Showing 75 items
matching melbourne - 1800's
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1897
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1897, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 6 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin was designed by Thomas Brock. The inscription’s translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith, Empress of India”. The reverse side of the coin was designed by Edward Paynter. The inscription "HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE" translates as "Evil be to him who evil thinks". AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 Spanish dollars were imported and converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then counter-stamped and used as the official currency. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced, removing the power from the States. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. This silver shilling is also of significance to Australia as part one of the British Colonies ruled by Queen Victoria. It is part of the special silver and gold coins minted 1887-1893 to celebrate the 50 years Jubilee of Queen Victoria’s reign 1837-1887. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1897. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Old Head’, looking left. Reverse; 3 shields (each crowned) - 3 passant lions (England), 1 rampant lion (Scotland), golden harp (Northern Ireland) - floral symbols between them – 1 open rose, 2 thistles. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA . DEI . GRA . BRITT . REGINA . FID . DEF . IND . IMP” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1897, Inner band, some letters hidden - HONI SO VI Y PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, british shilling 1897, thomas brock, edward paynter, great britain shilling, queen victoria currency, queen victoria 50 years golden jubilee shilling, colonial australia currency, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1897
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1897, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 6 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin was designed by Thomas Brock. The inscription’s translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith, Empress of India”. The reverse side of the coin was designed by Edward Paynter. The inscription "HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE" translates as "Evil be to him who evil thinks". AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 Spanish dollars were imported and converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then counter-stamped and used as the official currency. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced, removing the power from the States. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. This silver shilling is also of significance to Australia as part one of the British Colonies ruled by Queen Victoria. It is part of the special silver and gold coins minted 1887-1893 to celebrate the 50 years Jubilee of Queen Victoria’s reign 1837-1887. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1897. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Old Head’, looking left. Reverse; 3 shields (each crowned) - 3 passant lions (England), 1 rampant lion (Scotland), golden harp (Northern Ireland) - floral symbols between them – 1 rose, 2 thistles. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA . DEI . GRA . BRITT . REGINA . FID . DEF . IND . IMP” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1897, Inner band, some letters hidden - HONI SO VI Y PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, british shilling 1897, thomas brock, edward paynter, great britain shilling, queen victoria currency, queen victoria 50 years golden jubilee shilling, colonial australia currency, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1898
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1898, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 9 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin was designed by Thomas Brock. The inscription’s translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith, Empress of India”. The reverse side of the coin was designed by Edward Paynter. The inscription "HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE" translates as "Evil be to him who evil thinks". AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 Spanish dollars were imported and converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. This silver shilling is also of significance to Australia as part one of the British Colonies ruled by Queen Victoria. It is part of the special silver and gold coins minted 1887-1893 to celebrate the 50 years Jubilee of Queen Victoria’s reign 1837-1887. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1898. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Old Head’, looking left. Reverse; 3 shields (each crowned) - 3 passant lions (England), 1 rampant lion (Scotland), golden harp (Northern Ireland) - floral symbols between them – 1 rose, 2 thistles. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA . DEI . GRA . BRITT . REGINA . FID . DEF . IND . IMP” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1898, Inner band, some letters hidden - HONI SO VI Y PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, british shilling 1898, thomas brock, edward paynter, great britain shilling, queen victoria currency, queen victoria 50 years golden jubilee shilling, colonial australia currency, numismatics -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyNewspaper clipping, Diamond Valley Leader, Religion high on the hog, 08/08/2012
A story about Dave Fuller the All Saints Anglican minister at Greensborough in 2012 who is a Life Member of the God's Squad Motorcycle Club.All Saints Anglican church has been in Greensborough since the mid 1800's.A newspaper clipping with a colour photograph.Biro written datedavid fuller, all saints anglican church, god's squad motorcycle club -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, early 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons) and produced. In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "clear" glass. There are other milk bottles that have a "green" tint in them.Around the bottom side of the bottle and blown into the glass "ONE PINT" and on the opposite side "MILK". Below these markings is "This BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLES RECOVERY LTD" below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION. On the base of the bottle is molded a big "M". An identification mark of "90" over "9" is beneath the "M". glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles, milk, dairy, farms, kiewa valley -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid 1800's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the large volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36"This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against sunlight penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it 6/33 and next to this "ONE PINT" and under this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "4"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, circa mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt Beauty.This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head was manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle which contained milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it "6/18" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "3"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
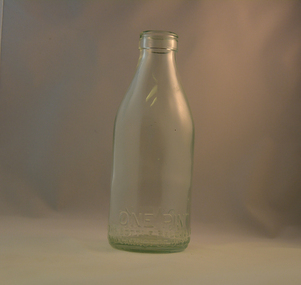 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) until the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt Beauty.This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottle along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it "6/36" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "15" glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up until the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under the house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt BeautyThis heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it "6/18" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "4"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded), until the time that cheaper containers were invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under the house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt BeautyThis heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle, to contain milk, required its thickness because of the extensive handling (man and machine) before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle is a circle within it "6/35" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "20"milk, dairy, glass bottle -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up until the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under the house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt BeautyThis heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottle along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a half pint capacity and is made from "clear" glass. There are other milk bottles that have a "green" tint in them and this tint was to protect the contents from sun damage. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the top half of this bottle is "MILK" and opposite "HALF PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base is "2 M" underneath this "8/11" and underneath is "ISM -169"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
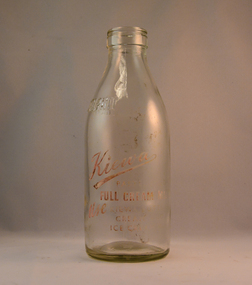 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, Circa mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons) and produced. In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" This particular one has "7/14".This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one Imperial pint capacity and is made from "clear" glass. There are other milk bottles that have a "green" tint in them. Around the bottom side of the bottle and blown into the glass "ONE IMPERIAL PINT". Below these markings and stenciled is "KIEWA" (in freehand style and underlined) underneath is "PASTEURISED FULL CREAM MILK" underneath this ,in freehand stiyle is "USE" next to this in block style "KIEWA BUTTER, CREAM, AND ICE CREAM MIX" to the left of this ,and barely readable is stenciled "THIS BOTTLE ALWAYS REMAINS/ THE PROPERTY OF/ NORTH EASTERN DAIRY Co. Ltd". On the base of the bottle is molded a big "2". with a smaller "m". An identification mark of "7" over "14" is within a circled boundary. Below this is moulded "RM - 15". glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySki Boots - Cross Country, mid 1900's
These cross country ski boots are part of the pioneer ski recreational sport in the Victoria Alps. The mid 1900's saw the Victorian Alps begin to be used for recreational skiing, especially cross country. The majority of skiers at this point in time were either from the SEC Vic. Kiewa Hydro Scheme or from Melbourne. International skiers had better ski fields (ski lodges etc.) in Europe, the U.S.A. and Canada. With greater and better coverage of the Winter Olympics and some medal wins, skiing became more interesting and rewarding for city dwellers in Melbourne and Sydney.These ski boots are of great significance to the Kiewa Valley as it demonstrates that winter sports in the region have and still do attract not only skiers but also provide an employment (even though seasonal) avenue which "livens up" a small rural community and provides for a diversity of land usage which did not exist in the 1800's. These brown cross country ski boots, "Grief" brand have "cherry" inserts with cream laces, within the main boot. The boots have red and black laces and crossover tie flaps (to allow for maximum front foot entry. These boots do not have any ski clips to hold firm those restraints (quick release) on the skis (like "modern boots and skis). The heel section has the red Greif "W" pattern.At the underside of the rubber sole in freehand script "Cresta"snow skiing, ski boots, winter recreational sports. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBadge - BMA Ladies Badge, Stokes, 1935
The badge was issued by the British Medical Association 'BMA'. It is known as the Female Relative's Bade or Ladies' Badge. It was manufactured in Melbourne in 1935 by Stokes of Melbourne. The BMA badge is one of a set of badges collected by Dr W R Angus from the organisations in which he was involved. They are now part of Flagstaff Hill’s comprehensive W.R. Angus Collection, donated by the family of Dr W R Angus, surgeon and oculist. The W.R. Angus Collection: - The W.R. Angus Collection includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. It includes historical medical and surgical equipment and instruments from the doctors Edward and Thomas Ryan of Nhill, Victoria. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1927 at Ballarat, the nearest big city to Nhill where he began as a Medical Assistant. He was also Acting House surgeon at the Nhill hospital where their two daughters were born. During World War II He served as a Military Doctor in the Australian Defence Forces. Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool in 1939, where Dr Angus operated his own medical practice. He later added the responsibility of part-time Port Medical Officer and was the last person appointed to that position. Both Dr Angus and his wife were very involved in the local community, including the planning stages of the new Flagstaff Hill and the layout of the gardens there. Dr Angus passed away in March 1970.This badge is significant for connecting Doctor Angus with organisations that support men and women who performed military service for Australia. The badge was specifically for a female relative of the person who did service, showing compassion for women. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The Collection includes historical medical objects that date back to the late 1800's.This BMA badge is an overall rectangular shape made in a silver metal. It has a raised oval section in the centre. The badge has embossed text and a basket weave background pattern within the metal. It is a Ladies Badge, made for the women connected to members of the British Medical Association. It was made in Melbourne in 1935. This badge is part of a set of badges collected by Dr W R Angus. the set represents organisations that he was involved in, and is part of the W.R. Angus Collection.Front embossed; “BMA” “LADIES” “BADGE. Back embossed; “MELBOURNE / 1935 “ “STOKES MELB”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, w.r. angus, badge, bma, british medical association, ladies’ badge, female relative's badge, military service, stokes, melbourne, w.r. angus collection -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyPostcard (item) - Colour tinted postcard, Nicholas John Caire, Cumberland Falls near Marysville, 1858-1918
One of a series of postcards of photographs taken by socialite photographer Nicholas John Caire. N.J. Caire had a great love for the area and in the late 1800's took many photographs of Marysville and its surrounds.One of a series of postcards of photographs taken by socialite photographer Nicholas John Caire. N.J. Caire had a great love for the area in and surrounding Marysville and in the late 1800's took many photographs of Marysville and its surrounds. N.J. Caire was born in 1837 in Guernsey. He arrived in Adelaide about 1860 along with his parents who encouraged his early interest in photography. He opened a studio in Adelaide in 1867 after traveling extensively throughout the Gippsland taking photographs. After marrying in 1870 he moved to Talbot in Victoria until 1876 when he opened a studio in the Royal Arcade in Melbourne. After 1885 N.J. Caire gave up his city work and made his home in South Yarra and devoted the rest of his life to outdoor photography, specializing in the bush, the gullies and the mountains of south-eastern Victoria. POST CARD Printed in Australia This space may be used for Correspondence/ within the Commonwealth without/ extra postage THIS SPACE FOR NAME AND/ ADDRESS Stamp/ Heremarysville, victoria, nicholas john caire, postcard, souvenir, cumberland falls -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyPostcard (item) - Black and white postcard, Nicholas John Caire, Cumberland falls, Marysville, 1858-1918
One of a series of postcards of photographs taken by socialite photographer Nicholas John Caire. N.J. Caire had a great love for the area and in the late 1800's took many photographs of Marysville and its surrounds.One of a series of postcards of photographs taken by socialite photographer Nicholas John Caire. N.J. Caire had a great love for the area in and surrounding Marysville and in the late 1800's took many photographs of Marysville and its surrounds. N.J. Caire was born in 1837 in Guernsey. He arrived in Adelaide about 1860 along with his parents who encouraged his early interest in photography. He opened a studio in Adelaide in 1867 after traveling extensively throughout the Gippsland taking photographs. After marrying in 1870 he moved to Talbot in Victoria until 1876 when he opened a studio in the Royal Arcade in Melbourne. After 1885 N.J. Caire gave up his city work and made his home in South Yarra and devoted the rest of his life to outdoor photography, specializing in the bush, the gullies and the mountains of south-eastern Victoria. Victorian one penny postage stamp Post Card The Address to be written on this side This space may be used for Correspondence/ within the Commonwealth at 1d rate./ Foreign, charged ordinary letter rate. AFFIX STAMP/ HERE Dear Mum/ Will you bring me/ over some/ milk. I cannot/ get any here./ Love to all/ from all/ Hilda Mrs Gregory/ Bay View Hotel/ Frankstonmarysville, victoria, nicholas john caire, postcard, souvenir, cumberland falls -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Book - Family History, Boxleigh, Avis, Box Family Stories - The Box Family of Sussex and Their Migration to Australia in the 1800's, 2009
A history of the Box family 1066 ---up till the late 1980s ( England America and Australia) The author has documented each branch of the family that she has known about.This is a spiral bound large book with pages that are copies of a computer file about the Box family Also refer to item no 00339 same title for more information.non-fictionA history of the Box family 1066 ---up till the late 1980s ( England America and Australia) The author has documented each branch of the family that she has known about.box family history, box cottage, william box -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tool - Farm Machinery, Horse-drawn Furrow Plough, Early 20th Century
Late 1800s-early 1900s A horse-drawn furrow plough is an example of the type of farm implement widely used by pioneer market gardeners in the Moorabbin Shire following 'Dendy's Special Survey' of 1841 and the Crown Land Sale in 1852. Land allotments were bought by pioneer settlers who established or rented allotments for market gardens in the area. They supplied produce to the markets in St Kilda and Melbourne. During the gold-rush of the 1850s the rapidly increasing population of Melbourne saw a huge demand and a rise in prices for all foodstuffs, including the vegetables and fruit grown in the Shire of Moorabbin. This heralded a time of prosperity for market gardeners, and an equally rapid expansion of the numbers of vegetable and produce growers in the area. The 'knock-on effect" resulted in an increased interest and development of the community in the Shire of Moorabbin.Following 'Dendy's Special Survey' of 1841 and the Crown Land Sale in 1852, land allotments were bought by pioneer settlers who established or rented allotments for market gardens in the area and they supplied produce to the markets in St Kilda and Melbourne. During the gold-rush of the 1850s the rapidly increasing population of Melbourne saw a huge demand and a rise in prices for all foodstuffs, including the vegetables and fruit grown in the Shire of Moorabbin. Circa late 1800's to early 1900s. A horse-drawn furrow plough was the most common type of agricultural implement used by the pioneers of the 1800s and continued on into the 1940s when motorised tractors came into use. This plough is an example of a two furrow, mullboard plough which would most likely have been pulled by two horses. The long handle was used to lower the silver plates, (mullboards), to the chosen depth of soil. Painted yellow. Although this Box Cottage museum plough is unbranded, the most widely used plough in the Shire of Moorabbin was made by Oliver. This plough appears to be identical to that brand. brighton, moorabbin, pioneers, fruit, bentleigh, vineyards, vegetables, plough, market gardens, plow -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Clothing - Clothing, lace collar, c1880
This heavy, detachable lace collar is an example of the dressmaking and needle work skills of the women of the families of the pioneer settlers and market gardeners of the Moorabbin Shire c 1880 The Maggs family settled in the Brighton district in the late 1800,s. After the Dendy's Special Survey of the Brighton area in 1841 land allotments were rented or sold to pioneers who established market gardens, dairy farms, fruit gardens and vineyards. The pioneer settlers and market gardeners of Moorabbin Shire had to be self reliant and made their own clothing and utensils. This is one of many items that exhibit the skill and craftsmanship of the women in these familiesThis heavy, lace collar is detachable and consists of hand crochet work.clothing, crochetwork, pioneers, early settlers, dendy henry, maggs geoff, brighton, bentleigh, moorabbin, market gardeners, craft working, dressmakers -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - FOUR BOOKS: 'THE QUEEN'S LONDON '
Four books -'The Queen's London ' - 32 Photographic Views for 6d , Cassell & Company , Limited ; London , Paris & Melbourne ( parts 6, 5, 4, 2 to be completed in 12 parts) ) / paper covers --'The Queen's London ' -surrounded by flowers , damaged , containing black and white photos -mid to late 1800's , inside front cover advert for 'Mellin's infant Food , G. Mellin's Food Works , Peckham , London , S.E. / inside rear cover shows an advert for Mellin’s Emulsion of Cod Liver oil , Food Biscuits and Lacto -Glucose / rear page shows photos of three infants and the words 'the following portraits are a few specimens of many thousands of strong healthy children reared on Mellin's Foods photos include - Temple bar , Harrow school, London bridge / architects drawing for ' Levels for Hanro Knitting Mills dated 20.6.26, Stamp showing 'Hanro' Australia Bendigo Knitting Mills Pty Ltd, stamp showing 'William Bocklie, consulting engineer 422-428 Collins St. Melboune.photograph, person, male / female, mellin's infant food / gustav mellin /baron justis von liebig, a famous dutch chemist -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - ALEC H CHISHOLM COLLECTION: BOOK ''THE PORTLAND BAY SETTLEMENT'' BY NOEL F LEARMONTH
Book. ALEC H CHISHOLM COLLECTION. 285 page hardback book on the history of Portland, Victoria from 1800 to 1851 by Noel Learmonth with a forward by A. S. Kenyon. Contains maps and B & W photos of the Hentys and other people. Published in 1934 by The Historical Committee of Portland. Printed by McCarron, Bird & Co. Melbourne. Catalogue sticker '2164 LEA' on spine. Handwritten in ink inside front cover ''A. H. Chisholm in gratitude for a few bird days. Noel F Learmonth Oct 25th 1944''Noel F. Learmonthbooks, collections, history, alec h chisholm collection, noel f. learmonth, portland, henty, history -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Medal, 1859
Objects. Token for G & W.H. Rocke , 18 Lonsdale Street, Melbourne. English Furniture Importer, with a Lion and shield on front. On reverse Melbourne, Victoria, 1859, person seated holding scales.numismatics, tokens, g & w h rocke, they used to live in another house in golden square, which was the site of a chinese market garden in the 1800's. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - HARRY BIGGS COLLECTION: ARTICLES FROM 'THE ARGUS', 1876
Six pages of newspaper clippings from 'The Argus' dated in the 1800's and pasted onto card, the name of the contributor is 'A Vagabond'. Article dated 13/5/1876 relates to the writers experience as an outpatient at the Melbourne Hospital. 20/5/1876 'The Outcasts of Melbourne' whose lives are one of misery, sin, crime but little shame. A warning to the authorities to 'take heed quickly' to prevent the continuation of these vices well into the future. 27/5/1876 'Sixpenny Restaurants' . Unknown date in 1876 'Three Days in the Benevolent Society' 10/6/1876 'Three Days in the benevolent Society' part 2.newspaper, human interest, the argus -
 St Kilda Historical Society
St Kilda Historical SocietyPhotograph, Cable tram, c. 1890s
... Carlisle Street St Kilda melbourne Swanston Street late 1800's ...black and white photographSwanston Street late 1800's. Carlton to Prahran tram.Talma Artist Photographer. Artistic Stationery Drawing Materials. J.T. Buxton Auctioneer and Valuers. Wm Ford and Co Chemists. Vita Studios. Exchange Hotel. -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionDomestic object - Flat Iron
These small heavy flat irons were used to iron clothes prior to electric irons being invented. They were heated on a wood fire stove top and used quickly before they lost heat to iron items of clothing and other small items. These irons were very heavy so that they retained the heat when heated by a wood fire stove top prior to electricity being connected to houses. Flat irons were used in the 1800's and in the early 1900's.Heavy black small flat iron with handle on top. Iron tapers from flat wide base to rounded point. It has a round logo on front under the handle.Unreadable round possibly manufacturers logo.social history, irons, ironing, domestic items, 1800's -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionDomestic object - Flat Iron
This iron is from Bayview Farm, Diggers Rest and believed to have been used there.Flat based irons were used to iron clothes and other items prior to electric irons being invented and electricity being connected to houses. They were used mainly in the 1800's and early 1900's.Heavy flat based iron with handle. Inscriptions on front, tapers from wide back to rounded point at front.on point of iron "6" on front "SILVESTER'S/PATENT..."cullinan, c, diggers rest, george evans collection -
 Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer Museum
Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer MuseumPhotograph - Yarrawonga Mulwala Photos - framed
Four postcard sized black and white photos of Yarrawonga and Mulwala area late 1800’s early 1900’s. Belmore Street looking south, Exchange Hotel Mulwala, Palms along Belmore St, Yarrawonga and Belmore Street looking north in 1882. These are all prints of original photos and are placed in a contemporary frame with matte surroundings belmore street, exchange hotel -
 Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer Museum
Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer MuseumPrize certificate, Special certificate for Crop competition, 1963
Crop Competitions have been held at local Shows dating from late 1800’s to todayCream card red and blue print. Hand printed details of winner and description of Crop Competition. Also has tractor and plough, silos, tractor and header logos on top and wheat head logos on sides and bottom.The Farm Competitions Association of Victoria. Special Certificate awarded to J C Thom, Winner of Open Wheat Crop Competition (40 acres) 1963. Variety exhibited - Olympic. Conducted by Yarrawonga Agricultural Society Signed by Deputy Chairman JW McCann, Hon Secretary R A Andrew -
 Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer Museum
Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer MuseumPrize certificate Yarrawonga A&P Association, Special certificate Crop Competition, 1957
Crop competitions have been held at local shows dating from late 1800’s to todayCream card Red and Blue print. Hand printed details of winner and description of Crop competition. Also has tractor and plough, silos tractor and header logos on top and wheat head logos on sides and bottom.The Farm Competitions Association of Victoria. Special certificate awarded to J C Thom ad P Bruce Open Wheat crop competition 1957 Area 40 acres. Variety Sherpa Conducted by Yarrawonga and Border Agricultural and Pastoral Society. Signed by Chairman Wm B Miller, Hon Secretary JWC McCann -
 Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer Museum
Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer MuseumStripper Harvestor, 1916
The first successful stripper harvestor ,a Nicholson & Morrow harvestor invented by James Morrow appeared at the Victorian Government trial at Dookie Experimental farm on Dec 27th 1883. Although the stripper harvestor was being manufactured in small numbers by the mid 1800's it did not take over from the tripper until 1904. Hugh McKay soon became the most successful manufacturer of stripper harvestors under the "Sunshine " name and by 1940 over 40,000 harvestors had been produced.This 1916 H.V. McKay harvestor Serial No.102736. The first machines looked like strippers ,but had a fan, sieves, elevators and a small grain storage bin.. The McKay Stripper Harvestor Sunshine
