Showing 71 items matching "anaesthesia equipment"
-
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryTool - Laryngoscope, Magill, A. Charles King Ltd, 1930
Magill laryngoscope with a battery in the handle was one of first of its kind This piece of equipment is made of stainless steel and has a canal on its left side and a handle to put batteries inside of it and it has attached a round screw to make it extendable. This object also has an stamped inscription and on the other side it has the manufacturer details. Stamped A.CHARLES KING.LTD Stamped REG.NO.749019 Stamped STAINLESSmagill, ivan, battery, laryngoscope, surgery, anaesthesia -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mouth opener, Heister
The advent of anaesthesia posed immediate problems for the oral surgeons and dentists who were used to operating on awake patients with intact airway reflexes. Early anaesthetics were very light and often created an uncooperative patient. Dentists were quick to complain they had trouble opening the mouth quickly enough and dental props soon made an appearance. Gags and tongue depressors proliferated, all initially devised to improve surgical and anaesthetic access, not to protect the airway. Other instruments for opening the jaws included the somewhat fearsome devices known as mouth openers. Heister's mouth opener was incorporated in anaesthetic practice but was not designed for this purpose. Lorenz Heister (1983 - 1758) used his device for mouth inspection and for operations on the palate, tonsils and teeth in the pre-anaesthesia era. He was not impressed with the way it was used by others in his life time and believed that it overstretched the jaw when used inappropriately. Despite its apparent brutality, the Heister mouth gag was still advertised for sale in 1983 and its useful mechanism has been incorporated into modern surgical retractors.Steel cork-screw shaped object with a twist top handle which will force the two arms apart. Each arm has ribbing toward the end to create friction when inserted in the mouth.Stamped into the twist top handle: MAYER & MELTZERheister, mouth gag, mouth opener -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Tube, Endotracheal, Uncuffed Rubber Nasal Tube
This is an early example of an endotracheal tube invented by Ivan Magill. The shattered faces and jaws of wounded soldiers presented real difficulties for the administration of anaesthesia. Ivan Magill and Stanley Rowbotham developed endotracheal tubes for these procedures that were more efficient and practical than the earlier insufflation catheters.The attached safety pin was used to prevent the loss of the tube down the patient's nose.Brown rubber tubing with three pairs of holes at one end and a bevelled edge at the other for nasal endotracheal intubation. There is a large safety pin stuck through the first pair of holes.magill, ivan, endotracheal, intubation, nasal, airway -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryBooklet - Book, Catalogue, A. Charles King Ltd, Anaesthetic Apparatus, Etc., Etc
Undated catalogue outlining all anaesthetic equipment available through A. Charles King Ltd.Brown cardboard covered book with white glossy pages, held together by a star clip.catalogue, anaesthetic, anaesthetic machine, anaesthetic device, anaesthetic apparatus, anaesthesia, medical history, medical device -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryBook - Book, Catalogue, Drug Houses of Australia Ltd, Surgical Instruments and Appliances, eighth edition
... anaesthetic equipment anaesthetic apparatus anaesthesia anaesthetic ...Grey/brown hardcover book with cloth covering produced as a trade catalogue for surgical instruments and appliances, including anaesthetic equipment and apparatuscatalogue, surgical instrument, anaesthetic device, anaesthetic equipment, anaesthetic apparatus, anaesthesia, anaesthetic, surgery -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Airway, Pharyngeal, Poe's, 1940
This is an example of an early airway management device for anaesthesia. Hollow curved metal tube with flat plate at one end and two tube coming out of it, one curved to the left, one curved to the right.Engraved by hand on curve of tube: POE'S / ASA 1940 Engraved by hand on flat plate: Wood Stamped into flat plate: REGGERairway, poe, american society of anesthesiologists -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Tube, Endotracheal, de Caux
Francis Percival de Caux invented this endotracheal tube which was devised for use during nitrous oxide/oxygen anaesthesia. Though he wasn't the first to use a two-tube method of anaesthesia, de Caux's invention was particularly effective; in 1930 he reported having given 20,868 nitrous oxide/oxygen anaesthetics in a four year period without a fatality. A long flexible metal tube formed from tightly wound metal with a small bulbous introducer at the distal end. The tube is mostly encased in a metal and rubber sheath. The proximal end has a finger ring and screw clamp.endotracheal, de caux, airway, nitrous oxide, anaesthesia -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Magill's Endobroncheal Tube
This endobronchial tube was invented by Sir Ivan Magill. It can be identified as pre 1948, as from that time on the wire spiral was eliminated from the body of the tubes. Sir Ivan Magill is famous for his involvement in modern anaesthesia. He worked closely alongside plastic surgeon Harold Gillies in the treatment of facial injuries sustained in World War 1. He was responsible for many items of anaesthetic equipment, but most particularly the single-tube technique of endotracheal anaesthesia.Tightly wound wire spiral tube with metal 'T' nozzle at the opposite end.magill, endotracheal, tube -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Tube, Endotracheal, Uncuffed, A. Charles King Ltd, c.1932
This is an early example of an endotracheal tube (c.1932) invented by Ivan Magill. The shattered faces and jaws of wounded soldiers presented real difficulties for the administration of anaesthesia. Ivan Magill and Stanley Rowbotham developed endotracheal tubes for these procedures that were more efficient and practical than the earlier insufflation catheters.The attached safety pin was used to prevent the loss of the tube down the patient's nose. Orange/brown rubber tubing with a bevelled edge at one end a safety pin stuck through the other end. This tube was used for nasal endotracheal intubation.Printed in black ink on tube: NO. 5 NASAL A. CHARLES KING LTD. MAGILL'S TUBE 27 / BRITISH MADEmagill, endotracheal, intubation, nasal, a. charles king ltd, england -
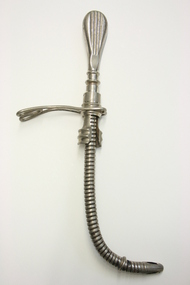 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Tube, Endotracheal, Kuhn, Circa 1900
The evolution of endotracheal intubation for anaesthesia was a slow process. Franz Kuhn (1806-1929), a head and neck surgeon working in Kassel, Germany, between 1902 and 1911, is said to have done more than any other to obtain general recognition for endotracheal anaesthesia. Kuhn's tube, is a flexible metal one inserted on a stilette which was then withdrawn. The tube was then secured with an elastic neck strap and connected by a rubber tube to a Trendelenburg cone. The glottis was packed with oiled gauze. Metal spiral tube with elaborate handle at one end and rounded at the other. There is a metal clasp at the base of the handle which all forms part of the endotracheal tube. Inside the tube is a curved metal piece that functions as an introducer.kuhn, endotracheal, airway, intubation -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Airway, Pharyngeal, Guedel
Captain Arthur Guedel was an American anesthetist who arrived at the Western Front with the American expeditionary force prior to America's official entry. He trained students in airway management and the monitoring of dept of anaesthesia using his chart board description of the signs and stages of anaesthesia. Black plastic tube, flattened and squared off, with a flat mouth plate. There is a metal inner tube which also has a flat plate.Stamped into metal flat plate: KING / 1 Moulded into plastic flat piece: KINGguedel, airway, pharyngeal, gilbert brown -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Wire, Ether, 1910
Mask used for administering ether anaesthesia. This mask also has a carbon dioxide inlet tube. Carbon dioxide was found to promote deeper breather which assisted in attaining faster anaesthesia. The mask was designed by an American anaesthetist James Tayloe Gwathmey, (1863-1944). Gwathmey invented a range of anesthesia equipment. In 1904, he introduced this mask as one part of a resuscitation apparatus. Gwathmey modified an existing mask to more closely fit the contours of the face. The holes in the rim allow for oxygen to be delivered for resuscitation or for the delivery of a combination of oxygen and anaesthetic. Wire framed mask in tear shape. There is a hinged top bracket which allows for a piece of flannel or domette to secured to the mask, onto which the ether would be administered. There is an inlet tube near the hinged bracket to allow for the administration of CO2 or oxygen and the rim is pierced with holes.james tayloe gwathmey, ether, anaesthesia, anesthesiologist, carbon dioxide, oxygen -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Guedel's Airway
Oral airways, such as the Guedel, make it easier for patients to be ventilated with manual resuscitators, such as the Porton and the Ambu bag. They depress the tongue and prevent it from falling to the back of the throat where it would obstruct the airway.Black rubber curved tube with metal insert at baseHallmarked on metal: [BRITISHMADE / 3]guedel, anaesthesia, ventilation, medical history -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Cylinder, Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide has been used for anaesthesia in dentistry since December 1844, where Horace Wells made the first 12–15 dental operations with the gas in Hartford. Its debut as a generally accepted method, however, came in 1863, when Gardner Quincy Colton introduced it more broadly at all the Colton Dental Association clinics, that he founded in New Haven and New York City. Hospitals administer nitrous oxide as one of the anaesthetic drugs delivered by anaesthetic machines. Nitrous oxide is a weak general anaesthetic, and so is generally not used alone in general anaesthesia. In general anaesthesia it is used as a carrier gas with oxygen for more powerful general anaesthetic drugs.Medium size empty blue coloured cylinder with rounded base and painted white neck once containing Nitrous Oxide. A large blue on white diamond shaped label is adhered onto the main cylinder body.Printed on manufacturer's label: 'CIG [logo] / [blank weights table] / DRY / NITROUS OXIDE / C.I.G. (Victoria) PTY. LTD. / 50 LA TROBE STREET, MELBOURNE C3 / Telephones: FJ 6681 / FJ 4164 / USE NO OIL / OR GREASE'nitrous oxide, dental anaesthesia, dental anesthesia, gardner quincy colton, colton dental association -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Cannula, Transfusion
Doctors trained in blood transfusion were essential to the development of Forward Resuscitation Teams during World War I. In 1918, Dr Alan Holmes a Court and his colleagues established a resuscitation team and, following their remarkable success at the battle of Hamel on July 4, teams were permanently established at each of the five Australian divisions. Each team consisted of one doctor trained in surgery, blood transfusion and resuscitation, another doctor trained in anaesthesia, resuscitation and blood donor classification, and four other assisting staff. This team moved out to the wounded, rather than waiting for them to be stretchered back. They provided on-the-spot, life-saving resuscitation. The wounded were then transported back to the Casualty Clearing Station or Regimental Aid Post for further treatment.A selection of metal cannula of various designs and sizes.blood, transfusion, intravenous, cannula -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Ramsay Surgical Limited
One of a range of metal face masks designed to have a cover which helps protect the patient's face.Wire frame mask designed to cover mouth and nose. There is a metal hook on the left hand side protuding from the base of the mask and wire mesh raised from the base with a circle in the middle.facemask, anaesthesia, ramsay surgical -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Resuscitator Unit, c. 1960
Mechanical resuscitation devices, such as the Pulmotor and Lungmotor, were popular in the early part of the twentieth century. Their use waned in the 1920s as significant bodies like the British Medical Research Council and American Red Cross refused to endorse them. The most popular of the resuscitators to emerge in the 1930s was the E&J (Ericson and Johnson) resuscitator. The device was soon widely available, vigorously promoted with support from many medical practitioners. They were soon to be found in hospitals, emergency services like the ambulance and fire brigade, and voluntary life-saving organisations. In Australia, Norman James, director of anaesthesia at the Royal Melbourne Hospital, developed an interest in equipment for ambulances and the resuscitation of drowning victims. Little in the way of practical, portable equipment was available to either the ambulances or the voluntary life-saving organisations, such as Surf Life Saving Australia (SLSA); American resuscitators, like the E&J, were expensive and bulky to import. James designed a simple portable resuscitation device for local use after being approached by Jack Conabere, secretary of the Elwood Life Saving Club (ELSC). The resulting Royal Melbourne Hospital resuscitator, or the R.M. resuscitator as it was marketed, was a simpler, manual version of those available overseas. It was gas driven with a plunger, marked “Press”, and a safety valve. The small working unit attached directly to the facemask. Once the patient was positioned facedown and the airway cleared of debris, the mask was placed firmly over the face. The plunger allowed gas to flow and lung inflation; releasing the plunger allowed expiration. This simple resuscitator was marketed by Commonwealth Industrial Gases (CIG) and became very popular in Australia with volunteer and professional rescue organisations. It represents one of the many innovations in resuscitation equipment that resulted from cooperation between volunteer life savers and medical practitioners. Norman James worked closely with Jack Conabere and the Government Pathologist to develop the equipment. ELSC was the first life saving club to use the resuscitator on the beach. While conducting an early training exercise on 23 December 1951, they used it to successfully resuscitate a man who had drowned after capsizing his home made yacht. The R.M. resuscitator was also used in more inventive ways. At Fairfield Hospital in Melbourne, a group of physiotherapists and doctors did some innovative work with polio patients, teaching them glossopharyngeal (or “frog”) breathing, as a means of becoming less dependent on ventilators. In 1981, the Australian Standards Association stated that the RM head failed to meet its revised standards and it was withdrawn from the market. Red leather suitcase with black leather trim with metal studs. There are clip locks for locking the suitcase in the closed position. The suitcase contains equipment for oxygen resuscitation. There is a space allocated for two oxygen cylinders, however there are no cylinders present.Embossed into metal plaque: The C.I.G. / Oxy-viva / PORTABLE UNIVERSAL OXYGEN RESUSCITATORresuscitation, portable, surf life saving australia, royal melbourne hospital, rm resuscitator -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Murray's Chloroform Mask, 1868
This small, neat, domette covered mask was widely used throughout Australia for the administration of chloroform anaesthesia.Triangular shaped mask with hinged arm at point of triangle that connects to upper frame section via a hook. Used for the administration of chloroform.chloroform, facemask, foldable, anaesthesia, anesthesia -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Bird Respirator Mark 7A with C.I.G. 'Ventviva' ventilator
The Bird ventilator Mark 7 is driven by medical compressed air or oxygen. It is not suited for anaesthesia unless using a special anaesthesia assistor controller attachment, which is essentially a “bag in a bottle” device.Apparatus attached to four castor stand with attached white wall connecting tubing.anaesthesia attachment, bag in a bottle -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Ether in Oil
Ether in oil was used for rectal anaesthesia. Rectal anaesthesia offered a way to administer anaesthesia when using a mask was impractical, such as oral or respiratory tract surgery. Undiluted ether was irritating to the bowel and even proved to be fatal. Ether in oil, developed in 1913, minimized irritation with no reported deaths.Empty clear glass bottle with cork stopper which has become dislodged and is now inside the bottle. The bottle has a white label with handwriting on the front. The bottle has been decanted.Handwritten in ink: Ether in Oil / = parts Stamped in red ink on top left corner of label: CAU... [faded and almost indecipherable]ether, ether in oil, rectal administration, anaesthesia -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Yankauer, c. 1904
Sidney Yankauer, M.D. (1872-1932), an ear, nose and throat specialist and pioneer in bronchoscopy, practiced at the Mount Sinai Hospital in New York. Dr. Yankauer, a prolific inventor of medical equipment, might best be known for the tube he designed for suctioning the mouth and throat. Yankauer introduced the wire-mesh anaesthesia mask around 1904. The drop method involved placing the mask over the patient’s nose and mouth, and then placing gauze over the mesh of the mask. Next, liquid anaesthetic, such as ether or chloroform, was applied in drops or lightly poured onto the gauze so that the patient breathed in evaporated anesthetic as well as air. The gutter around the base of the mask was designed to catch any residue of the harmful anaesthetic. (The Wood Library Museum, 2016; Museum of Healthcare Kingston, 2016)A metal tear-shaped mask with gauze wire dome, gutter around the base and detachable spring piece with open circular handle to secure cloth over gauze. Found inside medical carry box #899Stamped underneath neck of circular handle: HATRICKdr [e.s.] holloway, hatrick, yankauer, drop method, mask, gauze -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Murray
Seems to be a non- collapsible mask. Otherwise is a similar, thinner variety of Murray's mask, which was used for the administration of choloroform. John Murray was born in England, 1843 and described his wire mask in 1868 as a young chloroformist at Middlesex Hospital. It was wedge-shaped and made of thick wire and designed to be folded. The removable cover was originally made of several layers of flannel. Murray’s mask became very popular, especially in Australia, and was generally used with a single layer of flannel without an aperture or opening, as is this example. John Murray was an enthusiastic and innovative physician who also had an interest in nitrous oxide anaesthesia and conducted a series of experiments with J. Burdon Sanderson on dental patients comparing nitrous oxide to pure nitrogen. His career was short-lived and he died just before his 30th birthday. (Ball, C 1995, 'Cover Note: Murray's Chloroform Mask', Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, Vol. 23, No. 2, pg. 135)Triangular shaped wire mask covered by flannel. The flannel is sewn over frame and stitched around the base and along the vertical wire. The style and shape is similar to Murray's mask, which was used for the administration of chloroform, however this variation is not collapsible like Murray's mask.dr [e.s] holloway, mask, dr j. murray, chloroform -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Stopcock, Hewitt, George Barth & Co. Ltd, c. 1895
When Hewitt introduced his regulating stopcock in 1887, attempts were made to dilute the nitrous oxide with air and so obviate the element of asphyxiation. The method was to be seen in London, mainly in dentistry and minor surgery, so late as 1930. It was not very successful. To give even 10% of oxygen (which is not enough) the gas-mixture must contain 55% of air and 45% of nitrous oxide. The latter is thus so diluted by atmospheric nitrogen as to be incapable of producing anaesthesia except by asphyxiation. "Gas-air" was confined to analgesia, for example in midwifery. (Source: Penn catalogue)Brown leather facemask attached to metal inhaler and stopcock device that has been sectioned to reveal its inner workings. The various exposed channels have been painted either green, red, blue or purple.Engraved into side of stopcock: HEWITT'S / N20-02 / 1895 / G. Kaye sect. 1952. •Stamped into other side of stopcock: [indecipherable] BARTH & CO. / SOLE MAKERS / 54. POLAND STREET LONDON.W.frederic hewitt, stopcock, nitrous oxide, oxygen, gas-air -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Inhaler, Hewitt's (modified), Coxeter
Sir Frederick William Hewitt (1857-1916) wrote one of the earliest comprehensive textbooks on anaesthesia, and designed several pieces of anaesthetic equipment. In 1901, he described his wide-bore ether inhaler, a modification of the Clover Ether Inhaler. Unlike the Clover, it can be refilled with ether while still in use, and the mask is screwed into place so that it "cannot be unexpectedly detached." This version is a modified Hewitt's Inhaler which has a narrower 'ways' than the original Hewitt's, and no water compartment. Additionally, one side of the bowl is made of glass which enabled the person administering anaesthesia to see the level remaining in the bowl. Bowl shaped inhaler with a glass bowl base and metal dome top with a connector which appears to be for a rebreather bag. There is a metal switch at the base of the glass bowl to alter or regulate the flow.Stamped into central tube: COXETER LONDON Stamped into side of metal dome: 6460hewitt, wide-bore, clover, ether, anaesthesia, anesthesiology, anaesthesiology -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Inhaler, Probyn Williams (sectioned), Mayer & Co. London, c. 1900
Dr Geoffrey Kaye was a clinical anaesthetist at a time when very few full time anaesthetists existed. He was passionate about the training of future anaesthetists and would often section anaesthetic equipment to reveal its inner workings and show those to students. This Probyn Williams Inhaler is one apparatus which has been sectioned and the various elements of the inhaler have been painted to highlight the differences in function.Oval shaped metal inhaler with attached metal facemask. The inhaler has been sectioned to reveal its inner workings and the ether chamber has been painted black while the air-channel has been painted red. The manufacturer's logo, stamped into the inhaler, has been sectioned as well, leaving only half the information available.Engraved on dome side of inhaler: PROBYN WILLIAMS / G.K. sect. 1939 •Stamped into dome side of inhaler MAYER & / LONanaesthesia, anaesthetist, inhaler, ether, medical history -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Syringe
Pale blue cardboard box with white (discoloured) and blue manufacturer's label adhered to front. Inside the box is a cardboard rest holding a glass syringe with metal point and hand grip. The plunger has a metal end, with a rubber or plastic plunge. The manufacturer's label records it as a Record type hypodermic syringe, an Everett Product, and distributed by the Amalgamated Dental Co Ltd of Melbourne and Sydney. Additional information on the label suggests it have been marketed as The Laminex.medicine, anaesthesia, hospital -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Syringe
Glass and metal 10cc syringe with nozzle for connecting needle offset from the centre.anaesthesia, medicine -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Inhaler, Clover, The Holborn Surgical Instrument Company, 1877
Dr. Joseph Clover (1825-1882), an English physician, first described his Portable Regulating Ether Inhaler on Jan. 20, 1877. Clover was an especially sought after anesthesiologist and early pioneer in the specialty. This was the best-known of many inhalers that Clover designed. The dome-shaped reservoir was turned to points on a control dial to gradually increase or decrease the percentage of the air that passed over the ether. Several inventors based new inhalers on this, while the original continued to be manufactured as late as the beginning of WWII. Clover, to spare the patient the unpleasantness of induction with his "closed" inhaler (1877), suggested the "mitigated-ether" technique. The inhaler was fitted with a bypass tap for the reception of N2O. The bag was filled with the gas and anaesthesia was inducted a combination of N2O and asphyxiation. Ether was then admitted gradually by rotation of the bowl of the inhaler. When the patient had been duly "weaned over" to ether, the mask was lifted, the N2O allowed to escape, the bag refilled with exhaled air, and normal anaesthesia "a la Clover's inhaler" was continued.Metal domed chamber with a bulb attachment for rebreather bag, including a tap mechanism. Remnants of the paper rebreather bag are attached to the bulb. At the other end is a yellow facemask made of plastic (probably celluloid). The manufacturer's logo has been moulded into the dome of the chamber.Manufacturer's logo: THE HOLBORN / SURGICAL INSTRUMENT CO. LTD. / LONDON •Blue sticker with white writing: O.2.4.joseph clover, mitigated-ether, nitrous oxide, n2o, closed method -
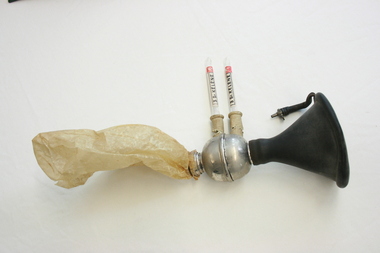 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Ethyl chloride inhaler, Mid 20th Century
The item was collected by Dr Geoffrey Kaye from a Vichy French military hospital during World war II.The inhaler comprises a black rubber face mask that connects to a metal circular chamber from which two white rubber valves are used to administer the anaesthetic agent. The ethyl chloride vials are labelled 'Kelene', a brand name. A waxed paper rebreather bag is attached to this metal chamer. mask, gas, anaesthesia, rebreather bag, world war ii, dr geoffrey kaye, ethyl chloride, kelene, french, vichy -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Venous pressure manometer, 1953
Hand-made manometer is mounted on a flat, rectangular chrome platform. It comprises three valves labelled A, B and C. Valve C is connected to a glass measuring cylinder via a curved metal pipe. Item also includes a small spanner and brown plastic mock leather case with metal clasp, hinges and studs.Engraved into the floor of the device are the instructions on what valves to open and shut for 'infusion, fill and read'. Engraved on spanner: Geoffrey Kaye Engraved on clasp of case: Kaye BJ.2749anaesthesia, dr geoffrey kaye, manometer, venous pressure manometer, measurement, spanner, chrome, invention, manufacture
