Showing 420 items matching "cash book"
-
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyaccount, 1st February 1912
William Haycox was a wholesale and retail butcher who was a cash buyer of hides, sheepskins and tallow. The Haycox Butcher shop was near the Club Hotel. Robert Pullar Cameron was a Shire Councillor for many years. He married Penuel Hossack and had a family of James, Flora, Penuel and Alex. This item is an example of book keeping in the early 20th century. It is from a business in Orbost and is a useful research tool.A white paper account with black print, blue ;lines and an illustration of cattle in the top left hand corner. It has a yellow duty stamp and is from William Haycox, butche,r to R.P. Cameron.on back -"Penalty McColl..." -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyaccount, April 1st, 1910
William Haycox was a wholesale and retail butcher who was a cash buyer of hides, sheepskins and tallow. The Haycox Butcher shop was near the Club Hotel. Robert Pullar Cameron was a Shire Councillor for many years. He married Penuel Hossack and had a family of James, Flora, Penuel and Alex.This item is an example of the book-keeping of an early Orbost business and is a useful research tool.A white paper account with black ink and blue lines from Haycox & Mc Henry, wholesale and retail butchers to R. Cameron. There is a duty stamp.haycox-butcher-orbost cameron-robert-pullar -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRecord Book, before 1897
... mechanics' institute records warrnambool record book c. 1897 Record ...This Record Book was printed and published in Melbourne by Sands & McDougall Limited and distributed to be sold by stationers for 1s. 6d (1 shilling and 6 pence) or with Blottings (blotting paper to soak up excess wet ink) for 2s. 6d..The back cover has advertising from the Colonial Mutual Life Assurance Society Limited, an insurance company based in Collins Street Melbourne.Inside the front cover is a Calendar for the year 1897 and a table with dates for Eclipses of the Sun and Phases of the Moon for that year. Contained within the diary is a loose page listing products and an order form for Sands & McDougall. There is also a section titled "Miscellaneous Information" that includes Weights and Measures, Postal Tarriffs, Holidays, Population of various towns and states, education and a Ready Reckoner for Hourly Wages. In UK in early 1800's the word 'mechanic' was applied to a broader range of skills such as working man, tradesman or artisan. Mechanics' Institutes were formed originally for voluntary, self-funded organisations, to improve the education of working men and to instruct them on their various trades. The germ of the idea came from a class formed in 1799 by Professor George Birbeck in Glasgow, Scotland, for journeymen mechanics (apprentice trade workers), with the first Institutes being organised in London and Manchester in the 1820's. By then the original aim had broadened and the Mechanics' Institutes were established as popular agencies of adult education. The Mechanics' Institutes were run by committees that provided facilities for a meeting room, hall suitable for lectures, and a library. Funding was raised locally and often supplemented by grants from government agencies for the purchase of books and other resources. Activities were community based. In Australia, Mechanics' Institutes were set up in New South Wales and in Tasmania in the late 1820's. Mechanics' Institutes began in Victoria, with the first one in Melbourne dating from 1839, providing similar services but in time offered services tailored to their specific area. Warrnambool's Mechanics' Institute (or Institution as it was sometimes called) was one of the earliest in Victoria. On 17th October 1853 a meeting was held where it was resolved to request the Lieutenant Governor of the Colony to grant land for the erection of a Mechanics' Institutes building. A committee was formed at the meeting and Richard Osburne chaired the first meeting of this committee. The land on the North West corner of Banyan and Merri Streets was granted but there were no funds to erect the building. The Formal Rights of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute's encompassed its aims and these were officially adopted in1859; "This Institution has for its object the diffusion of literary, scientific, and other useful knowledge amongst its members, excluding all controversial subjects, religious or political. "These objects are sought to be obtained by means of a circulating library, a reading room, the establishment of classes, debates, and the occasional delivery of lectures on natural and experimental philosophy, mechanics, astronomy, chemistry, natural history, literature, and the useful and ornamental arts, particularly those which have a more immediate reference to the colony." The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute opened its first reading room in November1884 in the National School building at the corner of Banyan and Timor Streets. The Institute was funded by member subscription, payable on a quarterly, half yearly or yearly basis. Samuel Hannaford, the Manager of the Warrnambool Bank of Australasia, was the first Honorary Secretary of the Mechanics' Institutes, and an early President and Vice-President. He also gave several of the early lectures in the Reading Room. Another early Secretary, Librarian and lecturer was Marmaduke Fisher, the teacher at the National School. Lecture topics included The Poets and Poetry of Ireland', 'The Birth and Development of the Earth', 'The Vertebrae - with Remarks on the pleasures resulting from the study of Natural History' and 'Architecture'. In q856 the Reading Room was moved to James Hider's shop in Timor Street, and by 1864 it was located in the bookshop of Davies and Read. In the 1860's the Mechanics' Institute struggled as membership waned but in 1866, after a series of fund raising efforts, the committee was able to purchase land in Liebig Street, on a site then called Market Square, between the weighbridge and the fire station. A Mechanics' Institute building was opened at this site in August 1871. The following year four more rooms were added to the main Reading Room and in 1873 the Artisan School of Design was incorporated into the Institute. The same year Joseph Archibald established a Museum; however it deteriorated when he was transferred to Bendigo in 1877. In 1880, with Archibald's return to Warrnambool, the Museum was re-established, and in 1885 a new building was built at the back of the Institute to accommodate the re-created School of Design, the Art Gallery and the Museum. In 1887 the Museum section was moved to the former court house in Timor Street (for some time the walls of the building formed part of the TAFE cafeteria but all is now demolished)). In 1911 the Museum was transferred back to the original building and the management of the Mechanics' Institute was handed over to the Warrnambool City Council. The Museum and Art Gallery became one and housed many fine works of art., and the Library continued to grow. The building was well patronised, with records showing that at the beginning of the 20th century there were between 500 and 800 visitors. During World War One the monthly figures were in the thousands, with 3,400 people visiting in January 1915. The Museum was a much loved Institution in Warrnambool until the contents of the Museum and Art Gallery were removed to make room for the Warrnambool City Council Engineers' Department. The contents were stored but many of the items were scattered or lost. In 1975 the original building was demolished and the site became occupied by the Civic Centre, which included the new City Library. (The library was temporarily located in the old Palais building in Koroit Street.) In the process of reorganisation the Collection was distributed amongst the community groups: - The new City Library took some of the historic books and some important documents, historic photographs and newspapers. - The Art Gallery kept the 19th Century art collection and some of the artefacts from the museum. - The Historic Society has some items - The State Museum has some items - Some items were destroyed - Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village has old newspapers, Government Gazettes, most of the Mechanics' Institute Library, ledgers and documents connected to the Mechanics' Institute Library, some framed and unframed art works and some photographs. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Library book collection is deemed to be of great importance because it is one of the few collections in an almost intact state, and many of the books are now very rare and of great value. NOTE: Pages of this book have been digitally recorded and archived.The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. Record book, Warrnambool Mechanics Institute Curator's Diary, 1897,June to Dec (Donations). Printed and published by Sands & McDougall, Melbourne. Australian Rough Diary 1897 No 4, Card covers printed with advertising, 7 days to an opening, lined with cash columns.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, warrnambool mechanics' institute, mechanics' institute records warrnambool, record book c. 1897 -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyminute book, 10.2.1950 - 11.5.1961
The Orbost Rifle Club existed in the early 20th century. (There are records from 1900). It folded in the late 1970's. The secretaries at the time of this book were D.Towers and ? Healey.arget shooting is one of the oldest organised sports in Australia. Records date back to the British Marines at Sydney Cove in 1788. The Victorian Rifle Association (VRA) was formed in 1860. One of the most important adjuncts to the militia system from 1903 to the re-organisation of 1912 was the role played by the Rifle Club movement in Australia. At the time, these clubs were seen as the reservoir of manpower for a potential guerrilla force should any invasion occur. For Australia, the invasion fear was uppermost in the minds of the population. So important were the rifle clubs for the defence of Australia that the Commonwealth provided the training staff, rifles and ammunition so the clubs could function. Members were drilled, wore uniforms and practised all the basic skills of soldiering as well as target shooting. The Orbost Rifle Club was active during this period.A light brown covered book with a brown fabric binding. There is a white sticker label on the front - "Single Cash" in black print. It contains minutes .orbost-rifle-club minute-book -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyAccount Book, Pencraft Productions, Ringwood State School Committee Accounts Book 1961-1968, 1961 - 1968
... The Pencraft Account Book. Treble Cash.... Committee as the Finance A/C, Petty Cash and Domestic A/C book ...Used by the Ringwood State School Committee as the Finance A/C, Petty Cash and Domestic A/C book.Account book - Ringwood State School Committee 1961 - 1968. Grey covered foolscap size with grey printing on front. Only one page unused.The Pencraft Account Book. Treble Cash. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Hemmer Foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Broad Hemmer Foot for a Wertheim sewing machine. Joseph Wertheim manufacturer, Germany, distributed by Hugo Wertheim William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Small Corder Foot, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin.The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Small corder foot for a Wertheim sewing machine. Joseph Wertheim manufacturer, Germany, distributed by Hugo Wertheim William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, small corder foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Seamer Foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Seamer foot; feller single seamer for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
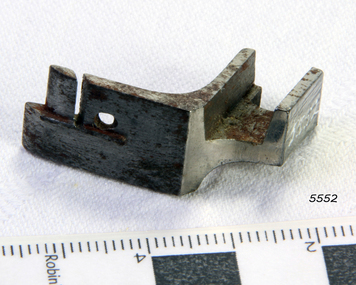 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Braider foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin.The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim.Wertheim braider; an accessory for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Sewing Machine Foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Foot accessory, metal, for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Binder, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin.The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Adjustable binder for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion, binder -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Tool Part, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Tool part for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Needle Plate, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Adjustable needle plate for a Wertheim sewing machine, made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, needle plate, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Sewing Tuck Marker, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
The tuck making tool is part of a set of tools and Instructions for a Wertheim New High Arm Sewing Machine as well as the "B' Medium, Cylinder Arm and Titania Machines. This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Tuck marker or creaser for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim , Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, sewing machine tool, sewing machine accessory, tucker, tuck maker, creaser, wertheim, joseph wertheim, germany, hugo wertheim, victorian era, sewing machine, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
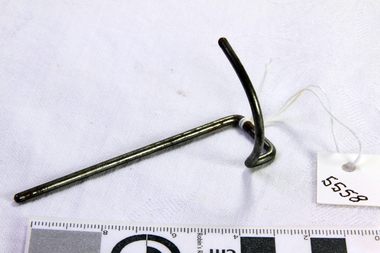 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Hook, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Hook; thin metal rod bent at one end into a curved upward arc. Thais sewing machine part was made for a Wertheim sewing machine by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Needle Plate, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Needle plate for a Wertheim sewing machine, made from a metal bar with machined holes for attaching and adjusting. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, needle plate, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Instruction Manual, Joseph Wertheim, Instruction manual for use and management of the Wertheim High Arm Sewing Machine, 23-07-1891
This instruction book was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains 12 accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The item is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim.Book with pale blue cover and 19 double-sided printed pages stapled together. The book is an instruction manual for using and managing the Wertheim High Arm Sewing Machine and other similar models. It was published in Frankfurt, Germany, by Joseph Wertheim, the machines' manufacturer. The Australian distributor of the machines was Hugo Wertheim, 173 William Street, Melbourne. Circa 1891.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessories, sewing machine instructions, wertheim instruction book, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, 23-7-1891, £6 6/-, mrs burrowes, burrumbeet, h. wertheim, wertheim sewing machines, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Receipt, Joseph Wertheim, Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, 23-07-1891
This receipt was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin.The receipt is significant for its connection with Victoria's northwestern district, the Melbourne distributor Hugo Wertheim, and the well-known German manufacturer of the early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. The stamp with Queen Victoria's profile also connects the receipt to the Victorian era and connects Melbourne to Colonial Australia. The receipt also gives a fixed date to the machine accessories and instruction book in our Collection, connecting them all to domestic life in the Victorian era.Receipt on cream paper, rectangular, with red horizontal and vertical lines. Printed letterhead and heading text. Handwritten details of the seller, owner, the item purchased, method of payment, and cost. Signed by two signatories. A one-penny stamp is attached. Sold by Wertheim Sewing Machines and Hapsburg Pianos,.dated 23rd July 1891 for £6 6/- from Mrs Burrowes, Burrumbeet, Victoria, for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine.Printed "From the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot" Handwritten "Mrs Burrowes, Burrumbeet" "July 23rd 1891" "Wertheim Sewing Machine" "£6 6" "Settled by Cash" Signatures "H. Wertheim" and (Looks Like) "John A Cherry" Ont the stamp, [image of Queen Victoria's profile] and "VICTORIA" "ONE PENNY" flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessories, sewing machine instructions, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, 23-7-1891, £6 6/-, mrs burrowes, burrumbeet, h. wertheim, wertheim sewing machines, domestic machines, dress making, home industry, fashion, receipt, queen victoria stamp, one-penny stamp -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Box, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This Wertheim Sewing Machine accessory box was donated with twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. the box's construction includes a coloured printed label and strong stitching on the joins of the edges. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The box is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim.Cardboard box, rectangular, with coloured printed labels. The top of the box has a city scene on it, depicting buildings, factories and figures. Made by Wertheim Sewing Machine Co. of Germany. The Box has been sewn around the edges. There is a handwritten pencil inscription on one of the sides (difficult to decipher)."Manufactured in Germany" "WERTHEIM" "The Wonderful Sewing Machines" Handwritten "Ste - - - B - - - - Wbool"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessories, sewing machine instructions, wertheim instruction book, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, 23-7-1891, £6 6/-, mrs burrowes, burrumbeet, h. wertheim, wertheim sewing machines, hand-stitched box, accessory box, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Foot tool, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Foot accessory tool for a Wertheim sewing machine. Mane by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBook - BOOK FROM GALLIPOLI, Cassel & Company Ltd, "THE ANZAC BOOK", C 1916
A compilation of articles, stories, poetry and illustrations written by men of the ANZACS in Gallipoli. In Nov 1915 a committee was established to produce the publication with cash prizes offered after evacuation correspondents, Charles Bean and Arthur Bazely edited the contributions.160 page soft cover book, brown in colour held by two large staples. Several front pages and one back page loose. Contents cover pictures, stories, poems and other writings set in the ANZAC Campaign.Heading 'THE ANZAC BOOK". "Written and illustrated in Gallipoli by the men of ANZAC". "For the benefit of Patriotic Funds connected with the A.N.Z.A.C." anzacs, gallipoli -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBook - Adult Education, At the Roadhouse, 1980
The South Australian Department of Education published books to educate adults in English Literacy. This one depicts Australian aborigines in the photos and may have been used in Aboriginal classes during the 1980's.Adult literacy in South Australia was targeted for varying groups including Aborigines. This book demonstrates the understanding of and attitude towards this group of people in 1980.Sepia coloured cover with cash register, coffee and woman serving a customer. The book is held together with 3 staples. Each page has a large black & white photo with large print at the top explaining the picture. Stamped on back and front cover: 'Myrtleford Adult Literacy Group'aborigines. adult education. literacy. -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncDocument - Series Listing, Fraser Faithfull et al, Series 71: Cash Receipt Books - Arts Related, 2000
A collection of 8 small Cash Receipt books and 4 larger Invoice and Statement books recording payments made to artists etc. One of the larger books dates from the 1970, the others from 1987-95. These books also record Art Award entries. Note: One book records purchases c. 1989/90 of the "Listening to the Landscape" oral hsitory project tape and book.shire of eltham archives, series listing -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncFolder, Eltham War Memorial Trust; Easter Gymkhana Committee Minutes, 19 Nov 1954-6 Jun 1958
Contents: Notice from Honoury Treasurer of Easter Gymkhana Committee regarding completion of 1954 event and expression of thanks and that committee is now going into recess prior to commencement of planning for 1955 Notice of Easter Gymkhana Committee Meeting, Monday 24th October, 1955 at the Shire Hall, Eltham Letter from B.T. Taylor, Hon. Secretary, Eltham Easter Show Committee regarding the sale of tickets (c.1957) Letter from B.T. Taylor, President, Eltham Easter Show Committee to Georges Ltd regarding the supply of The Georges Cup for the Eltham Easter Show, 11 April 1958 Letter from Georges Ltd to B.T. Taylor, President, Eltham Easter Show Committee with payment for the minitiares of The Georges Cup, 6 June 1958 Letter from Eltham Shire Secretary to B.T. Taylor, President, Eltham Easter Show Committee advising of new procxess regarding raffle, 5 May 1958 Letter from Lilian Heath, Secretary, Judge Book Village Auxiallary to B.T. Taylor, Eltham Easter Show Committee, 24 May 1958 Letter from Mrs R.J. Godfrey on behalf of M.A. Godfrey of Dandenong to B.T. Taylor, President, Eltham Easter Show under threat of legal action requesting replacement of cheque for £10 (second prize Open Jumping Contest), which was lost, 24 May 1958 Reply by B.T. Taylor, President, Eltham Easter Show Committee to Mrs R.J. Godfrey to her letter of 24 May explaining circumstances and denying responsibility to forward a replacement cheque as it was cashed at the Golf Club Hotel; 6 June 1958 History of the War Memorial Following the end of the First World War, communities across Victoria and Australia typically erected memorials which were predominantly statues, cenotaphs, avenues of honour and plaques. The Shire of Eltham established the Avenue of Honour at the gateway to the shire as well as an obelisk at the corner of Main Road and Bridge street and the Shire of Eltham War Memorial Tower at Kangaroo Ground. After the Second World War communities once again desired to preserve the memories of those who served and paid the ultimate sacrifice. Resources were scarce so there was a transition away from the traditional style memorials that sprang up post 1918 to one of building facilities that would provide ongoing benefit to the community. Even before the end of the Second World War, the citizens of Eltham began to consider an appropriate form of memorial for those from the area who fought and died in the First and Second World Wars. In 1943 the Eltham Women’s Auxiliary raised funds for the construction of buildings to be established on land to be purchased for the proposed War Memorial. On March 27th, 1945, the Eltham District Progress Association called a meeting of local people who in turn set up and registered the Eltham War Memorial Trust Inc. As a focus for the purpose of the memorial, the newspaper notice read:- ‘Those who have had a member of their family in the fighting services will want to see that the form of a memorial we are concerned with is the one which will be a constant reminder to us of those who fought for us and the little ones for whom they fought and died.’ At that meeting it was decided the Memorial should take the form of a baby health centre along with a creche and children’s library. In late 1945, the newly formed Eltham War Memorial Trust purchased the land at 903-907 Main Road Eltham from Miss Shillinglaw, which once formed part of the Shillinglaw farm on Lot 90 of Holloway’s 1851 “Little Eltham” subdivision. The Governor of Victoria, General Sir Dallas Brooks, laid the foundation stone on November 24th, 1950, in memory of those who fell in the Second World War. The Eltham Infant Welfare Centre was opened November 15th, 1952, the Pre-school on December 1st, 1956, and the Children’s Library in 1961. In late 1966 the children’s library service was integrated into the Heideberg Regional Library Service and the building was officially renamed the Eltham War Memorial Hall. Following the opening of the Eltham Infant Welfare Centre, work began in 1953 planning for the entrance to the grounds, which is signaled by a wrought iron arch entitled “Eltham War Memorial” . In 1954 the Eltham War Memorial Trust decided that a legacy provided by the late Councillor Ernest James Andrew (d. 29 March 1950) in memory of his wife, Mrs. Ellen Andrew (d. 13 July 1946) and who are both buried at Eltham Cemetery, should be used to fund the construction of the entrance. A metal plate inscribed to this effect was attached to the gates. Work on the Memorial Gardens was undertaken throughout the following decade, with a Memorial Forecourt included in the final 1956 plans for the Pre-School Centre. A quote was accepted by the Trust in 1963 for the implementation of a memorial garden, which included grading of a sixty-five foot strip at the rear of the Trust buildings and construction of concrete paths. The stone retaining walls at the front of the site were installed in 1968 when Main Road was widened and it is believed that the Memorial Gates were relocated at that time also. Eltham Senior Citizens Centre In 1964, Eltham Shire Council purchased a section of land from the Trust at the northern end of the site, as a provision for Country Fire Authority buildings. At the same time the Elderly Citizens Club proposed a Senior Citizens Centre on the south western section of the Trust’s property. This was approved by the Trust with the provision that the building was constructed in ‘accord’ with those already existing. In 1965 Council took on board the plans for the Senior Citizens Centre and applied for a government grant. These could only be awarded if Council owned the site. In 1962 the Trust had resolved to hand over the assets to Council once the Memorial Gardens were completed. This was in line with Health Department requirements that grants for the ongoing operation and maintenance of the three facilities would only be made once the the facilities were completed and handed over to Council. In 1965 the Department of Health further demanded substantial alterations to the Pre-School playground as a result of the pending impact of the planned Senior Citizens Centre and Main Road duplication. As a consequence, handover of the Trust’s assets to Council was initiated with a formal ceremony held in the Children’s Library on August 28th, 1965. The Trust continued on as a committee of management for another twelve months. Plans and specifications for the Senior Citizens Centre were prepared by March 1966. Council obtained a grant from the Government which covered one third of the cost and the building was completed by April 1967. Whilst the Senior Citizens Centre is contained within the original Eltham War Memorial building precinct, it was not part of the original Memorial and was not funded by the Eltham War Memorial Trust.Nine copies of letters/notices inserted loose in Minute Book, 33 x 21 x 1 cm, green faux crocodile skin hard board end-covers with black spine binding; 82 pages (last 38 blank)b.t. (ben) taylor, easter gymkhana committee, eltham war memorial trust, georges ltd, golf club hotel, judge book village auxilliary, lilian heath, minutes, r.j. godfrey, the georges cup -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchPersonal Records, Members pay book Royal Australian AIr Force
R A A F MEMBER PAY BOOK.Showing Cash payments ,Fines Forfeitures ,and other debits. Particulars of active pay and allowances .Medical records page24&25. This items significance is that it is a first hand account of financial aspects of our armed Forces .RAAF Pay Book - 74028 Oscar William Maxwell NILSON 1946Official No.74028. Pay Book No 148106 Surname NILSON ChristianNamesOSCAR WILLIAM MAXWELL,Top right corner a large hand printed M. Top left corner M/F 2. Centre front Australian Coat of Arms.Diagonal front cover Cancelled -Discharged 28/2/1946. -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionBook - Books, n.d
Port of Portland Collection -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBook - Ready Reckoner, The Express Ready Reckoner, circa 1920s
This item was produced for commercial shops and other traders in a period, 1800 to the 1950s. They were used because they were extremely cost effective, speedy, easy to learn and simple to use. It was also at a time before pocket calculators and electric cash tills were produced. The reckoners were a fast and accurate accounting book for a ever increasing bulk purchasing industry. These reckoners were at the start of a business principle "time is money" The reckoner was also looked upon as a way of reducing staff errors in the calculation field. This reckoner was highly valued to a rural industry in the Kiewa Valley because of the bulk produce being bought and sold here. Produce such as milk, tobacco, cattle, timber and fruits relied on weights and quantities calculation for cost pricing. Electrical machines were not of use in "the field or paddock" where important price negotiations took place. For a successful business to keep going accuracy was upper most to producers. It was still a time where honest transactions built reputations and tardiness ruined them. It was a time when a producer's word was his bond and a gentleman's handshake was as good as a contract. This attitude lasted a lot longer in rural regions than in the city. A producer's reputation was based on face to face negotiations and honesty.This hard cover book (blue in colour) contains 210 pages of black numbers and headings on light yellow pages (aged). The numbers refer to calculations of per unit price of goods and percentages.Top of front cover "Inglis Reckoners" underneath "The 'Express' Ready Reckoner", underneath "with All the Pence up to 1(pound symbol), Interest, Wages, Discount, Tables Etc." The spine: The Express Ready Reckoner with all the pence up to 1 (pound symbol) Interest Wages Discount Tables &c." underneath " The Express Series Vol 1" at the bottom of spine "Gall & Inglis"inlis, ready reckoner, imperial calculations -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Document - Younger Pty Ltd docket book, 1950s
This booklet of sales dockets came from the Youngers Stores in Warrnambool. John Younger came to Warrnambool from Beechworth in 1888 and established a general store in Liebig Street and quickly built up a thriving business. His store was one of the main reasons why Liebig Street became the main shopping precinct in Warrnambool by the beginning of the 20th century. John Younger was active in community affairs and was a Town Councillor from 1902 to 1918 and Mayor of the Town. He died in the 1930s and his store was continued by family members but taken over by Charles Moore in 1958. It closed in the 1980s. The maker of the docket book, Lamson Paragon Limited, was a British firm with factories and offices in Australia and it initially specialized in making sales docket books using a carbon paper process. The original founder of the firm, William Lamson of Massachusetts, U.S.A., was the first to introduce the system of paying for goods in a store using cash balls on tracks. This pad is of some interest as it shows the system of receipts issued by a Warrnambool firm in the 1950s. It is of particular interest coming from Youngers Stores, a major retailer in Warrnambool for over 90 years. This is a pad of dockets stapled together 30 pages). The pages are buff-coloured with red and black printing on every second page. Every second page has been left blank so that a second copy could be kept of every transaction using carbon paper. The pad originally had dockets for 50 transactions for Youngers Stores in Liebig Street, Warrnambool. The first three pages are badly torn. The back of every docket has an advertisement for Youngers stores.Docket front: ‘Phone 21, Terms, Nett Cash, M……………., Younger Pty Ltd, General Merchants, Registered Office, Liebig St., Warrnambool, We Buy for Cash and Sell for Cash, Sold by, Exd. By, Date, Lamson Paragon Limited.’docket book, younger pty ltd, general merchants, department stores, liebig street, warrnambool -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyBook, Borough of Ringwood Cash Expenditure Reports
... Bound book "Borough of Ringwood Cash Expenditure Reports"... Road Ringwood North melbourne Bound book "Borough of Ringwood ...Bound book "Borough of Ringwood Cash Expenditure Reports" -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Bank cheque, Sands & McDougall Limited, 03-12-1885
This bank cheque originated from the Bank of Australasia, Melbourne branch. It was issued on 3rd December 1885 to a person surnamed Slater for £71.11.5 (seventy-one pounds, eleven shillings and five pence). The parallel lines are called Cheque Crossed and mean that only Slater and no one else could receive the payment and that it would have been paid into Slater's bank account, not exchanged for cash. The embossed dots signify that the cheque amount was also paid to be the bearer of the cheque. Slater would have visited the bank to deposit the money into his or her own account. The cheque was printed by Sands & McDougall, a long-standing Melbourne printing and stationery company. It was then Stamped at the bank with its own unique number before it was issued to the customer. From its previously perforated edges, it is presumed that the cheque was part of a page of cheques, likely to be contained within a book of similar cheques ready for use. The Bank of Australia was incorporated by Royal Charter of England in March 1834. It had its Australian beginnings on 14th December 1835, opening in Sydney. The Acting Superintendent of the bank at that time was David Charters McArthur. He was Superintendent from 1867-to 1876. The Melbourne branch opened on 28th August 1838 in a two-roomed brick cottage on the north side of Little Collins Street, where two huge mastiff dogs were used at night to guard the bank. The government also provided an armed military sentinel. Due to the bank's rapid growth, a new building for the Melbourne branch was opened in 1840 at 75 Collins Street West. By 1879 the bank had been upgraded to a magnificent two-storey building on the corners of Collins and Queens Streets, with the entry on Collins Street. In 1951 the Bank of Australasia amalgamated with the Union Bank to form the Australia and New Zealand Bank, now known as the ANZ. Then in 1970, the ANZ merged with both the ES&A and the London Bank of Australia to form the ANZ Banking Group Limited. The ANZ Banking Group Ltd kindly donated a variety of historic items from the Bank of Australasia. BANK of AUSTRALASIA, WARRNAMBOOL – In 1854 Warrnambool had two banks, the Union Bank and the Bank of Australasia. Later, completely different bank businesses opened; in 1867 the National Bank of Australasia, then in 1875 the Colonial Bank of Australasia. The original Warrnambool branch of the Bank of Australasia was established in July 1854, and operated from a leased cottage on Merri Street, close to Liebig Street. The bank next bought a stone building previously erected by drapers Cramond & Dickson on the corner of Timor and Gibson Streets. Samuel Hannaford was a teller and then Manager at the Warrnambool branch from 1855 to 1856 and the Warrnambool Council chose that bank for its dealings during 1856-57. In 1859 Roberts & Co. was awarded the contract to build the new Bank of Australasia branch for the sum of £3,000. The land was on a sand hill on the northeast corner of Timor and Kepler Streets and had been bought in 1855 from investor James Cust. The new building opened on May 21, 1860. The bank continued to operate there until 1951 when it merged with the Union Bank to form the ANZ Bank, which continued operating from its Liebig Street building. Warrnambool City Council purchased the former Bank of Australasia building in 1971 and renovated it, then on 3rd December 1973 it was officially opened as the Art Gallery by Cr. Harold Stephenson and Gallery Director John Welsh. The Gallery transferred to the purpose-built building in Liebig Street in 1986 and the old bank building is now the Gallery club. Staff at the Bank of Australasia in Warrnambool included the following men but others were also involved: Samuel Hannaford, Teller then Manager from 1855-1856; W H Palmer, Manager from January 1857 until November 1869 when the Teller Basil Spence was promoted to Manager; H B Chomley, Manager from April 1873 and still there in 1886; A Butt, Manager in 1895-1904; J R McCleary Accountant and Acting Manager for 12 months, until 1900; A Kirk, Manager 1904; J Moore, staff until his transfer to Bendigo in December 1908; J S Bath was Manager until 1915; C C Cox, Manager until April 1923; Richard C Stanley, Manager 1923 to April 1928. The bank cheque has significance through its association with the Bank of Australasia. The early Australian bank was established in 1834 by Royal Charter and opened in Sydney, Australia, in Sydney in 1835. The bank had many Australian offices in November 1877, particularly on the east and south coasts. Victoria had 45 percent of all Offices. The bank cheque is significant as an early example of financial management of money and money exchange or transfer.Bank cheque of the Bank of Australasia, Melbourne branch. The rectangular paper has three sides that have been perforated. It is printed in blue with bank's Insignia of a heraldic shield of sheep hung by their waists and ships in full sail. Embossed Stamp Duty mark. Embossed dots. Handwritten black ink details Dated 3rd Dec 1885. Printed in Melbourne by Sands & McDougall. Diagonal parallel lines are across the cheque. Printed: "Bank of Australasia, MELBOURNE (75 COLLINS ST. WEST)." "454,358" "Sands & McDougall, Melbourne" Embossed stamp: Symbol of Crown above double oval lines " - STAMP DUTY" "ONE PENNY" Embossed dots forming test "7 PAID T2" Handwritten: "3rd Dec. [188] 5" "134 - Slater" "Seventy one pounds 11/S 5p" "£71.11.5" Signature: (undecipherable) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, bank cheque, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, bank of australasia, boa, union bank, australia & new zealand bank, anz bank, bank note, melbourne, slater, sands & mcdougall, chrssed cheque, embossed dots, paid cheque
