Showing 226 items
matching museum techniques
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Tatting Shuttle, Aero Needles Group Ltd, Mid to late 20th century
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots.The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century.Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic (as is item 8535.1). The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound (e.g. item 8535.2). The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace. One type of tatting shuttle produced by "Aero" from the 1930's to the late 1960's was an anodized grey coated aluminium shuttle with a sharp pick at one end. In the 1970's it was superseded by the grey plastic "Aero" which has a removeable bobbin which you can put on the end of the shuttle to make thread winding easier and an embedded crochet hook for joining picots. The "Aero" company developed in Redditch, England - a town renowned as a centre for manufacturing needles. Firms run by Henry Milward and Abel Morrall were based in Redditch and by the 18th century Redditch was manufacturing one million sewing needles per year. Abel Morrall Ltd launched the "Aero" brand in 1936 and greatly expanded the firm's product line to include tatting shuttles and knitting needles. The classic plastic "Aero" tatting shuttle was manufactured in England from the early 1970's until the 1990's. These items are significant as examples of easily accessible handiwork tools that enabled women in the 1930s -1960s to be able to decorate and personalize their household linen and clothing.Shuttle no. 8535.1 is a beige, boat shaped plastic shuttle with enclosed ends, small round central indentations on both sides and an enclosed black removeable bobbin. The shuttle has a grooved point at one end to hold a bobbin and a small metal crochet hook at the other end. Shuttle no. 8535.2 is a beige, boat shaped metal shuttle with pointed ends that are open but snug, small round central indentations and two smaller circular markings (on both sides) and two internal posts with cream thread wound around.Shuttle no. 8535.1 - "AERO" / "ENGLAND" Shuttle no. 8535.2 - "AERO' / "ENGLAND" "39c" (written in ball point pen)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, tatting shuttle, aero company, handwork, handwork tool, craft, handcraft, needlework, tatting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Plain Sewing Sampler, 1897
A "Plain Sewing Sampler" or "Darning Sampler" was intended to showcase the wide range of sewing techniques and skills a girl or woman had. These skills might include hand sewing techniques such as darning, patching, hemming, mending, structural sewing (making pleats, inserting gussets, joining fabric with seams) making buttonholes and embroidery. Samplers could also be intended for practicing a particular technique. There were several articles printed in Australian newspapers around 1889 referring to the "Plain Sewing Movement". In 1889 a Melbourne branch of the "London Institute for the Advancement of Plain Needlework" was formed by a group of ladies led by Lady Loch and Lady Clarke with the purpose of teaching "plain needlework' to women and girls. "Plain Sewing" included fundamental stitches and techniques that were essential for practical clothing construction and maintenance. Several years later in 1891, another meeting was held at Clivedon (the residence of Lady Clarke) to look into the possibility of improving the teaching of sewing in the state schools. This meeting was attended by several school inspectors and the committee of "the Melbourne Institute for the Advancement of Plain Needlework". This "Plain Sewing Sampler" was donated from the estate of Susan Henry OAM nee Vedmore (1944 - 2021). Susan's family (Harold and Gladys Vedmore) immigrated to Australia from Wales in 1955 and settled in Warrnambool. Susan was well known in the Warrnambool community for her work supporting children and families across the district - particular those with disabilities, or those who were homeless, unemployed or isolated. Susan was the founding trustee of the "Vedmore Foundation" - a Warrnambool philanthropic trust set up to support a range of charitable and not-for-profit causes by providing grant assistance. In 2021, she was awarded a Medal of the Order of Australia for services to the community. It has not been possible to identify the lady (with the initials L. L.) who made this item in 1897 but it was thought to possibly be a female relation in her maternal (or possibly, paternal) grandmother's family. It has many of the same elements and techniques that were taught by the "Plain Sewing Movement" that originated in England at the end of the nineteenth century.This item is a rare example of the handcraft skills learnt by women and girls in the late 1890's to construct and maintain practical clothing for their families.A cream cotton sampler made from three smaller rectangular shapes, displaying a wide variety of plain sewing techniques including hand stitched seams (french, bound and herringboned), inserted patch, buttonhole, button, gathering, a gusset, frills, pintucks, a placket, cross stitch initials and date (L L and 1897) and decorative embroidery.L L/1897flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, needlework, textiles, plain sewing sampler, darning sampler, handwork, sewing, great ocean road, susan henry oam, vedmore trust, hand sewing, sewing techniques -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Plain Sewing Sampler, 1897
A "Plain Sewing Sampler" or "Darning Sampler" was intended to showcase the wide range of sewing techniques and skills a girl or woman had. These skills might include hand sewing techniques such as darning, patching, hemming, mending, structural sewing (making pleats, inserting gussets, joining fabric with seams) making buttonholes and embroidery. Samplers could also be intended for practicing a particular technique. There were several articles printed in Australian newspapers around 1889 referring to the "Plain Sewing Movement". In 1889 a Melbourne branch of the "London Institute for the Advancement of Plain Needlework" was formed by a group of ladies led by Lady Loch and Lady Clarke with the purpose of teaching "plain needlework' to women and girls. "Plain Sewing" included fundamental stitches and techniques that were essential for practical clothing construction and maintenance. Several years later in 1891, another meeting was held at Clivedon (the residence of Lady Clarke) to look into the possibility of improving the teaching of sewing in the state schools. This meeting was attended by several school inspectors and the committee of "the Melbourne Institute for the Advancement of Plain Needlework". This "Plain Sewing Sampler" was donated from the estate of Susan Henry nee Vedmore (1944 - 2021). Susan's family (Harold and Gladys Vedmore) immigrated to Australia from Wales in 1955 and settled in Warrnambool. Susan was well known in the Warrnambool community for her work supporting children and families across the district - particular those with disabilities, or those who were homeless, unemployed or isolated. Susan was the founding trustee of the "Vedmore Foundation" - a Warrnambool philanthropic trust set up to support a range of charitable and not-for-profit causes by providing grant assistance. In 2021, she was awarded a Medal of the Order of Australia for services to the community. It has not been possible to identify the lady (with the initials L. L.) who made this item in 1897 but it was thought to possibly be a female relation in her maternal (or possibly, paternal) grandmother's family. It has many of the same elements and techniques that were taught by the "Plain Sewing Movement" that originated in England at the end of the nineteenth century.This item is a rare example of the handcraft skills needed by women and girls in the late 1890's to construct and maintain practical clothing for their families.A cream flannel sampler made from three smaller rectangular shapes, displaying a wide variety of plain sewing techniques including hand stitched seams (french, bound and herringboned), darned patches, inserted patches, pleats, buttonholes, buttons, a gusset, pintucks, a placket, cross stitch initials and date (L L and 1897) and decorative embroidery.L.L. / ?? Yr 1897flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, warrnambool, sewing, plain sewing, sewing sampler, plain sewing sampler, darning sampler, hand sewing, textiles, susan henry oam, vedmore foundation, sewing techniques -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Pie funnel, Thomas M Nutbrown, 1932 to 1940
A pie funnel is a hollow ceramic tool that bakers place in the center of pies to prevent bubbling over. They can also be called pie vents, because that hollow core allows steam to escape during baking. Thomas M Nutbrown started manufacturing kitchenware in 1927 from his factory on Walker Street, Blackpool. He registered the company in 1932 and over the following years his company was exporting goods all over the world. His company pioneered many unseen kitchen gadgets and utensils onto the market and had many products patented. Today Nutbrown continues original techniques and craftsmanship to produce kitchenware that give its products a distinctive character.A kitchen item that in the 1930s was a unique addition to any housewives kitchen from a UK company that is still producing these types of products today. Pie Funnel, ceramic white glaze, "Nutbrown" printed on side.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, pie funnel, porcelain pie funnel, baking utensil, cooking equipment, kitchenware, nutbrown pie funnel, nutbrown -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, Ivoryflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
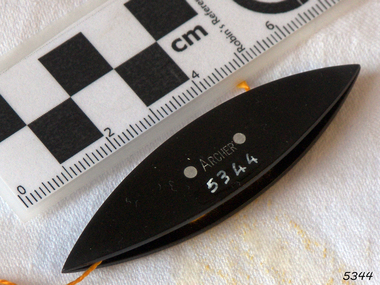 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, Black plastic, "ARCHER" inscribed. "ARCHER" inscribed.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, tortoise-shellflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, ivory, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, black plastic flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Pot
Modern iron cooking ‘ranges’ were being introduced from the late 18th century, however a vast number of people cooked in open fireplaces, well into the 1800s. Generally they were fitted with iron rods suspended above the fire or ‘cranes’ that could be swung in and out for easier and safer access to the pots that hung from them. These cooking systems may seem rudimentary, but a skilled cook knew how to manage pots, pans, cauldrons and pokers and expose them to the right type of heat by positioning them in various parts of the fireplace. They were also very versatile, enabling multiple cooking techniques – boiling, stewing, frying, roasting, toasting – all at the same time, using different types of vessels and utensils. https://blogs.sydneylivingmuseums.com.au/cook/hearth-fire-cookery/This type of item was used extensively over the centuries over open fires. It is still used in camping.Metal cooking pot with handle designed to hang the pot over an open fire.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, kitchenware, cooking, open hearth cookery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Serving Mallet, Unknown
A serving mallet is a tool to worm, parcel and serve a line and is to apply to the standing rigging multi-layered protection against chafe and deterioration. It is a technique not usually used on modern small boats but is found extensively on traditionally-rigged sailing ships. Worming, parcelling and serving —referred to collectively as "service"— is traditionally applied only to traditional twisted rope, either natural fibre or steel wire-rope, not the braided line almost exclusively used on modern vessels today. Parcelling means wrapping a rope line in a spiral fashion with long overlapping strips of thin canvas. This is wound from bottom to top, the edge of the progressing strip slightly overlapping the previous wrap to create a shingled effect, to prevent water from entering. Often the strips of the canvas are either saturated with Stockholm tar as they are applied, or painted with tar after the parcelling is complete, immediately before the process of serving. A serving provides an outer layer of protection and is formed by wrapping twine as tightly as possible around the line, each progressive turn of the twine laid as close as possible against the last, covering the rope completely. Following the rhyme above, it should have course run against the lay of the rope; this alternation helps prevent sideways chafe from opening up the protection. Traditionally hemp "marline" was and still is used for servicing on modern small craft with three-strand nylon "seine twine" often used. A serving board or serving mallet can be used to help get the outer twine as tight as possible. Despite the name (arising from its shape) the serving mallet is not used to hit anything, it forms a kind of guide and tensioning lever for applying the twine to the rope. An optional final stage for the permanent protection of "served" rope is to paint the outer layer of twine with a mixture of tar, varnish and black paint. This needs renewing periodically, and going aloft to paint foot ropes, shrouds, stays, and other served rigging is one of the regular maintenance tasks on many tall ships. The tar or "slush" is a mixture of Stockholm tar, boiled linseed oil, and Japan drier. Many "recipes" for slush exist, but the intent is always to allow a penetrating coat of preservative pine tar that then cures to a harder finish that will not so easily rub off on sails and crew. The term "slush" is also used to describe the grease applied to the masts to lubricate the “parallels” so that the yards can raise and lower freely.A tool used by sailors on board sailing ships as an aid in the preservation of ships rigging ropes by wrapping the rope in tar soaked canvas and covering the canvas by wrapping twine along the length of the rope. An item that is significant in that it tells a story of what sailors working lives were like onboard the early sailing ships and how these early vessels were maintained and sailed. Serving Mallet, used in Worming, Parcelling and Serving of rope - cylindrical handle with grooved wooden section attached. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Crochet Hook, Mid 19th Century
Crochet came from the Old French word crochet, meaning ‘small hook.’ This word comes from Croche. Croche comes from the Germanic word croc. Both mean hook and crochetage, which means a single stitch used to join separate pieces of lace together. People used this term in making French lace in the 1600s and the word crochet describes the hook and the craft. Evidence shows the starting point was the mid-1800s but as early as the late 16th and early 17th century, crocheted braiding was used in clothing and other products. Like on a man’s cape at the Victoria and Albert Museum. Crochet evolved in the early 1700s when stitching material on a tambourine reached Europe after going through India, Persia, North America, Turkey, North Africa and other places around the world. People removed the background fabric used for tambouring. The French named the new technique “crochet in the air.” In the early 1800s, shepherd’s knitting came about, along with the shepherd’s hook. It’s thicker than a modern crochet hook but still with a hooked end. By the mid-1800s, it became known as crochet or slip stitch crochet. In the 60s, the granny square and crocheted home ware appeared and became more popular.A significant domestic item used in crochet or craft work and recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg in the 1970s. For more information regard the wrecking of the Schomberg see note sect this document. The Schomberg has historical significance as one of the first luxurious ships built to bring emigrants to Australia. The collection of recovered artefacts from the Schomberg wreck and held at Flagstaff Hill Museum are significant because of their potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg and its passengers.Crochet hook made from Bovine Bone. It has two sections that screw apart. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg. Nonewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, crochet hook, crocheterage, craft -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tools, large Saw, 2 man, c1900
Early settlers had to clear the land of trees and shrubs to establish and maintain their farms and market gardens. Some settlers worked in the Gippsland region felling timber for transport by bullock wagons to Melbourne. Two-man crosscut saws were primarily important when human power was used. Such a saw would typically be 1 to 4 m (4 to 12 feet) long, and sometimes up to 5 m (16 feet), with a handle at each end. The technique in using a two-man saw involved a sawyer standing at each end and together the sawyers would alternate pulling the saw through the wood. If the kerf -slit- began closing, causing the saw to bind, wedges would be inserted behind the saw blade in order to keep the kerf open.Two-man saws were designed to cut in both directions. Careful tooth design was necessary to clear the sawdust during the cut. This is a typical two-man tree felling saw that was necessary to clear the land when the pioneers were establishing their market gardens and farms in Parish of Moorabbin c1850A long steel blade saw with 2 wood handles c1900tools, saws, axes, early settlers, pioneers, market gardeners, dairy farms, orchards, vineyards, timber mills, bullock wagons, tree felling, timber mills, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, parish of moorabbin, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman stephen, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tools, Blow-torch brass, 20thC
A blowtorch is a fuel-burning tool used for applying flame and heat to various applications, usually metalworking. Early blowlamps used liquid fuel, carried in a refillable reservoir attached to the lamp. Modern blowtorches are mostly gas-fuelled. Their fuel reservoir is disposable or refillable by exchange. The term "blowlamp" usually refers to liquid-fuelled torches still used in the UK. Liquid-fuelled torches are pressurized by a piston hand pump, while gas torches are self-pressurized by the fuel evaporation. In 1882, a new vaporizing technique was developed by C. R. Nyberg in Sweden, and the year after, the production of the Nyberg blow lamp started. It was quickly copied or licensed by many other manufacturers. The US blowlamp was independently developed with a distinctive flared base and was fuelled by gasoline, whereas the European versions used kerosene for safety and low cost.The family of Mr Howcroft were early settlers in Moorabbin ShireA brass blow-torch B.A. HJOP Co. STOCKHOLM SWEDENblowtorch, stockholm sweden, welding, moorabbin, cheltenham, bentleigh, early settlers -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Simpson's cranioclast used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Prior to the 1900s, complicated births, particularly where there was a disproportion between the size of the woman’s pelvis and the foetus’ head, often meant the death of the baby and the mother. Instruments for removing a dead or ailing foetus from within the mother were used to attempt to save the mother’s life. The cranioclast, first invented by Dr. James Simpson in the mid-19th century and later redesigned by others, was used for fetal destruction and removal. Fundamentally a strong pair of forceps, the cranioclast was used to crush the skull, decreasing its diameter. In some cases, this would allow normal uterine contractions to expel the foetus; in others, the physicians would use an obstetrical hook to pull the body out of the mother. Doctors disagreed as to the pelvic diameter that would necessitate this drastic intervention, but generally found that 3 to 3.5 inches was the smallest size through which a living infant could pass. Equally of debate was the pelvic size through which the dead fetus could be extracted. When vaginal extraction was deemed unadvisable, Caesarian section would be performed. As caesarean section became safer and more common with the advent of anaesthetics and antiseptic techniques, the use of cranioclasts and obstetrical hooks diminished. (Museum of Health Care, Kingston) Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Hinged metal tool with bakelite handles at one end and serrated teeth at other end. The instrument is in two sections. The right or upper blade has a black bakelite handle. There are two screws on the inside of the handle, 5.5cm apart. In the centre of the blade is a screw notch in the shape of a small horseshoe. On the inner side of the blade is a depression extending most of the length. The left, or lower, blade also has a black bakelite handle. There are two screws on the inside of the handle approximately 6cm apart. Mobile metal clasps in the shape of an 'S' , with three serrations, is attached to the distal end of the handle, which enables the blades to be opened or closed. destructive instruments -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Portable operating table used by Sir Victor Bonney, Allen & Hanburys, England, c. 1900
This operating table belonged to the famous gynaecological surgeon Dr Victor Bonney and was given to Dr Frank Forster in 1953 by his widow Mrs Annie Bonnie, a distant relative of Forster's. Dr Victor Bonney (1872 - 1953) followed his father into medicine and trained at St Bartholomew's and the Middlesex Hospitals. Writing his obituary in 1953, FW Roques said of Bonney that he "'made three great gifts to surgery. First, he was the pioneer of myomectomy; second, with Berkeley, he extended and perfected Wertheim's operation for carcinoma of the cervix; and third, he devised a fine surgical technique emulated by so many of his pupils. To theatre sisters, labour-ward sisters and young house-surgeons he will always be remembered as the discoverer of 'Bonney's Blue' [antiseptic solution].'" Bonney's utilitarian, portable operating table has a round, worn scrubbed patch showing traces of his famous blue solution.This portable operating table was owned and used by pioneering gynaecological surgeon Sir Victor Bonney in London, U.K. c 1900. Dr Bonney employed two theatre sisters and had two sets of instruments and portable operating tables. This made it possible for Dr Bonney to 'complete three or more operations a day by rotating staff and equipment with a chauffeur driven Lanchester or Rolls Royce', delivering them from one house to the next. The donor of the operating table, the late Dr Frank Forster, was a distant relative of Sir Victor Bonney's widow, Annie Appleyard, formerly of Tasmania. When he visited her in the UK after Bonney's death, she offered the operating table to Dr Forster for the RANZCOG Museum. It was still in a canvas bag in the boot of one of Bonney's cars. Sir Victor Bonney was the pioneer of myomectomy, the surgical procedure for removing uterine fibroids. In collaboration with Berkeley, he extended and perfected Wertheim's operation for carcinoma of the cervix. Bonney was an influential teacher, developing and promoting conservatism of surgical technique (minimal intervention) that has had a lasting influence in modern surgical practice. To theatre-sisters, labour-ward sisters and young house-surgeons he will always be remembered as the discoverer of Bonney's Blue an antiseptic that was characteristically blue.Portable, laminated operating table. Plywood rectangular table with two laminated plywood extensions, a head board, and a foot board. At the foot board are insets of canvas straps to support a patient's ankles. Two detachable stirrup poles, each with a canvas strap attached, fit into two holes at the lower end of the table. The table is supported by two timber trellis cross braces with metal bars, and supported at the centre by a metal rod that allows the table to pivot up and down. Two metal arcs with a locking mechanism fix the table at the desired elevation, allowing a Trendelenburg tilt ( a 45 degree tilt, with the patient's head downwards.) The operating table is demountable for transportation and re-assembly.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Rubin's tubal insufflator apparatus associated with St Vincent's Hospital, c1919
"Potential blockage in the Fallopian tubes was assessed using this apparatus. It was developed by American gynaecologist Isidor Clinton Rubin (1883-1958). It blows carbon dioxide, via a cannula, into the uterus. The ease with which gas escaped through the Fallopian tubes was reflected by pressure changes on an instrument called a manometer. Blockage of the tubes is often due to previous infection or surgery. It is a common cause of infertility. Rubin’s test formed a standard part of infertility investigations for many years. It was gradually replaced by an X-ray technique involving radio-opaque ‘dye’ injected into the uterus." Source: Science Museum Group. Rubin’s apparatus for uterotubal insufflation, New York, United States, 1928. A639503Science Museum Group Collection Online. Accessed 12 June 2024. https://collection.sciencemuseumgroup.org.uk/objects/co96774/rubins-apparatus-for-uterotubal-insufflation-new-york-united-states-1928-tubal-insufflator. There is no manometer to monitor gas pressure on this model so it is either incomplete or a manometer was not available in this possibly early model. This device may be dated c1919, 1920s, or 1930s. 1919 was the year Isidor Clinton Rubin (1883-1958) introduced this apparatus. Rubin's tubal insufflator apparatus. Consists of a large cylindrical glass canister, with three glass nozzles at top with long rubber tubing attached to each. The device is inside a portable plywood box with two door. One surgical steel introducer, and one glass introducer, are also attached to the device. -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1963
The Skylark 4, the final in the Slingsby Skylark series, dates from 1961. The design heralded a trend towards the use of plastics in the construction of gliders. Slingsby incorporated GRP (glass reinforced plastic) panels to achieve a streamlined fuselage nose and cockpit area while retaining the more traditional wood techniques for the rest of the aircraft. Another notable feature was the smooth wing surface that was obtained using a Gaboon ply skin across the ribs. Best glide performance of 1:33 was found to be comparable with the early full GRP glider designs. The Museum’s example (VH-GTB – C/N 1382) was built in 1963 and originally owned by Chuck Bentson of the UK. It was brought to Australia in 1967 by Jeremy Picket-Heaps and flown at various places including Benalla, Cooma and Gundaroo. In 1970 the glider was transferred to the New England Soaring Club. Many flights were made from Armidale and Bellata in Northern New South Wales. On one occasion, the glider was kept aloft for 8 hours 45 minutes and on another the pilot took it around a 500 kilometre triangle in nearly 8 hours. In 1980 it was sold to Ralph (“Feathers”) Crompton and was flown extensively in South Australia until 1988. The final owner before the glider was given to the Museum in 2004 was Ross Dutton of Melbourne. The last recorded flight occurred in 1992. The glider at that point had logged over 2000 hours flying time from about 2000 launches. The airframe is currently being restored to flying condition. Technically this aircraft represents the state of the art at the stage that sailplane design was changing from traditional wood construction to composites (GRP) The Slingsby Skylark 4 is high wing single seat sailplane of mainly wooden construction with plywood and fabric covering. However, the cockpit and forward part of the fuselage consists of glass reinforced plastic which was innovative at the time that the type was designed. The cockpit provides for a semi reclining position for the pilot protected with a full Perspex canopy. The wings are made up of a centre section with constant chord and tapered wing tips. The aircraft has a conventional arrangement for the tail stabiliser / control surfaces. The sailplane bears construction number 1382 and is registered in Australia as VH-GTBaustralian gliding, glider, sailplane, skylark, slingsby, bentson, picket-heaps, crompton, new england soaring club, dutton -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider –Sailplane, 1960
The FS-24 Phonix is the first sailplane design to be built using a moulded fiberglass sandwich technique. It was designed by Hermann Nagele and Richard Eppler leading a group setup for the purpose at Stuttgart Technical University in the early 1950s. Initial construction was undertaken at workshops of Wolf Hirth and the first prototype was completed at the Bolkow Aircraft Company where Nagele and another member of the group, Rudi Lindner, had gained employment. It flew on 27 November 1957. Two further prototypes were built incorporating a T-tail and other refinements. Eight in all were built before production was stopped in 1961. A number of gliding records were broken in Phonix sailplanes in Germany in 1962-1963. It was found to have a best glide ratio of 40:1. The Museum’s example, No. 403 was originally a prototype built on 25 May 1960 [Registration D-8354]. It was converted at Bolkow to a Phonix T in 1963 and sold to a private owner in Switzerland [Registration HB-746] and later then to gliding club Segelfluggruppe Solothurn in 1965. The glider returned to Germany in 1971 (Meersburg) and re-registered as D-0738. It moved to a new owner in Allershausen in 1976, and again to Lindhoft in 1982. In 1983 the glider was sold to owners at Hasselt, Belgium and given registration OO-ZQD. In 1989 a further change of ownership occurred and the glider went to Leusden in the Netherlands where it was registered as PH-949. In 2006 the Phonix No.403 was imported into Australia by John Ashford of the Geelong Gliding Club. On 30 January 2007, it was registered as VH-GRP. However, as at January 2016 it has not been flown in Australia. In the course of its flying history the glider was damaged several times and repaired. At one stage a larger rudder was fitted and later on this modification was reversed. With the original conversion to a Phonix T and subsequent repairs and changes to equipment the weight of the airframe increased from 182 kg to approximately 220 kg. Nevertheless, the wing loading is a modest 20kg/square metre. As at January 2016, minor repairs and airworthiness certification are required to return the glider to flying condition. This exhibit is highly significant as it is one of only eight of this pioneering sailplane design. It is the only one in Australia. Glassfibre single seat sailplane, finished white with blue stripes on fin and rudder.Australian registration GRP on rudder; Serial Number 403 and Vintage glider club of Netherlands plaque in cockpitaustralian gliding, sailplane, glider, fs-24, phonix, nagele, eppler, lindner, stuttgart technical university, bolkov aircraft company, segelfluggruppe solothurn, ashford, geelong gliding club. -
 Stratford and District Historical Society
Stratford and District Historical SocietyPortrait of Samuel Swan
This portrait is said to be in the technique of Alfred Bock, but the frame is dissimilar to the standard type on 80% of the collection in the Sale Museum. Samuel Swan died in 1880. It is unclear where the portrait hung, as Swan died before the Mechanics' Institute was built.An unsigned portrait, oil on canvas, of Samuel J Swan. He is shown looking left. It is framed in a gold coloured plaster frame, with relatively simple trimming on corners. The frame is chocked at the back with wooden wedges to hold canvas in place, and a framer's label appears at the top.'Samuel J Swan / Gippsland Pioneer' on brass plate bottom front. "Telephone 7231 Central / T.S. Glasier & Co Pty Ltd / Gallery of Art / Picture Frame Manufacturers &c / Union House / 284-6 Little Collins Street / No [in pencil] 2344, Melbourne" -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tubal insufflator associated with Dr Lorna Lloyd-Green, c1919
"Potential blockage in the Fallopian tubes was assessed using this apparatus. It was developed by American gynaecologist Isidor Clinton Rubin (1883-1958). It blows carbon dioxide, via a cannula, into the uterus. The ease with which gas escaped through the Fallopian tubes was reflected by pressure changes on an instrument called a manometer. Blockage of the tubes is often due to previous infection or surgery. It is a common cause of infertility. Rubin’s test formed a standard part of infertility investigations for many years. It was gradually replaced by an X-ray technique involving radio-opaque ‘dye’ injected into the uterus." Source: Science Museum Group. Rubin’s apparatus for uterotubal insufflation, New York, United States, 1928. A639503Science Museum Group Collection Online. Accessed 12 June 2024. https://collection.sciencemuseumgroup.org.uk/objects/co96774/rubins-apparatus-for-uterotubal-insufflation-new-york-united-states-1928-tubal-insufflator. Model may be dated c1919 or 1920s or 1930s. 1919 was the year Isidor Clinton Rubin (1883-1958) introduced the apparatus. Instrumant has a label with Cyrus Jones monogram " Donated by Dr Lorna Lloyd Green, 1986/ Rubin's Insufflator/ NB "sparklet holder separate" missing?Rubin's tubal insufflator apparatus, large cylidrical glass canister inside a portable carry box with two doors with three glass nozzels at top with long rubber tubing attached on each. One surigical steel introducer, one glass introducer attached. A blood pressure manometer is fixed on the inside door. infertility -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - Application Of Compliance Techniques For Studying Effect Of Side-Grooving On Stress-Corrosion Crack
Description: Publisher: Department of Civil Aviation Pages: 6 Binding: Permanent/Soft Level of Importance: National. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - An Ultrasonic Pulse-Height Difference Method Of Recording Crack Growth Over An Extended Period
Description: ISBN: AR-001-262 Date: April 1978 Author: W. J. Pollock Publisher: Defence Science and Technology Organisation Pages: 20 Binding: Permanent/Soft Keywords: Application of Compliance Techniques For Studying Effect of Side-Grooving On Stress-Corroasion Level of Importance: National. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (item) - Bill Prowse Collection WP14 See details in Description, Bill Prowse Collection WP14
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (collection) - Atar engine parts photographs, Technique Photographs for Atar Austenal and Shaw Precision Castings
Photos of precision castings -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Cloud-Seeding Techniques
Description: SUPPLEMENTS TO-1C-130E-4, PUBLISHED 1/2/1966. SUPERSEDES TO-1C-130E-4S-22, PUBLISHED 1/5/1977. 300 pages. Published by USAF. Published 5/10/1977. TO-1C-130E-4S-28. Operational Supplement for Technical Manual & Illustrated Parts Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Tool Catalogue For Wright Engines
Description: 120 pages. Published by CSIRO. Published 18/8/1967. Third Course of Instruction in Cloud-Seeding Techniques Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Techniques Of Oblique Aerial Photography Of Agricultural Field Trials
Description: 1 page. Published by Flight International. Published 16/3/1985. Single Page Extract from Flight International Magazine - First Flight of Locally Assembled F/A-18 Hornet Level of Importance: World. RAAF -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Jindivik Target Program
Description: 40 pages. Published by CSIRO. Published 1/1/1973. Division of Soils Technical Paper No. 19. Aerial Photography Techniques and Doctrines for Agricultural Field Trials. Level of Importance: World. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - Mirage Iii - Bulletins D'Evolutions Techniques
Description: Nomad, De-Icing, United Kingdom ,1979, Trials. Published by GAF in the year 1979. Level of Importance: .
