Showing 9017 items
matching pattern-making
-
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Domestic object - Kitchen Equipment, Tea Pot, Between 1885 and 1905 after which the backstamp changed to G & S LTD
Earthenware is lightly fired, readily absorbs water if not glazed, and does not allow light to pass through it. Coarse earthenware is made from clay and grog (ground up fired pot). There are two main types of glazed earthenware: One is covered with a transparent lead glaze; when the earthenware body to which this glaze is applied has a cream colour, the product is called creamware. The second type, covered with an opaque white .in glaze, is variously called tin-enamelled, or tin-glazed, earthenware, majolica, faience, or delft. G&S marking could be Grove & Stark, Longton, England (1871-1884). In the 19th century, J. & G. Meakin ,1851 based in Hanley, Stoke-on-Trent, Staffordshire, was known for the vast quantities of cheap ironstone china it produced for the domestic English market and for export to Australia, Canada, New Zealand and the United States. Grove & Stark were taken over by Meakin early 20thC The Mark could also be Gibson & Sons (Ltd), were notably manufacturers of earthenware Burslem, Stoke-on-Trent. Founded around 1885 and traded until the mid 1970's. They were previously Gibson, Sudlow & Co. Manufactured between 1885 to 1905. Small earthen-ware, black-glazed tea-pot. 8 sided. The body of the tea-pot is decorated with hand-painted gold flowers and raised cream flowers. The lid is also hand -painted with green leaves and flowers. This floral pattern is named "Garland" The lid is not of the same pattern as the base. The spout was broken when brush tailed possum entered Cottage via chimney 27/4/2014. Can be repairedOn the base of the tea-pot. Makers Mark is G & S. "Garland". (Pattern), Rg. No. 175153. Also 'Made in England'. Under glaze there is the word: England.crockery, earthenwarre, gibson & son ltd, grove & stark ltd, pioneers, early settlers, bentleigh, market gardeners, moorabbin, cheltenham, pottery, stoke- on - trent, england, longton, burslem, wedgwood -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Hughes Knitting Book no. 227, F. W. Hughes Pty. Ltd, 1959
One of a collection of 56 knitting pattern books donated by Mrs Hilma Carruthers. These books had been used by Mrs Carruthers, her mother and her two daughters. This book was produced by F.W. Hughes Ltd and contains patterns for knitted baby clothes.Knitting book, 16pp. Front cover printed in pink and black with a black and white photo of a finely knitted babies layette. Contains photos and patterns for knitted baby clothes.Hughes / KNITTING BOOK 227 / FEATURING / BABY'S / DESIGNS / 6 - 18 MONTHS / TWINPRUFE BABY WOOL / PRICE: 1'9handicrafts - history knitting, f.w. hughes industries ltd, handicrafts - history, knitting -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Pattern Book, Patons Knitting Book, No.805, Patons and Baldwins, 1980s
Twenty eight page knitting pattern book featuring black and white text and colour images. The colour cover features five children and a dog on skateboards and rollerskates, all wearing knitted jumpers (except the dog).front: [printed] Patons / EASY TO FOLLOW PATTERNS / ARAN / 8 ply / PURE NEW WOOL / BOOK 805 / PRICE CODE Kfashion, design, knitwear, home made, wool, pattern book, patons -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, Catchy Addresses, 2019
Mitcham streets reflecting Indian cities that were named by a well-known local who loved travelling there.Mitcham streets reflecting Indian cities that were named by a well-known local who loved travelling there. Vermont South streets named after Australia's best wine regions was testament to the suburb's wine-making history.Mitcham streets reflecting Indian cities that were named by a well-known local who loved travelling there. agra street, mitcham, calcutta street, mitcham, delhi street, mitcham, barossa avenue, vermont south, hunter valley road, vermont south, coonawarra drive, vermont south -
 Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer Museum
Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer MuseumKnitting, crochet and sewing books x 6, Paton's and Baldwin's, Madame Weigel's Journal of fashion x 2, Paton's knitting book x 2, Weldon's Socks and stockings, Enid Gilchrist's Toddlers clothes, 1942, 1943, 1950's
Madame Weigel's - monthly journal of fashion. Enid Gilchrist patterns - an Argus Production. Weldon's - printed in London, agent for NZ and Australia Gordon and GotchAll six books soft cover, colour print. Patons no 115 Bedjackets, Patons No 267 Jumpers, vest, cardigans, Weldon's sock and stockings for men and boys, Enid Gilchrist book has paper patterns inserted. Madame Weigel's includes advertisements, short stories, sewing, knitting, crochet patternssee photos -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Dowel Maker (Moot), Mid to late 19th Century indication of this date range is due to the engraved handles and brass ferrules often used on hand tools of this era
A dowel is a cylindrical rod, usually made of wood. In its original manufactured form, a dowel is called a dowel rod. Dowel rods are often cut into short lengths called dowel pins.These are commonly used as structural reinforcements in cabinet making and in joining large timbers together. To make a dowel, a piece of wood is split or whittled to a size slightly bigger than desired and to place the stock into a vice then rotate past a fixed knife, or alternatively, to rotate the knife around the stock such as the subject tool was used. Machines based on this principle emerged in the 19th century. Frequently, these are small bench-mounted tools, prior to this time dowels had to be cut by hand. The tool is an example of early to late 19th century hand tool used to make timber dowels. It is not associated with an historical event, person or place, makers provenance is unable to be determined at this time. Many small American and British tool manufactures were taken over by Stanley tools after 1843 when the company was established and this item could have been made by one of these. However the subject item appears to be rare and would be regarded as a collector's item.An adjustable woodworking tool know as a Moot, used for making Trunnels or Treenails (Dowels) for fastening joints in timber. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, moot, trunnels, treenails, circular, dowels, woodworking tool -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBag handle template, 1940
Used by internees at Camp 3 Tatura . Templates for the making of Handbagscamp 3, internee crafts, gisela wied, bag making -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Tool - Boot Last and Stand
Used for making Boots.No 8trades, bootmaking -
 Frankston RSL Sub Branch
Frankston RSL Sub BranchWebbing, Belt, Not known
1937 British Pattern web equipment was commonly on issue to Commonwealth forces including Australia up to the 1970's. Australian military forces changed colour from green blanco to black paint in the early 1960's.1937 pattern webbing belt with natural brass buckles and keepers. Outer surface stained black.Single engraved arrow on each inside surface of the belt fastening buckles. Printed owner's name "G. Boland" Printed identifier of former owner -3/773536(?) and initials "KFH" (?) -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Roombandolier
Designed from the experience of the British Army in the Anglo Boer War 1899-1902 for infantry and mounted troops. Bandolier included as part of the 1903 Pattern Bandolier Equipment ensemble. Dismounted troops very quickly rejected the Bandolier Equipment and it was replaced by the 1908 pattern Infantry web equipment. Australian horse mounted troops continued using the 1903 Bandolier equipment til they exchanged their horses for motorised vehicles in the early 1940's These bandoliers were worn by soldiers of the 4th, 17th, and 19th Light Horse Regiments and their precedent untis from c. 1905 to c.1942. Current 4/19th soldiers wear a bandolier styled on this bandolier when carrying a lance in Parades.Bandolier, 1903 pattern, 90 rounds mk. 2. Leather, Veg. tan, colour brown, brass buckles studs and triangle.M. A. RISK 1915 (Manufacturers mark and date of manuf.)leather, bandolier, 1903, accoutrements, equipment, 9 pockets -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchBook - ANZAC CENTENARY, Their journey is our story
The battles of the Great Warhave become well known; from the tales of dry air and dust that enveloped our soldiers at Gallipoli,to the cold, muddy horrors of Fromelles and other small towns along the Western Front where the long battle for peace played out.World War One (WW1)was one of the most significant events of the twentieth century, claiming the lives of more than 16 million people across the world.Rectangular shaped bookletANZAC CENTENARY.Sharing Stories & Making Connections.world war one history, victoria's world war one legacy, community resource guide -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph, Public Works, Road Construction, 1950s
An original photograph donated to the Kew Historical Society by the City's Engineering Department before the amalgamation of Kew into the City of Boroondara in 1994.While not all of the photographs are of Studley Park, Kew or East Kew, each photo provides a fine snapshot of the work of local government engineering departments of the period. They reveal they types of labour conducted, the techniques used and the equipment and machinery in the possession of the local government authority.Public works. Roadmaking machinery in the 1950s using a tip truck and other equipment. Inscription on reverse: "Road making. Date?" city of kew (engineering department), road construction maintenance -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph, Public Works, Road Construction, 1950s
An original photograph donated to the Kew Historical Society by the City's Engineering Department before the amalgamation of Kew into the City of Boroondara in 1994.While not all of the photographs are of Studley Park, Kew or East Kew, each photo provides a fine snapshot of the work of local government engineering departments of the period. They reveal they types of labour conducted, the techniques used and the equipment and machinery in the possession of the local government authority.Public works. Roadmaking in the 1950s using a steam roller. Inscription on reverse: "Road making. Date?" city of kew (engineering department), road construction building -
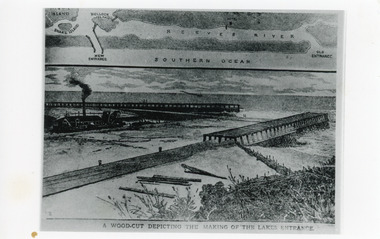 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - Entrance Works, 1880c
Photographic reproduction of woodcut drawing of the building of the entrance and map above of location.Black and white photograph of a woodcut showing dredge working between timber constructed piers on entrance from the lakes to the ocean Bass Strait. Piers unfinished, timber lying around, sand in the entrance. Map above showing position of the lakes, old and new entrances, southern ocean and sand dune vegetation. Lakes Entrance VictoriaA woodcut depicting the making of the Lakes Entrance.public works, dredging, waterways -
 Seaworks Maritime Museum
Seaworks Maritime MuseumParallel Rule- Prop
clear Parallel Rule with metal hinges with numbers and directions marked on itCapt Fields Pattern -
 Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright Museum
Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright MuseumLid
Brought to the Ovens Goldfields by Chinese men working in the area in the 19th century. Most likely made in China.Aldo Gios recorded the location of where most pieces in his collection were found. Some maps drawn by Aldo Gios, also give more detail. This detail is rare as most pieces of broken crockery were discarded and complete items were usually collected with no thought to recording the location where they were found. This object is part of one of the largest collections of Chinese ware found in the Upper Ovens area and the only one recording the location where found.Stoneware lid, glazed on upper surface. BrownChinese pattern on lid.chinese, ginger, jar, glaze, stoneware, lid -
 Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright Museum
Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright MuseumLid
Brought to the Ovens Goldfields by Chinese men working in the area in the 19th century. Most likely made in China.Aldo Gios recorded the location of where most pieces in his collection were found. Some maps drawn by Aldo Gios, also give more detail. This detail is rare as most pieces of broken crockery were discarded and complete items were usually collected with no thought to recording the location where they were found. This object is part of one of the largest collections of Chinese ware found in the Upper Ovens area and the only one recording the location where found.Stoneware lid, no glaze, slightly blackened - possibly been exposed to fire.Pattern on top of lid.chinese, ginger, jar, glaze, stoneware, lid, harrietville -
 Stanley Athenaeum & Public Room
Stanley Athenaeum & Public RoomDomestic object - Ashtray
Clear glass ashtray square in shape . pattern on side and base -
 Trafalgar Holden Museum
Trafalgar Holden MuseumFunctional object - Saddle cart/ van tree, Circa 1900
used circa 1900 in agriculture and on draught horsesAs manufactured and sold by Holden and FrostShaped to fit on horses back with two straps that fit around horses belly two metal rings for reins two brackets for strapping and a metal buckle on the end of the belly bandPattern etched on backsaddle cart, equine, agriculture -
 Working Heritage Crown Land Collection
Working Heritage Crown Land CollectionCeramic - Ceramic shard, Mint ceramic shard
Ceramic shard with white glazed finish and a blue decorative design. blue decorative patternpottery, ceramic, archaeology -
 Working Heritage Crown Land Collection
Working Heritage Crown Land CollectionCeramic - Ceramic shard, Mint ceramic shard
Ceramic shard with white glazed finish and a blue decorative design. blue decorative patternpottery, ceramic, archaeology -
 Working Heritage Crown Land Collection
Working Heritage Crown Land CollectionCeramic - Ceramic shard, Mint ceramic shard
Ceramic shard with white glazed finish and a blue decorative design. blue decorative patternpottery, ceramic, archaeology -
 Working Heritage Crown Land Collection
Working Heritage Crown Land CollectionCeramic - Ceramic shard, Mint ceramic shard
Ceramic shard with white glazed finish and a blue decorative design. blue decorative patternpottery, ceramic, archaeology -
 Working Heritage Crown Land Collection
Working Heritage Crown Land CollectionCeramic - Ceramic shard, Mint ceramic shard
Ceramic shard with white glazed finish and a blue decorative design. blue decorative patternpottery, ceramic, archaeology -
 Working Heritage Crown Land Collection
Working Heritage Crown Land CollectionCeramic - Ceramic shard, Mint ceramic shard
Ceramic shard with white glazed finish and a blue decorative design. blue decorative patternpottery, ceramic, archaeology -
 Working Heritage Crown Land Collection
Working Heritage Crown Land CollectionCeramic - Ceramic shard, Mint ceramic shard
Ceramic shard with white glazed finish and a blue decorative design. blue decorative patternpottery, ceramic, archaeology -
 Working Heritage Crown Land Collection
Working Heritage Crown Land CollectionCeramic - Ceramic shard, Mint ceramic shard
Ceramic shard with white glazed finish and a blue decorative design. blue decorative patternpottery, ceramic, archaeology -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook, Knitting, Lincoln Trio Knits Leaflet no. 45
This book was owned by the late Dr Elizabeth Kerr and was donated to the Museum by the executor of her estate, Margaret Cameron. It was produced by the Lincoln Mill, Coburg and contains a pattern for a womans cardigan.Lincoln Trio Knits / LEAFLET No. 45 / 1'6 / THIS PATTERN KNITS 5, 8 & 12 PLY / IN 4 SIZES / LINCOLN KNITTING WOOLS - THE BEST BUY IN ANY PLYknitting handicrafts - history, lincoln mills (australia) limited, knitting, handicrafts - history -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical SocietyLamp - kerosene, first half of 20th century
This lamp pattern was originally made in USA between 1880 and 1900. The pattern is called Feathered Cartouche and generally had a painted motif on each of the panels on the front. This lamp is probably a copy of the American lamp and made in Australia sometime in the first half of the 20th century. The lamp has an English style collar rather than an American one and the pattern is not as crisp as the American ones. There were several lamp patterns made here that were copies of American patterns and that style of collar was used on most of them. (ref Oil Lamp Antiques)This item is an important example of the early technology of artificial light. It has historical significance in demonstrating lighting devices used before the widespread use of electricity.Ornate clear glass kerosene lamp. Glass chimney is missing. Base is square and patterned with raised oval shapes, as is the stem. Both base and stem are hollow. At the top, the kerosene holder is squarish with round corners.. The wick holder is of brass and has a small wick adjustor.lamp, kerosene lamp, lighting - domestic -
 Chiltern Athenaeum Trust
Chiltern Athenaeum TrustThe Wells of Beersheba - book publication by Dalby Davison and Mahony, 1933
The Wells of Beersheba is a short romanticized account of the Battle of Beersheba, which took place on 31 October 1917 in Ottoman Palestine during the First World War between the attacking mounted infantry of Australia and New Zealand and the defending Ottoman garrison. It was written by the Australian author Frank Dalby Davison who was not present at the battle, but had been in the British cavalry during the war. Much of the book, which is more fictionalized reportage than novella, and in which no single character is drawn, reflects the codependency of horse and rider and the shock of battle. This booklet was first published in 1933. It was originally published in Sydney in 1933 by Angus & Robertson under the title The Wells of Beersheba. An Epic of the Australian Light Horse 1914-1918, with illustrations by Will Mahoney. WW1 semi-fictional association with the Battle of Beersheba - 4th Light Horse Brigade Australian Infantry Forces. October 1917. Ottoman Empire Palestine. Booklet titled "The Wells of Beersheba" by Frank Dalby Davison and illustrated by Will Mahony. Semi Cardboard Cover with parchment paper internally. The cover has a light rose colored pattern surrounding the title, author and illustrator details. Front cover has title "The Wells of Beersheba" and author Frank Dalby Davison with illustrator Will Mahony. There is a light rose colored pattern on the front cover. the wells of beersheba - charge of the 4th light horse brigade., book - the wells of beersheba, ww1 battle of beersheba october 1917.
