Showing 12906 items
matching warrnambool
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of the steam ship Barrgrove, (SH 038 Ships A - B).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, post card, barrgrove, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGreeting Card
Greeting Card, Black and White Christmas Card with photographs of 2 sailing ships the Buckingham and the barquentine Lahaina. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, buckingham, greeting card, lahaina -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black and White Photograph of a large Photograph of the barque Brilliant, Inscription on back read world's fastest oil - clipper. Steel 4 master .3765 tons 353feet long. SH 046 Ships A - B.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, photograph, brilliant, barque brilliant -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Coloured Postcard of the sailing ship Cedric the Saxon. (SH 052 Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, cedric the saxon., post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of M.V. Cheshire. (SH 053-1 Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, m.v. cheshire, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of the steam ship China. (SH 055 Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, steam ship china, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of the steam ship Changsha, Built (SH 056 Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, post card, changsha, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of S.S Celtic. 135mm x 85 mm. SH 057 Ships C - E.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, s.s celtic, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
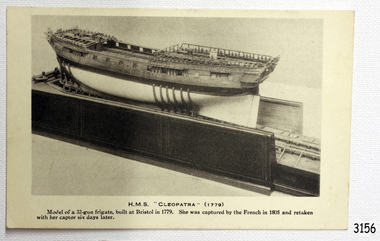
Black and White Postcard of a model of a 32 gun frigate, built in Bristol in 1779 H.M.S Cleopatra. She was captured by the French in 1805 and retaken with her captor six days later. (SH 056 [1] Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, h.m.s cleopatra, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of H.M.S. Conway. (SH 057[1] Ship C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, h.m.s. conway, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of U.S.S Constellation. (SH 058 [1] Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, u.s.s constellation., post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of a model of the Cutty Sark. (SH 063 [1] Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, post card, cutty sark, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Coloured Postcard of the Cutty Sark. Photograph taken by J Spurling. (SH 063 [2] Ship C - E.)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, post card, cutty sark, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black and White Photograph of S.N. Castle 254 mm x 208 mm. Inscription on reverse side reads S.N. Castle in English Harbour Fanning Island. From my own photo given by me to the skipper Capt. J.H. von Dahlern. Now in possession of Minna Wenzke of San Francisco, a niece of the skipper. 215 mm x 165 mm. SH 067 [1] Ships C - E.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, s.n. castle, fanning island, minna wenzke -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black and White Photograph of Postcard Schooner Eliza. 135 mm x 94 mm. SH 077 Ships C - E.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, post card, schooner eliza, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of S.V. Elizabeth Bandi. (SH 078 Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, post card, s.v. elizabeth bandi., postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of Enogerra. (SH 079 Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, post card, enogerra, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of Eumeralla. (SH 080 Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, post card, eumeralla, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of Eurypylus. (SH 082 Ships C - E).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, eurypylus, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of the sailing ship Fantome II . (SH 090[1] Ships F - H).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fantome ii, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard of the sailing ship Fairy Bell. (SH 091 Ships F - H).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fairy bell, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White postcard of the S.V.Garthpool ( SH 109 Ships F - H).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, s.v.garthpool, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White postcard, General Gordon. (SH 110.1 Ships F - H).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, general gordon, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White Postcard, General Gordon. (SH 110.2 Ships F - H).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, general gordon, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White postcard of M.T. Girl Pat. (SH 111 Ships F - H)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, m.t. girl pat, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White postcard of General de Sonis. (SH 112 Ships F - H).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, general de sonis, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard
Black and White postcard of the steam ship Glenmore. (SH 113 Ships F - H).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, steam ship glenmore, post card, postcard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Chair, Early 20th Century
The chair has been used since antiquity, although for many centuries it was a symbolic article of state and dignity rather than an article for ordinary use. "The chair" is still used as the emblem of authority in the House of Commons in the United Kingdom and Canada, and in many other settings. In keeping with this historical connotation of the "chair" as the symbol of authority, committees, boards of directors, and academic departments all have a 'chairman' or 'chair'. Endowed professorships are referred to as chairs. It was not until the 16th century that chairs became common. Until then, people sat on chests, benches, and stools, which were the ordinary seats of everyday life. The number of chairs which have survived from an earlier date is exceedingly limited; most examples are of ecclesiastical, seigneurial or feudal origin. Chairs were in existence since at least the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt (c. 3100 BC). They were covered with cloth or leather, were made of carved wood, and were much lower than today's chairs – chair seats were sometimes only 10 inches (25 cm) high. In ancient Egypt, chairs appear to have been of great richness and splendour. Fashioned of ebony and ivory, or of carved and gilded wood, they were covered with costly materials, magnificent patterns and supported upon representations of the legs of beasts or the figures of captives. Generally speaking, the higher ranked an individual was, the taller and more sumptuous was the chair he sat on and the greater the honour. On state occasions, the pharaoh sat on a throne, often with a little footstool in front of it.[ The average Egyptian family seldom had chairs, and if they did, it was usually only the master of the household who sat on a chair. Among the better off, the chairs might be painted to look like the ornate inlaid and carved chairs of the rich, but the craftsmanship was usually poor. The earliest images of chairs in China are from 6th-century Buddhist murals and stele, but the practice of sitting in chairs at that time was rare. It was not until the 12th century that chairs became widespread in China. Scholars disagree on the reasons for the adoption of the chair. The most common theories are that the chair was an outgrowth of indigenous Chinese furniture, that it evolved from a camp stool imported from Central Asia, that it was introduced to China by Christian missionaries in the 7th century, and that the chair came to China from India as a form of Buddhist monastic furniture. In modern China, unlike Korea or Japan, it is no longer common to sit at floor level. In Europe, it was owing in great measure to the Renaissance that the chair ceased to be a privilege of state and became a standard item of furniture for anyone who could afford to buy it. Once the idea of privilege faded the chair speedily came into general use. Almost at once the chair began to change every few years to reflect the fashions of the day. Thomas Edward Bowdich visited the main Palace of the Ashanti Empire in 1819, and observed chairs engrossed with gold in the empire. In the 1880s, chairs became more common in American households and usually there was a chair provided for every family member to sit down to dinner. By the 1830s, factory-manufactured “fancy chairs” like those by Sears, Roebuck, and Co. allowed families to purchase machined sets. With the Industrial Revolution, chairs became much more available. The 20th century saw an increasing use of technology in chair construction with such things as all-metal folding chairs, metal-legged chairs, the Slumber Chair,[ moulded plastic chairs and ergonomic chairs. The recliner became a popular form, at least in part due to radio and television. The modern movement of the 1960s produced new forms of chairs: the butterfly chair (originally called the Hardoy chair), bean bags, and the egg-shaped pod chair that turns. It also introduced the first mass-produced plastic chairs such as the Bofinger chair in 1966. Technological advances led to moulded plywood and wood laminate chairs, as well as chairs made of leather or polymers. Mechanical technology incorporated into the chair enabled adjustable chairs, especially for office use. Motors embedded in the chair resulted in massage chairs. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ChairThe chair is one of the most commonly used items providing comfort.Chair wooden varnished dark brown. Spokes for back support, front legs and spokes joining legs are patterned turned wood. Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chair, dining, carpentry -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Chair, Early 20th Century
The chair has been used since antiquity, although for many centuries it was a symbolic article of state and dignity rather than an article for ordinary use. "The chair" is still used as the emblem of authority in the House of Commons in the United Kingdom and Canada, and in many other settings. In keeping with this historical connotation of the "chair" as the symbol of authority, committees, boards of directors, and academic departments all have a 'chairman' or 'chair'. Endowed professorships are referred to as chairs. It was not until the 16th century that chairs became common. Until then, people sat on chests, benches, and stools, which were the ordinary seats of everyday life. The number of chairs which have survived from an earlier date is exceedingly limited; most examples are of ecclesiastical, seigneurial or feudal origin. Chairs were in existence since at least the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt (c. 3100 BC). They were covered with cloth or leather, were made of carved wood, and were much lower than today's chairs – chair seats were sometimes only 10 inches (25 cm) high. In ancient Egypt, chairs appear to have been of great richness and splendour. Fashioned of ebony and ivory, or of carved and gilded wood, they were covered with costly materials, magnificent patterns and supported upon representations of the legs of beasts or the figures of captives. Generally speaking, the higher ranked an individual was, the taller and more sumptuous was the chair he sat on and the greater the honour. On state occasions, the pharaoh sat on a throne, often with a little footstool in front of it.[ The average Egyptian family seldom had chairs, and if they did, it was usually only the master of the household who sat on a chair. Among the better off, the chairs might be painted to look like the ornate inlaid and carved chairs of the rich, but the craftsmanship was usually poor. The earliest images of chairs in China are from 6th-century Buddhist murals and stele, but the practice of sitting in chairs at that time was rare. It was not until the 12th century that chairs became widespread in China. Scholars disagree on the reasons for the adoption of the chair. The most common theories are that the chair was an outgrowth of indigenous Chinese furniture, that it evolved from a camp stool imported from Central Asia, that it was introduced to China by Christian missionaries in the 7th century, and that the chair came to China from India as a form of Buddhist monastic furniture. In modern China, unlike Korea or Japan, it is no longer common to sit at floor level. In Europe, it was owing in great measure to the Renaissance that the chair ceased to be a privilege of state and became a standard item of furniture for anyone who could afford to buy it. Once the idea of privilege faded the chair speedily came into general use. Almost at once the chair began to change every few years to reflect the fashions of the day. Thomas Edward Bowdich visited the main Palace of the Ashanti Empire in 1819, and observed chairs engrossed with gold in the empire. In the 1880s, chairs became more common in American households and usually there was a chair provided for every family member to sit down to dinner. By the 1830s, factory-manufactured “fancy chairs” like those by Sears, Roebuck, and Co. allowed families to purchase machined sets. With the Industrial Revolution, chairs became much more available. The 20th century saw an increasing use of technology in chair construction with such things as all-metal folding chairs, metal-legged chairs, the Slumber Chair,[ moulded plastic chairs and ergonomic chairs. The recliner became a popular form, at least in part due to radio and television. The modern movement of the 1960s produced new forms of chairs: the butterfly chair (originally called the Hardoy chair), bean bags, and the egg-shaped pod chair that turns. It also introduced the first mass-produced plastic chairs such as the Bofinger chair in 1966. Technological advances led to moulded plywood and wood laminate chairs, as well as chairs made of leather or polymers. Mechanical technology incorporated into the chair enabled adjustable chairs, especially for office use. Motors embedded in the chair resulted in massage chairs. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ChairThe chair is one of the most commonly used items providing comfort.Chair wooden varnished dark brown. Spokes for back support, front legs and spokes joining legs are patterned turned' wood. Backrest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chair, dining, carpentry -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Chair, Early 20th Century
The chair has been used since antiquity, although for many centuries it was a symbolic article of state and dignity rather than an article for ordinary use. "The chair" is still used as the emblem of authority in the House of Commons in the United Kingdom and Canada, and in many other settings. In keeping with this historical connotation of the "chair" as the symbol of authority, committees, boards of directors, and academic departments all have a 'chairman' or 'chair'. Endowed professorships are referred to as chairs. It was not until the 16th century that chairs became common. Until then, people sat on chests, benches, and stools, which were the ordinary seats of everyday life. The number of chairs which have survived from an earlier date is exceedingly limited; most examples are of ecclesiastical, seigneurial or feudal origin. Chairs were in existence since at least the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt (c. 3100 BC). They were covered with cloth or leather, were made of carved wood, and were much lower than today's chairs – chair seats were sometimes only 10 inches (25 cm) high. In ancient Egypt, chairs appear to have been of great richness and splendour. Fashioned of ebony and ivory, or of carved and gilded wood, they were covered with costly materials, magnificent patterns and supported upon representations of the legs of beasts or the figures of captives. Generally speaking, the higher ranked an individual was, the taller and more sumptuous was the chair he sat on and the greater the honour. On state occasions, the pharaoh sat on a throne, often with a little footstool in front of it.[ The average Egyptian family seldom had chairs, and if they did, it was usually only the master of the household who sat on a chair. Among the better off, the chairs might be painted to look like the ornate inlaid and carved chairs of the rich, but the craftsmanship was usually poor. The earliest images of chairs in China are from 6th-century Buddhist murals and stele, but the practice of sitting in chairs at that time was rare. It was not until the 12th century that chairs became widespread in China. Scholars disagree on the reasons for the adoption of the chair. The most common theories are that the chair was an outgrowth of indigenous Chinese furniture, that it evolved from a camp stool imported from Central Asia, that it was introduced to China by Christian missionaries in the 7th century, and that the chair came to China from India as a form of Buddhist monastic furniture. In modern China, unlike Korea or Japan, it is no longer common to sit at floor level. In Europe, it was owing in great measure to the Renaissance that the chair ceased to be a privilege of state and became a standard item of furniture for anyone who could afford to buy it. Once the idea of privilege faded the chair speedily came into general use. Almost at once the chair began to change every few years to reflect the fashions of the day. Thomas Edward Bowdich visited the main Palace of the Ashanti Empire in 1819, and observed chairs engrossed with gold in the empire. In the 1880s, chairs became more common in American households and usually there was a chair provided for every family member to sit down to dinner. By the 1830s, factory-manufactured “fancy chairs” like those by Sears, Roebuck, and Co. allowed families to purchase machined sets. With the Industrial Revolution, chairs became much more available. The 20th century saw an increasing use of technology in chair construction with such things as all-metal folding chairs, metal-legged chairs, the Slumber Chair,[ moulded plastic chairs and ergonomic chairs. The recliner became a popular form, at least in part due to radio and television. The modern movement of the 1960s produced new forms of chairs: the butterfly chair (originally called the Hardoy chair), bean bags, and the egg-shaped pod chair that turns. It also introduced the first mass-produced plastic chairs such as the Bofinger chair in 1966. Technological advances led to moulded plywood and wood laminate chairs, as well as chairs made of leather or polymers. Mechanical technology incorporated into the chair enabled adjustable chairs, especially for office use. Motors embedded in the chair resulted in massage chairs. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ChairThe chair is one of the most commonly used items providing comfort.Chair varnished dark brown. Spokes for back support, front legs and spokes joining legs are patterned turned wood. Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chair, dining, carpentry
