Showing 127 items matching "renaissance"
-
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncBook, Stawell Joint Venture, Stawell Joint Venture Reports 1976-1992, 1976-1992
Information on various aspects of the Stawell Gold Mine14 Yellow card with Black Plastic Ring Binders for spine. 3 Logos W.M.C. Central Norseman Limited Gold Corporation. Stawell Joint Venture. 2121: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. Progress report 1979 By R.B. Sloan. A Preliminary Look at the cost of establishing a Gold Production Operation at Stawell By N.R. Hook 1980 22: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. History of Exploration at Stawell By R.B. Watchorn & Stawell Development Proposal By R.B. Watchorn & N.R. Hooker 1980 23: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Stawell Joint Venture. Preliminary draft Stawell Gold Development Project A report on a proposed Exploration Drive. January 1981 24: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Stawell Joint Venture. Stawell Gold Development Project 1981 25: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. K Report No, 2595 Stawell Progress Report 1976-1981 26 Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. K Reort No. 2630 Stawell report on teh Wonga Mining Area with recommendations for exploration. 1982 27 Western Mining Corporation Limited ( Incorporated in Victoria). Acting Manager And Agent for and on behalf of the Stawell Joint Venture between Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited 28: Western Mining Corporation Limited. Stawell Gold Project: A report on proposed Operations. 1983 29: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. K Report No. 2870 A report on the Newington - Three Jacks area with recommendations for Exploration 1984 30: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. Report K 2885 THe Geology, Ore reserves & Exploration Potential of the Wonga Area, Stawell 1984 31: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Stawell Joint Venture. Stawell Gold Project: Davis Open Cut Environment Effects Statement 1986 32: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. Report. The Stawell Goldfield History of Exploration and Development & Chronology of the Discovery, History & Development of the Stawell Gold Field. 33: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. K Report 3392 Stawell Exploration Joint Venture Progress report 1982-1991 1991 34: Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. Three Fold out maps on the Treatment Plant. 1. Ball Mill Installation May 1989. 2. Vibrating Screen April 1992. By-Pass / Underflow / Oversize April 1992. 35Western Mining Corporation Limited & Central Norseman Gold Corporation Limited. Stawell - A renaissance. By S.H. Tan. 1986stawell gold mining -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Labassa, 4 Manor Grove, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages. HISTORY:-- From Victorian Heritage Database citation for Labassa https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/278 as at (26/10/2020) Labassa, Caulfield is one of Melbourne's most lavishly decorated nineteenth century mansions. It resulted from the extensive remodelling in 1890, of an earlier house, known as Sylliott Hill, which was begun in 1862-3 for lawyer, Richard A. Billing. The land at the corner of Balaclava and Orrong Roads was first acquired in 1854 by William Lyall, transferred to his partner, John Mickle, in 1859, who also acquired the adjoining allotment in Balaclava Road, and the three allotments were conveyed to Billing. His first eight-roomed house was extended significantly in 1873 into a twenty-roomed house by architects Crouch and Wilson, who were possibly also responsible for the first house. This reflected Billing's success as a barrister, and he resided at this property until his death in 1882. In 1883 prominent Melbourne businessman, Alexander William Robertson, leased the Sylliott Hill property from Billing's widow, and in 1885 he purchased the adjoining allotment in Balaclava Road. He purchased the Billing's property in 1887 and renamed the 6.31 hectare property, Ontario. In 1889-90, Robertson commissioned the German born architect, John A. B. Koch, to extensively remodel the house into a thirty-five roomed mansion. The existing house was extended and altered, largely resulting in the nineteenth century mansion as it now appears. After Robertson's death in 1896, the house was tenanted until it was eventually sold to the mining millionaire, John Boyd Watson, in 1904. He renamed the property Labassa and carried out repair and re-decoration work to the house. In the early twentieth century, many large estates were subdivided into smaller allotments as the demand for land grew and it became difficult to maintain such large estates. After Watson's death in 1911, portions of the Labassa estate were offered for sale, with Mrs Watson retaining a 1.73 hectare portion containing the house. In 1913 forty-six allotments were auctioned at Labassa Estate, with the formation of Labassa Grove and Ontario Street to the east of the property. Labassa was first recorded as containing flats in 1923 and in the late 1920s, the owner, Robert Hannon, built a red brick block of flats adjacent to the house. Subdivision continued, until the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) purchased the house in 1980 and subsequently purchased adjoining sites, one to the south-east in 1984 (house demolished in 1988) and to the west in 1988. Labassa as it now stands is substantially as it appeared when Koch completed the work in 1890. The original two storey house was transformed into a French Renaissance style mansion, with the addition of a two level L-shaped arcaded verandah and two prominent terminating bays to the south and the east. The building is of unpainted cement render with dressed bluestone plinths, balustraded parapet and steep, slate covered, flat topped mansard roofs behind. A truncated conical roof is a feature of the south bay and a helmeted head is incorporated in the parapet over the east bay. The main south and east facades incorporate many cast cement details, including sculptures, elaborate cornices, swagged Corinthian columns and caryatid consoles flanking the entrance porch, as well as pink marble panels and imitation marble, or scagliola, on curved surfaces. At the rear of the building is a two storey wing and a single storey cottage, the former being connected to the main house by a tower. This section of the house was constructed in 1873. The estate at its peak included stables (1873), conservatory (probably 1890) and a tennis pavilion (probably 1890). All of these outbuildings survive, with the stables and conservatory being converted for residential use after 1922. Internally a range of decorative treatments remain from the late nineteenth century and the early twentieth century, both from the Robertson and Watson periods of occupancy. These include wallpapers, ceiling decoration, chimney pieces, mouldings, joinery and decorative glass. From Victorian Heritage Database citation for H0135 Labassa 2/2A Manor Grove Caulfield North https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/278 as at (26/10/2020) HOW IS IT SIGNIFICANT? Labassa, Caulfield is of architectural, aesthetic and historical significance to the State of Victoria. WHY IS IT SIGNIFICANT? Labassa, Caulfield is of architectural significance as the most prominent example of a small number of houses built in Australia in the French Renaissance style. It is of further note due to the German interpretation of the style and the use of Hellenistic sources, via Germany. It is exceptional for its lavish treatment externally, including marble, scagliola, caryatids, swagged columns, mansard roofs and ornamental cresting. Labassa is of architectural significance as the most important surviving example of German architect, John Koch's domestic work. He undertook a large variety of work in Melbourne, including a number of houses, however Labassa is the most lavish example of his work. Labassa is of aesthetic significance for its outstanding assemblage of late nineteenth and early twentieth century European style interior decoration, which remain remarkably intact. These include a trompe l'oeil ceiling, painted ceilings, embossed imitation leather and other papers, chimney pieces, ceramic tilework, oak parquetry and stained glass, including a tripartite window by Ferguson and Urie, probably dating from the 1873 period. Labassa is of historical significance as an illustrative example of the wealth acquired by a number of prominent Victorian families in the second half of the 19th century. The early development of the property, Sylliott Hill, was due to the wealth acquired by Richard Billing, barrister and fifth Victorian to be appointed Queen's Counsel in 1878. The significant development in 1890 of Ontario, is illustrative of the wealth of Alexander Robertson, a partner in Cobb and Co., a director of Goldsborough Mort & Co., and a pastoral speculator. John B. Watson, whose father had acquired great wealth from the goldfields of Bendigo and subsequently invested in city and country properties, was the third resident to impact on the house, particularly the interiors. The Labassa estate is of historical significance as an illustrative example of the development that occurred in such suburbs as Caulfield in the 1880s due to the land boom, its proximity to Melbourne and the establishment of the Melbourne to Gippsland railway in 1879. It is also illustrative of an estate which succumbed to the pressures of subdividing in the early twentieth century, as properties became difficult to maintain and demand for land close to the city grew. It was typically divided into flats in the 1920s and was used as such for about sixty years. It is of historical significance for its associations with the remnants of the earlier estate which remain extant. These include the stables, conservatory (H2005) and tennis pavilion which all remain on separate sites. Also significant are the remains of early electrical wiring and fittings. Labassa was one of the first houses in Caulfield to be electrified and some of the original wires remain. [Online Data Upgrade Project 2004]Page 128 of Photograph Album with four photographs (two portrait and two landscape) of Labassa.Handwritten: "Labassa" 4 Manor Grove [top right] / Neg 232 8 Oct 1966 [under bottom right photo] / 128 [bottom right]trevor hart, bracketed eaves, slate roof, bay windows, decorative brackets, caulfield north, labassa, richard a. billing, balaclava road, orrong road, sylliott hill, william lyall, crouch and wilson, alexander william robertson, ontario, 1880's, john a. b. koch, mansion, john boyd watson, labassa grove, french renaissance style, l-shaped arcaded verandah, bluestone plinths, balustraded parapet, flat topped mansard roofs, conical roof, elaborate cornices, corinthian columns, caryatid consoles, marble panels, imitation marble, scagliola, tower, conservatory, stables, tennis pavilion, mouldings, decorative glass, caryatids, swagged columns, ornamental cresting, trompe l'oeil ceiling, embossed imitation leather, oak parquetry, stained glass, tripartite window, triple window, ferguson and urie, 1870's, flats, 1920's, electric wiring, 1860's, verandahs, curved windows, arched windows, italianate, terraces, gargoyles, ornamentation, ornate entrance, la bassa, manor grove, st kilda east, victorian, cast iron work, john koch, richard billing, architects, electrification, john mickle, land subdivision, mrs watson, labassa estate, robert hannon, national trust of australia (victoria), sculpture -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Labassa, 4 Manor Grove, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages. HISTORY:-- From Victorian Heritage Database citation for Labassa https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/278 as at (26/10/2020) Labassa, Caulfield is one of Melbourne's most lavishly decorated nineteenth century mansions. It resulted from the extensive remodelling in 1890, of an earlier house, known as Sylliott Hill, which was begun in 1862-3 for lawyer, Richard A. Billing. The land at the corner of Balaclava and Orrong Roads was first acquired in 1854 by William Lyall, transferred to his partner, John Mickle, in 1859, who also acquired the adjoining allotment in Balaclava Road, and the three allotments were conveyed to Billing. His first eight-roomed house was extended significantly in 1873 into a twenty-roomed house by architects Crouch and Wilson, who were possibly also responsible for the first house. This reflected Billing's success as a barrister, and he resided at this property until his death in 1882. In 1883 prominent Melbourne businessman, Alexander William Robertson, leased the Sylliott Hill property from Billing's widow, and in 1885 he purchased the adjoining allotment in Balaclava Road. He purchased the Billing's property in 1887 and renamed the 6.31 hectare property, Ontario. In 1889-90, Robertson commissioned the German born architect, John A. B. Koch, to extensively remodel the house into a thirty-five roomed mansion. The existing house was extended and altered, largely resulting in the nineteenth century mansion as it now appears. After Robertson's death in 1896, the house was tenanted until it was eventually sold to the mining millionaire, John Boyd Watson, in 1904. He renamed the property Labassa and carried out repair and re-decoration work to the house. In the early twentieth century, many large estates were subdivided into smaller allotments as the demand for land grew and it became difficult to maintain such large estates. After Watson's death in 1911, portions of the Labassa estate were offered for sale, with Mrs Watson retaining a 1.73 hectare portion containing the house. In 1913 forty-six allotments were auctioned at Labassa Estate, with the formation of Labassa Grove and Ontario Street to the east of the property. Labassa was first recorded as containing flats in 1923 and in the late 1920s, the owner, Robert Hannon, built a red brick block of flats adjacent to the house. Subdivision continued, until the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) purchased the house in 1980 and subsequently purchased adjoining sites, one to the south-east in 1984 (house demolished in 1988) and to the west in 1988. Labassa as it now stands is substantially as it appeared when Koch completed the work in 1890. The original two storey house was transformed into a French Renaissance style mansion, with the addition of a two level L-shaped arcaded verandah and two prominent terminating bays to the south and the east. The building is of unpainted cement render with dressed bluestone plinths, balustraded parapet and steep, slate covered, flat topped mansard roofs behind. A truncated conical roof is a feature of the south bay and a helmeted head is incorporated in the parapet over the east bay. The main south and east facades incorporate many cast cement details, including sculptures, elaborate cornices, swagged Corinthian columns and caryatid consoles flanking the entrance porch, as well as pink marble panels and imitation marble, or scagliola, on curved surfaces. At the rear of the building is a two storey wing and a single storey cottage, the former being connected to the main house by a tower. This section of the house was constructed in 1873. The estate at its peak included stables (1873), conservatory (probably 1890) and a tennis pavilion (probably 1890). All of these outbuildings survive, with the stables and conservatory being converted for residential use after 1922. Internally a range of decorative treatments remain from the late nineteenth century and the early twentieth century, both from the Robertson and Watson periods of occupancy. These include wallpapers, ceiling decoration, chimney pieces, mouldings, joinery and decorative glass.From Victorian Heritage Database citation for H0135 Labassa 2/2A Manor Grove Caulfield North https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/278 as at (26/10/2020) HOW IS IT SIGNIFICANT? Labassa, Caulfield is of architectural, aesthetic and historical significance to the State of Victoria. WHY IS IT SIGNIFICANT? Labassa, Caulfield is of architectural significance as the most prominent example of a small number of houses built in Australia in the French Renaissance style. It is of further note due to the German interpretation of the style and the use of Hellenistic sources, via Germany. It is exceptional for its lavish treatment externally, including marble, scagliola, caryatids, swagged columns, mansard roofs and ornamental cresting. Labassa is of architectural significance as the most important surviving example of German architect, John Koch's domestic work. He undertook a large variety of work in Melbourne, including a number of houses, however Labassa is the most lavish example of his work. Labassa is of aesthetic significance for its outstanding assemblage of late nineteenth and early twentieth century European style interior decoration, which remain remarkably intact. These include a trompe l'oeil ceiling, painted ceilings, embossed imitation leather and other papers, chimney pieces, ceramic tilework, oak parquetry and stained glass, including a tripartite window by Ferguson and Urie, probably dating from the 1873 period. Labassa is of historical significance as an illustrative example of the wealth acquired by a number of prominent Victorian families in the second half of the 19th century. The early development of the property, Sylliott Hill, was due to the wealth acquired by Richard Billing, barrister and fifth Victorian to be appointed Queen's Counsel in 1878. The significant development in 1890 of Ontario, is illustrative of the wealth of Alexander Robertson, a partner in Cobb and Co., a director of Goldsborough Mort & Co., and a pastoral speculator. John B. Watson, whose father had acquired great wealth from the goldfields of Bendigo and subsequently invested in city and country properties, was the third resident to impact on the house, particularly the interiors. The Labassa estate is of historical significance as an illustrative example of the development that occurred in such suburbs as Caulfield in the 1880s due to the land boom, its proximity to Melbourne and the establishment of the Melbourne to Gippsland railway in 1879. It is also illustrative of an estate which succumbed to the pressures of subdividing in the early twentieth century, as properties became difficult to maintain and demand for land close to the city grew. It was typically divided into flats in the 1920s and was used as such for about sixty years. It is of historical significance for its associations with the remnants of the earlier estate which remain extant. These include the stables, conservatory (H2005) and tennis pavilion which all remain on separate sites. Also significant are the remains of early electrical wiring and fittings. Labassa was one of the first houses in Caulfield to be electrified and some of the original wires remain. [Online Data Upgrade Project 2004]Page 129 of Photograph Album with three landscape photographs of Labassa. One of the photographs is of Labassa's drive and gates.Handwritten: 4 JUNE 1910 / SALE JUNE 28 1910 "LA BASSA' / "AUSTRALASIAN" FORMERLY "ONTARIO"/ RES OF JOHN B WATSON / 15 ACRES 3 ROADS [under bottom left photo] / 4 JUNE 1910 [under bottom right photo] / 129 [bottom left]trevor hart, bracketed eaves, intricate lacework, slate roof, bay windows, decorative brackets, caulfield north, labassa, richard a. billing, balaclava road, orrong road, sylliott hill, william lyall, crouch and wilson, alexander william robertson, ontario, 1880's, john a. b. koch, mansion, john boyd watson, labassa grove, french renaissance style, l-shaped arcaded verandah, bluestone plinths, balustraded parapet, flat topped mansard roofs, conical roof, elaborate cornices, corinthian columns, caryatid consoles, marble panels, imitation marble, scagliola, tower, conservatory, stables, tennis pavilion, mouldings, decorative glass, caryatids, swagged columns, ornamental cresting, trompe l'oeil ceiling, embossed imitation leather, oak parquetry, stained glass, tripartite window, triple window, ferguson and urie, 1870's, flats, 1920's, electric wiring, 1860's, verandahs, curved windows, arched windows, italianate, terraces, gargoyles, ornamentation, ornate entrance, la bassa, manor grove, st kilda east, gates, cast iron work, richard billing, architects, john koch, electrification, victorian style, drives, john mickle, land subdivision, mrs watson, labassa estate, robert hannon, national trust of australia (victoria), sculpture -
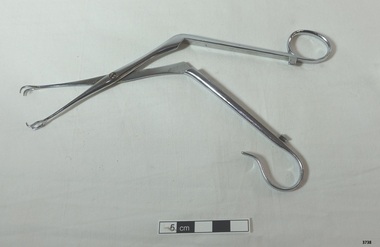 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928. Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community. They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine, administration, household equipment and clothing from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps from W.R. Angus Collection. Stainless steel, elbow shape in middle, hollow claw shape ends, one handle is open circle, handles clip together. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, department of defence australia, australian army, army uniform, medical treatment, medical history, medical education, forceps, surgery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th - early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. They are part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps from the W.R. Angus Collection. These are bonney forceps, often used when closing up after surgery. Blunt nose ends with V shaped teeth on each side that mesh together. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, medical equipment, surgical instrument, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, medical history, forceps, bonney forceps -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th - early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. Various types of forceps are still in common use today in modern surgery. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps from the W.R. Angus Collection. 'STAINLESS" & "LONDON MADE"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hillflagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w.r. angus, surgical instrument, forceps, dr ryan, medical equipment, surgical instrumentt.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, ear nose throat surgery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th - early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. Various types of forceps are still in common use today in modern surgery. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps, heavy duty, from the W.R. Angus Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, ear nose throat surgery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th Century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Stainless steel forceps, angled handles, ring shaped tips From the W.R. Angus Collection.Stamped "2" and crown, staff and snake insignia.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Stainless steel punch forceps from the W.R. Angus Collection. Ring on one end of tip and scoop on opposite side, angled handle.Stamped 'Ramsay'.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surger, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Stainless steel forceps, angled handles, ring shaped tips From the W.R. Angus Collection.'2' stamped on two parts.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps, angled handles, ring shaped tips From the W.R. Angus Collection."ALLEN & HANBURYS" & "LONDON"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Stainless steel angled forceps with scoop shaped ends.Inscribed "MEDICAL SUPPLY DEPOT": & "R" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surger, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Forceps, from the W.R. Angus Collection. Angled handles, crocodile teeth ends. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surger, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th century or early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Retractor forceps, from the W.R. Angus Collection. Crocodile teeth ends and locking handles.Inscribed "RERL" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th century or early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Retractor forceps, from the W.R. Angus Collection. Crocodile teeth ends and locking handles.Marked 'Stainless Steel' on both parts.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th century or early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Retractor forceps, from the W.R. Angus Collection. Crocodile teeth ends and locking handles.Inscribed "SURGI _ _ _ _ " & '1'flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Syringe set, 20th century
Whether it’s an anaesthetic, blood test, insulin, vitamin shot or vaccination, at a base human level something feels instinctively wrong about having a long thin piece of metal stuck deep into your flesh. And yet, in allowing physicians to administer medicine directly into the bloodstream, the hypodermic needle has been one of the most important inventions of medical science. In the beginning… Typically, it was the Romans. The word ‘syringe’ is derived from Greek mythology. Chased to the edge of a river by the god Pan, a rather chaste nymph by the name of Syrinx magically disguised herself as water reeds. Determined, Pan chopped the hollow reeds off and blew into them to create a musical whistling sound, thereby fashioning the first of his fabled pipes. Taking that concept of ‘hollow tubes’, and having observed how snakes could transmit venom, the practice of administering ointments and unctions via simple piston syringes is originally described in the writings of the first-century Roman scholar Aulus Cornelius Celsus and the equally famous Greek surgeon Galen. It’s unclear if the Egyptian surgeon Ammar bin Ali al-Mawsili was a fan of either of their scribblings, but 800 years later he employed a hollow glass tube and simple suction power to remove cataracts from his patients’ eyes – a technique copied up until the 13th century, but only to extract blood, fluid or poison, not to inject anything. Syringes get modern Then, in 1650, while experimenting with hydrodynamics, the legendary French polymath Blaise Pascal invented the first modern syringe. His device exemplified the law of physics that became known as Pascal’s Law, which proposes “when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined fluid, there is an equal increase at every other point in the container.” But it wasn’t until six years later that a fellow Renaissance man, the English architect Sir Christopher Wren took Pascal’s concept and made the first intravenous experiment. Combining hollow goose quills, pig bladders, a kennel of stray dogs and enough opium to fell a herd of elephants, Wren started injecting the hapless mutts with the ‘milk of the poppy’. By the mid-1660s, thinking this seemed like a great idea, two German doctors, Johann Daniel Major and Johann Sigismund Elsholtz, decided to try their hand at squirting various stuff into human subjects. Things didn’t end well, and people died. Consequently, injections fell out of medical favour for 200 years. Let's try again… Enter the Irish doctor Francis Rynd in 1844. Constructing the first-ever hollow steel needle, he used it to inject medicine subcutaneously and then bragged about it in an issue of the Dublin Medical Press. Then, in 1853, depending on who you believe, it was either a Frenchman or a Scot who invented the first real hypodermic needle. The French physician Charles Pravaz adapted Rynd’s needle to administer a coagulant in order to stem bleeding in a sheep by using a system of measuring screws. However, it was the Scottish surgeon Alexander Wood who first combined a hollow steel needle with a proper syringe to inject morphine into a human. Thus, Wood is usually credited with the invention. Sharp advancements Over the following century, the technology was refined and intravenous injections became commonplace – whether in the administering of pain relief, penicillin, insulin, immunisation and blood transfusions, needles became a staple of medicine. By 1946, the Chance Brothers’ Birmingham glassworks factory began mass-producing the first all-glass syringe with interchangeable parts. Then, a decade later, after sterilisation issues in re-used glass syringes had plagued the industry for years, a Kiwi inventor called Colin Murdoch applied for a patent of a disposable plastic syringe. Several patents followed, and the disposable syringe is now widespread. https://www.medibank.com.au/livebetter/be-magazine/wellbeing/the-history-of-the-hypodermic-needle/ This syringe set was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Syringe set (5 pieces) in container, from W.R. Angus Collection. Rectangular glass container with separate stainless steel lid, syringe cylinder, end piece and angle-ended tweezers. Container is lined with gauze and fabric. Scale on syringe is in "cc". Printed on Syringe "B-D LUER-LOK MULTIFIT, MADE IN U.S.A." Stamped into tweezers "STAINLESS STEEL" and "WEISS LONDON"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, syringe, b d syringe, luer-lok multifit, weiss london, surgical tweezers, hypodermic syringe, injections -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Syringe set, c. 1940s
Whether it’s an anaesthetic, blood test, insulin, vitamin shot or vaccination, at a base human level something feels instinctively wrong about having a long thin piece of metal stuck deep into your flesh. And yet, in allowing physicians to administer medicine directly into the bloodstream, the hypodermic needle has been one of the most important inventions of medical science. In the beginning… Typically, it was the Romans. The word ‘syringe’ is derived from Greek mythology. Chased to the edge of a river by the god Pan, a rather chaste nymph by the name of Syrinx magically disguised herself as water reeds. Determined, Pan chopped the hollow reeds off and blew into them to create a musical whistling sound, thereby fashioning the first of his fabled pipes. Taking that concept of ‘hollow tubes’, and having observed how snakes could transmit venom, the practice of administering ointments and unctions via simple piston syringes is originally described in the writings of the first-century Roman scholar Aulus Cornelius Celsus and the equally famous Greek surgeon Galen. It’s unclear if the Egyptian surgeon Ammar bin Ali al-Mawsili was a fan of either of their scribblings, but 800 years later he employed a hollow glass tube and simple suction power to remove cataracts from his patients’ eyes – a technique copied up until the 13th century, but only to extract blood, fluid or poison, not to inject anything. Syringes get modern Then, in 1650, while experimenting with hydrodynamics, the legendary French polymath Blaise Pascal invented the first modern syringe. His device exemplified the law of physics that became known as Pascal’s Law, which proposes “when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined fluid, there is an equal increase at every other point in the container.” But it wasn’t until six years later that a fellow Renaissance man, the English architect Sir Christopher Wren took Pascal’s concept and made the first intravenous experiment. Combining hollow goose quills, pig bladders, a kennel of stray dogs and enough opium to fell a herd of elephants, Wren started injecting the hapless mutts with the ‘milk of the poppy’. By the mid-1660s, thinking this seemed like a great idea, two German doctors, Johann Daniel Major and Johann Sigismund Elsholtz, decided to try their hand at squirting various stuff into human subjects. Things didn’t end well, and people died. Consequently, injections fell out of medical favour for 200 years. Let's try again… Enter the Irish doctor Francis Rynd in 1844. Constructing the first-ever hollow steel needle, he used it to inject medicine subcutaneously and then bragged about it in an issue of the Dublin Medical Press. Then, in 1853, depending on who you believe, it was either a Frenchman or a Scot who invented the first real hypodermic needle. The French physician Charles Pravaz adapted Rynd’s needle to administer a coagulant in order to stem bleeding in a sheep by using a system of measuring screws. However, it was the Scottish surgeon Alexander Wood who first combined a hollow steel needle with a proper syringe to inject morphine into a human. Thus, Wood is usually credited with the invention. Sharp advancements Over the following century, the technology was refined and intravenous injections became commonplace – whether in the administering of pain relief, penicillin, insulin, immunisation and blood transfusions, needles became a staple of medicine. By 1946, the Chance Brothers’ Birmingham glassworks factory began mass-producing the first all-glass syringe with interchangeable parts. Then, a decade later, after sterilisation issues in re-used glass syringes had plagued the industry for years, a Kiwi inventor called Colin Murdoch applied for a patent of a disposable plastic syringe. Several patents followed, and the disposable syringe is now widespread. https://www.medibank.com.au/livebetter/be-magazine/wellbeing/the-history-of-the-hypodermic-needle/ This syringe set was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Syringe set (8 pieces),part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Pocket syringe kit in oval stainless steel container with separate lid. Container holds syringe cylinder, plunger, 2 needles, blade and cap. Printed on syringe cylinder "FIVEPOINT BRITISH" and symbol of a red star. One needle stamped "22"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, medical history, medical education, medical text book, fivepoint syringe, general surgical co., injections -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Tooth Extractor, Late 19th - early 20th century
Toothaches have been with us since the evolution of teeth and extracting teeth. I wonder what poor Homo erectus did when suffering with a toothache. He probably just suffered and probably became very bad tempered. Ancient Dentistry Significant tooth decay did not appear until hunter-gatherer societies became agrarian. The change in diet included a large increase in carbohydrates which then led to tooth decay. Early man was primitive but he was also pretty smart. Some time around 8000 years ago someone in the area that is now Pakistan was using a drill to remove tooth decay. Examination of Neolithic skulls have revealed the handiwork of at least one very early dentist. A Sumerian text in about 5000 B.C. taught that the cause of tooth decay was tooth worms. Proposed cures for toothache were numerous. Early Egyptians wore amulets. An Egyptian named Hesy-Re, is known as the first dentist. Praise for his dentistry is inscribed on his tomb. Unfortunately it doesn’t delineate what he did to earn the praise. Pliny, the Elder, recommended finding a frog at midnight and asking it to take away the pain. The doctor to Emperor Claudius around 50 A.D. had his toothache patients inhale smoke produced by scattering certain seeds on burning charcoal and then rinsing the mouth with hot water. This was to expel the tooth worms. On the more practical side Aristotle and Hippocrates both wrote about the treatment of tooth decay. A primitive forceps was used for extracting teeth. Some dentists at that time were able to weave wire in the teeth to stabilize loose teeth. Medieval Torture From about 500 A.D. to 1100 A.D. monks were well educated and well trained and did some of the surgical procedures of the time. Barbers handled the rest of the operations, especially blood letting and tooth extractions. In 1163 the Pope put a stop to all surgeries by monks and the field was left open to the barbers. Barbers were, after all, very skilled with knives and razors. In fact, the barber pole, red and white spiraling stripes, is a symbol of the blood letting; red for blood. white for bandages. In the 1300s a Barbers’ Guild was established which divided the barbers into two groups: those with the skills and training to do procedures and those who were relegated to blood letting and tooth extractions. Pliers from a blacksmith’s foundry were the only device available. Barbers would often go to fairs and advertise painless tooth pulling. A shill in the audience would come on the stage, feigning severe toothache. The barber would pretend to extract tooth, pulling out a bloody molar he had palmed earlier. The supposed sufferer would jump for joy. The barbers set up near the bands at the fairs so that the music would drown out the screams of their patients. If the tooth was loose enough, the barber would tie a string around the tooth and yank hard to extract the tooth. This was a much less painful and dangerous procedure than the pliers. The pliers often fractured other teeth and sometimes the jaw. The procedure was far from sterile and infection was a common problem and some people bled to death. The Renaissance and the Rise of Tooth Decay In the 1400s refined sugar was introduced into Europe but only reached the tables of the wealthy. While their betters were munching on sweets, the poorer folk suffered fewer toothaches. Queen Elizabeth I was known for her blackened teeth. George Washington had a tooth extraction every year after age 22. He supposedly had a set of wooden false teeth but his dentures were actually ivory. The earliest instrument designed for tooth extraction was the dental pelican, which was shaped something like a pelican’s beak. The pelican was replaced in the 1700s by the dental key, which was fitted down over the affected tooth and was better able to grip the tooth. Both still often caused more damage than relief. The Development of Modern Dentistry Modern dental equipment began to be introduced in the 1800s about the time when dentistry became a profession and dental schools began to open. Ether was used starting in 1846 to anesthetize the pain and local anesthetics were introduced in the early 1900s. Modern dentists no longer have to seat their patients on the floor and have helpers to hold them down. Dentistry is as close to painless as possible now. There is no excuse to suffer the agony of a toothache these days. And extracting teeth is no longer dangerous. https://arizonadentalspecialists.com/the-surprising-history-of-extracting-teeth/ This tooth extractor was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Tooth extractor, dental surgical instrument. Metal with cross hatched pattern on handle. Stamped with maker's mark on hinge. Other stamps inside handles. Part of the W.R. Angus Collection.Stamped on hinge 'CASH & SONS ENGLAND'. Inside handles are 'C', 'P' and '27'.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, dental surgical instrument, tooth extractor -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Printmaking -Aquatint etching, 'Dog' by Geoffrey Ricardo, 1995
GEOFFREY RICARDO Born 1964, Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed limited edition print This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.art, artwork, geoffrey ricardo, printmaking, etching, aquatint -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionArtwork - bookplate, Geoffrey Ricardo, Ex Libris Geoffrey Ricardo, not dated
GEOFFREY RICARDO (1964- ) Born Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed bookplategeoffrey ricardo, bookplates, kangaroo -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, Geoffrey Ricardo, 'Monkeyshine' by Geoffrey Ricardo, 2000
GEOFFREY RICARDO (1964- ) Born Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed coloured aquatint on paper. Donated through the Australian Government's Cultural Gifts Programme by Katherine Littlewood.Under image in pencil ' T/P "Monkeyshine" Ricardo 2000'geoffrey ricardo, framed print -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, Geoffrey Ricardo, 'Dummy Throw' by Geoffrey Ricardo, 2000
GEOFFREY RICARDO (1964- ) Born 1964, Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed coloured aquatint on paperUnder image in pencil '4/20 "Dummy Throw" Ricardo 2000' geoffrey ricardo, framed print, printmaking, available, available framed, sport -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, Geoffrey Ricardo, 'Antelope' by Geoffrey Ricardo, 1997
GEOFFREY RICARDO (1964- ) Born Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed coloured aquatint on paperunder image in pencil 'G.P. Ricardo '97'geoffrey ricardo, framed print, printmaking -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, 'Personal Best' by Geoffrey Ricardo, 2000
GEOFFREY RICARDO (1964- ) Born Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed coloured etchingon paper. Donated through the Australian Government's Cultural Gifts Programme by Katherine Littlewood.Under image in pencil ' state proof ', "personal best" Ricardo 2000'. From Strange Games series. geoffrey ricardo, printmaking, framed print, available framed, available, sport -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, Geoffrey Ricardo, "The Urbane Heart" by Geoffrey Ricardo, 1999
GEOFFREY RICARDO (1964- ) Born Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed intaglio print from Geoffrey Ricardo's 'A Dark City, A Narrative' suite'. Donated through the Australian Government's Cultural Gifts Programme by Katherine Littlewood.Under image in pencil ' artists proof "The Urban Heart" Ricardo 99,geoffrey ricardo, printmaking, framed print, intaglio -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, Geoffrey Ricardo, 'Love Street' by Geoffrey Ricardo, 1999
GEOFFREY RICARDO Born 1964, Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed intaglio print from Geoffrey Ricardo's 'A Dark City, A Narrative' suite. Donated through the Australian Government's Cultural Gifts Programme by Katherine Littlewood.Under image in pencil '7/25 "Love street" Ricardo 99'geoffrey ricardo, printmaking, artworks, artist -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, Geoffrey Ricardo, Not known (Geoffrey Ricardo), 1997
GEOFFREY RICARDO (1964- ) Born Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Etching with aquatint on paper depicting a group of people pulling along a giant inflatable cow. Donated through the Australian Government's Cultural Gifts Programme by Katherine Littlewood.Lower left "State Proof" Lower right "Ricardo '97"geoffrey ricardo, printmaking, balloon, cow -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, Ricardo, Geoffrey, 'Veneer Deer' by Geoffrey Ricardo, 1997
GEOFFREY RICARDO (1964- ) Born Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed coloured aquatint.geoffrey ricardo, printmaking -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, Ricardo, Geoffrey, 'Lobster Chase' by Geoffrey Ricardo, 2000
GEOFFREY RICARDO (1964- ) Born Melbourne, Australia 1984-86 Bachelor of Arts (Fine Art), Printmaking, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1987-89 Printing Assistant at Bill Young Studios, Editioning intaglio prints, King Valley, VIC 1988 Full-time Studio Technician at Printmaking Department, Chisholm Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1989-90 Graduate Diploma (Fine Art), Printmaking, Monash University, Melbourne 1991 Traveled to England, France, Spain and USA (Winsor & Newton International Travelling Bursary, National Students Art Prize) Worked in private studios in Gaucin, Spain and New York, USA 1994-95 Master of Fine Arts, Monash University, Melbourne 1995 Guest Lecturer, Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne Traveled to Europe and America 1996 Guest Lecturer, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology, Melbourne 1990-98 Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne 1998 Traveled to America and Mexico 2001-05 Sessional Lecturer, The Victorian College of the Arts, Melbourne 2003-10 Printmaking Workshops, Warrnambool TAFE, Warrnambool, VIC 2004 Traveled to Europe, Mexico and Cuba 2005 Lecturer, National Art School (Summer School), Sydney Sessional Lecturer, Monash University, Melbourne Lecturer, Institution of Koorie Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC SOLO EXHIBITIONS 2012 ‘Collection of Works’ The Art Vault Mildura ‘Deeper Meanings’, The Incinerator Gallery, Melbourne ‘Three Projects’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney Melbourne Art Fair Stand F33, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 2009 ‘Anno Domino, Antarctica and The Anatomy Lesson’, Australian Galleries Derby Street, Melbourne The Art Vault, Mildura, VIC 2008 MV Orlova (Quark Expeditions), The Drake Passage, Antarctica 2007 ‘Herd’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney 2006 ‘Herd’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2004 ‘Recent work’, BMGArt, Adelaide 2003 ‘The Rapunzel Suite and Other New Works’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Recent Works’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Recent works’, Cowwarr Art Space, Cowwarr, VIC 2002 ‘The Rapunzel Suite’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Strange Games’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney 1999 ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘A Dark City Narrative’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne 1998 Cullity Gallery, School of Architecture and Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Delaney Gallery, Perth Chapman Gallery, Canberra BMGArt, Adelaide ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Menagerie’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1995 ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1994 Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth Graham Galleries + Editions, Brisbane ‘Wishful Thinking, Prints and Sculptures’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth 1992 ‘Prints, Sculptures and Watercolours’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney 1990 ‘Watercolours, Prints and Small Bronzes’, Australian Galleries, Sydney ‘Paintings, Prints and Sculptures’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne GROUP EXHIBITIONS 2013 ‘Sculpture by the Sea’ Cottlesloe, Western Australia 2012 ‘Brave New World’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Port Melbourne, VIC ‘Sculpture by the Sea’, Bondi, Sydney 2011 ‘Sculpture by the sea’, Aarhus, Denmark ‘Artwork to Tapestry’, Tarrawarra Museum of Art, Healesville, VIC Burnie Print Prize, Burnie Regional Gallery, Burnie, TAS ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Roylston Street, Sydney ‘large exhibition of small works’, Australian Galleries, Derby Street, Melbourne ‘Nature of the Mark’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Rick Amor Print Prize, Montsalvat, Eltham, VIC 2010 ‘Summer show’, Australian Galleries, Glenmore Road, Sydney ‘Summer stock show’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne ‘Sub10’, Substation, Melbourne ‘McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2010’, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘Artists’ Prints made with Integrity I’, Australian Galleries, Smith Street, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC 2009 ‘Artists’ ink: printmaking from the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, 1970-2001’, Ararat Regional Art Gallery, Ararat, VIC ‘Lorne Sculpture’ (Winner), Lorne, VIC 2008 ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Smith Street, Melbourne 2007 ARC Biennial (Art, Design and Craft), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane ‘Prints Tokyo: International Print Exhibition’, Tokyo, Japan Seoul International Print, Photo and Edition Works Art Fair, Seoul, Korea Guanlan International Print Biennial, Guanlan, China ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Antipodean Bestiary’, Project Space / Spare Room, RMIT University, Melbourne Montalto Sculpture Prize, Montalto Vineyard and Olive Grove, Red Hill South, VIC McClelland Sculpture Survey and Award 2007, McClelland Gallery + Sculpture Park, Langwarrin, VIC ‘2007: Works from the studio’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘50 - a print exchange portfolio’, Geelong Art Gallery, Geelong, VIC ‘Small Pleasures’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2006 ‘Partnership or perish’, Academy of the Arts, School of Visual and Performing Arts, University of Tasmania, Hobart Libris Awards, Artspace Mackay, Mackay, QLD ‘Summery’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Summer Stock Show’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Bookish’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne Melbourne Art Fair, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘50th Anniversary Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne 2005 ‘End of Year Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Works on Paper’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘Expansion’, Lancaster Press, Melbourne ‘The Art of Collaboration’, Singapore Tyler Print Institute, Singapore ‘Double take’, Arts Project Australia, Melbourne ‘Small Treasures - 20 emerging and established artists’, TILT Contemporary Art, Melbourne Jacques Cadry Memorial Art Prize, Fox Studios and State Library of NSW, Sydney ‘Tales of the City’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘A Decade of Collecting 1995-2005’, Cairns Regional Gallery, Cairns, QLD ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Surface Tension: 21 Contemporary Australian Printmakers’, University of Tasmania, Launceston, TAS ‘Neo-millenium’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne 2004 ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Group Exhibition’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Melbourne ‘Species’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Melbourne ‘In the presence of creatures great and small’, Australian Galleries Works on Paper, Sydney ‘Tapestries from the Victorian Tapestry Workshop’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Sculpture’, Australian Galleries Painting & Sculpture, Sydney ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, National Arts Club, New York, USA ‘Contemporary Australian Prints’, Gallery 101, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Australian Prints from the Collection’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney ‘Bridge’, Toyota Community Spirit Gallery, Melbourne ‘Vivid’, Fortyfive Downstairs, Melbourne Lake Gallery, Paynesville, VIC 2003 ‘Paper matters’, Lawrence Wilson Art Gallery, University of Western Australia, Perth ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Less is more’, BMGArt, Adelaide ‘The ink’s on me: Bill Young master printmaker’, Wangaratta Exhibitions Gallery, Wangaratta, VIC ‘Fantastic and Visionary Art’, Touring: Global Arts Link, QLD; Ipswich Regional Gallery, QLD ; Orange Regional Gallery, NSW; Manning Regional Gallery, NSW; Parramatta Heritage Centre, Sydney; Ballarat Regional Gallery, VIC 2002 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 2001 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Six Degrees of Collaboration’, RMIT Faculty of Art, Design and Communication Gallery, Melbourne ‘Reciprocal Moves’, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC International Print Triennial, Kanagawa, Japan ‘Fantastic Art’, Orange Regional Gallery, Orange, NSW ‘Dancing Made a Man out of Me’, The Switchback Gallery, Monash University, Gippsland, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Celebration’, Regional touring exhibition, VIC 2000-01 ‘Workings of the Mind: Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s’, Touring: Grafton Regional Gallery, NSW; Toowoomba Regional Art Gallery, QLD; Nolan Gallery, Canberra; Bendigo Art Gallery, VIC; PercTucker Regional Gallery, QLD 2000 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA The Hutchins Art Prize, Long Gallery, Hobart ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne 1999 Shell Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Space, Fremantle, WA ‘We are Australian’, George Adams Gallery, Victorian Arts Centre, Melbourne Rena Ellen Jones Memorial Print Award, Warrnambool Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC ‘National Works on Paper’, Mornington Peninsula Gallery, Mornington, VIC ‘Artists for Kids Culture’, Brightspace, Melbourne ‘Pleasure’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne 1998-99 ‘Australian Prints’, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney 1997 ‘KNOCK, KNOCK’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Woven Colour, The Art of Tapestry’, Dr Earl Lu Gallery, Singapore 1996 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Academy of Art & Culture, Calcutta, India ‘Synergy’, Touring: Lalit Kala Akademi, New Dehli, India; Jehangir Nicholson Gallery, Bombay, India; Birla, India ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Frederikshavn Kunstmuseum, Denmark; Australia House, London, UK 1995 ‘Interweave - Tapestry A Collaborative Art’, Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne ‘Contemporary Printmakers’, La Trobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC ‘Contemporary Australian Tapestry’, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Circus Capers’, Caulfield Arts Complex, Melbourne 1994 M.P.A.C. Print Award, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA Australian Universities of Visual Art, Australian High Commission, Singapore ‘Prints, Paintings and Sculpture’, BMGArt, Adelaide Fourth Australian Contemporary Art Fair, Royal Exhibition Building, Melbourne 1993 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA 1992 Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Transitional Times’, Print Council of Australia, Melbourne ‘Second Kochi International Triennial Exhibition of Prints’, Japan 1991 Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA ‘Table Top Sculpture’, Australian Galleries, Melbourne ‘Art 91’, London Contemporary Art Fair, London, UK 1990 M.P.A.C. Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Fremantle Print Prize, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle WA ‘The Christmas Show’, Intaglio Printmaker, London, England ‘Australian Contemporary Art’, AZ Gallery, Tokyo, Japan 1989 National Student Art Prize, Mitchell College, Bathurst, NSW Fremantle Print Award, Fremantle Arts Centre, Fremantle, WA City of Doncaster Acquisitive Print Prize, Manningham Gallery, Melbourne ‘Affiliations’, Monash University Gallery, Melbourne 1988 M.P.A.C. Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula Arts Centre, Mornington, VIC Henry Worland Memorial Print Prize, Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC 1987 ‘The Comedy Show’, Print Guild, Melbourne ‘Fluxus Art Flow’, Melbourne 1986 Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Acquisitive Print Prize, Mornington Peninsula, VIC Chisolm Institute of Technology, Graduating Students exhibition, Melbourne AWARDS 2013 King Valley Art Prize (printmaking) 2009 Lorne Sculpture Exhibition (Winner), Lorne, VIC 1989 Windsor and Newton International Travelling Bursary, UK Linbrook International First Prize for Printmaking, Australia COMMISSIONS 2005 Tapestry design for Bairnsdale Hospital (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Bairnsdale, VIC 1999 Tapestry design ‘Emblem’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1995 ‘A Night of Infectious Laughter’ Poster, St Kilda Festival, Melbourne 1994 Tapestry design ‘Elephant Gingham’ (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Australia 1993 Tapestry design for the Festival of Perth Official Poster (woven by the Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne), Perth RESIDENCIES & PROJECTS 2013 ‘Come In Outside’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool 2011 Mildura Wentworth Arts Festival Project, Mildura, VIC Residency, The Art Vault , Mildura, VIC 2010 ‘Wish’, Collaboration set design for Pocketfool, Artplay, Melbourne The Art Vault (included continuous public flag making workshops which were flown as part of The Wentworth Mildura Art Festival), Mildura, VIC 2009 The Art Vault (included two public printmaking workshops), Mildura, VIC 2008 Artist in residence, MV Orlova, Quark Expeditions, Antarctica 2003 Residency, Bairnsdale Regional Health Service, Bairnsdale, VIC 1998 Residency, School of Architecture & Fine Art, University of Western Australia, Perth 1997 Residency, La Salle/Fia, College of the Arts, Singapore 1996 Artist in residence, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, Melbourne 1993 Reduction Aquatint Workshop & Residency, Graphic Investigation Department, Canberra School of Art, Canberra NB: all residencies have included workshops involving students, children or the general public COLLECTIONS Artbank, Sydney Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Canson Australia Pty Ltd, Australia City of Box Hill, Melbourne City of Whitehorse, Melbourne Downlands College, Toowoomba, QLD Geelong Grammar School, Geelong, VIC Gold Coast City Art Gallery, Gold Coast, QLD Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD Helensvale High School, Brisbane Holmes à Court Collection, Perth Latrobe Regional Gallery, Morwell, VIC Monash University, Melbourne Mornington Peninsula Arts Council Collection, Mornington, VIC National Gallery of Australia, Canberra National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Parliament House Art Collection, Canberra Print Council of Australia, Melbourne Private collections in Australia, Switzerland, USA, UK, Singapore, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, Holland Queen Victoria Museum & Art Gallery, Launceston, TAS Queensland Art Gallery, Brisbane Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Shire of Diamond Valley, Diamond Valley, VIC Star of the Sea College, Melbourne The Melbourne Club, Melbourne University of Central Queensland, Brisbane University of Technology, Sydney Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, Wagga Wagga, NSW Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery, Warrnambool, VIC BIBLIOGRAPHY PERIODICALS AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 4, July-August 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol. 70, Issue 6, November-December 1998 AQ Journal of Contemporary Analysis, Vol.71, Issue 7, April 1999 Backhouse, Megan; “Going out of print and back to basics”, The Age, February 2003 Bellamy, Louise; “Renaissance of Western Art”, The Age (A2 section), 26 November 2005 Clabburn, Anna; “Fables and Foibles”, Art Monthly, September 1994 Dutkiewicz, Adam; “Edge of the sublime”, Advertiser, 1 December 2003, p. 76. Erickson, Dorothy; “The Festival that could have been”, The Bulletin, March 1994 Farmer, Alison; “Ricardo makes poster splash”, Sunday Times - Entertainment Extra, 19 September 1993 “Festival taps weaver’s art”, The West Australian, 11February 1994 Fiasco (web-page), March 2003 Jenkins, John; “A Dark City Narrative”, Imprint, Vol. 34, No. 4, 1999 Grishin, Sasha; “Multiplicity – collecting Australian prints”, Australian Art Review, Issue 13, March-June 2007, pp. 52-55 Grishin, Sasha; “Profiles in Print - Geoffrey Ricardo”, Craft Arts International, Issue 76, 2009, pp.1-4 Lloyd, Tim; “The elephant man”, The Advertiser (Review section), December 2007 Manzana Arné, Josep; “De L’Ex-Libris a L’Ex-Webis: Ex-Libris a Internet”, Ex-Libris, Associació Catalana D’Exlibristes, Barcelona, No. 27, July-December 2002, p.11 McDonald, John; “Dreams of hope and menace” The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 1995 McMillan, Peter; “Darkness visible”, The Age, 11September 1999 Nelson, Robert; “Circuses can be curated, but not cured”, The Age, 18 January 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Dream Weavers”, The Age, June 1995 Nelson, Robert; “Paen To Ricardo”, Imprint, Vol. 29, No.1, April, 1994 Nelson, Robert; “Revealed: Mother Nature’s vulgar past”, The Age, September 6, 2000 Nelson, Robert; “Riddled with hidden meaning”, The Age, September 8, 1999 Quadrant, April, 1995 Quadrant, Jan/Feb, 1995 Quadrant, October, 1995 Quadrant, November, 1994 “Ricardo’s surreal works at gallery”, Times-Spectator, 25 July 2003, p.7 Snell, Ted; “Art”, The Australian, 18 February1994 Snell, Ted; “Visual arts at the Festival of Perth”, Art Monthly, April 1994 Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Timms, Peter; “Geoff Ricardo: emerging from darkness”, Art Monthly, Issue 140, June 2001 Wallace, Dr Carmel; “Ways of seeing Australia”, Asian Art News, May/June 2004 BOOKS & CATALOGUES A Dark City Narrative, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 1999 ARC Biennial Exhibition (Exhibition catalogue), Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, 2007, pp. 78-79 Clabburn, Anna; “The Collaborative Spirit”, Australian Tapestries: Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 1995, p. 37 Fantastic Art, Orange Regional Gallery, NSW, 2001 Field, Caroline; Herd, catalogue essay, Australian Galleries, Sydney, 2007 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Identities in Printmaking, Wagga Wagga Regional Art Gallery, 2000 Grishin, Sasha; Australian Printmaking in the 1990’s, Craftsman House, 1997 Havighurst, Sophie (Illustrations by Geoffrey Ricardo); When Lester lost his cool, The University of Melbourne, 2007 Kolenberg, Hendrik & Ryan, Anne; Australian Prints, Art Gallery of New South Wales, 1998 Lawrence, Michel; Framed; photographs of Australian Artists, 1998 Modern Australian Tapestries, Victorian Tapestry Workshop, 2000 The Rapunzel Suite, Australian Galleries, Melbourne, 2002 Wallace, Dr Carmel (Essay); Surface Tension, Twenty One Contemporary Australian Printmakers, Gallery 101, Melbourne, 2004 Workings of the Mind : Melbourne Prints of the 1960s to the 1990s, Queensland University of Technology Art Museum, Brisbane, 2000 TELEVISION Sunday Arts, ABC TV, 6 May 2007 Inside Art TV, Channel 31, July 2012Framed coloured etching.geoffrey ricardo, printmaking, available, lobster
