Showing 79 items
matching architecture - japan
-
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph, postcard "Boiling the Billy" c1900, Early 1900's "Boiling the Billy", c1900
Early 1900's. "Boiling the billy". The term billy or billycan is particularly associated with Australian usage, but is also used in the UK and Ireland. It is widely accepted that the term "billycan" is derived from the large cans used for transporting bouilli or bully beef on Australia-bound ships or during exploration of the outback, which after use were modified for boiling water over a camp fire. Postcards developed out of the complex tradition of nineteenth-century printed calling cards, beginning with the advent of the Cartes-de-Visite in France. In the 1850s, Parisian photographer Andre Adolphe Eugene Disderi invented a photographic process involving egg white, albumen, and silver nitrate to create inexpensive portraits on paper cards. These photographic Cartes-de-Visites were 2 1/2 (75mm) by 4 inches (98mm) and became a popular, collectable form of "visiting cards" world-wide. Photographers would reprint portraits of famous individuals they had taken at their studios or during travel and sell them as collectable cards. Postcards as we know them now first began in 1861 as cards mailed by private post. In the 1870s picture postcards grew in popularity throughout the United States, Britain, Europe, and Japan. Cards were first permitted to have a "Divided Back," with text written on the left half of a dividing line and the address on the right half, beginning in England in 1902. Around 1900 the first postcards made of "Real Photos" rather than artwork began to circulate, aided in by advances in amateur photography equipment by companies such as Kodak. Kodak also introduced postcard paper for photographic development and photography studios began to offer portraits printed as postcards Many local town, countryside, and architectural images were captured during this period by local photographers, then printed and sold as postcards . Advances in amateur photography all contributed to a postcard craze that lasted from 1900 to the First World War. Postcards were the preferred means to send a quick note, whether across town or across a continent.Postcard with a black and white Photograph on the front and a 'Divided Back ' for the message and address. There are seven men surrounding the billy suspended over a camp fire. The ground has a lot of dead branches around. One man is bending down towards the billy. Two men on either side of the camp fire are carrying either a white bag across their shoulders or the fish in their hands. You can see, that there is some steam also coming out of the billy, which means that its hot. Court Post Card. / this space may be used for correspondence. / The address only to be written here.1900's, boiling the billy , postcards, photographers, england, hungary, america, cartes-de-visite, visiting cards, moorabbin, cheltenham, bentleigh, market gardeners, early settlers, pioneers, -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, Tokyo Cathedral, c. 1965
A detailed critique of Kenzo Tange's St Mary's Cathedral, Tokyo and experience of visiting the site. (later published asPublished as "A Cruciform Window onto Heaven" in "Architectural Forum", vol. 123, no. 2, September 1965, pp. 50-55.Typewritten (c copy), foolscap, 4 pages. (Three copies)st mary's cathedral, tokyo, kenzo tange, hiroshima, tokyo olympic games, hyperbolic paraboloid, japan, robin boyd, manuscript -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, Architecture in the Seventies
Boyd outlines the focus of the Modern Movement: function determining form and the rejection of ornamentation; outlines three phases of Modernism: the plain informal functionalist box style; 1950s monolithic sculptural forms (eg TWA terminal); and fragmented systematic expandable forms. Boyd proposes a new phase: a New Revolution Against Architecture, wherein the barriers between art and science are broken down and combined with technology; suggests looking to Japanese Metabolism.Typewritten, pencil edits, quarto, 21 pagesPage 1 refers to a chart (not attached). Sporadic annotations throughout. Appears to be a talk. Pages 6-8 refer to a chart, page 11 refers to an image of apartments by James Stirling, p14 refers to Robert Venturi's Guild House.page 1 refers to a chart (not attached). sporadic annotations throughout. appears to be a talk. pages 6-8 refer to a chart, page 11 refers to an image of apartments by james stirling, p14 refers to robert venturi's guild house -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, Kenzo Tange, 1946-1969, 1971
... melbourne Book review of "Kenzo Tange, 1946-1969. Architecture ...Book review of "Kenzo Tange, 1946-1969. Architecture and Urban Design", edited by Udo Kultermann, Praeger Publishers, 304 pp $29.50. Boyd praises Tange's unapologetic adherence to modernism and his adaptation of le Corbusier's ideas to tradition. He appraises the book's merits and problems (explanatory and not analytical writing, building omissions).Architectural Forum, Vol. 135, No.3, October 1971, p8. Book review by Robin Boyd of 'Kenzo Tange, 1946 - 1969, Architecture and Urban Design', edited by Udo Kultermann, Praeger Publishers,Typewritten (c copy), quarto, 3 pageskenzo tange, japanese architecture, modern movement, le corbusier, creative realism, expo, skoplje, yugoslavia, hiroshima, children's library at hiroshima, shizuoka olympic arena, tokyo, nichinan, robin boyd, manuscript -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, Antiarchitecture, 1968
Boyd argues that there is little that is truly avant-garde or revolutionary in architecture. Boyd defintes 'antiarchitecture' as architecture which rejects aestheticism, an approach explored by constructivists, Archigram and Venturi. Boyd indicates that he suspects that architecture can never fully escape aestheticism.Original manuscript of the article published in The Architectural Forum, Vol. 129, No. 4, November 1968, pp. 84-86.Typewritten (c copy), quarto, 6 pagesAnnotation on p2radicalism, venturi, archigram, reyner banham, buckminster fuller, new brutalists, constructivism, john m johansen, paul rudolph, charles moore, japanese metabolism, george nelson, aestheticism, robin boyd, manuscript -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, The Exhibitionist Expo, 1970
... or naive. Boyd is critical that Japan did not present a view ...Boyd discusses the exhibition buildings in Expo 70, Osaka, saying that they fall into two distinct categories, sophisticated or naive. Boyd is critical that Japan did not present a view of the future, which might have been expected of it. This manuscript was published under the title ‘Expo and Exhibitionism’ in 'Architectural Review 'Vol.148, No.882, August 1970.Original manuscript of article titled ‘Expo and Exhibitionism’ published in 'Architectural Review' Vol.148, No.882, August 1970, pp. 99 -100 & 109 &110.Typewritten (c copy), foolscap, 3 pages. (2 copies)osaka, expo 70, expo 67, archigram, metabolism, japanese architecture, kenzo tange, noriaki kurokawa, takamitsu azuma, sumitomo pavillion, takara pavilion, gas pavillion, yoshizawa ryusei, robin boyd, manuscript, ohm2022, ohm2022_31 -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, The Value of Expos
Primarily using the Osaka 70 World Expo, Boyd criticises the lack of depth of information of the event and the illusion each country provides for their audience. Boyd makes suggestions for improving audience engagement with the exhibitions and also for a new type of pavilion architecture which utilises the temporary nature of the buildings.Typewritten (c copy), pencil edits /notes, quarto, 6 pages. (Two copies)One copy annotated markers for slides for a talk or lectureosaka expo 70, japan, melbourne, robin boyd, manuscript, ohm2022, ohm2022_31 -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationBook, Robin Boyd, Kenzo Tange, 1962
... melbourne Kenzo Tange Japanese architecture modern architecture 20th ...Hardcover with Dust JacketRBF Acquisitionkenzo tange, japanese architecture, modern architecture, 20th century, walsh st library -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationJournal, Architectural Forum, Vol. 121, No.2, Aug/Sept 1964
This is a special issue on Architecture in Transition. It features articles is on 'Functional grid in Japan' (pp 130-135) and 'Bold Masses in Tokyo' (p 156-157) and 'Clean Sweep in Olympics' (pp 158-161) on the Tokyo Olympic buildings.Has a piece of paper with typed 'Journal Distribution' and a double columned list of initials: F.R., B.H., A.K., R.B., P.C., K.E.architecture, walsh st library -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationJournal, The Architectural Forum, Vol 135 No 1, July/Aug 1971
This issue is devoted to building for recreation. featuring a portfolio of vacation-time structures in Canada, Japan and the US. The piece on Japan is about a glass-walled college gym in Tokyo (pp 42-45).architecture, walsh st library -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationBook, Miya Inoka Hisa Henshu Jimusho, Yoshinobu Ashihara - Architect and Associates, 1966
... melbourne architecture japanese architecture Walsh St library ...Softcover Book, Japanese and English Textarchitecture, japanese architecture, walsh st library -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1967
Robin Boyd was appointed Exhibits Architect for the Australian Pavilion at Expo ‘67 in Montreal. The garden outside the pavilion featured a sculptural pool, a coral display, animal pool, a pit for kangaroos and Eucalypts and other native plants. The indoor exhibits covered aspects of Australian art and culture, architecture, industrial design and scientific innovation, such as the Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Power Scheme, the Parkes radio telescope, the design of Canberra, and the Australian way of life.Colour slide in a mount. Japanese Pavilion, Expo '67, Canada, Montreal (Architect: Yoshinobo Ashihara.) See also item S0109.Made in Australia / 4 / MAY 67M6 / 37 Handwrittenexpo 67, montreal, robin boyd, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1967
Robin Boyd was appointed Exhibits Architect for the Australian Pavilion at Expo ‘67 in Montreal. The garden outside the pavilion featured a sculptural pool, a coral display, animal pool, a pit for kangaroos and Eucalypts and other native plants. The indoor exhibits covered aspects of Australian art and culture, architecture, industrial design and scientific innovation, such as the Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Power Scheme, the Parkes radio telescope, the design of Canberra, and the Australian way of life.Colour slide in a mount. Japanese Pavilion, Expo '67, Montreal, Canada. (Architect: Yoshinobu Ashihara)Made in Australia / 3 / MAY 67M6 / 36 (Handwritten)expo 67, montreal, robin boyd, slide -
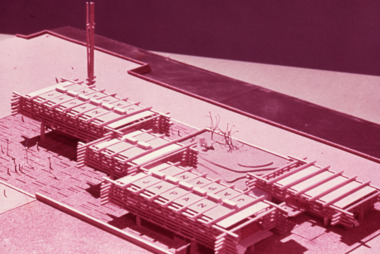 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Commercial, 1967
Robin Boyd was appointed Exhibits Architect for the Australian Pavilion at Expo ‘67 in Montreal. The garden outside the pavilion featured a sculptural pool, a coral display, animal pool, a pit for kangaroos and Eucalypts and other native plants. The indoor exhibits covered aspects of Australian art and culture, architecture, industrial design and scientific innovation, such as the Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Power Scheme, the Parkes radio telescope, the design of Canberra, and the Australian way of life.Colour slide in a mount. Model, Japanese Pavilion, Expo '67 Montreal. (Architect: Yoshinobu Ashihara.)Expo 67 Montreal Canada / Japan / April 28 - October 27 / Encircled 13 (Handwritten)expo 67, montreal, robin boyd, slide -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1967
Robin Boyd was appointed Exhibits Architect for the Australian Pavilion at Expo ‘67 in Montreal. The garden outside the pavilion featured a sculptural pool, a coral display, animal pool, a pit for kangaroos and Eucalypts and other native plants. The indoor exhibits covered aspects of Australian art and culture, architecture, industrial design and scientific innovation, such as the Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Power Scheme, the Parkes radio telescope, the design of Canberra, and the Australian way of life.Colour slide in a mount. USSR Pavilion, Expo '70 Osaka, JapanMade in Australia / 35 / MAY 67M6expo 67, montreal, robin boyd, slide -
 RMIT Design Archives
RMIT Design ArchivesDiazotypes, Robin Boyd's Sketch for combined project 60-64 Clarendon St + corner site, 1968
Robin Boyd’s unbuilt scheme for two residential towers for Carnich Pty Ltd in East Melbourne is one of his most striking late projects – remarkable for its daring scale, its indebtedness to the megastructural polemics of Paul Rudolph and Japanese Metabolism, and its prescience – a high-rise apartment building now sits on the same site. The drawing is spectacular: trays of space are held aloft on angled concrete props that branch off trunk-like vertical slabs. With balconies and spandrels highlighted in white, the scheme’s dynamism echoes El Lissitzky’s mad Wolkenbugel (‘Skyhooks’) while also signalling a tragic last hurrah before Boyd’s 1971 death. Philip GoadIncludes sketch of two structures and surrounding flora.Inscribed upper left of recto, "ROBIN BOYD'S SKETCH FOR / COMBINED PROJECT 60-64 / CLARENDON ST. + CORNER SITE"architecture, mid-century modern, emigre, rmit design archives -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, The Architect's Role in the Community
Appears to be a handwritten speech where Boyd discusses the architect's role in the community and describes architecture as "getting bigger". Boyd describes the shift in architect's thinking as moving away from the individual building to the city or the community. He argues that architecture inherently affects our lives if we live in ugliness, or in attractive surroundings and that the architect is responsible as moral and artistic leaders of the built environment.Handwritten (pencil), quarto, 1 pageNumbered paragraphs. Underlined phrases. Circles in margin.w.churchill, buckminster fuller, strategic plan for sydney, megastructure, community, park the length of swanston street, japan -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionCeramic - vessel, Woodfired Bulbous Pot by Greg Crowe, c1986
Greg CROWE (1953- ) Born England, arrived Australia 1963 Greg Crowe's intial training was in architecture. In 1980 Greg Crowe established the Hovea Pottery in the hills east of Perth and am constantly firing up new work there 30 years on.In 2008 Greg Crowe undertook a McKnight Residency for Ceramic Artists at the Northern Clay Center, Minnesota, U.S.A., and has demonstrated and exhibited elsewhere in the U.S.A. and Canada, Japan, France, Denmark, Ireland and Singapore. In 1985 he built a wood-fired salt kiln at Hovea with Fergus Stewart, and has specialised in wood-firing and salt-glazing since then, In 1992 he worked with wood firer Sven Bayer in Devon, UK. In 1996-1998 he built an anagama kiln in the south-west of Western Australia. y Texture and the unique, plastic responsive nature of claygre to stretching has been of great interest to Greg Crowe. Greg Crow signs his work with an impressed 'GC'. Thrown bulbous woodfired pot.greg crowe, ceramics, gippsland campus, jan feder memorial ceramics collection, hovea pottery, woodfire 86 -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionBook, Geoff Hocking, Australian Houses of the Twenties & Thirties, 1993
Australian domestic architecture of the period between the two world wars is a fascinating and complex subject. Our preconceived notions are based on the more obvious styles and impressions, so that visions of bungalows set row upon row spring to mind quickly. Influences in the designs of Australian houses of the 1920s and 1930s were extraordinarily diverse. Apart from their obvious origins, they can be traced to India, Japan, Switzerland, Holland, Germany, Italy, Spain, Mexico and even the American backwoods. Australian architects travelled to England, Europe and North America bringing back ideas and influences.Includes: index, bibliography. Australian domestic architecture of the period between the two world wars is a fascinating and complex subject. Our preconceived notions are based on the more obvious styles and impressions, so that visions of bungalows set row upon row spring to mind quickly. Influences in the designs of Australian houses of the 1920s and 1930s were extraordinarily diverse. Apart from their obvious origins, they can be traced to India, Japan, Switzerland, Holland, Germany, Italy, Spain, Mexico and even the American backwoods. Australian architects travelled to England, Europe and North America bringing back ideas and influences.Front page: Sue Barnettarchitecture, (mr) peter cuffley, dwellings, interior decoration, 1919 - 1929, 1930 - 1939
