Showing 64 items
matching adult training
-
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : September 1989
... in training [Adult literacy] / p4. Kew Band report / p4. Children's ...New Mayoral team looks to the future [Cr Michael Montalto, Cr Daryl Oldaker] / p1. Maternal and Child Health review / p1. Dates for September / p2. Head Lice Infection hits local Schools / p2. Commentary [Council Mission Statement] / Cr Michael Montalto / p3. Meet the Mayoral team [Cr Montalto & Cr Oldaker profiles] / p3. Kew Hawthorn Tenancy Week / p3. Notices / p4. Kew Neighbourhood Watch [meetings] / p4. Area 6 Traffic [Management Committee] / p4. Learning for leisure [Kew Recreation Centre] / p4. School holiday programs / p4. Tutors in training [Adult literacy] / p4. Kew Band report / p4. Children's Week / p5. Crackdown on dogs / p5. Aqua friends / p5. Kew's young concerned about health / p5. Rowing Four wins gold / p5. Hard of hearing seminar / p6. Government funding for Community Environment Groups / p6. Keep Kew Green [1990 Kew Festival] / p6. Open days for Kew's kindergartens / p6. Garden dedicated in ex-Principal's honour [Bicentennial Garden, Kew East Primary School, Graeme Lindsay] / p7. Deliverers wanted / p7. Awards for Kew Lions [and Lionesses] / p7. Bus volunteers [Kew Community Bus] / p7. Council taking a look at Kew's open spaces / p7. Letters to the editor / p8. Boroondara Bushwalkers [pollution, Yarra Bend Park] / p8. [Deepdene Uniting] Cricket Club recruiting new players / p8. Footy news [Kew Football Club] / p8. Keeping you informed [Consumer Affairs Kit] / p8.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fictionNew Mayoral team looks to the future [Cr Michael Montalto, Cr Daryl Oldaker] / p1. Maternal and Child Health review / p1. Dates for September / p2. Head Lice Infection hits local Schools / p2. Commentary [Council Mission Statement] / Cr Michael Montalto / p3. Meet the Mayoral team [Cr Montalto & Cr Oldaker profiles] / p3. Kew Hawthorn Tenancy Week / p3. Notices / p4. Kew Neighbourhood Watch [meetings] / p4. Area 6 Traffic [Management Committee] / p4. Learning for leisure [Kew Recreation Centre] / p4. School holiday programs / p4. Tutors in training [Adult literacy] / p4. Kew Band report / p4. Children's Week / p5. Crackdown on dogs / p5. Aqua friends / p5. Kew's young concerned about health / p5. Rowing Four wins gold / p5. Hard of hearing seminar / p6. Government funding for Community Environment Groups / p6. Keep Kew Green [1990 Kew Festival] / p6. Open days for Kew's kindergartens / p6. Garden dedicated in ex-Principal's honour [Bicentennial Garden, Kew East Primary School, Graeme Lindsay] / p7. Deliverers wanted / p7. Awards for Kew Lions [and Lionesses] / p7. Bus volunteers [Kew Community Bus] / p7. Council taking a look at Kew's open spaces / p7. Letters to the editor / p8. Boroondara Bushwalkers [pollution, Yarra Bend Park] / p8. [Deepdene Uniting] Cricket Club recruiting new players / p8. Footy news [Kew Football Club] / p8. Keeping you informed [Consumer Affairs Kit] / p8. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : February 1987
Kew's Premier Youth Theatre in performance / p1. SEC act threatens [street] trees / p1. Dates for February / p2. [Community] Notices / p2&8. Commentary - a challenging year ahead / Cr Joe Ormando, Mayor of Kew p3. Good gardening / Peter Davies p2. Kew Festival - eat your way through Fun Day / p3. Profile - Cr David Timms / p4. Calling artisans and craft persons [Senior Citizens' Week] / p3. After School program for Kew Primary School / p5. A gentle reminder about Kew's By-Laws [Mini bike riding] / p5. Get your entry in! [Images of Kew competition and exhibition] / p5. Kinder for there year olds [North Kew Municipal Kindergarten, 152 Pakington Street] / p5. Kew Community House [A new year starts; Volunteer tutoring for adult literacy; 1st semester pamphlet; Now open on Wednesdays] / Rhonda McCaw p6. Gymbaroo offers early learning / p6. Hassle free apprenticeship training [Inner Eastern Group Apprenticeship Training Scheme] / p7. Children's Services update [Kew Children's Services Consultative Committee] / p7. Care-Force needs volunteers [Care-Force Family Support Services] / p7. Footy news [Kew Football Club] / p8. Keeping you informed [Citizens' Advice Bureau] / p8. Babysitting? [Babysitting clubs] / p8.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fictionKew's Premier Youth Theatre in performance / p1. SEC act threatens [street] trees / p1. Dates for February / p2. [Community] Notices / p2&8. Commentary - a challenging year ahead / Cr Joe Ormando, Mayor of Kew p3. Good gardening / Peter Davies p2. Kew Festival - eat your way through Fun Day / p3. Profile - Cr David Timms / p4. Calling artisans and craft persons [Senior Citizens' Week] / p3. After School program for Kew Primary School / p5. A gentle reminder about Kew's By-Laws [Mini bike riding] / p5. Get your entry in! [Images of Kew competition and exhibition] / p5. Kinder for there year olds [North Kew Municipal Kindergarten, 152 Pakington Street] / p5. Kew Community House [A new year starts; Volunteer tutoring for adult literacy; 1st semester pamphlet; Now open on Wednesdays] / Rhonda McCaw p6. Gymbaroo offers early learning / p6. Hassle free apprenticeship training [Inner Eastern Group Apprenticeship Training Scheme] / p7. Children's Services update [Kew Children's Services Consultative Committee] / p7. Care-Force needs volunteers [Care-Force Family Support Services] / p7. Footy news [Kew Football Club] / p8. Keeping you informed [Citizens' Advice Bureau] / p8. Babysitting? [Babysitting clubs] / p8. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncClothing - Child's silk smocked dress, c.1910
The child's silk smocked dress with feather stitching is believed to have been worn by Mary Hodgetts, sister of the donor's mother. The dress is estimated to have been made in c.1919, but from its style it may date from the 1900s. This would not be uncommon as children's clothing was often 'passed-on' or reconfigured to fit a new wearer. Mary Hodgetts grew up in Kensington Park, Adelaide. As an adult, Mary enlisted in 1941 to the 1st AWAS camp. After six months she volunteers for the 58th AASL (Anti Aircraft Searchlight Battery). She was sent to Sydney where she attended Training School with 33 males and one other female. Mary was the first AWAS to receive a Commission in the RAA (Royal Australian Artillery). Mary Downer was one of many under Mary's command on returning to Adelaide. After a March through the streets of Adelaide, most of the unit transferred to Western Australia (Fremantle area) in 1943 and were scattered amongst the 55th and 65th AASL Batteries. At the conclusion of WW2, Mary travelled to Melbourne to be with her sister and studied Accountancy. She first lived in Mary Street, Hawthorn, and then bought a unit in Harcourt Street, East Hawthorn. During this period she worked as Bursar to St Catherine's Girls' School. On retirement, she purchased a house in Edgecombe Street, Kew, and lived there happily for many years. During this time she was active with the Kew Meals on Wheels, receiving her 10-years of service certificate. Mary Hodgetts died in 2018.Child's clothing associated with the history of a significant Australian woman who served with the 2nd AIFChild's silk smocked dress Shoulder width 26 cm / Length 52 cmmary hodgetts, 58th aasl (anti aircraft searchlight battery), children's clothing, women- ww2 -
![Notes for General Guidance of Officers in Charge of Idiot Children [Kew Cottages]](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/57a01b87d0cdd121042ac868/item-media/5e8a822a21ea671a7caf7140/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncDocument, Notes for General Guidance of Officers in Charge of Idiot Children
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]Framed document, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - ‘Notes for General Guidance of Officers in Charge of Idiot Children’kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Expression Australia
Expression AustraliaBooklet, Proposed Farm and Home for Aged Infirm and Feeble Minded Deaf Mutes
The Premier of Victoria, the Hon, Thomas Bent, has promised a grant of 2,000 pounds towards providing a Training farm for Feeble-minded, and home for Aged and infirm Deaf Mutes, conditionally that a further sum of 2,000 pounds be raised for the same purpose at once. The Committee of the Adult Deaf and Dumb Mission of Victoria having accepted this generous offer of the Government, produced this booklet with the desire to bring the scheme under the notice of the public with a view of appealing to it for the sum named.This booklet is significant as it marks the beginning of a major project, Lake Farm, Blackburn that sought to provide employment and residential facilities for aged and infirm Deaf adults in Victoria in the early years of the 20th Century.Size 13.5cmHx21.5cmW; 16 pagesdeaf, blackburn, thomas bent,ernest j. d. abraham, south australian farm and home for infirm deaf mutes, -
 Expression Australia
Expression AustraliaBooklet, Adult Deaf Society of Victoria Residential Independence Training Programme
Produced 19/5/80 to provide information generally about the residential programme and specifically for decisions on funding29.5cmHx21cmW, 12 pages, 2 copiesadult deaf society of victoria, residential independence training programme funding -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph, Miss Frances Emerson
Frances Emerson was born in Elsterwick in 1906 to Thomas James Emerson, a furniture manufacturer, and his wife Selina Sarah (nee Bowen). She had 3 siblings - Thomas George (1908-1977), Melvie Eleanor (1910-1965) and Hulett Moore (1915-1999). They lived at 18 Kent Road, known as 'Sunnybrae' and later as ‘Willacool’. Her mother died at 'Sunnybrae' a few months after the birth of her youngest brother. After attending state school, Frances went to Fintona. She trained as a kindergarten teacher at ‘Mooroolbeek’ Kindergarten Training College in Kew and taught during the 1930s. Her 1st appointment was at the Robert Cochrane Kindergarten in Auburn. She also worked at the City Free Kindergarten on the corner of Exhibition and Little Lonsdale Streets, where children came from very poor dwellings in ‘lanes off lanes’. See file on her work.A black and white photograph of four adults - two male and two female.clothing and dress, emerson, frances (miss), warren, frances (mrs), fintona, kent road, surrey hills, teacher, preschools, 1930-1939 -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society Collectionphotograph, Mr Joseph George of 26 Scheele Street, air raid warden
Mr Joseph George of 26 Scheele Street Pictured as an Air Raid Precautions Officer during the 1939 – 1945 war. ARP officers controlled the areas around their homes to check on tell-tale lights showing in the ‘brownout’ conditions and advising on the black-out of homes. Street lights were dimmed and screened downwards and Joseph’s daughter Marie remembered sewing black Italian cloth curtains to hang over the windows. Joseph taught adult first aid classes in local schools, church halls and at The Surrey Dive. Joseph conducted his practical training sessions at the Quarry in Grovedale Road, in case they had to deal with an emergency in such a site. Joseph (Joe) and wife Emily Ruth were English migrants; they bought their home in Scheele Street in 1919. Daughter Marie was born in 1914 when they are listed in the electoral roll at 'Hasland', Croydon Road, Surrey Hills; his occupation is given as a boilermaker. Emily (nee Sturgess) - d 15 November, 1960; buried Box Hill Cemetery - M-199A-0034 along with daughter Marie. Possible birth c Oct 1880, Birmingham (not confirmed); marriage to Joseph George c Jan 1905, Chesterfield, Derbyshire. The donor was his daughter, Marie, who was a school teacher and was on the staff at Chatham Primary School for a number of years. She died in February 1989.A black and white photograph of a man in uniform standing in a garden, with a small case beside him.(mr) joseph george, surrey hills, mont albert, scheele street, clothing and dress, uniforms, world war, 1939-1945, air raid wardens -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record - Text, Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind annual report 1962-1963, 1962-1963
Articles in annual report include: List of office bearers of the institute and officers of the institute, Confidence mobility, Annual report of the RVIB babies, Children and adults - 97 years of service and programmes - special appeal, Residence rehabilitation training centre, Conference mobility, Ten pin bowling, Deaf blind centre, Resident nursery and school, Worldwide literary competition, Higher education, Employment, Welfare, Recreation, Finance, Appreciation, Auxiliary, 3KZ Christmas appeal, Vice regal patronage, My friend the long cane - a new method of self-help for blind people, They're the workers, 36th annual report of the council of auxiliary. Events that occurred in 1962 : Hon. H.E. Bolte, Premier opened the appeal and announced a special grant of $20,000 pounds from the state government. Lieutenant General Sir Henry Wells accepted the board's invitation to become chairman of the appeal, at the Burwood school Cheng Ann Cheok a 15 year old Singaporean boy arrived to further his education and study music, he hopes to adopt music as his career. Through the kind offices of Dr Edward J. Waterhouse director of Perkins school for the blind of Boston and the generosity of its Board of Trustees a scholarship will be provided to the Institute for an Australian teacher to be trained as a specialist teacher within their school.1 volume of text and illustrationsroyal victorian institute for the blind, annual reports -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaFunctional object - Object, Harwill, Seeing Eye Dogs Australia tea towel
Blue edged tea towel with images of golden Labrador puppies and a black Labrador dog in a red harness. The words 'Our gift of independence' and 'Seeing Eye Dogs Australia' is printed amongst the images, on a white background. Common household items were often created to raise money for SEDA and to reinforce the work involved in training dogs from puppy to adult stage. 1 woven cloth tea towel with illustrationsseeing eye dogs australia, fundraising -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaFunctional object - Object, Bartel, Seeing Eye Dogs 2004: the calendar, 2003
a13 month calendar featuring photos of Labrador puppies each month with the wording 'Did you know you can sponsor me or one of my friends? Simply call 1800 787 797'. Calendar has part of the monthly image reprinted on un-used days, and a monthly wall planner inserted in the middle of the calendar. On the back of the calendar, all images are featured as well as a final appeal from the organisation. "Love without the leash. 1800 Puppys - As irresistible as our puppies are, not everyone can care for one. That's why you can sponsor an adorable pup for as little as .50c a day. All contributions are tax deductible, so giving couldn't be easier. Simply call 1800Puppys (1800 787 797)". Common household items were often created to raise money for SEDA and to reinforce the work involved in training dogs from puppy to adult stage.Paper calendar with coloured photographsseeing eye dogs australia, fundraising -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record - Text, Twentieth Annual Report of the Association for the Advancement of the Blind 1915, 1915
Annual report of the Association for the Advancement of the Blind outlined activities and events over the year, including the continued success of country concert tours in providing both an income for performers and raising awareness of the Association, return of wounded soldiers has prompted the need for support for those who have been blinded and the Minister of Defence has been approached to provide a list of those such affected so that the Association can provide assistance, advice and possible accommodation at Mair St, a sub-committee has been established to determine if massage training could be provided as an employment option, passing of active members Miss Faulkner and Rose Josephs, and the Honorary physician to the Adult Home for the blind (Dr Gray) has departed his position for overseas war service.1 volume of printed material with some illustrationsassociation for the advancement of the blind, annual reports -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBooklet - The Young at Bonegilla : Receiving young Immigrants at Bonegilla Reception and Training Centre. 1947 - 1971, Bruce J Pennay
Between 1947 and 1971 about 309,000 people arrived in Australia through the Bonegilla Reception and Training Centre in Northeast Victoria. Bonegilla was the largest and longest serving migration reception centre. It usually accommodated about 3,000 people but did hold up to 7,000 at one stage. It was a young person's place. Few of the adults were aged over 35 years old. This study analyses how Australia tried to meet the challenges involved in supporting young adults, teenagers and children. It also examines how those who were young remember their experiences at Bonegilla.non-fictionBetween 1947 and 1971 about 309,000 people arrived in Australia through the Bonegilla Reception and Training Centre in Northeast Victoria. Bonegilla was the largest and longest serving migration reception centre. It usually accommodated about 3,000 people but did hold up to 7,000 at one stage. It was a young person's place. Few of the adults were aged over 35 years old. This study analyses how Australia tried to meet the challenges involved in supporting young adults, teenagers and children. It also examines how those who were young remember their experiences at Bonegilla.bonegilla, immigrant experiences, young immigrants postwar -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumEphemera - Set of 10 Bus Service Sandringham - Monthly Tickets, Victorian Railways (VR), 1964
... except for one dated June 1962 and most likely used as a training... for one dated June 1962 and most likely used as a training set. AF ...Set of 10 Monthly tickets for the Sandringham based Co-ordinated Motor Coach service. See reference 165 and figure 7-78 for an example. Tickets were available for unlimited bus travel and were introduced in Sept. 1957. All dated July 1964 using blue card except for one dated June 1962 and most likely used as a training set. AF - Adult Female, AM - Adult Male 1 - Sandringham Beaumaris AF - 001, 002 2 - Sandringham Balcombe Rd AF 002, 004 and 005 3 - ditto - AM - 004, 005 4 - Sandringham - Royal Ave - AM - 001 5 - ditto - AF - 000 6 - Sandringham - Haydens Rd - June 1962, pink card - AM - unnumbered.Demonstrates a set of Victorian Railways monthly tickets used on the former Sandringham - Black Rock service replacement bus service.Set of 10 printed card tickets, all with trimmed or 45 degree corners.tickets, vr, vr trams, victorian railways, sandringham to black rock, buses, monthly -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaLetter - Text, Letter to a Life Member (1931), 9 February 1931
... Training Etc of Blind Adults, Homes Etc for Aged and Infirm Blind... and Maintenance of Blind Children, Industrial Professional Training Etc ...Letter to an unidentified Life Member asking for assistance in organising fundraising events to support Special Blind Appeal. The letter continues on to a second page, however this is missing. This is an example of a joint appeal between the RVIB and the AAFB, who usually preferred to work independently.1 photocopied letter with illustrations at topTop left hand corner is a lighthouse with the words 'Education and Maintenance of Blind Children, Industrial Professional Training Etc of Blind Adults, Homes Etc for Aged and Infirm Blind' written on the tower. The light that shines towards a female child and an adult male who are both wearing blindfolds, contains the wording 'Special 50,000 (pound) appeal for the Blind Children & Adults of Victoria". To immediate left of the people is written "Blind/and seeking the light/your generous donation will help them find it'. To the right of the rocks upon the which the lighthouse stands "Kindly address donations Hon. Treas. of Blind Appeal, The Lord Mayor of Melbourne, Cr. Harold Luxton M.L.A., Town Hall, Melbourne". Underneath the lighthouse against the left edge of the paper "Institutes participating in this appeal - The Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind and the Association for the Advancement of the Blind - these organisations care for the blind of Victoria from the cradle to the grave. Please address all correspondence S.W,. Hedger, Secretary Blind Appeal, Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind, St Kilda Road, Prahran, S.1. Vic, Phone W 6500. Blind Appeal Enquiry Office: Nicholas Building, 5th Floor Swanston Street, Melbourne, Phone F 6418."royal victorian institute for the blind, association for the advancement of the blind, fundraising -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - Public Health, Lakes Post Newspaper, 1992
Black and White photograph of Joan Harvey, Lynn Cann, Glad Metcalfe, Norma Thomas, Des Thomas, Betty Bryce, Margaret Wah, A Hill, Judy Jakins, President of Lakes Care, Pat Baird, Judy Young, Ute Wohl, Shirley Murray, Barbara Hughes at Lakes Care Group training course for volunteers Lakes Entrance Victoria health services, adult education -
 Box Hill Historical Society
Box Hill Historical SocietyBook, From Burwood to bestchance : 120 years of care and education, 2016
... , special primary education ( Cheshire School) and adult training ...Illustrated history of Burwood Boys Home, Child and Family Care, and bestchance, Child, Family Care. From original beginnings in 1895 when founder Robert Campbell Edwards established a home for the waifs of Melbourne, to the present organisation caring for families and children, providing child care, early intervention programs, special primary education ( Cheshire School) and adult training. In 2007, Ken Masterton's book "A Tea Merchant's Vision and Beyond - a history of the Burwood Boys' Home" (which is reproduced in full in this edition) begins with the vision of tea merchant Robert Campbell Edwards and "gives a valuable summary of the organisation's achievements".xvi, 202 pages : illustrations (some colour), portraits (some colour), colour maps; includes Appendices lists of leadership and Life Governors 1895 to 2016 non-fictionIllustrated history of Burwood Boys Home, Child and Family Care, and bestchance, Child, Family Care. From original beginnings in 1895 when founder Robert Campbell Edwards established a home for the waifs of Melbourne, to the present organisation caring for families and children, providing child care, early intervention programs, special primary education ( Cheshire School) and adult training. In 2007, Ken Masterton's book "A Tea Merchant's Vision and Beyond - a history of the Burwood Boys' Home" (which is reproduced in full in this edition) begins with the vision of tea merchant Robert Campbell Edwards and "gives a valuable summary of the organisation's achievements".burwood boys' home, child care, burwood children's home, bestchance, family day care -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - Diving, Lakes Post Newspaper, 1996
number in album 03532.01Black and white photograph at Aquadome Expo for older adults showing diver Rob Timmins instructing seven learner divers in the pool. Lakes Entrance Victoriarecreational facilities, training -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Boys Exercising, Kew Cottages, c.1900
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - 1973 [sic] Boys exercising. Boys of the Cottages. The Superintendent's Office, right (until 1973). Wards 12 and 13 left."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Matron Malloy, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - Matron Malloy 19..-1944. Matron Molloy of Kew CCE until about 1944"kew cottages, matron maud molloy, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kew Cottages, Yard
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families.Kew Cottages - Yard 1926/27. The yard of what was previously ward 26/27. New unit 7/8. kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - 12 Bed Dormitory, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families.Kew Cottages - Dormitory (12 beds). A dormitory at the Cottages.kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
![Airing Court Shed [demolished 1976], Kew Cottages](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/57a01944d0cdd121042a07ed/item-media/57a019f6d0cdd121042a4183/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Airing Court Shed, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families." Kew Cottages - Airing Court Shed demolished 1976. The building in the foreground was a so-called 'airing-court-shed'. The other building is an old Court Pell hut (ex Royal Park) transported here after World War II. There were two other such huts behind this. All these buildings were demolished in 1976 to make way for the Graham Perkins Unit."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Group of 30 Men, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - Group of 30 Men – Hospital Ward in Background. The Hospital Ward in the background."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Girls in front of Ward 25, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages. Girls in front of Ward 25."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Wards 11,12,13 & Old Conference Room, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Dr Cliff Judge in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families. [Conservation note: Broken glass to be replaced]"Kew Cottages - Wards 11,12,13 & Old Conference Room. Left to right - Wards 11, 12 and 13. Old Conference Room - Wards 23, 22 and 21."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Old Ward 21 (The Nursery), Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Dr Cliff Judge in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families. [Conservation note: Glass to be replaced]"Kew Cottages - Old Ward 21 (The Nursery). Old Ward 21, previously the 'nursery', and demolished in 1973 to make way for units 4 and 5. "kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Wards 11,12,13,13A, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - Wards 11,12,13,13A. Wards 11, 12, 13 and 13A. The Hospital Ward is in the background. Ward 13A was demolished in 1966."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Outside Old Ward 12, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Dr Cliff Judge in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - Outside Old Ward 12. Outside old Ward 12 (now Unit 10). The persons first, second and fourth from the left were blind."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
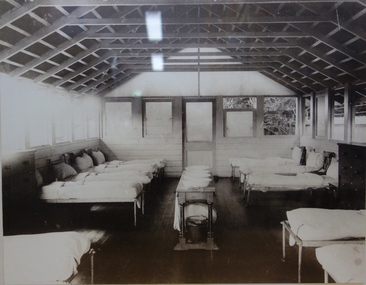 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Tent Dormitory, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by the Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."An old dormitory in the year 1973. It is still in use as a therapy room and store. Originally these buildings were called tents. Open air treatment was used to cure bad cases of insanity."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993
