Showing 107 items matching "rock specimen"
-
 Buninyong Visitor Information Centre
Buninyong Visitor Information CentreContainer - Ceramic bottle, K. Evans Potteries of Nottingham, Brown glazed stoneware bottle
Made in Nottingham, England by K. Evans. K. Evans Potteries in Nottingham has an intriguing history. During the construction of the Manchester, Sheffield & Lincolnshire Railway Company’s new London line (now known as the Great Central) through Nottingham, several objects of antiquarian interest were discovered. Among these treasures was an ancient pottery kiln, buried for centuries beneath the soft yellow Bunter sandstone rock that forms a significant part of the city’s foundation. The excavation took place near the point where Parliament Street intersects the railway, at a depth of ten to twelve feet below the original surface. The credit for rescuing many of these pottery fragments from destruction goes to Mr. C. B. Wright, of the late firm I. & I. C. Wright & Co., Bankers. His dedication and ingenuity allowed him to piece together broken parts, sometimes assembling as many as thirty or forty fragments to form a single complete specimen. These pottery pieces provide a fascinating glimpse into the past. Here are some details about the pottery found at K. Evans Potteries: Material: The pottery is made of coarse, reddish-brown clay. Construction: Evidence suggests that the potter’s wheel was used in their creation. Ornamentation: The vessels lack decorative patterns, except for indented or grooved handles. These handles exhibit a crude attempt at foliation, with the potter’s thumb leaving its mark. Function: The pottery likely served practical purposes, such as carrying water, ale, mead, or wine. Stew jars and drinking vessels were also part of this collection. This discovery remains almost unique, and its age continues to intrigue local antiquaries. While theories about its origin are scarce, the K. Evans Potteries offer a fascinating glimpse into Nottingham’s ancient craftsmanship. Cylindrical brown pottery jar (Bottle) with broken neck section. Uneven and work appearance of glazed surface.'... Stone bottles. K. Evans. ...Potteries of Nottingham'ceramics, pottery, bottles -
 Barwon Estuary Heritage Centre
Barwon Estuary Heritage CentreAnimal specimen - Echidna on Rock
... specimen Echidna on Rock ... -
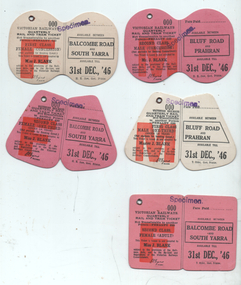 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumEphemera - Set of 5 sample - tram - rail quarterly tickets, Victorian Railways (VR), 1946
Set of 5 quarterly demonstration Victorian Railways tram - rail tickets for various uses and destinations on the Sandringham - Black Rock and rail line. All dated with an expiry date of 31 Dec. 1946. Not used as such, or does the reference does not show them being used.Demonstrates a set of tickets that were likely produced for discussion purposes for the Sandringham to Black Rock tram line.Set of 5 printed cloth faced tickets each with a metal eyelet and creased in the centre. All stamped "Specimen"tickets, vr, vr trams, victorian railways, sandringham to black rock -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Olivine Crystals, Unknown
... specimen olivine igneous rock volcanic gemstones volcanic bomb ...Olivine is mostly found on the Earth's surface in igneous rocks that are dark-coloured. It is common at divergent plate boundaries and at warm spots, such as volcanic areas. It crystalises and forms during the cooling of magma. Olivine is used in refractory sand, bricks, and gemstones. Olivine has been found on a number of meteorites, which might have originated from large asteroids or the mantle of a now-destroyed planet. This olivine crystal is thought to originate from Mount Noorat, with speculation that it could have originated from Mount Shadwell. Mount Noorat is a dormant volcano cone located in the Newer Volcanics Province of Victoria. Mount Noorat belongs to the Kirrae Wuurong people, who used the Mount as a place for meetings and gatherings prior to European settlement. Contact was first made between European settlers and the Indigenous people in 1841. The Mount has mostly been used for cattle and sheep grazing. Mount Shadwell is a well-known source of olivine and is the highest of a gathering of volcanic cones. The New Volcanic Province is located in South East Australia and covers 15000 square kilometres. It contains 400 explosive vents and small shield volcanoes. The last eruption is thought to have occurred 5000 years ago at Mount Gambier and Mount Schank. This olivine crystal has been identified as a volcanic bomb, which is a molten rock which was pushed out and ejected into the air when a volcano reupts. A rock needs to be larger than 65 mm in diameter to be classified as a volcanic bomb. This olivine volcanic bomb and its locality is historically and socially significant. The olivine was found in the Newer Volcanic Province, an area which contains over 400 dormant volcanoes. This olivine is one part of a volcanic bomb, which would have ejected when magma erupted out of a volcano. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid iron-magnesium silicate mineral with shades of green and brownburke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, olivine, igneous rock, volcanic, gemstones, volcanic bomb, meteorites, asteroids, plantes, mount noorat, mount shadwell, indigenous, kirrae wuurong people, newer volcanics province, victoria, european settlement, eruption -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Fossil Leaves
A fossil refers to any remains or traces of past life that are preserved in the rock. It could be remains of plants or animals. Fossil leaves are commonly found on different types of rocks. These fossils can go as far back as the Triassic Age just like the series of fossil plants collected at Denmark Hill, Ipswich in Queensland. Fossils leaves are formed when dead plants get buried by sediments like mud, sand, or volcanic ash. Often, it gets detached cleanly from stems along a special layer of weak cells, then twigs, and, less commonly, cones of conifers and fruits and seeds of flowering plants. Over time, the leaves or pieces of leaves get buried by more sediments and eventually gets 'lithified' or hardened into a rock. Erosions and mining can cause the rocks to break and reveal the fossils buried in it. Fossilisation frequently takes place at sites in the lowlands where deposits of clay, silt, sand are found. This is usually due to weathering and erosion of rocks. Fossil leaves can provide information about ancient Australia's way of living. It contributes to Victorian biodiversity records and its botanical collections. It also contributes information on the geographical profile of Victoria as fossilisation usually occur at estuaries and deltas of rivers, river flood plains, ponds and lakes. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Piece of light brown rock with fossilised leaves in shades of golden yellow and brown.Existing label: Fossil Leaves / Locality unknown / might be worth checking if this is Glossopteris, a Permian age plant. / C. William 16/4/21 geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, fossil leaves, fossilization, 1868 geological survey of victoria, lithified, rocks, fossilised leaf, rock, fossils, leaves -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Sphalerite, Unknown
Sphalerite or sphaelerite is named from the Greek word for 'treacherous' or 'deceiver' as specimens can vary widely in appearance, making them hard to visually identify. It is a zinc sulfide with the chemical composition (Zn,Fe)S, the most important ore of zinc. Specimens of sphalerite can contain iron as a substitute for up to 25% of the usual zinc present, as well as trace elements of gallium, cadmium, geranium and indium. Small amounts of arsenic and manganese may also be detected. Sphalerite is found in igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. It forms when carbonate rock encounters acidic, zinc-bearing fluid. It often forms in veins or in fissures of the existing rock, with colours and crystal shapes dependent on the composition of the the combining elements. It forms isometric crystal shapes including cubes, tetrahedrons, octahedrons, dodecahedrons. This specimen was collected in approximately 1852, in Broken Hill, NSW, as an adjunct to the Geological Survey of Victoria. It was donated to the Museum in 1868. Victoria and other regions of Australia were surveyed for sites of potential mineral wealth throughout the 19th Century. The identification of sites containing valuable commodities such as gold, iron ore and gemstones in a locality had the potential to shape the development and history of communities and industries in the area. The discovery of gold in Victoria, for instance, had a significant influence on the development of the area now known as 'the goldfields', including Beechworth; the city of Melbourne and Victoria as a whole.The specimen is significant as an examples of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries in Victoria and Australia, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century.A pipe-shaped specimen of sulfide-mineral zinc ore displaying patches of black, brown, beige and gold colouring. The main item has associated broken pieces. geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, mineralogy, indigo shire, geological survey, sphalerite, sphaelerite, zinc ore, broken hill, nsw, victoria, galena, fluorite, chalcopyrite, lead, cadmium, gallium, germanium, indium, iron -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Pyrite crystals in black slate, Unknown
... in similar metamorphic and sedimentary rock. This specimen is part ...Pyrite also known as iron Pyrite or fools gold is an iron sulfide with a chemical formula of FeS2 and is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Its metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold for which its nickname of Fools Gold comes from. There are a number of iron pyrite mines in Victoria and many would have been mined during Victoria's Gold Rush revolution in the 19th century. As it's lustrius yellow metallic look closely resembles gold, it is likely that it was often mistaken for gold as real gold was also often found in similar metamorphic and sedimentary rock. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these collections were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush). Collecting these specimens was an important part of Australia's early Geoplogical scientific discovery for mapping the earth's surface. It is unknown where in Victoria this specimen was mined from however; it shows strong provenance connections to Victoria's gold mining history and represents through larger economic and cultural structures the impact the Gold Rush had on Victoria during the 19th century. A solid coin-sized Pyrite crystal in black slate in shades of beige with tiny crystal structures. Pyrite / crystals / BB / in black slate / probably / victoria / (nice specimen)geology, geological specimen -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Ribbonstone-banded Chert
Chert is a sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz. While usually biological in origin, chert may also occur as a chemical precipitate or a diagenetic replacement--the product of petrified trees. Chert, also known as flint, was a common tool for early peoples during the stone age. It forms in limestone and chalk sediments as silicon dioxide microcrystals which grow into nodules of chert. Chert is found in many mines across the Northern Territory, however this specimen is sourced from the Mount Todd gold mine in Katherine. Its use in weaponry, both during the Stone Age and during the 18th century. Chert produces a spark when struck against steel, meaning t hat it can be used to start fires and fire guns. Chert was thus used in flintlock firearms, in which the gunpowder is ignited by a flint hammer striking a steel plate. Chert was commonly used in the Stone Age as a result of conchoidal fracturing causing very sharp edges, allowing early peoples to fashion weapons and cutting tools. It also rates a 7 on the Mohs Scale, making it a very hard and durable stone that maintains its sharpness. As a result, the significance of chert as a signifier of early indigenous Australian life makes this specimen important. It is also known that chert is a valuable mineral that was used as a trading commodity. Chert has also been valuable during the 1700s, proving itself to a be an important historical specimen in matters of war. A solid silicon dioxide mineral in shades of brown, white, and beigeburke museum, northern territory, chert, flint, minerals, geological specimen, katherine, mount todd gold mine, katherine northern territory -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Common Wombat, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Common wombats are short-legged, muscular, nocturnal marsupials that live in a wide variety of habitats throughout Australia. A common wombat can grow up to 1.2 metres in length and weigh up to 35 kilograms. The name “wombat” comes from the Darug language spoken by the Aboriginal Darug people, who originally inhabited the Sydney area. The wombat was first recorded in 1798 by explorer John Price on a visit to Bargo in New South Wales, however, wombats are depicted on Aboriginal rock-art that date back as far as 4,000 years ago. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century. Medium sized stocky wombat with a broad head and two muscular forelegs and two weaker hind legs that are met with long sharp black claws. The hair is long, thick and coarse in brown/yellow shades. The head features two small black eyes that have been made from glass, two short pointed ears and a bare nose pad. On wooden mount: BMM 5901 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, wombat, animalia, vombatidae, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, common wombat -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Thylacine, Reynell Eveleigh Johns, 1860-1880
The Thylacine or Tasmanian Tiger, was a large nocturnal carnivorous marsupial now believed to be extinct that was native to both Australia and New Guinea. The Thylacine is believed to have first appeared over two million years ago with documentation of the species appearing on rock-art that have been dated as far back as 1,000BC. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. The Burke Museum Thylacine is of great historic, scientific and cultural significance as Australia's most notable example of a species made extinct within living memory. Poignant images of the last known thylacine linger in national consciousness and remain an evocative symbol of the impact of humankind on the natural environment. The Burke Museum thylacine has immense social significance not only for its ability to tell a story to present and future generations, but also for embodying the mythic tiger that lives on elusively, we hope, in the Tasmanian wilderness. Attempts to clone the thylacine from material held in museums attest to the passion that this iconic animal evokes in the scientific as well as mainstream community. Medium sized lean female thylacine with four stocky legs and a stiff tail. The fur is short and coarse and in a light brown-yellow colour with 15 dark brown stripes across the width of the body. The head is long and narrow with two small pointy ears and a large jaw with up to 30 visible teeth.taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, thylacine, tasmanian tiger, rare -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Quartz veining in Breccia Conglomerate, Unknown
Quartz is one of the most common minerals in the world. It is formed by a 3d structure of silicon and oxygen. While it is a simple mineral, it can come in a variety of shapes and colours. When quartz is pure it is colourless, transparent and can appear glass-like. Better known and more rare variations of quartz include amethyst and smoky quartz. This specimen is a vein of quartz in Breccia Conglomerate. Breccia is coarse-grained clastic rock which is made up of broken rock fragments and held together by mineral cement. The locality of this specimen is unknown. While quartz is a very common mineral and does not have rarity, it is an important material in industrial settings. One of it's physical and chemical properties is that it is piezoelectric, which means it can be used to generate an electric charge. This has made it useful in the manufacturing of timekeeping devices. This specimen was donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880 among a larger collection of geological specimens. It was collected as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria which begun in 1852 as a response to the Gold Rush. Collections were distributed to organisations across Australia to encourage the further study of the scientific makeup of the Earth. A solid egg-shaped rock with a mineral vein forming a ring around the rock in shades of brown and beige.burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, 1852 geological survey of victoria, mineralogy, quartz, breccia, breccia conglomerate, conglomerate -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - Rock Samples from Bendigo
... specimen Rock Samples from Bendigo ...Identified as Bendigo rocks by a Geologist A box of rock samples from Bendigo with 12 Compartments. Number 1 Pink rock with striations, 2 Pink rock with striations, 3 Grey rock with white vein, 4 Dark grey rock with one shiny surface, 5 White rock with gold, 6 White rock with shiny inserts, 7 White rock with shiny inserts, 8 Light grey with gold, 9 Dark grey rocks, 10 Dark grey rocks with shinny inserts, 11 Brown rock with crystal inserts, 12 group of cubes two shinny and the remainder black. Part of the Amy Huxtable Collection. bengio, rocks, geology -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - Rock Sample
... . Geological specimen Rock Sample ...A very heavy rock sample, brown grey colour.rocks, geology -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - Rock Sample
... Geological specimen Rock Sample ...A grey pink rock with a yellow striperocks, geology -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - Rock Sample
... specimen Rock Sample ...An Ochre coloured rock samplerocks, geology -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - Rock Sample
... . Geological specimen Rock Sample ...A Rock sample, mid-grey sedimentary rock.rocks, geology -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Geological specimen - Rock Sample
... Rocks Geology A dark grey rock Geological specimen Rock ...A dark grey rockrocks, geology
