Showing 1239 items
matching codes
-
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyBook, Rupbert Lockwood et al, Humour is their Weapon, 1985
Paperback book 'Humour is Their Weapon - Laugh with the Australian Wharfies' by Ruper Lockwood. 96 pp, illustrated with cartoons and photosHas library codes on spine and inside back cover, stamped top and bottom 'St Kilda Public Library'piers and wharves - waterside workers, rupert lockwood, mark knight -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook, Knitting, Patons Book no. 845
This book was owned by the late Dr Elizabeth Kerr and was donated to the Museum by the executor of her estate, Margaret Cameron. It was produced by Coats Patons and contains knitting patterns for womens garments.BOOK 845 / PRICE CODE K / Patons / Lady's Handknits in / TOTEM 8 PLY / PURE NEW WOOLknitting handicrafts - history, coats patons (australia) limited, knitting, handicrafts - history -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchTool - "Pusser's" Dirk and Seaman's Paybook, Royal Australian Navy
Metal Dirk and Paper Booklet.Booklet Royal Australian Navy. Explanatory Notes on the Pay and Entitlement Provisions of the Naval Pay Code. January 1959. -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratGeneral Smuts (Don Woodward Collection), Millin, Sarah Gertrude, 1936
Biography of Jan Smuts (1870-1950) who was a South African soldier, statesman and politician. He promoted South Africa's role in the British Commonwealth.History - South Africa and British Commonwealth. Politics and government. Wars.Book; 394 pages. Cover: blue background; gold lettering; author's name and title.Library stamps: Carey Baptist Grammar. In black textacolour: 3973. In black textacolour: dewey decimal code on the spine.btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, smuts, jan, history - south africa, politics and government, biography, war, politics and government -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Pattern Book, Patons Knitting Book, No.684, Patons and Baldwins, 1980s
Sixteen page knitting pattern book featuring black and white text and colour images. The colour cover features a woman wearing a knitted jumper.front: [printed] Patons / The Magic of / Charm / 12ply / 684 / PRICE / CODE / F / 1 / EASY / TO FOLLOW / PATTERNSfashion, design, knitwear, home made, wool, pattern book, patons -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Pattern Book, Thorobred Tweed Collection, Thorobred Scheepjeswol Pty. Ltd, 1980s
Sixteen page colour knitting pattern book. The cover shows a man and woman wearing knitted jumpers.front: [printed] THOROBRED / We've fashioned the pleasure of knitting / TWEED / COLLECTION / with REAL TWEED / PRICE CODE Cthorobred scheepjeswol, fashion, design, knitwear, home made, wool, pattern book -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Pattern Book, Thorobred Playtime Volume 2, Thorobred Scheepjeswol Pty. Ltd, 1980s
Thirty two page colour knitting pattern book. The cover shows a child wearing a knitted jumper featuring a seal. There are nine other inset images of children wearing knitted jumpers.front: [printed] THOROBRED / PLAYTIME / VOLUME 2 / THOROBRED / We've fashioned the pleasure of knitting / PRICE CODE Dthorobred scheepjeswol, fashion, design, knitwear, home made, wool, pattern book -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchEquipment - Signal Lamp
This is a WW2 Morse code Signalling Lamp B 5A/2334 in its original wooden box. It was probably manufactured by BTH (British Thomson Houston), who were manufacturers of the iconic ‘Aldis Lamp.’ It was used for signalling ship to aircraft and ground to aircraft using morse code.Timber transit box with with hinged opening top secured by non return catches containing black metal round lamp with glass face attached to a low square stand. There are two metal bars attached to lid.Inside lid - Ref No 5A/2338 or 0? Hand painted in white SOS …—-… Box front face - printed in white and barely legible “small lamp” -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Army: Manual of Land Warfare, Part One: Vol.3, Pamphlet No.2: Aid To The Civil power, 1983
A gray coloured cover with black writing on it. The identification code is 7610-66-107-1143 and is in the top right hand side of the booklet. There are two punch holes on the left hand side of the booklet. The booklet is covered with a clear plastic coveraustralia - armed forces - service manuals, land warfare -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Military Forces: Staff Duties, (Australia) - copy 1, 1966
The aim of this handbook is to lay down the basic staff duties to be used by officers al all arms and services. A grey coloured plastic cover with black writing on it. There is the Australian Coat Of Arms in the middle of the cover. Near the top right hand is the code for the item 7610-66-021-5644. Also the date for Notification in ARO's for 31st December, 1966australia - armed forces - service manuals, staff duties -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPhotograph - Port Melbourne Police Station and lock-up, Jim Hillis, 1996
Taken by Jim HILLIS as a record of the buildingsOne of a set of photographs of Port Melbourne police station and lock up taken by Jim HILLIS in 1996 when PMH&PS representatives were given a tour after station was vacated by police: clipboard on wall with code of ethicsbuilt environment - civic, police, law, police station -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, Australian Army, Australian Military Forces: Staff Duties, (Australia) - copy 3, 1966
The aim of this handbook is to lay down the basic staff duties to be used by officers al all arms and services. A grey coloured plastic cover with black writing on it. There is the Australian Coat Of Arms in the middle of the cover. Near the top right hand is the code for the item 7610-66-021-5644. Also the date for Notification in ARO's for 31st December, 1966australia - armed forces - service manuals, staff duties -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, British Army, Manual of Map Reading, Air Photo Reading And Field Sketching. Part 3, Field Sketching, 1957, 1957
A red coloured cover with black writing on the front. In the middle reads Manual of Map Reading, Air Photo Reading And Field Sketching. Part 3, Field Sketching, 1957. Top Right corner reads WO Code No. 9085.british armed forces - service manuals, ministry of defence (army) -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, British Army, Recognition Booklet: Foreign Weapons and Equipment (USSR), 1964
A creamish coloured cardboard cove with black information on the front Top right hand corner reads Army Code No: 70009. there are two punch holes down the left hand side of the booklet and the booklet is held together with a metal staple.handbook, foreign weapons, foreign equipment, ussr -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MCCOLL, RANKIN AND STANISTREET COLLECTION: BUX TIN MINE/BADAK JUNGLE, 1920
Agreements between Bux Tin Mine/Badak Jungle. Badak Jungle to Henry Falconer Scarborough. Affidavit confirming siting of Company seal. Bux/Badak - Thomas West Orton, (Ronald Stanistreet), Scarborough, Clark, Frost, (Indenture paper). J. J. Stanistreet. Rules of North Blue Consolidated - Lord Nelson Consolidated, North Blue Consolidated. Correspondence Jungle Tin, coded cable, hand drawnmap of Tin Mine. Copy of code used. Re Badak Jungle(7) McColl Rankin & Stanistreet legal Managers Accountants etc Bendigo.MCCOLL RANKIN & STANISTREETorganization, business, gold mining, mccoll rankin & stanistreet -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPH NAVAL, MOUNTED, Exchange Studios, C.1900
The Steamer ASCANIUS became a troop Ship for the 1st AIF with the code name “HMAT A11”Photo B & W on light cream cardboard backing, photo is a 2 master, one funnel ship at sea, at the base is a Coat of Arms surrounded by the makers details in a circle. The rear has written details.On the rear in ink, “ ASCANIUS A11, Dear Exie, this is the old boat I am on, this photo was taken before she joined the Army”. On rear in pencil,” 9034. 1026 ........ 9 7/8. 6 3/4 .........”ascanius, troopships, aif -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook, Bentley's complete phrase code 1st ed 1928
"Bentley's complete phrase code 1st ed 1928"- E L Bentley compiler.wool sales wool brokering, wool sales, wool brokering -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratThe dark side of Camelot (Don Woodward Collection), Hersh, Seymour, 1997
Biography of J.F. Kennedy with insights into the Kennedy family and alleging that they "wrote their own moral code."USA politics. Biographical interest. Book; 498 pages. Cover: black background; black and white picture of J.F. Kennedy smoking; white and blue lettering; author's name and title. Green stamp with a ladybird and a heart.btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, kennedy, john f, presidents - united states, politics - united states of america, kennedy, joe, biography -
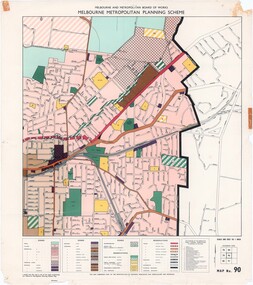 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyMap - Melbourne Metropolitan Planning Scheme, Municipality of Ringwood area - circa 1970
Colour-coded map marking proposed and existing business, industrial, transportation, public reservation, etc. planning zones within the City of Ringwood. Includes (undated) certification that this map is one of the maps constituting the Melbourne Metropolitan Planning Scheme Map.Scale: 800 feet to 1 inch. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instrument, Weighing Machine, c1970
In 2000 6 Staffmembers were asked if they had knowledge of this item. Barry Shearer remembered it well. Rob Greig, John Murray, Neville Gower, Stafford McKnight and Gael Ramsay had no knowledge of it. The weighing machine was used in the Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education Chemistry Laboratory until it was replaced by more modern weighing machines. A bench-top single pan weighing machine with built in ballance masses, applied by external colour-coded hand wheels. Fine adjustment used electric indication method. Sheet metal enclosure is painted green hammertone. Base is cast scientific instruments, stanton instruments, balance, weighting machine, barry shearer, chemistry -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, British Army, Field Engineering and Mine Warfare, Pamphlet No. 4: Mines- Individual Mechanisms 1961, 1961
A blue coloured cardboard cover with black information on it. top right hand corner reads WO Code No 9705. There are three punch holes and two metal staples down the left hand side. Inside of the booklet there are some loose pages.australia - armed forces - service manuals, field engineering, mine warfare -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, British Army, British Army: R.A.M.C. Training Pamphlet No. 1, Drills And Exercises, 1951, 1951
A brown cover whish has some water stains on it. The information on the cover is in black. Top right hand corner reads W.O. Code No. 6774. There are three punch holes and tow metal staples down the left hand side of the booklet.british army, r.a.m.c., training pamphlet, drills and exercises -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet, British Army, Field Engineering and Mine Warfare: Pamphlet No.6: Detection and Clearance of Mines, 1962 (Copy 2), 1962
A blue coloured cover with black writing. There is a rectangular square at the top with the word "Restricted" above the rest of the information. there is also a WO Code No: 9790 in the top right hand corner. There are three punch holes down the left hand side of the Manualbritish armed forces - service manuals, field engineering, mine warfare, detection and clearance of mines -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Instruction, Public Transport Corporation (PTC), "Code of Acceptable Behaviour", 8/01/1993 12:00:00 AM
Instruction - single A4 Photocopied sheet, titled "Code of Acceptable Behaviour", signed John McMillan CEO of PTC, reminding personal of their contractual obligations regarding public safety, equipment and disciplinary action. Dated 8/1/1993. Was faxed.trams, tramways, ptc, behaviour, staff, unions, personnel -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook, Knitting, Patons Book no. 483: Winter Warmers
This book was owned by the late Dr Elizabeth Kerr and was donated to the Museum by the executor of her estate, Margaret Cameron. It was produced by Coats Patons and contains knitting and crochet patterns for hats, scarves and gloves.WINTER / WARMERS / PATONS / Book 483 / 40 Designs for Hats, / Caps, Scarves, Gloves / and Mittens. / PRICE / CODE / Eknitting handicrafts - history crochet, coats patons (australia) limited, knitting, handicrafts - history, crochet -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Pattern Book, Thorobred Kashmir Mohair Designer Series Two, Thorobred Scheepjeswol Pty. Ltd, 1980s
Twenty four page colour knitting pattern book. The cover features two women and a man wearing coloured jumpers featuring geometric shapes.front: [printed] THOROBRED / We've fashioned the pleasure of knitting / KASHMIR / MOHAIR / DESIGNER SERIES / TWO / PRICE CODE Dthorobred scheepjeswol, fashion, design, knitwear, home made, wool, pattern book -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Pattern Book, Patons Knitting Book, No.1097, Patons and Baldwins, 1990s
Twenty six page knitting pattern book featuring black and white text and colour images. The colour cover features an image of three children lying next to each other wearing knitted jumpers.front: [printed] 1097 / PRICE / CODE / J / Patons / 18 PICTURE KNITS / FOR PRE-SCHOOLERS / IN PATONS 8 PLYfashion, design, knitwear, home made, wool, pattern book, patons -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Pattern Book, Patons Knitting Book, No.667, Patons and Baldwins, 1980s
Twenty six page knitting pattern book featuring black and white text and colour images. The colour cover features a woman wearing a pink, yellow, red and purple knitted jumper.front: [printed] Patons / belles in bluebell / 667 / PRICE / CODE / D / PURE NEW WOOL / EASY / TO FOLLOW / PATTERNSfashion, design, knitwear, home made, wool, pattern book, patons -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumSouvenir - CERAMIC MODEL, Swan China
Souvenir from England in WW1. Part of the collection of "Capt. Fred Baxter MC". Refer Cat No. 4219 for his service history.porcelain model of British soldier riding a motor bike. on side of front wheel is the shield emblem of Welwyn, a town in England. There is a hole in the bottom.on bottom is the stamp of a swan around which is written 'Swan China'. At bottom is written "Model of Despatch Rider" and a code number.baxter collection, fred baxter mc, souvenir, ceramic model, ww1 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, distant signal, signal, maritime signal, ball signal, signal shape, flagstaff signal, signal station, masthead signal, communications, marine technology, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, day shape, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897
