Showing 1379 items
matching iron ship
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Spoon, circa 1878
... square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7... square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7 ...This tea spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This teaspoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The following descriptions of maker’s marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. 1. A recessed Crown containing a raised Diamond outline and the initials “W” and “P” (the recognised trademark of William Page & Co) 2. An impressed Ellipse containing a raised, pivoted, Triangle in its lower part and bearing a Resurrection Cross on its upper section (a possible dissenting church symbol reflecting religious affiliation); OR a rounded Square impression containing a raised, ‘lazy’, letter “B” (possibly mimicking sterling silver hallmark signifying city of manufacture i.e. Birmingham) 3. An impressed rounded Square filled with a raised Maltese Cross (the base metal composite of nickel silver was also known as ‘German silver’ after its Berlin inventors in 1823) 4. A recessed Circle containing a Crab or Scarab Beetle image; OR a recessed Circle containing a rotated ‘fleur de lys’ or ‘fasces’ design 5. A depressed Diamond shape enclosing a large raised letter “R” and a small raised letter “D” (mimicking the U.K. Patent Office stamp which abbreviated the term ‘registered’ to “RD”, but also included date and class of patent) Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored tea spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and elongated bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. Only 15% of original electroplating remains with verdigris on 5% of spoon surface. Outlines of five makers marks are visible but details are obscured.flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, nickel silver, william page & co, birmingham, brass plating, makers marks -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSpoon, circa 1878
... square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7... square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7 ...This tea spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This teaspoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The following descriptions of maker’s marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. 1. A recessed Crown containing a raised Diamond outline and the initials “W” and “P” (the recognised trademark of William Page & Co) 2. An impressed Ellipse containing a raised, pivoted, Triangle in its lower part and bearing a Resurrection Cross on its upper section (a possible dissenting church symbol reflecting religious affiliation); OR a rounded Square impression containing a raised, ‘lazy’, letter “B” (possibly mimicking sterling silver hallmark signifying city of manufacture i.e. Birmingham) 3. An impressed rounded Square filled with a raised Maltese Cross (the base metal composite of nickel silver was also known as ‘German silver’ after its Berlin inventors in 1823) 4. A recessed Circle containing a Crab or Scarab Beetle image; OR a recessed Circle containing a rotated ‘fleur de lys’ or ‘fasces’ design 5. A depressed Diamond shape enclosing a large raised letter “R” and a small raised letter “D” (mimicking the U.K. Patent Office stamp which abbreviated the term ‘registered’ to “RD”, but also included date and class of patent) Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored tea spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and elongated bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. Only 10% of original electroplating remains as a dull bronze colour. Outlines of five makers marks are visible.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, nickel silver, william page & co, birmingham, brass plating, makers marks -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSpoon, circa 1878
... square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7... square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7 ...This tea spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This teaspoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The following descriptions of maker’s marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. 1. A recessed Crown containing a raised Diamond outline and the initials “W” and “P” (the recognised trademark of William Page & Co) 2. An impressed Ellipse containing a raised, pivoted, Triangle in its lower part and bearing a Resurrection Cross on its upper section (a possible dissenting church symbol reflecting religious affiliation); OR a rounded Square impression containing a raised, ‘lazy’, letter “B” (possibly mimicking sterling silver hallmark signifying city of manufacture i.e. Birmingham) 3. An impressed rounded Square filled with a raised Maltese Cross (the base metal composite of nickel silver was also known as ‘German silver’ after its Berlin inventors in 1823) 4. A recessed Circle containing a Crab or Scarab Beetle image; OR a recessed Circle containing a rotated ‘fleur de lys’ or ‘fasces’ design 5. A depressed Diamond shape enclosing a large raised letter “R” and a small raised letter “D” (mimicking the U.K. Patent Office stamp which abbreviated the term ‘registered’ to “RD”, but also included date and class of patent) Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored tea spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and elongated bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. 50% of original electroplating remains. Two of five makers marks are legible: (1) Trade Mark (4) Crab Designflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, nickel silver, william page & co, birmingham, brass plating, makers marks -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGeological specimen - Slate, c. 1886
... . Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts.... Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts ...This rectangular slate of 'beautiful, unusual, expensive, green' American roof tile was amongst tiles recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. Salvaging began in 1974 by volunteer divers, using local cray-fishing boats. An efficient system was devised that enabled the recovery of up to 4,000 of the still neatly packed slates a day. Many of 22,000 salvaged slates can be seen on roofs of eight buildings in the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The sought-after slate doesn't need any special treatment before use. Some of the slates have slight red staining that comes from over 70 years in the wrecked vessel's rusting hull. The four-mast iron barque 'Falls of Halladale' left New York in August 1908 and, due to a navigational error, floundered off the rocks at Peterborough, Victoria, in the following November. None of the 29 lives on board were lost. Crowds gathered for months to watch the tall ship slowly break up. The green American slates were carried on board as ballast. As well as over 56,000 of the American slates, the large cargo on the Falls of Halladale included benzine, costly timber, rolls of printing paper, coils of barbed wire, thousands of metal bolts, hardware items, tableware, American walnut desks and medicine. Some of the cargo was later recovered. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roof tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roof tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. This slate tile is significant for its connection with the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Unusual beautiful green American slate, rectangular shape, recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, green american roofing slate tile, roof tiles, slate, slate roof tiles, falls of halladale shipwreck, shipwreck cargo, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard - Local Postcards, Joseph Jordan Photographic Studio, Nov 1908 - early 1909
... ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft... ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft ...ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough southwest Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today in the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. These 5 postcards have photographic images taken while the Falls of Halladale was stuck on the reef near Peterborough. They are not stamped or dated but four of the images show the ship still in fairly good condition with her stern very low in the water so can be dated to around late November 1908 to January 1909 and the fifth image shows the ship beginning to disintegrate soon after. The image on Postcard 8658.3 was taken by Joseph Jordan (a well-known Warrnambool photographer who had his own studio in Liebig Street, Warrnambool). The other four images were supposedly taken by the sender (Bob) and converted to postcards. Amateur photography in Australia in the early 1900's was becoming very popular (and accessible) to the average person. Many newspapers published advertisements and articles about photography and photographic supplies. In 1903 in America, George Eastman designed and marketed the "Model 3A Folding Pocket Kodak" which used postcard-size negatives and provided the average person with a camera with which to make real photo postcards. As they became popular, George Eastman was able to develop and market a wide range of supplies for the amateur photographer to develop and print their own photographs onto a postcard backing at home. Four of the postcards were addressed to "Miss M. Kerr, Leura, Camperdown". Mary Agnes Kerr (1888 - 1943) was the daughter of William and Mary Ann Kerr (nee Spence) who owned "Leura Farm" at Camperdown. Mary Agnes Kerr went on to marry James Young Caldwell (a local tailor and mercer) in 1917. James Yong Caldwell came to Camperdown around 1908 and was employed as a draper. The postcards were signed "Bob". On postcard 5658.2 he has written his name with quotation marks around it - suggesting "Bob" is a nickname. He writes about the weather, meeting a friend, sending fish to Mary Agnes' family and the cargo expected to be washed up on the beach. On postcard 8658.4 he wrote about being busy after the wreck and supplying the shipwrecked crew with boots and pants which suggests "Bob" may be James Caldwell (the mercer and tailor).The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). These postcards are significant as examples of the continued interest the locals around the district of Peterborough showed towards the Falls of Halladale wreck and its disintegration during the next few months. Four of the postcards are also significant examples of the new hobby of photography that was available to the average person during the beginning of the 20th century.Set of 5 postcards showing different images of the Falls of Halladale sailing ship after it became stuck on a reef near Peterborough. None of the postcards are dated or stamped. Postcard 8658.1 has a sepia toned image of the Falls of Halladale, with its stern sitting very low in the water. It has many of its sails unfurled and there is a rocky headland in the foreground. A very small figure appears to be on the edge of the cliff. The back of the postcard has a handwritten message addressed to "Miss M Kerr, Leura, Camperdown" and is signed "Love Bob". Postcard 8658.2 has a sepia image of the Falls of Halladale taken some months after it had been stuck on the reef. Its sails are missing and only two broken masts remain. A large rock is visible in the front right hand side of the photo. There is a handwritten message on the back signed by "Bob". Postcard 8658.3 has a black and white image of the Falls of Halladale showing her almost side on with her stern very low in the water and still in full sail. The words "Falls of Halladale. No 1" are printed on the lower left side of the image. The back is labelled "Jordan Series". There is no message written on the back. Postcard 8658.4 has a sepia toned image of the Falls of Halladale facing two rocky headlands. She is showing full sail and the sea appears calm. There is a handwritten note on the back addressed to "Miss M Kerr" from "Bob". Postcard 8658.5 has a sepia image of a side view of the Falls of Halladale with her stern very low in the water and her sails are all up. The sea is calm and a rocky reef can be seen in the foreground. It has a handwritten note on the back from "Bob" to "Miss M Kerr" of Leura, Camperdown.Back of postcard 8658.1- "POST" "EMPIRE" "CARD" "FOR CORRESPONDENCE" "FOR ADDRESS ONLY" "STAMP" "Miss M Kerr / Leura / Camperdown" "Looking forward to letter today" "Hope fish arrived / allright. Don't / know for sure / what day I will / be going to Town / to buy. Some day / this week / Love Bob Back of postcard 8658.2 - "POST CARD"/ "CORRESPONDENCE" "ADDRESS ONLY" "93"/ "Friday / This is a contrast to the first/ I sent you. Having glorious weather / Saw Saw (Saul)? on Thursday at Peterborough / He is having a grand holiday / Expecting letter on /Tuesday Fondest Love / "Bob" Front of postcard 8658.3 - "Falls of Halladale. No 1" Back of postcard 8658.3 -"Post" "Card"/ Printed in Great Britain" /"This space may be used for Communication" "The Address to be written / here" "Jordan Series" Back of postcard 8658.4 -"POST" "EMPIRE" "CARD"/ "FOR CORRESPONDENCE" "FOR ADDRESS ONLY" / "STAMP" "Miss M Kerr/ Leura / Camperdown"/ "We are/ very busy. The / wreck is about / 11/2 other side of / Peterborough./ Fondest Love, Bob "Had to supply sailors with Boots Pants etc/ 25 pairs Boots, good order ah!" Back of postcard 8658.5 - "POST" "EMPIRE" "CARD" / "FOR CORRESPONDENCE" "FOR ADDRESS ONLY" / "STAMP"/ "Miss M Kerr / Leura / Camperdown" "Tuesday / Her estimated / value cargo included/ is (pounds)100,000. When / she breaks up the coast / will be strewn with / wreckage as the cargo / includes Rolls Paper./all sorts machinery thousands / cases Benzine etc/ love Bob flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, peterborough, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck, postcards, photographic images, mary agnes kerr, leura farm, camperdown, jordan series, handwritten notes, photographs, george eastman, 3a folding pocket kodak camera -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Anchor, Circa 1886
... . Configuration: Four-masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts... the title of “warehouse-type” ship and her iron masts and wire ...The anchor is one of four that were carried by the FALLS OF HALLADALE when she was wrecked near Peterborough in 1908. This Rodger’s Anchor was raised from the wreck site by Flagstaff Hill divers (Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden) in 1974 and is on permanent outdoor display at the Maritime Village. The imposing 2-tonne artefact required a raft of fourteen 44-gallon drums to raise it from the seabed before it was towed by a crayfish boat to the wharf crane at Port Campbell for loading onto land transport. Following Lieutenant William Rodger’s patent in 1831, anchor design moved away from the separate attachment of straight arms and flat flutes to each side of a long shaft. Rodger’s innovation included the forging of both arms and their flutes as a single uniformly curved piece which was then attached to the crown of the shank by a thick horizontal bolt. The two-inch diameter hole for the securing through-bolt at the crown is clearly visible in this example, the bolt dislodged by corrosion and now missing. The FALLS OF HALLADALE was a four-masted, iron-hulled barque, built by Russell and Co at Greenock in 1866 for the Falls Line of Wright & Breakenridge, Glasgow. The ship was 275 feet long, 42 feet wide, with a 24 feet draft and weighed 2,085 tonnes. She was built to carry as much cargo as possible rather than for speed. Her unmistakably square bilge earned her the title of “warehouse-type” ship and her iron masts and wire rigging enabled her to maintain full sail even in gale conditions. In 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo in her hold, the FALLS OF HALLADALE left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. 102 days later, at 3 am on the 14th of November, under full sail and in calm seas, with a six knots breeze behind and a misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a shelf of rock near Peterborough. There she stayed for nearly two months until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000-ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four-masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for the Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire.The shipwreck of the FALLS OF HALLADALE is of state significance – Victorian Heritage Register No. S255. She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).A large iron Rodger’s anchor recovered from the wreck of the FALLS OF HALLADALE. It has a rounded crown, curved arms and moulded flutes. Heavy duty iron stock with round eyes at either end, fitted over shank and fixed into position by a wedge-shaped metal locking pin. Shackle missing but severed securing bolt remaining in shank. The presence of an empty bolthole at the crown junction of shank and arms confirms Rodger’s type. Corroded from 66 years submersion in seawater but otherwise structure is sound.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, falls of halladale, rodger’s anchor, peterborough reef, 1908 shipwreck, anchor, last days of sail, great clipper ships -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMast Collar, c. 1886
... . Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts... ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft ...The husband of the donor of this mast collar chanced to be staying a night at a motel in Peterborough, along the Great Ocean Road in Victoria. He had a keen interest in maritime items and recognise the mast collar at the motel’s back fence line. The motel owner told his guest the story of a customer, a doctor, who had organised and paid for divers to raise the mast collar from a local shipwreck, the Falls of Halladale. Shortly afterwards the doctor passed away, so the mast collar had remained at the motel site. The owner was leaving the motel the following week and wasn’t at all interested in the artefact. He was very happy for his guest to remove it. It took five men to load the mast collar up for the trip to the new owner’s two storey shed in Ballarat. It stayed there undercover, in the company of his collection of 5 buggies, for the next 40 or so years until the property was for sale. A friend, who realised the significance of the mast collar, suggested that it be donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village where other artefacts from the Falls of Halladale, such as the slate tiles, were on display. This mast collar, or masthead, from the Falls of Halladale would have been used to join two sections of one of the tall masts. As sailing ships became larger there was a need for taller masts or spars, which became difficult or impossible to find. To overcome this problem mast was divided into sections; lower and top or upper mast (on some of the ‘tall ships’ a mast could be divided into three or even four sections). The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted British barque built-in 1886. On what turned out to be her fatal journey, she had left New York for Melbourne in late 1908. She ran aground on a reef close to the shore west of Peterborough, South West Victoria, on November 14th. All 29 crew eventually landed safely onshore. The wrecked ship stayed on the reef for several months as locals watched the sails slowly deteriorate. The salvaged cargo included slate tiles, as mentioned above, and many of these have been used on the roof of buildings at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. This mast collar is significant due to its association with the ship FALLS OF HALLADALE, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register, VHR S255 The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). Mast collar, steel, salvaged from the shipwreck FALLS OF HALLADALE, wrecked off the coast of Peterborough, South West Victoria. Oval shaped a band of metal with a straight band of same heights attached between the long sides. Two metal loops are attached to the outside of the oval shape, next to the crossing band. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough vic, sailing ship mast collar, masthead of sailing ship, falls of halladale mast collar, masthead, mast collar, ship rigging 1908, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument, 12-01-1882
... ” The S.S. Julia Percy (later named Leeuwin ) was an iron passenger...” The S.S. Julia Percy (later named Leeuwin ) was an iron passenger ...This hand written letter, in black ink script on blue lined paper, is impressed with the official stamp of the Victoria Steam Navigation Board. The left margin has the reference “S82/12" It is transcribed: "Victoria Steam Navigation Board, Melbourne, January 12th 1882 To Frederick Chapman, Master, S.S. "Julia Percy" You are herewith furnished with a copy of the report of the Official Court which assembled to enquire into the circumstances attending the collision between the steamers "Julia Percy" and "Nelson" off Apollo Bay near Cape Otway on the morning of the 25th December 1881, and you are hereby expected to attend at the Board Room, Custom House, Melbourne, at 2pm, on 13th January instant to show cause why you should not be censured accordingly. [Signature] Secretary" This document refers to the matter of a collision between two steamships, the Julia Percy and the Nelson, on 25th December 1881. The Julia Percy was at that time owned by her first owners, the Warrnambool Steam Packet Company, and she sailed under the command of Captain Chapman. She had left Melbourne the evening of 24th December, with about 150 passengers, sailing in fine weather through Port Phillip Heads around 9pm. She was headed for Warrnambool, Belfast (now named Port Fairy) and Portland. The Julia Percy was off Apollo Bay when Captain Chapman was woken by the ship’s whistle after midnight, the steamer Nelson being on a collision course with the Julia Percy.[See Link.] The Nelson struck Julia Percy midship. Boats were lowered from the ship (apart from a damaged lifeboat) and about 30-40 of the passengers boarded the Nelson. The engine room and the forehold were checked and found clear of water. The company manager, Mr Evans, had been on the Nelson, so he boarded and inspected the Julia Percy and the decision was made to continue on to Warrnambool with the passengers as there appeared to be no immediate danger. However, Captain Thomas Smith said the Nelson was taking on water, so Julia Percy followed her for about an hour towards Melbourne on standby in case of need. Then Julia Percy turned around towards Warrnambool again. Shortly afterwards the Nelson turned to follow her, the ships stopped and passengers were returned to Julia Percy, and three from Julia Percy boarded the Nelson. Both ships proceeded on their way. Julia Percy passed Cape Otway light afterwards, signalling that there had been a collision. It was discovered later that one of the passengers was missing, then thought to have boarded the Nelson but later thought to have fallen into the sea and drowned while trying to jump from Julia Percy to Nelson. There had been 3 tickets purchased under the same name of that passenger “Cutler”; a father, son and friend named Wordsworth, which had caused quite some confusion. No further mishap occurred to either ship and both the Julia Percy and the Nelson reached their destinations safely. An enquiry was instigated by the Victoria Steam Navigation Board regarding the cause of the accident between the two steamships, in connection with the death of Cutler who was supposed to have lost his life by the collision. The enquiry resulted in the following decision: "The Victorian Steam Navigation Board having taken into consideration the points urged by Captain Thos [Thomas] Smith and also by his legal advisers, is of opinion that the charge prepared against him has been sustained, but taking into consideration Captain Smith’s previous good conduct and character, the board suspends his master’s certificate No 227 issued by this board for a period of six calendar months from this date – Robert Fullarton, Chairman. “The Victorian Steam Navigation Board having beard the statement of Captain Frederick Chapman urged in his defense to the charge of dereliction of duty as master of the Julia Percy, in having no standing order on board that vessel to be called in the event of any approaching steamer’s lights being seen, find such charge sustained, and censure him accordingly – Robert Fullarton, Chairman.” ABOUT “JULIA PERCY” The S.S. Julia Percy (later named Leeuwin ) was an iron passenger-cargo steam ship built in 1876. At one point in time the Julia Percy would sail from Warrnambool to Melbourne every Friday and return from Melbourne to Warrnambool every Tuesday. The cost of a return ticket for a Saloon Fare was £1.0.0. She would sail “if practical and weather permitting”. Shipping was the cheapest and most practical means of carrying produce and goods during the period 1840-1890. Regular domestic steamer services commenced in the Warrnambool district in the late 1850’s and by 1870 the passenger trade was booming. Produce was loaded from the jetty into ‘lighters’ (small boats), which took it to the ships at anchorage in the bay. Passengers were taken to the ship’s side then climbed aboard up ladders or gangways. The coming of the railway in October 1889 meant the gradual decline and end of the steam shipping era. The Julia Percy was built in Glasgow by Thomas Wingate & Company, Whiteinch, in 1876 for the Warrnambool Steam Packet Company, which commissioned her for trade in Victoria’s western district. She was first registered in Warrnambool, Victoria in 1876. The Julia Percy changed hands several times. Her next owner was the Western Steam Navigation Co (1887), managed by Mr. T.H. Osborne (the company’s office was on the corner of Timor and Liebig Streets, Its north-western wall is now part of the current Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery. ) The Melbourne Steamship Co became the next owners (1890), followed by William Howard Smith and Sons (1901) for use in Queensland coastal trades, then she was bought by George Turnbull in 1903 and used for local mail contract in Western Australia. The Julia Percy was sold to the Melbourne Steamship Company Ltd. (1906) and re-named the “Leeuwin” but continued in her Western Australian coastal run. She was converted into a coal hulk in Melbourne in 1910 as a result of damaged caused when she was driven against the jetty at Dongara during a gale. The ship was eventually dismantled and scuttled in Bass Strait on 28 December 1934. The document is significant for its association with the wreck of the Leeuwin (Julia Percy), which is on the Victorian Heritage Register, VHR S413. . It is historically significant for being a rare artefact that has potential to interpret aspects of Western Victoria’s 19th century steamship trade and Victorian cultural history. The Leeuwin (Julia Percy) is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register as being historically significant ‘as one of only four wrecks of steamships in Victorian waters associated with the western district of Victoria’s coastal steamship trade. Reports of Victoria Steam Navigation Board about the collision on 25th December 1881 between the steamers " Julia Percy" and "Nelson". Letter from Victoria Steam Navigation Board, Melbourne to Frederick Chapman, Master, S.S. "Julia Percy", dated January 12th 1882. reference on letter in left margin "S82/12"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill –maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, victoria steam navigation board, captain frederick chapman, captain thomas smith, thomas wingate & company, steamer julia percy, steamer leeuwin, steamer nelson, steam ship, warrnambool steam packet company, t. h. ostorne, western steam navigation co., charles cutler -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societypulley
This pulley was found by Geoff Stevenson, on a beach near Cape Conran (east of Orbost). It probably came from a sailing ship which was wrecked there. Pulleys are simple devices for increasing mechanical advantage in a wire, chain or rope system. A pulley consists of a wheel with a specialized rim that rotates on an axle and carries some type of cable or chain. Ships used a variety of blocks (pulleys) for various tasks, such as stowing cargo or handling the sails. A large wooden pulley encased in iron. It was probably used on a sailing ship. pulley cape-conran sailing-ship maritime -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Cannon, circa 1825
HISTORICAL INFORMATION In an article dated 26 March 1963, the Warrnambool Standard reported: “A cannon which has lain on the ocean floor since the barque, Children, was wrecked at Childer’s Cove on January 15, 1839, was raised by three Warrnambool skindivers at the week-end…The cannon, weighing about 750 lb. and 4-ft. 6-in. in length…is in excellent order considering the length of time it has remained under-water”. No conservation measures were taken at that time, other than chipping off the marine growth with hammers and cold chisels. The minutes for the 4 February 1974 meeting of the Flagstaff Hill Planning Board recorded that “a cannon recovered some time ago was lying in the garden of [one of the three original divers] and that it could be picked up at any time”. Peter Ronald, past Manager and Diver for Flagstaff Hill, notes that the CHILDREN cannon would have been recovered by the other divers around 1964. When the cannon came into care of Flagstaff Hill it was given basic conservation relevant to the time. (At the same meeting the Board was advised of the recovery of an anchor from the wreck of the CHILDREN by Flagstaff Hill divers (Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden, and Hank Howey and Andrew Coffee), and its interim relocation in the sea at the end of the Warrnambool Breakwater while awaiting conservation). The CHILDREN was owned by the pioneering Henty family of Portland. She was en route from Launceston to Adelaide, when she foundered in rough conditions at Childers Cove on 14 January 1839. The CHILDREN was a small three-masted barque, only 29 metres long and 254 tons weight, with 14 crew members and 24 passengers (including 9 children) on board. The ship was also carrying an awkwardly ballasted cargo of 1500 sheep, 8 bullocks, 7 horses, 5000 London house bricks, 6 whaling boats, and general trade goods. When the CHILDREN was driven into the limestone stack at the entrance to the cove, the seas smashed her into pieces within half an hour, and 16 lives were lost. The CHILDREN was an all-wooden ship, built in 1825 at Liverpool, and her shipwreck in 1839 is one of colonial Victoria’s earliest and most significant maritime disasters. There is little left to mark the tragedy on the seabed now, apart from some of the house bricks intended for the Henty’s Portland Bay settlement. Despite its poor condition, the CHILDREN’s signal cannon remains an important and interpretable record of her demise, (along with her anchor, the bottom half of her ship’s bell, and portions of a brass porthole - artefacts that are also in the Flagstaff Hill collection). In 2015 the CHILDREN cannon will undergo further conservation. (Conservation Management Plan for Victorian Guns and Cannon, South Western Victoria, May 2008, ref W/F/06) The shipwreck of the CHILDREN is of state significance — Victorian Heritage Register No. S116.A 1.3 metre iron 6pdr cannon recovered from the wreck of the CHILDREN. The shape of the cannon tapers from a thick round breech to a flared muzzle, with an 8 centimetre bore, and two side trunnions for pivoting on a wooden gun carriage. It was recovered from the shipwreck site of the CHILDREN by local divers in 1963. This small muzzle-loading signal cannon is in poor and unrestored condition. The cannon’s upper profile of smooth grey metal casing has corroded off, leaving an extensively oxidised rough red surface of crumbling iron. The bottom half of the cannon remains intact although the outer smooth casing also appears to be separating from the iron core of the barrel. Original grey casting is also missing from the breech and muzzle ends of the cannon. Corrosion and spalling of the upper surface layer of the cannon has removed the maker’s marks and specificationsflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, the children, ship’s cannon, signal cannon, childers cove, 1839 shipwreck, conservation of marine artefactsm, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, cannon, 6pdr small bore cannon, children cannon, defence, children, shipwreck, 1839 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Cannon, Alexander Hall and Son, c. 1855
The Schomberg Cannon was recovered from the 1855 wreck of the SCHOMBERG in 1974 by Flagstaff Hill divers Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden. The wreck site was discovered in August 1973 by Stan McPhee and John Laidlaw. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG When SCHOMBERG was launched in 1855, she was considered the “Noblest ship that ever floated on water.” SCHOMBERG’s owners, the Black Ball Line, commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. The ship was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen at a cost of £43,103. It was constructed with three skins: one planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Its first-class accommodation was simply luxurious; velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple, mahogany, soft furnishings of satin damask; an oak-lined library and a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the SCHOMBERG’s 34-year-old master, Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, had promised Melbourne in 60 days, "with or without the help of God." James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; MARCO POLO and LIGHTNING. In 1852 in the MARCO POLO he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. There were 53 deaths on the voyage but the great news was of the record passage by the master. In 1954 Captain Forbes took the clipper LIGHTNING to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his own records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the SCHOMBERG’s maiden voyage, he was going to break records. SCHOMBERG departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6 October 1855 flying the sign “Sixty Days to Melbourne”. The ship departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, and 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. It also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and the cargo was insured for $300,000, a fortune in those times. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing SCHOMBERG’s journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, and Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the Third Mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off, Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26 December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to SCHOMBERG and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS QUEEN at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS QUEEN approached the stranded vessel and all of SCHOMBERG’s passengers and crew were able to disembark safely. The SCHOMBERG was lost and with her, Forbes’ reputation. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the SCHOMBERG. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot! Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach SCHOMBERG, salvage efforts were abandoned. Parts of the SCHOMBERG were washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand in 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck. The wreck now lies in 825 metres of water. Although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be seen due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. Flagstaff Hill holds many items salvaged from the SCHOMBERG including a ciborium (in which a diamond ring was concealed), communion set, ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and a photograph from the SCHOMBERG. One of the SCHOMBERG bells was in the old Warrnambool Library. The Schomberg cannon is currently on loan to the Port Campbell Visitor Information Centre.The SCHOMBERG collection is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S612. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the SCHOMBERG is significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the SCHOMBERG. The SCHOMBERG collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship. The shipwreck collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be the fastest and most luxurious of its day. The SCHOMBERG collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history.Cannon; 6-POUNDER (6pdr) smooth bore cannon, mounted on a wooden frame. The cannon has a metal lug on each side. It is commonly known as the Schomberg cannon. It was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg in 1974.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, cannon, the schomberg cannon, schomberg cannon, peterborough, 1855, sailing ship -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Sewing Machine, Singer Sewing Machine Company, 1922
In 1867 the Singer Company decided that the demand for their sewing machines in the UK was sufficiently high to open a local factory. Glasgow was selected for its iron-making industries, cheap labour, and possibly because at the time the General Manager of the US Singer Sewing Machine Company was George McKenzie, who was of Scottish descent. The company obtained a lease on land near Queen Street Station and machinery and machine parts were shipped over from the US. Demand for sewing machines outstripped production at the new plant and by 1873 a new larger factory was completed near Bridgeton Cross. By now Singer employed over 2,000 people in Scotland but still, they could not produce enough machines. In 1882 George McKenzie, the soon to become President of the Singer Sewing Machine Company undertook the ground breaking ceremony on 46 acres of farmland at Kilbowie, Clydebank and the largest Singer factory in the world started to be built. Originally two main buildings were constructed. Built above the middle wing of the factory was a huge clock tower with the 'Singer' name displayed for all to see from miles around. Many miles of railway lines were laid throughout the factory to connect the different departments and to aid in the shipping of their goods. Railway lines from the factory connected Glasgow, Dumbarton, and Helensburgh stations. The factory was regarded as the most modern facility in Europe at that time. As different departments in the factory were completed, the workers moved from the old sites to the new one at Kilbowie and the factory was finally finished in 1885. With nearly a million square feet of space and almost 7,000 employees producing on average 13,000 machines a week, making it the largest sewing machine factory in the world. The Clydebank factory was so productive that in 1905 the US Singer Company set up the Singer Manufacturing Company Ltd. as a UK registered company. The invention of the sewing machine had several very significant impacts on the lives of many people. It changed the domestic life of many women as more households began to own sewing machines, women as the ones who traditionally stayed home to do chores including making and repairing clothing, found themselves with more free time. Previously several days a week would be dedicated to sewing clothing for herself and her family, a housewife could now complete her sewing in merely several hours, allowing for more free time to pursue hobbies and attain new skills. Sewing and clothing production, in general, became more industrialized activities, taking place less in the home and more in large factories. Industrial sewing machines, in combination with the cotton gin, the spinning jenny, and the steam engine, made clothing production much easier and much cheaper. Sewing machine, treadle operated, "Branded Premier" 5-7-9-2-0-0-" Serial Number Y6243048 (denotes 1922 year of manufacture) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, sewing machine, hand operated, dressmaking, textile machinery, portable, premier sewing machine, premier, singer treadle sewing machine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Sewing Machine, Singer Sewing Machine Company, 1907 -1920 (see note section this document for further information regards model identification)
In 1867 the Singer Company decided that the demand for their sewing machines in the UK was sufficiently high to open a local factory. Glasgow was selected for its iron-making industries, cheap labour, and possibly because at the time the General Manager of the US Singer Sewing Machine Company was George McKenzie, who was of Scottish descent. The company obtained a lease on land near Queen Street Station and machinery and machine parts were shipped over from the US. Demand for sewing machines outstripped production at the new plant and by 1873 a new larger factory was completed near Bridgeton Cross. By now Singer employed over 2,000 people in Scotland but still, they could not produce enough machines. In 1882 George McKenzie, the soon to become President of the Singer Sewing Machine Company undertook the ground breaking ceremony on 46 acres of farmland at Kilbowie, Clydebank and the largest Singer factory in the world started to be built. Originally two main buildings were constructed. Built above the middle wing of the factory was a huge clock tower with the 'Singer' name displayed for all to see from miles around. Many miles of railway lines were laid throughout the factory to connect the different departments and to aid in the shipping of their goods. Railway lines from the factory connected Glasgow, Dumbarton, and Helensburgh stations. The factory was regarded as the most modern facility in Europe at that time. As different departments in the factory were completed, the workers moved from the old sites to the new one at Kilbowie and the factory was finally finished in 1885. With nearly a million square feet of space and almost 7,000 employees producing on average 13,000 machines a week, making it the largest sewing machine factory in the world. The Clydebank factory was so productive that in 1905 the US Singer Company set up the Singer Manufacturing Company Ltd. as a UK registered company. The invention of the sewing machine had several very significant impacts on the lives of many people. It changed the domestic life of many women as more households began to own sewing machines, women as the ones who traditionally stayed home to do chores including making and repairing clothing, found themselves with more free time. Previously several days a week would be dedicated to sewing clothing for herself and her family, a housewife could now complete her sewing in merely several hours, allowing for more free time to pursue hobbies and attain new skills. Sewing and clothing production, in general, became more industrialized activities, taking place less in the home and more in large factories. Industrial sewing machines, in combination with the cotton gin, the spinning jenny, and the steam engine, made clothing production much easier and much cheaper. Singer sewing machine treadle type wooden stand with six drawers plus instruction manual Lotus decoration to machinewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, sewing-machine, clothes repair, singer sewing machine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, circa 1888
This photograph was taken close to the time of the wreck of the "Edinburgh Castle". The “Edinburgh Castle”, three-masted iron barque, was built in Glasgow, Scotland, in 1863 by J.G. Lawrie. She was 53.7 meters long and weighed 627 tons. She was owned by shipping company T Skinner and Co and registered at Liverpool, England. She sailed from 1863 to 1885 along the trade route between Scotland, China, and Singapore. In 1887 the Master, Captain J.B. Darling, sailed the “Edinburgh Castle” for its new owners Gifford & Nicholson from London to Warrnambool. Her cargo was 4,900 casks of cement for the construction of the new Warrnambool Breakwater. Over the three month journey, the ship met with rough weather and even a hurricane. On January 15th 1888 the “Edinburgh Castle” approached Lady Bay where a welcoming crowd gathered. The Port’s relief Harbour Master, Pilot Carless took over to complete the docking. As he tried to guide her, the Lighthouse Keeper signalled that the ship was too close to shore. The pilot continued on his course, causing her to ‘miss stays’ (make an incorrect tack). The crew dropped anchors and tried to lighten the load by throwing some of the casks of cement overboard but this was to no avail, and she drifted sideways in calm waters, lodging in the sand. A distress signal was sent to the coastal steamer “Julia Percy”, which spent several hours trying to pull the stranded ship away, but it would not budge. Those involved hoped to re-float the ship but efforts to save the vessel were useless. The captain and some crew stayed on board. When the weather became rough the rocket crew brought its lifesaving gear to the shore, ready to launch a line to the ship. The three men on board sent those onshore a message in a bottle to assure the on-lookers that they were quite comfortable to stay aboard. After a night of bad weather, the crew were glad to accept the rocket crew’s help and were in turn safely hauled to shore in a breeches buoy. The ship broke up quickly. Very little of the cargo could be saved. A week later all that could be seen of her was the bow and some of the stern. The beach was littered with wreckage, including cement cask fragments, for weeks. Ironically, on the morning after the ship ran aground, the very same “Edinburgh Castle” was offered for sale at an auction in Melbourne, billed as “a sound ship with all the fittings and in the best order.” The sale was completed before they heard the news that the ship was totally wrecked! Over the decades the shifting sands concealed the wreck of “Edinburgh Castle”. However, in October 1985 two local divers, Peter Ronald and Colin Goodall discovered her near the Hopkins River mouth. Peter said in his book ‘Exploring Shipwrecks of Western Victoria’, “In the midst of this sand-cloud I could clearly see row after row of neatly stacked barrels”. He remarked, “I am privileged to have had at least a glimpse of one of Warrnambool's most significant wrecks.” Some 15 – 17 ships are believed to have sunk in Lady Bay, but only two have been discovered on the seafloor; the “Edinburgh Castle” and the “La Bella”. Both wrecks are popular diving sites and are preserved as significant historical marine and marine archaeological sites. The sailing ship “Edinburgh Castle” is of local and state and national significance. It is one of the only two shipwrecks discovered in Lady Bay, Warrnambool, out of the 15-17 shipwrecks in the bay. The “Edinburgh Castle” is significant for being one of the largest vessels lost in the bay. The significance of the wreck of the “Edinburgh Castle” was recognised by being listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR S209. She was declared an Historic Shipwreck on 17th January 1989 under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). The “Edinburgh Castle” wreck is also significant for the connection of its cargo with the building of the Warrnambool Breakwater, also listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR H2024. The “Edinburgh Castle” is included as one of the shipwrecks in Heritage Victoria’s Historic Shipwreck Trail on Victoria’s West Coast. Black and white photograph of the iron barque 'Edinburgh Castle' on breaking waves, land in the background. The ship was stranded and wrecked in Lady Bay, Warrnambool, on January 15th 1888. Figures are standing on deck. The masts are free from sails.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, great ocean road, edinburgh castle barque 1863, edinburgh castle shipwreck 1888, shipwreck 15-05-1888, glasgow ship, jg lawrie, t skinner and co, liverpool ship register, captain j.b. darling, gifford & nicholson, cement casks, cement barrels, warrnambool breakwater construction, breaches buoy, rocket crew, rocket launcher, lifesaving equipment, warrnambool harbour, lady bay warrnambool, ship pilot carless, lady bay shipwreck, peter ronald, colin goodall, lady bay diving site, marine archaeology, victorian heritage register, vhr s209 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Photograph of Edinburgh Castle' stranded and wrecked at Lady Bay, circa 1888
This photograph was taken close to the time of the wreck of the "Edinburgh Castle". The “Edinburgh Castle”, three-masted iron barque, was built in Glasgow, Scotland, in 1863 by J.G. Lawrie. She was 53.7 meters long and weighed 627 tons. She was owned by shipping company T Skinner and Co and registered at Liverpool, England. She sailed from 1863 to 1885 along the trade route between Scotland, China, and Singapore. In 1887 the Master, Captain J.B. Darling, sailed the “Edinburgh Castle” for its new owners Gifford & Nicholson from London to Warrnambool. Her cargo was 4,900 casks of cement for the construction of the new Warrnambool Breakwater. Over the three month journey, the ship met with rough weather and even a hurricane. On January 15th 1888 the “Edinburgh Castle” approached Lady Bay where a welcoming crowd gathered. The Port’s relief Harbour Master, Pilot Carless took over to complete the docking. As he tried to guide her, the Lighthouse Keeper signalled that the ship was too close to shore. The pilot continued on his course, causing her to ‘miss stays’ (make an incorrect tack). The crew dropped anchors and tried to lighten the load by throwing some of the casks of cement overboard but this was to no avail, and she drifted sideways in calm waters, lodging in the sand. A distress signal was sent to the coastal steamer “Julia Percy”, which spent several hours trying to pull the stranded ship away, but it would not budge. Those involved hoped to re-float the ship but efforts to save the vessel were useless. The captain and some crew stayed on board. When the weather became rough the rocket crew brought its lifesaving gear to the shore, ready to launch a line to the ship. The three men on board sent those onshore a message in a bottle to assure the on-lookers that they were quite comfortable to stay aboard. After a night of bad weather, the crew were glad to accept the rocket crew’s help and were in turn safely hauled to shore in a breeches buoy. The ship broke up quickly. Very little of the cargo could be saved. A week later all that could be seen of her was the bow and some of the stern. The beach was littered with wreckage, including cement cask fragments, for weeks. Ironically, on the morning after the ship ran aground, the very same “Edinburgh Castle” was offered for sale at an auction in Melbourne, billed as “a sound ship with all the fittings and in the best order.” The sale was completed before they heard the news that the ship was totally wrecked! Over the decades the shifting sands concealed the wreck of “Edinburgh Castle”. However, in October 1985 two local divers, Peter Ronald and Colin Goodall discovered her near the Hopkins River mouth. Peter said in his book ‘Exploring Shipwrecks of Western Victoria’, “In the midst of this sand-cloud I could clearly see row after row of neatly stacked barrels”. He remarked, “I am privileged to have had at least a glimpse of one of Warrnambool's most significant wrecks.” Some 15 – 17 ships are believed to have sunk in Lady Bay, but only two have been discovered on the seafloor; the “Edinburgh Castle” and the “La Bella”. Both wrecks are popular diving sites and are preserved as significant historical marine and marine archaeological sites. The sailing ship “Edinburgh Castle” is of local and state and national significance. It is one of the only two shipwrecks discovered in Lady Bay, Warrnambool, out of the 15-17 shipwrecks in the bay. The “Edinburgh Castle” is significant for being one of the largest vessels lost in the bay. The significance of the wreck of the “Edinburgh Castle” was recognised by being listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR S209. She was declared an Historic Shipwreck on 17th January 1989 under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). The “Edinburgh Castle” wreck is also significant for the connection of its cargo with the building of the Warrnambool Breakwater, also listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR H2024. The “Edinburgh Castle” is included as one of the shipwrecks in Heritage Victoria’s Historic Shipwreck Trail on Victoria’s West Coast. Black and white photograph of the iron barque 'Edinburgh Castle' stranded and wrecked at Lady Bay, Warrnambool, on January 15th 1888. The photograph shows wreckage along the shore and two standing figures looking on.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, great ocean road, edinburgh castle barque 1863, edinburgh castle shipwreck 1888, shipwreck 15-05-1888, glasgow ship, jg lawrie, t skinner and co, liverpool ship register, captain j.b. darling, gifford & nicholson, cement casks, cement barrels, warrnambool breakwater construction, breaches buoy, rocket crew, rocket launcher, lifesaving equipment, warrnambool harbour, lady bay warrnambool, ship pilot carless, lady bay shipwreck, peter ronald, colin goodall, lady bay diving site, marine archaeology, victorian heritage register, vhr s209 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, C. 1891
Photograph shows the ship FIJI where she met her demise, in Wreck Bay, on the shipwreck coast of South West Victoria. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Black and White Photograph of the ship "Fiji" taken from Wreck Creek. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, pocket watch, fob watch fiji, william vickers, william robe, bill robe, gebauhr, stansmore, carmody, wreck bay, moonlight head, fiji shipwreck 1891, port campbell rocket crew, wreck bay victoria -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Breeches Buoy and Traveller Block, 1860s to 1950s
The breeches buoy and traveller block are part of the beach rescue apparatus used by lifesaving crew overseas and in Australia in the 1860s to 1960s. The breeches buoy (or chair bucket or petticoat breeches) were invented by Lieutenant Kisbee by the 1850s. It looks like a pair of canvas shorts with a cork lifebuoy ring attached around the top. The set-up works similar way to a zip wire and allows for two-way travel. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria has had over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it, followed in 1864 by a rocket house to safely store the Rocket Rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost one hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain and improve their skills, summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The first use of a lifesaving rocket rescue system is often credited to Captain Manby and his invention of a life mortar, first used in 1808 to fire a line onto a ship to rescue lives. Henry Trengrouse’s invention of 1820 was the first to use a sky rocket’s power to throw a line, and his invention included a chair for carrying the shipwrecked victims to shore. In 1832 John Dennett invented a rocket specifically for shore to ship rescue. It had an iron case and an 8 foot pole attached and could shoot the line as far as 250 yards (about 230 metres). From the 1860s the rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It comprised a breeches buoy and traveller block that was suspended on a line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. Colonel Boxer, who had invented an early line-thrower, designed a rocket in 1865 with a range from 300 to 470 yards. It was the first two-stage rocket, with two rockets placed one in front of the other in a tube that carried the rescue line. The hemp line was faked, or coiled, in a particular way in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired, and the angle of firing the rocket was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol around 1920, which used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. Victoria’s Government adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain, which used Colonel Boxer’s rocket apparatus rescue method. The British Board of Trade published instructions in 1850 for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line attached, then firing it across the stranded vessel. A tally board was then sent out with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the continuous whip line and attach the whip block to a mast or sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a heavier hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser is then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rocket system could also be used from one ship to another. This item is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Breeches buoy and traveller lock; white canvas breeches (shorts) with lifebuoy ring attached to its waistband, with ropes for attaching it to the traveller block. Wooden traveller block has double brass inline sheaves and brass rollers on each cheek of the block, and each shell is scored for the strop. The thimble attached to the strop has a wooden slat for quick release of the breeches buoy. The ropes comprise of two equal lengths of rope that have been bunched together to form two loops, then bound together just below the loops, while the four hanging ends are looped around the lifebuoy, equally spaced, with each end finished in an eye-splice. The apparatus is suspended by the loops at the top and attached to the traveller block, which has a quick release device.flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, william schermuly, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, beach rescue set, traveller, block, running block, pulley, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, rescue boat, lifeboat, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, tramway jetty, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, captain manby, mortar, henry trengrouse, sky rocket, john dennett, shore to ship, colonel boxer, two-stage rocket, italian hemp, quadrant, schermuly, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, irish hand barrow, government of victoria -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessel - Sailing Ship, Falls of Halladale, After 13-11-1908
Falls of Halladale The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She was one of the first vessels to include fore and aft lifting bridges, which kept the crew safe and dry in as they moved around the decks in stormy conditions. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles, 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items (a list of items held at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village is included below). The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Photograph of the wrecked ship, the Falls of Halladale, sails still flying. The ship was wrecked at Peterborough on Nov 13, 1908. The outer frame is made from a piece of planking. Handwritten inscriptions in white ink on the top of the matt board, and on the lower right.BQE "Falls of Halladale" "Wrecked. Peterborough. Nov 13. 1908" "Frame. from piece of planking."flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwreck, photograph, falls of halladale, planking frame -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGlass
Falls of Halladale The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She was one of the first vessels to include fore and aft lifting bridges, which kept the crew safe and dry in as they moved around the decks in stormy conditions. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles, 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items (a list of items held at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village is included below). The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Porthole glass secured in wood, with a crack in the glass. Writing on wood "porthole Glass Falls of Halladale."Burnt into the wood are the words "porthole Glass Falls of Halladale."falls of halladale, wright, breakenridge & co of glasgow, californian blue roof slate, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, porthole glass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBinnacle, Early to mid 20th Century
Mr John Wilson Gillie was born on the 31st of March 1864. On the 31st of July 1880 he was apprenticed for four years to J.J. Wilson and Sons, Nautical Instrument Makers of Sunderland. Following the apprenticeship he spent six months to a year as an ‘improver’ in Glasgow, and then started a new company ‘Wilson and Gillie’ in North Shields. At this time sail had just given way to steam and wooden ships to steel, and the railways were competing with colliers for the carrying of coal from the North East of England to London and the South. In 1858 only seven out of 44 shipyards on the Tyne were using iron, but by 1862 there were ten, employing around 4,000 men. These changes had a significant effect on nautical instrument manufacturers, as the magnetic compass for a wooden sailing vessel was very simple and required little in the way of compensation. For steel vessels much more was required and this was a period of great development, both in the compass bowl and the binnacle in which it was housed. In 1870 Sir William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) designed his dry card standard compass, which completely replaced all previous designs. Wilson and Gillie started as agents for the Thomson compass, but later J.W. Gillie, using similar principles, redesigned the compass suspension and patented the ‘UNIT’ standard compass. It became popular with local shipowners and shipbuilders. In 1910 the firm of John Lilley and Son (which had been established in London in 1812), found themselves in financial difficulties and were saved with the help of John Wilson Gillie, who established, on the 8th of August 1911, a new firm of John Lilley and Son Limited. John Lilley and Son had been the sole London agents for Sir William Thomson, a very enviable position during this period, when the Thomson compass led the field. Unfortunately, Mr. Lilley had quarreled with the Glasgow company, who withdrew the agency and established their own branch in London (later to become Kelvin White and Hutton). On November 7th 1913, the firm of John Lilley and Son Limited of London amalgamated with Wilson and Gillie of North Shields, and after this date instruments manufactured by the two companies bore the name John Lilley and Son Limited of London and North Shields. During the 1930s many of the London nautical instrument makers were in difficulties, including John Lilley and Son Limited and Reynolds and Son, Dobbie and Clyde Limited, and Mr. J.W. Gillie arranged an amalgamation between these two companies. The new firm became Lilley and Reynolds Limited. In 1943, with estate duties in mind, the North Shields company was reconstituted and took the name of John Lilley and Gillie Limited, although the shareholders, directors and personnel remained unchanged In the early 1970s Lilley and Gillie developed close links with Observator in Rotterdam, who manufactured one of the first fully reliable transmitting magnetic compass systems. The Observator shareholders, Holland America Line, bought the share capital of John Lilley and Gillie Limited., but retained all the personnel and the directors. (See Links for more information)A significant item of early 20th century marine navigational equipment made by a leading manufacturer in the field from a company that is still producing marine navigational instruments today. John Lilleys company began in 1812 growing at a time when the transition of compasses from timber ships, to steel vessels. Compasses at this time required a method of compensation to allow their inclusion in steel vessels without magnetic deviation. This therefore was a period of great development, both in the compass bowl and the binnacle in which it was housed and the Lilley company were leaders in the field. Ships binnacle, wood with brass fittings, consists of 2 brass lamp holders, place for compass, Also has an inclinometer with a scale 40 to 0 to 40, one red and one green iron Kelvin compensation balls, one on each side of binnacle denoting port and starboard, a brass cylinder attached perpendicular at the rear for storing a Flinders Bar, 2 hinged cupboards containing adjustable wooden racks with drilled holes in them to hold iron Heeling error magnets.Textured brass plate attached to front stating "JOHN LILLEY & SON LTD (WILSON & GILLIE), NAUTICAL INSTRUMENT MAKERS, NORTH SHIELDS" . Inclinometer has "JOHN LILLEY & SON LTD (Wilson & Gillie) LONDON & NORTH SHIELDS" engraved. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, binnacle, john lillie & son ltd, compass -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaEquipment - Ship bell, Vickers, Barrow, SS Moreton Bay, 1920-1921
The Bell was presented to the Mission by the Aberdeen and Commonwealth Line in October 1957, after the ship made her final voyage to Australia in 1956 and it was broken up in Barrow in April 1957 by Thomas W Ward (UK). In the Annual Report 1957, Padre Oliver mentioned "the bell was found unsuited for the chapel belfry, it is to be mounted on a bracket and placed in the Celia Little lounge."Cast brass bell with wrought iron anchor and hook design wall mount: decoratively plaited cord in maritime knot pattern to resemble chain, sealed with a varnish and attached to cast iron clapper. Wrought iron hook secured by metal bolt. Bell is inscribed in upper case capital letters with MORETON BAY. Anchor attached with four flat headed hexagonal bolts with mighted wooden frame. Bell inscribed with upper case capital letters MORETON BAY. / Also brass presentation wall plaque (see image)bell, anchor, brass, ss moreton bay, ship's bell, plaque, celia little room, bracket, p&o, peninsular and oriental steam navigation company, passengers liners, passenger ships, emigrants, emigration -
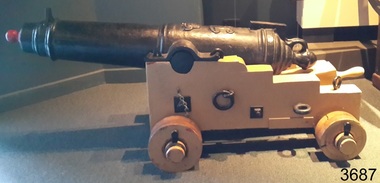 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Carronade, 1840
The carronade was designed as a short-range naval weapon with a low muzzle velocity for merchant ships, but it also found a niche role on warships. It was produced by the Carron Iron Works and was at first sold as a complete system with the gun, mounting, and shot altogether. Carronades initially became popular on British merchant ships during the American Revolutionary War. A lightweight gun that needed only a small gun crew and was devastating at short range was well suited to defending merchant ships against French and American privateers. The invention of the cannon is variously attributed to Lieutenant General Robert Melville in 1759, or to Charles Gascoigne, manager of the Carron Company from 1769 to 1779. In its early years, the weapon was sometimes called a "mellvinade" or a "gasconade". The carronade can be seen as the culmination of a development of naval guns reducing the barrel length and thereby the gunpowder charge. The Carron Company was already selling a "new light-constructed" gun, two-thirds of the weight of the standard naval gun and charged with one-sixth of the weight of the ball in powder before it introduced the carronade, which further halved the gunpowder charge. The theory of its design was to use less powder and had other advantages that were advertised in the company's sales pamphlet of the time, state. The smaller gunpowder charge reduced the barrel heating in action, also reduced the recoil. The mounting, attached to the side of the ship on a pivot, took the recoil on a slider, without altering the alignment of the gun. The pamphlet advocated the use of woollen cartridges, which eliminated the need for wadding and worming, although they were more expensive. Carronades also simplified gunnery for comparatively untrained merchant seamen in both aiming and reloading that was part of the rationale for adopting the gun. Other advantages promoted by the company were. The replacement of trunnions by a bolt underneath, to connect the gun to the mounting, reduced the width of the carriage that enhanced the wide angle of fire. A merchant ship would almost always be running away from an enemy, so a wide-angle of fire was much more important than on a warship. A carronade weighed a quarter as much as a standard cannon and used a quarter to a third of the gunpowder charge. This reduced charge allowed Carronades to have a shorter length and much lighter weight than long guns. Increasing the size of the bore and ball reduces the required length of the barrel. The force acting on the ball is proportional to the square of the diameter, while the mass of the ball rises by the cube, so acceleration is slower; thus, the barrel can be shorter and therefore lighter. Long guns were also much heavier than Carronades because they were over-specified to be capable of being double-shotted, (to load cannons with twice the shot, for increased damage at the expense of range), whereas it was dangerous to do this in a carronade. A ship could carry more carronades, or carronades of a larger calibre, than long guns, and carronades could be mounted on the upper decks, where heavy long guns could cause the ship to be top-heavy and unstable. Carronades also required a smaller gun crew, which was very important for merchant ships, and they were faster to reload. The small bore carronade and carriage is part of a collection of nineteenth Century Flagstaff Hill Guns and Cannon, which is classified as being of significance and was made a few years after the beginning of Queen Victoria's reign in 1837 and fires a 6 lb pound cannon ball. This nineteenth century artillery piece is a rare and representative item of artillery of this era, used predominately on ships, both military and merchant. The artillery piece, individually and as part of the collection, is highly significant for its historical, scientific and aesthetic reasons at the state, national and world level. This carronade represents the methods of artillery technology, its advancement and its modifications to suit dangerous situations that sailors encountered from attacks from free booters (pirates, living from plunder) or others at the time. Carronade firing a 6 lb cast iron ball, with a smooth bore barrel 6.5 cm in dia the item is mounted on stepped wooden carriage with wooden wheels. Cannon barrel can have its elevation adjusted via a wooden wedge. Gun carriage has loops for locating and holding in position to a deck by ropes. Carriage is a replica made 1982Cast into the barrel is the royal emblem of Queen Victoria (VR "Victoria Regina") indicating the carronade was cast during Queen Victoria's reign / 1840 & 4-2-0 denoting the weight of the barrel. Right hand trunnion has a serial number “8708”. Also on top of the barrel is the British "Board of Ordinance" identifying mark a broad arrow indicating the carronade was in military use. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, colonial defences, victoria’s coastal defences, warrnambool fortification, warrnambool garrison battery, warrnambool volunteer corps, ordinance, armaments, garrison gun, smooth bore cannon, carronade, black powder, 12 pounder, 1840, artillery, lieutenant general robert melville, charles gascoigne, carron company, mellvinade, gasconade -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSouvenir - Rope Sample, before September 1891
The rope was part of the distress rocket used during the time that the sailing ship Fiji was in distress, before it became a wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and distress rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Cartland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryan's Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to River nook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to River nook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967.This rope is part of the collection of artefacts from the wreck of the Fiji. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes).Rope, plaited, brown in colour, cut straight at one end, and the other end is separated into 3 pieces, from distress rockets used during the wreck of the sailing ship Fiji. Rope was in envelope printed with an address, and a description, and there was a display card with further details on it. Printed on the envelope: "Shire of Hampden / PO Box 84, Camperdown 3260" Hand written "rope of wreck of Fiji / 7cm / Mr Wm "Boyce" Display card with rope includes words "Piece of Rope from the Fiji distress rockets and was donated to Flagstaff Hill by a private donor in 1989"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, rope, the fiji, william boyce, distress signal, rocket rescue, life saving equipment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Copper Sheet, circa 1878
In 1984 the Commonwealth Government made available to Flagstaff Hill a collection of lead ingots and copper sheets recovered from the wreck-site of the LOCH ARD. They were presented to the Warrnambool City Council by the Hon. Tom Uren MHR, Minister for Territories and Local Government: “The Commonwealth recognises that shipwrecks like the LOCH ARD are our national heritage with important educational, recreational and tourist applications” (The Standard, Tuesday 8 May 1984). The LOCH ARD was wrecked in 1878. Unsuccessful salvage operations were then undertaken with the 90 ton paddle steamer NAPIER. In sudden bad weather this vessel too was sunk. The precise position of the LOCH ARD in the exposed and dangerous waters off Mutton Bird Island became lost to memory. The underwater location of the LOCH ARD was rediscovered in 1967 by a Warrnambool skindiver, Stan McPhee. In the two years following his find, the vessel was systematically pillaged by unauthorised salvagers. This led to the State and Federal Governments’ intervention in 1969. A roundup and seizure of recovered lead ingots and copper sheets was conducted by Commonwealth and Victorian Police. Offenders were charged and convicted. The “repossessed loot of the Tassie Boys” was placed into secure storage (Jack Loney, 1978, Wrecks & Reputations). The LOCH ARD manifest of cargo lists “Pig lead 50 tons, 994 pig & 37 rolls” and “Copper 33 plates, 53 bolts”. While the lead ingots have been subsequently described as “ballast”, the copper sheets are unlikely to have been associated with the ship’s normal complement in that way. Similar product lines in the cargo manifest are “Bar and rod iron 102 tons”, “Plate iron 3 tons” and “Zinc 12 tons”. These raw materials were used by colonial artisans such as blacksmiths and metal smelters to fashion, and repair, agricultural implements and industrial machinery. Copper was valued for its non-corrosive properties and its malleability, or ease of working. Both these qualities were useful, for example, in laying underground gas pipes that supplied lighting to residences, businesses and streetscapes in the mid-nineteenth century. As the nineteenth century progressed, the metal was also increasingly valued for its conductivity, with copper wiring linking colonial communities to each other, and the wider world, via the Telegraph system. The average weight of the copper sheets is 216 kilograms, calculated by "volume 0.1936m³ X Cu density 8930kgs/m³".The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Large heavy sheets or panels of copper metal raised from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The 10 sheets are of roughly similar dimensions and rectangular shape. They bear signs of prolonged submersion in seawater, with various degrees of limestone accretion, adhered marine growth, and green oxidisation. Three of the sheets are severely buckled, demonstrating the force of underwater explosives used in their salvage. One sheet appears cut or severed in a diagonal line downwards from its top left hand corner. One sheet has a 10cm X 10cm square cut out of its top right hand corner. All sheets are in sturdy, stable condition. No maker’s marks are visible.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, sailing ship, copper sheet, manutacturing materials, metal imports, muntz -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Pulley Block, Russell & Co, ca. 1886
A pulley block of this size would have many applications on a ship, including lifting loads such as cargo and sails. It was recovered from the wreck of the Halladale in the 1970s by divers Gary Hansen and Peter Ronald, former Director of Flagstaff Hill. The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque built in Glasgow, Scotland. It was used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. When the ship left New York in August 1908 it was bound for Melbourne and Sydney it’s the cargo in its hold consisted of roofing tiles, barbed wire, stoves, oil, benzene and many other manufactured items. On the 15th of November, 1908, after three months at sea and close to its destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland. The captain and 29 crew members survived but most of the cargo was lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not to any technical failure of the ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. The vessel was one of several designs of Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period between 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised its ship designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales. It was one of the last of the 'windjammers'. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have huge seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions.The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). The vessel was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the ship was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature that is still in use on modern vessels today. The block and pulley is an example of ship rigging equipment used on sailing ships during the 19th and early 20th centuries that transported goods around the world. It represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry and maritime history.A pulley block; metal frame with three sheaves. The block is in a fragile condition. It is also large and heavy. It was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale in the 1970s. warrnambool, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, clipper ship, windjammer, cargo vessel, falls of halladale wreck, shipwreck, 1908 wreck, breakenridge & co glasgow, russell & co ship builders, 1886 ship, shipwreck artefact, rigging, ship rigging, rigging equipment, sailing equipment, cargo equipment, marine technology, block, ship’s block, pulley block -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Deadeye, Russell & Co, Circa 1886
This deadeye was amongst artefacts recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. It would have been used on the ship to attach, hold and run ropes for the ship’s rigging. The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roofing tiles, barb wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject item is an example of ships rigging objects used on sailing ships during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods around the world the item is representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry and maritime history. Deadeye; wooden deadeye, three (3) holes, with metal surrounds and metal rigging cable attached. Recovered from the Falls of Halladale.Nonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, rigging equipment, sailing equipment, deadeye, falls of halladale wreck, breakenridge & co glasgow, russell & co ship builders, cargo vessel, 1908 wreck, rigging, ship rigging -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Buckle
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Set of 5 horse harness buckles, 2" x 2" Buckles are encased in concretion. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, horse harness, buckle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Ring
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Horse harness ring, 2" diameter Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, horse harness -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Ring
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Horse harness ring, 2" diameter Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, horse harness -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHarness Ring
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Horse harness ring, 1½" diameter. Ring has piece of metal fused to it. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, horse harness
