Showing 72 items
matching victorian gold fields
-
 Federation University Herbarium
Federation University HerbariumPlant specimen, Alexander Clifford Beauglehole, Acacia acinacea Lindl, 25/10/1978
Cliff Beauglehole was an orchardist at Portland, Victoria, who throughout hislife took an intense interest in the plants of Victoria. Over his lifetime he collected 90,000 plant specimens as part of a comprehensive study of Victoria's plants and wrote thirteen books under the heading The Distribution and Conservation of Vascular Plants in Victoria, each written to cover the 13 study areas of the Victorian and Conservation Council.A mounted botanical specimen.beauglehole herbarium, herbarium specimen, botany, herbarium, plant science, plant specimen, field naturalists' club ballarat, federation university herbarium, acacia acinacea, fabaceae, gold-dust wattle -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncDomestic object - Kerosene Lantern
During the Victorian goldrushes of the 1850s thousands of Chinese migrants arrived to seek their fortunes. At that time many came to the lucrative gold fields of Northeast Victoria. After the Gold rush, many Chinese migrants returned home. However, a number settled in the area as merchants, hawkers and market gardeners in surrounding towns including Wodonga, the Ovens, King, Buffalo River and Kiewa Valleys. They also rented lands and established themselves in the hops and tobacco farming industries. Items of Chinese origin made their way into many households. Importation of Chinese mass produced items such as this lantern continued well into the 20th century and were common domestic items across Australia before households were connected to electricity.This item is representation of kerosene / paraffin lamps used throughout Australia to provide lighting inside and outdoors prior to the widespread availability of electricity.A small hurricane lamp with a rounded tank and small carry handle attached to the top. A larger handle is also attached at the top of the frame. It has a lever to open the glass tank. It has a metal base which is filled with kerosene. It has a screw knob to open the kerosene receptacle. The metal hood also has vents. The Chinese characters around the base translate to "Shanghai Guanghuaheng".Around base : Chinese characters. On top : "Made in China KWANG HWA"kerosene lamp, domestic appliances, chinese artefacts -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Chinese Ceramic Spoons
During the Victorian goldrushes of the 1850s thousands of Chinese migrants arrived to seek their fortunes. At that time many came to the lucrative gold fields of Northeast Victoria. After the Gold rush, many Chinese migrants returned home. However, a number settled in the area as merchants, hawkers and market gardeners in surrounding towns including Wodonga, the Ovens, King, Buffalo River and Kiewa Valleys. They also rented lands and established themselves in the hops and tobacco farming industries. These spoons were found by Mr Robert Black when he was ploughing a paddock on his farm in Kergunyah, Victoria in the 1930s.2 small ceramic Chinese spoons. Spoon 1 has a clear light green glaze. Spoon 2 is decorated with a blue painted pattern.chinese immigration to victoria, chinese market gardens, chinese migration northeast victoria -
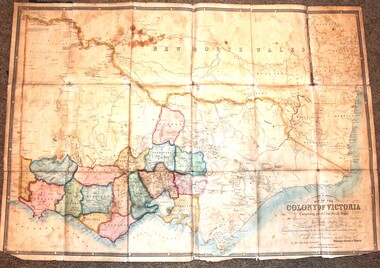 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncMap - Tulloch & Brown's Map of the Colony of Victoria, Tulloch & Brown, 1856
The map was created by Tulloch and Brown. David Tulloch was one of the earliest engravers and lithographers in the state of Victoria. He arrived in Melbourne from Greenock, Scotland, on 3 January 1849. Following the discovery of gold Tulloch went to the Victorian goldfields in 1851, commissioned to make sketches of the diggers and the diggings for Ham’s Illustrated Australian Magazine. In November 1852 Tulloch set up in business as engraver, draughtsman, copperplate printer and lithographer. Tulloch took a map engraver, James Davie Brown, into partnership in March 1853; the several maps and specimens of commercial engraving they showed at the 1854 Melbourne Exhibition were awarded a bronze medal. That year Tulloch and Brown also received a silver medal at the Victorian Industrial Exhibition. The partnership was dissolved towards the end of 1856.This is a very early map of the Colony of Victoria including Belvoir (now know as Wodonga).A foldable map mounted on linen and with a board cover. It records the Colony of Victoria according to Surveyor's Records revised in 1857. Areas of the map are shaded to highlight different counties.At bottom right hand section of map: Tulloch & Brown's map of the Colony of Victoria : comprising part of New South Wales, the boundaries, counties, also seaport & inland townships, the gold fields with the latest discoveries, roads, tracks, &c. &c. / compiled from drawings in the Survey Office and correctly revised till 1857. Respectfully dedicated by Permission, to the Honorable Captain Andrew Clarke R.E. Surveyor General of Victoria by His Obediant Servants Tulloch & Brown, Engravers & Publishers, Melbourne". At bottom right below border : Published as the Act directs by the Proprietors, Melbourne, 1st Feb. 1856. tulloch and brown maps, rare maps victoria, victorian cartography -
 Buda Historic Home & Garden Castlemaine
Buda Historic Home & Garden CastlemainePhotograph, c1858 - 1860
... around 1855 and made from gold found on the Victorian fields... around 1855 and made from gold found on the Victorian fields ...Gold and Redgum Inkstand made by Ernest Leviny, c1855-1858. Presented to Mr J.V.A. Bruce, contractor for the Melbourne and Murray Railway by the workmen, at Woodend on Monday 8th July 1861. This gold inkstand was Leviny's first major masterpiece commenced around 1855 and made from gold found on the Victorian fields. It featured four gold nuggets representing the Southern Cross from the goldfields of Ballarat, Bendigo Maryborough and Castlemaine. It was exhibited in Melbourne in 1858, and again in 1861 where it was awarded a 1st Class Certificate at the Victorian Exhibition in Melbourne. In 1862 it was exhibited at the London International Exhibition where it attracted a great deal of attention and was published in The Art Journal Illustrated Catalogue accompanying the exhibition. The whereabouts of the Inkstand is currently unknown.Matt, albumen print, mounted on lightweight card backing. Albumen photograph of a gold and redgum inkstand. Elaborate inkstand highly decorated with cast figures. Mounted on a redgum base.Stamp embossed on upper left corner. Crown in a circle with the words Bristol Paper. Handwritten in ink under image. "Gold inkstand presented at the opening of the Railway, designed by the late Ernest Leviny Esq. October 13th 1862. Made of almost pure gold and cost £700".inkstand, ornament, gold, goldsmithing, london exhibition 1862, melbourne and murray railway, photograph, woodend, 8 july 1861, mr j. v. a. bruce -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - Geological survey of Bendigo Goldfields
Three Geological survey maps of the Bendigo Gold Fields joined together. The three sections are Eaglehawk, Golden Square and Spring Gully. It shows geological conditions, gold reef lines and mine sights. Three sections are laminated together. The maps were produced by the Victorian Department of Manufacturing and Industry Development geological survey, bendigo gold fields -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - RESEARCH PAPERS: THE INIMITABLE CHARLES THATCHER, 2002
Charles Robert Thatcher (1831-1878) trained in England as a flautist before travelling to the Bendigo goldfields in 1853. He was unsuited and unsuccessful as a miner so decided to rely on his music to make his fortune. He was considered a 'comic vocalist' who wrote many songs about the observations he made on the goldfields. These songs were often satirical and were published in newspapers as poems. He travelled extensively around the Victorian goldfields and also toured New Zealand. In 1861 he married widowed singer Anna Vitellie who performed with him, singing sentimental ballads. In 1870 the family returned to England where Charles became an importer of curios, following in his father's footsteps. He travelled to China, Japan and India sourcing stock for his business and on one such trip he contracted cholera and died in Shanghai. His wife returned to Australia and taught singing in Moonee Ponds.A talk written by Jim Evans for the Bendigo Historical Society in September 2002 regarding the gold field entertainer Charles Robert Thatcher and his many chaotic adventures and performances across Bendigo and Australia. -
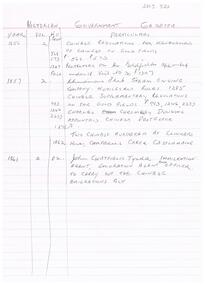 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MCCOLL, RANKIN AND STANISTREET COLLECTION: NOTES RE GOVERNMENT GAZETTES AND LIST OF PLANT
Two page, handwritten document on lined paper - front page reference to Victorian Government Gazettes and Chinese regulations, where listed in the gazettes and dates. Includes Chinese regulations for management of Chinese on Gold fields (1856) , Chinamans Flat Steam Engine company (1857), two Chinese murdered at Clinkers Hill, Castlemaine (1862) Charles Chromley Dowling appointed Chinese Protector (1857), John Chatfield Tyler Immigration agent, to carry out the Chinese Emigrations Act (1861) Back page dated 1947 lists "stocktake list of plant" On list - Deborah United 1946; North Hustlers; New Monument GMC, North Virginia, South Wattle Gully, Central Napoleon, Red, White and Blue Extended, Deborah Extended, New Don, East Clarence, Napoleon Reef, New Monument Battery, Deborah Extended. Possibly written by Albert Richardson.bendigo, mining, mccoll rankin & stanistreet -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPhotograph, ca1861
When Richard Daintree rejoined the Victorian Geological Survey as a field surveyor in January 1859, he pioneered the use of photography in field-work. The glass plates attributed to him by the State Library of Victoria show four images of the mines in Clunes, Victoria, Australia in the 1860'sBlack and white reproduction of Port Phillip Colonial & Gold Mining Co., Clunes, Victoria, Australia in a light wood timber frameOn Reverse: Handwritten in pencil Port Phillip Co. 1860's Nettleton Photography glass plate Latrobe Libraryport phillip and colonial gold mining co., richard daintree -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumBook, Fred Cahir, BLACK GOLD - ABORIGINAL PEOPLE ON THE GOLD FIELDS OF VICTORIA 1850-1870, 2012
Fred Cahir tells the story about the magnitude of Aboriginal involvement on the Victorian goldfields in the middle of the nineteenth century. The first history of Aboriginal–white interaction on the Victorian goldfields, Black Gold offers new insights on one of the great epochs in Australian and world history—the gold story. In vivid detail it describes how Aboriginal people often figured significantly in the search for gold and documents the devastating social impact of gold mining on Victorian Aboriginal communities. It reveals the complexity of their involvement from passive presence, to active discovery, to shunning the goldfields. This detailed examination of Aboriginal people on the goldfields of Victoria provides striking evidence which demonstrates that Aboriginal people participated in gold mining and interacted with non-Aboriginal people in a range of hitherto neglected ways. Running through this book are themes of Aboriginal empowerment, identity, integration, resistance, social disruption and communication. For more information on Aboriginal History Inc. please visit aboriginalhistory.org.au.BOUND FOLDER, BLACK CARDBOARD COVER 152 PAGESnon-fictionFred Cahir tells the story about the magnitude of Aboriginal involvement on the Victorian goldfields in the middle of the nineteenth century. The first history of Aboriginal–white interaction on the Victorian goldfields, Black Gold offers new insights on one of the great epochs in Australian and world history—the gold story. In vivid detail it describes how Aboriginal people often figured significantly in the search for gold and documents the devastating social impact of gold mining on Victorian Aboriginal communities. It reveals the complexity of their involvement from passive presence, to active discovery, to shunning the goldfields. This detailed examination of Aboriginal people on the goldfields of Victoria provides striking evidence which demonstrates that Aboriginal people participated in gold mining and interacted with non-Aboriginal people in a range of hitherto neglected ways. Running through this book are themes of Aboriginal empowerment, identity, integration, resistance, social disruption and communication. For more information on Aboriginal History Inc. please visit aboriginalhistory.org.au.first nations history, australia's victorian goldfields -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
... beechworth gold fields gold rush victorian gold rush gold ming ...This image is a reproduction of an 1899 original depicting the 'Williams Good Luck Mine' on the Mopoke Reef (also called 'Morepork Gully') in the Dingle Ranges, approximately three miles from Beechworth. A large opening to a mine can be seen behind the men in the photograph, with a wheeled cart on a track leading to the men's position, where the soil and rocks have been hauled away. This photograph interestingly contains dogs alongside the miners. While dogs have been recorded as deterrents to thieves in the Victorian goldfields, these dogs appear as companions to these men. Following the discovery of gold at Beechworth in 1852, rushes quickly followed at surrounding creeks and gullies in the district. In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, small syndicates of miners continued to work old or abandoned quartz reefs, often persisting without the assistance of heavy machinery to remove the large amounts of rock, in order to obtain yields at ever greater depths. The group of miners in this photograph are Mr. Roger Williams and Sons, who revived operations at the ‘Old Good Luck’ mine on the Mopoke Reef in the Dingle Range near Beechworth around 1892, working the site for more than two decades. An emigrant from Cornwall with experience in the tin mining industry, 19 year old Roger Williams senior sailed to New Zealand in 1840, then to Australia where he spent time in the Bendigo Gold Fields before settling in Beechworth in the early 1860s. Mr Williams senior worked on various mining activities in the district, including the Rocky Mountain Tunnel project. Conversant with the character of gold-bearing reefs in the area, the syndicate dug an eight hundred foot tunnel, digging down as far down as two hundred feet with little capital save their labour, to connect and provide better working access to the mass of reefs and veins in the vicinity. Progress was hampered by poor air quality charged with fumes from dynamite and large quantities of rock had to be crushed to obtain payable yields. The Victorian Goldfields are filled with ruins and remnants of the area's rich mining history, ranging from small alluvial diggings to the remains of huge mining companies. Site names often changed several times throughout the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Some sites were abandoned and forgotten, others were worked continuously over many decades. The names of mines were often repeated at different locations throughout the Victorian Goldfields. For example, there is a Mopoke Gully heritage mine near Fryers Creek, Victoria. 'Mopoke' is a common onomatopoeic name for Morepork and Australian Boobook owls.This image has historical, social and research significance for patterns of emigration during of the Victorian Gold Rush, and the historical, social and environmental impacts of mining at Beechworth at the turn of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. As gold became scarce and government support and large company investment waned, poor hard-working miners laboured intensively to make a living through periods of high unemployment. This image can be compared and studied alongside other historical mining photographs and objects in the Burke Museum Collection. It has potential to improve our understanding of miners working conditions and the shifting character of mining in the Beechworth district.Sepia coloured rectangular photograph printed on gloss photographic paper mounted on card. Obverse: Williams/ Good/ Luck Reverse: A02498/ 1997. 2498/ Good Luck/ Mine/ 1899/ Mopoke. burke museum, beechworth museum, beechworth, gold fields, gold rush, victorian gold rush, gold ming history, colonial australia, australian gold rushes, mining technology, beechworth historic district, indigo gold trail, migration, indigo shire, good luck gold mine, victorian goldfields, mining syndicates, gold fever, quartz-mining, small-scale mining, old good luck mine, mopoke gully, quartz reefs beechworth -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
... beechworth gold fields gold rush victorian gold rush gold ming ...This image is a reproduction of an 1899 original depicting the 'Williams Good Luck Mine' on the Mopoke Reef (also called 'Morepork Gully') in the Dingle Ranges, approximately three miles from Beechworth. The foreground of the image is littered with piles of smashed rock and detritus, known as ‘mullock’, beside a reinforced mine shaft, a vertical access passageway allowing miners to enter the mine and haul ore out using lifting technology such as a poppet heads, whims or windlasses. A group of miners and a dog appear close to an open-sided miner’s hut. Following the discovery of gold at Beechworth in 1852, rushes quickly followed at surrounding creeks and gullies in the district. In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, small syndicates of miners continued to work old or abandoned quartz reefs, often persisting without the assistance of heavy machinery to remove the large amounts of rock, in order to obtain yields at ever greater depths. The group of miners in this photograph are Mr. Roger Williams and Sons, who revived operations at the ‘Old Good Luck’ mine on the Mopoke Reef in the Dingle Range near Beechworth around 1892, working the site for more than two decades. An emigrant from Cornwall with experience in the tin mining industry, 19 year old Roger Williams senior sailed to New Zealand in 1840, then to Australia where he spent time in the Bendigo Gold Fields before settling in Beechworth in the early 1860s. Mr Williams senior worked on various mining activities in the district, including the Rocky Mountain Tunnel project. Conversant with the character of gold-bearing reefs in the area, the syndicate dug an eight hundred foot tunnel, digging down as far down as two hundred feet with little capital save their labour, to connect and provide better working access to the mass of reefs and veins in the vicinity. Progress was hampered by poor air quality charged with fumes from dynamite and large quantities of rock had to be crushed to obtain payable yields. The Victorian Goldfields are filled with ruins and remnants of the area's rich mining history, ranging from small alluvial diggings to the remains of huge mining companies. Site names often changed several times throughout the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Some sites were abandoned and forgotten, others were worked continuously over many decades. The names of mines were often repeated at different locations throughout the Victorian Goldfields. For example, there is a Mopoke Gully heritage mine near Fryers Creek, Victoria. 'Mopoke' is a common onomatopoeic name for Morepork and Australian Boobook owls.This image has historical, social and research significance for patterns of emigration during of the Victorian Gold Rush, and the historical, social and environmental impacts of mining at Beechworth at the turn of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. As gold became scarce and government support and large company investment waned, poor hard-working miners laboured intensively to make a living through periods of high unemployment. This image can be compared and studied alongside other historical mining photographs and objects in the Burke Museum Collection. It has potential to improve our understanding of miners working conditions and the shifting character of mining in the Beechworth district.Sepia coloured rectangular photograph printed on gloss photographic paper mounted on card.Obverse: Reverse: A02497/ 1997.2497/ 'Good/ Luck/ Mine'/ Morepork/ Gully/ Mrs Joyce/ Bright/ Tunnel/ 800 ft/ 1899. burke museum, beechworth museum, beechworth, gold fields, gold rush, victorian gold rush, gold ming history, colonial australia, australian gold rushes, mining technology, beechworth historic district, indigo gold trail, migration, indigo shire, good luck gold mine, victorian goldfields, mining syndicates, gold fever, quartz-mining, small-scale mining, old good luck mine, mopoke gully, quartz reefs beechworth
