Showing 597 items matching "physics"
-
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: G.F. Dainty
Black and white photograph portrait of G.F. DaintyOn front of image in ink: “4” On back of image: “5”, “No. 5 G.F. Dainty”. See History of Object for transcript. -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: H.D. Rathgeber
Black and white photograph of Henri Rathgeber looking through equipment. On front of image in ink: “6” On back of image in pencil: “No. 6 Henri Rathgeber” On back of image in ink: “6” -
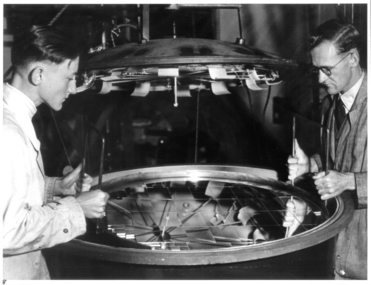 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: A.C. Goodwin & Peter Law
Black and white photograph of two scientists at work (A.C. Goodwin and Peter Law).On front of image in ink: “8” On back of image in pencil: “No. 8 A.C. Goodwin Peter Law” (L to R) On back of image in ink: “8” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: A.C. Goodwin & Peter Law
Black and white photograph of two scientists at work (A.C. Goodwin and Peter Law). On front of image in ink: “9” On back of image in pencil: “No. 9 A.C. Goodwin Peter Law” (L to R) On back of image in ink: “9” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: J.B. Wllis & P.G. Law
Black and white photograph of two scientists (J.B. Willis and P.G. Law) at work on microscope On front of image in ink: “31A” On back of image in pencil: “31A J.B. Willis, P.G. Law ” (L to R) On back of image in ink: “31A” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: ? Kahanine
Black and white photograph of male scientist (Kahanine) working on graphic design. On front of image in ink: “31” On back of image in pencil: “No. 31 Kahanine’ On back of image in ink: “31” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: Optical glass
Black and white photograph showing male hands preparing glass for fusing. Same photo as 144. On front of image in ink: “24” On back of image in pencil: “No. 24 Glass Preparation for fusing” On back of image in ink: “24” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: Notman
Black and white photograph showing young man (Notman) working on graphic designs at a draft board. On front of image in ink: “19” On back of image in pencil: “Notman No. 19” On back of image in ink: “19” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: G. Crickmore
Black and white photograph showing Gordon Crickmore using compass. Same photo as 136. On front of image in ink: “16” On back of image in pencil: “No 16 Gordon Crickmore” On back of image in ink: “16” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotograph, Optical Munitions: D. Huey
Black and white photograph Dick Huey at work assembling plate glass for making gla blocks. Same photo as 147 On front of image in ink: “27” On back of image in pencil: “No 27” On back of image in ink: “27” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumPhotographs, 2.8 MeV Betatron: Glass Donut
6 colour polaroid photographs showing different angles of Glass donut for 2.8 MEV Betatron (Reg 61) (269.1,269.2, 269.3, 269.4, 269.5, 269.6) Photographs are of Reg 61: Glass donut for 2.8 MeV Betatron -
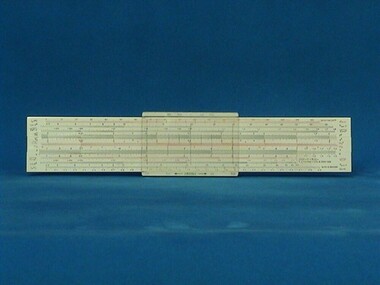 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumSlide rule, Faber-Castell
White Castell rectangular slide rule (270.1) stored in clear plastic Faber Castell case (270.2). On slide rule: printed - “Castell”, On case: stamped - “Made in Germany”, in pen - “451”, Paper label: “Castell 57/89” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumSlide rule , Castell
Plastic white rectangular Castell slide rule (271.1) stored in green lined rectangular case (271.2). On slide rule in green font: “Castell” -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumMeldometer, Joly
The Joly meldometer was created to determine the melting point of minerals. W.E. Wilson, an astronomer and author, stated in 1900 that the Joly meldometer consisted of a ‘a strip of platinum on which minute fragments of any mineral can be placed, while any alteration in its length can be determined by means of a micrometer screw which touches a lever connected with one end of the strip. The strip can be heated by an electric current, and is calibrated by observing the micrometer readings corresponding to the temperatures at which some substances of known melting-points melt’i . One reason why the Joly meldometer was seen as a successful addition to science was the small amount of any substance that it required for testing. Only a minute sample was needed for the instrument to work and so a tiny part could be taken from a delicate item without destroying itii . The instrument was originally manufactured by the Irish company Yeates & Son of Dublin. The Yeates family business was established in the early 1790’s and is thought to have operated until approximately 1922iii . Their business slogan was recorded as ‘Instrument makers to the University’, a slogan which proudly exhibited their relationship with Trinity College, Dublin. The company was located directly opposite Trinity College, the place where the Joly meldometer was created. Working in such close proximity must have assisted this business relationship. The inventor of this meldometer was Irishman John Joly. Joly was born in 1857 at the Church of Ireland Rectory, Hollywood House. His education led him to Trinity College Dublin where, by 1891, he had obtained a Bachelor of Engineering degree as well as a Doctorate of Science. The entirety of his working life appears to have taken place at Trinity College although he is known to have travelled in order to consult with other scientists such as the world renowned Sir Ernest Rutherford. The Joly meldometer was used for a variety of different purposes, with scientists often adapting the instrument to suit their own needs. For instance, the previously mentioned astronomer W.E. Wilson adapted the meldometer to assist him in measuring the radiation of the suniv . Joly used his device in an attempt to ascertain the age of the earth. In 1913, along with Sir Rutherford, Joly came to the conclusion that the earth was approximately 400 million years old. They did this by analysing the decay of radioactivity in minerals. According to our present knowledge of the earth this was a much more accurate date than the dates Joly had previously derived. He had first thought that the earth was 97 million years old due to the volume of sodium in the oceans. Joly’s second analysis of the topic had resulted in the age of 80 million years. This figure was based on the accumulation of sediment. Apart from designing his meldometer, Joly is also remembered for his work with colour photography. In 1894 Joly discovered a method for creating colour photographs from a single platev . He also studied the use of radiation as a treatment for cancer and persuaded the Royal Dublin Society to establish the Radium Institute to assist hospitals. In 1933 Joly passed away at the age of seventy-six. -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumX-Ray Spectrograph, Laby/Hilger
The spectrograph employs the principle of single crystal Bragg X-Ray Diffraction to measure wavelengths by interpolation from accepted standard lines. It is suitable for the identification and determination of the charateristic emissions of elements and thus for X-Ray spectrum analysis. The instrument was manufactured by ADAM HILGER Ltd. to the design of Professor Laby and is the best preserved instrument surviving from his research activity. A full description is given in the Hilger Pamphlet with the instrument; alternatively see duplicate in Appendix A5,A6 in Vol 2 of Laby ‘s COLLECTED PAPERS. -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumX-Ray Spectrograph, Laby
This is the prototype of Laby’s X-Ray Spectrograph (cat. no.274) and was constructed in the Nat. Phil. workshop. -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumInterferometer - Michelson
A student demonstration or general laboratory model capable of calibrating the pitch of the mechanical thread in terms of the wavelength ofvisible light, specifically a chosen emission line from the spectra of say mercury. -
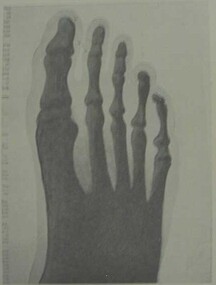 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumLyle Radiograph
Copies of the Lyle radiograph (see below) are on file with the letter (9Sept 1982) from J F Richardson (Australian Radiation Laboratory, as it was then called) detailing the description of the reproduction as follows: RADIOGRAPH OF PROFESSOR ORME MASSON'S FOOT! MOST PROBABLY THE FIRST RADIOGRAPH TAKEN IN AUSTRALIA. TAKEN BY PROFESSOR LYLE ON MARCH 3RD, 1896 USING A CROOKES DISCHARGE TUBE OF HIS OWN CONSTRUCTION -
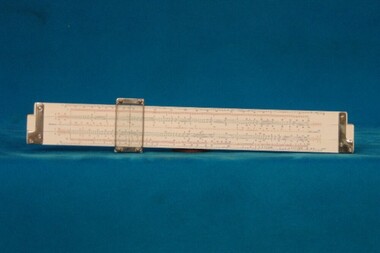 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumWhite & Gillespie Slide Rule
White & Gillespie “Dualface” comprehesive slide rule Model 432 In original cloth covered case“Dual face” Comprehensive Slide Rule Model 432 Melbourne > W&G -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum“MULTO” (Brunsviga)
ODHNER/BRUNSVIGA TYPE MULTO model 13or 113 keys: 10 x 8 x 13 same as F288/M1 -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumTRINKS - Triplex
A Brunsviga twin-system with keys 10x10x20 and 12x20. Plaque: TRINKS Double System / GRIMME NATALIS & Co / Braunschweig / AND Brunsviga Calculator Co. / London, Brunsviga House / Snow Hill EC1[London] / Manchester, WIlliam Brown Street / Glasgow, 20 West Campbell St. -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumS.C.M. HAMANN
S.C.M. HAMANN Mechanical Type 505 Ser. no. 501354 Donated by Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research keys: 9 x 8 x 16 ELECTRICAL! HANANN Rechenmaschinen GMBH Berlin SW61 (West G) -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumMILLIONAIRE (Ticket no 13) 10 keys
Sheet of operating instructions which mentions that O. Steiger is the Patentee. On separate stand about 600mms high Plaque: ‘Sole Agents for Australia / Peacock Bros. PtyLtd / Business Systems / Melbourne, Sydney, Adelaide, Brisbane, Perth’ -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumMILLIONAIRE (#2) 10 keys
Plaque: ‘Hans W Egli/Ingenieur / Fabrikation von flechenmashinen [sic; ?] / Pat. O, Steiger / Zurich II / No 2566. Sole Agents for Australia / Peacock Bros./ Business Systems Company / 558 , 560, 562 Collins St., Melbourne / and at / Sydney, Adelaide, Perth’ Plaque: ‘Presented to . / Department of Information Science / Melbourne University / by the / Gas & Fuel Corporation of Victoria / This calculating machine was used by Engineers of the Metropolitan Gas Co and Gas & Fuel Corporation / from 1917 to 1970’ -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumFACIT Mechanical Model C1-13
Plaque: Made by Atvidaberg - FACIT / Sweden keys: 8 x 13 x 13 -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumFACIT mechanical
-
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumFACIT Mechanical
keys: 16 x 9 x 16 Plaque: ‘Sydney Pincombe Pty Ltd, Sole Australian Agents Made by ....FACIT/ Sweden/ same as M11 -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumFACIT Mechanical
Keys: 10 x 19 x 10 Plaque: Made by Aktiebolaget FACIT/ ATVIDABERG / SWEDEN’ Black enamel, painted “V”; good working ordeer -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumFACIT Mechanical ModelCM 2-16
Keys: 16 x 9 x 16 ( A note states: ‘Possibly Model No LX (1945) See Sabielmy’s book (1939) Plaque: (See 297/M9 ....Sydney Pincombe ...) -
![MERCEDES-EUKLID [Arithmometer] Model 22](/media/collectors/500ce4da023fd719d872f684/items/59c8f25221ea680ef8f22ae4/item-media/59c8f26d21ea680ef8f24928/item-fit-380x285.jpg) The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumMERCEDES-EUKLID [Arithmometer] Model 22
Keys: 13 x 16
