Showing 501 items
matching baggage
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCopper Sheathing
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries the outside of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Piece of rectangular Muntz metal from the wreck of the Schomberg. Metal has been bent back on itself at one end. Evidence of nail holes. Metal has verdigris and marine encrustation. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Sheathing, ca. 1855
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the outsides of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 per cent copper and 40 per cent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three-masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the cover and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its dayCopper sheathing or "Muntz metal" - 60% copper and 40% zinc, used to line the hull of the Schomberg to prevent shipworm infestation. The sheet was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. It is irregular in shape with nail holes and slight encrustation.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building, late 19th century sailing ships -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Sheathing
This sheet of copper sheathing or Muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by the reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and has other damage that has caused the edges to break away or fold over. Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in seawater and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the outsides of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 per cent copper and 40 per cent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day This Muntz sheet was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. It has been folded, bent and wrinkled. It has nail holes, Verdigris, marine growth and slight encrustation. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building -
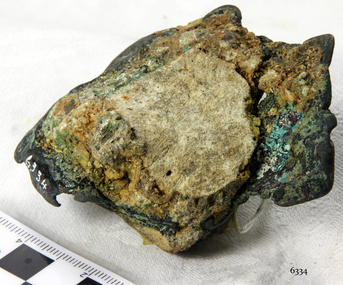 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCopper sheathing
This sheet of copper sheathing or muntz metal has been recovered from the sea. It has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea, it has encrustations from the sea such as sand, and other damage has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ Early timber sailing ships had a problem of the timber hulls being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries the outside of their ships were sheathed in copper sheathing or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oat with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper sheathing or Muntz metal in concretion. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, muntz, muntz metal, copper sheating,, copper sheathing, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumDocument - VIETNAM PAPERS - HERDMAN
5. Pocketbook issued to Australian Troops during the Vietnam War. Contents include: The War in South Vietnam, The People, Government Services, Armed Services, Viet Cong, Vietnamese Language, Useful information. 14. Details of Australia V US. Hill climb with program of Events, 22nd February 1970. 15. Details of dog races with fields listed on a six race program - 20th February 1970. 18. Document details departure itinerary (ex SVN) for K.J. HERDMAN. 27. Notebook contains names and addresses of US service personnel. Papers related to "Kevin John Herdman's" visit to South Vietnam from 18th February to 4th March 1970. Part of the Kevin John Herdman, No. 397661 Collection. See Cat. No. 5942P for details of his service. 27. Collection of documents related to K.J. Herdman. 1. Two page TAA flight ticket. Text in blue coloured type. Two baggage tickets stapled to front. 2. Single diary page with torn edge. Handwritten flight itinerary in section dated 16th February. 3. Two page QANTAS flight ticket. Text in red and black type. Flight details printed in purple type. 4. Printed flier outlining Australian Customs and Quarantine regulations. Recipient's name handwritten in black ink. 5. Green coloured soft cover pocketbook. 74 pages with cut edges. Black and white diagrams. Text in black type. 6. Small pamphlet with black type. Written in Vietnamese. 7. Foolscap sized 5 page document stapled on top LHC. Text in black type. Title "VISITS BY CMF OFFICERS TO VIETNAM". 8. A4 sized one page document with text in black type on one side only. Two sided pamphlet on blue paper stapled to top LHC. Black type on pamphlet. Title "NINE RULES FOR AUSTRALIAN ARMY FORCES IN VIETNAM." 9. Two page A4 sized document with text in black type. Text on one side of each page. Title "AUSTRALIAN FORCE VIETNAM, RTA BRIEFING NOTES - QANTAS CHARTER, SAIGON/SYDNEY". 10. Foolscap signed proforma oriented in landscape. Title: AUSTRALIAN MILITARY FORCES, VISITS BY CMF OFFICERS TO SYN". Details of personnel in black type. 11. Quarto sized two page document with printing on one side. Text in black type. Staple in top LHC. Title: "CMF VISITOR - LT. K.J. HERDMAN, (ITINERARY FOR LT. K.J. HERDMAN)". 12. Quarto sized two page document with printing on one side. Text in black type. Staple in top LHC. Title: " CMF VISITOR - LT K.J. HERDMAN (ITINERARY FOR LT. K.J.HERDMAN)" 13. A4 sized document with text in black type. Text on one side only. Title: CMF VISITOR - LT. K.J. HERDMAN". 14. Foolscap sized document with text in black type. Printing on one side. Title: "LONG HI HILL CLIMB". 15. Quarto sized document with text in black type. Printing on one side. Title: "DAT DO DOGS". 16. Foolscap sized 9 page document with text on one side. Printing in black type. Pages stapled together in top LHC. Title: "1 ATF G INSTRUCTIONS 14/69, SUPPLIES, POL AND AMMUNITION HOLDINGS". 17. A4 sized document with text on one side. Printing in black type. TITLE; "AMENDMENT 1 TO Q INSTRUCTION 14/69, DATED 23 OCT 69". 18. A4 SIZED DOCUMENT WITH TEXT ON BOTH SIDES. PRINTING IN BLACK TYPE. 19. Foolscap sized 3 page document with staple in top LHC. Text on page 1 in black type. Text on pages 2 & 3 in purple type. Pages are entitled "TEMA FLYING PROGRAMME - CH 47". 20. Foolscap sized 7 page document with text in black type. Printing on one side. Title: " OPERATIONS BREF - DET 52 SUP PL RAASC, REPUBLIC SOUTH VIETNAM (1967-69)", Dated 20 Sept, 69. 21. Foolscap sized 2 page document with text in black type. Printing on one side. Pages stapled on top LHC. Title: " Q INSTRUCTION 15/69, RETURN OF PRODUCE, " Dated 16 Oct 69. 22. Foolscap sized single page document with text in black type. Printing on one side. Title: " Q INSTRUCTION 19/69, RETURN AND DISPOSAL OF UNSERVICEABLE AMMUNITION" Dated 5 Nov 69. 23. Foolscap sized single page proforma with text and lines in black. No handwritten details. Title: "26 TRANSPORT COY RAASC VEHICLE SERVICEABILITY/AVAILABILITY STATE". 24. Foolscap sized single page proforma with text and lines in black. No handwritten details. Title: "DAILY EMPLOYMENT STATE, 85 TPT PL RAASC". 25. Foolscap sized single page document. Text and lines in purple. Reproduced on a spirit duplicator. Title: "INDENTING PROGRAMME FRESH". 26. Foolscap sized single sheet proforma with text and lines in black. No handwritten details. Title: DAILY MAINT MOVEMENT PLANNING TABLE". Printing on both sides. 27. Red and white covered note book. Title on front and details on back in black type. Lined pages. Handwritten information on most pages. 28. Illustrated Christmas Card. Illustration features an angel and the three Magi. Printing on inside in black. Handwritten message in black ink. 1. Passenger details handwritten in blue, carbon copy. 2. Itinerary notes handwritten in blue ink. 3. Handwritten in black ink: "CAPT K.J. HERDMAN". Flight details printed in purple coloured text. 4. Handwritten in black ink : "KEVIN JOHN HERDMAN". 7. Handwritten in black ink on page 1: LT. K. HERDMAN, 6 Coy RAASC, 17 Feb 70." Handwritten in black ink on last page: "1. Ensure teeth are all O.K., 2. Have you still got your tags Identity? (Signature). 11. Handwritten on top RHC of page 1: "CAPT A". 12. Handwritten on top RHC of page 1: "LT HERDMAN". 27. Handwritten notes in black ink on various pages. 28. Handwritten in black ink on inside of card: "Hello Kevin, Perhaps you remember the 62nd Trans. Company at Long Bing? I completely enjoyed your brief stay. If you are ever in the U.S. do stop by. Have a Merry Christmas to you and yours. Margo and Jack Olsen." vietnam war, army, training notes, kevin john herdman -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeremonial object - Chalice, 1855 or earlier
In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, found an ornate communion set used to celebrate the Eucharist or holy communion by a number of different Christian faiths was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery at Flagstaff Hill. The collection of artefacts from the Schomberg also contains ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and a photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald a former director of Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The Schomberg was a large three-masted full-ship rigged wooden ship built in 1855 by Alexander Hall and Co in Aberdeen, Scotland for James Baines' famous Black Ball Line at £43,103. The vessel was 288 feet (88 meters) in length, with a beam of 45 feet (14 meters), a depth of 29.5 feet (8.99 meters) of 2,284 tons. The mainmast was 210 feet (64 meters) high and she carried 3.3 acres of sail. The vessel was constructed with three skins. One planked fore and aft, and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). The Schomberg is one of only three clipper wrecks in Victorian waters that operated the England to Australia run. While the other two, Empress of the Sea and Lightning, were built by the famous American shipbuilder, Donald Mac Kay. Schomberg was an attempt to build a faster ship than Mac Kay and a vessel fast enough to break the sailing record to Australia. The Schomberg sailed on her maiden voyage from Liverpool on 6 October 1855, under the command of Captain James Forbes, on its maiden voyage to Australia with a general cargo, jewellery, spirits, machinery, and 2,000 tons of iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, plus 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. There were approximately 473 passengers and a crew of 105. It was hoped that Schomberg would make Melbourne in sixty days, setting a record for the voyage, but light winds at the equator dashed those expectations. The ship sighted Moonlight Head in south west Victoria on Christmas Day but through a deadly combination of wind, currents and unmarked sand spits, the vessel gently ran aground on 26 December 1855 on a spit that juts into Newfield Bay, just east of Curdies Inlet, and the present town of Peterborough. Fortunately, the SS Queen was nearby and managed to save all passengers and crew. The steamers Keera and Maitland were dispatched to salvage the passenger's baggage and the more valuable cargo. Other salvage attempts were made, but deteriorating weather made the work impossible, and within two weeks the Schomberg's hull was broken up and the vessel abandoned. The wrecking of the Schomberg caused quite the public stir particularly in light of the fact the vessel was supposed to be, the most perfect clipper ship ever built. Captain Forbes was charged in the Supreme Court under suspicion that he was playing cards with two female passengers below decks when his ship ran aground. Despite a protest meeting, two inquiries and the court proceedings, he was found not guilty and cleared of all charges. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime museum that also displays ship fittings and equipment, personal effects. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.This chalice is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century that is still in use today. The Schomberg has historical significance as one of the first luxurious ships built to bring emigrants to Australia to cash in on the gold rush era. And is included on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612). The collection of Schomberg artefacts held at Flagstaff Hill Museum is primarily significant because of the relationship between these recovered items having a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg and its foundering during a storm. The shipwreck is of additional historical significance for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the first passenger ship, which was designed not only to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day but foundered on its maiden voyage to Australia.Chalice; electroplated silver metal over metal, possibly nickle. The chalice has a wide bowl with an outer layer of intricately cut metal on the underside and a ribbon-like border of grapes and grapevine leaves is etched around it. It is supported by a tall stem with a circular knob partway down its length, and the stem is attached to a round base that is hollow underneath. The decorative pattern around the perimeter of the base is repeated on the knob on the stem. The base also has a pattern of lines around the vertical edge. There is a white sticker attached to the underside of the base. Its inscription is undecipherable. The chalice is part of a Communion set that was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. White sticker attached to the base of the chaliceflagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, schomberg, 1855, clipper ship, james baines & co, black ball line, luxury ship, emigrant ship, captain forbes, bully forbes, ss queen, peterborough shipwreck, communion set, religious service, communion service, ceremonial service, mass, chalice -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeremonial object - Cruet and lid, 1855 or earlier
In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, found an ornate communion set used to celebrate the Eucharist or holy communion by a number of different Christian faiths was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. The set comprised a cruet or jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery at Flagstaff Hill. The collection of artefacts from the Schomberg also contains ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and a photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald a former director of Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The Schomberg was a large three-masted full-ship rigged wooden ship built in 1855 by Alexander Hall and Co in Aberdeen, Scotland for James Baines' famous Black Ball Line at £43,103. The vessel was 288 feet (88 meters) in length, with a beam of 45 feet (14 meters), a depth of 29.5 feet (8.99 meters) of 2,284 tons. The mainmast was 210 feet (64 meters) high and she carried 3.3 acres of sail. The vessel was constructed with three skins. One planked fore and aft, and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). The Schomberg is one of only three clipper wrecks in Victorian waters that operated the England-to-Australia run. While the other two, Empress of the Sea and Lightning, were built by the famous American shipbuilder, Donald Mac Kay. Schomberg was an attempt to build a faster ship than Mac Kay and a vessel fast enough to break the sailing record to Australia. The Schomberg sailed on her maiden voyage from Liverpool on 6 October 1855, under the command of Captain James Forbes, on its maiden voyage to Australia with general cargo, jewellery, spirits, machinery, and 2,000 tons of iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, plus 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. There were approximately 473 passengers and a crew of 105. It was hoped that Schomberg would make Melbourne in sixty days, setting a record for the voyage, but light winds at the equator dashed those expectations. The ship sighted Moonlight Head in southwest Victoria on Christmas Day but through a deadly combination of wind, currents and unmarked sand spits, the vessel gently ran aground on 26 December 1855 on a spit that juts into Newfield Bay, just east of Curdies Inlet, and the present town of Peterborough. Fortunately, the SS Queen was nearby and managed to save all passengers and crew. The steamers Keera and Maitland were dispatched to salvage the passenger's baggage and the more valuable cargo. Other salvage attempts were made, but deteriorating weather made the work impossible, and within two weeks the Schomberg's hull was broken up and the vessel abandoned. The wrecking of the Schomberg caused quite a public stir, particularly in light of the fact the vessel was supposed to be, the most perfect clipper ship ever built. Captain Forbes was charged in the Supreme Court under suspicion that he was playing cards with two female passengers below decks when his ship ran aground. Despite a protest meeting, two inquiries and the court proceedings, he was found not guilty and cleared of all charges. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum that also displays ship fittings and equipment, and personal effects. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.This object is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century that is still in use today. The Schomberg has historical significance as one of the first luxurious ships built to bring emigrants to Australia to cash in on the gold rush era. And is included on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612). The collection of Schomberg artefacts held at Flagstaff Hill Museum is primarily significant because of the relationship between these recovered items having a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg and its foundering during a storm. The shipwreck is of additional historical significance for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the first passenger ship, which was designed not only to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day but foundered on its maiden voyage to Australia.Cruet and lid; electroplated silver metal over metal, possibly nickle. The cruet has a wide bowl large handle .The round domed lid has a pattern around the border. The cruet and lid are part of a Communion set that was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, schomberg jug or cruet, jug or cruet, schomberg communion set, jug, cruet and lid, cruet, communion set, religious service, communion service, ceremonial service, mass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper sheathing, c. 1855
This object is a piece of Muntz or copper sheathing, a sheet of metal used for lining a ship's hull as protection from sea worm or muntz worm. It has been salvaged from the Schomberg ship wreck. The muntz has been damaged by reaction of the metals to the sea. It also has encrustations from the sea such as sand. Other damage, such as movement of the sea or objects in the sea, has caused the edges to break away or fold over. ABOUT MUNTZ The hulls of early timber sailing ships had a problem of being eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called ‘sea worms’ or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and the bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by applying coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch onto the timber. In the 18th and 19th centuries ships were built with their hulls sheathed in sheets of copper or a combination of 60 percent copper and 40 percent zinc (called Muntz metal). The ships would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing remained effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oat with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. This piece of muntz sheathing is representative of building methods and materials used in late 19th and early 20th century ship building. The munts is also significant for its association with the Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper sheathing or Muntz metal in concretion. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, copper sheathing, muntz, muntz metal, teredo worms, sea worms, sea termites, ship building, 19th century sailing ships -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Container
When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen for £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, and oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately, there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. The land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in 825 metres of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. There have been many other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. This ceramic container was retrieved from the shipwreck site during early salvage efforts on the vessel. And was donated to the Flagstaff Hill collection of Schomberg shipwreck artefacts.The ceramic container is particularly significant in that along with other items from the wreck have helped in part to having legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter controls being employed to oversee the salvaging of wreck sites. This item forms part of the Schomberg collection at Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered Schomberg shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of additional significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes from society at the time of the wreck.Stoneware Container with lid, white in colour,Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, container, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Keg Spigot/Tap, Circa 1855
When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen for £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, and oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately, there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. The land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in 825 metres of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. There have been many other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. This item was retrieved from the shipwreck site during early salvage efforts on the vessel. And was donated to the Flagstaff Hill collection of Schomberg shipwreck artefacts.This artifact is particularly significant in that along with other items salvaged from the wreck have helped in part to having legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter controls being employed to oversee the salvaging of wreck sites. This item forms part of the Schomberg collection at Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered Schomberg shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of additional significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes from society at the time of the wreck. Brass keg spigot valve/tap, Schomberg Artifact Reg No S/94.Nonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, keg tap, brass keg tap -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Cannon, Alexander Hall and Son, c. 1855
The Schomberg Cannon was recovered from the 1855 wreck of the SCHOMBERG in 1974 by Flagstaff Hill divers Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden. The wreck site was discovered in August 1973 by Stan McPhee and John Laidlaw. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When SCHOMBERG was launched in 1855, she was considered the “Noblest ship that ever floated on water.” SCHOMBERG’s owners, the Black Ball Line, commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. The ship was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen at a cost of £43,103. It was constructed with three skins: one planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Its first-class accommodation was simply luxurious; velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple, mahogany, soft furnishings of satin damask; an oak-lined library and a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the SCHOMBERG’s 34-year-old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. The ship departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, and 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. It also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and the cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune in those times. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in 825 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and a photograph from the SCHOMBERG. One of the SCHOMBERG bells was in the old Warrnambool Library. The Schomberg cannon is currently on loan to the Port Campbell Visitor Information Centre.The SCHOMBERG collection is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history.Cannon; 6-POUNDER (6pdr) smooth bore cannon, mounted on a wooden frame. The cannon has a metal lug on each side. It is commonly known as the Schomberg cannon. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg in 1974.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, cannon, the schomberg cannon, schomberg cannon, peterborough, 1855, sailing ship -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Badge, Before 1855
The badge recovered from the Schomberg wreck is believed to depict one of the first steam engines. The engine's design by Charles Tayleur & Co. was to be produced for the Great Western Railway in England. The first nineteen of these locomotives were ordered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel for the Great Western Railway including six 2-2-2 Charles Tayleur locomotives. They were built by Charles Tayleur and Company, which later the Vulcan Foundry. The locomotives were unsuccessful and were rapidly supplemented by the Star Class locomotives ordered by Daniel Gooch once he had been appointed as the Locomotive Engineer. As built, they comprised two groups of three, the first group, was delivered in 1837. This locomotive was the first to run on the Great Western Railway when it was tested on 28 December 1837 from its shed at West Drayton. It was withdrawn in 1843 but was rebuilt as a 2-2-2T tank locomotive and returned to service in 1846, running in this form until 1868. It survived for two more years at Reading as a stationary boiler. It is named after the workshops where it was built, which themselves were named after the Roman god of fire. (Although a supposition, it is possible that the owner was a passenger on the ill-fated Schomberg and that they worked either for the Great Western Railway or the Vulcan Foundry that made the engine in the 1830s.) Wreck of the Schomberg: Schomberg was a large three-masted full-ship rigged wooden ship built in 1855 by Alexander Hall and Co in Aberdeen, Scotland for James Baines' famous Black Ball Line at £43,103. The vessel was 288 feet (88 meters) in length, with a beam of 45 feet (14 meters), a depth of 29.5 feet (8.99 meters) of 2,284 tons. The mainmast was 210 feet (64 meters) high and she carried 3.3 acres of sail. The vessel was constructed with three skins. One planked fore and aft, and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). The Schomberg is one of only three clipper wrecks in Victorian waters that operated the England to Australia run. While the other two, Empress of the Sea and Lightning, were built by the famous American shipbuilder, Donald Mac Kay. Schomberg was an attempt to build a faster ship than Mac Kay and a vessel fast enough to break the sailing record to Australia. The Schomberg sailed on her maiden voyage from Liverpool on 6 October 1855, under the command of Captain James Forbes, on its maiden voyage to Australia with a general cargo, jewellery, spirits, machinery, and 2,000 tons of iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, plus 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. There were approximately 473 passengers and a crew of 105. It was hoped that Schomberg would make Melbourne in sixty days, setting a record for the voyage, but light winds at the equator dashed those expectations. The ship sighted Moonlight Head in southwest Victoria on Christmas Day but through a deadly combination of wind, currents, and unmarked sand spits, the vessel gently ran aground on 26 December 1855 on a spit that juts into Newfield Bay, just east of Curdies Inlet, and the present town of Peterborough. Fortunately, the SS Queen was nearby and managed to save all passengers and crew. The steamers Keera and Maitland were dispatched to salvage the passenger's baggage and the more valuable cargo. Other salvage attempts were made, but deteriorating weather made the work impossible, and within two weeks the Schomberg's hull was broken up and the vessel abandoned. The wrecking of the Schomberg caused quite a public stir, particularly in light of the fact the vessel was supposed to be, the most perfect clipper ship ever built. Captain Forbes was charged in the Supreme Court under suspicion that he was playing cards with two female passengers below decks when his ship ran aground. Despite a protest meeting, two inquiries, and the court proceedings, he was found not guilty and cleared of all charges. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate, and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum that also displays ship fittings and equipment, and personal effects. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill.The Schomberg has historical significance as one of the first luxurious ships built to bring emigrants to Australia to cash in on the gold rush era. And is included on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612). The collection of Schomberg artefacts held at Flagstaff Hill Museum is primarily significant because of the relationship between these recovered items having a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg and its foundering during a storm. The shipwreck is of additional historical significance for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the first passenger ship, which was designed not only to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day but foundered on its maiden voyage to Australia.Gold coloured brass badge depicting an 1840's steam engine or locomotive with the figure of a fireman standing on the back. Smoke is coming from the smokestack. The reverse has three holes, possible where a mounting pin or fastener was attached. The badge was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, captain forbes, ss queen, badge, charles tayleur, great western railway, vulcan foundry, isambard kingdom brunel, locomoive, brooch -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCraft - Ship Model, S.S. Schomberg, 1988
This model of the clipper ship SS Schomberg was researched and constructed to a scale of 1:64 by David Lumsden in 1988. When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen for £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, and oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately, there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. The land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signaled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in 825 metres of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. There have been many other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. This item was retrieved from the shipwreck site during early salvage efforts on the vessel. And was donated to the Flagstaff Hill collection of Schomberg shipwreck artefacts.This artifact is particularly significant in that along with other items salvaged from the wreck have helped in part to having legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter controls being employed to oversee the salvaging of wreck sites. This item forms part of the Schomberg collection at Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered Schomberg shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of additional significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes from society at the time of the wreck.Wooden model of the clipper ship SS Schomberg. The three masts are rigged with lines but have no sails. The model is mounted on pedestals on a timber board, exhibited in a glass case. The scale of this model is 1:64.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ship model, schomberg ship model, 1855, david lumsden, ship model maker, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
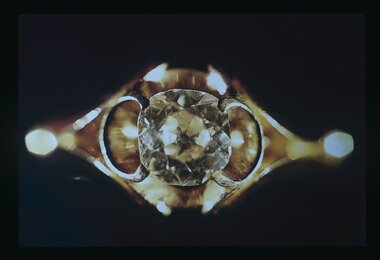 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Diamond ring, about 1855
In 1975, 120 years after the sailing ship Schomberg was wrecked, Flagstaff Hill divers (Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden) found an ornate communion set amongst the wreckage. The set comprised a jug, ciborium, lid, chalice and plate. The items, apart from the lid, were then displayed at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The lid had etchings that did not match the chalice and sat in storage for several years. Then in 1978, while the marine concretion inside the lid was being examined, a surface layer came loose and revealed a glint of gold that was assumed to be a piece of brass. The layers of concretion were carefully removed and a ring-like band emerged. Further treatment exposed a 'large faceted stone in an intricate gold setting. Weeks later a detailed examination estimated the value of the ring, known as the Schomberg Diamond, to be $7000. When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen at a cost of £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, an oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signaled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in 825 meters of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. The actual lid in which the ring was found has not yet been completely identified and could belong to a coffee pot, sugar bowl or maybe a jug or something similar. Although all survived the wreck no-one came forward to claim the valuable diamond. The Schomberg Diamond is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village along with the rest of the communion set. Other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. One of the Schomberg bells is in the Warrnambool Library.The Schomberg Diamond is particularly significant in that it played a crucial part in having the legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter control over the salvaging of items from wreck sites. This ring is registered as Artefact S/105 in the Schomberg collection, the Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significant because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. A mid-Victorian gentleman's solitaire diamond dress ring with a Brazilian cut diamond (cushion cut), one and one-third carat set within an 18 carat yellow gold ring consisting of four claws within an open scroll setting and a divided scroll shank. Colour is classified as 'J', clarity SII. The setting is handmade. warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, ciborium, ring, schomberg-diamond, schomberg-ring, gentleman's ring, dress ring -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWood sample, 1855
The artefact is a piece of ship’s timber from the wreck-site of the SCHOMBERG, a vessel which collided with the Peterborough reef on her maiden voyage in December 1855. This small wooden remnant of the disaster has been concreted on one side by the accrual of marine sediment while submerged. The build-up of sediment over the remains of the vessel is typical of the site as a whole. This artefact illustrates the reclaiming power of the ocean and the gradual disappearance of timber constructed vessels that have come to grief along this coastline (for example, the THISTLE in 1837, and the CHILDREN in 1838). The SCHOMBERG was a 2,000 ton clipper ship, specifically designed for the Australian immigration trade (back-loading wool for Britain’s mills), and constructed in Hall’s shipyard in Aberdeen, Scotland. She was owned by the Black Ball Line and launched in 1855. Alexander Hall & Son were renowned builders of sleek and fast 1,000 ton clippers for the China trade (opium in, tea out) and were keen to show they could also outclass the big North American ships built by Donald Mackay. Consequently the SCHOMBERG was ‘overbuilt’. Her hull featured five ‘skins’ of Scotch Larch and Pitch Pine overlaying each other in a diagonal pattern against a stout frame of British Oak. Oak has been favoured by builders of wooden ships for centuries. Its close, dense grain made it harder to work, but also gave it great strength and durability. In addition, the lateral spread of its branches supplied a natural curvature for the ribs of a vessel’s hull, as well as providing the small corner or curved pieces (‘knees’ and ‘elbows’) that fit them together. The shape and texture of this wood sample suggests a dense hardwood like Oak. The timber has been cut off at one end since its recovery from the sea, exposing a smooth and almost shiny surface. Seasoned English Oak has a similar light brown colour and tight grained finish. At the launch the SCHOMBERG’s 34 year old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. It also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in 825 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the SCHOMBERG. One of the SCHOMBERG bells is in the Warrnambool Library. The SCHOMBERG collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. A piece of wood, concreted in sediment, from the wreck of the SCHOMBERG (1855). The limestone accretion includes sand, shell grit and marine worm casings. The exposed surface of the wood is broken and worn smooth along the grain. One end of the timber has been cut or sawn off across the grain, presenting a smooth and shiny surface.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wood segment, schomberg, shipwreck timber, alexander hall and son, limestone concretion, oak-framed hull -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Bell, Before 1855
This small ship’s bell, possibly a ‘mess’ or dining room bell, was the smaller of the two bells rescued by the crew of the Schomberg when it was wrecked in 1855. All of the crew from the Schomberg wreck survived. They carried the two ship’s bells with them as they made their way along the coast, eventually arriving at the home of settler, John Manning, who lived at Hopkins Point near Warrnambool. Manning acquired the Schomberg bells, presenting them to two Warrnambool churches; the smaller one to St Joseph’s Catholic Church and the larger bell to St John’s Presbyterian church. This small bell developed a crack after about a year at St Joseph's church and could no longer be used. Thomas Manifold imported a new bell for that church and the cracked belled was stored at his farm and stored. The property was sold years later to John Logan, who donated the discarded bell to the Warrnambool Museum when it first opened in 1886. The Curator, Joseph Archibald, displayed the bell in the entry. The small bell was repaired and re-plated by Briggs Marine in 1986. The larger Schomberg bell was installed in St John’s Presbyterian Church. In 1887 a ‘massive’ new bell, made in Victoria, was installed at the Presbyterian Church, so the old bell was transferred to the nearby Woodford Presbyterian authorities. During World War II the 1887 bell cracked, and could not be repaired. In 1983 the old Schomberg bell from the Woodford church was loaned to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village. When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen at a cost of £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, and an oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the ship Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately, there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, and 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. The land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in 825 meters of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby.The bell is particularly significant in that along with other items from the wreck helped in part to having the legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter controls being employed to oversee the salvaging of wreck sites. This bell forms part of the Schomberg collection at Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered Schomberg shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of additional significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes from society at the time of the wreck. A small ship’s bell. The bell bears the ship’s name and year of construction on one side and the name and address of the ship’s builders on the other. These details are deeply engraved into the metal and formed in bold upper-case lettering. The bell has two bell stands, a left and a right side. Both stands have an Iron pipe made into an inverted ‘Y’ shape with a hole made in the single length, and feet attached to a rectangular metal plate at the other two ends. Feet are bolted into a timber base that has a hole drilled through the centre for mounting. Bell's front; “SCHOMBERG” with “1855” below. Bell's back “HALL & SONS (crack splits letter “N”) / BUILDERS (in italics) / ABERDEEN” (crack splits letter “B”).flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, schomberg, silver plated bell, mess bell, bell stands, captain ‘bully’ forbes, alexander hall and son, james baines and company, liverpool’s black ball line, bell, schomberg bell, ship's bell, small bell, st joseph's church, briggs marine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Menu, Bill of Fare ship Schomberg, circa 1855 - May 12 1856
A “Bill of Fare” is a menu or list of food offered for a meal. This Bill of Fare from the sailing ship Schomberg is handwritten in pen in hard-to-read script on the printed pages specifically for the Schomberg ship, of the Black Ball Line of Australian Packets. (‘Packets’ were vessels that had a regular trade run of cargo, passengers and mail; the sailing ship Schomberg was designed for long voyages between England and Australia.) These menus posed a puzzle as they have the handwritten dates of, May 10 and 12, 1856, by which time the Schomberg had sunk (she sunk on December 26, 1855). The donor of these pages of Bill of Fare is a stamp collector from Melbourne. He came across the menus in a package that he bought in 1980 at a stamp auction in Tasmania. He decided to give the menus to Flagstaff Hill this year during his annual family holiday in Warrnambool. A 1981 newspaper article about this donation included an interview with Flagstaff Hill’s curator Mr Peter Ronald, who said that the stationery of these menus is genuine. He went on to say that there would have been much stationery printed for use on the Schomberg although she sank on her maiden voyage. These menus could have been written at a dated late because the surplus Schomberg stationery could have been used for menus on other ships. We will probably never be sure of the answer but none-the-less the pages are still connected to the Schomberg. Below is what we believe the menu consists of although some of the writing is indecipherable - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (first menu) Roast Mutton Boiled Mutton? Ox Tail Mulligatawny? Or possibly Ox Tail Vegetables? Mutton Pies? ------------------------------- Vegetables Potatoes ---------------------------------- Dessert Fruit Puddings? Saturday May 10, 1856 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - AND - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (second menu) Boiled Mutton Roast Mutton? Roast Geese? Ox Tail?? Calves Head Broth? ------------------------------- Vegetables Potatoes ------------------------------- Dessert Tarts? Rice Pudding? ?...Maids?? Monday May 12, 1856 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Background of “SCHOMBERG” When SCHOMBERG was launched in July, 1855, she was considered the “Noblest ship that ever floated on water.” SCHOMBERG’s owners, the Black Ball Line (one of three companies by that name), commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen, UK at a cost of £43,103. She was constructed with 3 skins: one planked fore and aft, and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her first class accommodation was luxurious: velvet pile carpets; large mirrors; rosewood; birds-eye maple; mahogany; soft furnishings of gold satin damask; an oak-lined library; and a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. SCHOMBERG’s 34 year old master, Captain James ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days at the launch, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway as well as a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, and 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. SCHOMBERG also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to Forbes regarding a card game as more important than his ship, SCHOMBERG eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the steamer SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled it. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 salvage efforts were abandoned after two men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck of the SCHOMBERG lies in 825 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated, the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen surrounding the wreck, by divers. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed in concretion), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the SCHOMBERG. These Bills of Fare are significant due to their connection to Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg, which is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck S612. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The Schomberg collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day. The Schomberg collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Menu, or Bill of Fare, on cream coloured stationery from the sailing vessel “Schomberg”. Two rectangular pieces of paper, each bears the printed words “Black Ball Line of Australian Packets, Bill of Fare, Ship, Schomberg”, a printed symbol of the Black Ball line (a black ball on a red flag) and a decorative border. Both pages are handwritten, in similar but different sized writing, with a Bill of Fare and a date, Page (1) dated May 10th 1856 and (2) dated May 12th ’56, (Both dates are AFTER the Schomberg sank in December 26th 1855.) Both pages have three fold lines spaced across their width. To be used for the return voyage.Printed on the pages ““BLACK BALL LINE OF AUSTRALIAN PACKETS.” “Bill of Fare, / SHIP / “SCHOMBERG”.” Handwritten list of food, and on one page “Saturday May 10 1856” and on the other page “Monday May 12” warrnambool, peterborough, shipwrecked coast, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, maritime museum, great ocean road, flagstaff hill, sailing ship schomberg, shipwreck schomberg, black ball line of australian packets, bill of fare schomberg, menu schomberg 1856, food mid-1800’s, food on ships mid-1800’s, menu, may 10, 1856, may 12, 1856 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNail, 1855
The artefact is the lower portion of a rectangular shanked ‘planking nail’ with a straight-edged ‘flat point’. The distinctive ‘point’ of a planking/skirting nail was designed to be driven into timber across the grain in order to prevent the wood from splitting. This relic is from the shipwreck of the SCHOMBERG, which ran aground near Peterborough in 1855. It was retrieved in 1875 from a large section of the ship’s bow which had been carried by ocean currents to the western coast of New Zealand’s South Island. The nail is still fixed in a fragment of the original timber that it secured in the SCHOMBERG. The top portion, or ‘head’ of the nail, has corroded away but the pronounced rectangular shank and its flat point indicate its likely purpose and position on the vessel. Most fastenings used in sailing ship construction were either wooden treenails or copper bolts, which were relatively resistant to seawater corrosion. In addition, the preferred hull-frame timber of British Oak has a high content of gallic acid which rapidly corrodes unprotected iron work. The ferrous composition of this planking nail suggests it came from an internal and upper portion of the ship’s bow (protected from exposure to the sea or oak). According to an 1855 edition of the Aberdeen Journal, the five outer layers, or ‘skins’, of the SCHOMBERG’s pine hull were “combined by means of patent screw treenails”. However the “beams of her two upper decks” were of “malleable iron”, and “part of the forecastle” was “fitted for the accommodation of the crew”. It is therefore possible that iron nails of this description were used by the ship’s builders to secure floor and wall planks in enclosed areas of the crew’s quarters. (The same reasoning would apply to officer and passenger accommodation amidships and at the stern of the vessel, but it was the bow that floated to New.Zealand.) The SCHOMBERG was a 2,000 ton clipper ship, specifically designed for the Australian immigration trade (back-loading wool for Britain’s mills), and constructed in Hall’s shipyard in Aberdeen, Scotland. She was owned by the Black Ball Line and launched in 1855. Alexander Hall & Son were renowned builders of sleek and fast 1,000 ton clippers for the China trade (opium in, tea out) and were keen to show they could also outclass the big North American ships built by Donald Mackay. Consequently the SCHOMBERG was ‘overbuilt’. Her hull featured five ‘skins’ of Scotch Larch and Pitch Pine overlaying each other in a diagonal pattern against a stout frame of British Oak. Oak has been favoured by builders of wooden ships for centuries. Its close, dense grain made it harder to work, but also gave it great strength and durability. In addition, the lateral spread of its branches supplied a natural curvature for the ribs of a vessel’s hull, as well as providing the small corner or curved pieces (‘knees’ and ‘elbows’) that fit them together. At the launch the SCHOMBERG’s 34 year old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. It also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in 825 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the SCHOMBERG. One of the SCHOMBERG bells is in the Warrnambool Library. This nail is a registered artefact from the wreck of the SCHOMBERG, Artefact Reg No S/35 and is significant because of its association with the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. The object is the bottom end of a slightly curved iron planking nail with remnant of timber still attached, recovered from the wreck of the SCHOMBERG (1855). The shank of the nail is rectangular and it narrows to a flat (chisel like) ‘point’. The ‘head’ is missing although there is a quantity of dark red corrosion within the top of the surrounding wood, suggesting where it might have been. The artefact is from the wreck of the SCHOMBERG (1855) and was retrieved from part of the ship’s bow which was carried by sea currents to the South Island of New Zealand. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, planking nail, rectangular ship’s nail, cast iron nail -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWood encrustation, 1855
The object is a mass of small shipwreck debris that has been concreted together by sediment and marine growth. It was retrieved from the wreck-site of the SCHOMBERG, which ran aground near the mouth of the Curdies River near Peterborough in 1855. The conglomerate of preserved wood impressions, rusted metal pieces, a small square of copper alloy, and black glass-like stones, presents too disjointed a collection to provide information on their purpose or function on the ship. The natural and gradual process of limestone accretion is a significant feature of the wreck-site, which was rediscovered by fishermen and skindivers in 1973. In his book “Exploring Shipwrecks of Western Victoria”, experienced diver and former director at Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald writes that the SCHOMBERG’s “triple layered wooden hull has disintegrated almost without trace…The turbulent shallow waters have promoted particularly heavy marine growth which tend to disguise the wreckage…the most prominent feature being a corroded mass of railway iron…Close inspection reveals small artefacts firmly embedded in the marine concretion which…is quite literally as hard as iron”. The huge oblong mass of concretion that now distinguishes the site covers the remains of this heavy cargo. A contemporary account of the SCHOMBERG’s fate (told by two of her passengers to the Melbourne Argus) alleges the ship “was overloaded, drawing over 25 feet when she left, and the cargo was chiefly iron and plant for the Geelong Railway”. The SCHOMBERG was a 2,000 ton clipper ship, specifically designed for the Australian immigration trade (back-loading wool for Britain’s mills), and constructed in Hall’s shipyard in Aberdeen, Scotland. She was owned by the Black Ball Line and launched in 1855. Alexander Hall & Son were renowned builders of sleek and fast 1,000 ton clippers for the China trade (opium in, tea out) and were keen to show they could also outclass the big North American ships built by Donald Mackay. Consequently the SCHOMBERG was ‘overbuilt’. Her hull featured five ‘skins’ of Scotch Larch and Pitch Pine overlaying each other in a diagonal pattern against a stout frame of British Oak. Oak has been favoured by builders of wooden ships for centuries. Its close, dense grain made it harder to work, but also gave it great strength and durability. In addition, the lateral spread of its branches supplied a natural curvature for the ribs of a vessel’s hull, as well as providing the small corner or curved pieces (‘knees’ and ‘elbows’) that fit them together. The shape and texture of this wood sample suggests a dense hardwood like Oak. The timber has been cut off at one end since its recovery from the sea, exposing a smooth and almost shiny surface. Seasoned English Oak has a similar light brown colour and tight grained finish. At the launch the SCHOMBERG’s 34 year old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. It also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in 825 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the SCHOMBERG. One of the SCHOMBERG bells is in the Warrnambool Library. This object is listed on the Shipwreck Artefact Register, No S/49, and is significant because of its association with the ship SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. The object is an aggregate of limestone sediment that formed at the wreck-site of the SCHOMBERG (1855). It is an irregularly shaped conglomerate of sand, shell-grit and marine worm casings from the ocean floor, but also incorporates an assortment of manufactured metal pieces and pipe fittings (corroded with red rust), a small rectangular piece of copper sheet, some ‘petrified’ wood remains (hardened and a soft brown colour), and pieces of black shiny stone (roughly cube shaped and possibly glass or porcelain remnants). There is an impression left in the stone of a joist or plank end but the original timber that the sediment formed around has since been dispersed by the sea.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwreck timber, alexander hall and son, shipwreck debris, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaArticle, A Woman's Melbourne Letter
A detailed description of the Mission and its activities written by a woman: Western Mail (Perth, WA : 1885 - 1954), Friday 13 December 1918, page 34 A WOMAN'S MELBOURNE LETTER. Melbourne, Dec. 4. There is an idea abroad, which as regards Melbourne, at any rate, is quite erroneous, that our sailors are not as well looked after as our soldiers, and that the noble men of the Mercantile Marine are much neglected ! For once, perhaps, my readers will pardon a letter dealing with only one subject, but the steady, unostentatious work done by the Ladies' Harbour Light Guild, in connection with the mission to seamen in Melbourne could not be adequately explained if dismissed in the usual short paragraph. Some of the most prominent names in Melbourne are associated with this guild and with the Mission Chaplain, and Mrs. Gurney Goldsmith, the members have made the Seamen's Institute a real home for those sailors of the Mercantile Marine, who touch our port. What we as a community owe to those men by their heroism in recent hostilities is certainly more understood by this band of enthusiastic workers than by the community generally. By using their unflagging energies, and influence on the sailor's behalf they endeavour to discharge a debt to which in some way or other we could and should all contribute. Even the most casual person can, if he thinks at all, sum up a few of the things our sailors - other than those belonging to our glorious navy - have done for us. On the spur of the moment we remember that those of the Mercantile Marine, are the men who manned our transports, who carried our wheat and wool, to oversea markets; who kept us in touch with our loved ones abroad; who kept the fires going in the furnaces of the great leviathans, bringing our wounded soldiers home again; who never flinched when self-sacrifice was demanded; who cared, with that tenderness, innate in all sailors, for the women and children, when the passenger ships were struck a dastardly blow by the wicked enemy; who, mocking death, gave up life with a heroism all the more heroic because it was always taken as a matter of course! Is it any wonder, then, that the members of the Ladies' Harbour Light Guild make it their business to provide a bright, homelike, spot in Melbourne, where the sailors are always certain of a cherry welcome ashore? The members of the guild are admirably drafted! The 360 non-workers each pay £1 1s. per annum. The workers, of whom there are between 700 and 800, donate 2s. 6d. and school members - it is confidently hoped that gradually all the schools will take an active interest in the mission - 1s. a year. The knights of the guild - as the men members are designated - are responsible for any sum they wish to name, from 5s. a year upwards. Everything is paid for out of these revenues, with the exception of a small grant from the Home Mission Fund - and such is the organisation, and management, that the entire concern is quite free from debt. The Seamen's Church and Institute, where the "Harbour Lights" gleam so brightly, is situated right in the midst of all the bustle and turmoil of the wharves, at the end of Flinders-street. The building, comprising chapel, and institute under the one red tiled roof, is grey stuccoed, with a small tower, from which flaunts the flag of 'The Flying Angel" - the badge of the guild. A visit to the institute makes one fully appreciate the boon the place must be to the voyage worn, weary, sailor. The atmosphere is eminently social in its best sense. While the architecture imparts an elegance, and quiet dignity which soothes by the very subtlety of its charm. With its comfortable furniture, its wealth of flowers, and the happy, wholesome, feminine influence which prevails everywhere, the quality which stands for the magic word "home" abounds. The Chaplain in the course of conversation said: -"We try to make this really a free club for sailors." But the habitues would probably tell you it was far more than that to them. The Institute is excellently appointed, and every little corner seems to have its particular history. It was built after the model of one of the old mission churches in California, and retains something of the old world attraction, while yet it combines all the advantages of modern, practical, conveniences. On entering the door the first thing, one notices is a huge compass, inlaid upon the floor, evidently to indicate one's proper bearings for it points due north - to the chapel! Only one other seamen's mission in the world boasts such a compass. As the sailor swings through the entrance he finds the office on his right, and there is, here, always a smiling face to welcome the shy, or timid, new comer. Quite a real post office is staffed by members of the guild, and all the letters received are listed alphabetically. Therefore, the expectant sailor has just to run his eye down the list, and he can immediately see whether there is a letter for him or not. If he is fortunate, he comes up to the member in charge, who unlocks the box, and produces the longed for missive. The boys are always encouraged to answer letters - and to write them. Often a few words about their mother, and their own home, will provoke a sleeping memory into activity. The writing room is well stocked with paper, envelopes, pens, and ink. The tables are so divided to ensure the utmost privacy, and through a calculated chain of circumstances, many an anxious mother receives a letter from her sailor lad, who, perhaps, might not have written but for these kindly inducements. The central hall - where social evenings are held every other night besides two special concerts a week - is inviting in the extreme. A handsome piano affords opportunity for those musically inclined. The tables are strewn with papers. The walls are bright with pictures, and here, and there, is a carved model, of a ship. One, of especial interest, is a model of "The Roon" carved, and presented by a French sailor. This German vessel will always be remembered in Australia. For it was across her bows that the first hostile shot was ever fired in Australian waters. In the corner is the canteen. It was fitted up entirely from the proceeds of a quotation calendar compiled by one of the members. The sailors may at any time, get a teapot of tea, or a tray of eatables, at a nominal cost. Before the canteen was in existence they had to go out for refreshments! - and sometimes they did not come back! Groups of sailors sit chatting at the tables. Half a dozen Swedes laugh and talk among themselves, for the simple reason they know no other language than their own. Several British sailors cluster about a dark-eyed Welsh lad - a perfect Celtic type - who, although only about twenty years of age, has been the victim of the Hun five times. Mines and torpedoes sank the ships he was in, either in the Channel or off the English coast, four times; and it is to his fifth experience, when the Inverness was wrecked, that everyone is eagerly listening. "We were in the boats eight days," he was saying, "I was pretty well mangled when they picked me up. The sufferings we endured were awful. At last we managed to reach Rapa, a Hawaiian island. The natives thought we were Germans, and came at us with spears. When they found we were British, they were awfully good to us. They even cried when we left, and the day before the rescue boat arrived they begged us to go into the hills and hide." At another table a Canadian lad - once a sailor - then a soldier, who trained at the Broadmeadows camp - was telling his experiences : - "The voyage which will always stick in my memory," he said, "was to a place which must be nameless. We left the United States not knowing whether we were bound, or what we were going to do. After some weeks we sighted a group of wonderfully beautiful islands, and we headed for the most remote and most lovely of them all. Then, and only then, we learned our mission from the skipper. We were taking their year's supply to a leprosy station! Oh no! I don't blame the skipper for not telling us ! Someone has to do these things, you know. A naval guard saw they didn't come near - and we all got sixty dollars extra. When the job was over we were quarantined on another island for two months, and one little chap - the baby of the crew, not eighteen - developed leprosy, and died before we left. Yes! I'll never forget that voyage, mates! Sometimes, I seem to see Leper's Island yet, with its lavish tropical vegetation and the gorgeous sunsets which stained all the water with blood. Then, too" - here the voice deepened - "there was an English girl - a leper - there. We heard she used to be an actress, and she contracted the disease somehow or other. She was always alone, and always watching us. In the distance we could see her come to the water's edge, and from there she would watch. Just watch . .. . watch . . .watch. ..." "Here come a couple of North Sea chaps," broke in an elderly man after pause. "One of them wounded, too, poor lad." It is not strange that all the sailors flock to the Institute. It is so comfortable, and essentially inviting, besides being full of human interest. The men's quarters comprise reading, writing and dressing rooms - hot and cold baths are always available - billiard room, and a special baggage room, where any sailor may leave his kit for as long as he likes. The payment of 3d. covers its complete insurance. Upstairs are the officers' quarters. These also have their own billiard room, writing and reading rooms, bath and dressing rooms. Just close are the apprentices' quarters - "The Half Deck," as popular parlance has it! The lads also have a billiard room of their own, and indulge in an easy armchair - amongst others - which was a donation from the Milverton School branch of the Guild. It is hoped by the committee to some day utilise the huge empty rooms, which run the length of the whole building. Their ultimate intention is to fit them up as cubicles, or "cabins," as they are to be called. They trust these "cabins" will be donated, either in memory, or in honour, of someone dear to the donor. Another forward movement soon to be put in hand, now that materials are available, is the establishment of "Norla Gymnasium." In a sailors' club such facility for exercise is absolutely essential. The men both need, and miss, exertion. As one boy, who had been backsliding, once said pathetically : -"If only there was something to do to get me into a good sweat, I would be all right." Soon such an one will be helped to swing from the trapese of the Norla Gymnasium into the right track! Sunday is always a fete day at the Institute, for 40 or 50 sailors generally come into tea. The up-to-date kitchen, which is fitted with every labour-saving appliance - all paid for out of working members' half crowns - is then a hive of animation, and methodical order. A formidable row of teapots await filling. Mrs. Goldsmith -, the chaplain's wife - rightly thinks it is far more homely to pour out the tea from a pot, than to serve it straight from the urns. So tea is poured out by a member, who sits at the head of a table gay with flowers, and chats to the guests. These latter are of all nationalities. But the French, the Spanish, Scandinavian, Norwegian - or any other sailor is equally welcome with the British. Two enthusiasts belonging to the Guild actually learnt Norwegian, so that men of this nation would have someone to talk to, and so be less lonely when they reached this, to them, foreign port ! The members of the Guild have their own private suite where they arrange the flow-err and do other necessary odds and ends undisturbed. No one appreciates flowers like a sailor, and the earliest and most beautiful may always be seen adorning the tables and rooms. Teas are served and lectures are held in the "Celia Little Hall," one of the most beautiful portions of the institute. It was erected by the chaplain in memory of his aunt from whom the hall takes its name. The Gothic windows open upon the cloisters, where, in the hot weather, the sailors enjoy their meals out of doors. The cloisters, indeed, form an exquisite spot. They are between a series of sweeping arches which lead to the chapel, and are sheltered by the open balcony of the chaplain's quarters. Grace of contour marks the architecture on every turn. Just around the corner is the chaplain's garden - a patch of green and colour, transformed from a desert waste, by a well-known woman horticulturist. The book room is a department especially valued by the sailors. There are two secretaries, one for home and the other for foreign literature. Books in French, English, Spanish, Scandinavian, Norwegian, and German may be found on the shelves. Each week about 36 convenient parcels of reading stuff are made up. These contain illustrated papers, books in various languages, and magazines. These parcels are eagerly accepted by the sailor with a long monotonous voyage before him. But complete as is every corner of the institute, no part is so well equipped as the memorial chapel erected by the Ladies' Harbour Light Guild, in memory of the officers and men, who have lost their lives during the war. St Peter's - for it is called after the sailor's patron saint - with its hallowed gentle dignity is a veritable sanctuary of peace, perhaps all the more so because it sprang out of war. The fittings are entirely of Australian wood. The pews, given in memory of some loved one by one of the members, are of Tasmanian hardwood. The reredos and altar chairs of carved blackwood. The rich carpet was provided by the members' magical half-crowns. Already this chapel holds memorials of peculiar historical interest. The altar lectern was given in memory of Commander Elwell, who, it will be remembered, was killed at Rabaul, in the early part of the war. The font commemorates two heroes - Nigel Hockley and Fred Hyde, who lost their lives at the hands of the Germans, although they survived the actual torpedoing of their ships, the Galgorn Castle off the coast of Ireland. The mother of one of them wrote out that her son had died as an Englishman should - fighting for the right. This noble sentiment is suitably paraphrased upon the inscription engraved upon the font. Practically every-hing enshrined in the chapel has its own sentimental value. The alms salver of beaten copper, studded with agate, is fragrant with the memory of a saintly woman.The eye of the sailor is caught and held by the pulpit, which is fashioned like a ship's hull and only a twist of rope guides the chaplain up the steps. For the last 13 years the Rev. A. Gurney Goldsmith, M.A., has acted as chaplain to the Seamen's Mission in Melbourne. Before that he and his wife worked in China. Mr Goldsmith visits all the boats and gets in touch personally with the sailor, over whom he has great influence. He is not only their chaplain and friend, but, amongst a wide range of other things, their banker besides. An exchange system exists between the various Missions, and the sailor who has "banked" his money with the chaplain, upon going away, receives a cheque which is cashed - minus exchange - by the chaplain of the next port. Mr. Goldsmith will tell you he has a soft spot in his heart for on old sailor he calls "Paddy." This ancient mariner has been wrecked ten times. It was a long time before the chaplain prevailed upon "Paddy" to partake of the spiritual and secular advantages afforded by the institute. He would not come, he said, until he could do so "with a good heart." Finally he frankly admitted that he had no "friends like those of 'the Flying Angel,' " and that he eventually proved his own "good heart" will be shown in this story. One day he came in to the chaplain and said bluffly, "Well, sir, I've been payin' off some old scores up Carlton way, an' I tells yer, plain, sir, not one of 'em would have seen a penny of their money but for the Mission." The Ladies' Harbour Light Guild has over thirty working suburban branches, and the excellent results achieved at the Institute now will no doubt be considerably augmented in the future. The practical actions of the members do more than anything else to convey the subtle meaning of the name of the Guild. To the visiting sailors the word "ladies" signifies the bread givers; "harbour" safety ; "lights" welcome; "guild" the welding of fraternity, and they one and all tell you the ideals thus embodied are unselfishly carried out by all the ladies who have banded together to care for the sailors' welfare.The article describes the Mission and the use of several spaces a year after its opening and gives details about the daily activities.Digital copy of an article published in the Western Mail on the 13th of December 1918. 717 flinders street, seamen's mission, norla dome, lhlg, reverend alfred gurney goldsmith, celia little room, garden, frederica godfrey -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyLuggage tag, c1926
Property of E. Leason - Passenger to London.Luggage tag - with blue letter "E" printed on front. Has leather strap. On rear name of passenger.luggage, suitcases, baggage labels
