Showing 65 items
matching turner industries
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Ansett Australia Victorian Tourism Awards - University of Ballarat, 1999
A Submission to Tourism Victoria for the 1999 Ansett Australia Victorian Tourism Awards - Industry Education Category by Centre for Tourism University of Ballarat.White soft covered book of 24 pages and attachments.history and nature of our business, business success, contribution to the development of tourism at the local, regional and state levels, raising professionalism in the tourism industry, michael pearlman, jane picken, wendy liddell, arden joseph, mary hollick, alex ruggero, kendall airlines, john simos, sandra leach, monika heim, jeff floyd, jacqueline turner, nicole tangey, andrew duncan, deidre k. giblin, robert edwards, anne saunders, jenny nemeth, alice mills, nicole mackley, luis m diamonon, david riley, olivia hazledine, tourism victoria, jenny meaney, belinda pearce, peter freund, kerry kyriacou, mary hickey, ulla hiltula, ken hore, tracey hull, tom smith, liz seymon, meryl hodgson, rosie king, gerard ballantyne, emma cottis, david dunoon, customer service, ansett, tourism awards -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Magazine, Science and Industries Illustrated: The Official Organ of the Working Men's College, 30 October 1891, 30/10/1891
12 page magazine of the Working Men's College. Includes advertisements for Brooks, Robinson and Co; Australian Mercantile Loan and guarantee Co. Ltd;W. Watson and Sons; McCracken's City Brewery; Federal Building Society working men's college, rmit, brennan torpedo, edward s. prior, planet mars, wood workers' tools, brooks, robinson and co, australian mercantile loan and guarantee co. ltd, w. watson and sons, mccracken's city brewery, federal building society, c.f. rojo, a.e. illingworth, j. mcilwraith, baker and rouse, remington, w. detmold, g. stuckey, walter j. turner, g. james, hammond typewriter, havelock tobacco, tangyes limited, arnall and jackson, h.p. gregory and co, foster's lager beer, james mcewan and co, phoenix spouting, ridging and curving works, joh ndanks and son, walter j. anderson, herbery v. hampton, alcock and co -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Artafact, VIOSH - Occupational and Safety Certificate Course, Intake 7,1985, 1985
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. brown and gold framed photograph with title and names of students underneath.Framers details verso lls: "Artafact"viosh, viosh australia, occupatonal health and safety, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, john carlton, geoff dell, bob enright, tony franks, darryl hinks, kenneth kelman, jim mcristal, clarence mitchell, kevin munnings, michele patterson, pam prior, gill ross, brian simpson, colin stewart, mac story, robert sweeting, phillip turner, graeme walshe -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, VIOSH - Occupational and Safety Certificate Course, Intake 10 1997, 1997
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders in the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. Federation University VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree – on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge.Gold framed photograph with title and names of students underneath. Commenced January 1997viosh, viosh australia, occupatonal health and safety, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, stephen baldwin, paul brass, phil clark, dennis cordner, steve crawcour, steven duke, julie fitzgerald, david fitzgerald, gary lennon, patrick mcattackney, sue pannet, stephen pavlich, lloyd quarmby, noel read, tricia smith, robert turner, barrie wright -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale bone, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Baleen, or "Whalebone" The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The "bone" of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as "whalebone." Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone was an important commodity, used in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and toys.Whale bone piece. Advanced stage of calcification as indicated by deep pitting. Off white to grey.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale bone, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Baleen, or "Whalebone" The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The "bone" of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as "whalebone." Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone was an important commodity, used in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and toys.Whale bone piece. Advanced stage of calcification as indicated by deep pitting. Off white to grey.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips -
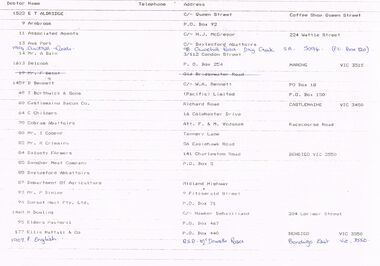 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BENDIGO SALEYARDS COLLECTION: DEFAULT RESPONSIBILITY - SALEYARDS
Four pages of Default Responsibility - Saleyards with the name and address. Date 22/3/90. Sheets are typed.bendigo, council, cattle markets, bendigo saleyards collection - default responsibility - saleyards, e t aldridge, arnbrook, associated agents, aus pork, austral meats, mr a bain, belcook, d bennett, t borthwick & sons, castlemaine bacon co, c childers, cobram abattoirs, i cooper, r crimmins, dalgety farmers, dandher meat company, daylesford abbattoirs, department of agriculture, p dinley, dorset meat pty ltd, m dowling, elders pastoral, ellis nuttall & co, p english, ferntree gully abattoirs, l fialli, foster abattoirs, g gathercole, gilbertson-greenham pty ltd, gilbertson group services, r grieve, hardwicks meat works p/l, heinz bros pty ltd, m herd, a j hill, hill & co, d hudson, r keech, n keogh, la franchi transports, r & lee, p llewellyn, r mcgregor & sons, w mckean & co, masons meats, meat exports sydney pty ltd, midfield meat co, miller-turner livestock, g mountjoy, f nevins & co, newman livestock service, oakey holdings, p o'connell. o'sullivans transport, overland meat export co, paynes transports, g pearce, penny & land, r plant, plants transports, plenty meat co, mrs pole, r & r meats, j ralph, g e rankin, riverland abattoirs, b rodwell & co, ross wholesale meat co, s rutland, t ryan, safeway supermarket (sy), i semmens, p siegel, e smith, smorgon consolidated industries, r stroud, talbot transports 244, talbot transports 1471, t tehan, traralgon meats p/l, trentham meats, j truscott, e vains & co, aus pork, victorian producers co-operative lt, n watkins, wagstaff cranbourne pty ltd, webster & company p/l, western district meat co 271, western district meat co 1473, wignalls transport co, r woodward, j wright -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - CAROUSEL, CAPITAL THEATRE, June 14, 1963
a/ Carousel, Capital Theatre, for six nights. Opening June 14th, 1963. Bendigo Operatic Society President: Mr J Mck. Cannon, Vice President: Mr E B Thomas, Hon. Secretary: Mrs R Boromeo, Hon. Treasurer: Mr B Ralph, Hon. Sub. Secretaty: Mrs J Cannon. Committee: Mesdames W Brown, J Smyth, Miss M Welch, Messrs. R Holyoake, J Smyth, V White. Photographs of: Miss Beatrice Oakley, Mary Ellis, Iaian Young, Fred Trewarne, Patricia McCracken, Joan Heard, Roger Sprawson, Reginald, Boromeo, Heather Lindhe, Peter Houston Annette Wilson, David Lea, Miss M Welch, Mrs R Conolan, Mr Max O'Loghlen. Synopsis of Story. Synopsis of Scenes. Bendigo Operatic Society presents By Permission of Chappell & Co. Ltd. 'Carousel' A Beatrice Oakley Production. Music by Richard Rodgers. Book and Lyrics by Oscar Hammerstein II. The Cast Carrie Pipperidge: Patricia McCraken, Julie Jordan, Mary Ellis, Mrs Mullin: Joan Heard, Billy Bigelow: Iaian Young, 1st Policeman: Peter Houston, David Bascombe: Reginald Boromeo, Nettie Fowler: Heather Lindhe, Enoch Snow: Roger Strawson, Boatswain: Alan Weatherley, 2nd Policeman: Graham Filcock, Captain: Victor White, Heavenly Friend (Brother Joshua): David Lea, Starkeeper: Robert Urquhart, Louise: Annette Wilson, Enoch Snow Jr.: Robert Wenn, Doctor Seldon: Robert Urquart, Principle: Peter Houston. Ladies of the Ensemble: Helen Ball, Patricia Barker, Heather Beer, Wendy Bertram, Berniece Boromeo, Marlene Bradley, Dawn Carr, Barbara Downing, Dorothy Field, Eileen Florence, Valerie Foulds, Marie Friswell, Edith Glen, Helen Gray, Joan Heard, Magaret Henderson, Jan Mollison, Shirley Moon, Bernadette Mulvahill, Anne Pearson, Margery Reed, Rhonda Scott, Mary Speedy, Shirley Unmack, Joan Crane, Olga Chew and Marion Shepperbottom. Gentlemen of the ensemble: Robert Aitken, Reginald Boromeo, Graham Filcock, Peter Houston, Max Rule, Roger Sprawson, Alan Weatherley, Peter White, Victor White, Robert Wenn. Ballet: Joan Hardin, Kaye Miller, Carol O'Sullivan, Melva Pennington, Sandra Searle, Barbara Sims. Children: Dianne Austin, Ray Austin, Carol Crane, Pamela Duffy, Leanne Dunbar, Win Davies, Larraine Kennard, Valda Kennard, Kaye Ruth Lyon, Cheryl Magee, Sharon Townsend, Lynette Reed, Karen Wilson. Bendigo Concert Orchestra: Violins: Miss A McNair, Mesdames A Bolton, A Foulds, F Robbins, C Messer, Dr Gault, Messrs. R Charlett, C Gill, J Jordan, O Turner, J Werry. Violas: Messrs. E Jarrett, S McNeill, Mrs. J Pinder. Cello: Mesdames C Bubb, J Borema, Miss L Slade, Mr A Rutland. Bass: Messrs. T French, S Anderson. Flutes: Mr C Bubb, Master D Bubb. Clarinets: Mr J McKay, Miss M Wilkinson. Trumpet: Mr N Pearce. Trombone: Mr J Allen. Tympani: Mr F Kennedy. Musical Numbers. Choruses from 'Carousel'. Advertisements: Allans, Music Store. Marin Washington, Portraits. John Brown Industries and Welmar Industries. Acknowledgments: Bendigo Advertiser, 3BO, BVC8, Mr B Bathe, K. Flat, Carousel Equipment, Frasers and all those people who have assister in any way. b/ Bendigo Advertiser article 15/6/63: Round and Round, 'Carousel' is Catchy, Bright. Apart from a few minor faults common on opening nights, warmly received by a small first-night audience. . . Bendigo Advertiser article 19/6/16 'Carousel' Scene. Carousel star Iaian Young, who plays the part of Billy Bigelow. . .Arthur Hocking Printprogram, music, bendigo operatic society, a/ carousel, capital theatre. june 14th, 1963. bendigo operatic society president: mr j mck. cannon, vice president: mr e b thomas, hon. secretary: mrs r boromeo, hon. treasurer: mr b ralph, hon. sub. secretaty: mrs j cannon. committee: mesdames w brown, j smyth, miss m welch, messrs. r holyoake, j smyth, v white. photographs of: miss beatrice oakley, mary ellis, iaian young, fred trewarne, patricia mccracken, joan heard, roger sprawson, reginald, boromeo, heather lindhe, peter houston annette wilson, david lea, miss m welch, mrs r conolan, mr max o'loghlen. synopsis. the cast carrie pipperidge: patricia mccraken, julie jordan, mary ellis, mrs mullin: joan heard, billy bigelow: iaian young, 1st policeman: peter houston, david bascombe: reginald boromeo, nettie fowler: heather lindhe, enoch snow: roger strawson, boatswain: alan weatherley, 2nd policeman: graham filcock, captain: victor white, heavenly friend (brother joshua): david lea, starkeeper: robert urquhart, louise: annette wilson, enoch snow jr.: robert wenn, doctor seldon: robert urquart, principle: peter houston. ladies of the ensemble: helen ball, patricia barker, heather beer, wendy bertram, berniece boromeo, marlene bradley, dawn carr, barbara downing, dorothy field, eileen florence, valerie foulds, marie friswell, edith glen, helen gray, joan heard, magaret henderson, jan mollison, shirley moon, bernadette mulvahill, anne pearson, margery reed, rhonda scott, mary speedy, shirley unmack, joan crane, olga chew and marion shepperbottom. gentlemen of the ensemble: robert aitken, reginald boromeo, graham filcock, peter houston, max rule, roger sprawson, alan weatherley, peter white, victor white, robert wenn. ballet: joan hardin, kaye miller, carol o'sullivan, melva pennington, sandra searle, barbara sims. children: dianne austin, ray austin, carol crane, pamela duffy, leanne dunbar, win davies, larraine kennard, valda kennard, kaye ruth lyon, cheryl magee, sharon townsend, lynette reed, karen wilson. bendigo concert orchestra: violins: miss a mcnair, mesdames a bolton, a foulds, f robbins, c messer, dr gault, messrs. r charlett, c gill, j jordan, o turner, j werry. violas: messrs. e jarrett, s mcneill, mrs. j pinder. cello: mesdames c bubb, j borema, miss l slade, mr a rutland. bass: messrs. t french, s anderson. flutes: mr c bubb, master d bubb. clarinets: mr j mckay, miss m wilkinson. trumpet: mr n pearce. trombone: mr j allen. tympani: mr f kennedy. musical numbers. choruses from 'carousel'. advertisements: allans, music store. marin washington, portraits. john brown industries and welmar industries. acknowledgments: bendigo advertiser, 3bo, bvc8, mr b bathe, k. flat, carousel equipment, frasers and all those people who have assister in any way. b/ bendigo advertiser article 15/6/63: round and round, 'carousel' bendigo advertiser article 19/6/16 'carousel' scene -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - JOHN BROWN INDUSTRIES BENDIGO
Large black and white drawing of John Brown Industries Bendigo, aerial prespective No Y1/29970, Stephenson and Turner architects 2/3/1956 J.R.bendigo, industry, john brown knitting mills -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BILL ASHMAN COLLECTION: CORRESPONDENCE
Letter, typed on paper with printed letterhead of Scalebuoys Limited. Astor House, Aldwych, London, W.C.2. Letter mentions the enclosure of a list of Foreign Agents. Also mentioned is the use of Scalebuoy water for the canning industry.sciences, instruments - general, scalebuoy, bill ashman collection - correspondence, scalebuoys limited, h c turner, scalebuoy company boston, w h cunningham & hill ltd, bendigo electronic company, scalebuoys (n.z.) limited, herr otto wulfrath, societe des chaudieres electriques francaises, don watson & co ltd, major t d hackett, commandante v betteloni, w h holt white, findlay durham & brodie, zuberbuhler & co, g kolovitch, g m b close, g p barker, l f norris -
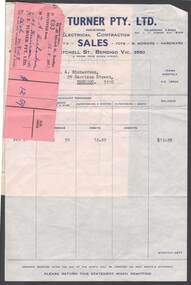 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - T.E TURNER PTY LTD
Invoice from T E Turner ,Electrical Contractor, dated 1st March 71 to Mr A Richardson. Feb 27th , 80/05 referenc 12- 59 pounds, with stapled receipt.bendigo, industry, hardware sales -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyDocument - Binder A3, source information for images used in Linking Us Together, Mary Mason, 11 Oct 2001
The book 'Linking us Together: A history of transport in the Port Phillip community' was designed and written on behalf of South Port Day Links in 2001 and the author's daughter, Mary MASON, prepared this reference to its 200 images.Linking us Together: A history of transport in the Port Phillip community'. (.02)- Black A3 binder containing source information, page by page, to each of the 200 images designed into the book. prepared for PMHPS by the designer. (.03) - Author's notes are packaged in the rear of the bindertransport, transport - tramways, transport - shipping, transport - railways, transport - aviation and aerodrome, transport - horse, transport - motor vehicles, transport - ferries, workers, industry, royal visits and occasions, piers and wharves - station pier, piers and wharves - princes pier, immigration, flood, business and traders - dairies, south port day links, wilbraham frederick evelyn liardet, wfe liardet, frank liardet, caroline frederica liardet, hector liardet, frederick liardet, liana thompson, r graham carey, swallow & ariell ltd, melbourne and metropolitan tramways board, mmtb, general motors-holden, gmh, faram brothers hardware, bert turner, james mcnab, eli (dick) edwards, jacob edwards, vincent 'ben' edwards, claude butcher, leonard george 'dugga' beazley, bicycles, cable trams, mary mason, pat grainger, frederick william maskell, linking us together -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyBook - Port Melbourne Council, John G Turner, Assistant Sanitary Inspector, Sanitary Inspectors Report Book, 1900
Sanitary Inspector's Reports to Port Melbourne Council May to August 1900. This volume details work of Assistant Sanitary Inspector appointed for three months; includes property to property inspections, notices served, follow-up actionlocal government - town of port melbourne, environmental issues, health - general health, business and traders, industry - noxious, nightsoil, built environment, j harrop - sanitary inspector, dr sandford - acting medical officer, john g turner - assistant sanitary inspector -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyDomestic object - Pack, Harper's spice, ground cinnamon, Robert Harper and Company Ltd, 1960s
This has been in Ken Turner's pantry for a long, long timeHarper's spice pack (Robert Harper and Co. Ltd.): 1 1/8 oz ground cinnamon c 1960s? Green and black on white cardboard container, tin coverindustry - manufacturing, robert harper & co ltd, spice -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyDomestic object - Pack, Harper's spice, ground nutmeg, Robert Harper and Company Ltd, 1960s
This has been in Ken Turner's pantry for a long, long timeHarper's spice pack (Robert Harper and Co. Ltd.): 2 oz ground nutmeg 1960s? Brown and black on white cardboard container, tin coverindustry - manufacturing, robert harper & co ltd, spice -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyDomestic object - Pack, Harper's spice, Star Brand ground ginger, Robert Harper and Company Ltd, c. 1940s
This has been in Ken Turner's pantry for a long, long time These spice products were made by Robert Harper & Co Ltd., which was established in 1865 and originally located in Flinders Lane, East Melbourne. The company transferred its operations to Port Melbourne in 1888 and became a registered company in 1896. Harper's & Co manufactured starch and a wide range of food product.Harper's spice pack (Robert Harper and Co. Ltd.): 1 oz ground ginger ('Star Brand'), c1940s?industry - manufacturing, robert harper & co ltd, spice -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPhotograph - Three employees of Swallow & Ariell in uniform and cap on beach, 1930s - 1940s
Photocopy from two snapshots loaned by Laura Irving McGILL in 1990. Three employees of Swallow & Ariel in uniform and cap on beach. May IRVING, centre, 1939 and Daisy IRVING with baby nephew John McGILL 1940s in rose garden then in Turner reserve. Laura Irving McGILL in background, and Irving family home at 41 Station St across the road.Ink - "S&A" "Rose Garden" Pencil : descriptionsparks and gardens, families, industry - food, may irving, daisy irving, laura mcgill nee irving, john mcgill, swallow & ariell ltd -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyBook, Mary Mason, 'Linking us Together: A history of transport in the Port Phillip community', 11 Oct 2001
A Centenary of Federation-funded project of South Port Day Links, coordinated, directed and designed by Mary MASON, written by Pat GRAINGER on behalf of PMH&PS'Linking us Together: A history of transport in the Port Phillip community' Soft cover, 72pp teal blue cover with '2001'graphic, brown spine. A Centenary of Federation Project printed Oct 2001transport, transport - tramways, transport - shipping, transport - railways, transport - aviation and aerodrome, transport - horse, transport - motor vehicles, transport - ferries, workers, industry, royal visits and occasions, piers and wharves - station pier, piers and wharves - princes pier, immigration, flood, business and traders - dairies, south port day links, wilbraham frederick evelyn liardet, wfe liardet, frank liardet, caroline frederica liardet, hector liardet, frederick liardet, liana thompson, r graham carey, swallow & ariell ltd, melbourne and metropolitan tramways board, mmtb, general motors-holden, gmh, faram brothers hardware, bert turner, james mcnab, eli (dick) edwards, jacob edwards, vincent 'ben' edwards, claude butcher, leonard george 'dugga' beazley, bicycles, cable trams, mary mason, pat grainger, frederick william maskell, linking us together -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook, Wool and the nation: a sketch of the wool industry in Australia
"Wool and the nation: a sketch of the wool industry in Australia"- Goldsbrough Mort and Company Ltd , 1946Brian S Turnerwool - history textile industry - history wool brokering, goldsbrough, mort and company limited, wool - history, textile industry - history, wool brokering -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Pamphlet, Your guide to better mowing, 1970s?
... Mitcham melbourne Lawn mowers Manufacturing industry Turner ...Operating instructions for a Turner 4-stroke rotary mower model 4CA.Operating instructions for a Turner 4-stroke rotary mower model 4CA.Operating instructions for a Turner 4-stroke rotary mower model 4CA.lawn mowers, manufacturing industry, turner manufacturing co. -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Stanley Works Pty. Ltd, 1977
In 1970, Stanley Works Pty. Ltd. took over toolmakers Turner Manufacturing Company, who were situated in Whitehorse Road, NunawadingColoured photograph of the head office of Stanley Works Pty Ltd, a tool making industry based in Nunawading. Photo taken in 1977 shows a sign over the entrance and shrubs in the left foreground.stanley works pty. ltd, tools, manufacturing industry -
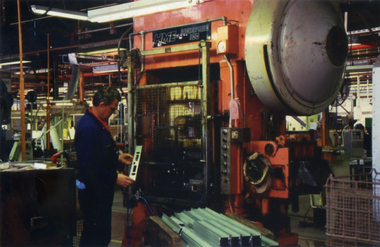 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Stanley Works Pty. Ltd, 1970+
In 1970 Stanley Works Pty. Ltd. took over toolmaker, Turner Manufacturing Company who were situated in Whitehorse Road, Nunawading.Coloured photograph of lock-broaching in the Stanley Works tool plant in Nunawading. Man to the left of photograph holding a steel object.stanley works pty. ltd. tools manufacturing industry nunawading -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Stanley Works Pty Ltd, 1970+
In 1970 Stanley Works Pty. Ltd. took over toolmaker, Turner Manufacturing Company, who were situated in Whitehorse Road, Nunawading.Coloured photograph of a male worker in a blue boiler suit in a Stanley Works machine room.tools, stanley works pty. ltd, manufacturing industry -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Stanley Works Pty. Ltd, 1972
... in 1993 stanley works pty. ltd tools manufacturing industry turner ...In 1970,Stanley Works took over toolmakers, Turner Manufacturing Company, who were situated in Whitehorse Road, Nunawading. Stanley Works Pty Ltd, shut their doors in 1993Coloured photograph of the head office at Stanley Works Pty. Ltd, Nunawading Circa 1972. Yellow Stanley sign on the roof. Cars parked in front of building. Power pole an left.stanley works pty. ltd, tools, manufacturing industry, turner manufacturing company -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Stanley Works Pty Ltd, 21/07/2010 12:00:00 AM
Stanley Works Pty Ltd took over Turner Manufacturing, Nunawading, in 1970. They closed their doors in 1992.Coloured photo of Stanley Works Pty Ltd building, with three signs - Stanley, Stanley Hardware, Hardware Divisiontools, stanley works pty ltd, manufacturing industry -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Black and white, 20 December 1945
Cheltenham is a suburb in the City of Kingston that was originally established as a rural market gardening community. The area is bordered by Highett, Mentone and Heatherton. The market gardens, farms and paddocks have gradually been sub-divided into housing and industrial estates. The Southland shopping centre is a major feature of the area.Cheltenham was established as a rural market gardening community. The Le Page family lived in Cheltenham since 1854 when Nicholas Le Page, a tailor from the Channel Island of Guernsey, bought two acres of land on Chesterville Road near Bernard Street to establish a market garden. Over the years the Le Pages purchased more land in the area. In 1875-76 Nicholas' son Frank and his wife Mary built 'Daphne Cottage' near the corner of Bernard and Wilson Streets. n the 1940s Frank's son, Everest Le Page, bought five more lots of land in Chesterville Road from the Tuck family. The Le Pages grazed horses, ponies and cows on this land, and grew pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, onions, potatoes and cabbages. Many buildings and locations within in Cheltenham commemorate the Le Page family's contribution to the Cheltenham community.Aerial photograph taken in 1945 of the Cheltenham district within the City of Kingston. The image includes Chesterville Road, the future site of Turner Road pool (now Waves) and Highett Reserve, (top left), Jellicoe Street, Argus Street, Bernard Street, Wilson Street, the Methodist Children Homes (now Southland), McIvor Street, Goulburn Street, Nepean Highway, Jamieson Street and Barker Street (bottom left), market gardens and paddocks. In the top centre of the image, "Daphne Cottage", the home of Frank T. Le Page is visible on the corner of Bernard and Wilson Streets. Much of the land depicted in this image was owned by the Le Page family. This image is possibly from the collection of aerial photographs commissioned by the Department of Crown Lands and Survey and taken by Adastra Airways.Black and white ink: 57250 White print: VIC-170 57250 20.12.45 Run 6 PROJ. No. 5 MELB. METROP AREA Black type 10200 FTS 30' LENS 20.12.45cheltenham, market gardens, industry, le page family -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyAudio - Oral History, Ken Turner, Chris Raeburn and Jo Swartz, Glen Stuart, 8 Jan 2001
Oral History of (1) Ken Turner, (2)Chris Raeburn, (3)Jo Swartz; recorded by Pat Grainger on 08.01.2002. (1)Conversation between Pat Grainger (PMHPS) and Ken Turner, former PM resident discussing shops in PM (research for 2001 calendar). (2) Councillor Chris Raeburn, Mayor, being interviewed by Bill Hartley on radio 3CR c1990 discussing Coode Island. (3)Jo Swartz, Mayor being interviewed by Romona Koval on radio 3CO discussing the Bayside Proposal. Recording duration 35:20.industry, built environment, town planning, oral history, bayside proposal, coode island, ken turner, josef (jo) szwarc, chris raeburn -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale Rib Bone, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Baleen, or "Whalebone" The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The "bone" of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as "whalebone." Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone during the 17th, 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries was an important industry providing an important commodity. Whales from these times provided everything from lighting & machine oils to using the animal's bones for use in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and many other everyday items then in use.Whale rib bone with advanced stage of calcification as indicated by brittleness. None.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whale bones, whale skeleton, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips, whaleling industry, maritime fishing, whalebone -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumBadge - Transport Health - Member 50 years, Transport Health Fund
Produced to celebrate a person being a member of the Transport Health Fund for 50 years. The fund started as the Tramways Benefit Society (a Friendly Society) in 1888 and was renamed during 1980s first as the Transport Friendly Society and then Transport Health. It was absorbed by HCF on 1/11/2021. Badge provided to Fred Turner, Inspecting Foreman (Rolling Stock) of the MMTB during the 1970s and 1980s.Tells part of the story of the Transport Industry health benefits funds.Badge - Metal - die stamped with Transport Health logo - enamel paint - green, gold and white with a lapel pin clip on the rear.tramways, tfs, friendly society, transport health, badges, benefit society, medical -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale bone, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Baleen, or "Whalebone" The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The "bone" of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as "whalebone." Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone was an important commodity, used in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and toys.Whale bone vertebrae. Advanced stage of calcification as indicated by deep pitting. Off white to grey.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips, whalebone
