Showing 2493 items
matching specimen
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionRocks, Azurite and Malachite Specimens, Moonta, South Australia
From the Ballarat School of Mines.Azurite and Malachite Specimens (and iron), Moonta, South Australiageology, rock, azurite, malachite, moonta -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPlant specimen, Flowers from the Holy Land, possibly c1949
This item was located in a book called The English Lakes which was owned by E.C. Holmes [Edward Carter Holmes was the name of my mother's, Elizabeth Mary [Elizabeth] Holmes family's pioneer settler. He arrived in Geelong on the 28th of June, 1849, with his wife Sarah and their first child Frances Harriet as assisted immigrants (people whose passage was subsidised by an assisted immigration scheme) to New South Wales at Port Henry, Geelong in the sailing boat ‘Larpent’. Sarah and Edward arrived two years before his mother, Harriet, arrived as unassisted passenger in Geelong on ‘The Eagle’. 200 of the " Larpent" passengers had been selected in England by Rev John Dunmore Lang whose wish was to encourage the migration of hard-working, God-fearing Protestants to the colony. He sponsored two ships, the "Travancore" and the" Larpent', to bring the settlers to Australia in 1849 with Dr Alexander Thomson, a Sydney Presbyterian minister, ready to receive and settle them. Thomson owned section 10 of the parish of Barrabool known as the Kardinia section — a square mile of undulating land west of Colac, still known today as Larpent. Among the 'Larpent' immigrants were many well-known Ballarat and District pioneers including Armitage, Mercer, Oddie and Scott. For more details about this migration scheme refer to: A thoroughly Protestant emigration: the emigration activities of the Rev. Dr. J.D. Lang / Ian Wynd.2006.] [source: Jane Dyer 2024] Printed card with a pressed botanical specimen glued onto it. Printed onto the card 'Flowers from the Holy Land. Placed on the Holy Sepulchrechatham family archive, chatham, holmes, ec holmes. holy land, relic, botanical, botany, holy sepulchre, botanical specimen -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - RANDALL COLLECTION: BALCONY AT SPECIMAN COTTAGE
Photograph, Balcony at Specimen Cottage, Hargreaves Street, Bendigo.photograph, building, speciman cottage -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryCrystalline Specimens
Box of 22 specimens of crystalline form, 3 missing -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Yellow Wattle Bird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Yellow Wattlebird is Australia's largest Honey-eater. This species is only found in Tasmania and is also known as the Tasmanian Wattlebird. The birds are active, noisy and conspicuous especially when the birds congregate in flocks. It lays two or three pinkish white eggs with light brown speckles. This particular Wattlebird specimen has been mounted in an accurate but stylised fashion by the taxidermist. When calling, this bird throws its head backwards to such an extent that the feathers on its crown may actually touch those on the bird's back. It then suddenly jerks its head forwards while releasing the call. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Yellow Wattlebird's has a distinct yellow belly and yellow-orange wattles on the sides of the head. The wattlebird's chest is white streaked with brown. The head, back and wings are brown. This specimen stands upon a wooden mount and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing-tag: 58a. / Wattled - Honeyeater / See catalogue page 18taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, bird, yellow wattlebird, tasmanian wattlebird, anthochaera paradoxa, australian birds, wattlebird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Little Pied Cormorant, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Little Pied Cormorant is commonly seen in Australia's wetlands. These birds reside amongst large flocks in locations where fish is plentiful. On the occasion that this bird is seen on inland streams and dams they will be solitary. This particular species willingly mixes with similar sized birds including the Little Black Cormorant. They feed on aquatic animals ranging from insects and yabbies and are labelled as benthic feeders because they find their prey on the seafloor. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Little Pied Cormorant specimen is a small bird with white and black colouring. The back of the head, neck, wings and tail are black while the undersides are a creamy white. The feet are webbed and are also dark in colouring. The bird has pale glass eyes and a medium sized bill and a long tail. This specimen is styled to look over it's left wing with its long neck bent to look in that direction. It stands on a wooden mount with a paper identification tag attached to the bird's right foot. The mount has the number 152 written on the wood.Swing tag: 21a. / Pied Cormorant / Catalogue page 41 / Mount: 152 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, cormorant, little piet cormorant, waterbird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Australasian Darter, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
An Australasian Darter is a waterbird with a distinctive long straight neck and a sharp bill. This feature has resulted in this bird sometimes being called the "snakebird" . This specimen is a slim bird with pale grey to white colouring. This colouring identifies this particular specimen as female. The Australasian Darter is commonly located around waterways in freshwater or brackish wetlands more than 0.5m deep. The Darter will perch on fallen trees and branches near the water and holds its wings out to the sides in an effort to dry them. The Noongar people of southwestern Australia called this bird "mimal". It has also been called the New Holland darter or the New Holland devil-bird. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.An Australasian Darter with a large, slim body and grey to white colouring. This specimen has a long snake-like neck and webbed feet. It has large powerful wings positioned flat against the rear of its body. The eyes are made of glass and are a pale yellow colour which is similar in colour to the long and sharp bill.Paper label: "154 New Holland Darter"taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, darter, bird, australasian darter -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Purple Swamphen, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Purple Swamphen can be readily located across eastern and northern Australia. They reside in areas with water including ponds, lakes, storm water drains, wetlands, swamps and marshes. These birds can often seen in urban locations including parks or along roadsides after a period of rainfall. Due to their adaptability, these birds often change environments. Purple Swamphens are omnivores and eat a wide variety of plants and animals. They live in large family groups and lay an average of five eggs which are the shared responsibility of both parents and occasionally the responsibility of young from a previous brood who may also assist caring for the eggs. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This taxidermy specimen is of a Purple Swamphen which is styalised standing on a wooden platform and has a paper identification tag tied to its upper left leg. The Purple Swamphen has dark colouring on its back and head with a purple-blue coloured neck, breast and belly. The bill is oversized and is orange/red which is the same colour as the frontal shield on the bird's face. The eyes are made from a red and black glass and the legs of this specimen are orange. The legs are elongated and the toes also long and unwebbed. 17e. / Purple Gallinule / Catalogue Page 35 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, swamphen, moorhen, purple bird, hen, purple swamphen, water bird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Gold-Sulphide Ore
This particular specimen was recovered from two hundred feet down in the Golden Mile in Kalgoorlie, Western Australia. The Golden Mile, named after the estimated sixty million ounces of gold worth around one hundred billion dollars, was the birthplace of the largest gold rush in Australia almost one hundred and thirty years ago when William Brookman and Samuel Pearce leased the Great Boulder mine. The Golden Mile is also the home of the Super Pit, Australia's most well-known mine.The majority of gold deposits will form as a native metal, however, on occasion, it can form a compound with another element, in this case, sulphur. Therefore, this specimen is a rare example of gold naturally forming into a compound mineral with sulphur. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A small gold-sulphide ore mineral specimen in shades of silver and grey with flecks of gold. Precious metals are often found in Sulphide Ores, as sulphides usually bind to these metals. They are also extremely symmetrical in crystaline form. Gold-Sulphide Ore occurs when gold forms a natural compound with other elements. In this form, gold can be present in one of two ways. It can be fully immersed in the sulphide, or a portion may be partially free. This specimen has minimal gold visible, with only a few flecks being partially visible.burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineralogy, gold-sulphide ore -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Masked Owl, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Masked Owls are an Australian barn owl species ranging across most of mainland Australia and Tasmania, generally within 300 km of coastline. Masked Owls are a medium sized bird averaging 390-500mm in length with wing spans up to 1250mm. There are several subspecies across Australia and the Tasmanian Masked Owl is the largest. Female Masked Owls are markedly larger than males. Masked Owls prefer forested, woodland, or timbered waterway habitats to open country, and nest in tall trees with suitable hollows and adjacent areas for foraging. They are territorial and hunt small mammals, rodents, rabbits, reptiles and small marsupials. Population numbers are in decline on the mainland and in Victoria the species is considered threatened. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century. This Masked Owl specimen is medium sized with a large head and distinctive heart-shaped facial markings. The plumage is mostly brown, patterned with flecks and patches of white, chestnut and light grey. The tail is short and largely concealed by long wing feathers. The face, feathered tarsi and underparts are much paler in contrast to the dorsal plumage, and the facial mask is edged by a distinct dark brown line. The eyes are large and yellow. This specimen stands on a wooden perch pedestal with identification tags attached to its leg. 12. / Delicate Owl / See Catalogue, page, 3 /taxidermy, taxidermy mount, masked owl, burke museum, australian museum, owls, birds of prey, heart-shaped faced owl, nocturnal birds, predator birds, barn owl, carnivore, tyto novaehollandiae, australian masked owl, tytonidae, tyto, territorial owl, threatened species, animalia, australian owls, tasmanian masked owl -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionGeological specimen, Petrified
14 specimens of petrified wood. Some smooth some rough.petrified wood, rock, geology -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - ESTELLE HEWSTON COLLECTION: SPECIMEN COTTAGE HARGREAVES STREET BENDIGO, Sept 1990
Two exterior photographs of Specimen Cottage, Hargreaves Street, BendigoEstelle Hewston -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - PHOTOGRAPH OF CARVED CHINESE CHAIR NO 7220
Photograph of Carved Chinese Chair No 7220 delivered to Specimen Cottage.photograph -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryGallium Residues
Gallium Residues (liquid). These are the earliest specimens from the Masson era -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryCrystalline Specimens
Number of parts: 27. Box of 26 specimens (glass) of crystalline -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyVase
White china specimen vase with pink flowers and green leaves.vases -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Crimson Rosella, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. The Crimson Rosella is relatively easy to see as it forages on the ground or among the leaves of eucalypts, with its spectacular combination of deep-crimson, royal-blue and black plumage. However, not all Crimson Rosellas look the same. Along the Murray River, Crimson Rosellas aren’t crimson at all — they are yellow, black and blue, with the yellow feathering replacing the crimson plumage. In southern South Australia they differ again, being roughly intermediate between crimson and yellow, with varying amounts of red and yellow in their plumage. Research featured in the 'State of Australia's Birds 2015' headline and regional reports suggest that the Crimson Rosella may be declining in the East Coast. There are several populations of the Crimson Rosella. Red (crimson) birds occur in northern Queensland, in southern Queensland to south-eastern South Australia and on Kangaroo Island. Orange birds are restricted to the Flinders Ranges region of South Australia, while yellow ones are found along the Murray, Murrumbidgee and neighbouring rivers (where yellow birds meet red birds they hybridise, producing orange offspring). Red birds have been introduced to Norfolk Island and New Zealand.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.There are several colour forms of the Crimson Rosella. The form it is named for has mostly crimson (red) plumage and bright blue cheeks. The feathers of the back and wing coverts are black broadly edged with red. The flight feathers of the wings have broad blue edges and the tail is blue above and pale blue below and on the outer feathers. This particular specimen has lost some feathers in its plumage and its colour is not as bright as that of a live specimen.Label: 77a / Pennant's Parakeet / See catalogue, page 22taxidermy, crimson rosella, bird, australian bird, rosella, crimson -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - GRAPTOLITE COLLECTION: DIDYMOGRAPTUS PROTOBIFIDUS (VARIANT) CHEWTONIAN
Sandy coloured rock, with two stiped graptolite specimen. Graptolite is very faint. On front sticker with 'Ch34'. Graptolite specimen was formerly held in the School of Mines Museum, Pall Mall, Bendigo. -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Wedgetail Eagle
The Wedgetail Eagle (aquila audax) is one of the largest birds of prey located in Australia, Indonesia and Papa New Guinea. It feasts mostly on rabbits but can target mammals as large as koalas, wombats, possums and small kangaroos. The darker the colouring, the older the bird is. A mostly dark brown feathering can suggest over 10 years old, though females are usually paler. This species mates monogamously for life. They circle high in the sky to avoid temperatures close to the ground and to assert their dominance over their territory. This specimen is lighter than many documented photographs of the species. They're usually less patchy / speckled with lighter colours on the chest and back. Documenting the wingspan of this specimen would be of interest because some have been measured up to 230cm. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This wedgetail eagle is posed with the head turned to the left. It has mostly dark brown feathers which is common for older birds in this species. Speckled light brown and white feathers cover it's neck, chest and a middle strip across the wings. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform. The bill is light grey and long legs dark brown. taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, wedgetail eagle, aquila audax, birds of prey, australian bird, eagle -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - GRAPTOLITE COLLECTION: ISOGRAPTUS CADUCEUS VAR. MAXIMO-DIVERGENS HARRIS
Isograptus caduceus var. maximo-divergens, Harris, Castlemainian. Pale brown rock, one graptolite specimen, one stipe not complete as rock is broken off. Sections visible are 3 cm in length. Sticker with 'Ca40' near specimen. Graptolite specimen was formerly held in the School of Mines Museum, Pall Mall, Bendigo. -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Ring Ouzel, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Ring Ouzel is a member of the Thrush family, Turdis, of which there are about 85 different species, commonly located in Europe. They are found in upland Scotland, northern England, north west Wales and Dartmoor. This species is identified by their dark colouring which contrasts to the white crescent across the breast and the white edging on the wings and some body feathers which provides a scale-like appearance. The diet of this species consists of invertebrates, some small vertebrates and a wide range of fruit. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Ring Ouzel specimen is stylised perched on a wooden platform. It is a medium sized bird of the thrush family. This particular specimen is a brown colour with pale edging to the wing feathers rather than the plumage being a darker black which can help identify this bird as female. The feathers have a white edging on the stomach giving this bird a scaly appearance. The bird has a small dark bill, two glass eyes, black legs and a long tail. Around the front of the upper breast, the bird has a striking white crescent shaped band. "Label 1 110a. / Ring Thrush / Catalogue Page 29 / Lable 2 Furdus torquaters / [illegible] 10 OCT. 1859 / near Leiden /"taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, european birds, ring ouzel, blackbird, ouzel -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Freshwater Crocodile, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Freshwater Crocodile can measure up to 3 meters and is generally not considered to be a threat to humans. They reside in Northern Australia, Western Australia and the northern part of Cape York Peninsula in Queensland. They live in freshwater environments and make burrows among the roots of trees which fringe the waters they can be found in. This species of Crocodile mainly feed on invertebrate and vertebrate prey which includes insects, spiders, frogs, fish and small birds and mammals. They are also recognized as "cannibalistic" with the older Freshwater Crocodile occasionally preying on young hatchlings. These crocodiles are known for their "high walk" which they do to move on land. It is named "high walk" because the animal lifts their body off the ground using their long legs for height. They are able to walk considerable distances on land using this technique. In captivity, Freshwater Crocodiles are known to be hostile and aggressive to others of its species. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Freshwater Crocodile has a slender snout which is much smaller and thinner than its Saltwater counterpart. This specimen has dark grey and brown colouring with the darker colours concentrated around the face and upper torso of the Crocodile. There are darker stripes along the tail which features triangular scales and is long in length. The teeth are visible and bright yellow glass has been used to replace the eyes of this particular specimen. The crocodile has long but thin limbs which protrude from the sides of the body.taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, crocodile, freshwater crocodile, johnstone's crocodile -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Common Buzzard, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860- 1880
The Common buzzard, a medium-sized raptor, is found across Europe and Asia, and in Africa in the winter months. It is the UK’s commonest bird of prey, found in nearly every county. Due to their large size and their brown color, they are often confused with other species, especially the Red kite and the Golden eagle. They may look the same from a distance, but the Common buzzard has a very distinctive call, like a cat’s mew, and a distinctive flying shape. When soaring and gliding, the tail is fanned and its wings are often held in a shallow 'V'. The colour of individuals varies from dark brown to much lighter, though they all have a finely barred tail and dark wingtips. This species occurs across Europe and Russia, and parts of Northern Africa and Asia in the cooler winter months. It lives in a range of habitats, especially woodland, moorland, pasture, scrub, arable land, marsh bog, villages, and sometimes towns and cities. This particular specimen has been mounted in a correct stylised fashion. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Common Buzzard is brown in colour with lighter markings on the chest. It has a white patch of feathers on the back of its head and it has darker wingtips and yellow feet. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing tag: 30 / Buzzard / Catalogue page 52. / Metal tag: 4043 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, common buzzard, bird of prey -
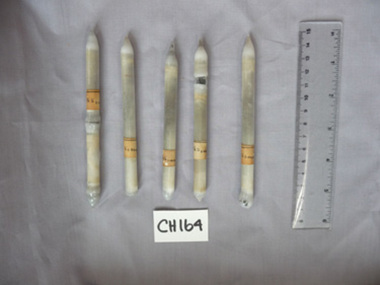 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryFes 1.064
Chemical specimens - 4 silica tubes containing Fe:S and Fe:O samples -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - GRAPTOLITE COLLECTION: TETRAGRAPTUS FRUTICOSIS (J. HALL) (3BR)
Tetragraptus fruticosis (J. Hall) (3br) Bendigonian. Dark grey rock, one specimen visible. 'Be.18' on sticker on rock. Graptolite specimen was formerly held in the School of Mines Museum, Pall Mall, Bendigo. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - GRAPTOLITE COLLECTION: TETRAGRAPTUS FRUTICOSUS (J. HALL) (3 BR.)
Tetragraptus fruticosus (J. Hall) (3 br.) Bendigonian. Cream coloured rock, 'Be19' on sticker next to graptolite specimen. Graptolite specimen was formerly held in the School of Mines Museum, Pall Mall, Bendigo. -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Goshawk, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This White Goshawk is the white colour morph of the Grey Goshawk. Is a moderate-sized hawk that measures 38 - 55 cm in length, and has a wingspan of 70 - 110 cm. It is native to Australia, and found in rainforest, forests, open forest and thickly-wooded watercourses. It mostly occurs in southeastern and northwestern Australia, and in Tasmania, all Grey Goshawks are white-phase. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This White Goshawk is white all over, with hints of beige around its eyes. The bird's legs are a yellow-beige colour, and its beak grey and white. This specimen stands on a perch, mounted upon a wooden platform, and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing tag: 5. / White Goshawk / See Catalogue, page 2 / Mount: 5 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, hawk, white goshawk, accipitridae -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Dusky Moorhen, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Dusky Moorhens are a medium sized, dark coloured water bird. They are located in the wetlands of eastern and south-western Australia. They can also be found in India, New Guinea, Borneo and Indonesia. These birds have a bright face shield located above the bill; however, the bright colour of this feature grows duller in females and young males during autumn and winter. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.A Dusky Moorhen standing on a wooden platform with a paper tag attached to its left leg. The specimen has a sooty-black plumage with a yellow bill and black/yellow legs/toes. It has remnants of what would have been a reddish-yellow shield on its forehead. "18c Australian Coot. See Catalogue, Page, 35"taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, dusky moorhen, waterbird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Grey Crow, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This specimen is named the Grey Crow on the swing tag but is more likely a Grey Currawong. There are six subspecies of Grey Currawongs and they can sometimes interbreed with other species of Currawong leading to a divergent series of appearances amongst the species. The species can be found in the south western to south eastern parts of Australia, including in Tasmania. It is an endangered species in the Northern Territory although the reasons why are not yet known. They prefer a wide range of habitats including coastal to arid and can also be occasionally found in suburban areas. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Grey Crow (or alternatively Grey Currawong) has mainly grey plumage with a white tail tip and darker undercarriage. It has yellow irises, made of glass, and brown claws. The bill is dark in colour. This specimen has been placed upon a wooden mount in a downwards facing position. It has a paper tag attached to its right leg.16a / Grey Cro [torn] / See Cat / [torn] /axidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, grey crow, grey currawong, currawong -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Grey Petrel, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Grey Petrel is commonly seen around New Zealand and rarely around mainland Australia. They are large birds with a grey-white-brown colouring who fly just above the water and are often solitary. They mainly eat squid and fish which they catch by shallow diving. Their scientific name, Procellaria cinerea, is derived from Saint Peter and the story of his walking on water. The Grey Petrel can appear to run on water as they prepare to take off. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Grey Petrel is a large bird with a grey and cream coloured plumage. It has short legs with webbed feet and a stout bill. The specimen stands on a wooden pedestal with a paper tag tied around its right leg. The eyes are small and made of a dark coloured glass.15a Great Grey Petrel - Catalogue, page 40.taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, grey petrel
