Showing 645 items
matching pressure
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - RAAF - Precision Pressure Test Set Model 156 (Texas Instrument Inc)
AAP 7640.036-2M -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - RAAF manuals on - non-return valves, valve box, cap assembly, mixer valve, springed rod, manual control unit, pressure switch, cold air unit
-
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncDomestic object - TILLEY Paraffin Pressure Iron, Tilley Lamp Company, 1950s to 1970s
Irons such as this were very popular prior to the widespread introduction of electricity in Australia. It was manufactured by the Tilley Lamp Company Ltd. In 1818 John and William Henry Tilley established W. H. Tilley, in Stoke Newington, London, England. During WW1 they started to use paraffin as a lamp fuel in pressurised containers. A production plant was established at Hendon, just north of London, and the first commercial lamps were produced after World War 1. During the 1920s the company diversified into domestic lamps. This expanded to other appliances such as heaters and eventually to irons. The use of paraffin or kerosene as a fuel was a much cleaner form of heat, especially when compared to older flat irons which used coal.This item is significant because it is representative of domestic appliances used in the Wodonga District prior to the introduction of electricity throughout the area.Cream coloured iron with a black Bakelite handle which attaches to the fuel tank. It has a steel sole plate. The heat of the iron is provided by a paraffin burner.On Metal plate: Model D.N. 250 Made in England British Pat. 524719 Australian Pat. 114305 On Knob at rear: ON/OFF TILLEYdomestic appliances, tilley paraffin iron, tilley lamp company ltd. -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Manual, Royal Australian Air Force, Royal Australian Air Force: Engineering Publication: A.C. Ratiometer Pressure Indicator Including Code Number 1ACR/MB (Smiths)
A yellow plastic cover with a clear window. There is the RAAf insignia near the top with Royal Australian Air Force and Engineering Publication under the insignia. Throug the window are the details of the manual on yellow paper. The manual is held together by a large metal slide which in on the inside of the coverroyal australian airforce - manuals, engineering publication, a.c. ratiometer pressure indicator -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Manual, Royal Australian Air Force, Royal Australian Air Force: Engineering Publication: Direct Reading Pressure Gauges Including Code No. 259 PG, 323 PG, 329 PG, PW1422 PG (Smiths)
A yellow plastic cover with a clear window. Under the RAAF insignia reads Royal Australian Air Force and Engineering Publication. Through the window are the details of the manual. The manual is held together by a large metal slide which is in the inside of the manual. The manual has what looks like oil/grease splats on the cover.royal australian airforce - manuals, engineering publication, direct reading pressure gauges -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - C.I.G. Regulator Type M, sectioned, Commonwealth Industrial Gases Ltd, c. 1960
The regulator was sectioned by I. Philpott in 1962.The regulator, designed to protect anaesthetic machines against sudden changes in pressure, consists of two main, rounded bodies, joined by a short connection. The lower section consists of a valve and a nut on the end that can be adjusted to provide a secondary pressure range. The upper section shows the gauge, which has had part of its face removed to show the inner workings. The valve on the reverse side has also been sectioned.anaesthesia, gas, pressure -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionSpeedy Moisture meter test kit
Used for pressure testing and recalibrating Speedy Moisture metersKit used pressure test Speedy Moisture metersforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
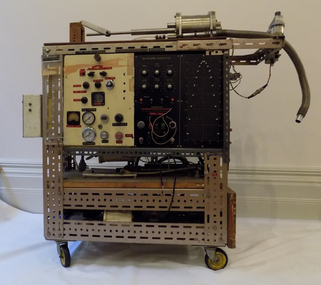 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Waveform Ventilator, 1970
Professor Arthur Barrington (Barry) Baker was the first Australian anaesthetist to gain a DPhil in anaesthesia. He completed his DPhil at Oxford University at the Nuffield Department of Anesthesia in 1971, titled, Physiological Responses to Artificial Ventilation. The Waveform Ventilator is the machine developed to illustrate his DPhil. The waveform ventilator was used in several scientific studies on 'the effects of varying inspiratory flow waveforms and time in intermittent positive pressure ventilation (IPPV)', published in the 'British Journal of Anaesthesia'. Professor Arthur Barrington Baker had an extensive career in research and clinical practice including holding the position as the Nuffield Professor of Anaesthetics at Sydney university (1992 - 2005) and also as the Dean of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) (1987-1990).The variable waveform ventilator is of national significance, due to its association with Professor Arthur Barrington Baker (Prof. Baker) the first Australian academic anaesthetist, and the representation of historical social themes and research and design, in anaesthesia. Historic significance – It is a rare type of ventilator in good condition and well provenanced. It is a tangible record of the beginning of the long established and distinguished career of Prof. Baker, the first anaesthetist in Australia to gain a DPhil. Prof Baker has a strong involvement in the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) organisation. The object is a product of Prof Baker’s Doctorate of Philosophy (DPhil) on respiratory physiology and is associated with the prestigious Oxford University and the well-known Nuffield Department of Anaesthetics. It also represents the social theme of migration to England from Australia in the 1960s and 1970s to access and experience academic and artistic opportunities limited in Australia at the time. Scientific Value – The object is of scientific value as it offers major potential for education and interpretation in anaesthesia. Although ventilators are common equipment, this specific design and construct prototype is one of a kind, designed and used specifically for research purposes. A rectangular shaped object on a trolley with four wheels. The top half of the object consists of two panels, one of cream coloured painted wood, the other black plastic, both containing several dials of different shapes and sizes. The wood surface also contains several gauges and a safety pressure clear plastic box. The plastic surface also contains a pin board. The bottom half of the object consists of two shelves. The whole object's perimeter is lined with perforated metals. The top wooden surface has several metal pieces of equipment and a long tube. The rear of the object contains numerous types of tubing and wire, a gas cylinder and two leather straps with buckles. The bottom half of one side of the objects has 3 electrical power outlets.Waveform Generator, Drs Colliss N Cowie, Dr Baker Dr Murray Willson, Dr Babbington, Safety Pressure, Error POS F/B, Position, Feedback, Set Balance, Reset, Full Stroke, Velocity, Converter Current, line Pressure, Low Pressure, Bias Pressure, Start, Stop, Stop, Reset Press, Max Press, W/G Output, A/CRO B/2.baker, arthur barrington, baker, barry, professor, academic anaesthetist, oxford university, nuffield department of anaesthesia -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, Lights coming up at last? Kerrimuir's new count, 1967
Box Hill Council has been pressured to erect traffic lights on the Springfield Road, Middleborough Road intersection.Box Hill Council has been pressured to erect traffic lights on the Springfield Road, Middleborough Road intersection. The pressure has come from Blackburn North State School Committee and Mrs N.G. Vance.Box Hill Council has been pressured to erect traffic lights on the Springfield Road, Middleborough Road intersection.city of box hill, blackburn north primary school, springfield road, blackburn north, middleborough road, blackburn north, vance, n. g. (mrs) -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - Article on the failure of Bendigo's Water Supply in 1870, Feb 06 2021
When work was being finished on the Back Creek syphon specially designed to push water uphill, metal plates on the pipelines were not strong enough to withstand the pressure. Damaged and loss of water was estimated to be 25,000 pounds. It was one of the biggest disasters in Vicotria's history.Bendigo Advertiser: Full page article entitled 'High pressure failure'.bendigo water supply, coliban system -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionWajax Mk 3 pump
The earlier Pacific Marine pumps were not replaced and were auctioned off during the 1980s. The ever reliable Wajax Mk3 remained a fire cache item ready to be called on should a specific need for a small transportable pressure pump arise. The Wajax Mk3 has been in circulation since the 1950’s, and through that time has undergone several upgradesHigh pressure Wajax Mk 3 pump With hand primerforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, fire pump -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Diving Compressor, Siebe Gorman & Co. Ltd, 1880-1890
This compressor was part of the E.G. Ward Collection. It is connected to the diving suit and boots also in our collection. Siebe Gorman & Company Ltd was a British company that developed diving equipment and breathing equipment and worked on commercial diving and marine salvage projects. The company advertised itself as 'Submarine Engineers'. It was founded by Augustus Siebe, a German-born British engineer chiefly known for his contributions to diving equipment. Siebe Gorman traded as an engineering firm for over 180 years from 1819 to 1999. The early success of the business was due to its founder, the Prussian immigrant Christian 'Augustus' Siebe (1788-1872). For business reasons, he applied for and was granted British citizenship in 1856. He was a gifted engineer who was able to translate theoretical problems into practical, working products. During the industrial Victorian period, the business traded as 'A. Siebe' at 145 High Street Holborn London, but in 1828 new premises were acquired at 5 Denmark Street, Soho. The family firm produced a wide range of manufactured goods including paper-making machinery, measuring machinery, water-pumps, refrigeration equipment and diving apparatus. Augustus Siebe specialised in submarine engineering early on and the company gained a reputation for the manufacture of safe, reliable diving apparatus. Augustus Siebe is best remembered for the development and manufacture of the ‘closed’ Diving Dress based on the ideas of Charles and John Deane, George Edwards and Charles Pasley. Apart from some small modifications to valves and diver communications, the basic 12 bolt ‘closed’ diving dress remained relatively unchanged after the 1870s. Later company successes were also based on innovation, with new products that could be successfully developed and manufactured to high standards. This was largely attributed to the inventive nature, foresight, engineering and entrepreneurial skills of Robert Henry Davis (1870-1965). In 1882, RH Davis joined the company of 'Siebe & Gorman' as a young 11-year-old office boy and he was to remain with the company until he died in 1965. Augustus Siebe retired in 1869 and handed over the company to a new partnership of Henry H. Siebe (1830-1885) and William A. O'Gorman (1834-1904). The new firm traded as 'Siebe & Gorman' (1870-1879) from premises in and around Mason Street, Westminster Bridge Road, Lambeth, London. The two partners soon recognised the potential of R.H. Davis and in 1894, aged 24, he became General Manager of Siebe & Gorman. Davis increasingly ran the company until the surviving partner (W.A. Gorman) died in 1904. The firm was disposed of to the Vickers (armaments) family and a new company 'Siebe Gorman & Co. Ltd.' (1905-1998) was formed. Under the chairmanship of Albert Vickers, R.H. Davis was kept on as Managing Director, and the company forged ahead. However, after WW1, the Great Depression caused manufacturing output and share prices to slump. In 1924 Robert Davis made a deal with the Vickers Board and acquired control of the company through majority shares. Under his leadership, the Siebe Gorman Company flourished and within time, four of his sons also joined the firm. The company gained a worldwide reputation for the manufacture of diving apparatus, decompression and observation chambers, and safety breathing apparatus of all types for use on the land, in the air and under the sea (including mine rescue, tunneling, aircraft, diving, submarine escape and in other hazardous environments). Close research and development links with the MOD (especially the Admiralty), also provided a lucrative outlet for the company products. In 1932, Robert Davis was knighted by King George V, principally for his invention of the ‘Davis Submerged Escape Apparatus’ (D.S.E.A.). Siebe Gorman essentially remained a family firm from the beginning (under A Siebe) until it became a public company for the first time in 1952. However, following WW2, British manufacturing stagnated through stifled investment and post-war austerity, and there was little innovation. Siebe Gorman fortunes began to decline as an ageing Sir Robert Davis failed to invest, or change the company business and management practices. In 1959, Siebe Gorman was acquired by the “Fairy Group” and the ailing Sir Robert was made Life President. Consequently, nothing changed and the slow decline continued until Sir Robert's death in March 1965. Around 1960, Siebe Gorman acquired the diving apparatus manufacturer C E Heinke, and for a brief period, it manufactured some diving equipment under the combined name of Siebe Heinke. Around 1964, Mr. E. 'Barry' Stephens was appointed as the new Managing Director to modernise Siebe Gorman. Changes were made, including a move to a new factory in Wales in 1975. The new company concentrated on fire fighting breathing apparatus and escape equipment, and the move coincided with the loss of many of the older, traditional craft skills. Between 1985 and 1998, Siebe expanded through acquisitions, and several other companies were acquired. The Siebe Gorman (diving apparatus) company has therefore traded as A. Siebe (1819-1870); Siebe & Gorman (1870-1879); Siebe Gorman & Co (1880-1904); Siebe Gorman & Co. Ltd (1905-1998).The compressor is a very significant item as it gives a snapshot into marine history and the development of diving equipment generally especially that used for salvage operations before and during WW2. Siebe & Gorman the company that made the equipment was a leading inventor, developer and innovator of marine equipment with its early helmets and other items eagerly sought after today for collections around the world. The items in the Flagstaff Hill collection give us an insight as to how divers operated and the dangers they faced doing a very necessary and dangerous job during the early days of marine exploration.A single cylinder divers' pump by Siebe Gorman & Co Ltd, London, eccentric hand cranked in brass mounted mahogany case with instructions to the underside of the lid, brass covered pressure gauge and air outlet, brass makers plaque to the front, water inlet and outlet to the rear, green painted lifting rings. Machinery has some blue painted areas on the metal.Plate on the back 'WATER SUPPLY" "WATER OVERFLOW" "WATER DRAIN-IN" Pressure gauge dial "BOURDON'S PRESSURE GAUGE" STEBE GORMAN & CO. LONDON", "LBS PRESSURE" "FEET OF SALT WATER" Plate on the front " PATENT, Siebe Gorman & Co Ltd Submarine Engineers" below emblem (Lion, Crown, Horse)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, maritime-museum, diving compressor, london, siebe gorman & co ltd, marine technology, life saving, deep sea diving, maritime museum, maritime village, manine history -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumInstrument - Pressure Gauge, Dane Taylor & Co. Pty. Ltd
Used in the Albion Mill to determine the pressure in the departments requiring steam such as the boiler and dyeing rooms. Circular brass object with black hand painted text and numbers, and a central dial. Printed: PRESSURE / GAUGE / LBS. PER INCH. DANE TAYLOR & Co. Pty. Ltd. / MELBOURNE [on base]: 277828instruments, pressure gauge, albion mill, dane taylor & co pty ltd, south melbourne, geelong, wool industry -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, Officers reign in spending, 1994
Article about City of Nunawading's triennial budget to be adopted 3 Oct 1994 in the knowledge that the City will be amalgamated shortly.Article about City of Nunawading's triennial budget to be adopted 3 Oct 1994 in the knowledge that the City will be amalgamated shortly. Council officers have prepared it under pressure to retain their jobs.Article about City of Nunawading's triennial budget to be adopted 3 Oct 1994 in the knowledge that the City will be amalgamated shortly.local government, city of nunawading, business and finance, amalgamations -
 Ambulance Victoria Museum
Ambulance Victoria MuseumSuction Unit, Jet, Laerdal, Laerdal
This pressure pack driven suction unit contains a lanyard to be placed around the neck (source Peter Naylon AHSV member and serving paramedic. 4 September 2016Clear plastic bottle with green and white screw on cap with external plastic tube. Plastic bottle contains a green and white pressure pack.vacuumised cartridge for jet suction Laerdal -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryTool - Manometer, Mercury, Elliotts & Australian Drug Pty. Ltd
In the 1600s, William Harvey realised a finite amount of blood circulates in one direction through the body. Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille introduced the mercury hydrodynometer in the early 1800s for measuring blood pressure. Karl von-Vierordt created the sphygmograph in 1855 and, in 1881, Samuel von Basch created the sphygmomanometer, distinct improvements on the hydrodynometer. In 1896, Scipione Riva-Rocci developed the mercury sphygmomanometer. American neurosurgeon, Harvey Cushing, was an early adopter, and advocate for monitoring patients during surgery and anaesthesia. Blood pressure monitoring is still an essential component of evaluating a patient’s condition.This blood pressure kit is housed in a rectangular, vinyl covered box with metal handle and press-stud lid release mechanism. The lid opens upwards and the glass blood pressure valve and plastic scale is attached to the underside of the lid. The measurements are written in black and go up in increments of ten, from 0 to 300. The glass valve has unidentified increments labelled in red, which is housed within a metal cylinder. The bellows is attached to the measuring valve via a dark green pressure cuff and rubber hose.Blue sticker affixed inside the kit: JOHN MARUM Ornate manufacturer's label: THE ARMOURED / ELLISCO / SPHYGMOMANOMETER / MADE BY / ELLIOTTS & AUSTRALIA DRUG / [indecipherable] LTD / CENTEN[indecipherable] MODELharvey cushing, blood pressure, measurement, anaesthetics, john marum, sphygmomanometer, elliotts & australian drug pty ltd, centenary model, cuff, bellows, ellisco, armoured -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, New tram link proves popular, 1979
Photocopy of article quoting Keith McCance, state member for Bennetswood commenting on the increase in patronage of the Burwood Road tram extension from Warrigal Road to Middleborough Road.Photocopy of article quoting Keith McCance, state member for Bennetswood commenting on the increase in patronage of the Burwood Road tram extension from Warrigal Road to Middleborough Road. Pressure is being applied to extend to Springvale Road.Photocopy of article quoting Keith McCance, state member for Bennetswood commenting on the increase in patronage of the Burwood Road tram extension from Warrigal Road to Middleborough Road. tram services, burwood road, burwood, mccance, keith -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPacific Marine pump Type Y
The Pacific Marine company was based in Seattle on the west coast of America and manufactured its first satisfactory portable fire pump 1925. These early Type N pumps were replaced in 1933 by the more familiar Type Y pumps. The updated pumps proved popular with the US Forest Service, and a large number were purchased by the Forests Commission as part of the equipment upgrade program in the wake of the 1939 bushfires. The Pacific Marine had a 9.8 Hp, two-cylinder, two-stroke petrol motor running with a high oil mix ratio of 16:1, so it blew vast clouds of blue smoke as the motor screamed at 4500 rpm. Part of its unique design was the water-cooled engine and muffler. But if the flow of water was interrupted the engine would quickly overheat and seize, so it needed constant monitoring and attention. Water was driven through a pair of bronze impeller gears which also needed a constant flow of water otherwise they would also self-destruct. When running properly, a Pacific Marine could pump 63 US gallons per minute, or about enough to fill a 200-litre drum. But its main feature was its high pressure of up to 225 psi. Pacific Marine pumps were often mounted on top of departmental fire tankers and used to spray water into the tops of burning trees. Compared to other pumps of the era it was light weight at only 70 pounds and was often mounted on a wooden stretcher frame. But they were cantankerous things to start with the rope pull and many exasperated novices came away with skinned knuckles. Modern Honda motors, which were more reliable and smoother running, replaced the Pacific Marines as the pump of choice for forest firefighters in the 1980s.High pressure Pacific marine Pumpforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, fire pump -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumIron, c. 1920
Coleman pressure iron with wooden handle and screw for adjusting pressureColeman -
 Ballarat RSL Sub-Branch Inc.
Ballarat RSL Sub-Branch Inc.Pressure Unit
"Pressure equalising vent"equipment/gear, ballarat rsl, ballarat -
 Hand Tool Preservation Association of Australia Inc
Hand Tool Preservation Association of Australia IncGauge
This item is part of the Thomas Caine Tool Collection, owned by The National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and curated by the Hand Tools Preservation Association of Australia.gauge, pressure -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Kerosene Searchlight, Circa 1935
The Tilley lamp derives from John Tilley’s invention of the hydro-pneumatic blowpipe in 1813 in England. W. H. Tilley were manufacturing pressure lamps at their works in Stoke Newington in 1818, and Shoreditch, in the 1830s. The company moved to Brent Street in Hendon in 1915 during World War I, and started to work with paraffin (kerosene) as a fuel for the lamps. During World War I Tilley lamps were used by the British armed forces, and became so popular that Tilley became used as a generic name for a kerosene lamp in many parts of the world, in much the same way as Hoover is used for vacuum cleaners. During the 1920s the company had diversified into domestic lamps, and had expanded rapidly after orders from railway companies. After World War II fears about the poisonous effect of paraffin fumes, and widely available electricity, reduced demand for domestic use. The company moved from Hendon to Ireland in the early 1960s, finally settling in Belfast. The company moved back to England in 2000.A significant item demonstrating the early use of kerosene under pressure as a lighting medium. These types of lamps were made by a company whose products became synonymous with oil lamps generally. Lamps that were used commercially, domestically and by the armed forces of many countries during the first and second world wars.Tilley Searchlight Projector, or search lamp, made in Hendon, England 1935. Metal kerosene pressure search lamp, glass front, fixed mirror at back, wooden carry handles. Mounted on fuel tank with pressure pump. Lamp has 8 airflow holes in the bottom and a covered outlet on the top. Glass is in 3 pieces, fitting together to make flat circle there is a maker’s plate on the pressure tank. “TILLEY / SEARCHLIGHT PROJECTOR / MADE AT / HENDON, ENGLAND”, “256” handwritten in red on one wooden handle, “9” or “6” hand painted in white on top on lightflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, tilley kerosene pressure searchlight, lighting, john tilley, pressure lamps -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionKerosene pressure lanterns
Used at fire basecampsKerosene pressure lanternsTilley 020forests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, camping equipment -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionKerosene pressure lantern in box
Used at fire basecampsKerosene pressure lanternTilleyforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, camping equipment -
 Maldon Vintage Machinery Museum Inc
Maldon Vintage Machinery Museum IncPressure Testing Pump
Hand operated pressure pump with water reservoir. High and low pressure hoses. Low pressure for filling reservoir, high pressure reinforced hose for delivering water to item to be pressurised. Brass fittings. Reservoir painted pale green and operating handle yellow & red. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Tilley Heater, John Tilley, 1930s
The Tilley lamp & heaters derives from John Tilley’s invention of the hydro-pneumatic blowpipe in 1813 in England. W. H. Tilley were manufacturing pressure lamps at their works in Stoke Newington in 1818, and Shoreditch, in the 1830s. The company moved to Brent Street in Hendon in 1915 during World War I, and started to work with paraffin (kerosene) as a fuel for the lamps. During World War I Tilley lamps were used by the British armed forces, and became so popular that Tilley became used as a generic name for a kerosene lamp in many parts of the world, in much the same way as Hoover is used for vacuum cleaners. During the 1920s the company had diversified into domestic lamps, and had expanded rapidly after orders from railway companies. After World War II fears about the poisonous effect of paraffin fumes, and widely available electricity, reduced demand for domestic use. The company moved from Hendon to Ireland in the early 1960s, finally settling in Belfast. It moved back to England in 2000.Item is significant as it was an early form of portable heating used in a domestic situation or any small room that required to be heated. This item fell out of use when electricity and electric heater became more available and affordable. Tilley kerosene pressure heater with large reflector dish. Fuel tank painted cream and wooden handle.Tilleyflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, kerosene heater, tilley lamps, john tilley, pressure heater, domestic use -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryGauge
g. Pressure gauge for the calorimeter -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Container - Manufactured glass, Codd bottle, c1888
The Codd Bottle was first invented by English manufacturer, Hiram Codd at Barnsley in 1870. The groove inside the top of the bottle held a rubber ring. A small glass balll was held against this ring by the pressure of the 'pop' or 'fizzy' carbonated drink inside the bottle. This style of bottle was widely manufactured and used in the production of mineral waters and lemonade. The glass has a slight green tint, known as aqua glass, and is what the Victorian era produced as 'clear glass'This glass Codd bottle with glass ball and partial rubber ring was probably imported from England by Bennetts Pty. Ltd of Richmond, Victoria for their Lemonade and sold as refreshment to early settlers of Moorabbin Shire c1880A slightly green tinted, glass bottle with a groove inside the top which held a rubber ring, against which, the small glass ball inside the bottle was held by the pressure of the 'fizzy' drink inside.BENNETTS / LEMONADE diagonally across bottlecodd hiram, glass manufacture, glass bottles, moorabbin, brighton, barnsley england, carbonated water, soft drink, mineral water, bennetts lemonade maker, richmond, early settlers, market gardeners, melbourne -
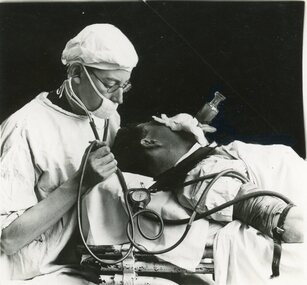 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPhotograph
The image, without a blackened out background was reproduced on page 21 in 'Practical Anaesthesia'. Practical Anaesthesia was the first text book on anaesthesia produced in Australia. Geoffrey Kaye was one of the contributors to this book, which included a foreword by F.H. McMechan, Secretary General, International Anesthesia Research Society. Blood pressure measuring enabled medicine to develop a greater understanding of shock and begin to develop more appropriate measures for resuscitation. Shock was not really understood until the introduction of routine blood pressure measuring in the early 20th century.This item is historically significant because it is a rare photograph of Dr Geoffrey Kaye, as well as being reproduced in Practical Anaesthesia, the first textbook on anaesthesia to be produced in Australia.Black and white photograph showing Dr Geoffrey Kaye during a demonstration of monitoring during anaesthesia in 1932. Dr Kaye is fully gowned and masked and is seated behind the head of the patient who is lying down. Dr Kaye is holding a blood pressure monitor in his right hand which is attached to the patient's arm. Handwritten in grey pencil on reverse: Fig 1 new bookgeoffrey kaye, blood pressure measuring, surgical gown, patient safety -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sphygmomanometer, Pre 1997
This Sphygnomanometer belonged to Dr Lorna Lloyd GreenSphygmomanometer, including arm cuff, rubbe tubing, rubber pressure bulb and metal pressure gauge and small black vinyl carry case.examination, blood pressure
