Showing 78 items
matching criminal record
-
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Administrative Record - Police Report Port Fairy Police Station, 10/07/1912
Hand written supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - saddle stealing, Port Fairy police stationport fairy police station report of criminal offence -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Police Report - Criminal Offence Horse Stealing Port Fairy, Victoria 1914, 27/11/1914
... supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - horse stealing, Port ...Hand written supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - horse stealing, Port Fairy police station, 27 Nov 1914 -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - Larceny 1914, 07/09/1914
Hand written supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - larceny, 8 bags of oats, Port Fairy police station. -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - Cattle stealing 1914, 28/08/1914
Handwritten supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - Cattle stealing (supposed) Casterton police station. -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Police Report - Criminal Offence Larceny Port Fairy, Victoria, 24/09/1913
... supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - larceny in a dwelling ...Hand written supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - larceny in a dwelling, Port Fairy police station -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Police Report - attempted arson, Heywood, 1914, 06/09/1914
Barry was a police officer stationed at Portland 1969 - 71. Stables were to be demolished. he was instructed to clean them out, and take the contents to the tip. He retained these documents and donated them to the Cultural Collection.Hand written supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence -attempted arson, Heywood police stationpolice report, arson, heywood -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Supplementary Police Criminal Offence report - Larceny 1913, 23/04/1913
... record Supplementary Police Criminal Offence report - Larceny ...Port Fairy Police Station recordsHand written , supplementary Police Criminal Offence report - Larceny, Port Fairy Police Station, 23 Apr 1913Front: Hand written - ' Please copy Portland & Heywood' -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Police Report- sheep stealing, Dunkeld, 1912, 04/06/1912
Barry was a police officer stationed at Portland 1969 - 71. Stables were to be demolished. he was instructed to clean them out, and take the contents to the tip. He retained these documents and donated them to the Cultural Collection.Hand written supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - sheep stealing, Dunkeld police station. 2 diagrams of ear notches and black star brandpolice report, theft, livestock theft, sheep stealing, dunkeld -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - Cattle stealing 1915, 01/04/1915
Heywood Police Station records.Hand written supplementary Police Report of Criminal Offence - Cattle stealing, Heywood Police Station, 1st April 1915. -
 Victoria Police Museum
Victoria Police MuseumCriminal records (Squizzy Taylor)
... of convictions, fingerprints for Squizzy Taylor Criminal records (Squizzy ...Police docket (with photograph), record of convictions, fingerprints for Squizzy Taylorsquizzy taylor, leslie taylor, david donoghue, leslie grout, michael mcgee, murder -
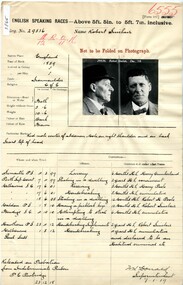 Victoria Police Museum
Victoria Police MuseumPrison record (Robert Sinclair), 23 December 1918
Robert Sinclair, a travelling entertainer, committed a variety of offences including housebreaking, having a skeleton/picklock key in his possession, being an habitual criminal. He had several aliases. Prison record for Robert Sinclair, prisoner registered number 29536, giving details of the prisoner, his crimes and the dates and places of his trials.robert sinclair, english speaking prisoner, larceny, housebreaking, stealing -
 Victoria Police Museum
Victoria Police MuseumPrison record (Edward Greenwood), 25 January 1919
In June 1915 was charged with stealing and unlawfully on premises. He was deemed an habitual criminal with prior offenses including obscene language, offensive behaviour, theft of money, larceny of eight bottles of beer. In September 1916 he was charged with forgery and uttering. His criminal career began in 1907 at the age of 22 years of age.Prison record for Edward Greenwood, prisoner registered number 32050, giving details of the prisoner, his crimes and the dates and places of his trials.edward greenwood, english speaking prisoner, obscene language, offensive behaviour, perjury, forgery, uttering -
 Victoria Police Museum
Victoria Police MuseumPrison record (Thomas Brooks), 14 June 1920
Thomas Brooks's had a long criminal career beginning in 1889 under various aliases. His crimes included forgery, imposition, horse stealing, and housebreaking (for which he received a sentence of 10 years). Most of his crimes were committed whilst under the influence of drink.Prison record for Thomas Brooks, prisoner registered number 22986, giving details of the prisoner, his crimes and the dates and places of his trials.english speaking prisoner, thomas brooks, horse stealing, imposition, housebreaking -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Touching the Full Redemption of Mankind by the Death and Blood of Christ Jesus (human skin cover), 1599
Anthropodermic Bibliopegy is the name given to the use of human leather to bind books. The name stems from the combination of the Greek root words, human (Anthropos), skin (derma), book (biblion), and fasten (pegia). The practice of creating anthropodermic books was popular throughout the 17th and 18th centuries. Most commonly, anthropodermic books are medical tomes, with the human leather taken from medical cadavers. Others were produced after criminal trials, with the criminal’s skin used to enclose the record of their own death sentences, creating a form of punishment that would surpass death. Other anthropodermic books contain poems or are religious texts. This book was written and printed in 1599 but most probably was rebound later when creation of anthropodermic books became more predominant. The book is a small tome of a religious nature containing the work of Bishop Thomas Bilson, who in a puritanical voice states that the primary argument articulated in this book is that “the metaphorical Calvinist interpretation of Hell as an exclusion from God was accurate then Christ's descent into hell after his crucifixion must refer to an actual existent hell as Christ was neither subject to sin nor able to be separated from the Divine.” The unusual cover of the book has led to many questions, the main being whether the book is covered with human skin. It was confirmed as such in 2014 with DNA testing undertaken by honours student Talanna Buckley at Federation University finding an 100% match to human DNA on the outside cover of the book. This is one of only two confirmed anthropodermic books in Australia, the other is housed at the National Library of Australia. Other forms of testing the leather of books have been found to be more accurate than DNA testing. For example, before DNA testing or PMF (Peptide Mass Fingerprinting) are undertaken many books have been identified as made from human skin through the close examination of the skins patterning. Hair follicles are the focus of the examination as certain patterns and sizes lend themselves to being human. However, many of these books have been proven to not be bound in human skin, the same can be said of books with inscriptions claiming them as anthropodermic. Peptide Mass Fingerprinting (PMF) testing has been found to be the most reliable way of confirming a leather bindings origin. This process involves the sampling of collagen-based materials, cutting the protein to gain specific amino acid combinations which form individual peptide sequences. Each mammal has an individual amino acid sequence in its collagen therefore its peptide mass combination is unique. This form of test can provide a more accurate outcome as collagen will be preserved for longer after the tanning process and will not be damaged in the same way DNA can be by the tanning process. DNA testing can also provide false positives as trace DNA from someone touching the book could be amplified and provide the reading instead of that of the leather itself. However, this book was tested with many controls as well as specific decontamination procedures in order to ensure that it was not trace DNA being tested. This book is historically and spiritually significant because it is a rare example of an early printed English Christian religious tract produced in Old English and Latin.. Its association with Thomas Bilson, who oversaw the final printing and publication of the King James Bible, is important. The covering of this book has been tested for human dna. Findings prove the book is covered with human skin, increasing the rarity of the object.420 page book with unusual leather cover. The book is written in Old English with passages in latin. There is a pressed petal between p.68 and 69. The covering of this book is made of human skin. The practice of binding books in human skin, also known as anthropodermic bibliopegy.Inside cover - James Hendy No 17 (Fu)gends Road Palmers Village Westminster. The gift of his mother Mrs Thomas Hendy. Some notes made through text eg p.112, and a passage written on the last page.religion, bible, edward lowe, edward lotos, thomas bilson, anthropodermic bibliopegy, james hendy, full redemption, religious, leather, wilson, winchester, jesus, puritanical, puritans, bungey, bilson, human skin, skin, human skin cover, human skin binding -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Police Report, 14/01/1914
Port Fairy Police Station police report 1914. -
 Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage Collection
Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage CollectionWork on paper - ink and watercolour, Annette Meikle, Karinga, 1977
In 1977, artist Annette Meikle undertook a commission to illustrate a book recording stories of places and people in the Bayside area. It was published in 1978 as Sandringham Sketchbook, with text by Elizabeth Waters. The sketches were intended to record remaining examples of Bayside’s early architecture and environment, as well as reflect newer architectural changes. Meikle went on to donate 22 of these sketches to Bayside City Council in 2003. This inter-war house located at 60 Bluff Road, Black Rock, was built in 1926 for former Scotland Yard and Criminal Investigation Branch detective Horatio Reginald Clarence McWilliams. When McWilliams died it was found that he had taken extreme measures to protect his security. All the windows were nailed shut, a network of burglar alarms ran through the house and a complicated underground air raid shelter had been built in the garden. The security measures were at odds with the name of the house – Karinga or Karinya – an Aboriginal word meaning peaceful, happy home. Later residents of ‘Karinga’ included Senator Don Chipp and his family. The property has since been demolished and apartments have been built on the land.Annette Meikle, Karinga 1977, ink and watercolour, 32 x 23.5 cm. Bayside City Council Art and Heritage Collection. Donated by the artist, 2003annette meikle, sandringham sketchbook, elizabeth waters, black rock, karinga, karinya, horatio reginald clarence mcwilliams, senator don chipp, historic house, bluff road -
 Public Record Office Victoria
Public Record Office VictoriaBrief for the Prosecution, 1854
VA 2825 Attorney-General's Department (previously known as the Law Department)Eureka Stockade:Brief for the Prosecution, Case no.16, Criminal Sessions Melbournetrial -
 Public Record Office Victoria
Public Record Office VictoriaLegal record (item) - Criminal Trial Brief for Harry Bruin and Benjamin Morris
... letters Legal record Criminal Trial Brief for Harry Bruin ...This collection of approximately 20 letters between Melbourne men Ben Morris and Harry Bruin, covering a period of several months in 1919, consists of original letters handwritten by Morris and carbon copies of Bruin’s replies. Love letters between men from this period are extremely rare in an Australian context, and globally. They were seized by police from Bruin’s home in Harcourt Street, Auburn in October 1919. The police were investigating a report that Bruin and Morris were conducting an intimate affair. The relationship came to light when the mother of one of Morris’ friends, having failed in her attempt to blackmail Bruin, went to the police. Blackmail was an ever-present danger to homosexual men at that time. Homosexual sex was against the law and even gossip alone could ruin reputations, careers and social standing. In refusing the demands of his attempted blackmailer, Bruin took an enormous risk. However, Morris and Bruin were lucky that their letters contained no descriptions of sex acts. It was not illegal to express love for a person of the same sex and when the matter came before the court, the police had no choice but to let the matter drop without laying charges. Letters like these are rare as potentially incriminating correspondence between men was usually destroyed by the writers or the recipients, to prevent it falling into the hands of the authorities, blackmailers, or disapproving third parties. These letters survived only because they were seized by the authorities for the purpose of prosecution. Morris and Bruin’s letters are also important because, together with the statements taken from the two men and others involved in the case by police prosecutors, they provide insight into the development of the liaison over an extended period. The emotional letters provide rare evidence of a deep romantic affection between two men in their own words. Quoted from "A History of LGBTIQ+ Victoria in 100 Places and Objects" by Graham Willett, Angela Bailey, Timothy W. Jones and Sarah Rood.
