Showing 107 items matching "ceremonial dress"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Tatting craft book, Paragon Art Needlecraft Pty Ltd, Tatting Designs, circa 1940's
... by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements... knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". It looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. Paragon knitting, crochet and tatting books have been distributed throughout Australia since the 1930's, originally by "Paragon Art Needlework Pty Ltd" of Sydney, N.S.W. From 1946 these books were designed and printed in Australia from patterns provided by British and Australian thread companies. Consequently these patterns may also appear in similar British and American publications. Paragon Book No. 104 is an instruction book designed for the "beginner" whilst Paragon book No. 105 is designed for the more experienced tatter. The layout of these books was typical of the 1940s period when paper was in short supply. Most of the pattern books were approximately 18 cms wide by 24 cms high and some were smaller at about 13cm by 21 cms. The type used was small (about four lines of text per centimetre) which was difficult to read. This item is an excellent example of a needle work pattern book available to women in the 1940's in Australia.A soft covered, 16 page instruction book titled "Tatting Designs". It has black and white photographs and detailed patterns for tatted doilies, a tray mat, a chairback and arm rests, a cheval set, a luncheon set, collars and edgings for an underskirt, gloves and handkerchief. It is published by Paragon Art Needlecraft of Sydney.Front cover - "Paragon's No 105" "PRICE 1/3" "Tatting Designs" "Household Linens * Personal Wear" Plus a stylized drawing of a deerflagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, tatting book, tatting patterns, craft, handiwork, handcraft, needlework, shuttle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Tatting craft book, Paragon Art Needlecraft Pty Ltd, Learn to Tat, circa 1940's
... by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements... knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". It looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. Paragon knitting, crochet and tatting books have been distributed throughout Australia since the 1930's, originally by "Paragon Art Needlework Pty Ltd" of Sydney, N.S.W. From 1946 these books were designed and printed in Australia from patterns provided by British and Australian thread companies. Consequently these patterns may also appear in similar British and American publications. Paragon Book No. 104 is an instruction book designed for the "beginner" whilst Paragon book No. 105 is designed for the more experienced tatter. The layout of these books was typical of the 1940s period when paper was in short supply. Most of the pattern books were approximately 18 cms wide by 24 cms high and some were smaller at about 13cm by 21 cms. The type used was small (about four lines of text per centimetre) which was difficult to read.This item is an excellent example of a needle work pattern book available to women in the 1940's in Australia.A soft covered 16 page instruction book with black and white photographs and detailed instructions explaining how to tat and eight tatting projects including how to make a collar and handkerchief edgings, published by Paragon Art Needlecraft of Sydney.Front cover - "PARAGON BOOK NO. 104" "PRICE 1/3" "Learn to/ TAT' Back Cover - "36/D5 E/A DO2" - handwritten in pencil flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, tatting, tatting pattern book, tatting instructions, handicraft, needlework, shuttle, tatting shuttle, paragon needlecraft, paragon craft book -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Safari Helmet, Early 20th century
... in tropical countries by both men and women and are part of the dress... countries by both men and women and are part of the dress ...A safari helmet was also called a pith helmet as it was made of sholapith material. It was first used by the Spanish forces in the Spanish East Indies and by the mid 19th century was used extensively by military forces in tropical countries and then became common civilian headwear for westerners in the tropics by the end of the 19th century. Safari helmets are still won today in tropical countries by both men and women and are part of the dress or ceremonial uniform for many members of the armed forces and music bands. This helmet has no known local provenance but is retained for display purposesThis is a pith or safari helmet made from a cream-coloured stiffened fabric. The crown has six segments with a small dome on top with three arch-shaped breathing holes. Around the edge of the crown is a white or stiffened cream cloth (puggaree) intertwined in layers and stitched onto the crown. The brim is peaked at the front and oblong at the back and tapered from front to back. The pleated cloth band is stiffened and has two brass clips. The edge of the brim is reinforced, perhaps with wire. Inside the helmet is the brass base of the top dome in eight circular sections. The interior of the helmet has green cloth in a damaged state. headwear, history of warrnambool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements... knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, Ivoryflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
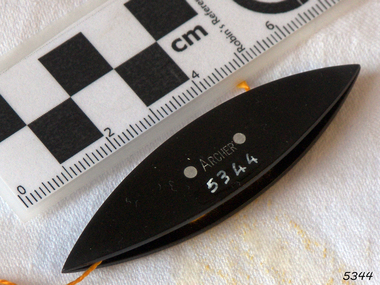 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements... knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, Black plastic, "ARCHER" inscribed. "ARCHER" inscribed.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements... knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, tortoise-shellflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements... knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, ivory, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements... knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, black plastic flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMAFunctional object, Gion Chigo Mochi, c. 1900s
... of Kyoto's entertainment districts, chigo are children dressed... entertainment districts, chigo are children dressed in ceremonial ...‘The Art of the Japanese Package’ was an exhibition that toured to 10 Australian and 11 New Zealand public galleries in 1979 and 1980. The touring exhibition comprised 221 objects of traditional Japanese packaging which extended from ceramics, wood and paper to woven fibre containers. At the conclusion of the tour, The Japan Foundation and the Crafts Board of the Australia Council donated the vast majority of the exhibition to the Ararat Gallery for its permanent collection. Combining the natural qualities of bamboo, paper and straw with delicate craftsmanship, these unique objects express Japanese aesthetics as applied through fibre crafts. In Japan, the qualities and traits of natural materials are exploited rather than hidden. The texture of straw, the septa of bamboo are not concealed but lovingly incorporated into the whole. In 1979 Hideyuki Oka, curator of ‘The Art of the Japanese Package’ wrote: “In no way self-conscious or assertive, these wrappings have an artless and obedient air that greatly moves the modern viewer. They are whispered evidence of the Japanese ability to create beauty from the simplest products of nature. They also teach us that wisdom and feeling are especially important in packaging because these qualities, or the lack of them, are almost immediately apparent. What is the use of a package if it shows no feeling?” The descriptions of the featured objects were written by Hideyuki Oka, curator of ‘The Art of the Japanese Package’, 1979. Gift of the Japan-Australia Foundation and the Crafts Board of the Australia Council, 1981An elegant wooden box, fashioned in the style of boxes used for gifts to the emperor some eight or nine centuries ago, is filled with a Kyoto confection called Gion Chigo Mochi. The Gion is one of Kyoto's entertainment districts, chigo are children dressed in ceremonial Buddhist costume for one of the city's numerous festivals, and mochi are cakes of steamed and pounded rice. The name of the confection derives from the style of the bamboo-sheath wrapping, which suggests the figure of a chigo. - Professor Hideyuki Oka, curator.japanese art, japanese packaging, tsutsumi, gift giving -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Tatting Shuttle, Aero Needles Group Ltd, Mid to late 20th century
... by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements... knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots.The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century.Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic (as is item 8535.1). The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound (e.g. item 8535.2). The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace. One type of tatting shuttle produced by "Aero" from the 1930's to the late 1960's was an anodized grey coated aluminium shuttle with a sharp pick at one end. In the 1970's it was superseded by the grey plastic "Aero" which has a removeable bobbin which you can put on the end of the shuttle to make thread winding easier and an embedded crochet hook for joining picots. The "Aero" company developed in Redditch, England - a town renowned as a centre for manufacturing needles. Firms run by Henry Milward and Abel Morrall were based in Redditch and by the 18th century Redditch was manufacturing one million sewing needles per year. Abel Morrall Ltd launched the "Aero" brand in 1936 and greatly expanded the firm's product line to include tatting shuttles and knitting needles. The classic plastic "Aero" tatting shuttle was manufactured in England from the early 1970's until the 1990's. These items are significant as examples of easily accessible handiwork tools that enabled women in the 1930s -1960s to be able to decorate and personalize their household linen and clothing.Shuttle no. 8535.1 is a beige, boat shaped plastic shuttle with enclosed ends, small round central indentations on both sides and an enclosed black removeable bobbin. The shuttle has a grooved point at one end to hold a bobbin and a small metal crochet hook at the other end. Shuttle no. 8535.2 is a beige, boat shaped metal shuttle with pointed ends that are open but snug, small round central indentations and two smaller circular markings (on both sides) and two internal posts with cream thread wound around.Shuttle no. 8535.1 - "AERO" / "ENGLAND" Shuttle no. 8535.2 - "AERO' / "ENGLAND" "39c" (written in ball point pen)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, tatting shuttle, aero company, handwork, handwork tool, craft, handcraft, needlework, tatting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Craft book, Norma Benporath, Tatting, circa 1940's
... by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements... knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doilies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. This book has photographs and detailed instructions for a wide range of tatted edgings and insertions suitable for household linens such as towels, doilies and tablecloths as well as patterns for whole mats. Stanley E. Mullen (a businessman) developed Semco Pty Ltd which began as a Melbourne based importation company in 1907. The first three letters of Semco's name were his initials. In 1915 it began manufacturing women's apparel, whitework and transfer patterns. In 1924 the company moved to Black Rock, Victoria and continued to produce an extensive range of needlework patterns and handcraft instruction booklets, threads etc. up until the late 1970's. Semco had a staff that included many young women. It was noted by E.J. Trait (editor of the local newspaper "Standard News") that the firm provided them with good working conditions and the correct rate of pay for women in a time of war - the starting rate for 15 year olds, mainly girls at Semco was 25 shillings per week. During World War 2, Manpower Regulations could be used to coerce workers to move into jobs that supported the war effort, but Trait argued that being employed at Semco could make this unlikely as the firm made some goods essential for the war effort. He even suggested that women be encouraged to produce needlework items (and play a part in the war effort) by sending them as presents, to the troops up north. He also heaped praise on the Semco workplace - noting that no Saturday work was the norm, allowing employees to shop and have "hair-do's" before enjoying a relaxing weekend! Semco also had a female cricket side in the women's Saturday association. After the war the firm stayed in production until the early 1990's when it was taken over by Coates-Paton Pty Ltd. Norma Benporath (1900 - 1998) was an expert in tatting techniques and taught and published extensively on the subject. She was born in New Zealand with impaired sight but cataract surgery restored 50% vision to one eye. She was inspired to learn tatting whilst watching her aunt tat and being told that tatting did not require as much sharp vision as embroidery. She quickly learnt to design her own patterns and published over 1000 tatted lace patterns between 1929 and 1952. She became a regular contributor to magazines (such as Home Beautiful) and newspapers across Australia. Her designs were also published in New Zealand, South Africa as well as the U.K. and U.S.A. When Semco, a thread manufacturer, noticed a rise in the sale of fine crochet threads, they realized they had an untapped market to explore. Norma designed a collection of tatting patterns for Semco that were used to help promote their threads. Norma also worked with Semco to produce a line of threads and shuttles specifically suited to tatting. In 1997, Norma was inducted into the "Order of Australia" for "Service to the craft of tatting as a designer and through the international publication of her patterns".This item is an excellent example of the needle work being enjoyed by women in the 1940's in Australia and the skills of the Australian designer, Norma Benporath. It is also an example of the trend that emerged for craft companies such as Semco to publish pattern books in order to advertise their own materials.A 32 page soft cover instruction book with green front and back covers showing two tatted doily designs. The book includes black and white photographs and written patterns by Norma Benporath.Front cover - "TATTING" "For / EXPERTS/ and / BEGINNERS" "By/Semco" "SEMCO INSTRUCTION BOOK" "No. 16" "WITH ILLUSTRATIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS" "9" Back cover - "FOR INSTRUCTIONS FOR WORKING SEE PAGE 22" "Published by Semco Pty. Ltd." "BLACK ROCK, 29, VIC"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, tatting, tatting instruction book, tatting patterns, tatting shuttle, semco, semco pty ltd, norma benporath, needlework, handcrafts, household linen, craftwork -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumCeremonial object - Ushabti of Taweret-Khaiti, Circa 1292 BC
Ushabti are tiny anthropoid (human-shaped) figures placed in the tombs of wealthy Egyptians. They were intended to do the work of the deceased in the afterlife. This purpose is implied through their name, which may have derived from the Egyptian word “to answer”. The Burke Museum in Beechworth is home to a particular ancient Egyptian Ushabti figure. This artefact was donated to the Museum in 1875. No details about how it left Egypt, arrived in Australia, and where it was located before this donation are known. The Nineteenth Century, when this artefact was donated, was a period when many museums acquired items of ancient Egyptian heritage. Many of these items were procured in less than desirable circumstances, having often been looted from ancient tombs and sold to tourists without documentation as to their original location and/or accompanying grave goods. These artefacts were also divested through partage (the trading of artefacts for funds); however, the latter is unlikely to have been the case for this artefact. Since the Ushabti was donated by an unknown donor, it is likely to have been in a private collection rather than an institution. Ushabti can be dated using iconographic analysis which is non-invasive and provides a comprehensive study of the artefact. The later period of the 18th Dynasty marked the beginning of an increase in both the inclusion of Ushabti as essential funerary items and the creation of Ushabti with tools. From this period, they are no longer depicted without tools. Depictions of tools including gardening hoes are frequently depicted grasped in the Ushabti’s hands whilst items like the seed-bag are depicted hanging on the back rather than in an alternative position. This Ushabti figure grasps a gardening hoe and a mattock and a small seed bag surrounded by a yoke bearing water jars are depicted on the upper back of the Ushabti. These features are essential in helping narrow this dating to the late 18th and before the early 20th Dynasty. The position of this seed bag also provides dating information. In the early 18th Dynasty this bag was consistently drawn on the front of the figurine; however, by the reign of Seti I, this feature moved to the back. Thus, since the seed bag is located on the back of this Ushabti, it cannot date to the early 18th Dynasty. By the 19th Dynasty, Ushabti’s were increasingly made from either faience or terracotta. The availability of these materials in Egypt resulted in the increase of Ushabti production with tombs containing many more figurines than previously seen. The Ushabti held by the Burke collections is made from terracotta. Terracotta was rarely used for Ushabti before and during the early 18th Dynasty with only the odd appearance until the late 18th Dynasty and becoming common through that period until the late Third Intermediate Period. Whilst the face has been damaged, there is no evidence for the Ushabti having been provided with an Osirian false beard. This omission rules out a dating of later than the 25th Dynasty when beards became prominent. The inscriptions also date the Ushabti to the New Kingdom. This is because of the use of sḥḏ (“to illuminate”) with Wsjr (“Osiris”) which only occurs in these periods. Therefore, considering all these elements, the Ushabti can be confidently be dated to between the late 18th to early 19th dynasty.Artefacts like this Ushabti are no longer exclusively representative of their origins in burial assemblages and significance in the mythology of the Egyptian afterlife but are also significant for the accumulated histories they have gained through travel. The movement of this artefact from Egypt to Australia allows insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century, and in particular, the reception of ancient Egyptian artefacts in small rural museums. The procurement of Egyptian artefacts was a social trend around the late 1800s to early 1900s. Egyptian artefacts were considered curiosities and recognised for their ability to attract public attention to museums. They were also utilised in Australian museums, like the Burke Museum, to connect the collection to one of the oldest civilisations known to man and since Australia was considered a “young” country by European settlers, this was vital and derived from an interest in Darwin’s “Origin of the Species” 1859. Furthermore, there was a culture of collecting in the 1800s amongst the affluent in English society which led to the appearance of many Egyptian artefacts in private collections. The acquisition of this Ushabti figure is not certain, but it was likely donated from a private collection rather than an institution. This particular artefact is significant as an example of a high-quality Ushabti representative of those produced during the late 18th or early 19th century. It provides insight into the individualism of an Ushabti and the mythology of ancient Egypt. It also provides an example of the types of items required in the tomb assemblages of this period and reinforces the importance of ensuring the successful afterlife of the deceased through art. This Ushabti belonged to a woman named Taweret-Khaiti, Chantress of Amun, in the late 18th Dynasty or early 19th Dynasty (c.1292 BC) of the Egyptian New Kingdom. It likely comes from an undetermined tomb in the locality of Thebes. This figure is made from Nile silt clay (a polyester terracotta; clay sourced from the banks of the Nile River) which was a popular material for Ushabti construction in the early 19th Dynasty. It is in a fair state of preservation (with the exception of a break through the centre) and originally made to a high quality. The face has been damaged but the eyes and eyebrows are clearly marked with black ink and the sclera painted white. The Ushabti is painted a light brown/yellow colour and features a vertical line of inscription down the lower front. The Ushabti wears a large wig and and a schematic collar. The arms are painted light brown and depicted crossed with bracelets around the wrists. It grasps a hoe and mattock. A yellow seed-basket is depicted on the Ushabti’s back. These features represent the likelihood that this particular Ushabti was intended to complete farm work for the deceased in the next life. There would have been additional Ushabti of similar design within the tomb who worked under the supervision of a foreman Ushabti. The foreman Ushabti would be depicted dressed in the clothing of the living. The inscriptions are painted freehand in black ink and written in a vertical column from the base of the collar to the foot pedestal on the front of the Ushabti. The owner of the Ushabti could elect to have the figures inscribed with their name, the Ushabti spell and any other details they deemed necessary. In the case of this example, the Ushabti is inscribed with the owner’s details and is an abbreviated version of the standard Ushabti formula. This formula ensured that the Ushabti would complete the desired task in the afterlife when called upon by the deceased. Ushabti which were not inscribed would represent their intended purpose through design; however, this Ushabti, like most made in the late 18th Dynasty, conveys its purpose both through both design and inscription. The inscription is as follows: sHD wsir nbt pr Smayt imn tA-wr(t)-xai(ti) mAa xrw which translates to: "The illuminated one, the Osiris (the deceased), the mistress of the household, Chantress of Amun, Taweret-Khaiti, true of voice (justified)"ancient egypt -
 Rye RSL Sub Branch
Rye RSL Sub BranchSword Ceremonial Turkish
A short dress sword thought to be turkish, with pointed etched blade including a crescent and star motif and brass hand guard also with etched crescent and star motif. -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPHS OF SOLDIERS, 38th BATTALION, 38 Bn, c1950-1962
38 Bn was raised in Bendigo in 1916. Post War it was the CMF Unit until 1967. The Mollison St Drill Hall was built by Contractor Mr. Midgley. First used Jan 1916. Shut down Circa 2002. The 38 Bn Colours are held within the RSL Military Museum, Bendigo.1. Photo of 4 Senior NCO's in battle dress in front of the Mollison Street Drill Hall. 38 Bn Northern Victorian Regiment. The four soldiers have .303 rifles. WO Burrell has the red sash of a Colour Sgt. His MM can be seen. 2. Photo of Regiment Colours 38 Northern Vic Regiment in front of Mollison St Drill Hall. Two Officers, Capt. Emonde holding Queens Colours - 4 Snr NCO's have rifles at the slope with ceremonial tips on their bayonets.1. On rear is written - Cenotaph party/ Warrant Officer 3 sets Guards. 2. On rear is written - '" ANZAC DAY" .38 bn, mollison st, drill hall, photographs -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPH, GROUP OF SOLDIERS MARCHING, Australian Army, c 1982 - 2000
... . Hattam with drawn sword. There are 18 male soldiers dressed... with drawn sword. There are 18 male soldiers dressed in khaki ...Colour photo mounted on cardboard. Squad led by Officer R. Hattam with drawn sword. There are 18 male soldiers dressed in khaki Ceremonial. They are carrying SLR rifles and wearing slouch hats. The female soldiers are wearing the winter ceremonial green uniform with light green hats. They are partially obscured and appears to be approx 12 of them.passchendaele barracks trust, cmf bendigo, 15 tpt sqn -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumUniform - MESS DRESS
Items issued to Francis William (Dinky) DEAN BEM, No's VX93960 2nd AIF, 3742 1RAR. Refer Reg No 124.2 for his service details.Pants, cummerbund, sash, peaked cap and white jacket, belonging to Frank (Dinky) DEAN.uniforms, army, costume, male ceremonial, military history -
 Frankston RSL Sub Branch
Frankston RSL Sub BranchWebbing, Belt, No maker discernible, Unknown
Used with dress uniform for ceremonious purposes.An example of the standard issue webbing belt used by Australian service personnel. The name "Bretterecker" and the number 360053, (possibly a post World War 2 service number) is written in black ink on the inside surface of the belt. The belt has been "blackened" for ceremonial use and has brass fittings, the 2 angled buckles normally located on the rear of the belt have been removed. The 1937 pattern equipment (also known as '37 webbing') was an item of military load-carrying equipment. Pattern 37 replaced the 1908 Pattern and 1925 Pattern—on which it was based—and was standard issue for British and Commonwealth troops from its introduction in 1937, throughout World War II, and in the post-war period until it was superseded by 58 pattern webbing. The design was confirmed on 8 June 1938 and wide-scale issue began in 1939. Towards the end of World War II, some 37 Webbing was produced in jungle green for troops fighting in the Pacific Theatre, although purpose-made 44 Pattern Webbing was then introduced for the humid jungle conditions, being lighter in weight, quicker drying, and rot-proofed.[ Although 44 Pattern continued in use with the British Army for jungle warfare in its various post-World War II colonial conflicts, it did not replace 37 Pattern in general service, which was in use up until the introduction of 58 Pattern. However, 37 Pattern was used for ceremonial purposes and still issued to Cadets in the 1990s. 1937 Pattern Webbing was made from cotton webbing, which was waterproofed and dyed before being woven. The fittings were made of stamped brass and it was produced by various manufacturers.Written in black ink on the inside "Bretterecker" and the number 360053, possibly a post World War 2 service number.webbing belt, dress webbing -
 Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub Branch
Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub BranchUniform - Sam Browne Belt, Sam Browne Belt (brown leather)
The Samuel Browne belt is named after Sir Samuel James Browne VC. In 1858, Browne lost his left arm in battle (as a result of a sword cut) and as the dress regulations of his regiment required officers to wear their waist belts under their tunics, Browne found this ungainly and devised an external belt supported on the left-hand (sword) side by a shoulder strap. The belt had two shoulder straps when a holster was worn. In the Australian Army, a brown leather version is worn on ceremonial occasions by officers and Warrant Officers Class One of all corps, except those who wear silver dress embellishments (Armoured, Aviation and Nursing Corps). These members wear a black Sam Browne belt. Wide brown pattern stitched brown leather belt with adustable shoulder strap, brass buckle and brass loop fittings (4 at the top and 2 at the bottom) attached to the belt by stitched leather straps.Nonesam browne, belt, clothing -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Ceremonial object - Clothing, child's dress-up costume, c1927
... with detachable cape Ceremonial object Clothing, child's dress-up costume ...A child's dress-up costume incorporating the Australian Red Ensign Flag made for a pageant c1927A child's dress-up costume c1927. An Australian Red Ensign Flag sleeveless top with detachable capeclothing, moorabbin, dressmaking, textiles, melbourme, velia dowdes house -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Clothing - BARBARA JOHNSON COLLECTION: CREAM SATIN UNDER-SKIRT OF WEDDING DRESS, 1958
Cream satin, full circle skirt, gathered onto a 4cm waistband. A rear opening has a 22cm placket, with metal zipper, and two metal hook and eye fasteners on the waistband. Handkerchief hem around the circular skirt. Two full length flat seams, one of which has a small blue ribbon bow sewn in for luck. Part of wedding dress collection 11400.528, 11400.529, 11400.530, 11400.531costume, female ceremonial, wedding skirt -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Clothing - BARBARA JOHNSON COLLECTION: WEDDING HORSESHOE, 1958
Small satin covered horseshoe, with a decorative frilled netting at front. Three 1.5cm ribbon bows are attached to the front. Three small chiffon “roses” and a wax orange blossom bud on a paper covered wire are attached to the front. Top of the horseshoe has once had a ribbon loop to carry over the bride’s arm, but this has been badly damaged. Part of wedding dress collection 11400.528, 11400.53029, 11400.530, 11400.531 Wedding dress worn at marriage of Barbara Johnson to her first husband Ian Bulte.costume, female ceremonial, wedding horse shoe -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Postcard - GLADYS DEAN COLLECTION: POSTCARD, 1906 - 1908
... is dressed in a ceremonial uniform with various medals... is dressed in a ceremonial uniform with various medals ...Black and white photograph of King Edward VII. He is dressed in a ceremonial uniform with various medals and decorations. Photograph has a 1cm border along the bottom edge with the printed words Konig Edward VII. von England. On the reverse card is addressed to Miss Dean McKenzie Street Golden Square. There is a one penny stamp affixed.Nonepostcard -
 Yarra Ranges Regional Museum
Yarra Ranges Regional MuseumEmpire Day Dress, Miss Mary Ryan, 1902
The dress was made by Miss Mary Ryan, a pupil at Lilydale Convent (now Mt Lilydale College) in 1902. It was worn to the Annual Empire Day Celebrations in Lilydale. Accompanying photo shows dress worn by Monica Ryan (no. 5089). The outfit also includes two hand made pockets for handkerchiefs and ties (nos. 735 & 736) Empire Day Dress; Cream silk, cotton lined, embroidered with kangaroos and emu holding shield, with Southern Cross stars above rising sun emblem. Banner below reads 'Advance Australia', embriodered with silk and cotton thread; also gold metalic braiding. Bodice of dress decorated with embroidered Australian and British flags, wattle branches and eucalyptus leaves, cotton, leather leaves(?); centre of dress and sleeve cuffs decorated with red, blue and white ribbons. Thin gold braiding around neckline. back of dress closes with hook and eye fasteners. 'Advance Australia' in gold metalic thread, bottom of dress. costume - childrens, costume - female ceremonial, lilydale -
 Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and Archives
Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and ArchivesSword + scabbard, Farquhar McCrae's sword + scabbard
Farquhar McCrae (1807-50) was born at Westbrook near Edinburgh, into a distinguished Scottish family. He was educated at the University of Edinburgh and graduated MD in 1827. After a sojourn in Paris he joined the staff of the general hospital at Chatham. Here he suffered an injury during a dissection, which impaired his health for the rest of his life. He was appointed curator of the museum at Chatham, and put together a notable collection of pathological specimens. In 1838 he sought to resign on the grounds of ill health, and was then offered a posting with the 6th (Inniskilling) Dragoons. But with his health still poor, he decided to emigrate to a kinder climate, and arrived in Melbourne aboard the barque Midlothian. McCrae set up practice in Bourke Street with his brother-in-law, David Thomas. Both were pioneers in the use of anæsthetics. McCrae was the first to introduce chloroform, Thomas ether. Sometime after 1841 McCrae moved to Sydney, where he was one of the first medical practitioners appointed to the staff of the Sydney Infirmary and Dispensary. He died in Sydney at the age of 43 years. The sword is a dress sword of the 6th Dragoons. Made by Henry Wilkinson of Pall Mall, it is 38 inches (96.5cm) long and has an elaborately engraved and highly polished steel blade. Being a ceremonial weapon, the blade is quite blunt, and the gilt guard bears the crown and monogram of Queen Victoria, which dates the sword to late 1837 or 1838. The grip is bound in snakeskin and the sword is carried in a leather scabbard with brass mounts. It remains as one of the important links to the pioneering days of Melbourne, and early medical practice in Australasia.Sword, ceremonial, steel with brass decoration and a steel handle, highly decorated, in a scabbard of patterned black leather covered metal, brass tipped, 100 cm long. It belonged to Farquhar McCrae. -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumPhotograph, Marie La Peyre with Japanese exchange student
Marie La Peyre with Japanese Rotary Exchange student wearing traditional Kimono dress. c1970s.tatura, exchange student, lapeyre m, locals, costume, female, ceremonial -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationCeremonial object - Academic dress hood
... Academic dress hood in red. Ceremonial object Academic dress hood ...Robin Gerard Penleigh Boyd was admitted to the degree of Doctor of Letters on the 21st day of October 1967 at University of New England. The family attended the outdoor ceremony and have slides of Robin Boyd in full academic dress. The Doctor of Letters Certificate (item D490) is also part of the Walsh Street Archive. Zelman Cowen was Vice Chancellor at University of New England 1967-1970. Robin Boyd designed the Zelman Cowen House at 34 Yarravale Rd in Kew in 1959. Academic dress hood in red.une, university of new england, zelman cowen, doctor of letters, robin boyd, ohm2022, ohm2022_42 -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPhotograph
A CEREMONIAL OCCASION AT A UNKNOWN CITY HALL. A MAYORAL PERSONAGE & VARIOUS OTHER WELL-DRESSED ONLOOKER.local history, photography, photographs, ceremony - unidentified -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Clothing - Wedding dress, 13.5.1945
Worn by Jessie Allan for her marriage to William Thomas Kenny on 13 May 1945 at St Stephens Church, Richmond. They lived in 19 Baldwin Road, Blackburn from 1965. Jessie deceased 1.4.2010. Funeral at St Alfred's Anglican Church, Blackburn South.1945 Cream satin wedding dress with a rouched bodice to a centre panel, high neckline and pointed collar. Bead work on centre panel and edge of bodice, long sleeves to a pointed wrist and beading. Thirty covered buttons down centre back. Skirt cut on cross and three metre train at back.|.2|Champagne coloured Wedding Veil - (approx 6ft in length) - complete with orange blossom 3 1/4' headdress. Headdress is handmade, attached to a wire frame|.3|Cream satin slipper. Machine stitched half in rows. Bow with satin loop and spray of wax orange blossom attached.|.4|Horse shoe shaped wedding item to hang over bride's arm. Rouched satin with ornamental - artificial (wax) orange blossom and buds with 2 mm ribbon to hang over arm. Cream coloured to match wedding dress.|.5|Satin horse shoe, rouched, with satin ribbon handle.|.6|Cream braided horse shoe with gilded wishbone and wax orange spray attached. A bow with long loop to hang on the arm.|.7|Satin Horseshoe Good Luck charm with 'petal' flowers surrounding it, made of cut material - ribbon bow with pearls in centre.|.8|Doll in taxi - Rosy-cheeked, dark hair, blue eyes, dressed in bridal dress with veil, with pearls and 'flowers' decorating the doll. The doll stood across the back seat, under the window. Lavender in base of stand.|.9|Bridal Ring Box - 'Good Luck' horseshoe charm box - in the shape of a prayer book. Cream box with silver motifs printed on.|.10|Groom's Buttonhole of spray of wax orange blossom - 4 flowers and 3 leaves. Cream flowers with yellow stamens - green leaves. 10 Items in total..7 'Wishing you all The Best' 'Good Luckcostume, female ceremonial -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Clothing - Bridesmaid Dress, 1950
Dress first worn at wedding of Miss Margery Rudd and then in 1973 for the wedding of Miss Sharlene Barry (now Draeger)1950's claret crushed velvet floor length dress with cream lace around the high square neckline and around cuffs on long sleeves. 25 velvet covered buttons down back. Waist comes to a point at back with inverted pleat falling from point at back waist line. Sash is separated with press stud fastening and a bow effect.costume, female ceremonial -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Clothing - Wedding Dress, 1978 c.February
Made for and worn by Jeanette Margaret Bennett at her wedding at Uniting Church, Riversdale Road, Wattle ParkWhite chiffon 1978 round neck line dress with high waist, long sleeves; with cuff and six covered buttons. Hem line and neck trimmed with satin. Dress lined with satin underskirt. See also 3597., Wedding Veilcostume, female ceremonial
