Showing 2242 items matching " usa"
-
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Commercial, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. New Orleans, Louisiana, USANew Orleans Balconies / RB / A (All Handwritten)mit bemis professorship, mit, robin boyd, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. Unknown location, probably USADate: 04819 / Subject / D (Handwritten) / Encircled 13 (Handwritten) / Encircled 76F (Handwritten)mit bemis professorship, mit, robin boyd, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Commercial
Colour slide in a mount. President and Mrs. Eisenhower on White House Lawn, Washington DC, USAMade in USA / Henry Cobb Shaw / 8 Bosworth St., Boston 8, Mass / WN6 / President & Mrs. Eisenhower on White House Lawnslide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1971
In April-May 1971, Robin and Patricia Boyd travelled to Honolulu, east coast USA and London. In London he was one of the judges for the Commonwealth-wide entries for the redevelopment of Whitehall and the Palace of Westminster. He was also researching overseas libraries, as background for plans for a new State Library of Victoria.Colour slide in a mount. Landscape, unknown location, probably Hawaii, USAInscribed Made in Australia / 5 / AUG 71M1slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. Crysler building in the distance, New York, New York, USAMade in Australia / 7 / JUL69M2 / Encircled 20 (Handwritten)slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. UMass, Dartmouth, Massachusetts, USA, 1963. (Architect: Paul Rudolph.)Made in Australia / 28 / JUL 69M2slide, robin boyd -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratThe autobiography of Benjamin Franklin with sayings of Poor Richard, hoaxes, bagatelles, essays, and letters, 1939
Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin who grew from poverty to become newspaper publisher, invented the lightning rod; he also became a politician and a signatory to the USA Declaration of Independence.Autobiographical, political, historical - USA. Book; 384 pages. Front cover: black background; coloured graphic of Ben Franklin; bookshop sticker - Lake Daylesford Book Barn; yellow, white, black, orange and green lettering; title.Title page: two prices - $8.55 and $4 - in pencil.btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, franklin, benjamin, autobiography, declaration of independence - usa, politics - united states of america -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. View from the Boyds’ apartment at Fernald Drive, Cambridge, MassachusettsMade in USA/ Patentedmit bemis professorship, mit, robin boyd, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. View from window with Patricia Boyd reading paperMade in USA / 14mit bemis professorship, mit, robin boyd, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. First Parish in Lexington, MAMade in USA / Patentedmit bemis professorship, mit, robin boyd, lexington, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France. Colour slide in a mount. Possibly New Orleans, Lousiana, USADate: 04819 / Subject: / E (Handwritten)slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. Red barns, unknown location, USAEncircled 64F (Handwritten)mit bemis professorship, mit, robin boyd, slide -
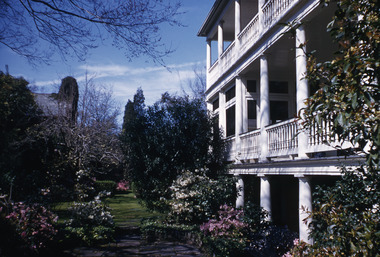 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. Unknown location, possibly southern USADate: / Subject / Encircled 67F (Handwritten) / Encircled 6 (Handwritten)mit bemis professorship, mit, robin boyd, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. Unknown location, possibly southern USADate: / Subject / Encircled 75F (Handwritten)mit bemis professorship, mit, robin boyd, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1971
In April-May 1971, Robin and Patricia Boyd travelled to Honolulu, east coast USA and London. In London he was one of the judges for the Commonwealth-wide entries for the redevelopment of Whitehall and the Palace of Westminster. He was also researching overseas libraries, as background for plans for a new State Library of Victoria.Colour slide in a mount. Building under construction, unknown location, probably USAInscribed Made in Australia / 9 / AUG 71M1slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. Wilde Lake Village Green, Columbia, Howard County, Maryland USAMade in Australia / 17 / JUL 69M6slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. Dulles International Airport, Chantilly, Virginia, USA. (Architect: Eero Saarinen.)Made in Australia / 15 / JUL 69M3slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. Dulles International Airport, Chantilly, Virginia, USA. (Architect: Eero Saarinen.)Made in Australia / 16 / JUL 69M3slide, robin boyd -
 Shepparton RSL Sub Branch
Shepparton RSL Sub BranchField Ration D, 1940
Kit emergency sustenance type E-3. Specification No 94-40441. Quantity 20,000 Stock No 8300-559158 Order No 43-29113AF MINTZ COMPANY PROPERTY AIR FORCES. USA ARMY Wrapped in waxed paper rectangle in shape with printed instruction and ingredients. -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Document, Schwerkolt Family: the Australian line, 2012
Account of Johann August Schwerkolt's early life, migration to Australia in 1849 and life there.Account of Johann August Schwerkolt's early life, migration to Australia in 1849 and life there. Also of August's youngest daughter Mary and her life and descendants in the USA.Account of Johann August Schwerkolt's early life, migration to Australia in 1849 and life there. schwerkolt, johann august, schwerkolt, paulina, schwerkolt, maria catherina wilhelmine, jackschowsky, mary elizabeth -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAudio - Gramophone Cylinder, B & H Jack, 1907
Edison Records was one of the early record labels that pioneered sound recording and reproduction, and was an important player in the early recording industry. The first phonograph cylinders were manufactured in 1888, followed by Edison's foundation of the Edison Phonograph Company in the same year. The recorded wax cylinders, later replaced by Blue Amberol cylinders, and vertical-cut Diamond Discs, were manufactured by Edison's National Phonograph Company from 1896 on, reorganized as Thomas A. Edison, Inc. in 1911. Until 1910 the recordings did not carry the names of the artists. The company began to lag behind its rivals in the 1920s, both technically and in the popularity of its artists, and halted production of recordings in 1929. Thomas A. Edison invented the phonograph, the first device for recording and playing back sound, in 1877. After patenting the invention and benefiting from the publicity and acclaim it received, Edison and his laboratory turned their attention to the commercial development of electric lighting, playing no further role in the development of the phonograph for nearly a decade. Start of the Recording Industry: In 1887, Edison turned his attention back to improving the phonograph and the phonograph cylinder. The following year, the Edison company introduced the ”Perfected Phonograph”. Edison introduced wax cylinders approximately 4+1⁄4 inches (11 cm) long and 2+1⁄4 inches (5.7 cm) in external diameter, which became the industry standard. They had a maximum playing time of about 3 minutes at 120 RPM, but around the turn of the century the standard speed was increased to (first 144) and then 160 RPM to improve clarity and volume, reducing the maximum to about 2 minutes and 15 seconds. Several experimental wax cylinder recordings of music and speech made in 1888 still exist. The wax entertainment cylinder made its commercial debut in 1889 at first, the only customers were entrepreneurs who installed nickel-in-the-slot phonographs in amusement arcades, saloons and other public places. At that time, a phonograph cost the equivalent of several months' wages for the average worker and was driven by an electric motor powered by hazardous, high-maintenance wet cell batteries. After more affordable spring-motor-driven phonographs designed for home use were introduced in 1895, the industry of producing recorded entertainment cylinders for sale to the general public began in earnest. Blank records were an important part of the business early on. Most phonographs had or could be fitted with attachments for the users to make their own recordings. One important early use, in line with the original term for a phonograph as a "talking machine", was in business for recording dictation. Attachments were added to facilitate starting, stopping, and skipping back the recording for dictation and playback by stenographers. The business phonograph eventually evolved into a separate device from the home entertainment phonograph. Edison's brand of business phonograph was called the Ediphone. The collection of three phonograph cylinders are an example of early recorded music use for domestic entertainment. They are significant as they represent the beginnings of the modern recording industry.Cardboard tube-shaped gramophone cylinder box with lid. The printed label on the outside of the box advertises the maker and patent details. The Catalogue Number and Title are either printed or hand written on the cylinder’s lid. This cylinder contained Record no. 49, “B & H Jack” and was made at the Edison Laboratory USA. C. 1905On lid “Edison Record No. 49”, written in pencil “B & H Jack” (it looks like this) On cylinder “EDISON GOLD MOULDED RECORDS ECHO ALL OVER THE WORLD” Patents listed for 1904 & 1905warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, gramophone record, gramophone cylinder, edison cylinder, edison record, home entertainment, music recording, edison laboratory orange nj, usa, national phonograph company of australia ltd sydney, thomas a. edison -
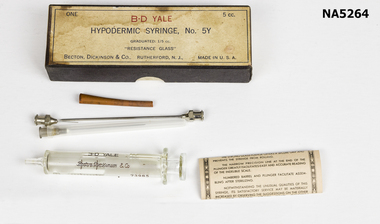 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Instrument - Hypodermic syringe, Becton, Dickenson & Co, Rutherford, N.J, Hypodermic syringe No.5Y, c 1947
Example of c1947 medical equipment.From equipment of a trained infant welfare nurse.Glass syringe with needles & "suggestions" (instructions!) in cardboard box. Dated June 1947.One 5cc. B.D Yale, hypodermic syringe, No 5Y, graduated 1/5 cc "Resistance glass" Becton, Dickenson & Co., Rutherford N.J. Made in USAmedical equipment -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumParaffin Section, 20th Century
Rectangular black box with metal scrapper and black instrument with round metal rod with screw tip and knob.Top of box: 'SPENCER BUFFALO USA' Label inside lid: 'PARAFFIN SECTIONS / [H]ONED NOV. 1952' Painted on box edge: 'W M 790'paraffin section, spencer buffalo, scientific equipment -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. Sculpture garden Museum of Modern Art, New York, New York, USAMade in Australia / 20 / JUL 69M2slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. Glazing detail, Dulles Airport, Dulles, VA, USA. (Architect: Eero Saarinen.)Made in Australia / 12 / JUL 69M3slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1969
Robin Boyd travelled to the USA and Britain for several weeks. He attended the opening of the new Australian Chancery in Washington DC, where he had designed an innovative exhibition with cylindrical display cases and sound recordings.Colour slide in a mount. Corner 5th Avenue and 56th St, New York, New York, USAMade in Australia / 25 / JUL 69M2slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. House, Possibly Charleston, South Carolina, USADate: 04819 / Subject: / Encircled 10 (Handwritten) / A (Handwritten) / 7 (Handwritten)slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1956-1957
Robin Boyd developed a close friendship with the founder of the Bauhaus in Weimar Germany, Walter Gropius, who had moved to the USA in the 1930s. Through this connection, Boyd was invited to be the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Bemis Professor at the School in the North American academic year 1956-7. Robin and Patricia Boyd, with their youngest daughter Suzy, were based in Cambridge, Massachusetts for the year. Boyd gave some lectures at MIT and he was also invited to give lectures at many other universities, allowing him to travel widely within the USA, especially on the East Coast. This gave him the opportunity to meet architects like Frank Lloyd Wright, Eero Saarinen, Paul Rudolph and many others, and visit the offices of Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, and places like Taliesin and the General Motors Technical Center Detroit. On the way home, the Boyds visited London, Berlin, Paris and Le Corbusier’s Ronchamp Chapel in France.Colour slide in a mount. Car park, possibly Los Angeles, USAEncircled 87F (Handwritten)mit bemis professorship, mit, robin boyd, slide -
 Anglesea and District Historical Society
Anglesea and District Historical SocietyKodak Camera and Brown Case, Eastman Kodak, No 1A Folding Pocket Camera, 1899 - 1905
This black folding Pocket Kodak camera comes with brown leather case and was on the market fron 1899 to 1905 and cost 12.00 US dollars. It uses film size A116.EKc on clasp. Case: KODAK CASE - MADE IN AUSTRALIA T.B. 25, 50 No.1. EKc - on top of lens. Shutter made in: ROCHESTER N.Y. USA by EASTMAN KODAK CO. - on bottom of lens 27258 F 7.9, 11, 16, 22, 32, 45 No 1A POCKET KODAK made in USA by EASTMAN KODAK COMPANY ROCHESTER N.Y. USE FILM SIZE A116 - on backcamera, folding, kodak, pocket -
 Queenscliffe Historical Museum
Queenscliffe Historical MuseumFour silver thumbles
Belonged to two grandmothers of donor - Emma Quimby, Maryland, USA and Anna Katherine Smailes Gilbert, Illinois, USA.1. Made in USA, Mt Patd. Thread cutter on side. 2. Handmade Victorian thimble, silver mark, fancy edge. 3. Silver thimble, floral edge. O for name. 4. Silver thimble size 8.
