Showing 110 items
matching volunteer force
-
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBadge - 2/23rd Battalion - Albury's Own
... -volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force and assigned to the 26th...-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force and assigned to the 26th ...Established at Victoria Barracks, in Melbourne, in June 1940, the 2/23rd Battalion was raised as part of the all-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force and assigned to the 26th Brigade. Under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Bernard Evans, a small cadre of experienced personnel drawn from Victorian Militia units were concentrated at Victoria Barracks prior to the battalion headquarters being relocated to Albury, New South Wales, where a large number of volunteers were completing their recruit training at the 4th Recruit Training Battalion. Upon the conclusion of this course, the recruits were posted to the 2/23rd and the battalion – over 900 strong– moved to Bonegilla, Victoria, just across the border, where more complex collective training was completed prior to departure overseas. A large majority of the battalion's initial intake of volunteers came from the Albury–Wodonga region and as a result, the 2/23rd became known as "Albury's Own"This item is part of a collection of items owned by Athur Lock, a member of the 2/23rd Battalion, an all-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force which served as part of the garrison during the Siege of Tobruk, then at El Alamein, New Guinea and Borneo. It has particular local significance as the battalion was know as "Albury's Own" because a large majority of the battalion's initial intake of volunteers came from the Albury–Wodonga region.Circular tin lapel button with pin back fastening. The front is made of paper and covered with clear plastic. The printed design on the front shows the post 1942 T-shaped colour patch of the 2/23 Battalion surrounded by the words "ALBURY'S OWN 2/23RD BN." There are 3 similar badges in our collection. Above colour patch "ALBURY'S OWN" Below colour patch "2/23RD BN."world war 11, rats of tobruk, tobruk, arthur lock -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPlaque - Plaque 2/23rd Battalion - Albury's Own
... -volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force and assigned to the 26th...-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force and assigned to the 26th ...Established at Victoria Barracks, in Melbourne, in June 1940, the 2/23rd Battalion was raised as part of the all-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force and assigned to the 26th Brigade. Under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Bernard Evans, a small cadre of experienced personnel drawn from Victorian Militia units were concentrated at Victoria Barracks prior to the battalion headquarters being relocated to Albury, New South Wales, where a large number of volunteers were completing their recruit training at the 4th Recruit Training Battalion. Upon the conclusion of this course, the recruits were posted to the 2/23rd and the battalion – over 900 strong– moved to Bonegilla, Victoria, just across the border, where more complex collective training was completed prior to departure overseas. A large majority of the battalion's initial intake of volunteers came from the Albury–Wodonga region and as a result, the 2/23rd became known as "Albury's Own"This item is part of a collection of items owned by Athur Lock, a member of the 2/23rd Battalion, an all-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force which served as part of the garrison during the Siege of Tobruk, then at El Alamein, New Guinea and Borneo. It has particular local significance as the battalion was know as "Albury's Own" because a large majority of the battalion's initial intake of volunteers came from the Albury–Wodonga region.A wooden plaque in the shape of a shield commemorating the 2/23rd Battalion known as "Abury's Own". It incorporates a representation of the 2/23rd Battalion colour patch worn after the Siege of Tobruk. At top of plaque "2/23RD AUST.IN.BN./ALBURY'S/OWN"world war 11, rats of tobruk, tobruk, arthur lock -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPlaque - Albury's Own 2/23rd Battalion 9th Division
... -volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force and assigned to the 26th...-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force and assigned to the 26th ...Established at Victoria Barracks, in Melbourne, in June 1940, the 2/23rd Battalion was raised as part of the all-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force and assigned to the 26th Brigade. Under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Bernard Evans, a small cadre of experienced personnel drawn from Victorian Militia units were concentrated at Victoria Barracks prior to the battalion headquarters being relocated to Albury, New South Wales, where a large number of volunteers were completing their recruit training at the 4th Recruit Training Battalion. Upon the conclusion of this course, the recruits were posted to the 2/23rd and the battalion – over 900 strong– moved to Bonegilla, Victoria, just across the border, where more complex collective training was completed prior to departure overseas. A large majority of the battalion's initial intake of volunteers came from the Albury–Wodonga region and as a result, the 2/23rd became known as "Albury's Own"This item is part of a collection of items owned by Arthur Lock, a member of the 2/23rd Battalion, an all-volunteer Second Australian Imperial Force which served as part of the garrison during the Siege of Tobruk, then at El Alamein, New Guinea and Borneo. It has particular local significance as the battalion was know as "Albury's Own" because a large majority of the battalion's initial intake of volunteers came from the Albury–Wodonga region.A plaque commemorating "Albury's Own" - the 2/23rd Battalion. It incorprates the Unit badge and a a list of battlefronts they served in as part of the 9th Brigade. The Latin in the centre of the badge translates as "I will either find a way or make one". In circular badge "ALBURY'S OWN/ 2/23 RD BN. AUT VIAM INVENIAM AUT FACIAM " On metal oblong "9th DIVISION /EL ALAMEIN -TOBRUK- LAE/ SATELEBERG - TARAKAN"world war 11, 2/23rd battailon, albury's own -
 Conservation Volunteers
Conservation VolunteersAward: Honour Roll, United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) - 1 June 2000 - The UNEP announced that the Australian Trust of Conservation Volunteers of Australia (ATCV), has been elected to the prestigious ranks of its Global 500 Roll of Honour for outstanding contributions to the protection of the environment, Award:United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) - 1 June 2000 - UNEP announced today that the ATCV has been elected to the prestigious ranks of its Global 500 Roll of Honour for outstanding contributions to the protection of the environment
... , whose mission is to attract and manage a force of volunteers..., whose mission is to attract and manage a force of volunteers ...THE AUSTRALIAN TRUST OF CONSERVATION VOLUNTEERS, ONE OF 14 INDIVIDUALS AND ORGANIZATIONS, TO RECEIVE UNITED NATIONS ENVIRONMENT AWARD NAIROBI, 1 June 2000 - The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) announced today that the Australian Trust of Conservation Volunteers of Australia (ATCV), has been elected to the prestigious ranks of its Global 500 Roll of Honour for outstanding contributions to the protection of the environment. ATCV is one of 14 individuals and organizations to receive this honour in 2000. Founded in 1982, ATCV is a national, not-for-profit community organization, whose mission is to attract and manage a force of volunteers in practical conservation projects for the betterment of the Australian environment. ATCV completes more than 4000 week-long conservation projects in urban, regional and remote areas of Australia each year. Activities range from bush regeneration, tree planting, seed collection, endangered species protection, weed control, flora and fauna surveys, walking trail construction, fencing, environmental monitoring and the protection of world heritage areas. ATCV community participation has resulted in more than 1.8 million trees being planted in 1999, and in more than 7.3 million trees planted over the past 10 years. Community involvement totalled 200,000 project days in 1999 and more than 700,000 days since 1989. To encourage the involvement of young people, ATCV developed and manages the federal government-funded programme Green Corps. Green Corps is a six-month traineeship for 17 to 20 year-olds, which incorporates conservation projects and accredited training. Since 1997, more than 4,000 trainees have completed the Green Corps programme. ATCV is a founding member of the International Conservation Alliance, which brings together organizations working in conservation volunteering, and is a member of the World Conservation Union (IUCN). " The award will be presented in Adelaide, Australia, at the World Environment Day ceremonies on 4 June 2000. World Environment Day, which is celebrated in some 120 countries around the world on 5 June, was established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1972 to focus global attention and action on environmental issues. Some 701 individuals and organizations, in both the adult and youth categories, have been honoured since UNEP launched the Global 500 award in 1987. Among prominent past winners are: French Marine explorer Jacques Cousteau; Sir David Attenborough, producer of environmental television programmes; Gro Harlem Brundtland, former Prime Minister of Norway; Anil Aggarwal, the prominent environmentalist from India; Ken Saro-Wiwa, the environmental and human rights activist from Nigeria who was executed for leading the resistance of the Ogoni People against the pollution of their Delta homeland; the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), Jimmy Carter, former President of the United States; Jane Goodall of the United Kingdom whose research on wild chimpanzees and olive baboons provided insight into the lives of non-human primates; and the late Chico Mendes, the Brazilian rubber tapper who was murdered during his fight to save the Amazon forest. To forge global links and to implement ideas, which can contribute to a more sustainable future, a network of all Global 500 laureates has been formed. Information about this unique network can be obtained at http://www.global500.org. The winners of UNEP's Global 500 Roll of Honour are members of a broad and growing environmental movement that is flourishing around the world. They have taken the path that most of us hesitate to take for want of time or caring," says UNEP's Executive Director, Klaus Toepfer. "In honouring the Global 500 laureates, UNEP hopes that others will be inspired by their extraordinary deeds."Certificatecva, conservation volunteers, conservation volunteers australia, conservation volunteers new zealand, colin jackson, better earth, environmental conservation, volunteers, volunteering, corporate volunteering, education – environmental, carbon footprint, climate change, ballarat, safety, training, partnerships, victoria, vic, nsw, queensland, act, australian capital territory, nt, northern territory, western australia, wa, south australia, sa, tasmania, new zealand, california conservation corps, atcv, unep, unep honour roll, united nations environment program -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societydeath notice/scroll, after 1919
In 1922 a Memorial Scroll was presented to the next of kin of those soldiers, sailors, and nurses who died while serving in the Australian Imperial Force or Royal Australian Navy during the First World War. Later they were presented with a Next of Kin Memorial Plaque. This was presented to Edward Lawless' mother, Elizabeth Lawless. This certificate is part of the Lawless Collection. The Lawless family lived in Orbost from 1907 - c 1920. John Francis Lawless had a saddlery shop. He died at an early age - 47 years - June 7 1912, leaving his wife, Elizabeth and seven children. The eldest son, Victor Rowland lawless volunteered for serv ice in WW1 but did not leave Australia because of illness. The second son, Edward Vincent Lawless (b 1895 d 1917) worked for McCoy & Co. in Orbost, coachbuilding, undertakers, general blacksmiths and farriers, prior to enlisting in WW!. He was trained as a signaller and was sent to France where he was killed in action on 9.10.1917. Elizabeth Lawless worked as a ladies' nurse (midwife) in Orbost prior to leaving the district in 1920. She lived to 6.6.1975 aged 104 years. On October 9, he was first recorded as missing in action and then confirmed killed in action. He was initially buried at Tyne Cot British Cemetry and then exhumed and buried at Passchendaele New British Cemetry, Plot 14, Row 2, Grave 2. Correspondence in his file dated April 7, 1925 providing the grave details show that his mother was still seeking that information. It was possibly due to the fact that his body was exhumed and reburied. While there is no correspondence to his mother about this move on file, the correspondence that is there indicates she had not received the specific information on his grave until 1925.These personal documents, medals, photographs and books give an insight into the human element of World War 1 ensuring that those who were part of the Orbost community and died while playing a vital role during this time are remembered.A death notice or memorial scroll which has the British Coat of Arms at the top and a message paying tribute to the soldiers who gave up "their own lives that others might live in freedom". The text is printed in calligraphic script beneath the Royal Crest followed by the name of the commemorated serviceman giving his rank, name and regiment. The scroll was sent on December 20, 1921. At the bottom - Pte. Edward Vincent Lawless 21st Ba. A.I.F.lawless-family certificate death-scroll ww1 -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societycertificate, 1945
The Volunteer Air Observers Corps was an Australian air defence organisation of World War II.It was formed on 31 December 1941 to support the Royal Australian Air Force by sighting and observing aircraft over Australia.It swiftly established observation posts across Australia and provided information to the RAAF's regional air control posts. As the threat to Australia declined its role was expanded to include coast watching, assisting air traffic control and weather reporting. The corps was staffed by civilian volunteers and reached a peak strength of 24,000 personnel and 2,656 observation posts in 1944. After the end of the war the VAOC was reduced to a cadre in December 1945 and was disbanded on 10 April 1946. The Volunteer Air Observers Corps was an Australian air defence organisation of World War II. This certificate is a record of the participation of members of the Orbost district. Anita Armistead, wife of Francis Armistead had a son, Sydney, who served as a gunner in Malaysia during WW11.A certificate of service awarded to Mrs F. Armistead for being a volunteer in the Air Observers Corps. It was awarded on 20 Sept, 1945 for one year's service.For King and Empire Presented to Mrs F. Armistead by the ROYAL AUSTRALIAN AIR FORCE As a record and in appreciation of patriotic response to the call of country by serving in the VOLUNTEER AIR OBSERVERS CORPS This 20th day of September 1945 signed G. Jones Air Vice Marshall Chief of Air Staff signed ? Unit Commanding Officercertificate ww11 air-observers-corps -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageClothing - Leather Leggings, 1899 to 1918
The subject leather leggings are associated with mounted troops known as the Australian Light Horse that served in the South African War from 1899 to 1902. After the war, Britain wanted to use fewer mounted troops and restructured its force around a style of combat that needed more infantry. But the defence of Australia still relied upon mounted military units as these were more mobile than infantry and could travel faster over long distances. Light Horse brigades in the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) mostly contained recruits who served in the Light Horse regiments of the Citizen Forces. Many young men from rural areas of Australia volunteered for the Light Horse regiments. They had to pass a riding test to join, this test was easier for men from the bush because horses were still the main method of transport on farms and in country towns. The army did not officially accept First Australians into the AIF until May 1917 when enlistment standards were relaxed to include 'half-castes' with a parent of European origin. Indigenous soldiers served as valuable members of the Light Horse and many possessed excellent horse handling skills and specialist tracking knowledge.The subject items are part of the uniform for the Light Horse Units that served in the Australian army from 1899 until 1918. These leggings were worn by soldiers on horseback and are significant as they represent a noteworthy time in Australia's early military history. It was a time when many young men gave their lives during the South African and First World Wars in the defence of the then British Empire as part of the Imperial Forces that were gathered from many British-controlled Colonial countries.A pair of two Leather Leggings used by Mounted Australian soldiers during the first world war. The leggings are dark tan in colour with stitching to attach buckles and fastener straps. The strap buckles are made of brass and the leather legging straps are of same leather as leggings. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, leggings, leather leggings, protective leggings, protective clothing, australian mounted light horse units, military equipment -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Article, Newspaper S McDonald, 1940’s
The Volunteers Air Observers was formed in 1941 with the aim of observing aircraft flying over Australia. There were over 24000 civilians volunteering their services and as the military threat to Australia subsided they took on roles as coast and weather watching. This photograph shows a group of local volunteers at their work. Mrs. S Hamilton, Mrs. J Lees, F/O E F English, Mrs. R Picton, Mr. Ralph Barnes and Miss S McDonaldA local item which relates to an organization which operated around Australia in the 1940’s. Small newspaper cutting with photograph with six people around a table. Text is underneath the photo. The back has an advertisement for Fletcher Jones clothingThe picture shows a control room manned by volunteer personnel. Here the plotters are marking positions of aircraft with symbols on a map of the surrounding district while the Teller in the raised chair sends reports on to the Air Force, which thus has a check of all planes left to right Mrs. S Hamilton, Mrs. J Lees, F/O E F English, Mrs. R Picton, Mr. Ralph Barnes and Miss S McDonald volunteer air observers corps,, volunteer air observers corps,, mrs. s hamilton,, mrs. j lees,, f/o e f english, mrs. r picton, mr. ralph barnes, miss s mcdonald warrnambool -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Book - Scrapbook, Ballarat School of MInes: Scrapbook of Newspaper Cuttings, Book 66, November 1994 to December 1994
Collection of newspaper articles related to Ballarat School Of Mines.They cover activities and advertisements for staff. The papers concerned are The Courier, Ballarat, The Australian, The Age over the period of 29 November 1994 to 29 December 1994.Book with yellow cover, front, spiral bound. teaching positions advertised, pre-employment courses, courses available, enrolment for smb courses, memorandum creates force, elder, young chefs on trial, nicole cobain, aaron taylor, francine briody, ararat courses increased, installation of geoffrey blainey, university of ballarat liftout, richard mcgarvie installs new chancellor, chancellor launches rich history, anne beggs sunter, smb training of water board staff, alice discovers computers at 80, smb presentation of volunteer tutors, peg johns, joan goldsmith, bob carmichael, david linder, heather bush, connie sadler, sue rattray, george burk, john vellenoweth, edleen tinker, lois morritt completes vce, neville love, ararat college plan approved, grants to build networks, mark judd, colin tonkin award for excellence, ruth kealy wins walker ceramics award, koori artists show works, fine art gallery, rubina burgoyne, bill blackall, kylie bird, ray muir, abraham baksh, anne beggs sunter uni origins -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchPhotograph, Lara 6th Battalion, 1940
Photograph of the Lara Members of the 6th Battalion Defence Force Corps 1940. All members listed under the photograph.Photo of Lara Defence Corps taken in 1940 include members from Lara Victoria. All members in the photograph named.Black and white Photograph on A4 paperLara Members of the 6th Battalion Volunteer Defence Corps 1940 Members listed under the photograph -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchPhotograph, Set 4 photographs. and others for Torquay Light Horse camp, 1940
These images capture for all time Light Horsemen travelling through Geelong on their way to camp at Torquay for the last Group meeting in Australia . information following - details obtained from .........https://torquayhistory.com/light-horse-brigade/ On Australia Day, 1997, Sir John Young unveiled this plaque on Point Danger, Torquay. Torquay history, Light Horse Training Camp, WW2 Plaque at Pt. Danger Note----- (See images to view plaque) The plaque identifies a significant event in Torquay’s history and the sentiments of ‘change’ for the Light Horse Brigade – from horses to machines. In 1940 the four Light Horse Regiments (4th, 8th, 13th and 20th), some 5000 Light Horse and 2000 horses camped and trained at Torquay. Three other regiments, formerly mounted on horses, were also at Torquay ‘mounted’ on privately owned trucks and cars. Division troops included Artillery, Engineers, Signals, Field Ambulance and other branches of the Army necessary to enable a Division to function. It wasn’t just the sheer numbers of men coming to this little town that made the event significant, it was also the fact that the men of the Light Horse were dramatic, almost glamorous figures and it is easy to see their exploits as some splendid adventure. Horses have played a special role in the story of Australia. They were the only means of transport across this huge country, so it was necessary for everyone to have the ability to ride a horse. When war broke out in 1899 between Britain and the Boers of South Africa (“Boer” was Dutch for “farmer”) Australia sent troops to fight. At first Britain was wary of using untried, unprofessional colonial cavalrymen but soon saw that the slouch-hatted Australian “bushmen” were a match for the fast-moving and unconventional mounted commandos of the Boers. The Australians proved themselves to be expert rough-riding horsemen and good shots. Bush life had hardened them to go for long periods with little food and water. They also showed remarkable ability to find their way in a strange country and use its features for cover, in both attack and defence. By 1914, when Australia joined the war against Germany, there were 23 Light Horse regiments of militia volunteers. Many men from these units joined the Light Horse regiments of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF). Men were given remounts (if not using their own horses) – army horses bought by Commonwealth purchasing officers from graziers and breeders. These were called “walers” because they were a New South Wales stockhorse type – strong, great-hearted animals with the strains of the thoroughbred and semi-draught to give them speed, strength and stamina. On 1st November, 1914, Australia’s First Infantry Division and the first four Light Horse regiments sailed for England in a fleet of transport ships. The first of the Light Horse arrived at Gallipoli in May without their horses. Back with their horses after Gallipoli, they were formidable combatants across the Sinai and Palestine. Some British commanders observed that the light horseman moved with a “lazy, slouching gait, like that of a sleepy tiger” but described how the promise of battle “changes that careless gait, into a live athletic swing that takes him over the ground much quicker than other troops”. They had Light Horse, Torquay, training campdeveloped a reputation as formidable infantrymen. The Turks called them “the White Ghurkas” – a reference to their deadly skill with the bayonet. The Arabs called them “The Kings of the Feathers”. The plume had originally been a battle honour of the Queensland Mounted Infantry for their work in the shearer’s strike of 1891. During WW1 it was adopted by almost all the Light Horse Regiments. It was the proud badge of the light horseman. The most famous of their battles was the attack on Beersheba- the charge of the 4th Light Horse Brigade. Mounted infantrymen and their superb walers had carried out one of the most successful cavalry charges in history – against what seemed impossible odds. They surprised the Turks by charging cavalry-style, when they would normally have ridden close to an objective then dismounted to fight. The fall of Beersheba swung the battle tide against the Turks in Palestine; and changed the history of the Middle East. While 19 men from the Surf Coast Shire served with the 4th Light Horse over the course of WW1, only four were involved in the charge of Beersheba- John GAYLARD, Philip QUINN.(Winchelsea); Wallace FINDLAY (Anglesea); Harry TRIGG (Bambra). After the war, Light Horse units played a key role in the Australian Government’s compulsory military training programme. The Citizen Military Forces (C.M.F.) thrived on the glamour of the wartime Light Horse tradition, ignoring the possibility that motor vehicles would soon replace the horses. When training was no longer compulsory, the C.M.F. regiments declined and horses became more of a luxury during the 1930s depression years of poverty and unemployment. Some regiments were motorised. Then, in 1939, Australia joined Britain in another world war. Training was increased for the militia at both home bases and regional training camps. The camp at Torquay in 1940, commanded by Major General Rankin, was at Divisional strength. By the end of the camp some felt that the Division was ready for active service. Gradually, over the next four years, the Australian Light Horse units were mounted on wheels and tracks and the horses were retired. Six men enlisted at the Torquay camp and another 57 men and women enlisted at Torquay for service in WW2. Those who served in the Militia provided valuable Officers and NCOs and men for the armed services during the war. Each infantry division of the 2nd AIF had a Light Horse regiment attached to it. But the day of the Australian mounted soldier hadn’t quite passed. During World War II, Australia’s 6th Cavalry Regiment formed a mounted unit they called “The Kelly Gang” which did valuable scouting work. In New Guinea, a mounted Light Horse Troop did patrol duty and helped carry supplies. Some fully equipped walers were flown into Borneo for reconnaissance in rugged mountain country. But by the end of the war, in 1945, the horse had disappeared from the Australian Army. References: Australian Light Horse Association www.lighthorse.org.au National Australia Archives Australian War Memorial Surf Coast Shire WW1 memorials www.togethertheyserved.com The Light horse- a Cavalry under Canvas Light Horse, Training Camp, Torquay, WW2 Late in 1939 it was decided to set up a Lighthorse training camp in Torquay to train both men and horses for the battles of the Second World War. Horses, men and equipment came on special trains from all over Victoria and NSW, and as you would expect horseman came from areas such as Omeo and Sale, the Wimmera and the Western District. They arrived at the Geelong racecourse for watering in the Barwon River and then were ridden across the ford at the breakwater and began their 11 mile trek to Torquay. Light Horse, Training Camp, Torquay, WW2 Tent city By the end of January 1940 the camp at Torquay accommodated some 5000 men and 2500 horses of the Second Cavalry Division. The rows of horses, tents and huts near Blackgate Road were quite a sight. While the cavalrymen engaged in exercises on the land and on the beaches, many of the troops took over the Torquay School for special training of men and officers. Mr Bob Pettit local farmer and Councillor for the Barrabool Shire, wrote about the Light horse in the Surf Coast Community News in 1985 saying “They used to travel about the district riding four abreast in one long convoy. To my annoyance they went through my property and shut all the gates behind them. I had certain gates open to let stock in to the water holes and it would take me three -quarters of an hour to follow the horsemen up and put all the gates right again” he continued “the men from the Light Horse were here when the fire went through in March 1940. He recalled an incident when early one morning, as some one blew the bugle, a soldier putting a white sheet on the line frightened the horses. They panicked and ran off in all directions. Six went over the cliff near Bird Rock, five were never found, and the rest were gathered up after nearly a fortnight in the bush around Addiscott and Anglesea" Light Horse, Training Camp, Torquay, WW2, Geelong Parade Geelong parade The training camp culminated in a parade through the streets of Geelong on March 12th 1940. The salute was given at the Town Hall and the troops continued on a route to the You Yang’s for a training exercise. Note-----(see media section for photograph) The Camp was abandoned in mid 1940 as it was deemed unsuitable for training during winter and the cost of a permanent camp could not be justified if it could not be used all year. Historic.......Rare,,,Interpretive.Sepia photographs.set of four ....post card size ....Horses &LighthorsemenNo 1, Lighthorsemen Regiment Geelong 1940......No 2 Light Horse at Breakwater Geelong 1938 to 1940....No 3 Light Horse at Breakwater Geelong 1938 to 1940.....No 4 Light Horse crossing Breakwater camped at Geelong Showgrounds. These markings are on reverse of photographs.light horsemengeelong 1940., world war 2 -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchPhotograph, Regiment of the Australian Light Horse on the March in Jerusalem in Palestine
By 1914, when Australia joined the war against Germany, there were 23 Light Horse regiments of militia volunteers. Many men from these units joined the Light Horse regiments of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF). Initially Australia promised four regiments of Light Horse, 2000 men, to fight in the British cause. By the end of the war, 16 regiments would be in action.The Light Horse were seen as the “national arm of Australia’s defence” and young men, most from the country, flocked to join. Framed and glass covered photo of a Regiment of the Australian Light Horse on the March in Jerusalem in Palestine"A Regiment of the Australian Light Horse on the March in Jerusalem in Palestine."ww1, world war 1, australian light horsemen, palestine, lara r.s.l. -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumNewspaper - THE AIF NEWS, 1941, Australian Imperial Force, 7.6.1941
The contents are mainly War news, maps, advertising and sports, rear page has photos of Women volunteers in the “WANS” Women’s Australian National Service.Newspaper, AIF news, Issued by the Australian Imperial Force Middle East, classed as 8 pages, yellowed, all print in black, illustrated with maps and photos.“The AIF News - Saturday June 7 1941”the aif news, middle east, 1941 -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Royal Commission into National Natural Disaster Arrangements, 2020
Two volume report into National Natural Disaster Arrangements, including a volume of attachments. This report is also known as the Bushfires Royal Commision. non-fictionroyal commission, natural disaster, bushfire, mark binskin, natural hazards, australian defence force, aerial, aircraft, evacuation planning, emergency information, abc, air quality, health, wildlife, heritage, indigenous land management, bushfire hazard reduction, fuel management, volunteers, disaster recovery, blue shield, dja dja wurrung clans aboriginal corporation, victorian farmers federation, black summer -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumAward - MEDALS VARIOUS, 1939, 1945,1947, 1965
.1) India, Volunteer Service Medal 1939-45 .2) Dutch (DHK 1940-45)Military, army, Navy, Air Force, Merchant Marine .3) India, 1947-48 General Service Jammu & Kashmir 25048 Separation. .4) Dutch, 1945-49 Issued to Dutch Army. War against Indon. Rebels. .5) India, 1965 Rausha Medalfor Bravery 1965numismatics - medals, india, dutch -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageUniform - Tunic, 1899-1903
This original tunic or jacket is part of the full dress uniform of the pre-Federation Victorian Permanent Artillery regiment. Its owner had the rank of Sergeant, as indicated by the three inverted chevrons. The Artillery design of the badges and buttons indicate the date of the tunic to be from 1893 to 1903. However the maker of the tunic, W. Moncton, began manufacture in Melbourne in 1899, so this the tunic can be dated between 1899 and 1903. The donor's grandfather was given this tunic but not the name of the original owner. It has since been suggested to the family that the tunic was worn by a local Western District Light Horse member. This could very well have been the case because mounted troops were officially referred to as the Light Horse in the late 19th to early 20th century. Several local men were involved in the Light Horse during the First World War. The donor's grandfather wore this tunic in the local district when riding a penny farthing bicycle. The donor's father also wore the tunic when dressed as a 'Captain' hosting a local disco dance. BRIEF MILITARY HISTORY- The Crimean War began In 1854 and many people in colonial Australia were afraid of a Russian attack. Volunteer forces were established to strengthen the British Imperial troops posted here. A battery of artillery was raised in Victoria as well as in other Australian states. In 1870 Australia became responsible for its own naval and military defence. The Volunteer Corps and Victorian Navy shared the responsibility of defending the existing forts, assisted by volunteer coastal and mobile field batteries. The Permanent Victorian Artillery force was established. It was disbanded in 1880 then re-formed in 1882 as the Victorian Garrison Artillery Corps. In 1895 the Geelong, Warrnambool, Port Fairy and Portland Batteries became part of the Western District Garrison Artillery. Many of the volunteers who served in the Artillery were from rural areas. They belonged to rifle clubs and were experience horsemen as well. Australia's defence at this time relied on these mounted troops, or Light Horse men. In 1899 the Victorian Garrison Artillery Corps amalgamated with the New South Wales and Queensland Permanent Artillery to become the Victorian Regiment of the Royal Australian Artillery (RAA). Then prior to Federation, the RAA and the Permanent Artillery of South Australia, Western Australia and Tasmania all combined, becoming the Royal Australian Artillery Regiment with two Batteries of Field Artillery; Battery A from Sydney and Battery B from Melbourne.This original uniform tunic of the pre-Federation Victorian Permanent Artillery is significant for its association with Australia's military defence and the fortifications of our district, state and country. The tunic is also significant, representing part of the history and evolution of uniforms in the Australian military forces. The tunic is also significant in its representation of Australia's independence in forming its own defences. The tunic has local significance in its connection with local social events.Tunic or jacket, part of the full dress uniform of the pre-Federation Victorian Permanent Artillery operating from 1893 to 1903. Original, single-breasted tunic of dark blue wool, red piping trim, black cotton lining in body. Sleeves lined with blue striped, white cotton. Front closure has eight brass buttons. Red band-style collar with hook-and-eye closure has gold bullion braid trim and a brass badge pinned each side at the front. Upper right sleeve has three inverted chevrons on red fabric with gold bullion braid trim (rank of Sergeant). Both sleeves have gold bullion braid 'Austrian knot' emblems stitched onto lower arm, with ends finishing on the inner sleeve. Shoulder epaulettes have red piping and smaller brass buttons. Closed back vent has vertical scalloped design with six brass buttons, in two columns of three, and red piping trim. Brass belt hook is attached to the left back waist, close to the seam (right side has a mark indicating a previous similar clip). Inside left breast is a concealed pocket. Tunic has both machine and hand stitching. All brass shank-style buttons have matching Artillery emblems with inscriptions on the back. The two brass collar badges have additional artillery emblems of exploding grenade and star as well as an inscription. Buttons were made for W. Moncton, of Melbourne and marked with his name. He traded from 1899, dating the tunic to between 1899 and 1903.Button front: Artillery emblem on front (field cannon facing left, in front of a muzzle-loading ram rod). Button back: engraved "W. MONCTON . MELBOURNE ." Collar badges: Artillery emblem (field cannon facing right | stars | exploding grenade | "AUSTRALIA")flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, uniform jacket, uniform tunic, garrison volunteer uniform, fortifications in victoria, victorian permanent artillery, pre-federation military uniform, sergeant's uniform, jacket, militia, victoria, victorian volunteer forces, victorian regiment, royal australian artillery, raa, field gun, sergeant, w. moncton, garrison, dress uniform, tunic, scarlet collar, red collar, scarlet piping, red piping, gold bullion, artillery emblem, light horse, artillery, mounted troops, victorian garrison artillery corps -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers Victoriaprogramme, Anzac Day Tuesday 25th April 1967, 1967
Several items were given by a seafarer, Mr Nicholas Garlick (1926-2009) into the care of Father Brady who retired from St Pauls Cathedral, Melbourne in 2018. Father Brady later donated the collection of; objects, documents and an extensive collection of cruise ship menus (1937-end of 20thC) to the Mission via the intermediary William Hastie, volunteer at the Mission for Seafarers.Possibly a pamphlet printed for VIP guests and families attending the ceremony.Two page Anzac Day memorial service pamphlet/leaflet. Smooth/shiny paper, two ink colours (magenta and bluish green), picture of slouch hat at top right corner, and the insignia of each Australian armed force (navy, army, airforce) along the bottom of the pamphlet. The order of ceremony is printed in red ink on the two inner pages. The back features a photo of the Brisbane Shrine of Remembrance and the poem 'The Glory of the Soldier' by Joyce Kilmer.1967, anzac day, brisbane, shrine of remembrance, brisbane, joyce kilmer, poetry, war memorials, william hastie, nicholas garlick, father brady -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Richard Pinn, Martina Neale addressing Hurstbridge Primary School students, Fergusons Paddock, Hurstbridge, c.1999, 1999c
Martina Neale was the driving force behind a group of volunteers who revegetated a part of Fergusons Paddock. On this occasion, students from Hurstbridge Primary School were given an environmental "walk and talk" in the area, as part of a program promoting interaction with the wider community.Four colour photographshurstbridge primary school, fergusons paddock, martina neale -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Richard Pinn, Tree Planting, Hurstbridge Primary School students, Fergusons Paddock, Hurstbridge, c.1999, 1999c
The woman in the light green top is Martina Neale, who was the driving force behind a group of volunteers who revegetated a part of Fergusons Paddock. On this occasion, most of the work was done by students from Hurstbridge Primary School, as part of a program promoting interaction with the wider community.Colour photographhurstbridge primary school, fergusons paddock, martina neale -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Richard Pinn, Tree Planting, Hurstbridge Primary School students, Fergusons Paddock, Hurstbridge, c.1999, 1999c
The girl looking to camera is Adele Neale (daughter of Martina Neale, who was the driving force behind a group of volunteers who revegetated a part of Fergusons Paddock).Colour photographhurstbridge primary school, fergusons paddock, adele neale -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Tree Planting, secondary school students, Fergusons Paddock, Hurstbridge, c.1999, 1999c
The woman in the reddish outfit in three of the photos is Martina Neale, who was the driving force behind a group of volunteers who revegetated a part of Fergusons Paddock. On this occasion, most of the work was done by a small group of secondary school students, who chose this activity from one of several options involving community groups. The man in the yellow shirt in two of the photos is Richard Pinn.Ten colour photographsfergusons paddock, martina neale -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societysaddle, Before 1915
By 1914, when Australia joined the war against Germany, there were 23 Light Horse regiments of militia volunteers. Many men from these units joined the Light Horse regiments of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF).This WW1 item is a reminder of the roles that men from Orbost played in that conflict.Large brown leather saddle used by the Light Horse Brigade in WW1. The saddle is built on a pair of felt-padded wooden "bars" which sat on either side of the horse's spine. These are joined by steel arches with a shaped leather seat laced between them. C G H F The saddle also has a few other numbers on it which are difficult to read with accuracy. saddle military-history army transport horse -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBadge - ACF Australian Comforts Fund badge, P J King Pty Ltd, 1940
This Australian Comforts Fund badge is part of a set of eleven badges collected from the 1920s to the 1940s by Dr W. R. Angus. The badge was sold by the ACF in 1940 to raise funds for gifts to send to the Australian troops serving overseas. The badge is one of a set of badges that represents various organisations that he had interests in. The Australian Comforts Fund was a mostly female, volunteer-run organisation officially recognised by the Government. It began in 1916 as an amalgamation of groups of people who wanted to support the Australian troops abroad with Items of comfort to supplement the essential items provided by the Australian Military Forces. The ACF raised funds to purchase goods, pack them and send them overseas. One of their fund-raising activities was 'button days' where buttons such as this one were given to those who gave donations. The ACF closed down after World War I but was re-formed at the start of World War II. Items that the ACF sent to the troops included personal toiletry items such as toothbrushes and toothpaste, magazines, pyjamas, singlets and socks. They also provided sporting equipment, recreational music, writing materials and postcards. Special hampers were sent to the troops at Christmas time. The maker, P J King, (Percy John King), originally established his engraving and ie casting business in Russell Street, Melbourne in 1893 in partnership with Charles Walder Bridgland, continuing on his own from 1899. Percy and his son John Howard King set up a new business P J King Pty Ltd in 1928 making uniform buttons. In the late 1980s, it merged with two other companies that then became J J Cash, now known as Cash's Australia. The set of badges was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” which includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) and Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. The W.R. Angus Collection: - The W.R. Angus Collection includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) and Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. It includes historical medical and surgical equipment and instruments from the doctors Edward and Thomas Ryan of Nhill, Victoria. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1927 at Ballarat, the nearest big city to Nhill where he began as a Medical Assistant. He was also Acting House surgeon at the Nhill hospital where their two daughters were born. During World War II He served as a Military Doctor in the Australian Defence Force. Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool in 1939, where Dr Angus operated his own medical practice. He later added the part-time Port Medical Officer responsibility and was the last person appointed to that position. Dr Angus and his wife were very involved in the local community, including the planning stages of the new Flagstaff Hill and the layout of the gardens there. Dr Angus passed away in March 1970.This badge represents the efforts of the women volunteers in Australia to support the Australian troops overseas in WWI and WWII. This badge is one of a set of significant badges that connects Doctor Angus with Australian organisations of the early-to-mid 20th century, including those relating to military service support. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The Collection includes historical medical objects that date back to the late 1800s.The ACF Badge is a star-shaped, gold, glittered red enamel and metal badge. The star has six points. The enamel surface is textured. The border and front inscription of the badge is gold. It is the badge of the Australian Comfort Fund, made by P.J. King and dated 1940. This badge is part of a set of badges collected by Dr W R Angus. the set represents organisations that he was involved in, and is part of the W.R. Angus Collection.Front: “ACF / 1940” Reverse embossed “P.J. KING”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, metal badges, enamel badges, organisation badges, acf, presbyterian brotherhood, oikumene, w.r. angus, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, australian comforts fund, button day, volunteer, australian military forces, christmas hamper, 1940 acf badge, fund-raising, p j king pty ltd, percy john king, donor's badge, world war ii, 1939-1945, australians at war, voluntary work, volunteers, home front, w.r. angus collection -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, University of Ballarat Volunteers Isolated Student Education 1997 Task Force: Internet to the Outback, 1997, 1997
University of Ballarat is a predecessor institution of Federation University Australia. Thirteen people pose for a photograph at Mount Helen Campus. university of ballarat, volunteers isolated student education, internet to the outback, marijke heywood, ed boyd, arno besse, ian bielenberg, tim mayes, helen richards, bob howey, brian sansom, bob rasmussen, mike stock -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageClothing - Leather Leggings, 1899 to 1920
The subject leather leggings are associated with mounted troops known as the Australian Light Horse that served in the South African War from 1899 to 1902. After the war, Britain wanted to use fewer mounted troops and restructured its force around a style of combat that needed more infantry. But the defence of Australia still relied upon mounted military units as these were more mobile than infantry and could travel faster over long distances. Light Horse brigades in the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) mostly contained recruits who served in the Light Horse regiments of the Citizen Forces. Many young men from rural areas of Australia volunteered for the Light Horse regiments. They had to pass a riding test to join, this test was easier for men from the bush because horses were still the main method of transport on farms and in country towns. The army did not officially accept First Australians into the AIF until May 1917 when enlistment standards were relaxed to include 'half-castes' with a parent of European origin. Indigenous soldiers served as valuable members of the Light Horse and many possessed excellent horse handling skills and specialist tracking knowledge.The subject items are part of the uniform for the Light Horse Units that served in the Australian army from 1899 until 1918. These leggings were worn by soldiers on horseback and are significant as they represent a noteworthy time in Australia's early military history. It was a time when many young men gave their lives during the South African and First World Wars in the defence of the then British Empire as part of the Imperial Forces that were gathered from many British-controlled Colonial countries.A pair of two Leather Leggings used by Mounted Australian soldiers during the first world war. The leggings are dark tan in colour with stitching to attach buckles and fastener straps. The strap buckles are made of brass and the leather legging straps are of same leather as leggings. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, leggings, leather leggings, protective leggings, protective clothing, australian mounted light horse units, military equipment -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Container - GRAHAM HOOKEY COLLECTION: BRASS 'COMFORTS' TIN
Brass gift box, presented to serving military personnel in World War 1. Attributed as being the brainchild of Princess Mary, daughter of King George V and Queen Mary. On top of tin the head of the Princess is surrounded by a laurel wreath. Embossed on top 'Imperium Britannicum', on bottom 'Christmas 1914' This tin was found in a secretaire given to Graham Hookey, inside the tin is gold woven epaulette, nibs for a dip pen and a small lock 'Miller' embossed on front. Also enclosed are two medals - one metal 'volunteered for active service' printed around outside of medal, other two appear to be off a uniform, another 'corps of engineers' gold badge. Rising sun medal with 'Australian Commonwealth Military Force' embossed.australia, military, brass comfort tin -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Melbourne University Publishing, The broken years, 2010
Before the First World War most Australians shared the emotions and traditions of the British Empire. Proud of their British heritage, anxious to raise the Imperial status of Australia, they were eager to fight and, if need be, to die in defence of their race and country. But the horror and tragedy of the conflict brought fundamental changes in outlook. Many of the pre-war enthusiasms persisted, but the days of unquestioning allegiance to Empire were beginning to come to an end, to be replaced by the bittersweet tradition of Anzac. Dr Gammage shows how and why these changes took place. Using the diaries and letters of one thousand front-line soldiers of the First Australian Imperial Force, most of them now part of a unique collection housed in the Australian War Memorial in Canberra, he reconstructs the motives and expectations with which these men volunteered and the experiences they encountered. He highlights and examines the new attitudes to war and to the homeland that developed and foreshadows the important effects in Australia of the changed outlook brought home by the survivors. Those who have returned from war will recognise immediately the raw realities faced by the 'diggers', the growing disillusionment, and the hopes for the future. Those with fathers, husbands, or brothers who served, and all those concerned with what happens to men at war, cannot fail to be moved by the simple dignity of the men{u2019}s accounts, or by the understated courage with which they wrote to their families of the miseries they endured. This book, written with sensitivity and scholarly care, must be read if we are to understand war and its impact on the ethos of a nation.Index, bib, ill, notes, p.288.non-fictionBefore the First World War most Australians shared the emotions and traditions of the British Empire. Proud of their British heritage, anxious to raise the Imperial status of Australia, they were eager to fight and, if need be, to die in defence of their race and country. But the horror and tragedy of the conflict brought fundamental changes in outlook. Many of the pre-war enthusiasms persisted, but the days of unquestioning allegiance to Empire were beginning to come to an end, to be replaced by the bittersweet tradition of Anzac. Dr Gammage shows how and why these changes took place. Using the diaries and letters of one thousand front-line soldiers of the First Australian Imperial Force, most of them now part of a unique collection housed in the Australian War Memorial in Canberra, he reconstructs the motives and expectations with which these men volunteered and the experiences they encountered. He highlights and examines the new attitudes to war and to the homeland that developed and foreshadows the important effects in Australia of the changed outlook brought home by the survivors. Those who have returned from war will recognise immediately the raw realities faced by the 'diggers', the growing disillusionment, and the hopes for the future. Those with fathers, husbands, or brothers who served, and all those concerned with what happens to men at war, cannot fail to be moved by the simple dignity of the men{u2019}s accounts, or by the understated courage with which they wrote to their families of the miseries they endured. This book, written with sensitivity and scholarly care, must be read if we are to understand war and its impact on the ethos of a nation. world war 1914-1918 - personal correspondence, world war 1914-1918 - social conditions -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph
The Battle of Tarakan was the first stage in the Borneo campaign of 1945. It began with an amphibious landing by Australian forces on 1 May, code-named Operation Oboe One. While the battle ended with success for the Allied forces over the Japanese defenders, this victory is generally regarded as having not justified its costs. 225 Australian soldiers of the 26th Brigade, 9th Division, 2nd Australian Imperial Force were once buried here. They were killed in the Battle of Tarakan (1 May - 21 June 1945) or died due to their wounds until 15 August 1945.The 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of a monument/cenotaph and lawn grave sites with white crosses.Handwritten on rear - Tarakan Cemetery2/24th battalion, wangaratta, tarakan -
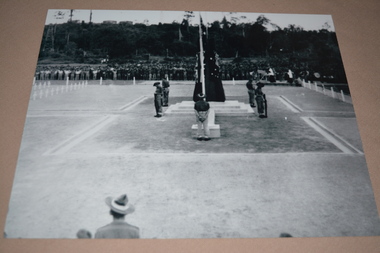 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph
September 30,1945 - The official dedication service and unveiling of the Cenotaph at Tarakan War Cemetery The Battle of Tarakan was the first stage in the Borneo campaign of 1945. It began with an amphibious landing by Australian forces on 1 May, code-named Operation Oboe One. While the battle ended with success for the Allied forces over the Japanese defenders, this victory is generally regarded as having not justified its costs. 225 Australian soldiers of the 26th Brigade, 9th Division, 2nd Australian Imperial Force were once buried here. They were killed in the Battle of Tarakan (1 May - 21 June 1945) or died due to their wounds until 15 August 1945.The 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of monument/cenotaph and catafalque party2/24th battalion, tarakan, cenotaph -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchFramed certificate, Certificate from Royal Australian Air Force to Henry F Zeffert for service in Volunteer Air Observers Corps. Dated 24th October 1945
Certificate from Royal Australian Air Force to Henry F Zeffert for service in Volunteer Air Observers Corps. Dated 24th October 1945
