Showing 87863 items matching " museums"
-
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBooklet - Cleckheaton No. 106, Country Spun, Cleckheaton, c.1970s
This book was owned by the late Dr Elizabeth Kerr and was donated to the Museum by the executor of her estate, Margaret Cameron. It was produced for Cleckheaton wool and contains knitting patterns for a jumper and a jacket.Knitting pattern book, 4pp. Cover printed in colour with an oval photo of a man and a woman wearing a chunky, textured knitted jumper in beige (her) and a shawl necked brown jacket with a belt tie (him).No. 106 / Cleckheaton / COUNTRY SPUNknitting handicrafts - history, cleckheaton, knitting, handicrafts - history -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook, Knitting, Vogue Knitting Book no. 65
This book was owned by the late Dr Elizabeth Kerr and was donated to the Museum by the executor of her estate, Margaret Cameron. It was published by English Vogue and contains knitting patterns for womens garments.VOGUE / Knitting / Book / no. 65 / Over 28 / new designs / suits / sweaters / dressesknitting fashion, vogue - english, knitting, fashion -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyBooklet - Sheet Music, Back to Rutherglen, 1935 (Exact)
Music and words written in 1935 by T.S. Parrott, at that time residing in Rutherglen, killed in motorcycle accident before the composition was published in 1936. Music donated to Museum by Fred Terrill."Back to Rutherglen" music composed by the late T S Parrott. Photo of composer on front page." "Back to Rutherglen" Words and Music by The Late T. S. Parrott. Souvenir of Back to Rutherglen Centenary Celebrations. Price: 2s."back to rutherglen., t s parrott, music, songs, centenary -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyImage, 1991
The old Court House was the Doctor's office for some years after it was closed as a court house, and is now a private residence. Some of the furniture from the Court House is now in the Museum.Two colour photographs on a single sheet, showing views of the interior of the Rutherglen Court House shortly after it was decommissioned.On the side of the top photo: "Rutherglen Court House 1991" On the side of the bottom photo: "Looking from Front Door" On back of photos: "Geoff Stewart"rutherglen court house -
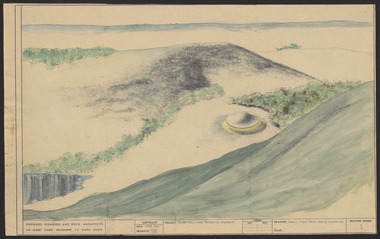 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDrawing - Aerial perspective, Tower Hill Lake Reserve Museum, Jun-61
Project: Tower Hill Lake Reserve Museum drawn by Robin Boyd of Grounds, Romberg & Boyd. Drawing no 1. Aerial perspective (same as item PL136 but watercolour and pastel)Sketch, Watercolour on dyeline -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Digital Image - set of 2, Peter Knife, New Museum views, 5/9/2023
Set of two digital images of the New Museum views - Maggie Knife and Chris Phillips with trams 1 and 2 in the view. Photo by Peter Knife 5/9/2023. Yields information about trams on display at the Museum.Set of two Digital images,tramways, tramcars, btm, tram 2, tram 1, new museum -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Ballarat Tramways - SEC - timetable board, Ballarat Tramway Museum (BTM), June 1994
Colour print showing two of the SEC tramway timetable boards, that was located at the City Tramway centre on display on the end of tram 39 before the construction of an entry into the Museum display.Demonstrates methods used to display information at the Museum during 1994. Colour photograph print on Fujichrome paper.museum, timetable boards, tram 39 -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Kodak Duplicate slide
Shows the truck of Ballarat tram 11 being cleaned, possibly before being loaded and transported to the Daylesford Museum, 9/1971. The tram has a Twin Lakes advertisement.Yields information about the work undertaken to clean trams possibly prior to being transported to a new location. The tram was given to the Daylesford Museum.Kodak duplicate colour slide, cardboard mount - TMSV Sales.In pencil "Ballarat Depot 35" and TMSV Sales stamp.sec, ballarat trams, cleaning, tmsv, tram 11, tramway, trams -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumEquipment - Tram Track Materials, Pandrol Australia, Sydney
Tramway Track materials used to reconstruct or replace Ballarat Tramway Museum track between Carlton St and Depot Junction Sept 2019. Follows the current practice in Melbourne.Demonstrates the materials used to replace BTM Tramway Track during 2019. Same materials used during the reconstruction of 2022.Group of rail fittings used during 2019 track relay by Fulton Hogan between Carlton St and Depot Junction. .1 - Section of tram rail - Ri57A - cut from an 18m long rail section. Rolled by voestalpine Railway Systems, Austria .2 - Group of three different sized Pandrol Rail insulators used between the rail and the clip. .3 - Pandrol resilient pad used between the concrete sleeper and the rail .4 - Pandrol clip used to secure the rail to the sleeper.tramways, ballarat, btm, trackwork, tramway rails, pandrol, voestalpine -
 Apollo Bay Museum
Apollo Bay MuseumAudio - Jan Lewis memories of Apollo Bay, May 2023
A chat collected at the museum residence during the Heart Maps project with Amy Tsilemanis, covering memories of Apollo Bay harbour, foreshore, dances, and being secretary of the Historical Society. apollo bay -
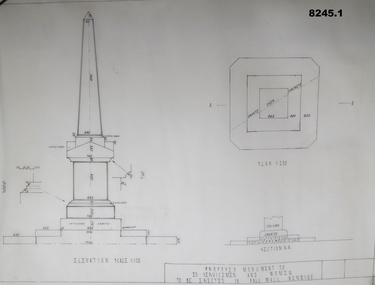 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPlan - MONUMENT PLANS, C.1992
These plans were for a proposed Memorial to Ex Servicemen and Women to be erected in front of the Soldiers Memorial Institute in Pall Mall Bendigo. This building is now known as "The Bendigo Military Museum".1) .2) Two Cronaflex .004 thick black ink plans , scale 1 - 100showing front elevation and plan of a proposed Monument. Both plans are slightly different showing plan sections."Proposed Monument to Ex Servicemen and Women to be erected in Pall Mall Bendigo"brsl, smirsl, monument, plan, -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumCertificate - WARRANT / CHARTER, 2008
PRESENTED TO THE HEPBURN SHIRE COUNCIL BY THE ALL NATIONS LODGE 28 TO COMMEMORATE 150 YEARS OF FREEMASONRY IN CLUNES. PRESENTED TO MAYOR TIM HAYES WHO THEN PRESENTED IT TO THE CLUNES MUSEUM.FRAMED COPY OF THE FOUNDATION WARRANT OF THE ALL NATIONS LODGE 28. ORIGINAL CHARTER FROM GRAND LODGE OF IRELAND DATED 9TH APRIL 1860 HAVING TAKEN 2 YEARS TO ARRIVE FROM IRELAND.local history, societies, freemasons, all nations lodge 28 -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Report, Dalgety Farmers Limited, Dalgety's Review (Australasia): 1914, 1 December 1914
"Dalgety's Review (Australasia): 1914". Part of the National Wool Museum Woolbroker's Office exhibit until late 1990's. Includes articles on the war and the Australian wool industry.Sixty page book, with cream soft cover and printed blue text. wool stores wool brokering world war i, dalgety and company limited, wool stores, wool brokering, world war i -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPrint, John Neeson, Fire in the Forest, 1973
John Neeson is a Postwar & Contemporary painter who was born in 1948. Numerous key galleries and museums such as Hill Smith Gallery have featured John Neeson's work in the past.Abstract composition in two panels. Left panel shows areas of three shades of grey. Right panel shows areas of grey, red and yellow. The centre image connects both panels with a triangular shape with red patterning, giving an appearance of flame and embers. Mounted in grey matt. In grey wooden frame with glass.Front: 1/25 (lower left) 73 (centre) John Neeson (lower right) (pencil) Back: (no inscriptions) -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPhotograph - W2 244 as the Christchurch NZ Restaurant tram, David Frost, c2005
The photo shows former Melbourne W2 class tram 244 modified by the Sydney Tramway Museum to be a Restaurant tram in Christchurch NZ. Photo taken at Cathedral Square c2005.Provides details of a Melbourne W2 class tram used as a Restaurant tram in Christchurch.Colour print of Christchurch Tramways W2 244 Cathedral Square printed on Kodak Royal paper.trams, tramways, w2 class, tram 244, christchurch, restaurant tram -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Speciality Knitting Book no. 49, Patons and Baldwins, 1930s
This book was owned by the late Dr Elizabeth Kerr and was donated to the Museum by the executor of her estate, Margaret Cameron. It was produced by Patons and Baldwins and contains knitting patterns for womens garments.Knitting pattern book, 24pp. Cover printed in colour with a photo of a woman wearing a light yellow cardigan heavily embroidered with colour flowers. She is standing in front of a rose bush. Contains knitting patterns and photos of womens garments.PATONS / AND / BALDWINS' / No. 49 / "P&B" / BRAND / SPECIALTY / Knitting Book / "P&B" / BRAND / TEN ULTRA - SMART MODELS . . . SIXPENCEknitting handicrafts - history, patons and baldwins (australia) ltd, knitting, handicrafts - history, fashion, clothing -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Bendigo 17 and Ballarat 28 - 100 years of electric trams, Steven Altham, 25/9/2005
Set of three photographs of Bendigo 17 and Ballarat 28 - on the celebration of 100 years of electric trams by the Ballarat Tramway Museum on 25-5-2024. Photo by Steven Altham.Yields information about the trams used to celebrate the 100 years of electric trams in Ballarat.Set of three Colour prints with photographers notes on the rear.In ink on all "25-9-05 and Steven Altham"tramcars, tramways, 100 years of electric trams, tram 17, tram 28, wendouree parade, btm -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - The Case for a Museum at Bendigo TAFE, Sat May 08 2021
Paul Howard MacGillivray was an international scientist who called Bendigo home. Bendigo historians are buiding the case to turn the McCrae Street's heritage listed TAFE building into a museum.Bendigo Weekly Story entitled 'Lost legacy rekindled' - one page article and four photos on the work of Paul Howard MacGillivray.school of mines, potential for museum, bendigo tafe, paul howard macgillivray -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Frame Fragment, Frame Fragment from 1860 J Wilder, Late 19th century
Joseph Wilder, a professional photographer, came to Warrnambool in 1860 and took a series of photographs, two of which survive today. One was of the local Volunteer Corps and the other was a series of photographs taken from Cannon Hill showing Merri Street and the town and buildings beyond. It seems that copies of these last-mentioned photographs were framed to produce a large panoramic view of 1860 Warrnambool and one of these was given to the old Warrnambool Museum in the 1880s by James Astley Bromfield. He had established a chemist’s shop in Warrnambool in 1854 and showed his interest in the history of the young town by producing a map in 1856 showing the first landowners, a seminal resource today for historians. He again demonstrated this interest when he included the names of the people and places in the 1860 photograph he gave to the museum in the 1880s. The frame fragment was found amongst the collection of items from the old Museum at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and brought to the Historical Society to accompany the original series of photographs. Bromfield went to live in Melbourne in the 1880s. It is presumed that the plastic cover has been placed on the frame fragment at a much later date than the 1880s.This frame fragment is interesting and very important for several reasons:- 1. It is one demonstration of the interest that James Astley Bromfield had in local history 2. It came from the old Warrnambool Museum and shows how that institution kept items of historical interest 3. It gives us the names of the people and places in the Joseph Wilder photographs of 1860 that placed together form a panorama that reveals what a major section of Warrnambool looked like only 13 years after its foundation. The list enables us to correctly identify the early places and people and so is invaluable for research purposes 4. It links a Museum exhibit of the 1880s with the original 1860 photographs which are held by the Historical Society This is a piece of wood broken from a frame containing a photograph. It has jagged edges. It contains the list of people and places depicted in the Joseph Wilder panorama photograph of Warrnambool in 1860. The list is handwritten in ink on paper which has been attached to the frame with a piece of plastic. Warrnambool in 1860 Photographed by Wilder. Showing children of the late Andrew Semple etc In red pencil – ‘Keep’, in ink, ‘Keep’ On separate piece of paper - Presented to Warrnambool Mechanics’ Muzeum by James Astley Bromfield, August 3rd 1886 joseph wilder 1860, panorama of warrnambool -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Eastern quoll, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Quolls are small carnivorous marsupials native to Australia and New Guinea. Tjilpa is the name given to the quoll amongst the Northern Arrernte language group of Australian Aboriginal people. Quolls are primarily nocturnal and spend most of the day in a den. Of the six species of quoll, four are found in Australia and two in New Guinea. The six species vary in weight and size, from 300g to 7kg. They live in coastal heathlands, sub-alpine woodlands, temperate woodlands and forests, riparian forests and wet sclerophyll forests. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from either the Trustees of the Australian Museum or from the amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880 and mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee around the same time. When all taxidermy mounts were completed, they were quickly put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.Small quoll with a small round head, long body, and long, thin tail perched on a branch attached to a wooden mount. The quoll has four skinny legs which have long, dark claws. The quoll's hair is a fawn colour with cream spots. There are two black eyes made of glass, two short pointed ears and black whiskers.On wooden mount: BMM5897 /taxidermy, quoll, animal, australia, burke museum, beechworth, reynell eveleigh johns, taxidermy mount, marsupial -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Crimson Rosella, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. The Crimson Rosella is relatively easy to see as it forages on the ground or among the leaves of eucalypts, with its spectacular combination of deep-crimson, royal-blue and black plumage. However, not all Crimson Rosellas look the same. Along the Murray River, Crimson Rosellas aren’t crimson at all — they are yellow, black and blue, with the yellow feathering replacing the crimson plumage. In southern South Australia they differ again, being roughly intermediate between crimson and yellow, with varying amounts of red and yellow in their plumage. Research featured in the 'State of Australia's Birds 2015' headline and regional reports suggest that the Crimson Rosella may be declining in the East Coast. There are several populations of the Crimson Rosella. Red (crimson) birds occur in northern Queensland, in southern Queensland to south-eastern South Australia and on Kangaroo Island. Orange birds are restricted to the Flinders Ranges region of South Australia, while yellow ones are found along the Murray, Murrumbidgee and neighbouring rivers (where yellow birds meet red birds they hybridise, producing orange offspring). Red birds have been introduced to Norfolk Island and New Zealand.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.There are several colour forms of the Crimson Rosella. The form it is named for has mostly crimson (red) plumage and bright blue cheeks. The feathers of the back and wing coverts are black broadly edged with red. The flight feathers of the wings have broad blue edges and the tail is blue above and pale blue below and on the outer feathers. This particular specimen has lost some feathers in its plumage and its colour is not as bright as that of a live specimen.Label: 77a / Pennant's Parakeet / See catalogue, page 22taxidermy, crimson rosella, bird, australian bird, rosella, crimson -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - American Crow, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The American Crow is common throughout North America. They reside in areas with open view and trees but can often frequent city parks, suburbs of large cities and along the seashore. The Crow is a robber and therefore, find living in locations which they can raid for food perfect. These birds are sociable animals and are often found in small groups made up of family members. All their lives they reside in the one location; however, they do migrate south during the autumn. They usually find their food by walking along the ground and eat both plant and animal foods. This includes worms, larvae, insects and fruits and nuts. Crows are also known to feed on small rabbits, frogs and mice. They are also identified as nest predators because they feed on eggs. In areas occupied by humans, the Crow will find their food source from trash and also road kill. The American Crow is not considered to be an endangered species and list them on the IUCN Red List as Least Concern. However, large amounts of crows are killed for sporting and during campaigns (having a desire to reduce the population of the Crow in America). This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This American Crow has black plumage which has slightly faded in colour. This colour fading could also indicate that the bird was molting because the feathers of the American Crow appear brownish when the are about to molt and these feathers give way to new glossy black feathers. The specimen has two black glass eyes, a dark bill and dark legs with talons. Both the edges of the bill and the talons are faded into a pale buff colour. It is likely that the legs and talons were painted a dark black by the taxidermist and the paint has either worn off or faded over the years. The bird is standing tall on a wooden mount and looking forwards. It has a paper identification tag attached to the right leg. The tail is short and the feathers are rounded at the ends.153a. / See catalogue page 61taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, america, crow, american crow -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Silver Gull, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Silver Gull is more commonly referred to as the 'Seagull'. Found all along the coast of mainland Australia and Tasmania, it can also be found in New Caledonia and New Zealand. These birds are a common nuisance at beaches and urban areas, such as shopping centres. Since the 1950s, humans have become increasingly wasteful, leading to an explosion of the Silver Gull population due to the availability of rubbish to scavenge. They feed mainly on small marine life, but they are a versatile scavenger. The population increase has impacted the breeding of other bird species, as Silver Gulls have dominated offshore island breeding grounds. Their breeding season is from August to December, when they nest on the ground, however mating can occur year-round. This species has a harsh, high-pitched call 'kwarwh', well known to all Australians. Although protected under Australian Environmental Law, there are many strategies in place to discourage increasing the numbers of Seagulls. This specimen is an inaccurate example of a Silver Gull, which although is in good condition and intact, does not look like an accurate representation of this species. The legs have been mounted too far towards the tail on this specimen, giving it an unbalanced appearance. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This adult Silver Gull has a white head, body, underpart and tail. Its wings are silver-grey, with black and white tips. It has an orange-red bill, feet and beak, indicative of its maturity. The irises are white. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing-tag: 11a / Silver Gull / See catalogue, page, 40. taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, seagull, silver gull, australian bird, nuisance -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Common Starling, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Common Starling is an introduced species to Australia (as well as widely throughout the world), and is considered a pest due to its attacks on fruits and seedlings, as well as competing with the native bird population. It was introduced to Victoria in 1861, and has since become abundant, whose sheer numbers cause many problems. These birds are a social species, which can mass in very large flocks (murmations), and show spectacular synchronised aerobatic displays. This species has a distinctive plumage, with glossy black bodies, white spots on their backs and wings, and a purple and green tinge to their underparts and wings. This species, when moving across the ground, has a distinctive 'walk' or 'run' rather than the traditional hopping of many other bird species. This bird is a noisy species, often becoming a nuisance to people. Starlings prefer to nest in holes in trees or buildings, yet there are at least two recorded cases of this species nesting on the backs of living sheep. This specimen is a good and intact example of this species. As the white spots are large and visible, as well as the purple and green shine, this specimen likely died close to Autumn and the breeding season, when these birds get their new bright plumage. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This adult Common Starling has glossy-black plumage with a metallic sheen, and white speckles throughout. The plumage has a purple and green shine. The irises are white. Its beak is black and pointed. This specimen appears to be male, with less white spots on its underparts. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg, and a metal tag tied around its foot.Swing-tag: 139a. / Starling / Catalogue Page, 59 / Metal-tag: 1250 (?)taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, sheep, common starling, starling, murmations, pest, australian bird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Grey-headed Woodpecker, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Grey-headed Woodpecker is a medium-sized woodpecker of the Picidae family, that is sometimes mistaken for the similar-looking Green Woodpecker. The species is known to have a grey face, neck, and underparts, with green wings and back, and underwing feathers that are a dark brown to dark grey-black with white dots. Although this can vary depending on location, with European and Northeast Asian birds having overall paler colours, to mainland Asian birds being darker overall. The species has a distinctive black mustache-like stripe on both sides of the face and the mature males have a red patch on the top of the head. These tree-clinging woodpeckers usually feast on ants, insects, and berries. This specimen differs in appearance from the common Grey-headed Woodpecker as its back feathers appear a dark grey, where in the wild these birds have sometimes quite vibrant green feathers. The eyes of the grey-headed woodpecker are also usually red with black iris, not white with black iris as in this specimen. The beak is also a pale yellowish colour on this bird, whereas commonly the species has a grey upper beak and pale yellow lower beak. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This male Grey-headed Woodpecker has a bright red head patch and distinctive black mustache-like stripes on both sides of the face, with additional black stripes running from the pale yellowish beak to the inner corner of the eye. The underbelly is a light grey and the back is a slightly darker grey. The underwing feathers are a light rufous-brown with white dots. The specimen is mounted on a sloping vertical wooden cylindrical stick attached to a mount. There are also two paper swing tags, one of which is torn in half.149a. / Unnamed / Catalogue page 60 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, woodpecker, grey-headed woodpecker, gray-headed woodpecker -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Red Wattle Bird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The red wattlebird is a passerine bird native to southern Australia. Measuring 33–37 cm (13–14.5 inches) in length, it ranks as the second-largest species among Australian honeyeaters. The species was first described by John White in 1790, and three subspecies are currently recognised. The red wattlebird is found across southeast Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, and southwest Western Australia, inhabiting open forests, woodlands, and urban gardens or parks. Known for its loud and conspicuous presence, the red wattlebird primarily forages in trees, although it occasionally searches for food on the ground. As one of the world's largest nectar-feeding birds, it consumes nectar from a wide variety of flowering plants, supplementing its diet with insects. Territorial and sometimes aggressive, it defends rich nectar sources from other bird species. Breeding occurs throughout its range, with the species constructing cup-shaped nests in trees and raising one or two broods annually. Despite localized declines due to habitat loss, the red wattlebird is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. This specimen was falsely identified as a yellow wattlebird in original catalogue records and is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The red wattlebird has predominantly grey-brown plumage, featuring red eyes, pale pinkish-red wattles on each side of the neck, white streaking on the chest, and a prominent yellow patch on the lower belly. Swing-tag: 58a. / Wattled - Honeyeater / See catalogue page 18taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, bird, yellow wattlebird, tasmanian wattlebird, anthochaera paradoxa, australian birds, wattlebird, red wattlebird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Australasian Swamphen, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Australasian swamphen is a visually striking and socially complex bird found across Oceania. It can be found in eastern Indonesia (specifically the Moluccas, Aru, and Kai Islands), Papua New Guinea, New Zealand, and Australia. As a member of the rail family (Rallidae), it belongs to the diverse order Gruiformes, which also includes cranes and other rail species. Like other rails, it possesses relatively short wings and a strong, elongated bill, both adaptations suited to its semi-aquatic wetland habitat. This swamphen is easily identified by its deep blue-purple plumage, prominent red frontal shield, and sturdy red legs. It primarily inhabits swamps, marshes, and other wet lowland areas, though its range has expanded to include pastures, roadsides, and farmland due to significant landscape modifications over the past 150 years. Unlike many wetland birds, it is highly adaptable and thrives in both natural and human-altered environments. Its diet is similarly flexible, consisting mostly of plant material such as grass stems, shoots, and leaves, but also including invertebrates and, on occasion, the young of other bird species. This specimen was misidentified as a Purple Swamphen in original catalogue records and is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This taxidermy specimen is of a Australasian swamphen which is mounted standing on a wooden platform and has a paper identification tag tied to its upper left leg. The specimen has dark colouring on its back and head with a purple-blue coloured neck, breast and belly. The bill is oversized and is orange/red which is the same colour as the frontal shield on the bird's face. The eyes are made from a red and black glass and the legs of this specimen are orange. The legs are elongated and the toes also long and unwebbed. 17e. / Purple Gallinule / Catalogue Page 35 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, swamphen, moorhen, purple bird, hen, purple swamphen, water bird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Southern Boobook, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Known for its distinctive ‘boo-book’ sound which gives it its name, the Southern Boobook owl inhabits a variety of environments, including woodland, rural, open desert and dense forest. It is found on mainland Australia as well as Tasmania and other costal islands. Some similar species can be located in New Zealand, New Guinea and Indonesia. Young Boobooks’ plumage is mostly off white, and there are slight variations in subspecies based on location - the Cape York rainforest owls are a larger, darker brown bird while the Tasmanian Boobooks are smaller and often have more white flecks on their plumage. Southern Boobooks hunt and eat nocturnally and, like most owls, their diet consists of smaller animals including smaller mammals and insects. While elements of this particular specimen are representative of the actual bird, the form and structuring of this specimen’s neck area appears to be somewhat out of shape in comparison to images of the actual bird, which present a distinct head structure. The eyes on this specimen are also problematic, as they are solely black - not aligning with accurate representations of this species that have a distinct golden yellow outer ring in their eyes around a large black pupil. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.One of the most commonly found Australian species of owl, the Southern Boobook is also Australia’s smallest owl. With a coating of dark chocolate brown coloured plumage on its wings, dorsal area, continuing onto the top of the head and around its eyes, the owl’s breast plumage is flecked with hazelnut brown and white feathers. Its chin and nose areas are a soft creamy white, and the owl’s beak is a darker grey. Traditionally, the eyes are yellow as are the legs and taloned feet. This particular specimen stands upon a wooden perch and an identifying tag hangs from its right leg.Swing-tag appears to read: '39. Boobook Owl / Catalogue page 53.' The 2 digit number at the beginning of the label could also be '3a'. taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, southern boobook, mopoke, australia, boobook, nocturnal, ninox novaeseelandiae, owl -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Colour Photograph/s - set of 3, Austin Brehaut, 5/11/2002 12:00:00 AM
Yields information about the appearance of Ballarat 28 following its repainting in ESCo colour scheme by the BTM 2002.Set of three colour photographs, from the same photograph of No. 28 running out into service across Wendouree Parade, first day in service following BTM Refurbishment, 5.11.2002. Photograph by Austin Brehaut. .1 - small print - car in the background - printed on Kodak Royal paper .2 - medium size print with the car in the background removed - see image 2 - printed on Canon hyper photo paper - colour inkjet print .3 - larger size print with the car in the background not removed - printed on Kodak picture maker paper - colour inkjet print.On rear in ink .1 - "63)" / "28 entering Wendouree Parade on first day back in revenue service 5.11.02 / Austin Brehaut" and "Returning into traffic after refurbishment over a 6 year period and carrying the company livery" .2 "63)" / Ballarat car 28 5.11.02, Ballarat Tramway Museum / Austin Brehaut pic / car returning into traffic after refurbishment over a 6 year period and carrying the company livery" "Modified image (background only) and a "William F Scott" address label .3 "photo Austin Brehaut: / Ballarat Tramway Museum / car 28 leaving the depot access track to enter into Wendouree Parade on its first day in service after extensive refurbishment an din the company livery 5.11.2002"trams, tramways, wendouree parade, depot junction, restoration, esco, tram 28 -
 Cheese World Museum
Cheese World MuseumDVD, Heywood Cheese; an oral history on film
For many years the Heywood Cheese Factory was an important part of life for Heywood and district farming and a vital place of employment for up to 40 men and 10 women. The factory opened in 1939 as a subsidiary of the Portland Butter Factory before becoming a world renowned cheese making enterprise. It was felt important to document its history from the surviving factory workers, including dairy suppliers and milk truck drivers. We hear their stories of the long hours and hard work without penalty rates, travelling unsealed roads and mixed with their humour of the bygone days is an important acknowledgement of that era. [blurb on back cover]This oral history provides significant material relating to the dairy industry in south west Victoria during the mid 20th century. The interviews give first-hand recollections of the interviewees involvement in the industry from a point of view of factory workers, milk pick-up drivers and farmers.Full colour DVD cover has photograph of Heywood Cheese factory and photographs of girls with calves, milk cans on a truck and workers in the cheese room, superimposed on a photograph of dairy cows grazing in a paddock. The DVD has the photograph of the cows grazing in the paddock.Heywood Cheese/An oral history on film (front) For many years Heywood Cheese Factory was ... [see historical information] Edited by Garry Kerr for the Heywood Pioneer Wagon Shed/ Museum History Group who wish to gratefully acknowledge the/ support of the Victorian Government and Public Records Office/ Victoria for making this project possible. Duration: 70 minutesallansford, heywood, cheese factories, cheese manufacturing, dairying, cheese
