Showing 6981 items matching "commission"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLetter - Loch Ard Centenary Letter, Koroit Council, March 1978
The Loch Ard was an iron hulled clipper, built in Scotland in 1873 and wrecked on the southwest coast of Victoria in 1878 at what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge, near Port Campbell. Fifty two crew and passengers died and only Tom Pierce and Eva Carmichael survived. The Loch Ard was the last sailing ship to lose emigrants' lives when negotiating the entrance to Bass Strait. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The Victorian History Advisory Council decided 1978 was an appropriate year to mark, not only the centenary of the sinking of the Loch Ard in 1878, but also commemorate the large part played by sailing ships in immigration, and through this, the development of Australia. The Victorian Government authorised the commemoration and a "Loch Ard Centenary Committee" was formed. It was established to create public interest and awareness for the 100th anniversary of the tragic Loch Ard shipwreck. Activities and events included student essays, exhibitions, videos, publications, competitions and historical information. A booklet called "Settlers Under Sail" by Don Charlwood was commissioned to be made available to all school children. The anchor of the Loch Ard was raised from the wreck and displayed at Port Campbell, a memorial plaque (erected by The National Park) was unveiled at Loch Ard Gorge, a special "Loch Ard Shipwreck Centennial Port Campbell" postmark was issued by the Post Office and a model ship competition was held. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village, together with other local towns and shires along the south-west coast participated in many of these commemorative activities. This letter is a significant reminder (and recognition) of the importance the Loch Ard (and other immigrant ships) played in the settling of Victoria and the dangers faced by the settlers who came to Australia in these ships. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best-known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Single page letter typed in blue ink, on behalf of Koroit Council, written on 14th March 1978 and addressed to the Chairman, Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village Advisory Board, in recognition of the "Loch Ard Centenary Commemoration 1878 - 1978". It has the "Borough of Koroit" stamp at the top of the page and a red "Borough of Koroit" seal on the bottom right-hand corner of the page. It is signed by the Mayor (Allan R. Waterson), a councillor (J. W. Smith) and the Town Clerk (Jim Macdonald). The letter is in a plain buff manilla folder labelled in blue type.Top left corner - "Address correspondence to:/TOWN CLERK / P.O. BOX 5/KOROIT, 3282" Top Centre - blue circular ink stamp of "BOROUGH OF KOROIT 1870" with coat of arms in the center Top right - "TOWN HALL,KOROIT/ PHONE KOROIT (055) 658230/After Hours (055) 658490" The letter is addressed to - "CR. J. S. Lindsay, /Chairman,/ Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village Advisory Board,/ WARRNAMBOOL. 3280" "LOCH ARD CENTENARY COMMEMORATION 1878 - 1978" (underlined) The letter begins - "It is with much pleasure that the Council of the Borough of Koroit, join with neighbouring municipalities, civic leaders and other organisations on this day, in commemorating the "Loch Ard" Shipwreck centenary. The "Loch Ard" operated as a cargo and passenger vessel for immigrants, for a period of five years, from 1873 to 1878. Its last voyage was from England to Melbourne, and the ship was sunk on the 1st June 1878, with only two survivors from passengers and crew of fifty-four. The celebrations being conducted throughout our district this day will help us all to remember and appreciate the determination and spirit shown by these people, for they had the faith to realise that their endeavours would be successful, even against great odds in comparison to present day standards and techniques, and their imprint on our history is record of this fact. This commemoration acknowledges the important role undertaken by sailing ships such as the "Loch Ard" and the vital role this ship played in the early settlement of the State of Victoria." The letter ends with -" the Common Seal of the Mayor, Councillors and Burgesses of the Borough of Koroit was hereunto affixed this 18th day of March, 1978." The letter is signed "Allan J. Waterson Mayor/J. W. Smith Councillor/ Jim Macdonald Town Clerk and a large red seal of the Borough of Koroit (with their coat of arms) is in the bottom right-hand corner. Front of manilla folder - "BOROUGH OF KOROIT / LOCH ARD CENTENARY COMMEMORATION/ 1878 - 1978" "4050" written in black ink top right-hand corner next to a scribbled out numberflagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, loch ard, port cambell, shipwreck, commemorative committee, loch ard centenary, koroit council, commemorative letter, loch ard commemorative committee -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Land League Committee Meeting, Dublin, 1864
The Irish National Land League (Irish: Conradh na Talún) was an Irish political organisation of the late 19th century which sought to help poor tenant farmers. Its primary aim was to abolish landlordism in Ireland and enable tenant farmers to own the land they worked on. The period of the Land League's agitation is known as the Land War. Within decades of the league's foundation, through the efforts of William O'Brien and George Wyndham (a descendant of Lord Edward FitzGerald), the 1902 Land Conference produced the Land (Purchase) Act 1903 which allowed Irish tenant farmers buy out their freeholds with UK government loans over 68 years through the Land Commission (an arrangement that has never been possible in Britain itself). For agricultural labourers, D.D. Sheehan and the Irish Land and Labour Association secured their demands from the Liberal government elected in 1905 to pass the Labourers (Ireland) Act 1906, and the Labourers (Ireland) Act 1911, which paid County Councils to build over 40,000 new rural cottages, each on an acre of land. By 1914, 75% of occupiers were buying out their landlords, mostly under the two Acts. In all, under the pre-UK Land Acts over 316,000 tenants purchased their holdings amounting to 15 million acres (61,000 km2) out of a total of 20 million acres (81,000 km2) in the country. Sometimes the holdings were described as "uneconomic", but the overall sense of social justice was undeniable. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Irish_National_Land_League, accessed 21 January 2014) The Irish National Land League was founded at the Imperial Hotel in Castlebar, the County town of Mayo, on 21 October 1879. At that meeting Charles Stewart Parnell was elected president of the league. Andrew Kettle, Michael Davitt, and Thomas Brennan were appointed as honorary secretaries. This united practically all the different strands of land agitation and tenant rights movements under a single organisation. The two aims of the Land League, as stated in the resolutions adopted in the meeting, were: ...first, to bring out a reduction of rack-rents; second, to facilitate the obtaining of the ownership of the soil by the occupiers. That the object of the League can be best attained by promoting organisation among the tenant-farmers; by defending those who may be threatened with eviction for refusing to pay unjust rents; by facilitating the working of the Bright clauses of the Irish Land Act during the winter; and by obtaining such reforms in the laws relating to land as will enable every tenant to become owner of his holding by paying a fair rent for a limited number of years. Charles Stewart Parnell, John Dillon, Michael Davitt, and others including Cal Lynn then went to America to raise funds for the League with spectacular results. Branches were also set up in Scotland, where the Crofters Party imitated the League and secured a reforming Act in 1886. The government had introduced the first ineffective Land Act in 1870, then the equally inadequate Acts of 1880 and 1881 followed. These established a Land Commission that started to reduce some rents. Parnell together with all of his party lieutenants, including Father Eugene Sheehy known as "the Land League priest", went into a bitter verbal offensive and were imprisoned in October 1881 under the Irish Coercion Act in Kilmainham Jail for "sabotaging the Land Act", from where the No-Rent Manifesto was issued, calling for a national tenant farmer rent strike which was partially followed. Although the League discouraged violence, agrarian crimes increased widely. Typically a rent strike would be followed by evictions by the police, or those tenants paying rent would be subject to a local boycott by League members. Where cases went to court, witnesses would change their stories, resulting in an unworkable legal system. This in turn led on to stronger criminal laws being passed that were described by the League as "Coercion Acts". The bitterness that developed helped Parnell later in his Home Rule campaign. Davitt's views were much more extreme, seeking to nationalise all land, as seen in his famous slogan: "The land of Ireland for the people of Ireland". Parnell aimed to harness the emotive element, but he and his party preferred for tenant farmers to become freeholders on the land they rented, instead of land being vested in "the people".(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Irish_National_Land_League, accessed 21 January 2014)Image of a number of men sitting around a table. They are members of the Land League Committee during a meeting in Dublin.ballarat irish, land league, land league committee, dublin -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
Taken in approximately 1900, this glass slide captures an image of a Mayday Hills Mental Asylum nurse. Also known as the Beechworth Lunatic Asylum, Mayday Hills was officially opened on the twenty-fourth of October 1867 and was commissioned following lobbying from Beechworth Municipal Council concerning a need for better living conditions for certain individuals confined to the town's gaol. These individuals, as well as many others who were brought from surrounding institutions, exhibited behaviours that were deemed to be unfit for mainstream society. At its peak, the asylum consisted of sixty-seven buildings and housed over twelve-hundred patients and five-hundred staff. At the time of Australian Federation in 1901 - just a year after this photograph was taken - the patient population numbered six-hundred and seventy-four. The designated site of the institution was chosen due to its scenery and altitude. It was argued that these picturesque surroundings would assist in curing the hospital's patients of their ailments. The asylum was officially closed in 1996. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register as being architecturally significant. The extensive complex of buildings are examples of Italianate-style, which is strongly associated with asylums of the 1860s - the period in which construction of this particular asylum began. Today the asylum offers tours to visitors: both daytime history tours and night-time ghost tours. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is socially and historically significant as it is representative of the lives of the nurses who worked at Beechworth's Mayday Hills Asylum in the early twentieth century. Thin translucent sheet of glass with a portrait image printed on the front. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, mayday hills, mayday hills mental asylum, beechworth asylum, beechworth asylum nurses, psychiatric nurses, psychiatric care, 1900 mayday hills, victorian heritage register, italianate style, 19th century asylums, asylums victoria -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Lantern Slide, c1900
Taken in approximately 1900, this glass slide captures an image of two Mayday Hills Mental Asylum nurses. Also known as the Beechworth Lunatic Asylum, Mayday Hills was officially opened on the twenty-fourth of October 1867 and was commissioned following lobbying from Beechworth Municipal Council concerning a need for better living conditions for certain individuals confined to the town's gaol. These individuals, as well as many others who were brought from surrounding institutions, exhibited behaviours that were deemed to be unfit for mainstream society. At its peak, the asylum consisted of sixty-seven buildings and housed over twelve-hundred patients and five-hundred staff. At the time of Australian Federation in 1901 - just a year after this photograph was taken - the patient population numbered six-hundred and seventy-four. The designated site of the institution was chosen due to its scenery and altitude. It was argued that these picturesque surroundings would assist in curing the hospital's patients of their ailments. The asylum was officially closed in 1996. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register as being architecturally significant. The extensive complex of buildings are examples of Italianate-style, which is strongly associated with asylums of the 1860s - the period in which construction of this particular asylum began. Today the asylum offers tours to visitors: both daytime history tours and night-time ghost tours. Lantern slides, sometimes called 'magic lantern' slides, are glass plates on which an image has been secured for the purpose of projection. Glass slides were etched or hand-painted for this purpose from the Eighteenth Century but the process became more popular and accessible to the public with the development of photographic-emulsion slides used with a 'Magic Lantern' device in the mid-Nineteenth Century. Photographic lantern slides comprise a double-negative emulsion layer (forming a positive image) between thin glass plates that are bound together. A number of processes existed to form and bind the emulsion layer to the base plate, including the albumen, wet plate collodion, gelatine dry plate and woodburytype techniques. Lantern slides and magic lantern technologies are seen as foundational precursors to the development of modern photography and film-making techniques.This glass slide is socially and historically significant as it is representative of the lives of the nurses who worked at Beechworth's Mayday Hills Asylum in the early twentieth century.Thin translucent sheet of glass with a portrait image printed on the front. It is held together by metal strips to secure the edges of the slide.burke museum, beechworth, lantern slide, slide, glass slide, plate, burke museum collection, photograph, monochrome, 1900 mayday hills, mayday hills, beechworth mental hospital, beechworth mental asylum, beechworth asylum nurses, psychiatric nurses, psychiatric care, victorian heritage register, italianate style, 19th century asylums, asylums victoria -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaDecorative object - Finial, c. 1920
Appearances to the contrary, the item is not a weathervane but a finial. It was the gift of Mr John Sanderson (Jottings Easter 1920), from John Sanderson & Co., wool merchants, stock and station agents, commission and shipping agents before he leaves for England to become senior partner in Sanderson Murray & Elder, London, import and export agents. It was designed by Walter & Richard Butler Architects. (sketch published in Building : the magazine for the architect, builder, property owner and merchant vol.33, no 193, 12 Sept. 1923). The finial was already drawn on the sketch of the Central Institute made by Walter Butler. The maker of the finial, was Henry Alfred George Arnold Saw (born June 1881 in Hotham, Victoria was the son of Edward Saw (1854-1926) a tinsmith and Catherine Barton (1863-1907). He worked as a metal artificer for a metal-working business located opposite the Trades Hall in Lygon Street and was given the job of making the copper ship finial. Henry married Florence Charlotte Reeder and they had four children. Also known as Harry Saw according to his grandson Brian, he died on 9th February 1960. Henry and Florence both died within two months of each other in 1960. It is not clear when the ship was actually installed on the roof, the earliest photograph dating from 1927. The windvane fell or moved several times because of gale forces: - In 1995 : After the funds were raised to repair it, it was treated by sculptor David Hope, and reinstalled in the 1998 (Ship to Shore #3 Sept 1998). - In 2017: Carmela Lonetti from the Grimwade Centre for Cultural Materials Conservation (Ship to Shore Autumn 2017) - In 2019: a generous passerby donated the necessary funds for the conservation. It was sent to Grimwade Centre for Cultural Materials Conservation (Ship to Shore 2019), treated by Evan Tindal (City of Melbourne Magainze Oct. 2020). It was reinstalled over the Summer of 2019-2020 (Ship to Shore Summer 2020). The weathervane was stolen during the night of the 6-7 March 2022. Copper price surge sparks rise in theft in Victoria in 2021-22 so it's likely the vane was stolen to be melted This sculpture is closely associated with the 1917 building and described in clippings and annual reports when the building was first newly opened. It can be seen in some of the earliest photographs of the new building and in the artist/architect Butler's impressions. The galleon is often a decorative design of Mission to Seafarers wind vane (London, Adelaide).Bronze and copper sculpture fashioned as a Wind Vane in the form of a Galleon style sailing ship with 2 pennants flying and two sails rigged atop with lower cross piece with wind directions N S E W . There is a decorative ornamental pierced scrollwork ferrule / finial with reinforcing chrome steel piping armature at base of main support which attaches to the roof or a base support. See also comments below weather vane, wind vane, sculpture, galleon, sailing ship, finial, henry alfred saw, david hope, windvane, weathervane, walter richmond butler (1864–1949), richard butler, john sanderson -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumMap - Map Extract - Charterhouse of Mendip, John James Raisbeck, Unknown
Map extract showing the towns of Cheddar, Rodney Stoke, Westbury and a smaller town of Easton. The area depicted is part of Somerset, England. Map is hand drawn by J.J. Raisbeck date unknown. John James RAISBECK was born on 4 July 1880 at Christchurch New Zealand. He served 4 years (Citizen Military Force - CMF) in 9th Australian Light Horse Regiment in Central VIC with the rank 2nd Lieutenant. He was the first Australian appointed to the Survey Section RAE, on 16 April 1910, as a draughtsman which was his civilian profession, with the rank Warrant Officer, honorary 2nd Lieutenant. He was required to resign his commission in the CMF. He supervised the draughting work of the Section in Melbourne and was largely responsible for the mapping standards and specifications set in the production of the Cowes one-inch-to-one-mile military map, which became the enduring Australian standard. He was also responsible for supervising the printing of the maps by the Victorian Government Printer. He was appointed 2nd Lieutenant in the AIF Survey Corps draft on 6 December 1917 (from Melbourne) embarking for England on 22 December 17. He was attached to the Australian Corps Topographic Section in France from 21 April 1918 to 5 March 1919 serving as Second-in-Command and as Officer Commanding. He was promoted Lieutenant 15 October 1918, attending the AIF Survey School, Southampton in 1919, returning to Australia 23 June 1919, before his AIF appointment was terminated 17 July 1919. He went on to serve the Survey Section RAE and Australian Survey Corps, including in the Second World War, having been promoted Captain then Major and Officer Commanding Army Headquarters Cartographic Section until February 1940. He retired after 33 years of service to military survey, and after serving the Corps in two world wars, on 4 July 1943 with the retired rank Lieutenant-Colonel. He was the author of the article ‘A Short History of the Military Survey of Australia, 1907-1936’, published in The Australian Surveyor, Sept 1, 1937Map extract slightly larger than A4. Scale: One Inch to One and a half Mile. 1:31680, 9 x copiesSignature of "J.J. Raisbeck" bottom right-hand cornerroyal australian survey corps, rasvy, fortuna, army survey regiment, army svy regt, asr -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Literary Work, John F. Moodie Heddle, Seven In the Half-Deck, 1949
This book is a true account of the experiences of seven Australian boys beginning their career as seamen on the last voyage of the ‘John Murray’ when they became stranded on a South Pacific Island. The author John F. Moodie Heddle was an apprentice on board at that time. The publisher firm of Longmans, Green & Co. was founded in 1724 in London by Thomas Longman under the name Longman. In August of that year, he bought the two shops and goods of William Taylor and set up his publishing house there at 39 Paternoster Row. The shops were called Black Swan and Ship, and it is said that the 'ship' sign was the inspiration for Longman's Logo. After many changes of name and management, including the name Longman, Green, Longman and Roberts from 1859 to 1862, the firm was incorporated in 1926 as Longmans, Green & Co. Pty Ltd. The firm was acquired by Pearson in 1968 and was known as Pearson Longman or Pearson PLC. The three-masted iron baque 'John Murray' was built and registered in Glasgow, UK, in 1877 as a general cargo vessel maned the 'Loch Ryan'. It traded between the UK and Australia from 1877 to 1909. In 1909 the Loch Ryan was purchased by the Defence Department of Victoria, refitted at Williamstown as a training vessel and renamed ‘John Murray’. It was commissioned from 1910 to 1917 for reforming juvenile offenders as seamen for the Navy and Merchant Navy. The training project ceased after reports of the treatment of the boys. Although 411 did their training under this scheme, the success rate of them qualifying to serve on other vessels was less than twenty per cent. The ship was named after John (Jack) Murray (1851-1916), who was born near Koroit. He was the 23rd Premier of Victoria (1909-1912), and a Warrnambool Member of Parliament for twenty years. In 1917 the John Murray was sold to the Government of Australia to serve during the Great War, World War I. The ship was loaded with a cargo of dynamite and petroleum at San Francisco then departed for Melbourne when, during its passage, it was wrecked at Malden Island reef in the mid-Pacific Ocean on May 29th, 1918.The book gives us a first-hand account of the wrecking of the sailing ship John Murray, named after a past Warrnambool Member of Parliament for twenty years and the 23rd Premier of Victoria, born locally, near Koroit. The book is significant for its association with the vessel John Murray, which was formerly the 'Loch Ryan' of the Loch Line General Shipping Company of Glasgow. The same company owned the Loch Ard, which was wrecked and tragically lost 52 lives. The book is significant as a record of one of the many clipper ships that traded between the United Kingdom and Australia, with goods collected from other countries along the way. The book has an important connection to Victoria's training ship John Murray, which aimed at reforming delinquent juveniles to be suitable as seamen for Australia's Navy or Merchant Navy.Seven In The Half-Deck: An account of the wreck of the Barque John Murray Author: John F. Moodie Heddle Publisher: Longmans Green & Co Date: 1949 Beige cloth hardcover book with colour sleeve pasted to front cover, depicting a lifebuoy with a sailing ship in the centre. Some words of the title are in rope-inspired writing. There are inscriptions on a label on the spine, a sticker on the front loose endpaper, and the image on the cover.. Label; typed text "RA 910.453 HED" Inside front loose endpaper has sticker "Warrnambool Children's Library" On lifebuoy: "JOHN MURRAY" "MELBOURNE"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, seven in the half-dec, true story, wreck of the barque john murray, shipwreck, john murray, barque, wreck, john f. moodie heddle, j f moodie heddle, longmans green & co, j moodie heddle, warrnambool children’s library, 1949, melbourne, the john murray, loch ryan, loch line, general shipping company, government of victoria, training ship, juvenile reformation, delinquent boys, james & george thomson, iron barque, three-masted ship, clipper ship, uk to australia trade, dynamite cargo, petroleum cargo, maldon island reef, 1909-1917, 1910, 1918, 23rd premier of victoria, warrnambool member of parliament, koroit, juvenile delinquent training, navy training, royal australian navy, merchant navy, first-hand account of a shipwreck -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDecorative object - Buggy Fitting, Circa 1855
This ornate fitting for a horse-drawn vehicle was amongst the items recovered from the Schomberg over one hundred years after it was wrecked. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. The Schomberg has historical significance as one of the first luxurious ships built to bring emigrants to Australia to cash in on the gold rush era. And is included on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612). The collection of Schomberg artefacts held at Flagstaff Hill Museum is primarily significant because of the relationship between these recovered items having a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg and its foundering during a storm. The shipwreck is of additional historically significance for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the first passenger ship, which was designed not only to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day but foundered on its maiden voyage to Australia.Ornate buggy or coach fitting with feather plumes on top, and a screw thread on the bottom. Silver plated,.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, artifact, ornate fitting, buggy fitting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Tap, Ca. 1855
The brass tap was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg sailing ship. It is severed at the pipe end before the position where the join would have been. This could have happened after the shipwreck or at the time of salvage. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This tap is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Brass tap, flat horizontal handle, horn-shaped finish above the spout. The fixture has been severed at the pipe connection end. The surface has since been polished. There is a hole in the side of the pipe near the vertical fitting. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, brass tap, plumbing fitting, water tap, tap -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Spur, Ca. 1855
Amongst the items of cargo recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg were riding spurs. This spur has been restored to show the type of finish the Spurs would have had when they were new. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three-masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oat with layers of Scottish larch. Schomberg departed Liverpool for Melbourne on 6 October 1855 under her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. Schomberg’s journey was slower than the predicted 60 days. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on an uncharted sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.This spur is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Spur; wish-bone shaped metal with a knob on one end, a drilled hole on the other and a hook shaped extension in the centre that has a hole through it. The edges are smooth and rounded. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg and has since been reconditioned.warrnambool, flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, silver plated spur, horse riding, spur, cargo, riding equipment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Harness Ring, Ca. 1855
The brass harness ring was one of many that were recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg sailing ship. It is a fitting used for horse straps and harness equipment. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This object is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Brass ring, a round tubular ring with a shiny surface. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, brass ring, harness ring, harness fitting, harness hardware -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Harness Ring, Ca. 1855
The brass harness ring was one of many that were recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg sailing ship. It is a fitting used for horse straps and harness equipment. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This object is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Brass ring, a round tubular ring with a shiny surface. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, harness ring, brass ring, brass harness ring, horse harness fitting, harness fitting, harness hardware -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Harness Ring, Ca. 1855
The brass harness ring was one of many that were recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg sailing ship. It is a fitting used for horse straps and harness equipment. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This harness ring is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Brass ring, a round tubular ring with a shiny surface. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, harness ring, brass ring, brass harness ring, horse harness fitting, harness fitting, harness hardware -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Button, Ca. 1855
The metal button was part of the cargo of the Schomberg vessel. Buttons are used for fastening two pieces of fabric together such as trousers, shirts, dresses and other similar items. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This button s significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century and the items carried on ships as cargo. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Button; round metal concave button with four holes. There is a decorative border on the edge and around the holes. The button was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, fastener, button, clothing accessory, clothing fastener, haberdashery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Button, Ca. 1855
The metal button was part of the cargo of the Schomberg vessel. Buttons are used for fastening two pieces of fabric together such as trousers, shirts, dresses and other similar items. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This button s significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century and the items carried on ships as cargo. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Button; round metal concave button with four holes. The outer edge and the holes each have a raised rim. The button was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, fastener, button, clothing accessory, clothing fastener, haberdashery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Shoe Buckle, Ca. 1855
The metal shoe buckle was part of the cargo of the Schomberg vessel. Buttons are used for fastening two pieces of fabric together such as trousers, shirts, dresses and other similar items. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This shoe buckle is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century and the items carried on ships as cargo. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Shoe buckle; two parts comprising a shiny metal rectangular piece and a hook piece. The shoe buckle was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, fastener, clothing accessory, clothing fastener, shoe accessory, shoe buckle, metal shoe buckle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Shoe Buckle, Ca. 1855
The metal shoe buckle was part of the cargo of the Schomberg vessel. Buttons are used for fastening two pieces of fabric together such as trousers, shirts, dresses and other similar items. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This shoe buckle is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century and the items carried on ships as cargo. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Shoe buckle; metal rectangular piece with a joining hook. The buckle has encrustations from the sea. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, schomberg, fastener, clothing accessory, clothing fastener, shoe accessory, shoe buckle, metal shoe buckle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Horse Brass
Amongst the cargo of the Shomberg were horse harness fittings and embellishments. Many of these were recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg over one hundred years later. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This object is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Heart shaped horse harness embellishment, brass. It has been reconditioned. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, schomberg, 1855, clipper ship, james baines & co, black ball line, luxury ship, emigrant ship, captain forbes, bully forbes, ss queen, peterborough shipwreck, harness fittings, horse harness, harness embelishments, horse brass, heart horse brass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Horse Brass
Amongst the cargo of the Shomberg were horse harness fittings and embellishments. Many of these were recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg over one hundred years later. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This object is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Shield shaped horse harness embellishment, brass. It has been reconditioned. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, schomberg, 1855, clipper ship, james baines & co, black ball line, luxury ship, emigrant ship, captain forbes, bully forbes, ss queen, peterborough shipwreck, harness fittings, horse harness, harness embelishments, horse brass, shield horse brass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Hub Nut
This hub nut was amongst the items recovered from the Schomberg over one hundred years after it was wrecked. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This object is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. Hub nut, brass, with octagonal head on round disc, on hollow threaded shank. Surface has some lacquer. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, schomberg, 1855, clipper ship, james baines & co, black ball line, luxury ship, emigrant ship, captain forbes, bully forbes, ss queen, peterborough shipwreck, brass fitting, hub net, wheel fitting, hardware -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Submission for Approval, VIOSH: Ballarat College of Advanced Education; Submission to the Victorian Institute of Colleges, 1978
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Ballarat College of Advanced Education had been trying for approval of a PG1 Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management during 1976 and 1977. This last application was 1978. They were hoping to introduce it in 1979. Present at this meeting held on Tuesday 8th August 1978 were representatives from: EAC Subcommittee; W J Robertson (Convenor), Dr K B Brown (Medical Officer}, Dr A J Christophers (Chief Industrial Hygiene Officer, Dept of Health, E O'Keefe (Secretary to the Committee) Ballarat CAE Course Advisory Committee; W Jinkins (Safety Engineer, Gas & Fuel), E Wigglesworth (Injury Research Unit, Royal College of Surgeons) Ballarat College of Advanced Education; D J Woolley (Head of School of Engineering), T D Norwood (Head of Dept Mechanical Engineering), D Viner (Course Co-ordinator}, G Fernandez (School of Business} Recommendation that the proposed course for the award of PG1 Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management at Ballarat College of Advanced Education be approved for introduction in 1979 at first year level. This still needs approval from the Tertiary Education Commission for the purposes of the expenditure of funds under the provision of the State Government.Ten A4 pages - typed. Four correspondence and six the Draft of course for the applicationLetterhead of Victoria Institute of Colleges and the Prime Minister, Canberra Signature: R I Viner - Minister assisting the Prime MInister in Public Service Matters Elizabeth O'Keefe - Secretary to the Academic Committee in Engineering, V.I.C.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, ballarat college of advanced education, pg1, graduate diploma in occupational hazard management, minister assisting prime minister, r i viner, elizabeth o'keefe, victoria institute of colleges, vic academic committee, w j robertson, k b brown, a j christophers, bcae advisory committee, w jinkins, e wigglesworth, bcad staff, d j woolley, t d norwood, d b viner, g fernandez, royal australian college of surgeons, department of health, gas and fuel corporation, medical officer olympic tyres, school of engineering, mechanical engineering, school of business, tertiary education committee, state government, state grants -
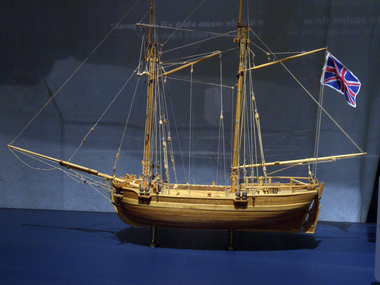 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCraft - Ship Model, H.M.S. Lady Nelson, 1988
This model of the ship H.M.S. Lady Nelson was researched and built as the vessel Lady Nelson by David Lumsden, a professional ship model builder. His Majesty's Armed Survey Vessel Lady Nelson was commissioned in 1799 to survey the coast of Australia. This vessel was purpose-built before the British Admiralty requested plans for a Schooner for Port Jackson. At the time large parts of the Australian coast were unmapped and Britain had claimed only part of the continent. The British Government were concerned that, in the event of settlers of another European power becoming established in Australia, any future conflict in Europe would lead to a widening of the conflict into the southern hemisphere to the detriment of the trade that Britain sought to develop. Against this background, Lady Nelson was chosen to survey and establish sovereignty over strategic parts of the continent. Lady Nelson left Portsmouth on 18 March 1800 and arrived at Sydney on 16th December 1800 after having been the first vessel to reach the east coast of Australia via the Bass Strait. Before that date, all vessels had sailed around the southern tip of Tasmania to reach their destination. Lady Nelson's survey work commenced shortly after she arrived in Sydney, initially in the Bass Strait area. She was involved in the discovery of Port Phillip, on the coast of Victoria, in establishing settlements on the River Derwent and at Port Dalrymple in Tasmania. She also successfully chartered much of the Victorian coastline and was heavily involved with the exploration of the Queensland coast with Matthew Flinders; investigated the Hunter River; made numerous visits to New Zealand and Norfolk Island and was involved in the founding of numerous settlements. In comparison to most colonial vessels, the Lady Nelson was technically unique she was fitted with sliding keels, or centreboards, and water-tight trunks reaching to the deck. Captain Schank invented these sliding keels that, when raised, reduced her draught to less than six feet. Her life as an exploration vessel ended while accompanying HMS 'Tamar' to Melville Island in 1825, the 'Lady Nelson' was captured and later abandoned by pirates off the island of Babar (Indonesia). This brought the vessel's 25 years of coastal exploration and navigation to a close.The Lady Nelson made was the first British ship to survey of the southern or south-western coast of Australia and traverse the Bass Strait. The vessel holds a special place in Australia's history of exploration as the first to explore and establish settlements in the then-new British colony of Van Diemans Land. The model gives an insight into what life must have been like onboard sailing vessels of the time and Australia's early history of establishment and exploration. This model acts as an important legacy of the full-scale ship which no longer survives. Ship model of the 60 ton British brig HMS Lady Nelson. Timber model of a two-masted brig with rigging but no sails, displaying the British Union Jack flag. The ship is in a glass exhibition display case on metal stand. HMS Lady Nelsonflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, by captain john schanck, sliding keels or centreboards, lady nelson, british brig hms lady nelson, david lumsden ship model builder, lieutennant james grant, bass strait discovery, surveying king island and port phillip bay, philip gidley king -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Perfume Bottle, Ca. 1854
The glass bottle and stopper were recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg over one hundred years afterwards. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. The Schomberg has historical significance as one of the first luxurious ships built to bring emigrants to Australia to cash in on the gold rush era. And is included on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612). The collection of Schomberg artefacts held at Flagstaff Hill Museum is primarily significant because of the relationship between these recovered items having a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg and its foundering during a storm. The shipwreck is of additional historically significance for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the first passenger ship, which was designed not only to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day but foundered on its maiden voyage to Australia.Perfume bottle, clear glass, hexagonal. Bottle has a glass stopper seal and has contents. Glass has imperfections. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. Paper label is attached to basewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, perfume phial, phial, perfume bottle -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Container - World War 1939-45 Ration pack, c1940
AMF Operational Ration This ration pack was developed by Sir Stanton Hicks. It contained three meals, each waterproofed (a vital consideration for the tropics), which offered a balanced selection of meat, vegetables, fruit and vitamin supplements. Before the development of this ration pack, Australian soldiers were supplied with quantities of preserved food that were difficult for a man to carry and divide, and which often did not provide a nourishing diet. Sir Cedric Stanton Hicks (1892-1976), university professor and army catering officer, was born on 2 June 1892 at Mosgiel, New Zealand. University of Otago (B.Sc., N.Z., 1914; M.Sc. Hons, 1915; M.B., Ch.B., 1923) 1916-18 Hicks served as a non-commissioned officer in the New Zealand Expeditionary Force and he assisted Professor J. K. H. Inglis in the synthesis and production of Chloramine-T for use against meningitis among the troops. Hicks was appointed government analyst in 1918. On a Fellowship 1923, he travelled to England and studied at Trinity College, Cambridge (Ph.D., 1926) and caried out research in Switzerland, Germany and the United States of America. 1927 he was appointed to the new chair of physiology and pharmacology at Adelaide University, which he was to hold until 1957. During the Depression he studied the dietary patterns of five hundred families receiving relief. 1940 Hicks was appointed temporary captain, Australian Military Forces, and performed part-time duty as catering supervisor. Moved to Melbourne as chief inspector of catering, he began a campaign for applying scientific principles to the feeding of troops. 1943 the Australian Army Catering Corps was formed. Hicks altered the basis of the allowance for military rations from a monetary to a nutrient entitlement, improved the pay and promotion opportunities of cooks, established schools of cooking and catering, devised new methods for preparing food, supported the service's adoption of the Wiles steam-cooker, and designed jungle-patrol, emergency and air-drop rations. His 'Who Called the Cook a Bastard?' (Sydney, 1972) gave an account of his experiences in military catering.Men from most families in the City of Moorabbin area served in the Australian Military Forces during World War 2.A tin container , khaki colour, used for the storage of a food ration item for a soldier serving in the Australian Military Forces World War 11.TURN KEY ← TO OPEN CAN / diagram of key / A.M.F. / OPERATION/ RATION/ 02 / D↑Dworld war 11, australian military forces, sir cedric stanton hicks, army catering corps, soldier rations, food supplys, australian diggers, food preservation -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, C. 1950s
Extract from The Spectator of June 12, 1946: "From the Queensland 'Methodist Times'. Dreams do come true. At any rate, that is what the Rev. Cliff Lanham believes, who after the lapse of several years finds that his early dream of a Flying Patrol for the Inland is now an actuality. The Methodist Inland Mission Board has purchased from the Disposals Commission of the R.A.A.F. a De Haviland Fox Moth Biplane. Indeed, two machines have been bought, but one will be broken up for spare parts. This 'new angel of the air' is fitted with a 130 h.p. engine and possesses a cruising speed of 100 miles per hour. The petrol consumption is only that of a big six-cylinder car—18 miles per gallon. In addition to the pilot there is room for three passengers, and a stretcher is installed whereby urgent cases of sickness or accident can be flown to the nearest hospital. In this machine, Mr Lanham proposes to cover the whole of S. W. Queensland and a portion of the Northern Territory from his headquarters at Mt Isa. It takes little imagination to realise what a boon the 'flying parson' will be to those of the great outback." …. "Before [Mr Lanham] inaugurated the scheme [the idea of a flying parson] he spent his first furlough from inland mission work (and incidentally £60) learning to fly. 'In a month,' he says whimsically, 'I was a pilot of sorts.' Mr Lanham is a son of the Church. His parents were staunch Methodists, and their home offered generous hospitality to mininsters and preachers. His brother, the Rev. Percy Lanham, M.A., died in Libya when on active service as a chaplain. His widowed mother must be proud of her tall, stalwart son, whom the Church now sends forth on his flying mission for the Lord. May he ever be wafted through inland skies on two wings and a prayer." It is of interest to note that although Cliff Lanham's brother, Percy, is listed in the Methodist Church of Australasia's Ministerial Index (9th Edition, Revised to 1961) Cliff Lanham himself is not listed as either active or deceased.Three B&W identical photographs of Lanham standing next to a Methodist Inland Mission bi-plane. Lanham and an unidentified man are holding a stretcher between them with a boy of about 10-11 on it. They seem to be exiting the plane. The original photograph F69-1 is a 110x65 mm Kodak print; the other two are 195x145 mm enlargements. Lanham is wearing a white shirt and grey trousers, the other person is wearing a safari helmet.All three photos identify "Rev. Cliff Lanham" on the back. They seem to have been originally used or intended for use by The Spectator.lanham, cliff, queensland, methodist inland mission, flying parson -
 Duldig Studio museum + sculpture garden
Duldig Studio museum + sculpture gardenCeramic, Karl Duldig, Gumnut Bowl by Karl Duldig c.1948, c. 1948
Karl Duldig’s ceramic bowl is a particularly interesting example of Karl’s ability to creatively respond to a new environment with a fresh visual repertoire, in this case, the flowering Eucalyptus in a design reminiscent of traditional European folk art. The bowl is an excellent example of the utilitarian and decorative studio pottery produced by Karl and his wife Slawa Horowitz-Duldig between 1944 and 1960. Clay was an important medium for Karl. When he was forced to flee Austria for Switzerland, working with clay became a convenient medium; and he continued to expand his use of clay in Singapore. In Australia his work in clay extended from domestic hand-made pottery to public sculptures and architectural reliefs. In 1944 Duldig purchased a kiln, which was installed in the garage of the family’s St. Kilda flat, soon after a pottery wheel was acquired. It was the beginning of a cottage industry that supplemented the family income during the war years and beyond. Duldig initially sold his decorative ceramic wares through a local florist in St. Kilda, and subsequently through shops such as the Chez Nous French Art Shop (Howey Place) and Light and Shade (Royal Arcade), and the Primrose Pottery shop in Collins Street. The Primrose Pottery shop was an extremely important commercial outlet, and hub, for emerging artists, potters and designers from 1929 until 1974. Its proprietors Edith and Betty MacMillan worked closely with their suppliers, commissioning and taking items on consignment. In the post war period important Melbourne studio potters such as Allan Lowe, Arthur Boyd, John Perceval and Neil Douglas exhibited and sold domestic wares in the Primrose Pottery shop. The Duldigs studio pottery provides a counterpoint to the ceramics produced at Arthur Merric Boyd Pottery in Murrumbeena, which was established in 1944 by Arthur Boyd, John Perceval and Peter Herbst. The emphasis on painterly decoration was important and the AMB potters also produced simple household wares decorated with Australian flora and wildlife, for example Neil Douglas also made small bowls decorated with the fairy wrens, lyrebirds, gumnuts and eucalypts. Ann Carew 2016The Duldig Studio’s collection of ceramics has national aesthetic and historic significance. It contains a representative sample of works of art in ceramics created by Karl Duldig during his lifetime, including small sculptures, as well as functional and novelty items for the tourist market during the 1956 Melbourne Olympic Games. The artist’s working methods and the development of his practice are comprehensively demonstrated in the collection. This in-situ collection demonstrates the philosophy of the Vienna Secession and its inheritors that handcrafted, simple functional domestic wares might enrich both the lives of the maker and the user. This bowl is part of a collection of ceramics that has national historic significance in providing a rich illustration of an immigrant and artistic experience, and touching on the themes of settlement adaptation of artistic practice. The collection is also associated with places of cultural and historical significance in Melbourne such as the Primrose Pottery Shop, and the story of Australian studio ceramics in the post-war years. Ann Carew 2016Cream earthenware bowl with flowering gum motif and sponged green background.Duldig in script incised under. -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photograph, Dorothy Wickham, Winter's Swamp, Ballarat, January to April 2014
Study of Winter's Swamp commissioned by BEN and completed by BHS. The swamp was named after one of the first European settlers in the district. Winter Swamp LAT -37 32 LONG 143 47, Parish of Dowling Forest, County of Grenville Winter Swamp, on the southwest corner of Ballarat West Town Common, was not included in the original proclamation of the Common in 1861. However, being marshland, it was not considered suitable for grazing, so was added to the Common soon after 1861. Winter Swamp is a large wetland with native and exotic pasture significant for wildlife. John Winter (Jock) was born in Berwickshire, Scotland. He married Janet Margaret Irving the daughter of Robert Irving, advocate, Bonshaw, Dumfries, Scotland. Winter died in Ballarat in 1875 and was buried at the Ballaarat Old Cemetery. He took up the run Bonshaw from 1841; Leigh River Buninyong 1842-46; Junction, Delatite, March 1851 to September 1862; with sons: Carag Carag and Corop, April 1857 to September 1872; Colbinabbin and Stewart’s Plains, April 1857 to December 1872; St Germains February 1867 to March 1871. (The name became Winter-Irving in 1890). Mr John Winter, who died on August 22 at the age of 72, was a man of some note it the mining community of Ballarat. He was a self-made man, and one of our oldest colonists, it being over a quarter of a century age since he took up county about Ballarat and settled at Bonshaw. He died very rich. It is calculated that if he had retained an interest in all his runs, his income must have been not less than £10,000 or £50,000 a year. Some eight or ten years ago he sold his Bonshaw pre-emption to the Bonshaw Gold mining Company for £20,000, and a few years later the ground belonging now to Winter's Freehold Company brought him £50,000 more, the payment being made at the requisition of the deceased in sovereigns. In these relations Mr. Winter has been closely identified with the mining industry at Ballarat. The deceased was a native of Lauder, in Berwickshire, and landed in Victoria several years before the gold discovery.The principle task of this project was the delivery of a report outlining the history of European settlement in the Skipton and Cardigan/Ballarat districts as pertinent to the use of and impact on the natural environment of the two reserves Skipton Common and Winter Swamp. The report was delivered in digital form only. The report, upon completion, was presented to the Network’s Committee in order to discuss the project. The report identified and described the uses of Skipton Common and Winter Swamp, and their impacts. In particular, this report examined farming/grazing (official and informal), mining, vegetation removal (including the removal of woodlands for timber, grasslands for pasture improvement) & use of riparian areas for access to water and timber removal. Recording the more benign and environmentally friendly uses such as picnicking, community activities, nature walks and the roles of organisations such as Field Naturalists’ and Bird Observers’ clubs, school and scout/guide groups will be relevant in helping to depict overall community attitudes towards the reserves; e.g.: has the Common generally been viewed as little more than a grazing paddock and fire hazard; has Winter Swamp always been the unknown natural asset that seems to have been its lot for at least the past 40 years? In this regard, the more contemporary history of actions surrounding the use and management of the reserves is of particular interest, in view of the extant evidence at both reserves; e.g. the actions of the Shire of Ballarat in the 1980s in establishing Winter Swamp as something of a competitor to Lake Wendouree but with a more environmental bent (although almost none of the plants used are indigenous species, but that is part of the story); the trotting track constructed on Skipton Common in the 1960s following representations to Premier Henry Bolte and the cropping of the western section of the Common to raise funds for the town’s new swimming pool, the fertilizing of the land putting an end to the native grassland vegetation. There are obviously multiple sources of information to source in preparing the report, however sources that the contractor is specifically requested to consult are the Skipton Historical Society, the former Skipton Common managers (specifically Graeme Pett), the Cardigan Windermere Landcare Group and the Learmonth Historical Society (believed to hold many of the former Shire of Ballarat’s records pertaining to the Council’s role as the Committee of Management for both Winter Swamp and the Ballarat West Town Common – Winter Swamp was split between 2 separate Crown Land tenures). The contractor is also encouraged but not required to utilise community newsletters, such as the Skipton Community Newsletter, to publicise and seek information about the project. Skipton Historical Society (Mary Bradshaw) contacted on Thursday 12 June 2.30pm. Mary lived on a farm out of Skipton but is currently living in the township. She remembers walking along the creek of the Common especially in spring and autumn in bare feet and that it was a very pretty place. There were a few snakes around the waterway in summer. People put cows and a couple of horses on the commonage to graze. Graeme Pett has always lived close to the Common and would know a lot about it. Other possible contacts would be Nicole Petress, Secretary of the Progress Association, and the Corangamite Council, Camperdown. Digital images of Winter's Swampwinter's swamp, ballarat, john winter, ballarat environmental network, mullawullah -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumVehicle - Lifeboat, A McFarlane and Sons, Lifeboat Queenscliffe, 1926
QUEENSCLIFFE was built in 1926 to a Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI) design called the Watson Class. The double-diagonal planked vessel was built by A McFarlane and Sons in Port Adelaide SA, commissioned on the 6th of March 1926, and then officially named and launched on the 9th of April 1926. The original Wayburn petrol engine was replaced with a Gardner diesel. This gave QUEENSCLIFFE a top speed of 7.5 knots with a range of 350 miles. The equipment carried aboard included a VHF Radio Telephone, HF radio transceiver, visual signals, life rafts, hand rocket gun, flare gun, generator, search light and first aid supplies. In the tradition of many shore based lifeboats, QUEENSCLIFFE had its own shed and slipway and was always ready for launching when required to go to sea in response to an emergency call. Its area of operation included 'the Rip' at Port Phillip Heads and the Bass Strait seas immediately offshore. She was taken out of service in 1976 by the Marine Board of Victoria and subsequently offered to the Borough of Queenscliffe for care and display. The Lifeboat is listed on the Australian Register of Historic Vessels (ARHV). During her 50 years of service the Queenscliffe attended many calls for assistance both inside and outside the Heads. Some of the vessels and calls for help the lifeboat attended were: 1960 - Army Commandos lost in the Rip 1967 - The search for the late Prime Minister Harold Holt 1974 - The last attendance to a vessel was to the Brisbane Trader which was on fire The shed which housed the lifeboat is located on the Queenscliff 'New' or 'Steamer' Pier (built in 1884). This shed includes the internal section of the slipway used to launch and retrieve the lifeboat. The external slipway and some other structures associated with the lifeboat shed have been removed. Originally fitted with two masts, the stern mast being removed in the 1960's. A retractable centre plate was used when under sail. Delivered with an 80 hp Wayburn petrol motor which was later replaced by a 72 hp Gardiner diesel. Top speed of 7.5 knots and a range of 350 miles.QUEENSCLIFFE is a wooden lifeboat built in 1926 in South Australia. It has a long association with the Victorian port of Queenscliff. It was manned voluntarily by their local fishermen and is therefore closely attached to families of the Queenscliff community. It is a rare surviving example of the coastal shore-based lifeboats that were based around the Australian coastline.The lifeboat 'Queenscliffe' a Watson Class LifeboatQueenscliffelifeboat, rescue, watson class boat -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyPhotograph - No. 1 Headrace Tunnel, Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme Workshops, 1952
MEYER COLLECTION - FALLS CREEK PHOTOS In 1947 a determined group of like-minded State Electricity Commission (SEC) staff including Ray Meyer, the chief surveyor of the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme, had a common interest that revolved around the skiing potential of the snow-covered high plains which included what is now the resort of Falls Creek. The six SEC employees, Toni St Elmo, Ray Meyer, Jack Minogue, Lloyd Dunn, Adrian Ruffenacht and Dave Gibson (together with their families) banded together to secretly build a 'hut' that was the first ski lodge at Falls Creek. Using a road built in 1930s to gain access to Falls Creek, their hut project was carried out in secret as efforts by other skiers were blocked by H.H.C. Williams – the engineer in charge of the Hydro Scheme. In 1946 Ray Meyer made a trip to the Lands Office in Melbourne. He came away with a 99-year lease on three acres that was ideally suited for a hut designed by Lloyd Dunn. Adrian Ruffenacht (Design Engineer for the KHS) had suggested where the group should build because of easy access to a spring for water. Much of the building material required was scavenged from derelict huts on the high plains. Due to the need for secrecy, the determined group worked on the hut in the evenings and weekends to avoid detection. During the building period the group had met at Echidna Rock (now known as Eagle Rock) where Skippy St Elmo announced, "This is my favourite ‘Skyline’.” And so the first lodge in the area at Falls Creek Ski Resort came into existence. With the development of the International Poma in the 1970s, the Skyline Lodge, which was sited between the ski-lift’s pole one and pole two, was demolished. However, the legacy of Ray Meyer, Toni St Elmo, Jack Minogue, Lloyd Dunn, Adrian Ruffenacht and Dave Gibson and Skyline lives on in the vibrant atmosphere of Falls Creek Resort. The MEYER COLLECTION documents developments on the Kiewa Hydro Scheme and their life at Falls Creek from the mid 1930s to 1950s.This image is significant because it documents development of the Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme.A black and white image of the No 1 Headrace Tunnel, Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme showing workshops and the McKay Aditkiewa hydroelectric scheme, ray meyer -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyPhotograph - No. 1 Headrace Tunnel, Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme, 1952
MEYER COLLECTION - FALLS CREEK PHOTOS In 1947 a determined group of like-minded State Electricity Commission (SEC) staff including Ray Meyer, the chief surveyor of the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme, had a common interest that revolved around the skiing potential of the snow-covered high plains which included what is now the resort of Falls Creek. The six SEC employees, Toni St Elmo, Ray Meyer, Jack Minogue, Lloyd Dunn, Adrian Ruffenacht and Dave Gibson (together with their families) banded together to secretly build a 'hut' that was the first ski lodge at Falls Creek. Using a road built in 1930s to gain access to Falls Creek, their hut project was carried out in secret as efforts by other skiers were blocked by H.H.C. Williams – the engineer in charge of the Hydro Scheme. In 1946 Ray Meyer made a trip to the Lands Office in Melbourne. He came away with a 99-year lease on three acres that was ideally suited for a hut designed by Lloyd Dunn. Adrian Ruffenacht (Design Engineer for the KHS) had suggested where the group should build because of easy access to a spring for water. Much of the building material required was scavenged from derelict huts on the high plains. Due to the need for secrecy, the determined group worked on the hut in the evenings and weekends to avoid detection. During the building period the group had met at Echidna Rock (now known as Eagle Rock) where Skippy St Elmo announced, "This is my favourite ‘Skyline’.” And so the first lodge in the area at Falls Creek Ski Resort came into existence. With the development of the International Poma in the 1970s, the Skyline Lodge, which was sited between the ski-lift’s pole one and pole two, was demolished. However, the legacy of Ray Meyer, Toni St Elmo, Jack Minogue, Lloyd Dunn, Adrian Ruffenacht and Dave Gibson and Skyline lives on in the vibrant atmosphere of Falls Creek Resort. The MEYER COLLECTION documents developments on the Kiewa Hydro Scheme and their life at Falls Creek from the mid 1930s to 1950s.This image is significant because it documents development of the Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme.Two black and white images of the McKay Adit, Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme' kiewa hydroelectric scheme, ray meyer
