALT JAR
Cut glass Watkins Celery Salt shaker with black bakelite screw lid, green, cream & black paper label with green & black lettering.Trade Mark J R Watkins Made in Australiadomestic equipment, containers, bottle -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Tool - Bottom swage, c1920
Bottom swage used with top swage to round up rods etc.rural industry, farm machinery, trades, blacksmithing -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Thermometer, 20th century
Thermometer made to the specifications of Dr. Forbes. Used to measuring temperatures from freezing to boiling. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Thermometer, glass, part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Scale 15 - 240, "Dr Forbes Specifications." Made in Germany. "Freezing" up to "Warm Boil" Paper label inside thermometer has "Dr Forbes Specifications." Made in Germany. "Freezing" up to "Warm Boil" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, scientific instrument, medical instrument, thermometer, heat measurement, dr forbes specifications, german made thermometer -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th - early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. Various types of forceps are still in common use today in modern surgery. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps, heavy duty, from the W.R. Angus Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, ear nose throat surgery -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumMachine - Skycraft Scout, 1970
Historical Details: . Description: The Skycraft Scout is perhaps the aircraft that can be credited with starting the modern ultralight flying movement. Built in Sydney and utilising many yachting components including sail booms for the wing spars and sailcloth for the wing covering, the Sc. Level of Importance: Regional -
 Trafalgar Holden Museum
Trafalgar Holden MuseumVehicle - Calibra YE
Designed in Germany as an Opel, but sold in the UK as a Vauxhall, in Australia as a Holden. Elsewhere was also known under the Chevrolet badging.In an effort to introduce a smaller sporty sedan the Calibra was introduced into AustraliaDark blue 2 door sports sedan, with glass sunroof, high polish alloy wheels, body protector on bonnet. Open slot grille. Stop light mounted centre of boot.Round Holden emblem mounted both grille and boot centre. Boot LHS Calibra 16V, RHS HOLDEN badgevehicle, calibra, holden -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Toy Cream Can
Possibly toy dairy equipmenttoys, general -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Spokeshave, Prior to 1950
A spokeshave was made with a wooden body and metal cutting blade. With industrialization metal bodies displaced wood in mass-produced tools. Spokeshaves can be made from flat-bottom, concave, or convex soles, depending on the type of job to be performed. They can include one or more sharpened notches along which the wooden shaft is pulled in order to shave it down to the proper diameter. Historically, spokeshave blades were made of metal, and the body and handles were wood. Unlike a drawknife, but like a plane, spokeshaves typically have a sole plate that fixes the angle of the blade relative to the surface being worked. By the twentieth-century metal handles and detachable blades had become the most common. A convex, wooden, variant of the spokeshave is called a travisher; at one time mostly used in chairmaking.A tool of the cooper and other woodworking tradesmen that has been in use since the making of barrels and wooden buckets for hundreds of years without much change to the design or how the tool is used.Spokeshave, with two wooden handles on either side. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, coopers tools, spokeshave, barrel making, wood plane, wagon making, joiners tools, carpenter tools -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Tool - PITTOCK COLLECTION: VARIOUS TOOLS
Pittock saddler's bos: six varios tools steel spanner - 200 mm x 55 mm x5mm thick wooden tool handle, with steel straps, used - 115mm x 30mm diam steel rasp - 250mm x25mm metal punch, ussed - 165mm x17mm x 10mm thick, 12mm pinch wooden and steel leather work tool - 135mm x 14mm x 10mm thick lead solder, triangular - 170mm x10mmnil -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Functional Object, Ration pack (x2) gold plated tin
1) metal tin with the following contents - curry powder pouch, matches, instant coffee, several unidentified pouches. 2) closed tin 2x food ration tinsration pack -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Stencil Set
The incomplete set of copper stencils was used some time ago to print Old English letters. They still have the remains of black ink on them. The user places the stencil on top of the surface to be labelled, then paints, rolls or brushes ink onto the surface of the stencil, allowing the ink to cover the surface that is exposed by the cutout in the stencil. Stencils in a variety of materials have been in use for thousands of years to reproduce images and letters; examples include wood, metal, cardboard, paper and wax. The box once contained a Silver Stork brand feather pen.The stencil set represents a form of manually produced printing and labelling. The process has been used Stencils, copper; twenty-two stencils of the old English alphabet, stored in a pale green cardboard rectangular box that once contained a feather pen called The Silver Stork feather pen. Box is labelled "The Silver Stork" "A Scribbling Pen" Image; [a feather' with text "Silver Feathers" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, stencil set, copper stencils, silver stork, feather pen, printing, labelling, reproduction, stencilling -
 Stanley Athenaeum & Public Room
Stanley Athenaeum & Public RoomFunctional object - Photo Frame, Frame for Christina Muter photo
Wooden with gold metal border frame on black mountboard. made approximately 1990's -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - BACK PACK, SMALL, 1969
Item commonly called by soldiers, “bum pack”Small pack, webbing, canvas & inside lining waterproof. Has adjustable straps, buckles, metal, on rear metal clips for attachment to webbing belt & harness.“018465-823-7622 RP 1969--C105961” “Written: 3798215 THOMAS”military equipment - army, uniforms - accessories, metalcraft -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumFunctional object - TOY WASHBOARD
HANDMADE CHILD'S WASHBOARD MADE FROM WOODlocal history, toys, general -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - KIT BAG
Part of the "Kevin John Herdman", No.397661 Collection. See Catalogue No. 5942P for details of his service record.Green coloured canvas bag closed with heavy duty plastic zipper. Two handles made from thick dark green canvas. Each is attached and reinforced with Khaki coloured stitching. A clear plastic pocket is sewn onto one side to house a name card. Below this is a pocket closed in a plastic zipper. On the inside of the bag are two large canvas pockets.Handwritten in black on outside above the clear plastic pocket "HERDMAN".equipment, kitbag, kevin john herdman -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Trunk, late-19th to mid-20th century
Trunk is made strong for long journeys and rough use. Tray compartments would have been fitted inside the lid for storage of smaller items such as hats, umbrellas and underclothing. The illustration pasted inside the lid is similar to those shown in women's fashion journals of the 1880s and 1890s. A similar trunk was found in the catalogue of Anthony Hordern & Sons, a large and famous late 19th to mid 20th century retailer in Sydney,.This trunk is an example of the typical travel luggage of people migrating to the Colony of Australia in the late 19th century.Wooden cabin trunk, rectangular, brown in colour. Lid has arched top, front has a strong padlock, sides have leather strap handles. Corners and edges are reinforced with iron, iron bands and extra wooden slats. Lid is divided into tray compartments. A print of a female in 19th century costume is attached to the inside the lid in one compartment. flagstaff hil, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, trunk, cabin trunk, travel trunk, cargo, storage, women's fashion, late 19th century fashion, travel luggage, travel goods -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Sand anchor, Mid-19th to mid-20th Century
The rocket rescue crews used a sand anchor at a beach rescue site to weigh down the rescue apparatus. The crew would connect the steel cables to the connecting cable and then join heavy ropes or chains to the connecting cable. They would then bury the anchor in a trench about three-quarters of a metre deep, keeping the connecting cable’s end free. The length of heavy rope or chain was attached to a pulley block onto the heavy hawser line. The block and a crotch pole were used to keep the hawser line high and taught, keeping the survivors above the sea as they were hauled to shore on a line or in a breeches buoy. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s, the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This sand anchor is part of the rocket rescue equipment and is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.The sand anchor comprises a plank with steel cables and a connecting cable. The rectangular wooden bevelled-edged plank with two pairs of square metal plates bolted through it. Each metal plate has an eyelet and the two steel cable lengths are permanently attached by their eyelets to the plates. The eyelets at each end of the cable lengths are reinforced with rope work and one length also has a ‘U’ bolt shackle connection. The steel connecting cable also has reinforced eyelets at both ends. The plank has a black stencilled inscription on the upper surface. Stencilled in black paint "ANCHOR" "BACKER"flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket equipment, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faked line, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, whip line, endless whip, harbour board, sand anchor, rocket set, anchor backer, rescue anchor, beach anchor, backer, anchor, steel cable, wire cable, connecting cable -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionTool - Tools, n.d
Port of Portland CollectionBack: Wrench driver: 'SIDCHROME' -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumFunctional object - KEROSENE LANTERN
LANTERN WAS USED FOR OUTDOOR LIGHTING.1 METAL LANTERNS WITH GLASS TO ENCLOSE LIGHT; .2 METAL WELL AT BASE TO CONTAIN KEROSENE, WITH CARRY HANDLE, ONE WITH RED LAMP GLASS.LANORA - AUSTRALIAkerosene & oil, lighting -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Tool - Bottom swage, c1920
Bottom swage used with top swage to round up rods etc.rural industry, farm machinery, trades, blacksmithing -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer, Griffiths Bros, 1900 - 1940
In 1873, English grocer James Griffiths migrated to Melbourne with his wife and cousin in order to start a tea business. By 1875 Griffiths Brothers Teas had become a sensation, providing tea, coffee, cocoa and chocolate all over Australia. The Sydney outlet of the Melbourne-based company was built in 1915. In a memorable advertising campaign, a series of Griffiths signs were situated at varying intervals along the rail lines on fences and building, designed to allow travellers to count down the miles until they could drink up. In 1925, James Griffiths was killed by a train and the tea company was sold to Robur Tea, which itself lasted until 1974. Griffiths’ death meant downsizing within the company with the Sydney building being transferred to the Sydney City Council, who then leased it back to Griffiths Teas. The tea craze was over by 1965, and Griffiths relinquished control of the building to a variety of tenants. Griffiths tea became an intrical part of Australian life, during the late 19th to mid 20th century. The company became a household name through the clever use of outdoor advertising with their blue and white enamel “Griffiths Tea” signs. These were visible Australia wide on railway fences, stations and other buildings. Griffiths signs let the rail travelers know the distance to where their tea could be enjoyed, with distances being shown as “miles to Griffiths Tea”, These signs were well known along the eastern states railway lines. Tea container tin Griffiths blue tin with round lid, not hinged. 7lbs net Choice Tea Griffith Bros 7lb net in white on a blue labelflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumFunctional object - Match Tin with lid, 1940
Originally held wax vesta matches, used by internees at Camp3Small tin for wax matches with lid attached ( hinged) and rasp like panel on the bottom for striking the match.Duncans Waterproof Wax Vestas.tatura, containers, industrial -
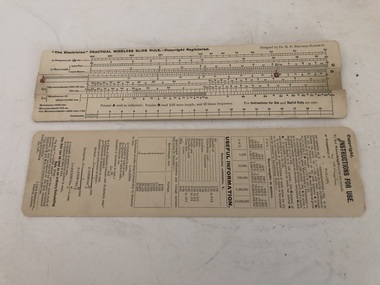 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionEquipment, "The Electrician" Practical Wireless Slide Rule
Henry Sutton is a talented world-wide accepted inventor with inventions relating to the telephone, photography, wireless, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles as well as many more inventions. Henry was also one of four brothers that ran the Sutton's Music Store after the death of their Father Richard Sutton. Henry Sutton taught Applied Electricity at the Ballarat School of Mines in 1883 to 1886."The Electrician" Practical Wireless Slide Rule, By Dr H.R. Belcher-Hickman in paper envelope including instructions for use associated with Henry Sutton. Stored in leather wine box2/6 netthenry sutton, "the electrician", practical wireless slide rule, dr. h.r. belcher-hickman, instructions -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - COMPASS JAPANESE, C. 1939 - 45
Item souvenired by Leslie John Kupke No VX93892 2nd AIF. Refer 2054.2 for his service history. Japanese compass with hinged cover. Casing made of metal. N,S,E,W in Japanese. Case has loops for attaching to a strap.PATEN 2908 stamped on back (worn but visible)surveying-terrestrial, military - equipment, japan -
 Australian Commando Association - Victoria
Australian Commando Association - VictoriaEquipment - Rutsack and frame
-
 Parks Victoria - Cape Nelson Lightstation
Parks Victoria - Cape Nelson LightstationFunctional object - Flag set, navigational
The flags were used for communicating messages to passing ships. Knowledge of visual signaling was mandatory for all lightkeepers and all stations maintained a set of these flags. Although used for centuries, visual flag signaling formally developed in the nineteenth century and was published internationally as a system in 1857. By the early twentieth century it had developed into an effective means of conveying all kinds of short range visual messages.The Cape Nelson Lightstation is architecturally and scientifically (technologically) important as the most intact complex of lightstation buildings in Victoria. The octagonal signal station is a unique feature which is all the more important for its complete set of signal flags’. Cape Nelson Lightstation’s complete set of 41 alphabetic and numeric visual signaling flags (including substitute and answering pennants) are made of bunting, a coarse fabric of worsted (open yarn wool) in various colour combinations, and some of the fabric is hand sewn and bears inscriptions. Attachments include handmade wooden toggles, brass clips and hemp rope. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Pulley Block, Russell & Co, ca. 1886
A pulley block of this size would have many applications on a ship, including lifting loads such as cargo and sails. It was recovered from the wreck of the Halladale in the 1970s by divers Gary Hansen and Peter Ronald, former Director of Flagstaff Hill. The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque built in Glasgow, Scotland. It was used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. When the ship left New York in August 1908 it was bound for Melbourne and Sydney it’s the cargo in its hold consisted of roofing tiles, barbed wire, stoves, oil, benzene and many other manufactured items. On the 15th of November, 1908, after three months at sea and close to its destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland. The captain and 29 crew members survived but most of the cargo was lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not to any technical failure of the ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. The vessel was one of several designs of Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period between 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised its ship designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales. It was one of the last of the 'windjammers'. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have huge seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions.The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). The vessel was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the ship was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature that is still in use on modern vessels today. The block and pulley is an example of ship rigging equipment used on sailing ships during the 19th and early 20th centuries that transported goods around the world. It represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry and maritime history.A pulley block; metal frame with three sheaves. The block is in a fragile condition. It is also large and heavy. It was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale in the 1970s. warrnambool, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, clipper ship, windjammer, cargo vessel, falls of halladale wreck, shipwreck, 1908 wreck, breakenridge & co glasgow, russell & co ship builders, 1886 ship, shipwreck artefact, rigging, ship rigging, rigging equipment, sailing equipment, cargo equipment, marine technology, block, ship’s block, pulley block
