Showing 850 items matching "male / female"
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Grey Butcher Bird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
... of a male/female pair (see Relationships). Many birds ...Grey Butcherbirds live in wooded habitats, including suburban areas, from the north of Western Australia, across different parts of the top of the country, through to mid-eastern Queensland, and then south along the eastern side of the country all the way down to Tasmania. They have a 'lovely, lilting song', and are fiercely protective of their nests and chicks, swooping at presumed attackers with enough strength to sometimes draw blood. Adult Grey Butcher Birds are typically a light grey colour with dark heads and white underparts. The brown colouring on this animal suggests that it is a young bird, with its grey adult feathers coming in. This bird appears thinner than most Grey Butcher Birds, but it is unclear if this is because of its age or because of inaccurate taxidermy. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is particularly special in the Burke Museum Collection as it is part of a male/female pair (see Relationships). Many birds in the collection were originally donated in male/female pairs, but at least one specimen has been lost, leaving these as one of the few surviving sets.This Grey Butcher Bird (likely female, based on size) has a light grey and brown bill with a sharp hook. The majority of the feathers on its back and tail are an olive-brown colour. The feathers of its underparts, the patches on either side of its bill, and two stripes coming up either side of its neck are a yellow-white colour. There are some light grey feathers coming through in small patches, particularly across the back, the top of the underparts, and along the upper half of the legs. The eyes are brown. The bird stands on a brown, wooden perch with a circular bar, curved stand, and circular base. It has an identification tag tied around its right leg.18a. / Collared Crow. Shrike / See Catalogue; Page 10. /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, australian birds, butcher bird, butcherbird, grey butcher bird, collared crow-shrike, australian butcherbird, tasmanian butcherbird, tasmania, bird pair -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Red-Winged Blackbird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The red-winged blackbird is native to North America. They live in a verity of places from southern Alaska at its northern most point, to the Yucatan peninsula in the south and covers the greater part of the continent reaching from the Pacific coast of California and Canada to the eastern seaboard. Populations that are most northerly migrate south after the mating season, but some of the populations in the central and western United States, Central America and the Gulf Coast are resident year-round. In the breeding season, Red-winged blackbirds are found in a range of fresh and saltwater environments, including in small trees and bushes along marshes and watercourses, in agricultural areas and dry meadows. During migration, they can be found in, pastures, prairies and cultivated fields. They are polygamous. In the north, the early arrival and tumbling song of these birds are welcome indications of spring's return. The Red-winged blackbirds are known for their scarlet and yellow shoulder patches on this specimen are rather dull and the feathers are not as glossy black as they are in other images. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This is one of the most common birds in North America and is the most boldly coloured one. The males are glossy-black with shoulder patches of scarlet and yellow which they are able to puff up or hide according to their level of confidence. Females look like a big, dark sparrow, being a subdued, streaky brown. This specimen has the colouring of the male Red-Winged Blackbird which helps to identify it as such.Swing-Tag: 137a. / Red-winged Starling / Catalogue page, 58 / Tag: A. 4429taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, american birds, north america, red-winged blackbird, red-winged starling, migratory, alaska, canada, saltwater -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Red-Winged Blackbird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The red-winged blackbird is native to North America. They live in a verity of places from southern Alaska at its northern most point, to the Yucatan peninsula in the south and covers the greater part of the continent reaching from the Pacific coast of California and Canada to the eastern seaboard. Populations that are most northerly migrate south after the mating season, but some of the populations in the central and western United States, Central America and the Gulf Coast are resident year-round. In the breeding season, Red-winged blackbirds are found in a range of fresh and saltwater environments, including in small trees and bushes along marshes and watercourses, in agricultural areas and dry meadows. During migration, they can be found in, pastures, prairies and cultivated fields. They are polygamous. The Red-winged blackbirds are known for their scarlet and yellow shoulder patches but on this specimen are rather dull and the feathers are not as glossy black as they are in other images. It is mounted accurately but the feathers appear to be ruffled. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Red-Winged Blackbird is one of the most common birds in North America and is the most boldly coloured one. The males are glossy-black with shoulder patches of scarlet and yellow which they are able to puff up or hide according to their level of confidence. Females look like a big, dark sparrow, being a subdued, streaky brown. The colouring of this particular specimen identifies it as male.[torn] page 58 / Tag: A. 4423taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, american birds, north america, red-winged blackbird, red-winged starling, migratory, alaska, canada, saltwater -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Regent Honey-Eater, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Warty-faced honeyeater Formerly more widely distributed in south-eastern mainland Australia from Rockhampton, Queensland to Adelaide, South Australia, the Regent Honeyeater is now confined to Victoria and New South Wales, and is strongly associated with the western slopes of the Great Dividing Range. The Regent Honeyeater is found in eucalypt forests and woodlands, particularly in blossoming trees and mistletoe. It is also seen in orchards and urban gardens. This species is critically endangered. They are native to Southeastern Australia. Specimen is mounted accurately. Colour around the eyes is red whereas they are yellow normally. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The striking Regent Honeyeater (Warty-faced honeyeater) has a black head, neck and upper breast, a lemon yellow back and breast scaled black, with the underparts grading into a white rump, black wings with conspicuous yellow patches, and a black tail edged yellow. In males, the dark eye is surrounded by yellowish warty bare skin. Females are smaller, with a bare yellowish patch under the eye only, and have less black on the throat. Young birds resemble females, but are browner and have a paler bill. The colouring of this particular specimen helps identify it as male.Swing-tag: 56a. / Warty-Faced Honeyeater / See Catalogue, page 18taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian bird, honey-eater, warty-faced honey-eater, regent honeyeater, critically endangered, yellow -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - White-Throated Treecreeper, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
... with their long, curved beak.The females are distinct from males through... with their long, curved beak.The females are distinct from males through ...The White-throated Treecreeper is a commonly small bird of the Climacteridae family, that has a loud, piping, whistle-like call. Living in permanent territories and rarely seen on the ground, this species is found in forested areas of south-east and southern mainland Australia. The name tree-creeper comes from their foraging patterns, in which they spiral up the trunk of trees (usually eucalypts for their preferrable rough bark) head-first, probing for ants or nectar with their long, curved beak.The females are distinct from males through orange marks on the sides of their face. The colour of these specimens differ from white-throated tree-creepers, whose plummage on the head and back is usually a dark gray-brown. The beaks of these specimens are also an orange-brown colour whereas these birds usually have a black beak. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This mount includes two White-throated treecreepers secured on a stick, one above the other. The top specimen is female, distinguished by a distinctive orange mark on the sides of its face underneath the eyes. Both specimens have white throat, chest and streaks on the flank. The top of the head and back are both a brown to dark-brown colour, with streaks of those colours on the flank as well. The stick and specimens are mounted on a wooden platform and a swing tag is secured around a part of the stick.Swing tag: 67a. / White-throated treecreeper / See catalogue, page 20 / Wooden Mount: 85taxidermy mount, taxidermy, burke museum, beechworth, bird, treecreeper, australian birds, white-throated, white-throated treecreeper, reynell eveleigh johns -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Green Woodpecker, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This fairly large woodpecker of the Picadae family is widely distributed across most parts of Europe and the UK, with some occurrence in Western Asia. Preferring semi-open habitats such as woodlands, heathlands and gardens, the species is unique amongst woodpeckers as it prefers to hunt and feed on the ground for its ant prey. This species has a distinctive bright red crown, black moustasche-like stripes, mostly green back plumage and a paler green to yellow breast. This is a female of the species as the male has a red centre to the moustache stripe at the side of the beak. This specimen is a fairly accurate depiction of a Green Woodpecker. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Green Woodpecker has a distinctive red crown on its head that appears patchy. It has a black face, a black moustache-like stripe on each side of the beak, pale eyes and long light yellow-orange beak. The back of the bird is green, and its flank and breast is a pale cream-yellow colour. It has slightly visible distinct white-dotted brown feathers folded into its wings. The specimen is mounted on a wooden perch, with a metal tag tied around its right leg and a paper tag around each leg.Swing tag: 1e. / Green Woodpecker / Catalogue page 66 / Metal tag: 4308 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, woodpecker, green woodpecker, eurasian green woodpecker -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Satin Bowerbird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Satin Bowerbird is a medium-sized common bird found from Queensland to Victoria in rainforests and wet sclerophyll forest. During the summer, the diet consists mostly of fruit, with insects as a supplement. They're famous for their courtship behaviour and for decorating stick-structured nests with blue sparkling objects. With it's stunning glossy blue-black feathers, which evolve from green-brown in appearance, this Satin Bowerbird is more than seven years old, and therefore not any younger as they are often mistaken for females, which are supposed to look like the green catbird. The eyes of this mature male are violet-blue, and the bill is pale bluish white. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.Satin Bowerbirds are medium-sized birds. The adult male has striking glossy blue-black plumage, a pale bluish white bill and a violet-blue iris.47a / Satin Bower-bird / See Catalogue, page 16 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, satin bowerbird, bowerbird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Satin Bowerbird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Satin Bowerbird is a medium-sized common bird found from Queensland to Victoria in rainforests and wet sclerophyll forest. During the summer, the diet consists mostly of fruit, with insects as a supplement. They're famous for their courtship behaviour and for decorating stick-structured nests with blue sparkling objects. With it's stunning glossy blue-black feathers, which evolve from green-brown in appearance, this Satin Bowerbird is more than seven years old, and therefore, not any younger as they are often mistaken for females, which are supposed to look like the green catbird. The eyes of this mature male are violet-blue, and the bill is pale bluish white. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.Satin Bowerbirds are medium-sized birds. The adult male has striking glossy blue-black plumage, a pale bluish white bill and a violet-blue iris.Swing tag: National Museum Victoria / Satin Bowerbird / Ptilonorhynchus Violaceus / B2027 / (Vieillot) / W. Shaw Collin. / Mount: PTILONORHYNCHUS / VIOLACEUS / SATIN BOWERBIRD / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Nankeen Kestrel, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Nankeen Kestrel, also known as the Australian Kestrel, is a common native to the open country's grasslands and farmlands, preferring agricultural areas. They are drawn to animal pests like mice, insects, small animals, reptiles, and birds. Due to the shape and ability of their tail feathers, which allows them to hoover over their prey, they do not rely on speed to catch their meal like most falcons in their family group. These birds are among the smallest raptors in the Falcon family, having well-known face characteristics and body shapes. The females of the species are distinguished by their darker patterns and red-brown (rufous) tones, as well as their larger size, whilst the males are more greyish. The yellow markings around the eyes and top of the beak, as well as the noticeable black dipped wings, distinguish each species. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Nankeen Kestrel is a small raptor in the Falcon family. It has a stockier appearance, with the upper parts of its body, such as the head and the tops of its wings, being a light red-brown (rufous) colour and the tips of its wings appearing dipped in black. The top of the beak and the eye rings are both yellow, and this bird's falcon appearance shows its inherent dark streak markings visible near the eyes and on the chest. The underparts are pale, with a tail feather that spreads out to help it hover and is ornamented with fine black decorations.20. / Unnamed / Catalogue page 5 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, nankeen kestrel -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Nankeen Kestrel, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Nankeen Kestrel, a small type of falcon, can be found all over Australia, usually in grassland or farmland areas. This falcon is carnivorous and hunts all manner of small prey including mice, lizards, insects, and other birds. When hunting, Nankeen Kestrels can be seen hovering in the air searching for prey. Nankeen Kestrels are generally monogamous, staying with the same breeding partner for multiple seasons. The Nankeen Kestrel is known for its reddish-brown feathers, spotted with a distinctive black pattern on its back, and have black-tipped wings and tail band, a stark contrast to its white chest. Females tend to be larger, and males will have a grey head and neck area. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Nankeen Kestrel is relatively small and slender. It is mostly reddish-brown, streaked with darker coloured areas. The tips of the wings and tail feathers are tipped in black. The chest is white with streaks of reddish-brown. The areas around its eyes, beak, and feet are a bright yellow. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing-tag: 19. / Unnamed / Catalogue page, 5 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, nankeen kestrel, falcon -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Magpie-Lark, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Magpie-Lark, also commonly known as a Mudlark, is a carnivorous bird found in many regions of Australia, Indonesia, Timor, and Southern New Guinea. They are a non-migratory species and are extremely adaptable to a variety of environments. These environments include dry forest, savannah, grassland, and even urban areas. Magpie-Larks are typically monogamous and are often found in pairs. They are black and white, with a white underbelly, long legs, and a long, thin beak. The females of this species have a white throat, while the males have a white eyebrow and a black throat. While juveniles have dark eyes, mature adults have light irises. This information helps identify this specimen as an adult male. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Magpie-Lark is a small to medium-sized bird which has distinctive black and white colouring. The bill is long and thin and is a whitish colour which differentiates it to other Magpie species. When mature, like this particular specimen, the Magpie-Lark have distinctive light irises. The glass eyes provided for this specimen are accurate in colour. This male specimen has a white 'eyebrow' marking and a black chest or bib. This Magpie-Lark stands on a wooden mount with a swing tag attached to its leg.Swing-tag: 20a. / Reed Grallina / See catalogue page 10 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, mudlark, magpie-lark -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Barn Owl, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 16-1880
... , with wing spans between 800-950mm. Females are larger than males..., with wing spans between 800-950mm. Females are larger than males ...Barn Owls are the most widely distributed owl species in the world and one of the most widespread of all bird species, including in Australia. Barn Owls are sedentary and prefer open habitats such as grasslands, farmlands, and open woodlands, where they forage and hunt small mammals, particularly rodents, at night. Barn Owls nest in deep hollows in old trees, especially eucalypts, but also in caves, rock cavities, and sometimes cavities in buildings. Barn Owl's have a highly distinctive white heart-shaped face and pale underbelly feathers. They can be seen circling low above grassland areas at dusk or at night, and their drawn-out shrieking, hissing, and 'eerie' rasping sounds have led some rural populations to consider they have magical powers. Barn Owls vary in size but average 330-390mm in length, with wing spans between 800-950mm. Females are larger than males and most are a mix of white, pale brown and shades of grey speckled with fine black tear-shaped spots. They have a distinctive flat heart-shaped facial mask with oversized oblique black eye-slits and black irises. A ridge of feathers sits above the beak resembling a long nose. The feet vary in colour from pink to grey, and beaks can be pale to dark buff, corresponding to general plumage hue. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Barn Owl is medium sized with long wings and a short squarish tail. Its underbelly is pale and speckled with dark spots. The wings and tail feathers are light brown, grey and white with small, dark, tear-shaped speckles on the upper parts. It has a distinctive white heart-shaped facial disc with large black eyes and curved beak. This specimen stands on a wooden perch pedestal and it has metal and paper identification tags attached to its legs. Swing tag: 36. / Barn [torn] / Catalogue [torn] / Metal tag: 4058 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, owls, birds of prey, tyto alba, heart-shaped faced owl, nocturnal birds, predator birds, 'harbingers of misfortune', demon owl, ghost owl, death owl, magical animals, lich owl, birds as omens, barn owl, carnivore, hissing owl -
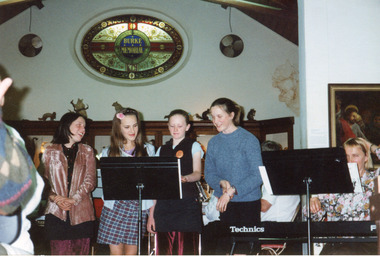 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c1999/2000
This photograph depicts female singers accompanied by members of the Beechworth Band at a 'Liedertafel' concert in the main hall at the Burke Museum in 1999. The concert related to an exhibition titled, 'From the Liedertafel to the Skating Rink: Entertainment in Beechworth 1852 - early 1900s', which celebrated the rich and diverse entertainments that were part of Beechworth life in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. 'Liedertafel' is a German tradition that accompanied European settlers to Australia. It refers to a friendly society of men united by an enthusiasm for singing. The Beechworth Liedertafel was established 14 March 1894 at the London Tavern, Camp Street, Beechworth, by president, Mr. A.A. Billson, and a visiting conductor, Mr. H. Fielder. The Beechworth Brass Band was formed by Mr. H. Vandenberg in 1887. Marching bands, choirs, circus acts, theatrical performances, races, and seasonal activities, such as Mr. Spiller's roller skating rink, which was founded in the late 1860s, were among the entertainments on offer in Beechworth.This photograph of the Beechworth Band playing at the Burke Museum is historically significant for the information it conveys about an exhibition at the Burke Museum between September and November 1999. The use of the contemporary Beechworth Band in a 'Liedertafel' performance provides insight into curatorial approaches at the turn of the twenty-first century and improves our understanding of how exhibitions use objects in the Burke Museum's Collection to tell stories about the past in the present. The image is historically and socially significant for attesting to the enduring appeal of local musical associations, which were a popular means of entertainment that fostered social connections among settlers from diverse ethnic backgrounds. Liedertafel choirs were originally male-only, therefore, the presence of female singers at the 1999 exhibition reflects progressive social and community values with regard to gender and inclusion.Rectangular colour photograph printed on matte photographic paper.Reverse: 7030 / Label: Burke Museum / Liedertafel Exh / Emily Messen, Luetta / Schier, Hannah / Routledge, Sarah / McKinley 2000 (?) / 2000 (?) / liedertafel, beechworth band, burke museum, exhibition 1999, from the liedertafel to the skating rink, entertainment in beechworth 1852 - early 1900s, past exhibitions, performances at the burke museum, european settlers, german community, german choral societies, brass bands, male choir, colonial passtimes, colonial entertainments, cultural traditions, gold rush, immigration, beechworth's german heritage, london tavern beechworth, camp st beechworth, beechworth historic district, beechworth's first brick tavern, spiller's skating rink, vandenberg's beechworth brass band, benevolent societies, intellectual societies, protestantism, billson brewery beechworth, teetotallism, fancy dress carnivals, skating carnivals, fundraising societies, german musicians, crimean war, beechworth german association, freemasonry, yma's, beechworth athenaeum, beechworth skating rink -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Morepork, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Morepork is a small brown and white spotted owl found in New Zealand, Tasmania and Norfolk Island. It is known by around twenty different names which are all onomatopoeic which emulate the birds distinctive two-pitched call. They are mostly nocturnal and carnivorous (eating insects and small vertebrates). They reside in habitats with trees, they sleep in roosts and hunt mainly in the evenings and early morning. Females are slightly bigger than males. This species attains full plumage in its third or fourth year. They can turn their heads 270 degrees." In Māori tradition the morepork was seen as a watchful guardian. It belonged to the spirit world as it is a bird of the night. Although the more-pork or ruru call was thought to be a good sign, the high pitched, piercing, ‘yelp’ call was thought to be an ominous forewarning of bad news or events." (NZ Department of Conservation). This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Morepork (also known as the Masked Owl) is covered in brown and white plumage on its head and body. The white feathers delineate its round yellow eyes. Its belly and back are brown and white with the white feathering appearing spotted. This Morepork specimen sits on a wooden perch with his head turned to the left. A swing tag is attached to its left leg.Swing tag: 10 / Masked Owl / See Catalogue, page 3 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, ruru, spotted owl, tasmanian spotted owl, morepork, mopoke, new zealand owls, new zealand birds, tasmanian owls, tasmanian birds, norfolk island owls, norfolk island birds -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Black Shouldered Kite, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Black Shouldered Kite is commonly found throughout mainland Australia in grasslands and other open habitats. It is a raptor (bird of prey) that will eat mice and other small rodents. The species is monogamous and will find a mate by the male giving food to the female while both are in flight. It is sometimes confused with the letter-winged kite though there undercarriages when in flight are very different with the letter-winged showing the letter W or M and the black shouldered kite showing black wing tips with white towards its belly area. The feathers of this species when alive and in the wild are more white than this specimen. The iris is usually red in mature birds so this specimen may not have been a mature bird as its eyes are brown. However, this is difficult to ascertain because it is also possible that the taxidermist who replaced the original eyes with the current glass ones provided a colour which was not accurate to the age/species of the bird. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Black Shouldered Kite has a white face and front of body with a grey posterior from the top of its head to its tail. It has black on its wings/shoulders. Its face is white with its eyes delineated by small black apostrophe like shapes from the inner eye to the top of the eye. The specimen stands on a wooden perch and has a swing tag tied around its right leg. Its eye colour is brown rather than red, indicating it is not a mature specimen.9. / Black Shouldered Kite / See Catalogue, page 3 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, black shouldered kite -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Morepork, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Morepork is a small brown and white spotted owl found in New Zealand, Tasmania and Norfolk Island. It is known by around twenty different names which are all onomatopoeic which emulate the birds distinctive two-pitched call. They are mostly nocturnal and carnivorous (eating insects and small vertebrates). They reside in habitats with trees, they sleep in roosts and hunt mainly in the evenings and early morning. Females are slightly bigger than males. This species attains full plumage in its third or fourth year. They can turn their heads 270 degrees." In Māori tradition the morepork was seen as a watchful guardian. It belonged to the spirit world as it is a bird of the night. Although the more-pork or ruru call was thought to be a good sign, the high pitched, piercing, ‘yelp’ call was thought to be an ominous forewarning of bad news or events." (NZ Department of Conservation). This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Morepork (also known as a Masked Owl) is covered in brown and white plumage on its head and body. The white feathers delineate its round yellow eyes. Its belly and back are brown and white with the white feathering appearing spotted. He sits on a wooden perch with his head turned to the left. A swing tag is attached to its leg.11 / Masked Owl / See Catalogue, page 3 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, ruru, spotted owl, tasmanian spotted owl, morepork, mopoke, new zealand owls, new zealand birds, tasmanian owls, tasmanian birds, norfolk island owls, norfolk island birds -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Merlin
... that this particular specimen is female. This is because male Merlin's... that this particular specimen is female. This is because male Merlin's ...This Merlin specimen is large for the falco columbarius species. It is brown and white in colouring which suggests that this particular specimen is female. This is because male Merlin's are usually blue, black, silver or grey. This species is predominantly found in the Northern Hemisphere. They are small, fast and highly skilled in hunting. The Merlin is generally a solitary bird outside of the mating season when it will socialise with other Merlins. The Merlin will consume smaller birds, mammals and bugs. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Merlin has a medium brown back with light brown and white speckled chest. The edges of her wings are dark brown and underneath her tail is white but also patterned in spots of light brown. It's bright yellow eyes are framed by tan coloured feathers and elaborate spotted patterns throughout it's body. Her small hooked beck ranges from orange to dark brown and feet are a faded yellow.Swing tag: 28 / Merlin / Catalogue, page 6 / Other swing tag: 56 / Falco / Cesalon Metal tag: 4033 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, bird, northern hemisphere, falcon, falco columberius, merlin, pigeon hawk -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Superb Lyrebird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Superb Lyrebird is a large ground-dwelling bird with powerful legs and long tail. Found in rainforest habitats in southeastern Australia, it forages in leaf litter for food. It has a very powerful song and is known for mimicking other species. The males have spectacular long tail comprising a variety of feather types, where juveniles and females lack the longer tail feathers. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This male Superb Lyrebird is primarily grey/brown. It has striking tail feathers that are white, beige and darker brown that vary in size. Aside from the middle of its tail feathers, the parts of the bird which are darker brown include the top of its head, wings and back. The bird has strong legs and a small beak. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform.taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, superb lyrebird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Superb Lyrebird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Superb Lyrebird is a large ground-dwelling bird with powerful legs and long tail. Found in rainforest habitats in southeastern Australia, it forages in leaf litter for food. It has a very powerful song and is known for mimicking other species. The males have spectacular long tail comprising a variety of feather types, where juveniles and females lack the longer tail feathers. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This male Superb Lyrebird is primarily grey/brown. It has striking tail feathers that are white, beige and darker brown that vary in size. Aside from the middle of its tail feathers, the parts of the bird which are darker brown include the top of its head, wings and back. The bird has strong legs and a small beak. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform. taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, superb lyrebird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Superb Lyrebird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Superb Lyrebird is a large ground-dwelling bird with powerful legs and long tail. Found in rainforest habitats in southeastern Australia, it forages in leaf litter for food. It has a very powerful song and is known for mimicking other species. The males have spectacular long tail comprising a variety of feather types, where juveniles and females lack the longer tail feathers. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Superb Lyrebird is primarily grey/brown. It has shorter tail feathers than the male, which are dark and light brown, and vary in size. The bird's wings, chest and belly are a lighter grey/brown, and there are hints of yellow-white in the edges of the feathers and through the bird's chest. The bird has strong legs and a small beak. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform.37a. / Lyrebird / See Catalogue, page [illegible] /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, superb lyrebird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Powerful Owl, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860- 1880
... birds, male Powerful owls are larger and stronger than females... birds, male Powerful owls are larger and stronger than females ...The Powerful owl is native to south-eastern and eastern Australia and is the largest owl on the continent. It is found in coastal areas and in the Great Dividing Range rarely more than 200 km (120 mi) inland. An apex predator in its narrow distribution, the Powerful owl is often an opportunist like most predators, but generally hunts arboreal mammals, in particular small to medium-sized marsupials. It is a typically territorial raptorial bird that maintains a large home range and has long intervals between egg-laying and hatching of clutches. Unlike most raptorial birds, male Powerful owls are larger and stronger than females and so the male takes the dominant position in the mating pair, which extends to food distribution. This example of a Powerful Owl show lighter brown coloured feathers and slight discolouration. The Powerful Owl has darker colourings and whiter feathers in real life. This example also show discolouration in the feet and they are brighter yellow in colour in real life. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th centuryThis Powerful Owl has medium brown to dark grey-brown above, with white barring, and off-white front. The glass eyes are yellow, set in a dark grey/brown facial mask. The legs are feathered with yellow feet and talons. The specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has no identification tags attached. Swing-tag: n/a Metal tag: n/a Mount: no markings taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, owl, powerful owl -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Powerful Owl, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1086- 1880
... birds, male Powerful owls are larger and stronger than females... birds, male Powerful owls are larger and stronger than females ...The Powerful owl is native to south-eastern and eastern Australia and is the largest owl on the continent. It is found in coastal areas and in the Great Dividing Range rarely more than 200 km (120 mi) inland. An apex predator in its narrow distribution, the Powerful owl is often an opportunist like most predators, but generally hunts arboreal mammals, in particular small to medium-sized marsupials. It is a typically territorial raptorial bird that maintains a large home range and has long intervals between egg-laying and hatching of clutches. Unlike most raptorial birds, male Powerful owls are larger and stronger than females and so the male takes the dominant position in the mating pair, which extends to food distribution. This example of a Powerful Owl show lighter brown coloured feathers and slight discolouration. The Powerful Owl has darker colourings and whiter feathers in real life. This example also show discolouration in the feet and they are brighter yellow in colour in real life. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Powerful Owl has medium brown to dark grey-brown on its wings and back, lighter patterning on its chest lightening with white barring, and off-white front. The eyes are yellow, set in a dark grey/brown facial mask. The legs are feathered with yellow/browning feet and talons. The specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has no identification tags attached. Swing-tag: n/a Metal tag: n/a Mount: wooden with no markings.taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, owl, powerful owl -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Snowy Owl, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860- 1880
The Snowy owl is a large and powerful bird. It is one of the largest species of owl, and in North America, it is on average the heaviest owl species. The adult male is virtually pure white, but females and young birds have some dark spots; the young are heavily barred, and dark spotting may even predominate. Thick plumage, heavily feathered taloned feet, and coloration render the Snowy owl well-adapted for life north of the Arctic Circle. This Snowy Owl example is slightly discoloured and in real life the Snowy Owl displays much more brilliant white feathers. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Snowy Owl adult male is virtually pure white with brown spot markings and a pale brownish wash. It has thick plumage and heavily feathered taloned feet. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing tag: [torn] snowy owl / See catalogue, page 54 / Metal tag: 4054 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, owl, snowy owl, arctic circle -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, E-Gee Printers, Middleton & Manning's Gippsland Directory 1884-5, 1983
The 1884-1885 Directory was the first year of publication for the Middleton and Manning's Gippsland Directory. It was first published by Ale Middleton and Francis Beresford Manning. Beginning with advertisements from local businesses of the time, this is followed by a short gazetteer of places around the region, as well as general information on the districts of Gippsland. The main part of the Directory consisting of about 100 pages, is the Alphabetical Directory. Listed alphabetically by surname under each region, this lists heads of household (mostly male but there are a few females mentioned), together with their occupation and address.The list includes farmers, labourers, coach painters, dairywoman, teacher, saddler, brickmaker, merchant, laundress, hotel keeper, minister of religion, dressmaker, grocer, grazier, gasfitter, seedsman, coachbuilder, engineer, auctioneer, upholsterer, fowler, journalist, surveyor, musician, traveller, watchmaker, solicitor, restaurant keeper, blacksmith and miner. It is not just "business owners" mentioned in this directory it is everyone. (ref Gen E Books)This is a useful reference tool.A 135 pp soft covered book with an orange/brown cover. On the front cover in black print is a range of advertisements or local businesses. It contains a short gazetteer of places in the region as well as general information on the districts of Gippsland. The main part of the directory is an alphabetical list of the household , with occupations and addresses. This is a reprint of the original.directory-gippsland book-middleton-manning-1884-5 -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Hardhead, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Interestingly, the name "Hardhead" does not refer to the density of this species skull. Instead, it refers to the difficulty encountered by early taxidermies in styling the bird's head. This particular breed of Duck is smaller than average and are often found in the coastal regions of Australia. They are also known to reside in New Guinea, New Zealand and the Pacific Islands. This species was formerly known as the 'White-eyed Duck"; however, since the female Hardhead have dark eyes, this species was renamed the "Hardhead" Duck. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Hardhead specimen is a stocky medium-sized duck with chocolate brown colouring. The bird has paler white/ cream coloured plumage on the stomach and neck. The bill is a grey black colour and the eyes are made of a grey glass with a black pupil. The lighter brown colour of this specimen's head could refer to its identification as female or could be due to the taxidermy process or the impact of age on the colouring of the specimen. Female Hardheads have brown eyes, while the male have strikingly pale white/grey eyes. The bird has large webbed feet which are attached to the wooden platform it stands upon. The platform is inscribed on the left with the number 138.7a. / White-eyed Duck / See Catalogue, Page 39. / 138 on the wooden platformtaxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, heron, duck, australaisian shovelor, shovelor -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Gang Gang Cockatoo (female), Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Gang-gang Cockatoo can be found throughout much of south-eastern Australia. They reside in mountainous forests and open woodlands, often in small groups or larger flocks at sources of food and water. They eat mainly seeds from native trees and shrubs along with wattles, eucalypts and hawthorns. The Gang-gang Cockatoo is also known to incorporate berries, nuts, fruits and insects to their diet. The sound made by this type of Cockatoo is often described as a rasping screech which resembles the sound of a rusty hinge being moved.This type of call is made when the bird is in flight. These birds also fond of attention and can pick their own feathers if they are bored. The name "gang gang" derives from a New South Wales Aboriginal language, either the Ngunnawal or Wiradjuri. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Gang-gang Cockatoo has a grey head and crest with brown glass eyes. The beak is hooked and a pale bone colour. The neck and torso of the cockatoo is patterned with orange and black stripes. The feathers of the underparts and back are slate-grey with an edging of pink and yellow. The female cockatoo has more yellow in their feathers than the males which gives them a further barred appearance. taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, australaisian shovelor, shovelor, cockatoo, gang-gang cockatoo, cockie -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Belted King Fisher, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Belted Kingfisher is commonly seen near bodies of water or coasts in Canada, Alaska and the United States. During migration periods these birds may stray far from their usual habitat. Interestingly, the female of this species, as is the case for this specimen, is often larger than the male. They are also more brightly coloured. This species feed on amphibians, small crustaceans, insects, small mammals and reptiles. They lie await perched on a tree located close to water and remain there watching until they see their prey. When they have located their prey, the Belted Kingfisher plunges its head into the water and catches its food. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Belted Kingfisher stands upon a wooden perch with a light brown paper tag attached to leg. This specimen has pale cream/white and slate grey/blueplumage. The head and back are coloured the blue-grey while the neck and stomach are cream/white. The bird has a black ring around its upper chest. The stomach has a chestnut brown band which identifies this particular specimen as female. The bill is long and pointed and the eyes and legs black. The bird is small and stocky with a large head and a square-tipped tail.95.a / Belted / Kingfisher / Catalogue page, 25 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, kingfisher, small birds, belted kingfisher, king fisher, female bird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Red Necked Avocat, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This particular species is native to Australia and can be located throughout the mainland, preferably in the south-western interior. It is known for its distinctively upturned bill, the males of this species have a slightly more upturn to their bill than the female. This style of bill is unusual among birds and is used to assist them forage in the water of shallow wetlands. These birds feed on aquatic insects, crustaceans and seeds. The name of this species is derived from the distinctive chestnut brown/red colouring of the head and neck. Interestingly, the call of this bird has been described as a "yapping" sound which is similar to the sound of dogs barking when performed by a flock in flight. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Red Necked Avocat specimen is stylized in a standing position upon a wooden platform. There is a pale brown identification tag tied around its left leg. The bird has long pale grey coloured legs and a characteristic long, thin and black upturned bill. The plumage of this species is largely white. It has a chestnut brown/red coloured head which is where this species gets its name. The wings are white with black tips.25c. / Avocet / Catalogue, page, 36. / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, large bird, red necked avocat, avocat -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Red-Necked Avocat, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This particular species is native to Australia and can be located throughout the mainland, preferably in the south-western interior. It is known for its distinctively upturned bill, the males of this species have a slightly more upturn to their bill than the female. This style of bill is unusual among birds and is used to assist them forage in the water of shallow wetlands. These birds feed on aquatic insects, crustaceans and seeds. The name of this species is derived from the distinctive chestnut brown/red colouring of the head and neck. Interestingly, the call of this bird has been described as a "yapping" sound which is similar to the sound of dogs barking when performed by a flock in flight. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Red Necked Avocat specimen is stylized in a standing position upon a wooden platform. There is a pale brown identification tag tied around its left leg. The bird has long pale grey coloured legs and a characteristic long, thin and black upturned bill. The plumage of this species is largely white. It has a chestnut brown/red coloured head which is where this species gets its name. The wings are white with black tips.24c. / Avocat / Catalogue, page, 36. /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, large bird, red necked avocat, avocat -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, circa 1870
Taken circa 1870, depicting twenty-eight staff members divided by gender standing in front of the Beechworth mental asylum. Constructed between 1864 and 1867 to the designs by the Public Works Department (PWD) is the Beechworth Lunatic Asylum that was renamed Mayday Hills. The decommissioned asylum was one of the largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria and consisted of sixty-seven buildings, one thousand two hundred patients and five hundred staff members. The asylum was predominately inhabited by long-stay patients but there was active out-patients. The asylum was one of the first asylums to focus on treatment and rehabilitation instead of institutional confinement. At the asylum active works was considered imperative and workshops were located near the male accommodations and laundries and drying yards near the female accommodation. The asylum closed in 1995 and was sold to La Trobe University before being closed and sold again in 2011 to a private owner. This photograph is historically significant as it provides insight into the importance of Beechworth mental asylum as the asylum demonstrates the changing approaches to the treatment of mental illness in Victoria from confinement to treatment and rehabilitation. Sepia rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper mounted on card Reverse: 1997.2489/ Beechworthbeechworth, mental asylum, beechworth mental asylum, mental asylum administration building, mayday hills, mayday hills mental asylum, beechworth lunatic asylum
