Showing 3719 items
matching instruments-measuring
-
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - COMPASS, PROTRACTOR, RULER, Est WWI
... instruments-measuring ...The 3 items belonged to Sgt Jack Grinton No 1043, 38th Batt AIF. The ruler was broken by a small piece of shrapnel which then passed through a wallet containing photos. Refer Cat No 1280 for service details. Refer 1317P, 1320P, 1241.22P, 1278.2. Part of the Grinton collection which included hundreds of negatives and developed photos that he took during the War..1) Pocket compass, metal and glass, mirror backed. .2) Protractor-wooden, metal stud and ring. .3) Ruler, wood, in 2 parts..2) "Veare wood" .3) One inch and centimetre increments.instruments-measuring, surveyors-terrestrial -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, Budget blowout, 1991
Nunawading Council is facing a potential $3.3 million budget blowout and could go into the 1991-92 budget with a $1m deficit.Nunawading Council is facing a potential $3.3 million budget blowout and could go into the 1991-92 budget with a $1m deficit. Mayor Bruce Atkinson said the present $2m deficit was covered by the measures taken in the mini budget.Nunawading Council is facing a potential $3.3 million budget blowout and could go into the 1991-92 budget with a $1m deficit. city of nunawading, atkinson, bruce, local government finance -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionInstrument - Scientific Instrument, E. & G.W. Blunt, Sextant
A sextant is an instrument generally used to measure the altitude of a celestial object above the horizon. Sextant with a black timber (ebony?) frame, ivory graduated scales and brass attachments : vernier scale radial arm, mirrors and optical filterssextant, astronomy, scientific object, scientific instruments -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneEquipment, The Lane Poole Recording Caliper
Measuring instrument for tree diameters. 3x metal components in fitted timber case.EquipmentM.U.Forestry -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Cup, Chemist Measure cup
This measuring container would have been used by chemists, doctors and nurses to accurately measure a tablespoonful of medicine or other liquid or substance equivalent to half an ounce in weight. It could also have been used in households for the same purpose. It would have been in use in the 19th century and perhaps the first six decades of the 20th century. Today glass or plastic containers would be used. This container, although damaged, is of interest as an example of the type of measuring container used by chemists and doctors in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It has no known local provenance but will be useful for display. This is a cream-coloured ceramic medicine measuring container. It will hold half an ounce or a tablespoonful. It is circular in shape, tapering down from the top to the bottom. It has a rim at the top which is cracked and partly broken away. ‘½ oz. To Lower Rim (a tablespoonful)’ chemists in warrnambool, history of warrnambool, medical aids, ceramic medicine glass -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyCarpenters Measures
2 Carpenters measures, both with 66 foot measure. a. Cloth measure in brass case. b. Metal measure in metal case.measures, measuring instruments, carpentry tools -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Instrument - Spring Balance
... instruments ...Metal instrument for weighing - possibly in a butcher's shop. Round ring at top attached to a round dial measuring pounds(lbs) up to 200 lbs. Indicator on dial. Large hook at base of dial to attach the item to be weighed.0 - 200 Salter's Spring Balance British Made Silvester's Patent to Weigh 200 lb.instruments, weighing -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyDomestic object - Scales, L.F. & C, Pocket Balance Scales, 1900 c
Small, very old pocket balance scales 0 L.F. & C. Made in New York. Possible belonged to and used by the Bishop family 1900's/30's. The front plate is brass. The wording on the scales is "Not Legal For Use In Trade". The scales measure up to 25lb.Small very old pocket balance scales, front plate is brass. The wording on the scales is Not Legal For Use In Trade,. Scales measure up to 25lb.scales, kitchenware -
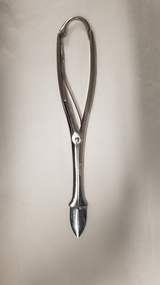 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Naegele-style perforator associated with Dr Michael Kloss
This instrument was part of a collection of instruments associated with Dr Michael Kloss and his medical practice. Dr Kloss subsequently donated this collection to the College.Metal perforator. Instrument consists of two straight, pointed blades with screw joint, and a spring loaded insert. Also includes a connecting spring bar at top of handle. Perforator is engraved with the word 'Kloss'. Inner aspect of perforator is engraved with a three digit number , '21...'. The third number is illegible.'Kloss'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Urinary catheter used by Dr Michael Kloss
This instrument was part of a collection of instruments used by Dr Michael Kloss in his medical practice. Dr Kloss subsequently donated this collection to the College.Metal uterine catheter. Thin, small, curved instrument in the shape of a narrow tube. There is a circular fitting at one end of the tube, and the tube curves as it reaches a rounded, hollow tip at the other end. A strip of metal topped by a rounded fitting extends from the hollow end of the tube, forming a circular loop.obstetrics -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneEquipment
Caliper style measuring instrument. Measurements in cm along length. Fixed and moveable bars (red)Equipment -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Collin's-type pelvimeter used by Dr Fritz Duras
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany , and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. Metal pelvimeter. Consists of a device with two arms, which curve into rounded points at their ends. A semi-circular measuring gauge is attached to the end of the pelvimeter.obstetrics -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Instrument, Soprano saxaphone and Box
This musical instrument belonged to Donald Robert McDonald who was a member of a prominent South Warrnambool family. As his army service number is on the case it is presumed that he had the musical instrument with him during his wartime service (World War Two). Donald Robert McDonald (b. 1908) enlisted in 1942 and was discharged in 1946. He was a bombardier in the 2/4 Aust. Composite A/A Regiment.The instrument is significant because it belonged to a member of a prominent South Warrnambool family. It had historical and social significance as an example of the musical entertainment common in the 1940s (perhaps Donald McDonald played in a local band or a military band)Silver-coloured soprano saxophone; end taped with mouthpiece missing; Black case for holding a musical instrument made of moulded cardboard and lined with black velvet. It has a leather handle and metal catches and studs. ‘Trade Mark Boosey’ ‘Boosey and Co Makers London 25081’ ‘British Throughout’ donald robert mcdonald, south warrnambool, south warrnambool, 2/4 aust. composite a/a regiment., warrnambool -
 Victoria Police Museum
Victoria Police MuseumPhotograph (police car)
Holden van with two MTS police sitting on the tailgate in full uniform, including hats, coats, breeches, boots and recording instruments, presumably for speed. Circa 1967. Operating an Amphometer speed measuring device. St.Georges Rd North Fitzroypolice vehicles; motor transport branch; motor transport section; holden courtesy van -
 Learmonth and District Historical Society Inc.
Learmonth and District Historical Society Inc.Scales, "Circa 1863"
This set of scales would have been used to check the acuracy of Weights and Measures.Where it was used is unknown, but it may have always been part of the Shire.The maker was J.D.Potter,Poultry,London Middlesex,U.K. One of several sets of scales of various sizes in collection of Learmonth And District Historical Society Inc.To measure precise weights,the instruments used were a set of precise balanced scales. Set on a wooden box,( which would have contained the weights).It is made of brass and has a brass beam balance,steel pointer with index and twin pans. Date 25/1/1865.Various hallmarks similar to "jewellers".tools, and, scales, weights, measures, potter london, measuring devices -
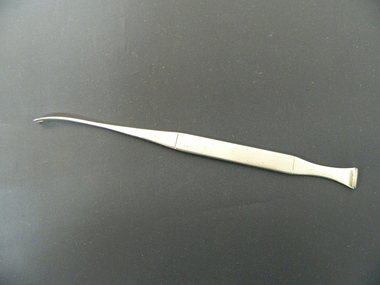 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyTonsil Dissector and Pillar Retractor
This medical instrument was used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was built in the 1950s specifically for the increase in population due to the Kiewa Hydro Scheme. Historical: Shows the development of scientific hospital equipment. Provenance: Used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was remote and therefore required good equipment.Metal instrument that is shaped like a elongated fish with a long pointy 'face' that is slightly curved. When turned on its edge 2 teeth can be seen at the end. Retracts the membrane (pillar) in front of the tonsil.medical instrument. hospital equipment. tawonga. mt beauty. tonsil -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instrument, Goniometer
A goniometer is an instrument that either measures an angle or allows an object to be rotated to a precise angular position. The term goniometry is derived from two Greek words, gōnia, meaning angle, and metron, meaning measure. (Wikipedia)Goniometer in a timber box. (eleven parts)galvometer, ganiometer, j. swift and sons -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncMemorabilia - Realia, 1900's
One Chain Measure. Used for Survey or Farm Measurestawell -
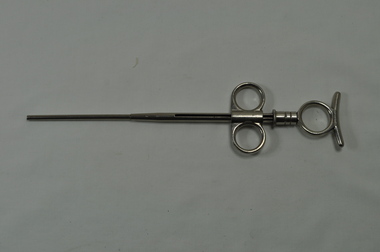 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyTonsil Snare
This medical / hospital instrument was used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was built in the 1950s specifically for the increase in population due to the Kiewa Hydro Scheme.Historical: Shows the development of scientific hospital equipment. Provenance: Used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was remote and it therefore required good equipment.Long metal instrument with sliding two finger piece. The other end is hollow and fitted with a very fine wire which was used to snare the tonsil (or nasal polyps). Note: incomplete - wire to be fitted into holes.BRITISHMADE at handle end.medical equipment. hospital equipment. tawonga. hospital. mt beauty. medical instrument. nurse. medical. tonsil. -
 Parks Victoria - Maldon State Battery
Parks Victoria - Maldon State BatteryScales, platform
Similar to railway platform scales and may have been relocated from the nearby Maldon Railway station. The history of its use at the battery is unknown.Large cast iron platform scale, white painted base with 2 wheels. The cast iron plate sits on top of a base with an inscription. There is white and green floral decoration on the frame, which is attached to the base. The white decorative stand with tray and weight measure attached has an inscription.base- "W. & T. Avery Ltd/makers/London &/Birmingham". Platform- "W. & T. Avery Ltd. Weight measure- LB 14 12 10 8 6 4 2" -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instrument, Orsat Apparatus
The Orsat was returned to the Historical Collection by Len Taylor, former staff member of SMB. For a period of time it was with Gary Price who rebuilt the Orsat to working order. Gary used a similar apparatus at Sidchrome and Ballarat Heat Treatment Pty. The Orsat apparatus is used to measure volumes of Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen, and Carbon Monoxide within a fixed volume of a sample of gas.Timber box with lift up front revealing a number of valves, pressure measure and glass container of red liquid attached to hose. Gas analysis apparatusorsat, len taylor, gary price, carbon dioxide, oxygen, carbon monoxide, gas, measure, apparatus -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumW&M Fl. Oz. Measuing Kit
8692.1 - Large grey painted metal box with hinged lid, metal latch and a black handle on top. 8692.2 - Glass measuring jug. 8692.3 - Glass measuring jug. 8692.4 - Glass measuring jug. 8692.5 - Glass measuring jug. 8692.6 - Glass measuring jug. 8692.7 - Glass measuring jug.8692.1 - W&M 8692.2 - VIC - 1 Pint - 20 Fl. Oz. 8692.3 - VIC - 4 Fl. Oz. - 32 Fl. Dr. 8692.4 - VIC - C 68° F - 16 FLDR - 2 FLOZ. 8692.5 - VIC - 8 FLDR - 11 FLOZ. 8692.6 - VIC - 4 FLDR - 240 MIN. 8692.7 - VIC - 2 FLDR - 120 MIN. -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumGunter chain (broken)
8653.1- Rusty measuring chain. 8653.2 - Rusty measuring chain. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionAmmeter, Henry Sutton (probably), Ammeter attributed to Henry Sutton, 1883 (estimated)
W.B Withers wrote of Sutton: "In the realm of science Ballarat has become of world-wide fame through the inventions by Mr Henry Sutton, a native of the place. His skill and acquirements in electricity, telegraphy, telephony, photography and also in astronomical and microscopal studies have won for him a high position as a practical scientist, and the credit is the greater as he is a self-taught student … Mr Sutton, before he was fourteen years old, had read every book on science to be found in the library of the Ballarat Mechanics' Institute." The Ballarat School of Mines (SMB) was fortunate to have this genius appointed as the lecturer-in-charge of the new Electricity and Magnetism department from 23 April 1883. Although Henry Sutton submitted his resignation to the Council of SMB in October 1884 it was resolved that he be asked to reconsider, and Mr Sutton continued to teach at SMB until the end of 1886. He was a prominent member of the Camera Club, and many of the other SMB clubs. Sutton had an active and fertile brain, and was known for his inventions, especially his work on the telephone, telephane and carbon lamps. Sutton presented a vacuum pump, worked by water jet, for use in SMB Chemistry classes. His report of 1883 states: ‘A telephonic circuit has been laid down between the [SMB] engine-house and workshops, to be used for experimental purposes.’ Henry Sutton spent much thought on artificial flight, and made some interesting experimental studies with flying birds. The storage of electricty also attracted his attention, and, after much work and thought evolved the Sutton Secondary Battery. A paper on this battery was presented to the Royal Society, London, and was afterwards printed in the 'Transactions'. Henry Sutton is listed on the Federation University Honour Roll at https://www.federation.edu.au/curator/honour-roll/honourroll_sutton.shtmlA crude scientific instrument that measures amps, with a timber base and frame. Terminal posts and sliders contacts are positioned on top of the base, with flex attached. Henry Sutton lectured at the Ballarat School of Mines (SMB) in Electricty and Magnestism between 1883 and 1886. In 1883 Sutton reported: ‘…The class has been unfortunately situated, by having to wait for instruments of precision ordered from England, but which have not come to hand. The delay has caused us to start constructing instruments, which it is hoped will bear favourable comparison with those of older date.'ammeter, henry sutton, electrical, inventor, electricity and magnetism, sutton, scientific instruments -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumX-Ray Spectrograph, Laby/Hilger
The spectrograph employs the principle of single crystal Bragg X-Ray Diffraction to measure wavelengths by interpolation from accepted standard lines. It is suitable for the identification and determination of the charateristic emissions of elements and thus for X-Ray spectrum analysis. The instrument was manufactured by ADAM HILGER Ltd. to the design of Professor Laby and is the best preserved instrument surviving from his research activity. A full description is given in the Hilger Pamphlet with the instrument; alternatively see duplicate in Appendix A5,A6 in Vol 2 of Laby ‘s COLLECTED PAPERS.Laby Bibliography by R W Home “Physics in Australia 1945” pp 106-08; also reproduced by permission as Appenix C in “A Man Ahead of his TImes”By E G Muirhead References. nos 45, 41, 47, 52, 53 -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumX-Ray Spectrograph, Laby/Hilger
The spectrograph employs the principle of single crystal Bragg X-Ray Diffraction to measure wavelengths by interpolation from accepted standard lines. It is suitable for the identification and determination of the charateristic emissions of elements and thus for X-Ray spectrum analysis. The instrument was manufactured by ADAM HILGER Ltd. to the design of Professor Laby and is the best preserved instrument surviving from his research activity. A full description is given in the Hilger Pamphlet with the instrument; alternatively see duplicate in Appendix A5,A6 in Vol 2 of Laby ‘s COLLECTED PAPERS. -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneEquipment, Universal Avometer
Instrumentass. No. 38 -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumInstrument - PH Meter For Use in Woollen Mill, c.1940
A complex instrument used to determine the pH factor of liquid samples, in this case, dyes. Without this instrument to measure the pH level of dyes before use, it would be impossible to ensure successful and repeatable results when dyeing wool.pH meter contained within dark wooden box, opened with two brass clasps. Contains dials, an electrode, glass bottle of potassium chloride and instructions for use on card inside lid.textile testing, dyeing, woollen mill, ph, scientific instument -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Surgical Instrument Roll, C early 1900's
This surgical instrument roll has loops into which various surgical instruments would be placed. The flaps of the fabric would then be folded inwards over the instruments, then rolled up, then the long ties would be tied up to create a secure kit. The 'roll' would be very portable and could also keep the instruments together whilst being sterilised. it is most probable that it belonged to Dr. Tom Ryan and was later handed on to Dr. Angus, dating the roll then to the late 1800's. This instrument roll was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1941-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Surgical instrument roll, part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Cloth fabric, custom made with loops and ties for organising and storing surgical instruments, making them easily carried and accessed.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, medical history, surgical instrument roll, fabric case for holding surgical instruments, portable surgical instrument container -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Instrument - Mathematical Instruments
... instruments ...Believed to be 70 years old.Flat grey box containing four set squares in the lid, one compass, one ruler, two pieces of cork (not numbered), two pencils (not numbered), and an eraser (not numbered).The School Set of Mathematical Instrumentsinstruments, measuring
