Showing 166 items matching "anaesthesia"
-
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPhotograph
The Lidwill machine was designed by Mark Lidwill in 1913, for the purpose of mechanical or insufflation anaesthesia. It was manufactured by Elliott Bros. of Sydney.Colour photograph of a Lidwill anaesthetic machine sitting on carpet. A circular metal ether vaporiser sits on a brown wooden base, with brown tubes connecting to a trap bottle and metal valves, and a brown tube connected to the valve is coiled on the floor.anaesthetic equipment, lidwill anaesthetic machine, mark lidwill, ether vaporiser, elliott bros sydney -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - De Ford Somniform Inhaler, E. De Trey & Sons Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
The De Ford Inhaler was introduced in 1913 and was designed to allow anaesthesia to continue through the nose while dental surgery was happening.This inhaler is composed of metal and rubber. The oral mask and rubber covered nasal mask are connected to a curved rubber covered support that was placed on the patient's forehead to hold the inhaler in place. The gas was administered via a long tube; the terminus designed to allow for the placement of a vial containing the anaesthetic drug and a rebreather bag mount. Inscribed on the back of the mouth inhaler: 'Dr De Ford's Universal Inhaler for Somniform Nitrous Oxide etc. E. De Trey & Sons Phila. PA U.S. Pat. Pending.'anesthesia, dentistry, somniform, surgery, medical instrument, de ford, 1913, e de trey and sons, vial, rebreathr bag mount, inhaler -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Cylinder, Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide has been used for anaesthesia in dentistry since December 1844, where Horace Wells made the first 12–15 dental operations with the gas in Hartford. Its debut as a generally accepted method, however, came in 1863, when Gardner Quincy Colton introduced it more broadly at all the Colton Dental Association clinics, that he founded in New Haven and New York City. Hospitals administer nitrous oxide as one of the anaesthetic drugs delivered by anaesthetic machines. Nitrous oxide is a weak general anaesthetic, and so is generally not used alone in general anaesthesia. In general anaesthesia it is used as a carrier gas with oxygen for more powerful general anaesthetic drugs.Medium size empty blue coloured cylinder with rounded base and painted white neck once containing Nitrous Oxide. A large blue on white diamond shaped label is adhered onto the main cylinder body.Printed on manufacturer's label: 'CIG [logo] / [blank weights table] / DRY / NITROUS OXIDE / C.I.G. (Victoria) PTY. LTD. / 50 LA TROBE STREET, MELBOURNE C3 / Telephones: FJ 6681 / FJ 4164 / USE NO OIL / OR GREASE'nitrous oxide, dental anaesthesia, dental anesthesia, gardner quincy colton, colton dental association -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Magill's Endobroncheal Tube
This endobronchial tube was invented by Sir Ivan Magill. It can be identified as pre 1948, as from that time on the wire spiral was eliminated from the body of the tubes. Sir Ivan Magill is famous for his involvement in modern anaesthesia. He worked closely alongside plastic surgeon Harold Gillies in the treatment of facial injuries sustained in World War 1. He was responsible for many items of anaesthetic equipment, but most particularly the single-tube technique of endotracheal anaesthesia.Tightly wound wire spiral tube with metal 'T' nozzle at the opposite end.magill, endotracheal, tube -
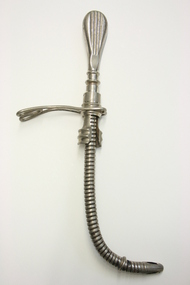 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Tube, Endotracheal, Kuhn, Circa 1900
The evolution of endotracheal intubation for anaesthesia was a slow process. Franz Kuhn (1806-1929), a head and neck surgeon working in Kassel, Germany, between 1902 and 1911, is said to have done more than any other to obtain general recognition for endotracheal anaesthesia. Kuhn's tube, is a flexible metal one inserted on a stilette which was then withdrawn. The tube was then secured with an elastic neck strap and connected by a rubber tube to a Trendelenburg cone. The glottis was packed with oiled gauze. Metal spiral tube with elaborate handle at one end and rounded at the other. There is a metal clasp at the base of the handle which all forms part of the endotracheal tube. Inside the tube is a curved metal piece that functions as an introducer.kuhn, endotracheal, airway, intubation -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryDomestic object - Wine coaster, MAPPIN & WEBB, 1985
In February 1984, Dean WM Crosby of ANZCA, admitted Dr. William Derek Wylie to the Honorary Fellowship of the Faculty of Anaesthetists of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons. Derek Wylie is one of the best known British Anaethetists and during his career devoted much of his attention to medical negligence and its prevention. He lectured and wrote extensively and is noted as the co-author of one of the most widely read textbooks on anaesthesia, 'A Practice of Anaesthesia', which was translated into several languages.Sterling silver wine coaster with ribbed pattern on top border and turned wooden base.With gratitude DEREK WYLIE HON. FFARACS, 1984 Engraved on base: MAPPIN & WEBB LTD. Hallmarks [Makers mark/ image of lion passant/ image of lion head / cursive script L]wylie, derek, mappin & webb -
 Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and Archives
Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and ArchivesTool - Schimmelbusch anaesthetic mask, Mid 20th Century
This anaesthetic mask has a screw missing from the right hand side. Made of stainless steel with light tarnish. mask, surgery, anaesthesia -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - C.I.G. Regulator Type M, sectioned, Commonwealth Industrial Gases Ltd, c. 1960
The regulator was sectioned by I. Philpott in 1962.The regulator, designed to protect anaesthetic machines against sudden changes in pressure, consists of two main, rounded bodies, joined by a short connection. The lower section consists of a valve and a nut on the end that can be adjusted to provide a secondary pressure range. The upper section shows the gauge, which has had part of its face removed to show the inner workings. The valve on the reverse side has also been sectioned.anaesthesia, gas, pressure -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - McKesson Nargraf Machine, McKesson Appliance Co, c. 1930
The McKesson Nargraf machine is affixed to a four-legged metal stand with castors. The head of the machine has two reduced pressure gauges on top: one each for oxygen and nitrous oxide. Below each pressure gauge is a cylindrical drum, where the green-painted faces are directed outwards. There is a pressure control valve with a dial on top of the machine between the two pressure gauges, and a large mixing valve in the centre of the machine head that regulates the proportions of oxygen and nitrous oxide. In front of the mixing valve is a glass cylinder with fabric threads hanging down from the top surface inside.anaesthesia, oxygen, nitrous oxide -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Cylinder top and valve
The top part of a metal gas cylinder, including the shoulder, neck, and attached brass valve. The cylinder has been painted blue with a section painted siler, and the metal shows effects of rusting. A series of numbers indicating former capacities are pressed into the shoulder and neck of the cylinder. Stamped into valve. "COXETER/LONDON"gas, anaesthesia, valve -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Amplon cyclopropane cylinder, sectioned
The narrow, silver metal cylinder, known as an "amplon", once was used to contain cyclopropane, a potent anaesthetic agent. The cylinder has been sectioned at the neck and shoulder to show part of the cream-coloured exterior and orange walls. The inflow screw section, a narrow opening in the neck, has been painted red.anaesthesia, gas, cyclopropane -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Parrett's Somnoform Inhaler, sectioned, George Alfred James Parrett, c. 1912
Sectioned by Dr. Geoffrey Kaye.A metal inhaler which has been sectioned to reveal the interior, painted in red and blue to indicate direction of air flow. The large, bowl-like opening with metal gauze for attachment of a rebreather bag has been painted red, and the metal mask at the other end has been painted brown. The mask and bag mount meet at a 90-degree angle. inhaler, somnoform, anaesthesia -
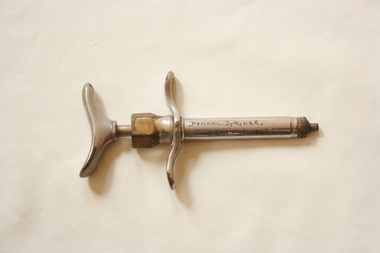 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Dental syringe, sectioned
Sectioned by Dr. Geoffrey Kaye in 1946.Cross-sectioned silver metal dental syringe, which injects at a high pressure of c.10 atmospheres. It was used for raising intradermal wheals, injecting the cranial foramina and infiltrating fibrous tissues. Hand-written inscription on barrel. "DENTAL SYRINGE/G Kaye sect. 1946"anaesthesia, dentistry, dental -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Syringe kit (empty), Chas F Thackray Ltd
Steel box holding syringe parts. There are four hollow metal rods resting in metal clasps attached to a baseboard inside the tin. Some of the rods appear to have metal wire threaded through (purpose unknown). There are a number of clasps attached to the baseboard and top-plate which indicate syringes would have been housed there.Maker's mark stamped into tin: THACKRAY / LEEDShospital, medicine, anaesthesia -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Syringe kit
Stainless steel box containing a baseboard with clips to hold objects in place, a glass syringe with metal tip and glass plunger, along with two stainless steel syringe points.medicine, hospital, anaesthesia -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Ramsay Surgical Limited
One of a range of metal face masks designed to have a cover which helps protect the patient's face.Wire frame mask designed to cover mouth and nose. There is a metal hook on the left hand side protuding from the base of the mask and wire mesh raised from the base with a circle in the middle.facemask, anaesthesia, ramsay surgical -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Syringe
Pale blue cardboard box with white (discoloured) and blue manufacturer's label adhered to front. Inside the box is a cardboard rest holding a glass syringe with metal point and hand grip. The plunger has a metal end, with a rubber or plastic plunge. The manufacturer's label records it as a Record type hypodermic syringe, an Everett Product, and distributed by the Amalgamated Dental Co Ltd of Melbourne and Sydney. Additional information on the label suggests it have been marketed as The Laminex.medicine, anaesthesia, hospital -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMedal - Medal, Dean, Garrard & Co. Goldsmiths & Silversmiths, 1953
Dr Bernard Johnson was elected on December the 6th December 1952 as the Faculty's first honorary Fellow. At the time, Johnson was the Dean of the Faculty of Anaesthetists, Royal College of Surgeons, England. He was invited to visit Australia to receive his award and in 1953 Johnson received his award and brought with him a notable gift being the local Dean's medal of office which was presented on behalf of the Royal College of Surgeons. Johnson had previously met with Ivan Jose and H.J. Daly by providing advice for the establishment of an Australasian Faculty. Johnson is a significant figure as a pioneer into intravenous anaesthesia into Great Britain. He then turned his attention to improving dental anaesthesia. Working with fellow colleagues R R Macintosh and W S McConnell, they established the ‘Mayfair Gas Company’, primarily for dental anaesthesia, but also provided anaesthesia for general surgery during honorary hospital sessions. Johnson participated in the development of the Faculty of Anaesthetists within the Royal College of Surgeons. A founding member of the Board of Faculty, he served as Vice-Dean and then was the second Dean (1952-5), a role which provided a seat on the council of the RCS England. A 9 carat gold [375] oval shaped Dean's Medal of the Faculty of Anaesthetists, Royal Australasian College of Surgeons secured onto a red coloured woven tape by two large gold links. Obverse depicts in coloured enamel secured onto base the RACS coat of arms and crest. Engraved around the sunken diameter are the Faculty and College names. The reverse side has the presentation details inscribed onto a plaque secured onto the main piece with three rivets with hallmarks on both the message plaque and the outer rim. The original red leather box is in poor condition. Printed on the inside silk cover are the maker's marks.[obverse] THE FACULTY OF ANAESTHETISTS / ROYAL AUSTRALASIAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS [reverse] PRESENTED / BY THE DEAN / DR BERNARD JOHNSON / ON BEHALF OF THE BOARD OF / THE FACULTY OF ANAESTHETISTS / OF THE ROYAL COLLEGE OF / SURGEONS OF ENGLAND / AT THE INAUGURAL MEETING / 17th APRIL 1953 [hallmarks on reverse] GAS CO LTD 9 375 R Edinburgh? [black print on inside box cover] By appointment silversmiths to / THE LATE KING / GEORGE VI / THE [goldsmith's logo] / GOLDSMITHS & SILVERSMITHS / COMPANY LTD / CROWN JEWELLERS / incorporating GARRARD & CO / 112 REGENT STREET, LONDON W. I.dean medal, mayfair gas company, rcs england, johnson, bernard -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMedal - Medal, Orton, c. 1986
The Robert Orton Medal is awarded at the discretion of the Council of the College (formerly the Board of the Faculty), the sole criterion being distinguished service to anaesthesia. The award was established by the Faculty of Anaesthetists, Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, in 1967. Robin William Smallwood was Dean of the Faculty of Anaesthetists at the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons from 1986 - 1987. Smallwood died 6 October 1987 after a brief illness. Smallwood completed medicine at the University of Melbourne in 1958 and decided on anaesthesia as a career, attaining his FFARACS in 1964. The Orton Medal was awarded posthumously.Die cast medal mounted in a hard blue velour base, with a wooden gold frame. The medal is placed inside the base, with a red velvet ribbon coming out from underneath, used for removing the medal. Underneath the medal is a two cent coin, stuck to the base. Where the medal rests is covered in red velvet as well.Moulded in relief around perimeter of medal: THE ROBERT ORTON AWARD R.A.C.S. •Handwritten in black ink on reverse: THE ROBERT ORTON MEDAL OF THE FACULTY / OF ANAESTHETISTS, ROYAL AUSTRALASIAN COLLEGE / OF SURGEONS, PRESENTED POSTHUMOUSLY TO / ROBIN WILLIAM SMALLWOOD AT THE R.A.C.S. / G.S.M. MAY 7 1989 •Stamped in black ink on reverse: PORT MELBOURNE PRINTS & FRAMING / 276 BAY ST., PORT MELBOURNE 3207 / TELEPHONE No 646 4000 •Etched around the rim of the medal: ROBIN WILLIAM SMALLWOOD OCTOBER 1987orton, robert, smallwood, robin, distinguished services, faculty of anaesthetists, faculty board -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Vial, Hydrochloride of Cocaine, T Morson & Sons
Cocaine was the first topical anaesthetic. It quickly numbs the area after application. Synthetic drugs provide better local anaesthesia without negative side-effects of cocaine. It is now only used for nasal surgery to prevent bleeding.Small clear glass vial with cork stopper and discoloured [white] manufacturer's label with black printing. There is a small amount of white powder in the vial, presumably hydrochloride of cocaine as per label.Black print on manufacturer's label: Hydrochloride of Cocaine / POISON / T. MORSON & SON / London Englandlocal anaesthetic, hypnotic, cocaine, sedative, morson & son, london -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Electroconvulsive therapy machine
In 1940 doctors started experimenting with curare for use with electric shock therapy. Electric shock therapy regularly caused broken bones, including vertebrae, and all sorts of dislocations. The intensity of convulsions was high and couldn’t be controlled. During the 19th Century curare was unsuccessfully used to treat rabies, tetanus and epilepsy. By 1935, Harold King had isolated tubocurarine, curare’s active ingredient. In 1942, Harold Griffith successfully used standardised curare (Intocostrin) with cyclopropane. Within five years synthesised muscle relaxants were available. Intocostrin, combined with an anaesthetic agent, was a break-through for this treatment.Solid wooden box with three separate sections inside box. First section contains electrical lead for attaching unit to mains power. Second section contains ECT unit and controls. Third sections contains electrical lead ending in plugs for holding in hands. Sections cannot be separated out, they form one unit.Etched on to the face of the internal unit: PROPERTY OF / THE ROYAL WOMEN'S HOSPITAL Label tape affixed to top of the lid: E.C.T. UNIT OP. THEATRES R.W.H.anaesthesia, muscle relaxants, electroconvulsive shock therapy, women -
 Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses League
Ballarat Base Hospital Trained Nurses LeagueEther for Anaesthesia
Round metal containerWriting on Labelether, anaesthesia, metal, container -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Renton circle valve absorber, sectioned, Dr Douglas Renton, 1931
The Renton circle valve absorber has been sectioned to show the valve connection points. The inside is a creamy brown colour, encased in black on the outside. A larger silver metal valve runs through the centre, and to it attaches a flat, reflective silver metal disc as a dial indicating "EXH", "ABS", and "REB", with a black needle. The system includes tubes and valves for oxygen entry, gas expiration, connection to soda lime cannister, rotary valve, and rebreather bag, with a broken, deteriorated segment of the bag still attached.valve, anaesthesia, soda lime, rebreathing -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Wire
Wire framed face mask with a hinged outer layer which can be opened to insert gauze or flannel on which to administer ether. The domed portion is attached by inserting wire edges into slots in the rim, which ends in a handle with a loop at the end.mask, ether, anaesthesia, open method -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Coxeter-Mushin carbon dioxide absorber MK II, sectioned, c. 1945
The Coxeter-Mushin carbon dioxide absorber consists of the main metal body, painted aquamarine, fixed to a stand. The cylindrical silver metal cannister on the left was used to contain ether, while that on the right contained soda lime. The apparatus has been sectioned to show the inside of the two cannisters, the right of which has an arrow drawn inside to indicate the flow of air breathed out by a patient. The front cover over the control dials has also been removed to show the mechanism. The two circular holes above the dials, facing forward, are where two corrugated tubes would attach; both of these tubes attached to the mask of the patient. The round yellow knob in the centre controls the Compensating Valve, which allowed the anaesthetist to raise or lower the rebreathing bag to allow air into the circuit or expel anaesthetic gas.anaesthesia, carbon dioxide, ether, soda lime -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Oxygen cylinder, sectioned, George Barth and Company
The oxygen cylinder is a small, round-based cylinder painted in black that has been sectioned in the shoulder, neck, and valve area for teaching purposes. The sectioned valve area is wooden and has been colour-coded with red and blue paint for teaching purposes. There is a metal screw embedded into the wooden valve. The manufacturer's name, "G. BARTH & CO.", has been stamped into the back of the valve.Inscription on back of valve. "G. BARTH & CO."anaesthesia, oxygen, gas, sectioned -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Guedel's Airway
Oral airways, such as the Guedel, make it easier for patients to be ventilated with manual resuscitators, such as the Porton and the Ambu bag. They depress the tongue and prevent it from falling to the back of the throat where it would obstruct the airway.Black rubber curved tube with metal insert at baseHallmarked on metal: [BRITISHMADE / 3]guedel, anaesthesia, ventilation, medical history -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryAccessory - Facemask
Pear shaped metal mask for attaching to Probyn Williams inhaler. The edge of the facemask is surrounded by a black leather cushion, with a tube on the top. The facemask is metal with a thumb action lever on connector.anaesthesia, inhalational, probyn williams, facemask -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Vaporiser, Penthrane, Cyprane Ltd, c. 1982
This vaporiser has a main cylindrical body with a step up to the dial plate with a small red latch to lock dial in to place.On the front of the body sits a square gauge to indicate the level FULL along with a long rectangular shape.There is an Inlet and outlet valve that sits behind the metal dial.There is a manufacturers plate sitting on top of the dial and the inlet/outlet valve. Inscribed on top plate: KEEP UPRIGHT/ PENTEC 2/ WHEN CHARGED •Inscribed on inlet & oulet valve plate: PENTEC 2/ SERIAL NO 252939/ PATENTS PENDING •MADE IN / ENGLAND BY/ CYPRANE LTD / KEIGHLEY •Metal dial has inscribed: OFF/.2 .5 1 1.5 2 Max •Inscribed on front plate in green writing: USE ONLY/ PENTHRANE/ (METHOXYFLURANE)penthrane, vaporizer, anaesthesia, anaesthetic machine -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Bottle, Chloroform
Chloroform began to be used as an anaesthetic agent in 1847. It was administered by dropping the substance on to a handkerchief held over the patient's nose and mouth.Clear glass bottle with frosted neck and fluted lip with a glass lid that has a frosted stopper and heart shaped handle piece for lifting the lid out of the bottle. The bottle is housed in a black circular cardboard case with red inner lining. Cotton padding has been stuffed in the top of the lid to protect the bottle stopper.Printed in gold leaf on top of case lid: CHLOROFORMchloroform, anaesthesia, surgery, administration
