Showing 170 items matching "landscape plants"
-
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionPhotograph, John Gray Memorial Rotunda in Surrey gardens, Union Road, Surrey Hills, c 1925, c 1925
The rotunda was built in 1912 by Clarence Montgomery for the Surrey Hills Progress Association and the local community and dedicated to John Gray, "a highly respected and revered citizen". Surrey Hills Brass Band regularly gave concerts in the rotunda, provided music for regular 'loyal' celebrations and also for silent films held in the gardens. The rotunda was quite elevated off the ground due to the slope of the gardens and the bioscope was stored in the room underneath. This was later used as the infant welfare centre until the Progress Association built a dedicated facility for these purposes. The rotunda was demolished in 1972. Clarence Montgomery, carpenter, was living in Sunbury Crescent in 1914. By 1916 he had moved to 83 Croydon Road where he lived for the rest of his life. Clarence was born in 1869 in Taradale, son of John Montgomery and Jane Ford. He married Sarah Ann Ingram in Echuca in 1894. Their children were: 1. Annie (Mrs P Paynter) born Echuca in 1895 2. William Henry born Echuca in 1897 3. Christina Mary (Mrs F Meyers) born Echuca in 1898 4. Violet (Mrs G Ewing) born Echuca in 1902 5. Clarence George Ingram born Echuca in 1906 and died aged 7 months. Violet became a tailoress and Christina a dressmaker. William became a carpenter like his father. Sarah Ann Montgomery died at their home in June 1932 aged 62 years. Clarence died in August 1946 aged 77 years. They are buried in Box Hill Cemetery (P-EB-0020). John Gray was "actively associated with all movements for the benefit of neighbours and fellow citizens". [Quote from the official tribute on his death in 1909.] He was very active in the Surrey Hills Progress Association in the early 1900's. The rotunda built in the Surrey Gardens by the Progress Association in 1912 was dedicated to him. John Gray was born in 1861 in Eldorado. He died on 7 December 1909 in Surrey Hills and is buried in Box Hill Cemetery (M0472). He married Emma Beckett in 1888 at 'Guildford Villa' in Essex Road, the Beckett home. They are listed in both the 1903 and 1906 electoral rolls in Arundel Crescent; his occupation is given as bootmaker. The Alan Holt property register identifies this as 24 Arundel Crescent, known as 'Tumberumba'. John and Emma had a large family: (Gunner) John Robert Gray (1888, Surrey Hills - 21 June 1917, France) Benjamin Walter Gray (1890, Surrey Hills - 1949, Heidelberg) Herbert Harry Gray (1892, Surrey Hills - 1959, Queensland) William Beckett Gray (1897, Surrey Hills - 1899, Surrey Hills) Norman Douglas Gray (1901, Surrey Hills - 1947, Sydney) Evelyn Lizzie Gray (1906, Surrey Hills - 1983) Evelyn married Reginald Roberts and donated a number of photos to the collection. The donor Violet Ewing (nee Montgomery) was Clarence's daughter. She married George Isaac Henry Ewing (blacksmith) in 1934. They inherited the family home at 83 Croydon Road. Although constructed 5 years after their opening, this rotunda was a central feature of the Surrey Gardens which was planted to a design adapted from one suggested by the renowned landscape gardener and botanist William Robert Guilfoyle (1840-1912). Rotundas were a key feature of many late nineteenth and early twentieth century public parks. This particular rotunda was notable for the Chinoiserie influence reflected in its roof. Surrey Gardens are now regarded as one of the City of Boroondara's heritage gardens and this image is significant as evidence of the design of the rotunda which is no longer extant. It is also significant as evidence of the extent of the role of the Surrey Hills Progress Association in the provision of public facilities. A black and white photo of an octagonal rotunda situated within Surrey Gardens taken from the perspective of the main entrance. It is a largely wooden structure with a domed chinoiserie-style roof. The rotunda is enclosed by established gardens. There are 4 people in the photo, with 2 women standing on the steps at the rotunda's entrance. A man and a young person are seated within the rotunda. It has 8 support pillars, which are open with balustrades to 7 sides.rotundas, surrey gardens, union road, surrey hills progress association, surrey hills brass band, parks and reserves, 1925, john gray, clarence montgomery, box hill cemetery, cinema, john gray memorial rotunda, bandstands -
 The Dunmoochin Foundation
The Dunmoochin FoundationScreenprint, Leda and the Emu, 1980
Painting depicting a reclining female nude and two blackboy plants with emu against an orange background. Inscribed (L.l) 'AP VIII/VIII Leda and the Swan' and signed (L.r) 'Clifton 80'.clifton pugh, screenprint, leda and the emu, female nude, landscape -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Black and white print, College photographs, Administration Building, 1949
... Boulevard Richmond melbourne administration building planting ...Black and white photograph. Newly completed Administration Building. Some new planting around it. Flag flying.administration building, planting, landscaping, emily gibson, flag, publicity -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Black and white print, Administration Building, 1949
... branch assembly hall library pavilion planting landscaping ...Note by T.H. Kneen 20.02.1991, Early stages of landscaping for the new building. Note young Magnolia grandiflora planted to soften stark wall. The building comprised right to left Principal's office, office for school teaching staff, offices for Fruit Preserving Branch, Agrostology Branch and future Plant Breeding Branch (branches of the Department of Agriculture), four class rooms, Assembly Hall, Library and student change rooms. The old Pavilion was demolished earlier.3 copies black and white photographs. Very similar views of the newly constructed Administration Building. Planting around the building. Flag flying.principal's office, fruit preserving branch, agrostology branch, plant breeding branch, assembly hall, library, pavilion, planting, landscaping, magnolia grandiflora, staff room, class rooms, student change rooms -
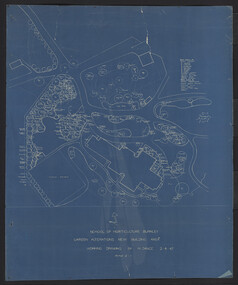 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, Hilda Marriott ( Dance), Garden Plans by Hilda Marriott (Dance), 1947-1981
Set of 8 plans, including blue-prints, of various gardens, dated c. 1947 - 1981. See paper catalogue for complete list.Plans by Hilda Marriott Dance (1) Sketch plan and 2 blueprint copies of School of Horticulture Burnley. Garden Alterations New Building Area, Working Drawing by H. Dance, Scale ⅟₂₀"=1', 2/4/47, on reverse handwritten,"Proposed Garden Lay-out for New School Building (H. Dance-plan)." (NB Emily Gibson was also involved in the planning of this site.) (2) Tracing paper, paper and blueprint copies of Ararat & District Hospital Garden Plan - MacDonald Memorial & Court, Landscape Architect - H. Dance, Scale 1 inch=8 feet. Includes handwritten note, "Replacement for Ararat Hospital Nov. 1979," list of plants. (3) Blueprint Proposed Design for Garden Watermill Farm, Newbury for Norman Gadsden Esq., Scale ⅟₄₀"=1 ft. (4) Sketch Plan for Garden, Barcombe, Buangor - January 1981 by Hilda Marriott, Scale - Approximate Only - 1:40. (5) Tracing paper copy of plan of Garden at Plumhill, Templestowe, for Mr. & Mrs. Colin Smith. Hilda Dance, Designer 26/4/47, Scale ⅛"=1'. (6) Blueprint Garden House - Sketch. (7) Tracing paper and paper copies Ararat Medical Centre Courtyard Garden, Landscape Architect - Hilda Marriott, Scale - 1:25, Date 8.5.79. (8) Tracing paper copy National Trust of Australia (Victoria) The Heights, Newtown, Geelong Garden Plan, Scale 1:250, Drawn by - Hilda Marriott, Date 12.10.79.(1): on reverse handwritten,"Proposed Garden Lay-out for New School Building (H. Dance - plan)." (2): Includes handwritten note, "Replacement for Ararat Hospital Nov. 1979," list of plants.hilda marriott ( dance), burnley school of horticulture, students -
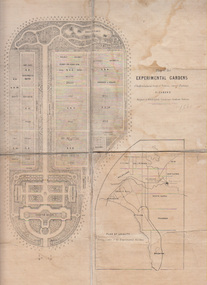 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, Alfred Lynch, Plan of the Experimental Gardens of the Horticultural Society of Victoria. Survey Paddock. Richmond, 1861
Subsequently the area was not fully developed in this manner following flooding in 1863. Some remnants remain.Plan on paper with cloth backing. Inscription, "Designed by Alfred Lynch. Landscape Gardener, Prahran. Printed by De Guchy & Leigh." An inset plan shows position of Experimental Gardens related to the City of Melbourne and Bay. Plan shows layout and plantings of the designated area - fruit, vegetables: the conservatory, nursery, exhibition buildings. This plan was owned by E.E. Pescott. Inscription on cover, "Burnley. E.E.P.." "Ed. E. Pescott." Subsequently the area was not developed in this manner. See inscription on copy made for Centenary Exhibition B92.633. Other copies given to College by N. Lothian (graduated 1934). Jim Sanders, a friend of his, gave them to Dr. G. Moore in 1991. A larger copy, inscribed on reverse, '1861', 'Early proposals for Horticultural Gardens for Horticultural Society of Victoria (now Royal). The lithograph was included as an insert in the Farmers Journal and Gardeners Chronicle 21 June, 1862. It is only in one of the copies held by the State Library of Victoria. 1 large and 1 small photographs of plan. Several photocopies of the plan.Inscription, "Designed by Alfred Lynch. Landscape Gardener, Prahran. Printed by De Gruchy & Leigh." / Inscription on cover, "Burnley. E.E.P.." "Ed. E. Pescott."alfred lynch, experimental gardens, conservatory, nursery, e.e. pescott, n. lothian, jim sanders, dr. g. moore, horticultural socoety of victoria -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, Swan Street Entrance. Also see B15.0352, 1988-1998
(1) 1 coloured and 2 copies, hand drawn , and 4 tracing paper sketches. Concept and Drawing by Steve Mullany, Lecturer V.C.A.H. Burnley, 09.12.1988. (2) 2 copies on tracing paper, original on paper with some additional notation and 3 copies of Landscape Plan by Steve Mullany 3 Feb 1989. (3) Photocopy of Project Eden, Swan Street, Richmond - Landscape Plan LA2 Project No 682 by Mark Mc Wha Pty. Ltd. Nov 1997. Includes Irrigation and Plant Schedule. (4) Coloured, Swan St Frontage Planting Scheme by P. Tulk for AMRAD 19.2.1998. -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, Mark Burns, 3 Stage Therapy Garden Merve Irvine Nursing Home, 1996
Laminated and coloured Planting Plan by Mark Burns dated 07.10.1996, File No B33 Sheet No 3 of 4. Scale 1:100.mark burns, merve irving nursing home, landscape design, therapy garden, water features -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, ACM Landscape Architecture, Courtyard & Entrance, 1995
Photocopies of sketches of Set out plan, Planting plan & surface finishes details. Typed description of works by ACM Landscape Architecture. Not sure if this relates to Burnley or is Student work.acm landscape architecture, burnley, courtyard garden -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, Jacqueline Fraser, The Chivers House 34 Finlayson Street Malvern East, 1991
(1) Jacqueline Fraser - Site Inventory and Analysis dated 5.11.91, Conceptual Design dated 1.11.91, Planting Plan and Section Elevation dated 8.11.91. Scale 1:100. (2) Troy Watchorn - Site Analysis and Inventory, Concept Plan, Planting Plan, Section Elevation, dated 14.11.1991. Scale 1:100. (15 sheets)jacqueline fraser, troy watchorn, landscape design, malvern -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, S. Soerono, Project Xerophytic Garden, 1989
... Boulevard Richmond melbourne s. soerono landscape design xerophytic ...Planting Plan and Coloured Elevation from Pt A to A₁ by S. Soerono, dated 10.11.1989s. soerono, landscape design, xerophytic gardens -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Colour prints, Miscellaneous Quad and Other
(1-3) Quad landscaping. (4) Bull Paddock with staff carparking (created 1974). (5) Wisteria at entrance to Administration Building. Remainder plants and roots in soil.quad, landscaping, bull paddock, wisteria, administration building, staff carpark -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesWork on paper (item) - Student Work, Anton Bialylew, Kneebone Project Landscape Design, Uncertain, probably 2017-2018
Made as an assignment for HORT90035, a subject at Burnley Horticultural College coordinated by Andrew Laidlaw. -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesWork on paper (item) - Student Work, Sandra Brizga, Andembach - Riverside Garden Planting Plan, 8 November 2018
Made as an assignment for HORT90035, a subject at Burnley Horticultural College coordinated by Andrew Laidlaw. assignment, burnley horticultural college, hort90035 -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesWork on paper (item) - Student Work, Iroshan Gangodawialge, Blackney Residence Garden Landscape Design, 2017
It was made as an assessment for HORT90035 Landscape Construction and Graphics, a subject at Burnley Horticultural College coordinated by Andrew Laidlaw. assignment, burnley horticultural college, hort90035 -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesWork on paper (item) - Student Work, E. Johnston, Mooney Residence Landscape Design, September 2017
Submitted as an assignment for an unspecified subject at Burnley Horticultural College, probably HORT90035 coordinated by Andrew Laidlaw. assignment, burnley horticultural college -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesWork on paper (item) - Student Work, Lucas McGarrigle, Landscape Design Plan, 2018
Made as an assignment for HORT90035, a subject at Burnley Horticultural College coordinated by Andrew Laidlaw. assignment, landscaping, burnley horticultural college, landscape construction and graphics, hort90035 -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesWork on paper (item) - Student Work, Jane McKenzie-Smith, Ironbark Designs Landscape Design, 2015
The sheets were submitted as part of a landscape design project, most likely for HORT90035, 'Landscape Construction and Graphics,' a subject at Burnley Horticultural College coordinated by Andrew Laidlaw. It seems there is a third sheet missing that would have been the site analysis component of this project. assignment, landscaping, burnley horticultural college, landscape construction and graphics -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan (Item) - Landscape design, Landscape Design Plant List & Graphic interpretation - For?
... Landscape Design Plant List & Graphic interpretation - For? ... assignment showing plant list and graphic interpretation Landscape ...amy willis, landscape design -
 Friends of Ballarat Botanical Gardens History Group
Friends of Ballarat Botanical Gardens History GroupWork on paper - Victoria Park Precinct, City of Ballarat, Victorian Heritage Database place details -19/9/2017, 19/9/2017
Victoria Park is associated with gold mining in the 1860's, military manoevres in the late 19th century; as an army base during World War 2 and a recreation area.Victoria Park is a "landmark cultural landscape" in the city of Ballarat. This parkland established 1890-1910, was modelled on English country estates and London Parks. It demonstrates the civic pride of Ballarat citizens and is an important parkland for the local community. There is a collection of exotic and early planted native trees and areas of native grasslands.6 pages of print. p.1. is a front page with a map and Victoria Park marked in purple with a bibliography on p.4 and footnotes on p.6.None.john garner, victoria park, friends of ballarat botanical gardens, heritage overlay, gold mining, parkland, late nineteenth century, native grasslands, exotic and native trees, royal park, mullock heap, mount holled-smith, arbor day, messrs clegg&nicholls, william guilfoyle, w.o.allen, significant tree register, john garner collection, gardens, ballarat -
 Phillip Island Conservation Society Inc.
Phillip Island Conservation Society Inc.Work on paper - Photocopy of newspaper cutting, "PHILLIP ISLAND/A place to fall in love"
This article was written by an English visitor named Elsa Christian who was touring Australia and New Zealand with her husband Frank in their own small van. The article was published in the Australian Women’s Weekly, magazine, March 1966. Elsa writes she wanted to visit four Australian locations before she died: Ayers Rock (actually Uluru), the Snowy River project, dolphins at Coolangatta and the Penguin Parade at Phillip Island. These destinations were all very popular in the 1960s for both Australian residents and overseas visitors. Because the roads were becoming better too many locations, self guided tours in small vans for cars towing bond would caravans were becoming more popular means of seeing AustraliaThe article is significant in many ways. 1. Indicates the places English visitors commonly wish to see in Australia. 2. Describes the growing trend to self- drive van/camping holidays. 3. Gives the route taken from Melbourne to Phillip Island during the 1960s. 4. Describes the appearance of the roadsides and locations visited. 5. It is written in a descriptive and lyrical style designed to appeal to Women’s Weekly magazine readers, who were probably wondering how they could visit Phillip Island with their husbands or families themselves, and what there was to see there. 6. Gives the visitors’ view of how the Penguin Parade operated at the time. 7. Includes a description of potter and artist Eric Juckert’s renowned garden at Grossard Point, Ventnor. 8. Indicates how introduced plants such as Hawthorn pushes and Kate weed were common in the area. 9. Describes Phillip Island as “a place to fall in love” because of its natural beauty, fauna and coastal seascapes. 10. As a visitor Elsa describes the housing estates as a blot on the landscape, but also sees the value as a way of their owners escaping from the hustle and bustle of Melbourne. 11. Gives the visitors’ interpretation of the behaviour of wildlife the RC in the wild, as well as Elsa’s knowledge about some of the species she encounters.Photocopy of full page article with 5 columns of text, a map and 2 photographs. Black ink on white paper. Photographs blackened in photocopying processphillip island, cape woolamai, penguin parade, seal rocks, nobbies, township of rhyll phillip island, princes highway, dandenong, pakenham, kooweerup, carinya creek, officer, san remo, gippsland highway, holiday homes, fort dumaresq, kitty miller's beach, wreck of the speke, hereford cattle, fleetwood manor, koalas, ventnor, eric juckert, little penguin behaviour -
 Merri-bek City Council
Merri-bek City CouncilLithograph, John Wolseley, After the Fire - Leaf Surge, 2003
British born artist John Wolseley relocated to Australia in 1976, where he travelled extensively through the outback mainly recording the natural history of remote north Australia in large, minutely detailed paintings. Since 2009, he has travelled to Darwin annually to continue his exploration of the Top End, visiting Arnhem Land and Daly River to work with Indigenous artists to research and capture the detail and essence of particular landscapes. His works reflect how landscape can be thought of as fields of energy in which plant forms move or dance with rhythmic life. After The Fire - Leaf Surge represents the vibrant regrowth of new foliage emerging from a landscape recently ravaged by fire. -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionDrawing, Stratford, Noella, 'Avenue of Desire' by Noela Stratford, 2005
Noela STRATFORD Dr Noela Stratford explores Australian landscapes, and considers their contextual systems in her personal interpretations. This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 2000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.A framed drawing of agave plants along an isolated place in southern Spain. art, artwork, noella stratford, flowers, flora, spain, agave, noela stratford -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Graves of Thomas Sweeney and family, Eltham Cemetery, Victoria, 27 January 2008
... in a new section called Ashes Walk. Local landscape architect... in a new section called Ashes Walk. Local landscape architect ...The grave of Thomas Sweeney, former convict turned respectable citizen. The Murray and Sweeney families were both early settlers of the Eltham district and connected by marriage. Their family plots are located side by side in the Catholic section of the Eltham Cemetery. Irish-born Thomas Sweeney is regarded as the first settler in Eltham. He was transported to Sydney in 1823 after being convicted of arson. He was granted his freedom in 1838 and married Margaret Meehan in the same year. They moved to Melbourne and in 1842 Thomas purchased 110 acres beside the Yarra River in the vicinity of present-day Sweeneys Lane. He called the property ‘Culla Hill’ and built a small slab hut (reputedly with Wurundjeri help; Margaret is said to have run an informal hospital for them in return). This was followed in 1846 by more substantial buildings consisting of a three-roomed Irish-style ‘longhouse’ and a barn made of stone and handmade bricks, with doors large enough to accommodate a fully loaded wagon. When the gold rush came, Thomas prospered by selling meat and potatoes to the prospectors, enabling him to purchase a further 308 acres in 1856. He promoted the construction of a bridge over the Plenty River and the establishment of a school at Eltham. Roman Catholic Church services were held at Culla Hill in the early years. When he died in 1867, he was regarded as a respected member of the community. Thomas and Margaret are buried in Eltham Cemetery with many of their descendants. Their first son John continued to farm Culla Hill until his death in 1909. Culla Hill passed out of the Sweeneys' possession in 1939. The house and barn remain today, though lesser outbuildings have gone. The facade of the house is much the same as it was in the 1840s. Sacred To the memory of Thomas Sweeney Who died Sep 6th 1867 Aged 65 years May his soul res in peace Also his wife Margaret Died Oct 3rd 1884 aged 73 years And their daughters Annie Died Aug 22nd 1860 aged 21 years Johanna Died Aug 19th 1872 aged 22 years Margaret Died 7th Sep 1913 aged 72 years R.I.P. Also In Memory Of John Sweeney Died 24th May 1909 Aged 65 years Also of his wife Ellen Died 8th March 1910 Aged 64 years R.I.P Also In Memory Of Caroline Infant daughter of John & Ellen Sweeney Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p55 From the piety and poverty of 19th century Eltham, 20th century artists and environmentalists, to today’s comfortable middle class, Eltham Cemetery records it all — and more. A visit to Eltham Cemetery reveals an important social record since its beginnings in 1858. The cemetery was situated on about six acres (2.4ha) (now around 4.8ha) at the corner of Mount Pleasant and Metery Roads.1* It is thought that Metery Road was originally called Cemetery Road, but in the early 1940s, a resident, possibly a councillor, objected to the name resulting in the change.2 Much can be gleaned about the developing Eltham community from burial styles and the names of former local residents. Originally the cemetery was divided into Christian denominations, like others of that time, following the United Kingdom burial system. In 1861 the cemetery included Church of England, Presbyterian, Roman Catholic and Wesleyans (later Methodist) sites. Graves also indicated social class. Some had grand tombstones, perhaps fenced with ornamental cast iron railing, but most in the 1860s and 1870s were constructed of modest stone slabs.3 This indicated the poverty of the district, which was largely inhabited by farmers on small landholdings. A poignant reminder of the high rates of infant mortality of those times, are the many infants and young children recorded on the headstones. Major changes occurred in the cemetery in the late 20th century as Christian adherence weakened and society became more egalitarian and informal. In the early 1970s a non-denominational lawn section for burials was established. Since then all new areas have been non-denominational to accommodate the more diverse local community. Now, instead of large ornamental headstones, some mourners have chosen boulders, reflecting the natural Eltham style, while others choose graves in the lawn areas or niches in walls. In the late 1970s, the University Donor Section was established north-west of Candlebark Lawn for those who donated their bodies for The University of Melbourne medical research. In the early 1980s the natural Australian garden style, popular in Eltham, was mirrored in a new section called Ashes Walk. Local landscape architect Gordon Ford, who had popularised this style, designed the Walk using boulders shaded by native plants beside curved pathways. Landscape architect Robert Boyle later redesigned Ashes Walk and developed other parts of the cemetery in keeping with this style.4 Appropriately Ford, who died in 1999, was interred in the Native Garden Section in a cluster of sites shaded by a large eucalyptus tree.5 By 2007, about 6400 interments were recorded in the Eltham Cemetery. Close inspection reveals notable names in the district’s history. The grave of Thomas Sweeney, a former convict who became a respected citizen, can be found in the Roman Catholic section near the path. Eltham Primary School’s first headmaster, David Clark, is buried in a modest grave in the Church of England section to the east of the path from the main entrance. Sir William Irvine, Victorian Premier from 1900 to 1902, whose grave is in the north-east Presbyterian section was at various times Victoria’s Chief Justice, Deputy Governor and Treasurer.6 Further south is the grave of social reformer Bertram Wainer, born in Scotland in 1928 and died in 1987. He campaigned to legalise abortion and exposed police corruption in allowing illegal ‘backyard’ abortions. Other prominent local residents interred in the cemetery include: Justus Jörgensen, who founded Montsalvat; Alistair Knox, the mud-brick housing pioneer and Eltham Shire Councillor from 1971 to 1975 and President in 1975; Clem and Nina Christensen, who had a major influence on the literary development of post World War Two Australia. Others were: composer Dorian Le Gallienne; artist Peter Glass; Stephen Dattner, a prominent Melbourne furrier; ALP parliamentarian for Greensborough, Pauline Toner and political scientist and commentator, Professor William Macmahon Ball.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, annie sweeney, caroline sweeney, ellen sweeney, eltham cemetery, graves, gravestones, johanna sweeney, john murray, john sweeney, margaret sweeney, mary ellen drain, mary murray, thomas murray, thomas sweeney -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Wingrove Cottage, Main Road, Eltham, 8 June 2006
Wingrove Cottage built 1858-1859 of hand made bricks is historically significant for its long association with Charles Wingrove, a prominent figure in Victorian local government, as secretary to the Eltham District Road Board and Shire Council from 1858 to 1904, and Shire Engineer and Secretary to the Heidelberg Road Board. The cottage was used as the office of the Eltham District Road Board and Council for many years It is one of the Shire's oldest dwellings, and one of the few surviving 19th century buildings associated with early Eltham and located in the original Eltham Village Reserve. The symmetrical planting of a pair of Pencil Pines (not visible in photo) is also historically and aesthetically significant as characteristic of the early period of planting in the district and because they are a distinctive landscape feature. In October 2002 new owners demolished the outbuildings attached to the rear of the cottage. Community protest at the demolition resulted in Council issuing a Stop Work order. The owner was issued with a court order in September 2003 to develop a conservation management plan and restore the heritage listed property. The owner sold the property in 2005 to Cameron Construction in 2005 who undertook the restoration work. In 2007 a planning application to build two offices and seven dwellings at the rear of the property was ultimately rejected. The cottage is now the main office for Cameron Construction. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p57 Wingrove Cottage on Main Road beside Eltham Primary School, is one of the Shire’s most important historical buildings and was central to local government for almost 50 years. The cottage was built in stages from 1858 to 1888 for Charles Symons Wingrove JP. He was the Eltham District Road Board’s first paid secretary and later the Shire Secretary when the board became the Eltham Shire Council. Wingrove held those positions, and that of engineer for a time, for 46 years. He was also one of the main figures in the Municipal Association of Victoria. As Eltham’s first paid municipal officer, Wingrove used one room in his 11 – (originally two) roomed home, as the office for the board then the council. Meetings were held there from the late 1850s (as well as at more central locations) until Wingrove’s retirement in 1904. The cottage is a rare example of a local government office occupying a Road Board /Shire Secretary’s purpose-designed house. The cottage is also significant because it is the oldest largely intact building from the original Eltham township reserve (south of Dalton Street).1 The township had its origins in the 1848 Nillumbik Parish Plan and was one of the state’s earliest township reserves. The rectangular house of handmade bricks, roofed with grey slate tiles and with a veranda encompassing three sides, is reminiscent of those in the central goldfields including Castlemaine. Its overhanging eaves and gables were unlike houses in Melbourne at the time. Wingrove, who was born in 1827, had been a gold digger and a road surveyor. Impossible to imagine in today’s world, Wingrove was also the Shire of Heidelberg’s secretary and engineer for part of the time that he was secretary in Eltham. Living next door to the primary school was a mixed blessing. Wingrove and his wife Katherine, who had ten children, sent their eight surviving children to the school. But they had occasional disputes with the school authorities when their cattle wandered into the schoolyard. Eltham showed Charles Wingrove its appreciation of his services by giving him two illuminated addresses, one after ten years and the other at retirement. Wingrove died in 1905 aged 76 and was buried in the St Katherine’s Church of England cemetery in St Helena. His grave is surrounded by those of family members including his wife, Katherine and two babies, Henry, 12 months and Isobella, 15 months, who died in the mid-1860s. Cottage ownership passed to his wife, then to daughter Caroline and then to daughter Bessie, a Melbourne University graduate and artist. During the Great Depression their brother Walter was the ratepayer. At one stage the Wingrove property extended to Metery Road and included a small creek. The family ran a small dairy and orchard, with associated farm buildings, which were later removed. In 1949 part of the property was compulsorily acquired by the Eltham Primary School, which infuriated owner Bessie Wingrove. She protested in a letter about this ‘monstrous act of unmitigated tyranny’.2 She was the last Wingrove to occupy the cottage and died in 1955. Wingrove descendants sold the house in 1974 and the property was subdivided. In the 1960s the Eltham Shire named the park opposite the cottage in Wingrove’s honour. The cottage has since had several owners including psychiatrist Dr Daniel Kahans, who practised there. In October 2002 late rear additions which had been substantially altered were demolished contrary to council planning controls. This caused a community outcry and resulted in legal proceedings against the owner. Fortunately the historical significance of the demolished section was not as great as the older front part of the building, which has been retained and was later restored.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, cameron construction, charles symons wingrove, eltham, eltham road district board, eltham shire council, main road, wingrove cottage -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Former home of Alistair and Margot Knox, King Street, Eltham, 16 January 2006
Situated in King Street, Eltham, Alistair Knox built his home and office in 1962-1963 with mud-bricks made from the local soil and recycled materials blending the house with bush around it. Knox popularised the Eltham earth building movement, begun by Montsalvat founder, Justus Jorgensen. Alistair Knox (1912-1986) was also an Eltham Shire Councillor 1971-1975 and Shire President in 1975. Knox established the inaugural Eltham Community Festival in 1975. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p145 Lack of money was a strong incentive for Alistair Knox to do what he did best when he built his house and office at King Street, Eltham in 1962-63. He used mud-bricks from local soil and recycled materials, characteristically blending the house with the bush around it. The result was a work of art. Knox popularised the Eltham earth building movement,1 begun by Montsalvat founder Justus Jörgensen. He was also an Eltham Shire Councillor from 1971 to 1975 and Shire President in 1975. For Knox mud-brick building was not just a building style, but a spiritual experience and a way of relating with nature. At 40 he rediscovered God and his building reflected his theological, political, philosophical and particularly environmental world view, which was far ahead of its time.2 He also contributed to building development in his use of concrete slab foundations when stumps and bearers were the norm. Knox was introduced to mud-brick construction in 1940 by Jörgensen, then shortly after, Knox joined the Navy. In 1946 Knox studied Building Practice and Theory at Melbourne Technical College (now RMIT University). There he befriended fellow student and artist Matcham Skipper who belonged to what was then called the Jörgensen Artists’ Colony. Knox decided to build an earth building in Eltham, partly because the post-war huge building demands resulted in expensive and scarce building materials. He asked artist Sonia Skipper for help who, with Matcham, had constructed mud-brick buildings at the Artists’ Colony. The simple rectangular low-lying house at King Street is framed by native plants and a 3.6 metres wide pergola surrounds the building. Wedded to the landscape, a door in every room at the perimeter, opens outside. The property also includes a forge, a small hut built by son Macgregor at 15, and a mud-brick tower for chickens. Building materials were foraged from a wide variety of sources. Some of the joinery material came from old whisky vats. When the Oregon of the highest quality ‘was put through the wood-working machines, it gave off a deep smell of whisky that made the whole atmosphere exotic and heady’.3 Amateur builders, including schoolboys from Knox’s Presbyterian Church, made some of the mud-bricks. But the building was finished with the professional help of Yorkshire builder, Eric Hirst. Inside, the light is subdued with the mud-brick, beamed timber ceilings and floors of slate, timber or orange-brown tiles. Skylights, with rich blue and red leadlighting, illuminate one entrance area and this feature is repeated as edging on the door. The centre of the house is like a covered courtyard, with rooms built around it. The central room, 11 metres x 7 metres, was built in the same proportions as Knox’s mud-bricks. Clerestory windows on four sides infuse the room with a soft light. A huge brick fireplace extends beyond one corner and opposite is a small one where timber can only be placed vertically. The slate for the floor was discarded from the Malthouse Brewery now used as a theatre in Southbank. In the middle is a large refectory table and benches that seat 18. Like much of the house, it is rugged, yet beautiful. Made of Western Australian Jarrah by Macgregor with a chain saw and an adze, it retains knot and nail holes. Each wall has an opening, 2.4 metres at the ends and 3.6 metres at the sides. Only one has doors and these concertina doors are made of the backs of old church pews. The main bedroom has an ensuite with a marble hand basin discarded from the Victorian Parliament building; and a dressing room, where two wardrobes of polished timber recovered from a tip are attached to the walls. Separate from the house is the strikingly original circular-shaped office made of bluestone sourced from the original Army campsite at Broadmeadows.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, alistair and margot knox house, alistair knox design, mudbrick construction, eltham, king street -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Hawthorn hedges, Eltham-Yarra Glen Road, Kangaroo Ground, 3 October 2006
Hawthorn hedges are important reminders of Kangaroo Ground's Scottish heritage. They are Registered on the Victorian Heritage Register. They are "historically significant because the planting of hawthorn hedges reflects the adoption of Eurorpean farming techniques by the Kangaroo Ground population in the period following settlement and because the grid pattern of paddocks that the Hawthorn hedges define is very different to today's farm landscapes." Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p21 Hawthorn hedges bordering Kangaroo Ground’s gently rolling farmlands are important reminders of its Scottish heritage and are rare so close to Melbourne.1 As early as the 1840s newly arrived farmers from Scotland planted hawthorn hedges around their properties, to protect crops from the numerous kangaroos and wallabies. Many of these hedges survive today. These farmers had the good fortune to settle some of the most fertile land available for cropping in the Colony of Victoria. At that time the black volcanic soil could sustain an amazing two crops a year. By the mid 1850s, 500 acres (202ha) of wheat were growing in Kangaroo Ground. But the crops were threatened by kangaroos, which were so plentiful, that Surveyor-General, Robert Hoddle, named the district Kangaroo Ground in 1838. As post-and-rail fences proved inadequate barriers for the bounding kangaroos, the Scots planted hawthorn hedgerows as they had done in Scotland. Some also used the hedges to net birds, presumably for the table. Interestingly the farmers in the bordering townships of Panton Hill and Christmas Hills, did not plant hawthorn hedges around their properties. Perhaps it was because by the time they settled in the 1860s and 1870s most of the wildlife had been gunned down by residents.2 The canny Scots planted the hedges on public land outside their own farms, as the hedgerows could spread to about five yards (five m) in width. With this impenetrable barrier Kangaroo Ground’s industrious farmers flourished to gain the economic power that saw the Shire of Eltham governed from Kangaroo Ground for 79 years (1858-1937). The Scots jealously guarded their land, so hard to get in Scotland. That is why they refused to release any of it ‘for local roads to follow easier grades as was the case in surrounding districts where roads generally followed ridgelines or streams’.3 Instead the roads were built in accordance with the magnetic bearings of their first survey in 1847 whether that suited the steep topography or not. This could force traffic to diverge when wet through Greensborough and Diamond Creek. Until 1921, the Eltham-Yarra Glen Road beside Wellers Restaurant, ‘dipped down into the upper reaches of Stony Creek’.4 Later some corners were compulsorily cut for the increasing motor traffic. As late as the 1960s, corners were cut to form sweeping curves above and alongside the Kangaroo Ground Cemetery and opposite the Emergency Operations Centre. In the latter case, the farmers – understanding their hedgerows as important heritage – insisted upon their reinstatement to conform to the altered road alignment. Kangaroo Ground’s ancient manna gums also point to the district’s history and to that of the hedgerows. The Aboriginal people had transformed the original forests into grasslands with the fires they lit to attract kangaroos, (which the Scots were to exclude by planting hedgerows). But the Wurundjeri hunters left the gums (Eucalyptus vimminalis cygnetensis), on the grasslands as ‘stalking trees’ to hunt kangaroos. The hawthorn hedges in Kangaroo Ground were neglected for around 60 years from about the middle of the 20th century. Bushfires had created gaps and the hedgerows were not trimmed. Then in late 2005, local historian Mick Woiwod, formed a group to lobby the Nillumbik Shire to restore the hedges, which could last for many centuries. Some hedges in parts of Britain date back to AD 800.5 Although the original Scottish farmers have gone, the hedges are a reminder of when they flourished in the district, which has changed little in 150 years.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham-yarra glen road, hawthorn hedgerow, kangaroo ground -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, St Andrews Hotel, 2 February 2008
The c1860 St Andrews Hotel, with the c1930 additions, and the Canary Island Palm, and the surrounding site to the title boundaries are historically, socially and aesthetically significant to the Shire of Nillumbik. The St Andrews Hotel is historically significant because it may have given its name 'St Andrews' to the town (another suggestion is that the name came from St Andrews church) and for its connection to Ewen Hugh Cameron (1831-1915) the prosperous local farmer, member of the Eltham Roads Board/Shire Council and local MP. It is also significant as the oldest hotel building in the former Shire of Eltham, as one of the few surviving buildings connected with the Caledonian goldfields era and as one of a handful of early structures to have survived the 1960s bushfires; the additions and alterations to the hotel reflect its long life. The hotel is socially significant because it has served as an important meeting place for more than 160 years. The Canary Island Palm is historically significant as a rare example of exotic tree planting in this rural area. The tree is aesthetically and historically significant as a local landmark and for its contribution to the streetscape and landscape value. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p71 Built around 1860, St Andrews Hotel has changed little since it first welcomed thirsty gold diggers from the Caledonia Goldfields. The timber building, with gabled roof, beamed ceilings and a massive fireplace, is Nillumbik Shire’s oldest hotel and has always been an important community centre, particularly in its early days. Fortunately, the hotel and the near-by Canary Island Palm Tree, which is quite rare in this area, survived the 1960s bushfires, along with a few other early buildings. St Andrews (formerly Queenstown) was founded on gold, as were Panton Hill (formerly Kingstown), Research and Diamond Creek, from the mid-1850s to the 1860s. But by the early 20th century common use changed the name Queenstown to St Andrews, possibly after this hotel or after the church or the mining district.1 The Caledonia Diggings were probably named by Scottish settlers after the Roman name for Scotland, despite this land bearing little similarity to their homeland.2 Queenstown, which was proclaimed as a township in 1861, was the gold-mining centre on the Upper Diamond and in the 1850s had up to 600 European inhabitants and a small camp of Chinese on the flats along the creek. Queenstown was the administrative centre of the Upper Diamond with three hotels, a brewery and a slaughterhouse.3 It is unclear which hotel was the district’s first, as distinct from the earliest unlicensed grog shops, some of which operated in tents. John Corke Knell was one of eight unlicensed storekeepers supplying drink to miners at Caledonia in 1857, named by Sgt. McNamara of the Caledonia Police Station.4 In February 1859, Knell apparently bought most of the present hotel’s site at the first township land sales. As he was a local storekeeper, he might have first established a store there.5 Knell and his wife Eliza were early licensees of the St Andrews Hotel. The hotel had eight bedrooms – including three for public use – and the dining-room seated 30 people. It is thought they named the hotel St Andrews after Eliza’s hometown of St Andrews in Scotland. St Andrews Hotel was an important local centre in several ways. In the same building the Knells also operated a post office and general store. In 1867 Mrs Knell was appointed Deputy Registrar of Births and Deaths for Queenstown. The hotel was also used to hold inquests into people’s deaths when the police residence became too small.6 The hotel also became a fashionable destination at Christmas for parties from Melbourne. In 1868, possibly following her husband’s death, Mrs Knell applied for a temporary licence, which was then transferred to Robert Smith after their marriage in 1869. But then, possibly after Robert’s death, Mrs Smith operated the hotel until 1892. This contradicts a report in The Evelyn Observer 1882 that JC Knells of the St Andrews Hotel was granted a publican’s licence in the Queenstown Police Court. At that time he was supposed to have been dead for around 14 years! Although Mrs Smith was a respected citizen, known for her geniality and as an ideal hostess, she had a minor brush with the law when she was fined ten shillings for not lighting a lamp outside her licensed premises.7 From 1892 several publicans owned the hotel including W Atkins, from 1895. In 1909 the licensee was apparently Mrs Smith’s son, Walter Knell, who held the licence until at least the 1920s. Not surprisingly, this old hotel has attracted romantic stories. Mrs Smith is said to be seen roaming the pub in her nightdress – even though she was buried in the Queenstown Cemetery in 1911.8 A musical The Hero of Queenstown, set in the hotel, was written and produced by local actor Reg Evans in the 1970s.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, st andrews hotel -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Gordon Ford's Garden, 'Fulling', Pitt Street, Eltham, 10 November 2006
'Fulling', the half-hectare property at Pitt Street, Eltham was the home of landscape designer Gordon Ford and his wife Gwen. Ford bought the property in 1948, originally part of an orchard. The garden encapsulates the major trends of Australian garden design in the second half of the 20th century. The garden design is based on mass (plants) and void (paths and pools), textures and forms. It epitomises the Eltham style because of its relaxed informality and attraction to native wildlife. The mud brick house and designed and built by Ford commenced in 1948. Several extensions were added up to 1970 and were built by Graham Rose (Source: information panel for exhibition, n.d.) Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p147 A narrow timber gate opens onto a garden that has had a huge impact on natural garden development in Australia since the 1950s.1 Fulling, the half-hectare property at Pitt St, Eltham, was the home of the landscape designer, Gordon Ford, who died in 1999. The garden ‘encapsulates the major trends of Australian garden design in the second half of the 20th century...and epitomises the Eltham style of garden’.2 It in turn, was influenced by several Victorian major landscape designers of the mid 20th century – Ellis Stones, Peter Glass and Edna Walling. The gate opens onto a sandy gravel path, one of several, which wind around dramatic pools and what appear to be natural bush, but on close inspection are carefully integrated native, indigenous and exotic plantings. Retaining walls and steps of rock through the garden link different terrace levels. Lichen-covered boulders serve as steps across a pool, leading to the triple level mud-brick house. Ford bought the property, which was originally part of an orchard, in 1948. As the son of a Presbyterian minister, Ford received a good education, which included learning Latin. This was advantageous when he worked in plant sales for the Forestry Commission, before the Second World War. In the late 1940s, however, Ford turned to building and landscape gardening. He worked on the Busst house, an early mud-brick building designed by Alistair Knox and at the same time, Ford was employed by Ellis Stones. Knox described Ford as, ‘one of the funniest men of the district. ...Rocky’s (Ellis Stones) Depression stories and Gordon’s memory and quick tongue made the jobs the most enjoyable of all those hysterical times that made Eltham the centre of the eternal laugh, between the years of 1945 and 1950’.3 Ford’s house, like so many after the war, was built progressively, as more space was needed and formerly scarce materials became available. It began with an army-shed of timber-lined walls, now used as the kitchen. Ford then built what is now the lounge room, and the house grew ‘like topsy and on a shoestring,’ says his widow Gwen. A lot of second-hand materials such as window frames were used, a style made famous particularly with their extensive use at Montsalvat, the Eltham Artists’ Colony. The house was constructed as a joint venture with friends, including artist Clifton Pugh, who built Ford’s bedroom for £10. The polished floorboards and solomite (compressed straw) ceilings, interspersed with heavy beams, exude warmth. The result is a home of snug spaces, with soft light and garden vistas. Several other mud-brick buildings were constructed as needed, including a studio and units for bed-and-breakfast clients. The garden, which has been part of the Open Garden Scheme since the mid 1980s, is based on a balance of mass (plants) and void (paths and pools), textures and forms. It epitomises the Eltham style because of its relaxed informal ethos and attracts native animals. Wattlebirds, scrub wrens, pardalotes, currawongs, owls and even kangaroos, have been seen at Fulling. Gwen, a former English teacher who has worked on the garden since around 1970, urged and helped Ford write his book, The Natural Australian Garden.4 Several of Ford’s favourite trees are in the garden, including the native Casuarina or She-Oak. In spring, the garden is dusted with the purple Orthrosanthus multiflorus or blue native irises and rings with the calls of birds attracted to plants like the callistemons, correas and grevilleas.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham, fulling, gordon ford garden, pitt street, eltham mud brick buildings, mud brick house -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Eltham Community and Reception Centre, 2 October 2006
The Eltham Community and Reception Centre was Australia's first public mud-brick building. Commissioned in 1977 by Eltham Shire Council, led by Shire president (and architect) Robert Marshall, architects Whitford and Peck were asked to design a multipurpose facility in mud-brick and timber. The official opening was performed by the Hon. R.J. Hamer; E.D., M.P., Premier of Victorai on Saturday, April 22, 1978. Architects: Whitford & Peck Pty Ltd Quantity Surveyor: D.J. Cant & Associates Structural Civil Engineers: Charlett & Moore Pty Ltd Landscape: Peter Glass, Dennis Edwards Mech Elec: Lobley Treidel & Partners Pty Ltd Acoustics: Riley Barden & Kirkhope Builder: L.U. Simon Pty Ltd Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p177 The Wiggles performed there, so has the ABC’s Play School. New citizens have made their vows, volunteers have been honoured, school children have performed, weddings celebrated and people mourned at funerals. Since 1978 the Eltham Community and Reception Centre at the corner of Pitt Street and Main Road, has provided a beautiful and quintessential Eltham environment for people from all over Melbourne. Recognised as Australia’s first public mud-brick building, the centre was built partly on the site of the parsonage of the former Methodist Church (now the Uniting Church).1 Commissioned by the Eltham Council headed by President Robert Marshall, architects Whitford and Peck were asked to design a multipurpose facility in mud-brick and timber. Following public consultation, it was agreed to build a centre for dances, exhibitions, films, plays or concerts. The results – at a cost of around $620,000 – captured the Eltham rustic style. The building – in soft tones of mud-brick and timber and immense floor-to-ceiling windows – overlooks the Diamond Creek and sporting fields. Eltham’s strong artistic heritage is reflected in the centre. Although the lighting is not ideal for a gallery and labels cannot be placed on walls, the centre hosts the Nillumbik Art Awards and displays around ten to 20% of the Nillumbik Shire Art Collection, usually for around a year at a time.2 On permanent display, close to the entrance, is local artist Clifton Pugh’s White Choughs in the Landscape. Further to the right is the Walter Withers Gallery, named after a local member of the Heidelberg School of artists. As part of the Eltham Gateway opposite the Eltham Hotel, the centre stands on what was once part of the Eltham Town Centre along this section of Main Road, then known as Maria Street. On the same site once stood the house and flour mill owned by Henry Dendy, best known as the founder of Brighton, although he lived longer in Eltham. Beside the drive is a wheel-rim tool with accompanying plaque, illustrating a technology important during the horse-powered age and now almost completely gone, as has the blacksmith’s shop that had housed it nearby. The implement is a platform for fitting iron tyres to the wooden rims of cartwheels. Beneath it is a capsule placed in 1985 to commemorate Victoria’s 150 years, which is to be opened in 2035. Although the plants, forming part of the landscaping by Peter Glass and Denis Edwards, are largely indigenous and other native species, some exotic plants are protected as an important link with the site’s past. Planted at the front around 1920, is a large Peppercorn tree with two joined trunks growing from the base, and close by is a Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa). Three other Peppercorn trees fringe the drive. The building includes two halls – the larger seating 250 people – and a large foyer overlooking trees and ovals. Both halls have retractable rear walls providing varying spaces as required, and guests can use several external decks. A site for outdoor theatre has been carved out of the natural slope outside the entrance. The Bricklayers Union refused to use the traditional mud-bricks, which weigh more than 22kg. As a result the mud-bricks were redesigned to reduce their weight and were laid back-to-back to produce a wall of normal thickness.3 The centre’s massive timber frame is reminiscent of timber bridge construction, with infill panels of mud-brick.4 In accord with the rustic style are colossal rough-sawn posts, bolts and steel brackets. The combination of mud-brick, exposed feature timber framing and creative design in this centre, characterises Eltham’s innovative buildings and the social movement behind them from the 1940s to the 1970s.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham community and reception centre, mudbrick construction
