Showing 72 items
matching featherston
-
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Cane, c. 1952
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Unknown
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Unknown, 2 pieces, 1939-1950
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Shields (pair of curtains), 1965
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Periwinkle
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Ararat Gallery TAMA
Ararat Gallery TAMATextile, Frances Burke, Fabric piece, framed
Frances Burke: Designer of Modern Textiles Australia’s most influential and celebrated textile designer of the mid-20th century, Frances Burke (1904-1994), employed Australian native flora, garden flowers, marine subjects, Indigenous culture and increasingly, abstract motifs in her stunning modern fabrics. A confident, determined designer and businesswoman; Burke made the shift from fine art to design in 1937. While she began by designing dress fabrics for Melbourne’s fashionable Georges Department store, printing them on linen using lino blocks, she was an early adopter of the screen-printing process and during the war years began printing on cotton. Burke’s furnishing fabrics took their place in influential modern buildings Australia-wide through collaborations with leading architects and interior designers. They included Robin Boyd’s 1949 House of Tomorrow, Roy Grounds’ Quamby flats, Guilford Bell’s Royal Hayman Island Resort for Ansett Airlines, and Yuncken, Freeman Brothers, Griffiths and Simpson’s Canberra Civic Centre Theatre. In the post-war period, Burke made regular trips to the United States and Europe, on her return advising homeowners and manufacturers on the latest trends in products, colours and home design in lectures and interviews. At New Design her fabric showroom and interior design consultancy Burke introduced furniture by emerging designers Clement Meadmore and Grant Featherston in the early 1950s and presented local and imported homewares, mostly from the United States. She was enthusiastic about the convenient and comfortable lifestyle experienced by ordinary American women. Her fabrics and advice were regularly featured in Australian Home Beautiful, Australian House and Garden and the newspapers of the day. Some of Burke’s designs had remarkable longevity. Tiger Stripe (1938) for example, continued to be produced in a wide range of colours until 1970 and Crete (1946) remained a popular choice for interiors into the 1960s. Drawing from a rich variety of sources including Indigenous culture in Goanna (c.1954) and Pacific Island tapa cloth designs in Bird and Tree (1940), Burke also looked to Japan in designs such as Plum Blossom (1948) and Zen (1965). She loved exploring the potential of native flora, seen in designs including Waratah (1955) and Flannel Flower (1955), while garden flowers were the source for many other designs including Belladonna (1940), Periwinkle (n.d.) and Rose (1947). Burke’s clever interplay of a single striking printed colour with lively gestural lines revealing the white base fabric, gave her designs a vibrancy that characterised the optimistic post-war era. This can be seen in Burke’s fabrics for Hayman Island including Angel Fish and Seapiece (both 1949) which expressed the freshness and excitement of the luxurious new tropical resort and led to further commissions. Burke’s three decades in business (1937-1970) were an unparalleled success in the story of Australian design. Her fabrics have been collected by the NGA, the Powerhouse Museum, NGV, RMIT Design Archives and Sydney Living Museums in addition to Ararat Gallery TAMA. Written by Nanette Carter and Robyn Oswald-Jacobs. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LA TROBE UNIVERSITY BENDIGO COLLECTION: BENDIGO TEACHERS' COLLEGE PRE GRADUATION LUNCHEON 1968
A white document titled Bendigo Teachers' College. Pre Graduation Luncheon. 11th December, 1968. Below the title is a copy of the Menu being offered and an outline of the Program: Chairman - Mr. F. Courtis. Grace - Mr. Rob Davis. Welcome - Mr. F. Courtis. Loyal Toast and Graduation cake - Miss Lorraine Silke and Mr. Rob Davis. Principal - Mr. J. M. Hill. Guest Speaker Mr. J. Witney. Also included Mrs. H. Chatfield and Miss Lorraine Silke. On the back of the card is a list of the Students of 1966 - 1968. Trained Infant Teacher's Certificate: Linda Boxall, Carole A. Campbell, Maureen J. Carter, Alice M. Chiswell, Robyn J. Clemson, Lynn F. Dewhurst, Rosslyn D. Doble, Elizabeth J. Duvall, Nola L. Flynn, Dawn E. Freemantle, Dawn E. Gray, Louise Hadfield, Laurel Y. Harrison, Beth A. Harrop, Jennifer N. Hildebrand, Merren J. Hurlston, Helen M. Jasper, Glenise F. King, Rosalie D. King, Wendy J. Lanyon, Anne T. Luddington, Bernadette M. Moore, Judith M. Olsen, Cheryl D. Peace, Janet E. Pollock, Glenda J. Ritchie, Sandra F. Ross, Patricia Scott, Lorraine M. Silke, Kaye E. Speers and Robyn M. Walker. Students of 1967 - 1968. Trained Primary Teacher's Certificate: Garry D. Aitchison, David C. Allsop, Susan M. Blacket, Leonie J. Bock, Coral M. Brown, Glenys M. Brown, Helen E. Campbell, Merril A. Campbell, Dianne J. Cheong, Roslyn O. Chisholm, Lloyd R. Christopher, Therese A. Curran, Tanyth M. Dainton, Robert J. Davis, Elaine Duncanson, Janice Eddy, Joyce P. Evans, Kerrie F. Featherston, Heather F. Fehring, M. Selby Fidler, E. R. Lia Filisone, Lindsay J. Fisher, Jennifer K. Goode, Kaye D. Gribben, Patricia J. Grigg, Susan A. Haines, Rhonda M. Hall, Mary J. Hallinan, Raymond C. Harvey, Neil J. Harrington, Robin C. Hill, Gayle L. Hinks, Carol A. Hitchens, Aileen M. Hooley, Susan M. Hunt, J. Maree Hutchins, Rhonda E. Jobling, Cherrill J. Johnson, Roslyn M. Jordan, Leonard J. Jude, Mary Kappadais, James C. Kennedy, Cheryl A. Little, Helen M. Lynas, Brian D. McDonald, Elaine T. Mace, Patricia Mackin, Christine E. Maddern, Michael J. Maher, Janet F. Markey, Averil N. Miles, Helen A. Moait, Kenneth D. Molyneux, Edna M. Morrison, Jillian M. Morrison, Noelene E. Morrison, Marilyn F. Nadenbousch, Christine D. Napier, Sandra Nesbit, Maxine J. Nicolson, Jane L. Nisbet, Jeanette M. Norman, Shane J. O'Brien, Jillian R. Ogden, John G. Pease, Pauline E. Peck, Peter C. Powles, Denise M. Quinn, Georgia A. Radcliffe, John Reid, Kaye Retallick, Glenice W. Rice, Kirtis R. Richards, Judith H. Richards, Pamela M. Schroeter, Marjorie R. Shaw, Christopher F. Sharpley,Beverly L. Smith, M. Anne Stuchbery, Heather Sutherland, Elaine R. Sutton, Ian H. Taylor, Julie A. Thirwell, Margaret A. Thomas, Jennifer R. Thorne, Faye E. Tonkin, Rosemary D. Turner, Robert R. Walsh, Helen J. Watt, Glenda K. Wilson and Eugeniusz Zolnieczyk.bendigo, education, bendigo teachers' college, la trobe university bendigo collection, collection, bendigo teachers' college, bendigo, education, teaching, teachers, students, menu, graduation luncheon, lunceon, tertiary education, graduates, graduands, graduation, bendigo teachers' college staff, bendigo teachers' college students -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncNewspaper - Folder, A Look at Local Government, July 27, 1976
Supplement to Diamond Valley News, Tuesday, July 27, 1976. Includes photos, Statement by the Shire President, Profiles of Councilors, articles and information on community services. Folder 70 from Harry Gilham Collection. 8 pageseltham living and learning centre, don maling, bill hale, peter graham, allan horsley, robert marshall, graham bride, frank maas, norm williams, arthur traynor, w. r. featherston, community services, diamond valley news, shire of eltham, 1976 -
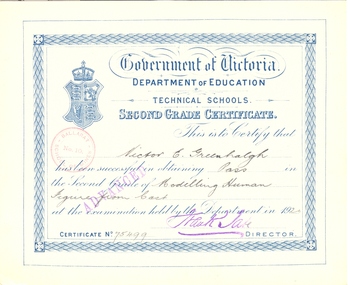 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionCertificate, Education Department, Victoria, Victorian Education Department Certificates, 1916-1928
Ballarat Technical Art School was a division of the Ballarat School of Mines.373 certificates in 2 boxes. Most appear to be related to subjects undertaken at the Ballarat Technical Art School. Director of education stamped signature Frank Tate.Stamped Ballarat School of Mines No.10 Stamped signature "Frank Tate"ann duke, plain needlework, victor greenhalgh, frank tate, ballarat technical art school, arnold j. allen, florence allen, m.a. ansen, dressmaking, modelling human figure from cast, ruby e. allison, drawing fro memory, nancy b. angwin, maude arberry, douglas w. arch, muriel j. arch, eileen bailey, annie c. baker, percy j. baker, general design, light metal work, bessie m. barbery, commerical arithmetic, decorative needlework, bert bernaldo, drawing from a flat example, lorna m. mccallum, brush drawing, stanley g.a. barnett, millinery, mavis g. beacham, theodore k. beckwith, isabel j. bell, kelva e. bellingham, leslie bennett, olive van berkel, elizabeth e. berry, beatrice m. blake, thomas g. blake, catherine m. bowers, nancy w. bowe, clarice v. branagh, harold r. brown, architecture, modelling the head from life, henry bull, light metalwork, ivan d. brown, thyra j. brown, henry j. bull, leila m. burford, embossed leathwork, lettering, drawing fro dressmakers, irene m. burke, josephine m. callery, modelling, mona r. callow, herbert cameron, lillias cameron, william e. carlyon, doris l. carter, ruth e. catt, hiram e. chamberlain, stephen chambers, jack d. chand, jack d. chard, clara v. clegg, beryl e. coad, john c. collins, keith m. collins, robert g. collins, kathleen m. conway, athol b. cornish, ballantyne cottier, douglas s. cotton, lilith s. christmas, perspective, doreen coughlan, ivy g. crompton, phyllis culliver, joan m. cuthbertson, alan r. cutter, john l. daniel, arthur dansey, katherine d'arcy, dorothy f. darling, myrtle f. darling, reginal a. davey, gwladys h. davies, annie dellaca, henry a. deller, ivy f. denovan, joyce doepel, bessie donacaster, charles o. dowie, horace b. dowsing, walter dunstan, mary dwyer, allan r. egglestone, melville g. ellingsen, hugh o. elliott, beryl r. ellis, cecil f. engish, allan e. evans, matson l. eves, olive j. fairlie, robert j. falla, mavis felstead, lena featherston, albert c. ferguson, alma ferguson, hilda m. ferguson, john f. ferguson, beatrice m. field, clarice f. fisher, philip h. fleischer, building construction, olive p. francis, agnes fraser, essie gale, gilbert foster, pearle fricke, effie gascoigne, enid m. gates, clarice gear, james a. geary, sylvia f. greenhalgh, evelyn f. geddes, thomas j. gibson, wavie b. gilbert, edna m. gilmer, nancy govan, eula h. gower, doris e. gray, lesley j. gower, henry n. graham, victor e. greenhalgh, melva e. gribble, human anatomy, roy k. griggs, jack gullan, robert gullan, alma m. gunn, dorothy j. hallan, lucy hamilton, james hammer, dorothy e. hamond, christopher j. hanlon, catherin hardess, lily haymes, gladys hedges, irene h. hewitt, john hill, victor j. hill, olive hillings, john a. hobill, frances k. holmes, gertrude m. hopkins, alice horan, marjorie hudson, linda m. hughes, lydia hughes, winifred humphreys, commercial english, agnes a. humphries, colin hunt, kathleen hutchinson, francis n. king, jean king, hilda knox, john kopke, isabel a. kopke, hazel jackson, freda jacobi, agnes james, william r. james, alexander johnson, edward j. jones, eleanor w.h. jones, nellie kau, thomas kean, francis kelly, roy k. kelly, thomas g. kierce, theo e. leonard, esther f. leviston, bessie lockett, norman h. long, ena mackay, gwenda e. mann, robert v. maddison, herbert w. malin, dorothy m. marriott, john c. mcarthur, james p. mcculloch, doris mcdougall, cyril mcgibbony, thelma mcgibbony, jean mcgregor, kenneth mciver, constance m. mckenzie, elsie j. mckissock, alexander k.mcleod, grace b. mclean, john f.w. mclean, rebecca mcphan, vera meeny, edna merritt, dougald miller, florence h. mingst, agnes m. monteith, doreen j. montgomery, jean e. montgomery, robert w.p. montgomery, margaret b. moore, harry e. morrish, james mow, gwendoline r. neagle, gerald r. newson, robert j. nicol, helen f. nicholl, george m. norton, edward s. oliver, mavis e. oliver, hector h, osborne, henry parker, norma e. parr, doris m. patterson, elsie pearce, celia pearlman, leslie pearlman, edna pearson, william j. perriman, eulalie perry, ernest b. pinney, charles e. peverill, clarence r. pittock, raymond b. pitts, phyllis polson, cynthia b. power, bessie puzey, john m. punshon, evelyn a.v. ramsay, robert i ramsay, william a. rattray, drawing for builders and artisans, george h. reed, fred reeves, mavis i. regelhuth, george r. renkin, annie e. reynolds, lizzie rice, eileen l. richards, henry c. riegelhuth, gladys m. riley, charles a. rimmington, amy robson, ernest w. robson, florence a. rogers, dorothy rppney, kathleen rooney, hugh n. ross, stella m. rowe, agnes w. ryan, rosaling e. sage, cora sandberg, eric c. sanders, douglas f. scott, sylvia e. selkirk, dorine a. shearer, gladys sheldon, emily e. simper, veri slattery, florence c. smith, hilda m. spencer, rose spiers, mopna g. spiller, alma m. stapleton, joyce w. stark, marcus m. stone, commercial correspondence, beatrice m. stuart, ena v. sullivan, margaret a. sydes, rita tainsh, norman b. tamlyn, arthur w. thane, alma m. thomas, david e. thomas, william h. thompson, william m. thomas, edgatr j.t. tippett, sidnet tippett, gladys tongway, mavis toop, hugh d. trainor, annie e. treloar, john h. treloar, eilleen trumain, linda f. treewk, percival a. trompf, percy trompf, jean tunbridge, ruth e. tunbridge, allan j. twaits, irene m. utting, elizabeth van beek, william a. wade, agnes a. walker, james a. walker, vera v. aller, john walsh, marjorie walters, rex warrillow, edith watson, bernice e. webb, constance i weeks, ina m. westcott, pearl whan, violet wheeler, myrtle d. whitfield, annie whitl, richard l. whitla, charles f. whitla, grace a. wilcock, murray a. wilkie, andrew w. william, arthur williams, baden p. williams, david d. williams, grace f. williams, maude h. williams, mavis m. williams, james williamson, ivy wilson, hector g wilson, frederick w.r. wilson, david s. wood -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyBook - Receipts, Abel Tasman, c. 1989
Carbon Copy book of service to shipping receipts, Abel Tasman, June - September, 1989"12" Handwritten on front covermelbourne harbor trust - port of melbourne authority, piers and wharves - station pier, hmas warrnambool, ray c mcgillin, j ryan, l featherston, abel tasman, hmas bendigo, hmas canberra, j flaherty, a johnson, b revell, j oldani, g pearce, t mallia, g webb, w hughes, g krekos, a phillips, s kostakakis, m lucovic, i koster, j parriera, r costello, k ranginui, s gallagher, j bitmead, f aquilina, h l philistin, g rhodes, v camilleri, w hatty, w thompson, j files, a jukic, s aquilina, j aquilina, w hamilton, g miller, r lowerson, j mantzis, a albisi, b bell, e molnar, j cull, j douglass, f konkol, g rembelos, a arostopoulos, m vuk, j brojba, k nedelkovsk, v de cunto, t phelivianis, i borg, r wilson, j benstead, j domanski -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Script, Robin Boyd, University of the Air. Design in Australia 5. Architecture, 1964
Robin Boyd was involved in creating several TV series for the ABC University of the Air. 'Design in Australia' was an eight part series. (Items D184-D193 contain all the manuscripts except part six titled 'Communications'.) In Part 5, Boyd identifies three styles of interior decoration in Australia. The first, Exhibit A is directly influenced by the fashions of Paris, London and New York and does not integrate the interior with the exterior. Exhibit B is the Australian architectural style of the 1960s. Exhibit C is characterised by practical, cheerful and easy to clean up interior fittings based on colourful plastics. Boyd refers to this style as "Australian pop art". He continues by explaining why Exhibit C came to be the preferred Australian style over Exhibit B. He suggests that the Australian public is ill-informed and misguided, ultimately concluding that Australian interior design reflects the public's lack of taste. (Same content as item D193, differing side notes on left side of pages)This is a draft script for the ABC television program 'University of the Air', subtitled 'Design in Australia', broadcast in 1965.Typewritten (c copy), foolscap, 15 pages (compared to D193, 11 pages) (Two copies)One copy has crisper letters typed over on pages 1 and 5.university of the air, design in australia, australian style, interior decoration in australia, frederick ward, lester bunbury, frances burke, grant featherston, modernage fabrics, manuscript -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Script, Robin Boyd, University of the Air. Design in Australia. 5. Interiors. Working Script, 24.11.1964
Robin Boyd was involved in creating several TV series for the ABC University of the Air. 'Design in Australia' was an eight part series. (Items D184-D193 contain all the manuscripts except part six titled 'Communications'.) In Part 5, Boyd identifies three styles of interior decoration in Australia. The first, Exhibit A, is directly influenced by the fashions of Paris, London and New York and does not integrate the interior with the exterior. Exhibit B is the Australian architectural style of the 1960s. Exhibit C is characterised by practical, cheerful and easy to clean up interior fittings based on colourful plastics. Boyd refers to this style as "Australian pop art". He continues by explaining why Exhibit C came to be the preferred Australian style over Exhibit B. He suggests that the Australian public is ill-informed and misguided, ultimately concluding that Australian interior design reflects the public's lack of taste. (Same content as item D188, differing side notes on left side of pages)This is a script for the ABC television program 'University of the Air', subtitled 'Design in Australia', broadcast in 1965. Item D188 is the draft version.Typewritten, foolscap, 11 pages, (compared to D188, 15 pages)university of the air, design in australia, australian style, interior decoration in australia, frederick ward, lester bunbury, frances burke, grant featherston, modernage fabrics, manuscript, ohm2022, ohm2022_30
