Showing 3071 items matching "scales"
-
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Air Power Development Centre, Operation Pelican : The RAAF in the Berlin Airlift, 1948-1949, 2008
In 1948 Britain, France and the United States of America found themselves opposed to their former wartime ally, the Soviet Union, over matters regarding control of the capital of the defeated Nazi German regime. When the Soviets imposed a blockade of the city, the Allies had no option but to begin flying in the necessities of life for the two million inhabitants of the zones under their administration. Thus began the first large-scale humanitarian airlift in history. When Britain turned for support to its Dominion partners, the transport element of the Royal Australian Air Force had recently ceased flying a regular courier service for Australian occupation forces involved in garrisoning another defeated Axis power of World War II, Japan - this role having been handed over to a commercial airline. By September 1948 an unnumbered Australian squadron had joined other RAAF transport crews already engaged as part of the massive allied undertaking. To the Americans the fifteen-month-long operation was codenamed Vittles, while the British called it Plainfare. But to the Royal Australian Air Force personnel involved, the Berlin Airlift was known as Pelican. Here the story is told of the events that made the airlift necessary, what the undertaking entailed and the part that Australians played in it, as well as the outcome and achievements of Operation Pelican.Ill, maps, p.82.non-fictionIn 1948 Britain, France and the United States of America found themselves opposed to their former wartime ally, the Soviet Union, over matters regarding control of the capital of the defeated Nazi German regime. When the Soviets imposed a blockade of the city, the Allies had no option but to begin flying in the necessities of life for the two million inhabitants of the zones under their administration. Thus began the first large-scale humanitarian airlift in history. When Britain turned for support to its Dominion partners, the transport element of the Royal Australian Air Force had recently ceased flying a regular courier service for Australian occupation forces involved in garrisoning another defeated Axis power of World War II, Japan - this role having been handed over to a commercial airline. By September 1948 an unnumbered Australian squadron had joined other RAAF transport crews already engaged as part of the massive allied undertaking. To the Americans the fifteen-month-long operation was codenamed Vittles, while the British called it Plainfare. But to the Royal Australian Air Force personnel involved, the Berlin Airlift was known as Pelican. Here the story is told of the events that made the airlift necessary, what the undertaking entailed and the part that Australians played in it, as well as the outcome and achievements of Operation Pelican.cold war - history, berlin airlift 1948-1949 -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncDocument - Folder, Smith, Sydney and Rebecca
Sydney Smith (1821-1886) came to Australia as a young man. After marrying and some years in Epping, he moved to the Diamond Creek area. Contents Photocopy typed notes, undated, on Sydney Smith, family and descendants. Newspaper clippings, A4 photocopies, etcsydney smith, william smith, elizabeth smith, henty family, rebecca lee, william lee, elizabeth lee, john matthews, mary ann lee, ship maitland, william henny, rebecca matthews, mary ann matthews, scale family of epping, emma smith, thomas smith, robert smith, james smith, rebecca smith, reuben smith, sarah sussannah smith, emma jane smith, midhurst at arthur's creek, arthur's creek road, frank kurnell, elizabeth smith nee johnson, william johnson, sarah johnson, st john's church diamond creek, arthur j pickering, charlotte harrison, sarah janes laura smith, william sydney smith, rebecca edith maud smith, thomas james leslie smith, elizabeth mary mabel smith, florence ellen isobel smith, albert percival smith, evelyn hazel walher smith, elsie may smith, jack's creek waterworks, toorourrong reservoir, doctors gully road, harold bassett, hazel glen state school, wesleyan sunday school hazel glen, middle station creek glenburn, glenburn school, allan ferguson, diamond creek state school, haley's gully road arthur's creek -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumBook, The Best Show Ever, First printed 2010
AUGUST 1943 WAS A TURNING POINT FOR THE CLUNES AGRICULTERAL SOCIETY. IT MARKED THE DEATH OF MR JOHN ROBINS CARTER OF "SCALE-PARK" CLUNES...SOFT COVER BOOK, WHITE COVER, AN IMAGE OF A DRAUGHT HORSE, (LINO TYPE) STEPPING OFF. 215 pagesnon-fictionAUGUST 1943 WAS A TURNING POINT FOR THE CLUNES AGRICULTERAL SOCIETY. IT MARKED THE DEATH OF MR JOHN ROBINS CARTER OF "SCALE-PARK" CLUNES...150th anniversary, clunes and district agricultural society, john robinson carter -
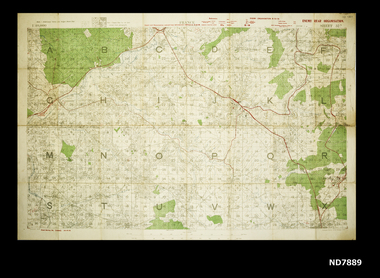 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Map - WW1 map of France, WW1 map of France - regional. Field Survey Map of Enemy Rear Organisation, 08/10/1918
Enemy Rear Organisation map Scale 1 : 40,000Field Survey Map of Enemy Rear Organisationnon-fictionEnemy Rear Organisation map Scale 1 : 40,000maps, world war 1914 - 1918 -
 Narre Warren and District Family History Group
Narre Warren and District Family History GroupBook, Bev Rasker, Nilon family. Michael Nilon and his family in Australia, 2000
In the early 19th Century rural Ireland was experiencing severe economic and social problems Population continued to grow as couples married at 16 or 17 and proceeded to have an average of 9 children. At the bottom end of the social scale labourers and the very smallest of farmers were in dire poverty. For the more comfortable farmers with 20 acres or so circumstances were better as they were in a position to grow additional crops which generated extra valuable income. Crop failures in 1822 and 1837 and again in 1845 to 1848 brought about unendurable hardship and famine. It was against this backdrop that Michael Neylon (Nilon) left his native Benvoran, Kilmurry McMahon Co Clare in search of opportunity and a better life. Now Beverley Rasker (nee Nilon) has fully researched his arrival in Australia in 1841 and she has taken up his story and that of his many descendants. Having communicated with Beverley for some time, I eventually had the pleasure of meeting her in September 2000, during her 2nd trip to Ireland in connection with her research. She has now put together an excellent record of interesting and informative material, which indeed makes us all proud of the achievements of the Neylon (Nilon) family. As we say in Irish'Molann an obair an fear' Sean Neylon, Kilkee, Co Clare Ireland. November 2000non-fictionIn the early 19th Century rural Ireland was experiencing severe economic and social problems Population continued to grow as couples married at 16 or 17 and proceeded to have an average of 9 children. At the bottom end of the social scale labourers and the very smallest of farmers were in dire poverty. For the more comfortable farmers with 20 acres or so circumstances were better as they were in a position to grow additional crops which generated extra valuable income. Crop failures in 1822 and 1837 and again in 1845 to 1848 brought about unendurable hardship and famine. It was against this backdrop that Michael Neylon (Nilon) left his native Benvoran, Kilmurry McMahon Co Clare in search of opportunity and a better life. Now Beverley Rasker (nee Nilon) has fully researched his arrival in Australia in 1841 and she has taken up his story and that of his many descendants. Having communicated with Beverley for some time, I eventually had the pleasure of meeting her in September 2000, during her 2nd trip to Ireland in connection with her research. She has now put together an excellent record of interesting and informative material, which indeed makes us all proud of the achievements of the Neylon (Nilon) family. As we say in Irish'Molann an obair an fear' Sean Neylon, Kilkee, Co Clare Ireland. November 2000michael nilon, bolong (nsw), cootamundra (nsw) -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Ribbonstone-banded Chert
Chert is a sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz. While usually biological in origin, chert may also occur as a chemical precipitate or a diagenetic replacement--the product of petrified trees. Chert, also known as flint, was a common tool for early peoples during the stone age. It forms in limestone and chalk sediments as silicon dioxide microcrystals which grow into nodules of chert. Chert is found in many mines across the Northern Territory, however this specimen is sourced from the Mount Todd gold mine in Katherine. Its use in weaponry, both during the Stone Age and during the 18th century. Chert produces a spark when struck against steel, meaning t hat it can be used to start fires and fire guns. Chert was thus used in flintlock firearms, in which the gunpowder is ignited by a flint hammer striking a steel plate. Chert was commonly used in the Stone Age as a result of conchoidal fracturing causing very sharp edges, allowing early peoples to fashion weapons and cutting tools. It also rates a 7 on the Mohs Scale, making it a very hard and durable stone that maintains its sharpness. As a result, the significance of chert as a signifier of early indigenous Australian life makes this specimen important. It is also known that chert is a valuable mineral that was used as a trading commodity. Chert has also been valuable during the 1700s, proving itself to a be an important historical specimen in matters of war. A solid silicon dioxide mineral in shades of brown, white, and beigeburke museum, northern territory, chert, flint, minerals, geological specimen, katherine, mount todd gold mine, katherine northern territory -
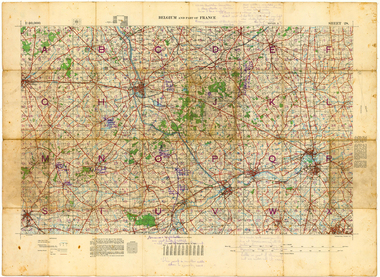 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Map - Belgium and part of France map WW1, Belgium and part of France map WW1with penciled annotations by Charles H. Honybun, Nov 1917
WW1 map of Ypres and Menin. Sheet 28 Edition 3 Scale 1: 40,000 Nov 1917Map bounded by Balleul, Poperinghe, Ypres, Menin, Moorsele, Tourooingnon-fictionWW1 map of Ypres and Menin. Sheet 28 Edition 3 Scale 1: 40,000 Nov 1917world war 1914 - 1918, world war 1914 - 1918 battle of ypres, maps -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual - Flight radios, Flight Radio Licence Manual
Photocopied pages of radio procedures, frequencies & wave propogation. Era unknownPhotocopied pages in manila foldernon-fictionPhotocopied pages of radio procedures, frequencies & wave propogation. Era unknownreadibility scales, procedures words & phrases, radio transmission of numerals, aircraft id, aeronautical station id, other radio topics -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
This image is a reproduction of an 1899 original depicting the 'Williams Good Luck Mine' on the Mopoke Reef (also called 'Morepork Gully') in the Dingle Ranges, approximately three miles from Beechworth. A large opening to a mine can be seen behind the men in the photograph, with a wheeled cart on a track leading to the men's position, where the soil and rocks have been hauled away. This photograph interestingly contains dogs alongside the miners. While dogs have been recorded as deterrents to thieves in the Victorian goldfields, these dogs appear as companions to these men. Following the discovery of gold at Beechworth in 1852, rushes quickly followed at surrounding creeks and gullies in the district. In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, small syndicates of miners continued to work old or abandoned quartz reefs, often persisting without the assistance of heavy machinery to remove the large amounts of rock, in order to obtain yields at ever greater depths. The group of miners in this photograph are Mr. Roger Williams and Sons, who revived operations at the ‘Old Good Luck’ mine on the Mopoke Reef in the Dingle Range near Beechworth around 1892, working the site for more than two decades. An emigrant from Cornwall with experience in the tin mining industry, 19 year old Roger Williams senior sailed to New Zealand in 1840, then to Australia where he spent time in the Bendigo Gold Fields before settling in Beechworth in the early 1860s. Mr Williams senior worked on various mining activities in the district, including the Rocky Mountain Tunnel project. Conversant with the character of gold-bearing reefs in the area, the syndicate dug an eight hundred foot tunnel, digging down as far down as two hundred feet with little capital save their labour, to connect and provide better working access to the mass of reefs and veins in the vicinity. Progress was hampered by poor air quality charged with fumes from dynamite and large quantities of rock had to be crushed to obtain payable yields. The Victorian Goldfields are filled with ruins and remnants of the area's rich mining history, ranging from small alluvial diggings to the remains of huge mining companies. Site names often changed several times throughout the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Some sites were abandoned and forgotten, others were worked continuously over many decades. The names of mines were often repeated at different locations throughout the Victorian Goldfields. For example, there is a Mopoke Gully heritage mine near Fryers Creek, Victoria. 'Mopoke' is a common onomatopoeic name for Morepork and Australian Boobook owls.This image has historical, social and research significance for patterns of emigration during of the Victorian Gold Rush, and the historical, social and environmental impacts of mining at Beechworth at the turn of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. As gold became scarce and government support and large company investment waned, poor hard-working miners laboured intensively to make a living through periods of high unemployment. This image can be compared and studied alongside other historical mining photographs and objects in the Burke Museum Collection. It has potential to improve our understanding of miners working conditions and the shifting character of mining in the Beechworth district.Sepia coloured rectangular photograph printed on gloss photographic paper mounted on card. Obverse: Williams/ Good/ Luck Reverse: A02498/ 1997. 2498/ Good Luck/ Mine/ 1899/ Mopoke. burke museum, beechworth museum, beechworth, gold fields, gold rush, victorian gold rush, gold ming history, colonial australia, australian gold rushes, mining technology, beechworth historic district, indigo gold trail, migration, indigo shire, good luck gold mine, victorian goldfields, mining syndicates, gold fever, quartz-mining, small-scale mining, old good luck mine, mopoke gully, quartz reefs beechworth -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
This image is a reproduction of an 1899 original depicting the 'Williams Good Luck Mine' on the Mopoke Reef (also called 'Morepork Gully') in the Dingle Ranges, approximately three miles from Beechworth. The foreground of the image is littered with piles of smashed rock and detritus, known as ‘mullock’, beside a reinforced mine shaft, a vertical access passageway allowing miners to enter the mine and haul ore out using lifting technology such as a poppet heads, whims or windlasses. A group of miners and a dog appear close to an open-sided miner’s hut. Following the discovery of gold at Beechworth in 1852, rushes quickly followed at surrounding creeks and gullies in the district. In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, small syndicates of miners continued to work old or abandoned quartz reefs, often persisting without the assistance of heavy machinery to remove the large amounts of rock, in order to obtain yields at ever greater depths. The group of miners in this photograph are Mr. Roger Williams and Sons, who revived operations at the ‘Old Good Luck’ mine on the Mopoke Reef in the Dingle Range near Beechworth around 1892, working the site for more than two decades. An emigrant from Cornwall with experience in the tin mining industry, 19 year old Roger Williams senior sailed to New Zealand in 1840, then to Australia where he spent time in the Bendigo Gold Fields before settling in Beechworth in the early 1860s. Mr Williams senior worked on various mining activities in the district, including the Rocky Mountain Tunnel project. Conversant with the character of gold-bearing reefs in the area, the syndicate dug an eight hundred foot tunnel, digging down as far down as two hundred feet with little capital save their labour, to connect and provide better working access to the mass of reefs and veins in the vicinity. Progress was hampered by poor air quality charged with fumes from dynamite and large quantities of rock had to be crushed to obtain payable yields. The Victorian Goldfields are filled with ruins and remnants of the area's rich mining history, ranging from small alluvial diggings to the remains of huge mining companies. Site names often changed several times throughout the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Some sites were abandoned and forgotten, others were worked continuously over many decades. The names of mines were often repeated at different locations throughout the Victorian Goldfields. For example, there is a Mopoke Gully heritage mine near Fryers Creek, Victoria. 'Mopoke' is a common onomatopoeic name for Morepork and Australian Boobook owls.This image has historical, social and research significance for patterns of emigration during of the Victorian Gold Rush, and the historical, social and environmental impacts of mining at Beechworth at the turn of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. As gold became scarce and government support and large company investment waned, poor hard-working miners laboured intensively to make a living through periods of high unemployment. This image can be compared and studied alongside other historical mining photographs and objects in the Burke Museum Collection. It has potential to improve our understanding of miners working conditions and the shifting character of mining in the Beechworth district.Sepia coloured rectangular photograph printed on gloss photographic paper mounted on card.Obverse: Reverse: A02497/ 1997.2497/ 'Good/ Luck/ Mine'/ Morepork/ Gully/ Mrs Joyce/ Bright/ Tunnel/ 800 ft/ 1899. burke museum, beechworth museum, beechworth, gold fields, gold rush, victorian gold rush, gold ming history, colonial australia, australian gold rushes, mining technology, beechworth historic district, indigo gold trail, migration, indigo shire, good luck gold mine, victorian goldfields, mining syndicates, gold fever, quartz-mining, small-scale mining, old good luck mine, mopoke gully, quartz reefs beechworth -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - United States Camouflage WW II from Scale Productions Texas
