Showing 1145 items matching "peterborough"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Ship Compass Sections, 1886
A ship's compass played an extremely important role in navigating the ship from the port to its destination. If there was a slight inaccuracy in its calibration the ship could miss its destination and crash or be wrecked. The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roofing tiles, barb wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject model is an example of an International Cargo Ship used during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods worldwide and represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The compass sections are also significant for belonging to the compass of the Falls of Halladale. It was a critical part of the ship's equipment. Compass sections, two; brass disc with a round object on a pedestal, together with a glass disc with a metal frame and insert in the centre. Both items were recovered from compass on the wreck of Falls of Halladale. Nonewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, compass sections, falls of halladale, wreck of halladale, ship compass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Step Tread Protector, Russell & Co, 1886
The ornate brass step protector was used to protect stair treads and was fitted to the front edge of a tread to minimise wearing of the wooden tread. This item was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roofing tiles, barbed wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject model is an example of an International Cargo Ship used during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods around the world and representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. Step tread protector; brass with fancy cutouts. Lower section has screw holes drilled through. Recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, shipwreck artefact, step tread protector, ship fitting, falls of halladale -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Lamp Glass, 1886-1908
The lamp glass was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. It was blown into a mould, as evidenced by ripples in the base of the glass. The frosted inside area is likely to be from abrasive sediment inside the glass on the sea bed. The encrustations has also come from the sea. The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roofing tiles, barb wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in 1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breckenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject model is an example of an International Cargo Ship used during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods around the world and representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. Lamp glass, scalloped pattern around top lip, bulbous body. Slight encrustation on body. Glass has ripples in base area. Inside body is opaque in about a 1/5 ofr the area.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, glass, russell & co., wreck, artifact, lamp glass, kerosene lamp, lighting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - "S" Hook Buckle, Ca. 1855
The "S" hook buckles were grouped together under the sea as part of the cargo of the vessel Schomberg. "S" hook buckles are used for fastening two ends of fabric together such as harness belts, trouser belts and similar items. The buckles were recovered in October 1980 by the Flagstaff Hill Sub-Aqua Group, Peter Ronald, Barry Lowther and Jeff Bell. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This group of "S" hook buckles and conglomeration of buckles is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century and the items carried on ship as cargo. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. "S" hook buckles; oval silver alloy buckles contained within a conglomeration of materials from the sea. The group was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, horse harness fitting, harness hardware, "s" hook buckle, "s" hook buckles, conglomeration of buckles, belt buckle, fastener, quick release fastener, flagstaff hill sub-aqua group, peter ronald, barry lowther, jeff bell -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Pulley Sheave, Circa 1886
The pulley sheave comes from the Falls of Halladale, a four-masted iron-hulled barque that was built in 1886 for the long-distance bulk carrier trade. The vessel was built for the Falls Line (Wright, Breakenridge & Co., Glasgow, Scotland) at the shipyard of Russell & Co., Greenock on the River Clyde, she was named after a waterfall on the Halladale River in the Caithness district of Scotland. The ship's design was advanced for her time, incorporating features that improved crew safety and efficiency such as elevated bridges to allow the crew to move between forward and aft in relative safety during heavy seas. The Falls of Halladale was the seventh vessel in a series of eight similar iron-hulled sailing ships, all built by Russell & Co and all named after waterfalls in Scotland. The Falls of Halladale was preceded by the Falls of Clyde (1878), the Falls of Bruar (1879), the Falls of Dee (1882), the Falls of Afton (1882), the Falls of Foyers (1883) and the Falls of Earn (1884). The Falls of Halladale was followed by a sister ship, the Falls of Garry (1886). The Falls of Clyde is afloat today and is a major attraction at the Hawaii Maritime Center in Honolulu. The Falls of Halladale is best known for her spectacular demise in a shipwreck near Peterborough, Victoria on the shipwreck coast of Victoria, Australia. On the night of 14 November 1908, she was sailed in dense fog directly onto the rocks due to a navigational error. The crew of 29 abandoned ship safely and all made it ashore by boat, leaving the ship foundering with her sails set. For weeks after the wreck, large crowds gathered to view the ship as she gradually broke up and then sank in the shallow water. Soon after the accident the ship's master, Capt. David Wood Thomson was brought before a Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne and found guilty of a gross act of misconduct, having carelessly navigated the ship, having neglected to take proper soundings, and having failed to place the ship on a port tack before it became too late to avoid the shipwreck. Capt. Thomson's punishment included a small fine and he had his Certificate of Competency as a Master suspended for six months. Today the Falls of Halladale is a popular destination for recreational divers. The wreck is easily accessible by scuba divers about 300 m offshore in 3 to 15 m of water. The hull lies on its collapsed starboard side. Some of the original cargo of 56,763 roof slates remains at the site of the wreck along with corroded masses of what used to be coils of barbed wire. Twenty-two thousand slates were salvaged in the 1980s and used to provide roofing at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. An anchor that was recovered in 1974 is on display at the village. The pulley sheave is significant as a salvaged item from the Victorian heritage-listed Falls of Halladale wreck. As an artifact from the wrecked ship, it helps us to remember today the story of the wrecking and is an important reminder of a marine incident in Victoria's maritime history. Wooden Pulley Sheave from the vessel Falls of HalladaleNoneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wooden pulley sheave, falls of halladale -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, post 1889
The photograph shows the three-masted iron and steel bark "Newfield" sailing in open seas. It event would have been between 1889-1892 during the ship's working life. ABOUT THE NEWFIELD The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast and at about 1:30am ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The Port Campbell rocket crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. A local man, Peter Carmody, volunteered to swim one mile to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. One of the men, apprentice William McLeod, was rescued by local woman Margaret E. MacKenzie. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum has several artefacts that have been salvaged from the wreck. The report from SHP documented the following in regards to the Newfield collection: Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, because of its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of its relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as it is the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 (Living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck. Black and white photograph of the three-masted sailing ship “Newfield” in the open sea, sails unfurled. The ship was built in 1859 by Alexander Stephen and Sons Limited of Dundee, Scotland. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, barque newfield, photograph, 1880s sailing ship -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Key, 1886
The key was recovered from the Falls of Halladale, a four-masted iron-hulled barque that was built in 1886 for the long-distance bulk carrier trade. The vessel was built for the Falls Line (Wright, Breakenridge & Co., Glasgow, Scotland) at the shipyard of Russell & Co., Greenock on the River Clyde, she was named after a waterfall on the Halladale River in the Caithness district of Scotland. The ship's design was advanced for her time, incorporating features that improved crew safety and efficiency such as elevated bridges to allow the crew to move between forward and aft in relative safety during heavy seas. The Falls of Halladale was the seventh vessel in a series of eight similar iron-hulled sailing ships, all built by Russell & Co and all named after waterfalls in Scotland. The Falls of Halladale was preceded by the Falls of Clyde (1878), the Falls of Bruar (1879), the Falls of Dee (1882), the Falls of Afton (1882), the Falls of Foyers (1883) and the Falls of Earn (1884). The Falls of Halladale was followed by a sister ship, the Falls of Garry (1886). The Falls of Clyde is afloat today and is a major attraction at the Hawaii Maritime Centre in Honolulu. The Falls of Halladale is best known for her spectacular demise in a shipwreck near Peterborough, Victoria on the shipwreck coast of Victoria, Australia. On the night of 14 November 1908, she was sailed in dense fog directly onto the rocks due to a navigational error. The crew of 29 abandoned ship safely and all made it ashore by boat, leaving the ship foundering with her sails set. For weeks after the wreck, large crowds gathered to view the ship as she gradually broke up and then sank in the shallow water. Soon after the accident the ship's master, Capt. David Wood Thomson was brought before a Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne and found guilty of a gross act of misconduct, having carelessly navigated the ship, having neglected to take proper soundings, and having failed to place the ship on a port tack before it became too late to avoid the shipwreck. Capt. Thomson's punishment included a small fine and he had his Certificate of Competency as a Master suspended for six months. Today the Falls of Halladale is a popular destination for recreational divers. The wreck is easily accessible by scuba divers about 300 m offshore in 3 to 15 m of water. The hull lies on its collapsed starboard side. Some of the original cargo of 56,763 roof slates remains at the site of the wreck along with corroded masses of what used to be coils of barbed wire. Twenty-two thousand slates were salvaged in the 1980s and used to provide roofing at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. An anchor that was recovered in 1974 is on display at the village. The key is significant as a salvaged item from the Victorian heritage-listed Falls of Halladale wreck. As an artifact from the wrecked ship, it helps us to remember today the story of the wrecking and is an important reminder of a marine incident in Victoria's maritime history. KeyNoneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co., key -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Rope
The encrusted rope probably used on rigging comes from the Falls of Halladale, a four-masted iron-hulled barque that was built in 1886 for the long-distance bulk carrier trade. The vessel was built for the Falls Line (Wright, Breakenridge & Co., Glasgow, Scotland) at the shipyard of Russell & Co., Greenock on the River Clyde, she was named after a waterfall on the Halladale River in the Caithness district of Scotland. The ship's design was advanced for her time, incorporating features that improved crew safety and efficiency such as elevated bridges to allow the crew to move between forward and aft in relative safety during heavy seas. The Falls of Halladale was the seventh vessel in a series of eight similar iron-hulled sailing ships, all built by Russell & Co and all named after waterfalls in Scotland. The Falls of Halladale was preceded by the Falls of Clyde (1878), the Falls of Bruar (1879), the Falls of Dee (1882), the Falls of Afton (1882), the Falls of Foyers (1883) and the Falls of Earn (1884). The Falls of Halladale was followed by a sister ship, the Falls of Garry (1886). The Falls of Clyde is afloat today and is a major attraction at the Hawaii Maritime Centre in Honolulu. The Falls of Halladale is best known for her spectacular demise in a shipwreck near Peterborough, Victoria on the shipwreck coast of Victoria, Australia. On the night of 14 November 1908, she was sailed in dense fog directly onto the rocks due to a navigational error. The crew of 29 abandoned ship safely and all made it ashore by boat, leaving the ship foundering with her sails set. For weeks after the wreck, large crowds gathered to view the ship as she gradually broke up and then sank in the shallow water. Soon after the accident the ship's master, Capt. David Wood Thomson was brought before a Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne and found guilty of a gross act of misconduct, having carelessly navigated the ship, having neglected to take proper soundings, and having failed to place the ship on a port tack before it became too late to avoid the shipwreck. Capt. Thomson's punishment included a small fine and he had his Certificate of Competency as a Master suspended for six months. Today the Falls of Halladale is a popular destination for recreational divers. The wreck is easily accessible by scuba divers about 300 m offshore in 3 to 15 m of water. The hull lies on its collapsed starboard side. Some of the original cargo of 56,763 roof slates remains at the site of the wreck along with corroded masses of what used to be coils of barbed wire. Twenty-two thousand slates were salvaged in the 1980s and used to provide roofing at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. An anchor that was recovered in 1974 is on display at the village. The encrusted rope is significant as a salvaged item from the Victorian heritage-listed Falls of Halladale wreck. As an artifact from the wrecked ship, it helps us to remember today the story of the wrecking and is an important reminder of a marine incident in Victoria's maritime history.Piece of encrusted rope. Artifact Reg No FoH/1.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co., rope -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Pulley Sheave, Circa 1886
The pulley sheave comes from the Falls of Halladale, a four-masted iron-hulled barque that was built in 1886 for the long-distance bulk carrier trade. The vessel was built for the Falls Line (Wright, Breakenridge & Co., Glasgow, Scotland) at the shipyard of Russell & Co., Greenock on the River Clyde, she was named after a waterfall on the Halladale River in the Caithness district of Scotland. The ship's design was advanced for her time, incorporating features that improved crew safety and efficiency such as elevated bridges to allow the crew to move between forward and aft in relative safety during heavy seas. The Falls of Halladale was the seventh vessel in a series of eight similar iron-hulled sailing ships, all built by Russell & Co and all named after waterfalls in Scotland. The Falls of Halladale was preceded by the Falls of Clyde (1878), the Falls of Bruar (1879), the Falls of Dee (1882), the Falls of Afton (1882), the Falls of Foyers (1883) and the Falls of Earn (1884). The Falls of Halladale was followed by a sister ship, the Falls of Garry (1886). The Falls of Clyde is afloat today and is a major attraction at the Hawaii Maritime Center in Honolulu. The Falls of Halladale is best known for her spectacular demise in a shipwreck near Peterborough, Victoria on the shipwreck coast of Victoria, Australia. On the night of 14 November 1908, she was sailed in dense fog directly onto the rocks due to a navigational error. The crew of 29 abandoned ship safely and all made it ashore by boat, leaving the ship foundering with her sails set. For weeks after the wreck, large crowds gathered to view the ship as she gradually broke up and then sank in the shallow water. Soon after the accident the ship's master, Capt. David Wood Thomson was brought before a Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne and found guilty of a gross act of misconduct, having carelessly navigated the ship, having neglected to take proper soundings, and having failed to place the ship on a port tack before it became too late to avoid the shipwreck. Capt. Thomson's punishment included a small fine and he had his Certificate of Competency as a Master suspended for six months. Today the Falls of Halladale is a popular destination for recreational divers. The wreck is easily accessible by scuba divers about 300 m offshore in 3 to 15 m of water. The hull lies on its collapsed starboard side. Some of the original cargo of 56,763 roof slates remains at the site of the wreck along with corroded masses of what used to be coils of barbed wire. Twenty-two thousand slates were salvaged in the 1980s and used to provide roofing at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. An anchor that was recovered in 1974 is on display at the village. The pulley sheave is significant as a salvaged item from the Victorian heritage-listed Falls of Halladale wreck. As an artifact from the wrecked ship, it helps us to remember today the story of the wrecking and is an important reminder of a marine incident in Victoria's maritime history. Wooden Pulley Sheave from the vessel, Falls of HalladaleNoneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wooden pulley sheave, falls of halladale -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Vent Cover, circa 1886
The vent cover comes from the Falls of Halladale, a four-masted iron-hulled barque built in 1886 for the long-distance bulk carrier trade. The vessel was built for the Falls Line (Wright, Breakenridge & Co., Glasgow, Scotland) at the shipyard of Russell & Co., Greenock on the River Clyde, she was named after a waterfall on the Halladale River in the Caithness district of Scotland. The ship's design was advanced for her time, incorporating features that improved crew safety and efficiency such as elevated bridges to allow the crew to move between forward and aft in relative safety during heavy seas. The Falls of Halladale was the seventh vessel in a series of eight similar iron-hulled sailing ships, all built by Russell & Co and all named after waterfalls in Scotland. The Falls of Halladale was preceded by the Falls of Clyde (1878), the Falls of Bruar (1879), the Falls of Dee (1882), the Falls of Afton (1882), the Falls of Foyers (1883) and the Falls of Earn (1884). The Falls of Halladale was followed by a sister ship, the Falls of Garry (1886). The Falls of Clyde is afloat today and is a major attraction at the Hawaii Maritime Center in Honolulu. The Falls of Halladale is best known for her spectacular demise in a shipwreck near Peterborough, Victoria on the shipwreck coast of Victoria, Australia. On the night of 14 November 1908, she was sailed in dense fog directly onto the rocks due to a navigational error. The crew of 29 abandoned ship safely and all made it ashore by boat, leaving the ship foundering with her sails set. For weeks after the wreck, large crowds gathered to view the ship as she gradually broke up and then sank in the shallow water. Soon after the accident the ship's master, Capt. David Wood Thomson was brought before a Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne and found guilty of a gross act of misconduct, having carelessly navigated the ship, having neglected to take proper soundings, and having failed to place the ship on a port tack before it became too late to avoid the shipwreck. Capt. Thomson's punishment included a small fine and he had his Certificate of Competency as a Master suspended for six months. Today the Falls of Halladale is a popular destination for recreational divers. The wreck is easily accessible by scuba divers about 300 m offshore in 3 to 15 m of water. The hull lies on its collapsed starboard side. Some of the original cargo of 56,763 roof slates remains at the wreck's site along with corroded masses of what used to be coils of barbed wire. Twenty-two thousand slates were salvaged in the 1980s and used to provide roofing at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. An anchor that was recovered in 1974 is on display in the village. The pulley sheave is significant as a salvaged item from the Victorian heritage-listed Falls of Halladale wreck. As an artifact from the wrecked ship, it helps us to remember today the story of the wrecking and is an important reminder of a marine incident in Victoria's maritime history. Vent cover taken from the top of an iron Bollard. Recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, vent cover, falls of halladale, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Sheathing, Ca. 1855
This sheet of copper sheathing or Muntz metal has been recovered from the site of the wrecked ship Schomberg. It has been damaged by the reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and another damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. Early sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in seawater and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Early shipbuilders applied coatings of tar, was, lead or pitch onto the timber to prevent this. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the outsides of ships’ hulls were encased in either copper sheathing or Muntz metal, which is a combination of 60 per cent copper and 40 per cent zinc. The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. About the SCHOMBERG- James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned the luxury sailing ship, Schomberg, to be built for its fleet of passenger liners The three-masted wooden ship was launched in 1855, designed by the Aberdeen builders to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. The material used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. The Schomberg’s master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes commanded the ship on its maiden journey between Liverpool and Melbourne, departing on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. After sailing for 78 days she ran aground on a sand spit at Curdies Inlet near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December 1835. At dawn on the next day, the ship’s Chief Officer signalled a passing steamer, SS Queen, for help and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The passengers’ baggage and some of the cargo were later collected from the Schomberg. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and the remaining cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo that was still on board. They eventually sold it and after two of the men drowned in the salvage efforts the job was abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including former Director, Peter Ronald, explored the Schomberg wreck site and recovered many artefacts that are now on display at the Museum.The copper sheathing is significant for its connection with the Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large and fast clipper ship that sailed on the England-to-Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they can interpret the story of the ship, Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day.Copper sheathing; rectangular sheet of copper, shaped for use on a ship's hull, buckled, with fibres protruding from one edge. The object was recovered from the wreck of the SCHOMBERG.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, ship construction, copper sheating, sheathing, sea worm, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, shipbuilding -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Welsh Theological Dictionary - 2 volume, William Jones, A THEOLOGICAL DICTIONARY, 1837 & 1839
The Theological Dictionaries belonged to David and Alice Ellis, a young couple married in Dublin in 1855. They left for Australia on the Schomberg clipper ship on October 6 that same year, joining the other passengers for the luxury sailing ship’s first voyage, bound for Melbourne, Australia. The Schomberg was grounded on a sand spit near Peterborough. All passengers and crew were safely rescued. They had been allowed to take something small with them when leaving the sinking vessel, and as such, Alice took a small cane basket and coin purse. The Dictionaries were also amongst the couple’s possessions, along with a metal trunk, a Bible and a pair of candlesticks. These items were all later retrieved from the ship’s deck by the crew of a steamer sent from Melbourne. At that time, David was 23 years old (born in Wales, in 1832) and Alice was 26 (born in Ireland, 1829). The couple lived in Tasmania for a short period before settling in the Western Districts of Victoria. David worked as a gardener and, when land in the area was available to purchase, David and Alice claimed a selection on Noorat Road near Terang. They settled there for the remainder of their lives, expanding the property that they named, ‘Allambah’, and had six children. David died in 1911, aged 79, and Alice passed away the following year, aged 83. Two of David and Alice’s children, David jnr. and Grace adopted a daughter Nell Margaret Crick (nee Ellis). The Dictionaries were passed onto Nell with the misunderstanding (due to being written in the Welsh language) that they were Bibles. Nell pasted a piece of paper onto the front of the first volume recording ‘Welsh Bible 90 yrs old. April 3rd 1844’. The April date relates to the inscription inside both volumes and the 90 yrs old relates to the year Nell possibly received them, 1934. She has also added to the inscription page inside the first volume again recording ’Welsh Bible 90 yrs old. Miss. G Ellis “Allambah” Terang’. This implies that Grace Ellis had been the ‘keeper’ of the dictionaries. Grace and David Ellis were devout Christians which they passed on to their adopted daughter Nell, and were prominent members of the Noorat and Terang Presbyterian Churches. As David and Alice Ellis came out on the Schomberg in 1855, and the inscription inside both volumes of the Dictionary carries the date April 3rd 1844 and the name Thomas Ellis, it could be presumed that this was a family gift of significance to the couple as they began their new life in a country far away.The theological dictionaries are part of a group of donated possessions of David and Alice Ellis that have great significance as personal belongings, providing an insight into what emigrants considered important possessions to bring as they began a new life on the other side of the world. They are part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg shipwreck, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612). All items had been saved from the sinking luxury clipper ship, the Schomberg, in 1855. The ship has historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, built to carry emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. The ship’s design included the technical advances needed to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. The relationship of the objects in Flagstaff Hill’s Schomberg collection allows potential interpretation of the story of the Schomberg. The collection of objects is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship, as it represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history, in addition to its association with the shipwreck and the ship.A two volume set Theological Dictionary in Welsh. Both books are covered in brown leather with gold embossed patterns and words on the spine. The words 'GEIRIADUR DUWINYDDOL' (Theological dictionary) are on both spines towards the top and towards the bottom the number 1 or 2 dependent on the volume. The first volume, at around 900 pages, is slightly larger than the second volume, around 740 pages. The first volume has had a plain piece of paper glued to the front with the words 'Welsh Bible, 90 yrs old, April 3rd 1844'. Each volume has an inscription to Thomas Ellis inside the front cover, the date April 3rd 1844 and other words in Welsh. The first volume has added writing (in different handwriting) on the inscription page. The books are laid out in dictionary format with the first volume going from ABE to HYP. The second volume begins at IAC and ends at YST, followed by an Appendix and Index. The first volume was published in 1837 and the second volume in 1839.Volume 1 - Thomas Ellis ... 6 words in Welsh ... Aprill 3/44 (Handwriting 1) - Welsh Bible 90 yrs old, Miss G. Ellis, "Allambah" Terang. (Handwriting 2) Volume 2 - Thomas Ellis ... 6 words in Welsh (same as volume 1) ... Aprill 3/44flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, theological dictionaries, welsh theological dictionaries, welsh bible, schomberg, sailing ship, schomberg passengers, schomberg ship, 1855, 1855 shipwreck, peterborough shipwreck, david and alice ellis, david ellis jnr, grace ellis, nell ellis, nell crick, allambah terang, terang presbyterian church -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Compass, mid-19th Century
Captain Robilliard: James Arthur Robilliard was a sea captain and tentmaker, born on the 19th April 1843 at Saint Helier, Jersey. He trained there in his father's sail loft as a sailmaker. His first job as a sailor was in Liverpool, England and 1875 James Robilliard migrated to Australia as mate on the "E.M. Young". James Robilliard and his family were amongst the early settlers that arrived along the Curdies River in the Heytesbury district of Western Victoria. In 1877 he became a Captain and would have used his compass from ship to ship. On 28th May 1877 in that same district a small 3-masted, schooner the "Young Australian" was wrecked. This schooner had been built 1864 at Jervis Bay, NSW. She had been on her way from Maryborough Queensland to Adelaide, under the command of Captain Whitfield, when she lost her mainmast in a heavy gale. She was beached at Curdies Inlet in Peterborough, Victoria, Captain Robilliard was placed in charge of the salvaging operation and recovered a good portion of the cargo. Not long after this incident a Warrnambool shop owner David Evans found employment for James Robilliard with Evan Evans, who produced tents, sails, tarpaulins and similar goods; James already had the necessary skills for this work. Evan Evans was the same sailor rescued from the “Young Australian” soon after his rescue Evan recalled he had a relative in Australia in a town called Warrnambool and while walking in Timor Street, Warrnambool, he saw a sign over a shop that said “David Evans” and once the two men met, Evan was warmly welcomed. David then helped his relative to establish a tent and tarpaulin-making business there. Evan later transferred his successful business to a shop in Elizabeth St, Melbourne, under the name Evan Evans Pty. Ltd.) James Robilliard, a committed Christian, and accredited Lay Preacher with the Methodist Church. He travelled around the local district leading the settlers in worship. On 14th November 1879, Captain Robilliard married Helen Beckett. Alfred and Selina Beckett and their family all attended the church at Brucknell where Captain Robilliard preached. He was said to have been taken by their young daughter Helen. James and Helen had ten children; James Arthur (Jnr), Henry William, Nellie Jessie, Alfred Albert, Rubena Nellie, De Jersy Norman, Clifford Beckett, Olive Ida, Frances Ridley Havergal and Nellie Elvie, all born in Victoria. In the 1880s James Robilliard captained the cutter "Hannah Thompson" into Port Campbell, Victoria. This vessel was the first coastal trader to operate between Melbourne and Port Campbell. At one time Captain Robilliard had to beach the "Hannah Thompson" for repairs. In 1923 she was blown ashore in a gale and wrecked at Oberon Bay, at Wilson's Promontory. In 1889 the compass was saved by Captain James Arthur Robilliard from his sinking brigantine "Mary Campbell" in 1889. This vessel was used to carry equipment for the Sydney Sugar Refinery's Mill in Southgate, NSW. The ship had been built in 1869 and traded for the next 20 years between Australian ports and rivers along the east coast as well as regular ports in New Zealand. She was recognised by the Sydney Morning Herald as one of the best "carrying vessel in the timber trade". She had several owners over this time, the last one being Captain James A. Robilliard. On 29th April 1889 the "Mary Campbell", with Captain James A Robilliard as captain and owner, was on her way from Clarence River, NSW to Melbourne, Victoria with a cargo of railway girders for the Melbourne Harbour Trust. Captain Robilliard encountered a storm off Port Macquarie. He sailed the vessel south to about 40km east of Cape Hawke, near Tuncurry. At around 7 pm, he discovered that the cargo had shifted during the storm and the heavy girders had damaged the hull, causing a leak. The pumps were inadequate to stem the fast-flowing leak water soon filled the hull during the next two hours. Some of the crew began throwing the cargo overboard to lighten the vessel, hoping to keep it afloat until daylight. When the water reached over 2 meters in the hull they realised their efforts were in vain. On the 30th April 1889, the crew left the vessel the ship was sinking fast, so they made for the shore. While still miles off Cape Hawke all seven crew members, including the Captain, were rescued by the Government Tug "Rhea" and taken to Port Macquarie Hospital and later returned to Sydney in the vessel "Wellington". No cargo had been saved and the consignment had been under-insured, only covered for half its value. The name of the last ship Captain Robilliard sailed is currently unknown, however, he sailed that ship from the port of Marlborough, Queensland, carting steel railway girders for the Geelong-to-Camperdown railway line. On this trip the ship hit a storm, the cargo shifted and the ship was wrecked along the NSW coast. After this, Captain Robilliard retired from the sea and began farming in Peterborough. In about 1897, verging on retirement, Capt. Robilliard superintended the Melbourne Sailors’ Home in Spencer Street, Melbourne, before being asked to leave this position in 1902 for trying to shut down a local hotel. On 6th May 1917 Captain James Arthur Robilliard J.P. died at Blackwood Park, in the Cobden district of Brucknell, the first Robilliard family homestead in Australia. He was buried in the Melbourne General Cemetery, Victoria. His wife Helen passed away in 1947. This compass, once belonging to Captain James Arthur Robilliard, is of local and state historical significance for its use by the Captain with his vessel the "Mary Campbell", a trading vessel that was bringing railway girders to the Melbourne Harbour Trust. He also used this compass on the "Hannah Thompson", listed on the Victorian Heritage Register and known as being the first coastal trader to operate between Melbourne and Port Campbell. The compass is also a very fine example of maritime navigational instruments manufactured and used in the mid-19th century. Marine compass, brass, in wooden box with separate, fitted lid. The compass card has sixteen points. The four principal points are marked; North with a star shaped, South with an “S”, East with and “E” and West with an “O” (French word OUEST). Each quadrant of the circle is numbered from 0 – 90 degrees. The card is floating in a liquid. The compass gimbal is attached to the sides of the box and to the front and back of the compass’ cylindrical brass frame. The mahogany coloured timber storage box is joined with brass nails. The centre of the lid has a folding decorative brass handle. The lid fits over base and closes with a brass screw and hook on both front and back. Maker; Dubas Watchmaker Optician, Nantes, France, c 1860-1870. Compass came from the ship “Mary Campbell”, which sank off the NSW coast in 1889, near Forster. The compass, as well as the ship, belonged to Captain James Arthur Robilliard and was donated by his family. “DUBAS MANTES” stamped into side of gimbal. “DUBAS HORLOGER OPTICIEN. NANTES.” printed around centre of card. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, marine compass, navigation instrument 19th century, marine instruments, dubas mantes, captain james arthur robilliard, j.a. robilliard, helen beckett, ship young australian, ship young australia(n), ship hannah thompson, ship mary campbell, melbourne sailors home, david evans, evan evans, curdies inlet, brucknell church, curdies railway, great lakes museum -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHandle, c. 1859
This brass handle was found on Sea Elephant Bay beach in King Island, Tasmania, in 1913. The donor identified it as being from the wreck of the Newfield. It would could have been part of the fittings or amongst the cargo on the ship. ABOUT THE "NEWFIELD" The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast and at about 1:30am ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The Port Campbell rocket crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. A local man, Peter Carmody, volunteered to swim one mile to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. One of the men, apprentice William McLeod, was rescued by local woman Margaret E. MacKenzie. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum has several artefacts that have been salvaged from the wreck. A report from SHP documented the following in regards to the Newfield collection: Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, because of its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of its relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as it is the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 (Living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck. The Newfield collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criteria A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history Ornate brass handle, round plates each end, each with 4 round fixing holes. Found washed up on Sea Elephant Bay beach, King Island 1913, identified by donor as being from the wreck of the Newfield.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, barque newfield, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ornate handle, sailing ship fitting, sea elephant bay, king island -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Bulls Eye, 1886
Context: A deadeye or bullseye is an item used in the standing and running of sail rigging in traditional sailing ships. It is a smallish round thick wooden disc (usually lignum vitae) with one or more holes through it, perpendicular to the plane of the disc. History Falls of Halladale: The wooden bullseye comes from the Falls of Halladale, a four-masted iron-hulled barque that was built in 1886 for the long-distance bulk carrier trade. The vessel was built for the Falls Line (Wright, Breakenridge & Co., Glasgow, Scotland) at the shipyard of Russell & Co., Greenock on the River Clyde, she was named after a waterfall on the Halladale River in the Caithness district of Scotland. The ship's design was advanced for her time, incorporating features that improved crew safety and efficiency such as elevated bridges to allow the crew to move between forward and aft in relative safety during heavy seas. The Falls of Halladale was the seventh vessel in a series of eight similar iron-hulled sailing ships, all built by Russell & Co and all named after waterfalls in Scotland. The Falls of Halladale was preceded by the Falls of Clyde (1878), the Falls of Bruar (1879), the Falls of Dee (1882), the Falls of Afton (1882), the Falls of Foyers (1883) and the Falls of Earn (1884). The Falls of Halladale was followed by a sister ship, the Falls of Garry (1886). The Falls of Clyde is afloat today and is a major attraction at the Hawaii Maritime Centre in Honolulu. The Falls of Halladale is best known for her spectacular demise in a shipwreck near Peterborough, Victoria on the shipwreck coast of Victoria, Australia. On the night of 14 November 1908, she was sailed in dense fog directly onto the rocks due to a navigational error. The crew of 29 abandoned ship safely and all made it ashore by boat, leaving the ship foundering with her sails set. For weeks after the wreck, large crowds gathered to view the ship as she gradually broke up and then sank in the shallow water. Soon after the accident the ship's master, Capt. David Wood Thomson was brought before a Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne and found guilty of a gross act of misconduct, having carelessly navigated the ship, having neglected to take proper soundings, and having failed to place the ship on a port tack before it became too late to avoid the shipwreck. Capt. Thomson's punishment included a small fine and he had his Certificate of Competency as a Master suspended for six months. Today the Falls of Halladale is a popular destination for recreational divers. The wreck is easily accessible by scuba divers about 300 m offshore in 3 to 15 m of water. The hull lies on its collapsed starboard side. Some of the original cargo of 56,763 roof slates remains at the site of the wreck along with corroded masses of what used to be coils of barbed wire. Twenty-two thousand slates were salvaged in the 1980s and used to provide roofing at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. An anchor that was recovered in 1974 is on display at the village.The pulley sheave is significant as a salvaged item from the Victorian heritage-listed Falls of Halladale wreck. As an artifact from the wrecked ship, it helps us to remember today the story of the wrecking and is an important reminder of a marine incident in Victoria's maritime history.Carved wooden Bulls Eye/Deadeye, varnished.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co., bulls eye -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Buckle
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Set of 5 horse harness buckles, 2" x 2" Buckles are encased in concretion. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, horse harness, buckle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Ring
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Horse harness ring, 2" diameter Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, horse harness -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Ring
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Horse harness ring, 2" diameter Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, horse harness -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Ring
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Horse harness ring, 1½" diameter. Ring has piece of metal fused to it. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, horse harness -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Ring
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Horse harness ring, 1½" diameter Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHandle
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Ceramic handle. Handle is white with a small piece broken from end. 4" long. Retrieved from the Schombergflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, handle -
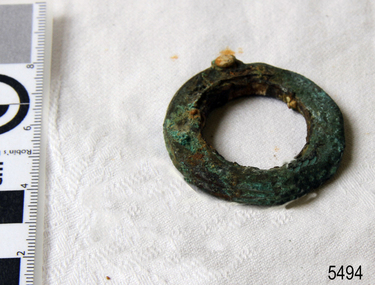 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWasher
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Flat brass washer diameter 1". Has some concretion. Retrieved from the Schombergflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, washer, brass washer -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNut
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Brass Hex nut 9/16". Retrieved from the Schombergflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEye Bolt
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Eye bolt, screw part visible. Bolt has a lot of encrustation. Length 4" Width 2½" Retrieved from the Schombergflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, eye bolt -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Buckle
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Part of a horse harness buckle, t-shaped. Retrieved from the Schombergflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoor knob
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Door knob section. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoor knob
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Door knob section. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNail
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper nail from the Schomberg. Small piece of concretion on the nail. Nail is bent.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, nail -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePrint - Maritme, Colonial Clipper Schomberg, 1992
This framed print of the famous clipper ship “Schomberg” is associated with Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the wreck of the “Schomberg”. The original was painted in 1992 by maritime artist Philip J. Gray. This limited edition print is number 9/1000. ABOUTH THE SUBJECT – “Schomberg” The Schomberg was a luxury ship built in 1855 to bring immigrants from the UK to Australia in superior comfort. The voyage could take three months or longer but Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes thought that he could sail the Schomberg from Liverpool to Melbourne in a record time of 60 days. On October 6th 1855 the Schomberg left Liverpool on its maiden voyage. She carried 430 passengers plus 3000 tons cargo including rail lines for Geelong and iron for a bridge in Melbourne. After 78 days at sea, on December 27th, Schomberg ran aground near Peterborough, Victoria. All on board were rescued the next day by the passing steamer SS Queen. Gray is well known for his depiction of maritime history. His meticulous attention to detail shows the enormity of the immigrant clipper with its huge billowing sails compared to the tiny figures at work on the deck. The busy crew can be seen attending to the rigging, as can a group of sailors working on the bow under supervision. He identifies the company logo of the Black Ball Ship Line by the flapping white flag with its black circle. Divers from Flagstaff Hill including Peter Ronald (former director) salvaged artefacts and personal effects from the wreck, to be preserved and displayed. Amongst these is the famous Schomberg Diamond ring. ABOUT THE ARTIST – Philip James Gray “Philip is one of Australia’s leading maritime artists and his meticulous research and social commentary paintings of ships, such as, the Loch Ard and Schomberg form an important part of Warrnambool’s Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum.” [ref. Dr Marion Manifold, Artist and Art Historian, 2014] Philip James Gray was born in London but has lived most of his life in Australia. He graduated from a London school of art as an illustrator, specialising in technical and scientific illustration as well as other commercial and applied art. He was also a student for a time of Fyffe Christie - British figurative artist, mural painter and humanitarian – who had a great influence on his career. Philip has always worked as a professional artist and illustrator. Many publications on maritime history have featured his work. His paintings have been released and sold all over the world as limited edition prints. The State Library of Victoria’s ‘Latrobe Collection’ holds two of his paintings. His street painting of ‘The Ashes Contest’ decorates the brick wall of Old Bakery Laneway in Sunbury and a Sunbury café owner commissioned him to paint the ‘Sunbury Pop Festival’ as a remembrance of local history. [ref. Sunbury Leader, Nov 15 2013] Philip has been an active member of the Sunbury Art Society in Victoria for several years, serving on the committee for some of that time and being involved in exhibitions. He enjoys helping new artists and sharing his skills and experience. The subject of the sailing ship “Schomberg” is significant for is connection with the 1800s vessel “Schomberg” and the historic role the ship, and other similar ships, played to transport migrants and goods into Australia. The print is significant as it is a limited edition of an Australian maritime artist. Print in gilt timber frame. "The Colonial Clipper Schomberg" by Australian maritime artist Philip J Gray, 1992. Signed and numbered, Limited Edition print 9/1000. Depicts clipper ship “Schomberg”, in full sail at sea with land in background. Backing of frame has illegible adhesive label and pencilled text. Stamp In pencil “FLAGSTAFF HILL” and “FLAGSTAFF C”. Illegible text on adhesive label. Signature [Philip J Gray] Stamped as a limited edition of SCHOMBERG Handwritten edition "9/1000"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, sailing ships, schomberg, clipper ship, colonial clipper, limited edition print, 9/1000, philip j gray, marine artist -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageButton
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day 1¼" brass button from the wreck of the Schomberg. Part of the button is cracked.warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, button
