Showing 64 items
matching mayday hills hospital
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Isabel Wells, 24th February 2000
... Mayday Hills Hospital... in the region, like Mayday Hills Hospital and The Ovens and Murray Home... in the region, like Mayday Hills Hospital and The Ovens and Murray Home ...Isabel Wells was born in Beechworth in 1914. Her father, Mr. Newey, was a butcher; his shop was in Ford street and he took over from his grandfather. The family business, along with the local residents, was supplying the main government institutions in the region, like Mayday Hills Hospital and The Ovens and Murray Home, making a large percentage of his profit. Mr. Newey was also a captain of the fire brigade and Isabel mentioned that there were more fires happening in those days. The menace of a huge fire was impending in Beechworth for many years, due to the lack of adequate water supply and the absence of trained firefighters. The first fire brigade in the town was voluntary and was formed in 1858 under Superintendent Luke Reilly. A few other schemes deployed the following years, with all failing to sufficiently control the fires that occurred, until the creation of the first reliable fire brigade in the 1870s. The worst fire in the town's history happened on 23rd March 1867; it swept through many shops and the post office, leaving behind a damage cost estimated at £12,000. Isabel's mother was in a wheelchair, suffering from osteoarthritis; thus, Isabel had taken over the responsibility for looking after her mother and assisting her with daily living needs and personal care activities. She used to play golf and tennis and she was a member of the town tennis club. In terms of social life, Boxing Day was a big occasion for the town, with horse-races and games taking place. According to her narration, the use of cars was a turning point in the town's social activities, since people were able to visit nearby places and take day trips, such as having a picnic at Lake Kerferd or Buffalo. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke. Isabel's account of her life in Beechworth and the local area during the 20th century is historically and socially significant as it offers valuable information about the business activity in the region and provides a deeper insight into the operation of butcher shops and meat supply during the first half of the previous century. Additionally, it offers invaluable information about the everyday life of people living in Beechworth, and highlights aspects of the overall social life and activities.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mrs Isabel Wells/ isabel wells, beechworth, mr. newey, ford street, butcher, mayday hills hospital, the ovens and murray home, fire brigade, 23rd march 1867, fire, osteoarthritis, boxing day, horseraces, lake kerferd, buffalo, picnic, cars, firefighters, luke reilly, wheelchair -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPostcard, George Rose, c.1945
... of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth... of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth ...The Rose Stereograph Company first began producing postcards, identified as the 'P' series (like this particular example) in 1913 and continued in this business until 1967 after which they switched to machine manufactured colour postcards printed by an external company. These were produced by Victorian-era photographer George Rose (1861-1942) often reputed as one of the best photographers in Australia during the later 19th Century and early 20th Century. Rose was born in 1861 in Clunes and began his photography business in 1880 when he founded the Rose Stereograph Company. He later switched to producing postcards after stereographs lost popularity in the early 1920s. The Mayday Hills Hospital was one of these locations photographed by George Rose and published as a postcard. Beechworth's Mayday Hills was chosen as the site of Victoria's newest asylum, at the time, due to the landscape and altitude. The hilltop atmosphere and the native fauna, it was argued, would assist in the cure of the patients kept at the hospital (Wood 1985, 122). The positioning of the hospital had a beneficial effect on the rural town. A pamphlet published by James Ingram and Son (1849) reveal that famous landmarks in Beechworth which included the Post Office, Gaol, Courthouse and Asylum "demonstrate the appreciation of Beechworth by the Government not only as as important district center, but also as a site unrivaled as a sanitarium". There were other locations in contention at the time, but ultimately Beechworth was chosen (Craig 2000,33). Prior to the creation of the Asylum in Beechworth, those charged with having mental illnesses or, as it was termed, "insanity" were unable to be properly cared for in the Gaol (which is where they were often sent). John Buckley Castieau wrote, in 1861 for the Ovens and Murray Advertiser, that the Gaol was unable to properly care for those classified then as "insane" but that they would endeavor to treat them above the other inmates (which he notes is not always the case in other establishments). Castieau wrote this in favour of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth. It was stated that at the time the Mayday Hills Hospital was built, there were 83 prisoners kept in the Gaol who were to be rehoused to the Hospital on the grounds of "insanity". The classification as someone as "insane", in this period of time is a reflection on the inability to cure and understand illnesses of the mind during the mid to late 1800s. Opening on the 24th of October 1867, the Mayday Hills Hospital was originally named the "Ovens Lunatic Asylum", a title which is very much a product of its time. Whilst controversial, changes to the name is part of the history of the Hospital and can provide much insight into the understanding of mental illness throughout history and the use/disuse of this term provides information into the reception/changing opinions of mental illness in society. The Hospital would later become known as the "Mayday Hills Asylum" and/or "Mayday Hills Hospital" with the latter being the most commonly used title. An article in the Ovens and Murray Advertiser notes that on the 7th of March 1865, the foundation stone of the Hospital was laid (it would officially open in 1867) and that it was such a moment of accomplishment and joy for Beechworth that a letter to the editor even suggested that there should be a holiday dedicated to the day the foundation stone as laid. This reveals an extent to which the townspeople of early Beechworth valued the construction of the Hospital in their town. It provided the town with a sense of prestige and honour. At first glance, the remains of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth, Victoria, inspire tragedy, trauma and beauty. The buildings themselves, with their Italianate style Renaissance architecture designed by J.J. Clark (Craig 2000, 49 & Smith 2016, 203) reflect a bygone period of European and Australian history. The gardens provide a sense of tranquility and beauty. The experience of those within these walls remains a valuable area of study to provide a more complete understanding. This particular hospital is considered the fourth of its like and one of three identified as the largest of their kind. The Mayday Hills Hospital is a sister to the Kew and Ararat Asylums in Melbourne which are both located in relative proximity. Understanding the role of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth history is integral to understanding the development of the goldfields town, but also for providing important information as to the history of caring for, and the reception of, mental illnesses in Australian and wider European history. Mayday Hills provides a case study which can be researched through oral history, an analysis of the grounds/buildings and through images like this postcard which portray the structure in a highly deliberate manner. Images like this depict the strong façade of the Hospital and provide a glimpse into the tranquility of the gardens. This has been done deliberately to provide a sense of comfort and healing about the building to those looking from the outside. Further research into the importance of the Hospital in Beechworth and it's connection to the town will be supported through images like these kept in the Mayday Hills photo album in the collection of the Burke Museum.Pale sepia toned rectangular postcard printed on matte card.Obverse: THE ROSE SERIES P. 4689 / COPYRIGHT / ADMINISTRATIVE OFFICES, MENTAL HOSPITAL, BEECHWORTH, VIC / Reverse: Published by the Rose Stereograph Co. / Armadale, Victoria / POST CARD / THE "ROSE" SERIES / DE LUXE / A REAL PHOTOGRAPH / PRODUCED IN AUSTRALIA /mayday hills, asylum, mental hospital, hospital, beechworth -
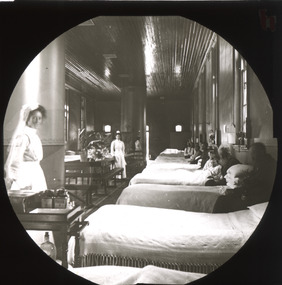 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
... Mayday Hills Hospital... at Mayday Hills Mental Asylum. Also known as the Beechworth Lunatic... Mayday Hills Mayday Hills Hospital Mayday Hills Asylum Beechworth ...This glass slide captures a scene from a male hospital ward at Mayday Hills Mental Asylum. Also known as the Beechworth Lunatic Asylum, Mayday Hills was officially opened on the twenty-fourth of October 1867 and was commissioned following lobbying from Beechworth Municipal Council concerning a need for better living conditions for individuals confined to the town's gaol. These individuals, as well as many others who were brought from surrounding institutions, exhibited behaviours that were deemed to be unfit for mainstream society. At its peak, the asylum consisted of sixty-seven buildings and housed over twelve-hundred patients and five-hundred staff. At the time of Australian Federation in 1901 - just a year after this photograph was taken - the patient population numbered six-hundred and seventy-four. The asylum was officially closed in 1996. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register as being architecturally significant. The extensive complex of buildings are examples of Italianate-style, which is strongly associated with asylums of the 1860s - the period in which construction of this particular asylum began. Today the asylum offers tours to visitors, including daytime history tours and night-time ghost tours. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is socially and historically significant as it is representative of the lives of the nurses and patients at Beechworth Mayday Hills Asylum in the early twentieth century. It is also historically significant as it is representative of the changing style of treatments and attitudes towards mental illness. Thin translucent sheet of glass with a circular image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.Obverse: h /lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, mayday hills, mayday hills hospital, mayday hills asylum, beechworth lunatic asylum, beechworth mental asylum, psychiatric hostpital, beechworth, burke museum, beechworth municipal council, beechworth patients, psychiatric patients, victorian heritage register, 1900, 1900 mayday hills, italianate style, 19th century asylums, asylums victoria, male ward mayday hills -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mr and Mrs Don Hayes, 20th May 2000
... Mayday Hills Hospital... as Mayday Hills (est. 1862) and continued working there for the next... at Mayday Hills Mental hospital from the 1950's. Hearing the stories ...In this interview we hear from Don and Bobbie Hayes who met and were married in Beechworth. Mrs Hayes was born in Beechworth to a blacksmith and a teacher who had moved to the area not long before she was born in 1925. She discusses her family and the struggle her mother had being a city woman relocated to the bush and into a family who didn't accept her for her Methodist religious beliefs as they were a staunch Catholic family. After working in the Tannery when they first moved to Beechworth from Melbourne, Don got a job in the 1950's at the Beechworth Mental hospital known as Mayday Hills (est. 1862) and continued working there for the next thirty six years. Starting as a nurse Don would be one of three or four staff known then as attendants, who would oversee up to forty patients in a ward taking them out to work the land and gardens or chop wood on the grounds. Mrs Hayes also worked in the Hospital and discusses the need at the time to be earning to pay for large medical bills that came from two of their children, one having a congenital heart problem which was not covered by hospital benefits and the other displaced hips that required surgery. By the end of his time working at the hospital, Don was in charge of the patient training centre where those destined for discharge would be trained on how to cope in the world outside of the hospital grounds they were so used to. Both talk openly and with heartfelt candour, recalling their years spent among the patients of the hospital community, their sense of humour and compassion are evident and although the times and the jobs were definitely hard and the wages low, this couple cared deeply about the people they worked with and sit among those people from the local area who established Beechworth as a significant social welfare region. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.The significance of this oral history lies in the firsthand accounts from two people who were directly involved in the significant nursing work undertaken at Mayday Hills Mental hospital from the 1950's. Hearing the stories from those who were there and had lived experience, adds depth and we gain valuable insight into how and what the asylum was like for those who worked there and colourful details about the kinds of patients they encountered too, it adds human and personal context to what could otherwise become statistic and abstract information about a historic site. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.listen to what they say, beechworth, oral history, burke museum, mayday hills hospital, may day hills, beechworth mental asylum, mental hospital, asylum, nursing, hospital, patient training centre, patients, social welfare -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mrs Beth Miller, 8 June 2000
... in 1949. A working contract and position at the Mayday Hills... immigration Mayday Mayday Hills Mental Hospital Asylum Black Spring ...Mrs Beth Miller was born in February, 1924 in Latvia. Her family left for Germany after Russian occupation was implemented in Latvia, and eventually sailed for Australia from Naples, Italy in 1949. A working contract and position at the Mayday Hills Mental Hospital brought her to Beechworth, where she settled with her husband and parents. Mrs Miller recounts the daily work in the Mental Hospital during the 1950s, life in Black Spring and the isolation of the immigrant experience. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Mrs Beth Millers account of her life in Beechworth and the local area during the 20th century is historically and socially significant to the cultural heritage of the region. She gives important insights into the life of post-war European immigrants in the area. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mrs Beth Miller /beechworth, beth miller, miller, listen to what they say, jennifer williams, oral history, latvia, bonegilla, immigration, mayday, mayday hills, mental hospital, asylum, black spring, bakery, lutheran, immigrant -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mrs Elva Hill & Mrs Mary Martina, 22nd August 2000
... mayday hills mental hospital... Hospital', the full name of which was the Mayday Hills Mental... Hospital', the full name of which was the Mayday Hills Mental ...This oral history interview was conducted with two sisters, Mrs Elva Hill and Mrs Mary Martina. They describe growing up in Beechworth, living a fairly well-off life compared to others around them. Mrs Martina in particular talks about going to school, becoming a teacher, and helping to set up Beechworth Secondary School. She talks briefly about gender roles for girls in the classroom and how teaching has changed over time. Mrs Hill and Mrs Martina describe the Beechworth community as friendly, including towards migrants, and suggest they were not particularly involved in political movements except for protesting after the dismissal of the Whitlam Government. They discuss visiting the Albury Show. The sisters briefly discuss 'them pushing the wheelbarrow to Mt Buffalo'. This refers to a publicised wager between garage proprietor Tom Parkinson and Post Office Hotel licensee Tony Evans in 1935. Evans challenged Parkinson to push him in a wheelbarrow for over 80km (with an elevation of 1000m) from the Beechworth Post Office to Mt Buffalo in just eight days, with the winner awarded twenty pounds. A brochure was published with official rules, and the incident made international news in the New York Times. They briefly discussed that their parents worked at the 'Mental Hospital', the full name of which was the Mayday Hills Mental Hospital, known at other points as the Beechworth Asylum and the Beechworth Hospital for the Insane. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.The statement captures a personal perspective on the teaching profession and education at rural schools during the mid-twentieth century, with a focus on the experience of young girls and women going to school. It specifically discusses the establishment of Beechworth Secondary School. Mrs Hill and Mrs Martina also provide insights into the social dynamics of the town, as two girls from a well-off family discuss how they believed people from different backgrounds interacted with one another. The interview also puts Beechworth into a wider social context, as the women discuss how they were perceived when they went to College and how they interacted with wider politics. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mrs Elva & Mrs Mary Martina /listen to what they say, beechworth, oral history, burke museum, hill, martina, sisters, boarding school, rural school, primary school, beechworth secondary school, mayday hills mental hospital, gender, gender at school, entertainment, albury show, dress codes, wealth gap, whitlam dismissal -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, W. D. Gibbon, 1905
... mayday hills mental hospital... asylum beechworth mental hospital mayday hills mayday hills ...Taken 1905 by photograph W.D Gibbons the photograph depicts a pathway leading to the administration building of the Beechworth Mental Asylum. There are three well-dressed young men lounging on the grass as another is jumping behind them. This is significant as it demonstrates that the asylum was not a prison and that the mentally ill patients were allowed their freedom. The Beechworth 'Lunatic' Asylum was constructed between 1864 and 1867 to the designs by the Public Works Department (PWD) and was later renamed the Mayday Hills Mental Asylum. The decommissioned asylum was one of the largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria and consisted of sixty-seven buildings, one thousand two hundred patients and five hundred staff members. At the asylum, active work was considered imperative and workshops were located near the male accommodations and laundries and drying yards near the female accommodation. The administration building itself highlights the architectural and aesthetic significance of the asylum to the State of Victoria. This photograph is historically significant as it demonstrates the architectural and aesthetic significance of the asylum but also the changing approaches to treating mental health. Black and white rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper mounted on grey cork Obverse: W.D Gibbon/ Beechworth Reverse: 79.1701beechworth, beechworth lunatic asylum, beechworth mental hospital, mayday hills, mayday hills mental hospital, asylum, administration building, wd gibbon, photograph -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, About 1880
... mayday hills mental hospital... drawn carriage mayday hills mental hospital beechworth lunatic ...Taken about 1880, this photograph depicts nine people and a horse-drawn carriage in front of the Administration building of Beechworth Mental Asylum. Constructed between 1864 and 1867 to the designs by the Public Works Department (PWD) is the Beechworth Lunatic Asylum which was renamed Mayday Hills Mental Asylum. The decommissioned asylum was one of the largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria and consisted of sixty-seven buildings, one thousand two hundred patients and five hundred staff members. The asylum was predominately inhabited by long-stay patients but there were active out-patients. The asylum was one of the first asylums to focus on treatment and rehabilitation instead of institutional confinement. At the asylum, active work was considered imperative and workshops were located near the male accommodations and laundries and drying yards near the female accommodation. The asylum closed in 1995 and was sold to La Trobe University before being closed and sold again in 2011 to a private owner. This photograph is historically significant as it shows one of the main buildings of the Beechworth Mental Asylum that was pivotal in changing the approaches to treating the mentally ill.Sepia rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper mounted on card.Reverse: 1997.2458/ Front view/ Beechworth/ about 1880/ Lunatic Asylum/ administration building, mayday hills, beechworth, beechworth lunatic asylum, beechworth mental asylum, horse drawn carriage, mayday hills mental hospital, beechworth lunatic asylum administration building, psychiatric hospitals -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
... Mayday Hills Asylum in the early twentieth century. Burke Museum ...Taken in approximately 1900, this glass slide captures an image of two Mayday Hills Mental Asylum nurses. Also known as the Beechworth Lunatic Asylum, Mayday Hills was officially opened on the twenty-fourth of October 1867 and was commissioned following lobbying from Beechworth Municipal Council concerning a need for better living conditions for certain individuals confined to the town's gaol. These individuals, as well as many others who were brought from surrounding institutions, exhibited behaviours that were deemed to be unfit for mainstream society. At its peak, the asylum consisted of sixty-seven buildings and housed over twelve-hundred patients and five-hundred staff. At the time of Australian Federation in 1901 - just a year after this photograph was taken - the patient population numbered six-hundred and seventy-four. The designated site of the institution was chosen due to its scenery and altitude. It was argued that these picturesque surroundings would assist in curing the hospital's patients of their ailments. The asylum was officially closed in 1996. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register as being architecturally significant. The extensive complex of buildings are examples of Italianate-style, which is strongly associated with asylums of the 1860s - the period in which construction of this particular asylum began. Today the asylum offers tours to visitors: both daytime history tours and night-time ghost tours. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is socially and historically significant as it is representative of the lives of the nurses who worked at Beechworth's Mayday Hills Asylum in the early twentieth century.Thin translucent sheet of glass with a portrait image printed on the front. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, 1900 mayday hills, mayday hills, beechworth mental hospital, beechworth mental asylum, beechworth asylum nurses, psychiatric nurses, psychiatric care, victorian heritage register, italianate style, 19th century asylums, asylums victoria -
 Department of Health and Human Services
Department of Health and Human ServicesPhotograph, Portrait of man assumed to be Joe White, 1800s
... and the Mayday Hills Hospital. TRIM NUMBER DRC/18/1022... and the Mayday Hills Hospital. TRIM NUMBER DRC/18/1022 The back ...This photograph is of unknown origin but was identified in a collection of Mayday Hills Beechworth photographs. Research has failed to identify a connection with this individual and the Mayday Hills Hospital. TRIM NUMBER DRC/18/1022Black and White photograph mounted in cardboard frame. The back of the photograph has the name Joe White. In darker handwriting is Best Wishes from "The Original" The photographers stamp is of David S King Photographer Moore St East, Ararat. -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
... photograph depicts 25 members of the Mayday Hills Hospital Staff... photograph depicts 25 members of the Mayday Hills Hospital Staff ...Photographed in the early 1900s, this black and white photograph depicts 25 members of the Mayday Hills Hospital Staff. Five men sit in front of the group, upon the ground and behind them, in bright white clothing, sit eight female nurses upon a long bench (one of these nurses is identified on the rear as Miss A.J. Ross). Behind these women stand 12 men. The men are all wearing dark clothing and several have 'Kepi' style hats. The staff photograph was captured by Frazer and Vallance Photographers Melbourne. This image was originally combined with 1997.2490 but these images have since been torn apart and catalogued separately. Beechworth's Mayday Hills was chosen as the site of Victoria's newest asylum, at the time, due to the landscape and altitude. The hilltop atmosphere and the native fauna, it was argued, would assist in the cure of the patients kept at the hospital (Wood 1985, 122). The positioning of the hospital had a beneficial effect on the rural town. A pamphlet published by James Ingram and Son (1849) reveal that famous landmarks in Beechworth which included the Post Office, Gaol, Courthouse and Asylum "demonstrate the appreciation of Beechworth by the Government not only as as important district center, but also as a site unrivaled as a sanitarium". There were other locations in contention at the time, but ultimately Beechworth was chosen (Craig 2000, 33). Prior to the creation of the Asylum in Beechworth, those charged with having mental illnesses or, as it was termed, "insanity" were unable to be properly cared for in the Gaol (which is where they were often sent). John Buckley Castieau wrote, in 1861 for the Ovens and Murray Advertiser, that the Gaol was unable to properly care for those classified then as "insane" but that they would endeavor to treat them above the other inmates (which he notes is not always the case in other establishments). Castieau wrote this in favour of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth. It was stated that at the time the Mayday Hills Hospital was built, there were 83 prisoners kept in the Gaol who were to be rehoused to the Hospital on the grounds of "insanity". The classification as someone as "insane", in this period of time is a reflection on the inability to cure and understand illnesses of the mind during the mid to late 1800s. Opening on the 24th of October 1867, the Mayday Hills Hospital was originally named the "Ovens Lunatic Asylum", a title which is very much a product of its time. Whilst controversial, changes to the name is part of the history of the Hospital and can provide much insight into the understanding of mental illness throughout history and the use/disuse of this term provides information into the reception/changing opinions of mental illness in society. The Hospital would later become known as the "Mayday Hills Asylum" and/or "Mayday Hills Hospital" with the latter being the most commonly used title. An article in the Ovens and Murray Advertiser notes that on the 7th of March 1865, the foundation stone of the Hospital was laid (it would officially open in 1867) and that it was such a moment of accomplishment and joy for Beechworth that a letter to the editor even suggested that there should be a holiday dedicated to the day the foundation stone as laid. This reveals an extent to which the townspeople of early Beechworth valued the construction of the Hospital in their town. It provided the town with a sense of prestige and honour.At first glance, the remains of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth, Victoria, inspire tragedy, trauma and beauty. The buildings themselves, with their Italianate style Renaissance architecture designed by J.J. Clark (Craig 2000, 49 & Smith 2016, 203) reflect a bygone period of European and Australian history. The gardens provide a sense of tranquility and beauty. The experience of those within these walls remains a valuable area of study to provide a more complete understanding. This particular hospital is considered the fourth of its like and one of three identified as the largest of their kind. The Mayday Hills Hospital is a sister to the Kew and Ararat Asylums in Melbourne which are both located in relative proximity. Understanding the role of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth history is integral to understanding the development of the goldfields town, but also for providing important information as to the history of caring for, and the reception of, mental illnesses in Australian and wider European history. Mayday Hills provides a case study which can be researched through oral history, an analysis of the grounds/buildings and through images like this postcard which portray the structure in a highly deliberate manner. Images like this depict the strong façade of the Hospital and provide a glimpse into the tranquility of the gardens. This has been done deliberately to provide a sense of comfort and healing about the building to those looking from the outside. Further research into the importance of the Hospital in Beechworth and it's connection to the town will be supported through images like these kept in the Mayday Hills photo album in the collection of the Burke Museum.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on photographic paper mounted on cardFrazer & Vallance Photographers Melbournemental asylum, beechworth -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c.2000
... of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth... of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth ...This photograph was captured on an undisclosed date and by an unidentified photographer. It was printed in colour through the company AGFA which is a Belgian-German Multinational Corporation. This business prints, develops, manufactures and distributes digital imaging products, software and systems. It was founded in 1967 and continues to operate today. Beechworth's Mayday Hills was chosen as the site of Victoria's newest asylum, at the time, due to the landscape and altitude. The hilltop atmosphere and the native fauna, it was argued, would assist in the cure of the patients kept at the hospital (Wood 1985, 122). The positioning of the hospital had a beneficial effect on the rural town. A pamphlet published by James Ingram and Son (1849) reveal that famous landmarks in Beechworth which included the Post Office, Gaol, Courthouse and Asylum "demonstrate the appreciation of Beechworth by the Government not only as as important district center, but also as a site unrivaled as a sanitarium". There were other locations in contention at the time, but ultimately Beechworth was chosen (Craig 2000, 33). Prior to the creation of the Asylum in Beechworth, those charged with having mental illnesses or, as it was termed, "insanity" were unable to be properly cared for in the Gaol (which is where they were often sent). John Buckley Castieau wrote, in 1861 for the Ovens and Murray Advertiser, that the Gaol was unable to properly care for those classified then as "insane" but that they would endeavor to treat them above the other inmates (which he notes is not always the case in other establishments). Castieau wrote this in favour of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth. It was stated that at the time the Mayday Hills Hospital was built, there were 83 prisoners kept in the Gaol who were to be rehoused to the Hospital on the grounds of "insanity". The classification as someone as "insane", in this period of time is a reflection on the inability to cure and understand illnesses of the mind during the mid to late 1800s. Opening on the 24th of October 1867, the Mayday Hills Hospital was originally named the "Ovens Lunatic Asylum", a title which is very much a product of its time. Whilst controversial, changes to the name is part of the history of the Hospital and can provide much insight into the understanding of mental illness throughout history and the use/disuse of this term provides information into the reception/changing opinions of mental illness in society. The Hospital would later become known as the "Mayday Hills Asylum" and/or "Mayday Hills Hospital" with the latter being the most commonly used title. An article in the Ovens and Murray Advertiser notes that on the 7th of March 1865, the foundation stone of the Hospital was laid (it would officially open in 1867) and that it was such a moment of accomplishment and joy for Beechworth that a letter to the editor even suggested that there should be a holiday dedicated to the day the foundation stone as laid. This reveals an extent to which the townspeople of early Beechworth valued the construction of the Hospital in their town. It provided the town with a sense of prestige and honour.At first glance, the remains of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth, Victoria, inspire tragedy, trauma and beauty. The buildings themselves, with their Italianate style Renaissance architecture designed by J.J. Clark (Craig 2000, 49 & Smith 2016, 203) reflect a bygone period of European and Australian history. The gardens provide a sense of tranquility and beauty. The experience of those within these walls remains a valuable area of study to provide a more complete understanding. This particular hospital is considered the fourth of its like and one of three identified as the largest of their kind. The Mayday Hills Hospital is a sister to the Kew and Ararat Asylums in Melbourne which are both located in relative proximity. Understanding the role of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth history is integral to understanding the development of the goldfields town, but also for providing important information as to the history of caring for, and the reception of, mental illnesses in Australian and wider European history. Mayday Hills provides a case study which can be researched through oral history, an analysis of the grounds/buildings and through images like this postcard which portray the structure in a highly deliberate manner. Images like this depict the strong façade of the Hospital and provide a glimpse into the tranquility of the gardens. This has been done deliberately to provide a sense of comfort and healing about the building to those looking from the outside. Further research into the importance of the Hospital in Beechworth and it's connection to the town will be supported through images like these kept in the Mayday Hills photo album in the collection of the Burke Museum.Coloured rectangular photograph printed on gloss photographic paper.Reverse: AGFAbeechworth, mayday hills, mayday hills asylum, mental health, history of mental health, asylum, 1860s, gold town, north-east victoria, kew asylum, ararat asylum -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
... of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth... of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth ...This photograph was captured in approximately 1900 and depicts the on site nurses homes. During the 1880s, these detached cottages were constructed and provided accommodation for the staff (in this case, the nurses) who lived within the hospital walls. Within the image are weatherboard buildings, a number of nurses and water tanks. Beechworth's Mayday Hills was chosen as the site of Victoria's newest asylum, at the time, due to the landscape and altitude. The hilltop atmosphere and the native fauna, it was argued, would assist in the cure of the patients kept at the hospital (Wood 1985, 122). The positioning of the hospital had a beneficial effect on the rural town. A pamphlet published by James Ingram and Son (1849) reveal that famous landmarks in Beechworth which included the Post Office, Gaol, Courthouse and Asylum "demonstrate the appreciation of Beechworth by the Government not only as as important district center, but also as a site unrivaled as a sanitarium". There were other locations in contention at the time, but ultimately Beechworth was chosen (Craig 2000, 33). Prior to the creation of the Asylum in Beechworth, those charged with having mental illnesses or, as it was termed, "insanity" were unable to be properly cared for in the Gaol (which is where they were often sent). John Buckley Castieau wrote, in 1861 for the Ovens and Murray Advertiser, that the Gaol was unable to properly care for those classified then as "insane" but that they would endeavor to treat them above the other inmates (which he notes is not always the case in other establishments). Castieau wrote this in favour of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth. It was stated that at the time the Mayday Hills Hospital was built, there were 83 prisoners kept in the Gaol who were to be rehoused to the Hospital on the grounds of "insanity". The classification as someone as "insane", in this period of time is a reflection on the inability to cure and understand illnesses of the mind during the mid to late 1800s. Opening on the 24th of October 1867, the Mayday Hills Hospital was originally named the "Ovens Lunatic Asylum", a title which is very much a product of its time. Whilst controversial, changes to the name is part of the history of the Hospital and can provide much insight into the understanding of mental illness throughout history and the use/disuse of this term provides information into the reception/changing opinions of mental illness in society. The Hospital would later become known as the "Mayday Hills Asylum" and/or "Mayday Hills Hospital" with the latter being the most commonly used title. An article in the Ovens and Murray Advertiser notes that on the 7th of March 1865, the foundation stone of the Hospital was laid (it would officially open in 1867) and that it was such a moment of accomplishment and joy for Beechworth that a letter to the editor even suggested that there should be a holiday dedicated to the day the foundation stone as laid. This reveals an extent to which the townspeople of early Beechworth valued the construction of the Hospital in their town. It provided the town with a sense of prestige and honour.At first glance, the remains of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth, Victoria, inspire tragedy, trauma and beauty. The buildings themselves, with their Italianate style Renaissance architecture designed by J.J. Clark (Craig 2000, 49 & Smith 2016, 203) reflect a bygone period of European and Australian history. The gardens provide a sense of tranquility and beauty. The experience of those within these walls remains a valuable area of study to provide a more complete understanding. This particular hospital is considered the fourth of its like and one of three identified as the largest of their kind. The Mayday Hills Hospital is a sister to the Kew and Ararat Asylums in Melbourne which are both located in relative proximity. Understanding the role of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth history is integral to understanding the development of the goldfields town, but also for providing important information as to the history of caring for, and the reception of, mental illnesses in Australian and wider European history. Mayday Hills provides a case study which can be researched through oral history, an analysis of the grounds/buildings and through images like these. Images like these depict the strong façade of the Hospital and provide a glimpse into the tranquility of the gardens. This has been done deliberately to provide a sense of comfort and healing about the building to those looking from the outside. Further research into the importance of the Hospital in Beechworth and it's connection to the town will be supported through images like these kept in the Mayday Hills photo album in the collection of the Burke Museum.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on photographic paper mounted on card"Early nurses quarters, Beechworth Mental Hospital, now May Day Hills Hospital."may day hills hospital, nurses quarters, beechworth, mayday hills, asylum -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
... of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth... of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth ...These images are copies of a photograph (3448) captured in approximately 1900 and depicts the on site nurses homes. During the 1880s, these detached cottages were constructed and provided accommodation for the staff (in this case, the nurses) who lived within the hospital walls. Within the image are weatherboard buildings, a number of nurses and water tanks. Beechworth's Mayday Hills was chosen as the site of Victoria's newest asylum, at the time, due to the landscape and altitude. The hilltop atmosphere and the native fauna, it was argued, would assist in the cure of the patients kept at the hospital (Wood 1985, 122). The positioning of the hospital had a beneficial effect on the rural town. A pamphlet published by James Ingram and Son (1849) reveal that famous landmarks in Beechworth which included the Post Office, Gaol, Courthouse and Asylum "demonstrate the appreciation of Beechworth by the Government not only as as important district center, but also as a site unrivaled as a sanitarium". There were other locations in contention at the time, but ultimately Beechworth was chosen (Craig 2000, 33). Prior to the creation of the Asylum in Beechworth, those charged with having mental illnesses or, as it was termed, "insanity" were unable to be properly cared for in the Gaol (which is where they were often sent). John Buckley Castieau wrote, in 1861 for the Ovens and Murray Advertiser, that the Gaol was unable to properly care for those classified then as "insane" but that they would endeavor to treat them above the other inmates (which he notes is not always the case in other establishments). Castieau wrote this in favour of supporting the building of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth. It was stated that at the time the Mayday Hills Hospital was built, there were 83 prisoners kept in the Gaol who were to be rehoused to the Hospital on the grounds of "insanity". The classification as someone as "insane", in this period of time is a reflection on the inability to cure and understand illnesses of the mind during the mid to late 1800s. Opening on the 24th of October 1867, the Mayday Hills Hospital was originally named the "Ovens Lunatic Asylum", a title which is very much a product of its time. Whilst controversial, changes to the name is part of the history of the Hospital and can provide much insight into the understanding of mental illness throughout history and the use/disuse of this term provides information into the reception/changing opinions of mental illness in society. The Hospital would later become known as the "Mayday Hills Asylum" and/or "Mayday Hills Hospital" with the latter being the most commonly used title. An article in the Ovens and Murray Advertiser notes that on the 7th of March 1865, the foundation stone of the Hospital was laid (it would officially open in 1867) and that it was such a moment of accomplishment and joy for Beechworth that a letter to the editor even suggested that there should be a holiday dedicated to the day the foundation stone as laid. This reveals an extent to which the townspeople of early Beechworth valued the construction of the Hospital in their town. It provided the town with a sense of prestige and honour.At first glance, the remains of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth, Victoria, inspire tragedy, trauma and beauty. The buildings themselves, with their Italianate style Renaissance architecture designed by J.J. Clark (Craig 2000, 49 & Smith 2016, 203) reflect a bygone period of European and Australian history. The gardens provide a sense of tranquility and beauty. The experience of those within these walls remains a valuable area of study to provide a more complete understanding. This particular hospital is considered the fourth of its like and one of three identified as the largest of their kind. The Mayday Hills Hospital is a sister to the Kew and Ararat Asylums in Melbourne which are both located in relative proximity. Understanding the role of the Mayday Hills Hospital in Beechworth history is integral to understanding the development of the goldfields town, but also for providing important information as to the history of caring for, and the reception of, mental illnesses in Australian and wider European history. Mayday Hills provides a case study which can be researched through oral history, an analysis of the grounds/buildings and through images like these. Images like these depict the strong façade of the Hospital and provide a glimpse into the tranquility of the gardens. This has been done deliberately to provide a sense of comfort and healing about the building to those looking from the outside. Further research into the importance of the Hospital in Beechworth and it's connection to the town will be supported through images like these kept in the Mayday Hills photo album in the collection of the Burke Museum.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on gloss photographic papermental hospital, mayday hills, beechworth, copy, nurse, nurses quarters, on-site dwelling, 1900s, 1880, beechworth asylum -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, J. Collins, c.1940-1950s
... style of the Mayday Hills Hospital in close proximity... style of the Mayday Hills Hospital in close proximity ...This photograph was captured sometime between an estimated 1940s-1950s. It depicts the Beechworth Benevolent Asylum (later the Ovens and Murray Hospital for the Aged) which was built in 1862. It is located on an elevated site in Beechworth, Victoria because it was believed the height was beneficial to the health of the patients at the Benevolent. Later wings were added to the original building between 1867 and 1890. The building was constructed in an unusual Flemish Gothic Revival style which contrasts with the classical style of the Mayday Hills Hospital in close proximity to the Benevolent. The Hospital was designed in Italianate Revival architecture. The appearance of buildings like the Mayday Hills Hospital and the Ovens Benevolent Asylum are representative of the importance of Beechworth as a town shortly after the goldrush. During the 1850s and 1860s, administration buildings were erected alongside churches, shops and structures of justice. This marks a movement away from the "chaotic" structure of life on the goldfields and towards a more civilised and cultural lifestyle. This social phenomenon is also witnessed in Melbourne with the creation of buildings like the State Library and the University of Melbourne. The Beechworth Benevolent Asylum was renamed the Ovens Benevolent Home in 1935. The Asylum had been set up to provide accommodation and care for permanently injured gold miners, and for women and children who were penniless, homeless, or whose parents were guests of the state. In 1954 it was renamed as The Ovens and Murray Home (as pictured in this photograph). The purpose of this building was to provide a refuge for the poor and destitute, homeless older men, deserted women and children along with providing care for the mentally ill. These buildings were built at the government's expense and are of great historical and architectural significance.This photograph depicts the Ovens and Murray Home (previously the Ovens Benevolent Home) during the 1940s or 1950s. Since this building is of great historic and architectural significance, photographs like this are especially valuable in reconstructing the use history and any changes/additions to the building over a period of time. This building is important for what it can reveal about society in Beechworth and also architectural styles. This building is made in the Flemish Gothic Revival style which is quite unusual for the 1860s. It is important as an early example of a building constructed for a specific purpose, in the case of this particular building: caring for the aged/destitute. This building is important for research into the civic development of Beechworth as an early Gold Rush town located in Victoria's North-East. During this period, Beechworth was developing as the main center of administration in this region which made it a very influential and quickly developed town. Photographs like this one which depict a building during one period in history can reveal important information for the use and alterations of a building and for preferences in architectural style. It can also be studied for what it reveals about society in Beechworth and compared and contrasted to similar institutions across Australia and with additional photographs in the Burke Museum collection.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on gloss photographic paperObverse: OVENS & MURRAY HOME / Reverse: KODAK PAPER / 727 / J. Collins BMM 8689.1 /mayday hills, beechworth benevolent asylum, ovens benevolent home, asylum, refuge, poor and destitute, goldrush, flemish gothic revival, architecture -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, J. Collins
... style of the Mayday Hills Hospital in close proximity... style of the Mayday Hills Hospital in close proximity ...This photograph was captured sometime between an estimated 1940s-1950s. It depicts the Beechworth Benevolent Asylum (later the Ovens and Murray Hospital for the Aged) which was built in 1862. It is located on an elevated site in Beechworth, Victoria because it was believed the height was beneficial to the health of the patients at the Benevolent. Later wings were added to the original building between 1867 and 1890. The building was constructed in an unusual Flemish Gothic Revival style which contrasts with the classical style of the Mayday Hills Hospital in close proximity to the Benevolent. The Hospital was designed in Italianate Revival architecture. The appearance of buildings like the Mayday Hills Hospital and the Ovens Benevolent Asylum are representative of the importance of Beechworth as a town shortly after the goldrush. During the 1850s and 1860s, administration buildings were erected alongside churches, shops and structures of justice. This marks a movement away from the "chaotic" structure of life on the goldfields and towards a more civilised and cultural lifestyle. This social phenomenon is also witnessed in Melbourne with the creation of buildings like the State Library and the University of Melbourne. The Beechworth Benevolent Asylum was renamed the Ovens Benevolent Home in 1935. The Asylum had been set up to provide accommodation and care for permanently injured gold miners, and for women and children who were penniless, homeless, or whose parents were guests of the state. In 1954 it was renamed as The Ovens and Murray Home (as pictured in this photograph). The purpose of this building was to provide a refuge for the poor and destitute, homeless older men, deserted women and children along with providing care for the mentally ill. These buildings were built at the government's expense and are of great historical and architectural significance.This photograph depicts the Ovens and Murray Home (previously the Ovens Benevolent Home) during the 1940s or 1950s. Since this building is of great historic and architectural significance, photographs like this are especially valuable in reconstructing the use history and any changes/additions to the building over a period of time. This building is important for what it can reveal about society in Beechworth and also architectural styles. This building is made in the Flemish Gothic Revival style which is quite unusual for the 1860s. It is important as an early example of a building constructed for a specific purpose, in the case of this particular building: caring for the aged/destitute. This building is important for research into the civic development of Beechworth as an early Gold Rush town located in Victoria's North-East. During this period, Beechworth was developing as the main center of administration in this region which made it a very influential and quickly developed town. Photographs like this one which depict a building during one period in history can reveal important information for the use and alterations of a building and for preferences in architectural style. It can also be studied for what it reveals about society in Beechworth and compared and contrasted to similar institutions across Australia and with additional photographs in the Burke Museum collection.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on gloss photographic paperBack of photograph. Handwriting: "For John Beckingsale"mayday hills, beechworth benevolent asylum, ovens benevolent home, destitute, gold town, beechworth, victoria, north-east vic -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
... Mayday Hill Hospital...), and the Mayday Hills Hospital (opened in 1867). Lantern slides...), and the Mayday Hills Hospital (opened in 1867). Lantern slides ...This image shows 5 nurses of Mayday Hills Mental Asylum gathered on the porch and staircase of a building. Beechworth has a long history of nursing, beginning with the establishment 3 medical facilities in the mid-1800s, the Ovens District Hospital (opened in 1857), the Ovens Benevolent Asylum (opened in 1863), and the Mayday Hills Hospital (opened in 1867). Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and Woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniquesThis glass slide is significant because it provides insight into Beechworth's social amenities and religious infrastructure in the late Nineteenth Century. It is also an example of an early photographic and film-making technology in use in regional Victoria in the time period.Thin translucent sheet of glass with a square image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metals strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, nurses, nursing, mayday hill hospital -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Barry Pope, 26/6/2000
... Mayday Hill Hospital... a job as a kitchen-hand at the Mayday Hill Hospital. Taking up... a job as a kitchen-hand at the Mayday Hill Hospital. Taking up ...Barry Pope left Melbourne at the intentions of travelling around Australia, met a local girl in Beechworth and decided to stay. He worked firstly in logging operations at the mill in Stanley, had some bartending jobs at Beechworth hotels, then got a job as a kitchen-hand at the Mayday Hill Hospital. Taking up new opportunities to advance his career and earning potential, he trained as a prison officer, working for several months at Pentridge Prison and Fairlea Women's Prison in Melbourne. He then returned to Beechworth to work in the prison system. In his story Mr Pope discusses many aspects of prison life for both prisoners and prison officers, from the food and daily routine, attitudes to discipline and rehabilitation, industries and opportunities available to prisoners and how prisoners were viewed in society after their period in prison was finished. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. These cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Barry Pope's account of his career is historically and socially significant as it details practices within the prison industry in the Twentieth Century as well as the operations of regional hospitals. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the 20th century, many of which will have now been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Barry Pope /beechworth, 1960s, 1970s, 1980s, stanley mill, logging, hotel wentworth, oral history, hospital garden, mayday hill hospital, met hospital, social welfare department, loyola, lyolla, pentridge prison, fairlea women's prison, prison officer training, drug crimes, prison daily life, prison farm, prison wood workshop, prison industry, prison escapes, beechworth prison, prison suicides, prison violence, prisoner attitudes to crime, mental health, isolation cells, walking dog scheme, guide dogs, prison concerts, prison plays, george smee, prison food, prison officer accommodation -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAudio - Oral History, Jennifer Williams, Mrs Sheila Parkinson, 3 January 2000
... as a psychiatric nurse at Mayday Hills hospital prior to the second World... as a psychiatric nurse at Mayday Hills hospital prior to the second World ...Mrs Sheila Parkinson was born in Wagga in 1916 and came to Beechworth as a young woman around 1938. Sheila trained as a psychiatric nurse at Mayday Hills hospital prior to the second World War. At that time, unmarried women were accommodated and received nursing training on-site. Shiela was obliged to cease professional training and employment when she married in 1941, which disrupted completion of her final nursing examinations. Following post-war changes to the law that allowed married women to work, Sheila returned to Mayday Hills. Sheila's husband, Don, returned to Beechworth after four years abroad as a serviceman in the Australian Air Force. Beechworth's institutions were a major source of local employment throughout the twentieth century. As well as providing limited employment opportunities to young women like Shiela, post-war European migrants from Bonegilla Migrant camp found at Mayday Hills, encouraging European migrant settlement in the district. Mayday Hills was renamed several times since its establishment in 1867. At the peak of operations, it comprised sixty-seven buildings housing over twelve hundred patients patients and five hundred staff. The hospital officially closed in 1998. Today, the decommissioned two-storey Italianate style main building stands on eleven hectares of botanical gardens under National Trust protection. The site remains a popular cultural heritage destination for visitors. This oral history recording was part of a project conducted by Jennifer Williams in the year 2000 to capture the everyday life and struggles in Beechworth during the twentieth century. This project involved recording seventy oral histories on cassette tapes of local Beechworth residents which were then published in a book titled: Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth century Beechworth. The cassette tapes were digitised in July 2021 with funds made available by the Friends of the Burke.Employed as a psychiatric nurse at one of Beechworth's large welfare institutions, Mayday Hills, Mrs Sheila Parkinson recalls the conditions faced by staff and patients at the hospital, which cared for chronically ill people from the Ovens region and patients from the Yarra Bend Asylum, Melbourne, which closed in 1925. When Sheila first began her nurse training, Mayday Hills suffered from a lack of resources and rudimentary facilities and patients frequently suffered from the cold due to poor heating and inadequate clothing and bedding. However, as the twentieth century progressed, Sheila recalls how conditions and treatments improved as a result of increased government funding of services and advances in psychiatry and pharmaceutical medicine. Mrs Sheila Parkinson's oral history recording is historically and socially significant for its witness to life in Beechworth in the pre- and post-WWII period. Sheila's story enriches our understanding of processes of modernisation with regard to psychiatric and welfare services, while the course of Sheila's professional training and employment brings attention to systemic and socio-economic barriers faced by women, as well as the valuable contribution women and migrants make in the delivery of care and ancillary services. This oral history account is socially and historically significant as it is a part of a broader collection of interviews conducted by Jennifer Williams which were published in the book 'Listen to what they say: voices of twentieth-century Beechworth.' While the township of Beechworth is known for its history as a gold rush town, these accounts provide a unique insight into the day-to-day life of the town's residents during the twentieth century, many of which would have been lost if they had not been preserved.This is a digital copy of a recording that was originally captured on a cassette tape. The cassette tape is black with a horizontal white strip and is currently stored in a clear flat plastic rectangular container. It holds up 40 minutes of recordings on each side.Mrs Sheila Parkinson /twentieth century beechworth, mayday hills, psychiatric care, benevolent asylums, nursing, wwii, psychiatric treatment, country women, psychiatric hostpital, beechworth's institutions, local employment, government institutions, listen to what they say, oral history, burke museum, sheila parkinson, beechworth lunatic asylum, beechworth mental hospital, beechworth hospital for the insane, the kerferd clinic, bonegilla migrant camp, working women, white australia policy -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
... ), and the Beechworth Mental Hospital (opened in 1867 and renamed Mayday Hills... in 1867 and renamed Mayday Hills Hospital at Centenary ...This image appears to show nurses at what is now the Mayday Hills Mental Asylum arriving for work in approximately 1900. These individuals are part of a long history of nursing in Beechworth. Three medical or social welfare facilities opened in the mid-1800s as part of a push by the township to become a regional centre for Government services. These were the Ovens District Hospital (opened in 1857), the Ovens Benevolent Asylum (opened in 1863), and the Beechworth Mental Hospital (opened in 1867 and renamed Mayday Hills Hospital at Centenary celebrations in 1967). It was recognised that the unsettled living conditions, poverty and relative isolation of the Goldfields environment could produce 'mental disturbances' which required local treatment facilities as services in Melbourne were too far away. Carole Woods' publication 'A Titan's Field' describes activities undertaken by patients at Beechworth Mental Hospital as including monthly balls and occasional concerts as well as work to make the facility self-supporting such as farm work and making clothes. She mentions a report in 1870 that the approximately 300 patients were clean and neat with 'no-one in restraint or seclusion' but that by 1905 the organisation had 623 patients which placed strain on building infrastructure such as heating and water supplies, leading to high turnover of nurses and other issues. A program of building works to extend and improve facilities followed over subsequent decades. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and Woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques This glass slide is significant because it provides insight into Beechworth's social and medical amenities in the early Twentieth Century, around the time of Australia's Federation into one nation. It is also an example of an early photographic and film-making technology in use in regional Victoria in the time period.Thin translucent sheet of glass with a rectangular image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metals strips to secure the edges of the slide.Obverse: i /burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, magic lantern, indigo shire, north-east victoria, nineteenth century, 1900s, twentieth century, emulsion slides, nursing, nurses, mental hospitals, lunatic asylums, asylums, social services, social welfare, insane asylums, mental health, infrastructure -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
... Mental Hospital (opened in 1867 and renamed Mayday Hills Hospital...), and the Beechworth Mental Hospital (opened in 1867 and renamed Mayday Hills ...This image appears to show nurses at what is now the Mayday Hills Mental Asylum in approximately 1900. These individuals are part of a long history of nursing in Beechworth. Three medical or social welfare facilities opened in the mid-1800s as part of a push by the township to become a regional centre for Government services. These were the Ovens District Hospital (opened in 1857), the Ovens Benevolent Asylum (opened in 1863), and the Beechworth Mental Hospital (opened in 1867 and renamed Mayday Hills Hospital at Centenary celebrations in 1967). It was recognised that the unsettled living conditions, poverty and relative isolation of the Goldfields environment could produce 'mental disturbances' which required local treatment facilities as services in Melbourne were too far away. Carole Woods' publication 'A Titan's Field' describes activities undertaken by patients at Beechworth Mental Hospital as including monthly balls and occasional concerts as well as work to make the facility self-supporting such as farm work and making clothes. She mentions a report in 1870 that the approximately 300 patients were clean and neat with 'no-one in restraint or seclusion' but that by 1905 the organisation had 623 patients which placed strain on building infrastructure such as heating and water supplies, leading to high turnover of nurses and other issues. A program of building works to extend and improve facilities followed over subsequent decades. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and Woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is significant because it provides insight into Beechworth's social and medical amenities in the early Twentieth Century, around the time of Australia's Federation into one nation. It is also an example of an early photographic and film-making technology in use in regional Victoria in the time period.Thin translucent sheet of glass with a circular image printed on the front and framed in a black backing. It is held together by metals strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, magic lantern, indigo shire, north-east victoria, nineteenth century, 1900s, twentieth century, emulsion slides, nursing, nurses, mental hospitals, lunatic asylums, asylums, social services, social welfare, insane asylums, mental health, infrastructure -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, 27/01/2010
Taken on the 1st of April 1928 and copied from a private collection on the 27th of January 2010 the photograph depicts three well-dressed men and a small child standing around a fountain at the back of the administration building of Beechworth's 'lunatic' Asylum The asylum was constructed between 1864 and 1867 to the designs by the Public Works Department (PWD) and was later renamed Mayday Hills Mental Asylum. The decommissioned asylum was one of the largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria and consisted of sixty-seven buildings, one thousand two hundred patients and five hundred staff members. The asylum was one of the first asylums to focus on treatment and rehabilitation instead of institutional confinement. At the asylum, active work was considered imperative and workshops were located near the male accommodations and laundries and drying yards near the female accommodation. The asylum closed in 1995 and was sold to La Trobe University before being closed and sold again in 2011 to a private owner.This photograph is historically significant as it demonstrates the freedom and safety of those who visited the asylum while also highlighting this instutions mission to treat and rehabiliate patients instead on institutionalising them.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on photographic paperReverse: 7606-1/ Copied 27 Jan 2010/ Copied from private collection/ Inscribed on the back of original/ J.Pinfold 1-4-1929/ May Mental Hospital for the Insane. beechworth, beechworth mental asylum, beechworth lunatic asylum, beechworth mental hosptial, mayday, mayday hills, mayday hills mental asylum, administration building, fountain -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c1900
... Beechworth Mental Asylum Beechworth Mental Hospital Mayday Hills ...Taken around 1858, depicting a row of five business buildings on a rocky, sloping hillside at New Town, with a view across to residences and open land. Businesses included, Joseph E. Bishop, Coach Builders; Straughair Duncan, Engineers, Blacksmiths & Farriers; Straughair Duncan, Beechworth Foundry; Wholesale & Retail Est. 1855, Mackenzie Family Store ; and T. Pratten, Grocer. The Mental Hospital can be seen in the background. Mark Straughair and John Duncan, established the Beechworth Foundry, Newtown in 1858 and went on to build an important industry, employing around sixteen men, after acquiring Alexander Roger's New Ford Street Foundry in the late 1860s. Making and repairing mostly mining and agricultural machinery for the Ovens District and a Beechworth brewery, the business continued to function after Straughair's death in 1882, up until the death of Duncan in 1896, when the business folded. This photograph is historically significant because it shows the development of the businesses in Beechworth from the early establishment of the town.Sepia rectangular photograph printed on photographic paper mounted on boardObverse: [Pin holes from circular tacks in all four corners] Reverse: 84.216-1/ Newtown/ 1997.2650/ 21/ BMM3056/new town, newtown, newtown beechworth, local business, 1858, 1850s beechworth, joseph e. bishop, coach builder, coach, mark straughair, m. straughair, straughair and duncan, john duncan, j. duncan, beechworth foundry, mackenzie family store, t. pratten, grocer, beechworth grocers, beechworth mental asylum, beechworth mental hospital, mayday hills mental asylum, mental hospital, alexander rogers, new ford street foundry, 1860s beechworth, 1860s, mining machinery, agricultural machinery, manufacturing, bridge road -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, Circa 1858
Taken around 1858, depicting a row of five business buildings on a rocky, sloping hillside at New Town, with a view across to residences and open land. Businesses included, Joseph E. Bishop, Coach Builders; Straughair Duncan, Engineers, Blacksmiths & Farriers; Straughair Duncan, Beechworth Foundry; Wholesale & Retail Est. 1855, Mackenzie Family Store ; and T. Pratten, Grocer. Eleven men may be seen outside the Foundry building. The Mental Hospital can be seen in the background. Mark Straughair and John Duncan, established the Beechworth Foundry, Newtown in 1858 and went on to build an important industry, employing around sixteen men, after acquiring Alexander Roger's New Ford Street Foundry in the late 1860s. Making and repairing mostly mining and agricultural machinery for the Ovens District and a Beechworth brewery, the business continued to function after Straughair's death in 1882, up until the death of Duncan in 1896, when the business folded. This photograph is historically significant because it shows the development of the businesses in Beechworth from the early establishment of the town.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on photographic paperReverse: [Agfa wordmarks: diamond-shaped watermarks for Agfa photographic paper] 1997.2642/ refer to/ 1997 2650/ 3056joseph e. bishop, mark straughair, john duncan, mackenzie family store, beechworth foundry, coach, coach builder, engineer, blacksmith, farrier, t. pratten, beechworth grocers, grocer, new town, newtown beechworth, newtown, foundry, 1858, local business, new ford street foundry, alexander rogers, victorian agricultural history, mining machinery, beechworth brewery, ovens district, mayday hills mental asylum, beechworth mental hospital, beechworth mental asylum, mental hospital, mental -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumSculpture - Carving, c1977
Carving of a large male head made by a patient of Mayday Hills Asylum. The sculpture has been roughly hewn from a single piece of wood.Mayday Hills Asylum was one of the three largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria, and played an important role in the treatment of mental health illnesses from its establishment in 1867 to its closure in 1995. As part of prescribed treatment, many patients participated in craft activities were they were able to create an array of objects. A limb of a tree roughly carved into the shape of the man's face featuring heavy eyebrows, moustache and beard.beechworth, burke museum, mayday hills asylum, carving, wooden sculpture -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumSculpture - Carving, c1977
Carving of a small female head made by a patient of Mayday Hills Asylum. The sculpture as been roughly hewn from a tree limb with multiple branches.Mayday Hills Asylum was one of the three largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria, and played an important role in the treatment of mental health illnesses from its establishment in 1867 to its closure in 1995. As part of prescribed treatment, many patients participated in craft activities were they were able to create an array of objects. A limb of a tree roughly carved into the shape of a face, featuring a wide nose, protruding eyes, and flat mouth. On a limb section that extends above the head is a carving of a small totem-like face. Two small limb sections protruding from the back. Pen lines and figures on nose and ears.beechworth, burke museum, mayday hills asylum, sculpture, wood carving -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumSculpture - Carving, c1977
Carving of a small female head made by a patient of Mayday Hills Asylum. A grid has been drawn across the top with Romanian letters written within the cells.Mayday Hills Asylum was one of the three largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria, and played an important role in the treatment of mental health illnesses from its establishment in 1867 to its closure in 1995. As part of prescribed treatment, many patients participated in craft activities were they were able to create an array of objects. A limb of a tree roughly carved into the shape of a woman's face, featuring a thick hair style, slanted eyes, delicate mouth, and long neck. Pen notations on top of sculpture.beechworth, burke museum, mayday hills asylum, sculpture, wood carving -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumDocument - Magazine, CENTENARY ISSUE / 1867 / The New Open Door / 1967, 1967
Centenary issue of the Open Door Magazine that was produced by both staff and patients. The title reflects Mayday Hills "open door" approach to patient care.Mayday Hills Asylum was one of the three largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria, and played an important role in the treatment of mental health illnesses from its establishment in 1867 to its closure in 1995. As part of prescribed treatment, many patients participated in craft activities were they were able to create an array of objects. 13-page A4 paper magazine with 4 copper staples.CENTENARY ISSUE / 1867 / The New Open Door / 1967 [The Australian National Coat of Arms]beechworth, burke museum, mayday hills, magazine, centenary -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumDomestic object - Rocking Horse, c1977
Child-size rocking horse made and sold by a patient of Mayday Hills Asylum. Purchased in 1978 and used by a family for generations.Mayday Hills Asylum was one of the three largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria, and played an important role in the treatment of mental health illnesses from its establishment in 1867 to its closure in 1995. As part of prescribed treatment, many patients participated in craft activities were they were able to create an array of objects. A small wooden rocking horse painted in green, white and brown, with carpet lining on seat.beechworth, burke museum, mayday hills asylum, rocking horse, children's toys -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumTextile - Handbag, c1970
A knitted handbag made by patients of Mayday Hills Asylum.Mayday Hills Asylum was one of the three largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria, and played an important role in the treatment of mental health illnesses from its establishment in 1867 to its closure in 1995. As part of prescribed treatment, many patients participated in craft activities were they were able to create an array of objects. A blue and white knitted handbag with cane handles, made by a patient of Mayday Hills.beechworth, burke museum, mayday hills asylum, knitting, handbag, bag, craft, fibre art
