Showing 52 items matching "one mile hill"
-
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - The last train at Barker Station, 1952
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of the last passenger train at Barker Railway Station in 1952. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society."Last train at Barker Station / 1 August 1952"kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), barker railway station, kew branch line -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Barker Station, August 1952
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of the last passenger train at Barker Railway Station in 1952. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society."Barker Station / August 1952"kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), barker railway station, kew branch line -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kew Railway Station: Denmark Street entrance, 1952
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of the entrance to Kew Station from Denmark Street in 1952. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society.kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), kew branch line, kew railway station -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kew Station 22/4/51, F3
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of Kew Railway Station, looking south to Barker Station. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society.kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), kew branch line, kew railway station -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kew Branch Line : The Hawthorn Grove crossing, August 1952
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of the Hawthorn Grove crossing, August 1952. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society.kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), kew branch line, hawthorn grove -- hawthorn (vic.), railway crossings -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Seven Carriage Train at Barker Station
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of a seven carriage train approaching Barker Railway Station. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society."Seven Carriage Train at Barker Station"kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), barker railway station, kew branch line -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Farewell to 'Our Lady of Fatima'. Xavier College 22/4/51
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of a train leaving Kew Station with the Xavier Chapel on the hill in the background, hence the ironic title provided by the photographer. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society."Farewell to 'Our Lady of Fatima'. Xavier College 22/4/51"kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), kew branch line, xavier college, kew railway station -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kew Branch Line: Looking along cutting towards Barker Station 22/4/51
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot looking along cutting towards Barker Station 22/4/51. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society."Looking along cutting towards Barker Station 22/4/51"kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), barker railway station, kew branch line -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - The last train at Kew Station, August 1952
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of the last passenger train at Kew Railway Station in 1952. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society."The last train at Kew Station, August 1952"kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), kew branch line, kew railway station -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kew Branch Line: Weeds at Kew Station 14/51
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of how the Kew Branch Line was allowed to run down. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society.kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), barker railway station, kew branch line -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kew Railway Station, May 1950
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of Kew Railway Station inMay 1950. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society."Kew Railway Station, May 1950"kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), kew branch line, kew railway station -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kew Railway Station, 1951
The Kew railway was opened in 1887, and diverged from the main (Box Hill–Lilydale) line about half-way between Hawthorn and Glenferrie. From the point of divergence the line was slightly less than one mile long, and it had only one intermediate station — Barker. There were four road over-bridges and two level crossings, including one over the busy Barkers Road. The line supported a passenger and goods service, and was electrified in December 1922, at the same time as the main line to Box Hill. There were a number of peak hour services which ran from Flinders Street station (Melbourne) to Kew, but in 1938 all but one of these were diverted to the Ashburton line, where traffic was growing. This had an adverse effect on Kew traffic, as passengers from Kew needed to cross over a footbridge at Hawthorn to change trains, and the main line trains were usually already crowded by the time they reached Hawthorn. At about the same time the off-peak trains were replaced by road buses. In 1952 all passenger trains were withdrawn, but the road bus service continued for many years. Goods trains were finally withdrawn in 1957, and the railway was dismantled in 1958-59. (Source: Frank Stamford, 'The Hawthorn - Kew Railway')Small black and white snapshot of Kew Railway Station in 1950. The photograph, one of 12, is part of a larger album of newspaper clippings, timetables, tickets and photos relating to the Kew Railway Line, taken and compiled by Lachlan Richardson, while a resident of Kew. The album dates from the 1950s. The album is part of a larger subject file on the Kew Line, compiled over time by members of the Kew Historical Society."Kew Station / 14/51 / 22/4/51 F5"kew railway line, transport -- railways -- kew (vic.), kew branch line, kew railway station -
 Trentham and District Historical Society
Trentham and District Historical SocietyBook - Log book, Observers Log - Volunteer Air Observers Corps
Used during WW2. Trentham Air Observers Corps logbook of plane traffic spotted from Cranney's Hill lookout. The lookout was located one mile east of Trentham township. The Observers were volunteers, mainly women.Foolscap sized book with brown paper cover. Hand-written entries.trentham, volunteer air observers corps, spotters, cranney's hill, shirley trewella, gamble, world war 2, home front, log-book -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionBook, Australian Houses of the Forties and Fifties, 1993
The classic triple-fronted brick veneer is one of the best-known styles of the forties and fifties. The distinctive colour schemes, furniture, fabrics, gardens and memorabilia are also discussed.Includes: index, bibliography. The classic triple-fronted brick veneer is one of the best-known styles of the forties and fifties. The distinctive colour schemes, furniture, fabrics, gardens and memorabilia are also discussed.Front page: Sue Barnettarchitecture, (mr) peter cuffley, dwellings, interior decoration, 1940-1949, 1950-1959 -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph, Carnival Day at Surrey Dive, Possibly 1909
This photo records one of the swimming carnivals held at the Surrey Dive, the first of which was organised in 1907. It was at the 1907 carnival that champion swimmer Frank Beaurepaire won the one-mile championship in record time. In the era before purpose-built municipal swimming pools, Surrey Dive was a popular destination for swimming and people came to it from many Melbourne suburbs. It operated from 1905 to 1967. It was the newly formed Surrey Park Swimming Club (established in 1905) that petitioned the Box Hill Council to purchase the former quarry site associated with the Box Hill Brick Works. A ramp, bathing sheds, springboards, and eventually a 10-lane course were developed, making the Dive the first Olympic standard pool in Australia. The carnivals attracted huge crowds. The original use as a quarry explains the notorious depth of the swimming hole and the sheer, steep cliffs surrounding it. These posed obvious safety issues, as did the water quality. Ivy Lavinia Weber, who was the second woman to be elected to the Victorian parliament (the first at a general election) and renowned for her commitment to health and physical fitness, campaigned for State government assistance to build new baths. These were built adjacent to the Dive and were opened in 1939. The Dive continued as a facility used by experienced swimmers until 1967 when it closed due to the drought causing the water to dry up. Today the site has been turned into an ornamental lake. This image was used as a mural in the refurbishment of the Box Hill Aqualink. The image has strong associations with early industry (brick making), recreation and particularly the early history of the sport of swimming.Black and white photo with a white border. Scan shows image only. It shows 3 men diving from a wooden platform into an area of water beneath higher banks. There is a boat in the background, a building to the LHS of the photo and many spectators in boater hats on the platform, some in bathing suits along a ledge and many around the top of the bank. Two men in the LH foreground may be officials.Printed long the bottom edge of the frame: "An image from history - Carnival Day at the Dive. / (photo: Box Hill Council)"surrey dive, box hill brick works, swimming, surrey park swimming club, (mr) frank beaurepaire, (mrs) ivy lavinia weber, swimming carnivals -
 Victorian Harness Racing Heritage Collection at Lord's Raceway Bendigo
Victorian Harness Racing Heritage Collection at Lord's Raceway BendigoPhotograph - Framed photo finish, Greg Matthews Photo, Glamour Chief, 21 January 1975
Glamour Chief won the Bendigo Pacing Cup on the 21 January 1975, followed by Yallara and Go Van. Glamour Chief owned by M Robinson, WR Lanyon, B & C Hill, was trained and driven by RA Robinson. Glamour Chief raced from 1970 (2yo) through to 1976 (8yo). Career: 29 wins 9 seconds 4 thirds 59 starts. Refer to Identifier 15.127 (Media) for Full Career Performance Record. Two colour photographs, one small one large in a white frame. At the top: Bendigo Trotting Club 21-1-75/ Pacing Cup At the bottom: Left corner: Distance 2615 metres/ Mile rate 2.6.2/5 / Greg Matthews Photo Centre: Glamour Chief (Chief Rainbow - Dainmont) / Yallara 2nd / Go Van 3rd Right corner: Owned by- M Robinson, WR Lanyon, B & C Hill/ Trained and driven by - RA Robinsonbendigo harness racing club, horses, race, winner, bendigo trotting club, pacing cup, driver, trainer, owner, 1975, glamour chief, ra robinson, m robinson, wr lanyon, b & c hill, yallara, go van, rex robinson -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Maroondah Aqueduct Siphon Bridge over the Plenty River, 26 January 2008
Opened in 1891, the bridge formed part of the Maroondah Aqueduct carrying water from Watts River near Healesville to the reservoir at Preston where it joined Melbourne's metropolitan water system. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p99 Built to supply thirsty Melbourne in the late 19th century, the siphon bridge spanning the Plenty River off Leischa Court, Greensborough, was part of an engineering masterpiece. Opened in 1891, the bridge formed part of the Maroondah Aqueduct carrying water from the Watts River near Healesville to the reservoir at Preston where it joined the metropolitan distribution system. A major link in Melbourne’s water supply, it also had a huge impact on communities, which mushroomed along its route. Named after the Aboriginal word for the area around the Maroondah Reservoir, the Maroondah Aqueduct was fully operational until the 1970s. Since the 1980s the land along parts of the aqueduct have been used for walking and bicycle riding, shaded in places by Monterey Pine trees planted to stabilise the surrounding ground. From 1857 the Yan Yean Reservoir supplied Melbourne’s water but the growing city needed additional catchments.1 In 1886 work began on a weir on the Watts River to enable the aqueduct to carry most of the river water 41 miles (66km) to Melbourne. The aqueduct, built by the Board of Works, is the oldest remaining aqueduct near Melbourne and was probably the first built with concrete.2 Although the aqueduct is now only used between the Maroondah and Sugarloaf Reservoirs, it can still be traced across the Shire. It extends from the Maroondah Reservoir through Christmas Hills, Kangaroo Ground, Research, Eltham, St Helena and then previously wound west through Greensborough to Reservoir.3 Built by horse and manpower the aqueduct gravity fed 25 million gallons (113.6ML) of water a day to Melbourne along a gradient of one foot to the mile. It included 25 miles (41km) of open concrete and brick channel, six miles (10km) of tunnels, and nine miles (15km) of 14 inverted siphons of riveted wrought-iron across creeks. Bricks for the aqueduct were made from clay found near the sites and remains of several kilns can still be found between Kangaroo Ground and Christmas Hills. Building the aqueduct transformed local communities. An abattoir was established at Christmas Hills. Grog shanties and labourers’ camps sprang up and local courts dealt with cases of ‘petty pilfering and boisterous behaviour’.4 The Kangaroo Ground school population jumped to 91, crammed into a room with one teacher. Miners who built the tunnels camped just north of Churinga in Greensborough – then called Tunnel Hill Camp – and adjacent to the Evelyn Arms Hotel. The miners’ high spirits were sometimes quenched in horse troughs or by a ‘welt under the ear and kick on the behind’ as the local constable calmed them down rather than lock them up.5 But the growing city of Melbourne needed more water, so the O’Shannassy catchment, east of Warburton, was added to the system in 1914. In 1920 work began on the present concrete Maroondah Dam one mile (1.6km) from the weir on the Watts River. The aqueduct capacity was thus doubled to 50 million gallons (227ML) a day.6 Intense land development threatened to pollute the open water supply, so channel sections were replaced with large pipes. In the late 1960s a large water main was built from the tunnel outlet at Research and extended through St Helena and Greensborough, so this section of the aqueduct was taken out of use. Long sections of the unused open channels in Greensborough and Bundoora were destroyed, but the old channel in Research and Eltham North remained largely intact. In the 1970s, the Sugarloaf Reservoir was constructed, inundating 445 hectares of land in Christmas Hills. Sugarloaf was officially opened in 1980 and serves as a water storage and treatment plant supplying Melbourne. In the early 1980s pipes replaced the section from Sugarloaf Reservoir to the tunnel entrance at Kangaroo Ground. The Research-Kangaroo Ground tunnel operates as part of the pipeline system.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, maroondah aqueduct, pipe bridge, siphon bridge -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Sweeney's Cottage, Sweeneys Lane, Eltham, 30 January 2008
Part of the original cottage named Culla Hill built by Thomas Sweeney (a former convict) remains as a small section of today’s house. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme National Estate National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Local Sifgnificance Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p19 Thomas Sweeney, a former convict who became a respected citizen, once lived on a property at what is now the corner of Sweeneys Lane and Culla Hill, Eltham. As Sweeney was one of the district’s first settlers, the property is registered by the National Trust. Thomas Sweeney was born in 1802, son of impoverished tenant farmers in Tipperary County, Ireland. He became a ploughman, then at 21 he was sentenced to hang for setting on fire the house of Patrick Guyder at Gullshill. It is said the arson was due to a dispute over undelivered guns to a social justice guerilla group, the White Boys, of which Sweeney was a member. But the sentence was commuted to life transportation to Australia in 1823.1 Apparently in Sydney he became a servant to James Chandler at Botany. Soon James Chandler leased his farm and became a catechist on the Hawkesbury River, so Sweeney was reassigned to a former convict, John Brown, at Liverpool. Later Sweeney was assigned to George Brown of Lake Illawarra. In 1831, Sweeney was granted a ticket-of-leave and bought a boat to carry goods between Illawarra district and Sydney Town. He married his first wife who had come to Australia as a free woman. However she drowned after bearing him a daughter. In 1838, one month after he had received a conditional pardon, Sweeney married a blacksmith’s daughter, Margaret Meehan, newly arrived from Ireland. They then moved to Port Phillip and squatted on the south side of the Yarra River, about seven miles (11km) from Melbourne. Around 1842, Sweeney bought 110 acres (44.5ha) in the parish of Nillumbik for £110. He built a slab hut 12 x 10 feet (3.6m x 3m) and then his homestead, Culla Hill, a typical Tipperary style cottage, now known as Sweeney’s Cottage. It was here that many generations of Sweeneys lived for almost 100 years. Culla Hill became a social centre for the district and the Catholic community used it as a church. Sweeney was apparently on good terms with a tribe of Aborigines living on the river nearby, who helped him build his house.2 Sweeney proved himself a civic-minded leader. In 1844, he led a call for a bridge over the Plenty River. He was on the first school board and supplied the first grain for Eltham’s mill. Sweeney profited during the gold rush, not by gold digging, but by providing supplies for nearby fields and others as far away as Beechworth.3 Thomas Sweeney died in 1867 and was buried at the Eltham Cemetery, leaving two sons, five daughters, and 300 acres (121.4ha), as well as Culla Hill. Culla Hill – by then reduced to 75 acres (30ha) – was sold out of the family in 1939, then renamed Sweeneys. The present Sweeneys Lane, running diagonally through the original holding, was the track to the house. Part of the original cottage remains as a small section of today’s house. The dining-family room fronted by a veranda is original, and although there have been some changes, the cedar door and most of the small 12-paned wooden-framed windows are original. The walls are made of the original hand-made brick. After buying the property in 1952 Mr and Mrs Burston demolished a dilapidated slab hut, a three-roomed detached kitchen and cellar, as materials needed to restore them were very difficult to obtain so soon after the war.4 However the barn remains almost in its original condition. It is believed to have been built from stone quarried on the property. Now roofed with iron sheets it was probably originally thatched. The sandstone barn has a peaked roof supported by the original saplings and a doorway large enough to accommodate a fully loaded wagon.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, culla hill, eltham, sweeney's cottage, sweeneys lane, thomas sweeney -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Hourglass
An hourglass or sandglass is an instrument for measuring a defined time and can be used perpetually by simply turning it over immediately the top bulb empties. The clear blown glass is shaped into two equal sized bulbs with a narrow passage in the centre and contains uniform sized sand or glass particles in the lower bulb. The width of the neck regulates the constant flow of the particles. The glass is held in a stand with top and bottom of equal shape and size. Hourglasses can measure an infinite variety of time by gauging the size of the particles, the shape and size of the bulbs and the size of the passage between the bulbs, thus measuring hours or minutes or even seconds. Generally an hourglass sits between discs of wood at the ends, which are joined by long wooden spindles between the ends and tightened by screw caps. The length of time can be adjusted by adding or removing sand particles. The use of the marine sandglass (or hourglass) has been recorded in the 14th century in European shipping. A one minute sandglass was used in conjunction with the ship’s log for ‘dead reckoning’, (see below) that is, for measuring the ship’s speed through the water. They were also used to regulate ringing the ship’s timetable; for example a 4 hour sandglass was used for the length of the sailors’ watch, and a half hour timer for taking of readings for the ship’s log; the ship’s bell would be rung every half hour. It was usually the role of the cabin boy to watch and turn the sandglasses over at the exact time of them emptying their upper chambers and to ring the ship’s bell. Hourglasses have been used historically for many hundreds of years. Some have been used for timing church sermons, in cooking, in industry and at sea. Even today they are used for measuring the cooking time of eggs and timing a player’s turn in games such as Boggle and Pictionary. The sandglasses at sea were gradually replaced in the late 1700’s to early 1800’s by the more accurate chronometers (marine clocks) when they became reliable instruments. DEAD RECKONING (or Deduced Reckoning) Dead reckoning is the term used to describe the method of calculating the ship’s position from its speed and direction, used in early maritime travel, mostly in European waters. Both the (1) speed and the (2) direction of travel were recorded on a Traverse Board at half-hourly intervals during a helmsman’s watch of 4 hours. The navigator would record the readings in his ship’s log, plot them on his navigational chart and give his updated course directions to the next helmsman on watch, along with the cleared Traverse Board. This was a very approximate, but none-the-less helpful, method of navigation. The wooden Traverse Board was a simple pegboard with a diagram of a compass with eight peg holes along the radius to each of the compass points, plus a grid with ascending half hours in the left column and increasing ship’s speed in knots in a row across the column headings, with a peg hole in each of the intersecting cells. A number of wooden pegs were attached to strings on the board. By placing one peg consecutively in the direction’s radius hole, starting from the centre, and the speed holes when the half hourly reading was taken, a picture of speed and direction for the whole 4 hour watch was created. (1) To measure the ship’s speed a one minute hourglass timer was usually used to measure the ship’s speed through the water and help to calculate its longitude. A rope, with knots at regular standard intervals and a weight such as a log at the end, would be thrown overboard at the stern of the ship. At the same time the hourglass would be turned over and a seaman would start counting the number of knots on the rope that passed freely through his hands as the ship travelled. When the timer ran out the counting would be stopped. A timer of one minute (one-sixtieth of an hour), knots spaced one-sixtieth of a nautical mile apart, and simple arithmetic easily gave the speed of the ship in nautical miles per hour ("knots"). This would be recorded every half hour. The speed could however be inaccurate to the travel being affected by ocean currents and wind. (2) To calculate the ship’s direction a compass sighting would be recorded each half hour.Marine hourglasses or sandglasses were used from around the 14th to 19th century during the time of sailing ships. This hourglass is representative of that era, which is during the time of the colonisation of Australia. Hourglass or sandglass; an instrument used to measure time. Two equal sized clear glass bulbs joined with a narrow passage between them, containing equal sized particles of sand grains in lower bulb. Glass sits in a brass collar at each end, in a frame comprising 3 decorative brass columns or posts, each attached top and bottom, using round screw-on feet, to round brass discs. Disc have Roman numerals for the numbers 1 - 12 pressed into their inner surfaces and hieroglyphics on the outer surfaces. Roman numerals on inner surface of discs " I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X XI XII " Hieroglyphics impressed on outer surface of discsflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, horology, hourglass, hour glass, sandglass, sand glass, timing instrument, dead reckoning, deduced reckoning, finding latitude at sea, sandglass with hieroglyphics and roman numerals, hourglass with hieroglyphics and roman numerals, brass hourglass -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ALBERT RICHARDSON COLLECTION: BLACK FOREST COMPANY
Five page handwritten and typed document with information about the Black Forest Gold Mine on the Hustler's line of reef. The Black Forest mine was situated one mile north of the Eaglehawk Post Office. To the west was the South New Moon on the Garden Gully line of reef and to the east was the Lightning Hill line of reef worked by open cutting to a depth of over 100 ft by Pascoe and Simonds. A party of Germans named 'Rothacker and Party', first worked the claim on the Black Forest mine approx. 1860. Other mines worked on the Hustler's line north of the Black Forest were: Martha Company. Johns and company and Meaner (unclear) and Co.bendigo, mining, black forest gold mine -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - KANGAROO HYDRAULIC COMPANY OPENING 25TH JANUARY 1894
4 page typed document, typed copy of article in Bendigo Advertiser 25th January, 1894. The Kangaroo Hydraulic Company had its plant south of Diamond Hill and 'a couple of miles from Kangaroo Flat'. The company had a Pelton Wheel to drive the crushing battery, 'one of the first in the colony'. Extensive detail on the operation. John Delbridge mechanical engineer was the engineer under who 'the plant has been erected' Mrs McGowan broke a bottle of champagne over the wheel. Thompson and Co., Castlemainer were involved in the build of the plant. Mr. C. Jorgensen was commended for his work.Bendigo Advertiserbendigo, mining, kangaroo hydraulic company -
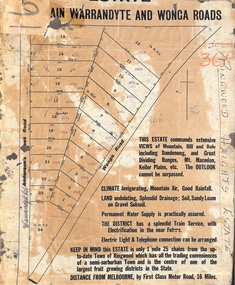 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyMap, Partially Trimmed Copy of Ringwood Heights Estate, Ringwood, Vic. - circa 1923
Clipped copy of a subdivision advertisement on cardboard backing. Sales notations on numbered allotments in Andersons's Creek Road (later Warrandyte Road) and Wonga Road, Ringwood. Handwritten title reference - LP7305. Captions - This Estate commands extensive views of mountain, hill and dale including Dandenong and Great Dividing Ranges, Mt. Macedon, Keilor Plains, etc. The outlook cannot be surpassed. Climate invigorating, mountain air, good rainfall. Land undulating, splendid drainage; soil, sandy loam on gravel subsoil. Permanent water supply is practically assured. The district has a splendid train service, with electrification in the near future. Electric light & telephone connection can be arranged. Keep in mind this estate is only 1 mile 25 chains from the up-to-date town of Ringwood which has all the trading conveniences of a semi-suburban town and is the centre of one of the largest fruit growing districts in the state. Distance from Melbourne by first class motor road, 16 miles.
