Showing 42 items matching "sanitation"
-
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, Sewer Treatment Plant, 11/09/2017 12:00:00 AM
Frank Sedgman Reserve could become a giant sewage farm servicing householders in Manningham.Frank Sedgman Reserve could become a giant sewage farm servicing householders in Manningham.Frank Sedgman Reserve could become a giant sewage farm servicing householders in Manningham.frank sedgman reserve, yarra valley water, sewerage and sanitation -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
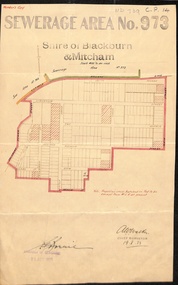
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Document, Sewerage Area, 19/08/1933
Map dated 19 - 8 1933 showing sewerage area no. 973 in the Shire of Blackburn and Mitcham. Note that View Street on the plan is now Linum Street.sewerage and sanitation, shire of blackburn and mitcham, acacia avenue, blackburn, salisbury avenue, laburnum street, view street, derby street, myrtle grove, south parade, the avenue, main street, laurel grove, pakenham street, blackburn., linum street -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
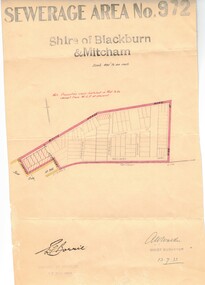
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Document, Sewerage area, 13/07/1933 12:00:00 AM
Plan of sewerage area no. 972, Shire of Blackburn and Mitcham, scale 400' to an inch. 13 July 1933. Note that the area including Stuart Street on the map is now the Thiele Court area.sewerage and sanitation, shire of blackburn and mitcham, whitehorse road, blackburn, railway road, vine street, lithgow avenue, downing street, frankston street, stuart street, thiele court -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Map, Sewerage reticulation, 1933
Melbourne & Metropolitan Board of Works plan of reticulation area no 731 in the Shire of Blackburn and Mitcham 1933 and correspondence.sewerage and sanitation, melbourne and metropolitan board of works, pope road, blackburn, whitehorse road -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
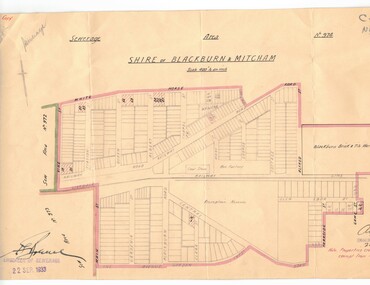
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Document, Sewerage area, 22/09/1933 12:00:00 AM
Plan of sewerage area no. 974, Shire of Blackburn and Mitcham. Scale 400' to an inch. 22 September 1933.sewerage and sanitation, shire of blackburn and mitcham, whitehorse road, blackburn, vine street, parkside street, alfred street, main street, the avenue, gordon crescent -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, Sewage Plan, 2018
Yarra Valley Water named Eram Park as the 'ideal site' to recycle sewage from 5500 new homes in the Doncaster Hill precinct and Tullamore Estate development, but local residents are totally opposed it.sewerage and sanitation, yarra valley water, city of whitehorse, eram park -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Document, Sewerage, 1933
Plan of M.M.B.W. reticulation area no 708,Shire of Blackburn and Mitcham; sewer through council property.Plan of M.M.B.W. reticulation area no 708,Shire of Blackburn and Mitcham; sewer through council property. Scale 40' to 1' [1933?] with correspondence between MMBW and the Shire, March - April 1933.Plan of M.M.B.W. reticulation area no 708,Shire of Blackburn and Mitcham; sewer through council property.sewerage and sanitation, melbourne and metropolitan board of works, shire of blackburn and mitcham, pope road, blackburn, whitehorse road -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
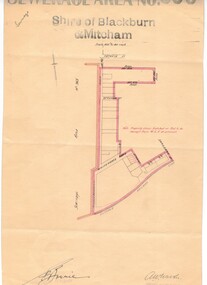
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Map, Sewerage area No 966, 1/06/1933 12:00:00 AM
Map of sewerage are no. 965 covering part of North Blackburn.Map of sewerage are no. 965 covering part of North Blackburn. Note that Stuart Street is now part of Thiele Court. Map of sewerage are no. 965 covering part of North Blackburn. middleborough road, blackburn, sergeant street, stuart street, thiele court, blackburn north, attunga street, walker, a. w., borrie, e., shire of blackburn and mitcham, sewerage and sanitation -
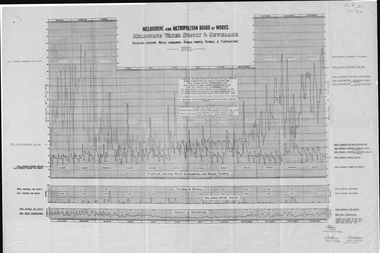 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Document, Melbourne water supply, 1932
Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works, Melbourne water supply and sewerage diagrams showing water consumed, sewage pumped, rainfall and temperature, 1931.melbourne and metropolitan board of works, sewerage and sanitation, rainfall, temperature -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncArchive (Sub-series) - Subject File, Kew Historical Society, Garbage Disposal (Kew), 1958
Various partiesReference, Research, InformationSecondary Values (KHS Imposed Order)Subject file containing primary resources/publications and newspaper articles/clippings. The oldest item in the file is a ‘Report on the Sub-Committee of the Conference of Municipalities on the Best Means of Disposing of Street and House Refuse, Street Sweepings and other Garbage of the Metropolitan Area (Brunswick, Slobom & Co., Printers, 1 Union Street, 1901). The other publication dates from 1993 and is City of Kew: Your guide to total waste management.sanitation - kew (vic), garbage - kew (vic.)sanitation - kew (vic), garbage - kew (vic.) -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Document/Letter, 1900
A letter dated 8th May 1973 details how the letter from Florence Nightingale was forwarded to Mrs E.G. (Janet) Wilson in 1955 by Gwendolen, Florence Nightingale's niece. The explanatory letter was forwarded by Elsa Halenstein and given to Royal District Nursing Service and remains in its Archives. From 1948 Mrs. Wilson served on the Committee of Management of Melbourne District Nursing Society (later Service), serving as President from October 1964-1967. In 1949 Mrs. Hallenstein served on the MDNS Committee of Management, becoming President of the now Royal District Nursing Service from 1967-1974. Florence Nightingale was the founder of modern nursing. Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) only employed Trained nurses from its inception in 1885. They followed Florence Nightingale's basic rules of good hygiene, cleanliness, good nutrition and fresh air, which they learned during their Nursing Training at a Hospital, and taught to their patients by instruction and demonstration. In those days Trained nurses were called 'Nurse'. In 1892 MDNS employed Lucy Smith who, through the Nightingale Fund, did her nursing training at the Nightingale Training School at St. Thomas's Hospital in London. She was the first nurse from this school to work at MDNS. Florence Nightingale, born on the 12th of May 1820, was named after the place of her birth in Italy. Born into a wealthy family she was schooled at home where she excelled in her studies; spoke several languages fluently, and was taught home management. She believed she was ‘called’ to reduce human suffering and tended to ill members of her family and tenants on the family estate. She worked as a nurse at Salisbury Infirmary where she learned about nursing sanitation and hospital practice. Florence then enrolled at the Institution of Protestant Deaconesses at Kaiserswerth, Germany where she learned basic nursing skills, the importance of patient observation, and hospital organization. In 1853 she became Superintendent of the Institution for Sick Gentlewomen in Distressed Circumstances in London, where she reformed health care, working conditions, and hospital efficiency. The Crimean War broke out in late 1853 and a newspaper reported the injured and sick soldiers were being cared for by an “incompetent and ineffective medical establishment and that most basic supplies were not available for care”. After an outcry from the public, Florence was asked to lead a group of 38 nurses, whom she had trained, to Scutari where the wounded soldiers were sent. After arriving at the Barrack Hospital in October 1854, she found the soldiers were being cared for in overcrowded and filthy conditions; contaminated water, faeces on the floors and rats running freely. There were few supplies and equipment. Florence bought supplies and equipment and found help to assist in the laundry. The wards were scrubbed from floor to ceiling. Florence set a high standard of care with fresh air, hygiene, clean clothing, sufficient food and regular dressing of wounds being carried out. She realized the importance of psychological needs, and soldiers were assisted to write letters to relatives, and took part in education and recreational activities. Of a night Florence walked through the wards, carrying a lamp to light her way, to check on ill and wounded soldiers and became known as “The Lady with the Lamp”. She gained the respect of the soldiers and the establishment, and later, the public through the soldier’s letters and reports in the newspaper. After visiting Crimea she contracted ‘Crimean Fever’ from which she never really recovered. When she returned to London she was regarded a heroine. The public had given freely to buy her a gift but Florence preferred this money be used to establish a fund, which became known as the Nightingale Fund. Florence had kept excellent records on the running of the Barrack Hospital, medical and nursing staff efficiency, and the causes of illness and death. Many nurses from the training school became Matrons in many countries throughout the world. Florence pushed the Government for legislation to improve drainage and sanitation in homes and in the building of hospitals with fresh air a priority. She wrote the book ‘Notes on Nursing’ and many writings on health reform. She died, aged 90 years, in her home at 10 South Street, Park Lane on the 13th of August 1910. A handwritten letter, written in lead pencil, by Florence Nightingale. It is written to her niece Gwendolen.. The letter is on buff coloured paper and has the date 'Oct 17 1900'/ written in the top right hand corner; below this is, in capital letters, the two line black printed address - '10, South Street,/ Park Lane, W'/ is stamped. The bulk of the letter reads over eight lines: "Dearest Gwendolen",/ "Thanks for your / dear note,/ I shall gladly look / forward to seeing you, / on Friday at 5 ,/ ever your loving, / Aunt Florence./ . rdns, royal district nursing service, miss florence nightingale, mrs e.g. (janet) wilson, mrs d. (elsa) hallenstein -
 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History Collection
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History CollectionBook - Illustrated book, Thornton Butterworth Limited, Florence Nightingale 1820-1856: a study of her life down to the end of the Crimean War, 1931
This book focuses on the early life and work of Florence Nightingale, particularly her contribution to healthcare and nursing, up to her involvement in the Crimean War. The book also explores Nightingale's experiences in the Crimean War, where she helped establish a hospital and improved sanitation, leading to better care for the soldiers. The book also delves into the impact of her work and its influence on civilian hospital reforms in Great BritainIllustrated book has been covered with adhesive dark blue plastic. Handwritten in silver on the spine are the words 'Hist of N I' and the number 9non-fictionThis book focuses on the early life and work of Florence Nightingale, particularly her contribution to healthcare and nursing, up to her involvement in the Crimean War. The book also explores Nightingale's experiences in the Crimean War, where she helped establish a hospital and improved sanitation, leading to better care for the soldiers. The book also delves into the impact of her work and its influence on civilian hospital reforms in Great Britainflorence nightingale, military nursing-history, nurses-biography, nursing-history, crimean war 1853-1856-medical care
