Showing 1058 items matching "mrs hill"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Birthday Book, Raphael Tuck & Sons et al, The Dickens Birthday Book, 1901-1911
Birthday Books are personal record books for names and birth dates of friends and relatives. This book includes a quote from Charles Dickens for each day of the year. The books were published in many editions, with different publishers, illustrators, covers and designs. This Dickens Birthday book was presented as a gift to fifteen-year-old Clara Skirrow on January 19th 1911, by Mr and Mrs B Watson, perhaps the 'Benji Watson' in the book, whose birthday was July 1st, 1887. The entries in the book include several with the surnames Watson and Skirrow. Interestingly, names are entered in various writing styles, perhaps because each entry was written by the person of that name, similar to an autograph book. Curiously, there are two entries for Connie Watson, one in brackets on March 16th, the other on March 23rd, without brackets. The artist, Pilford Fletcher Watson (1892-1907), was born in London. He moved to Sydney, where he became a prominent and well-established artist and a founding member of the Academy of Arts, Australia, established in 1891. His works included local scenery, architecture, and the interiors of historic buildings. Many of his pieces were bequeathed to the State Library of New South Wales. The firm, Raphael Tuck & Sons Ltd, was a printer and publisher that operated in London from 1866 to 1960. Its logo was the artist's easel, palette and brush. The firm that specialised in greeting cards and produced puzzles. It also became the world’s largest postcard publisher. In 1960, the firm amalgamated with others to become the British Printing Corporation. The fly page states that Ralph Tuck & Sons, Ltd. was the publisher to Their Majesties, the King and Queen, and Their Royal Highnesses, the Prince and Princess of Wales. This would suggest that this book was published from 1901 to 1910, when King Edward VII and Queen Alexandra, and Prince George and his wife Princess Mary were permitted to use these titles. NAMES LISTED IN THE BIRTHDAY BOOK (the museum has photographs of every entry in the book, which are available on enquiry): - January 1 Mrs J (or S) Watson January 11 Wilfred Skirrow, 1904 January 16 Elsie Watson, 1897 January 17 Elsie Hartley, 23/06/2012 [error?] January 21 Frances Victoria Haieck January 29 Annie Skirrow, 1884 February 14 Willie Illingworth February 17 Bessie Watson February 19 Mrs Butterfield, 22 Apperley Rd, Idle [UK] February 27 William Ernest Futter ? March 13 Carrie Barker March 16 Connie Watson March 19 Hilda Graham March 20 Mrs W. Illingworth March 23 Connie Watson April 5 Mrs Ruth Ann Skirrow April 6 William Dickinson Goldsbrough April 11 Norman Goldsbrough April 16 May Jessen April 19 Mrs A Dixon April 20 Mrs S Watson April 23 John Fred Stansfield, 1912 April 24 Reginald Goldsbrough May 12 Bertha Ellis May 18 Gladys McInnes May 28 Mrs Arthur Watson June 3 Jack Watson, 1910 June 10 Mr James Watmough June 18 Miss Hilda Hodgson, 1895 June 26 Sarah Atkinson, 1894 June 30 Mary A Bannister, 1896 July 1 Benji Watson, 1887 July 1 Ester Watmough, 1896 July 2 Clara Skirrow, 1896 July 2 Aunt Jinni July 2 Aunt Hannah July 10 Ellen Gertrude Connolly July 11 Violet Mathieson July 23 Hady Rogers July 26 Sarah Atkinson August 2 Allan Watson August 3 George Skirrow August 6 Thomas Skirrow August 6 Gladys Patten August 8 John Waite, 1909 August 21 Lilian Pattison, 1909 August 25 Ethel Watson, 1889 August 25 Evellyn Goldsbrough September 4 Miss Frances Barker September 12 Ernest Hartley, 1888 September 14 Harry Stansfield, 1895 September 20 Harry Padgett September 25 Leslie Watson September 26 Florrie Wise, 1896 September 27 Dorothy Watson, 1909 October 1 Madge Ferrier October 3 Elizabeth Padgett, 1896 October 5 Violet Altridge, 1895 October 13 Elsie Hodgson, 1893 October 18 Arthur Watson October 21 Emily Bradshaw November 14 Mr A Dixon December 27 Laura Hartley, 1890 December 29 Arther Skirrow, 1894 December 29 Dolly GrahamThis early 20th-century Birthday Book is significant for containing quotes by the famous writer Charles Dickens. It is also connected to the popular and prolific publisher and printer, Raphael Tuck & Sons Ltd, and the renowned illustrator and artist, Pilford Fletcher Watson. Ownership of a rare and beautifully presented book like this indicates the value placed on keeping records of family and friends, and remembering their birthdays, in the early 1900s. The book is highly significant for the entries of local family names, some with birth dates. Book: small book with padded maroon leather hard cover and embossed with gold text on cover and spine; cover also has a gold motif. The pages include coloured illustrations, sketches, and lines for personal entries. The first pages are about Charles Dickens. Title: The Dickens Birthday Book, with six illustrations in Colour by P. Fletcher-Watson Publisher: Raphael Tuck & Sons Ltd, Britain Printed in England 1901-1910 Artist: P. Fletcher-Watson This padded red leather hardcover book has embossed gold text on the front cover and spine. The six colour illustrations throughout the book were by artist P. Fletcher-Watson; one is a portrait of Dickens. Each day has a quote from Charles Dickens' works and blank lines below. The drawing on the fly page depicts a stone building with side pillars and a logo in the centre of the horizontal beam. It has a gift inscription for Clara Skirrow on January 19th, 1911. There are handwritten entries under many of the dates, some include years that range from 1884 to 1912, and one includes an address in the U.K.. Embossed on cover and spine: “The DICKENS Birthday Book” Handwritten in black ink: "From Mr & Mrs B. Watson / To Clara Skirrow / With Best wishes / January 19th 1911" Illustration on fly page: Logo [artist's palette, brush and easel] Publisher information: “Raphael Tuck & Sons Ltd, London, Paris, Berlin, New York, Montreal,” “Publishers to their Majesties the King and Queen, and T.R.H. the Prince and Princess of Wales” “Printed in England” Handwritten entries with names, some dates, and one address. flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, birthday book, p. fletcher-watson, raphael tuck & sons ltd, 1901-1910, illustrated, 19-01-1911, mr & mrs b. watson, clara skirrow, red cover, british printing corporation, king and queen and trh prince and princess, king edward vii and queen alexandra, antique book, rare book, atkinson, bannister, barker, bradshaw, butterfield, connolly, dixon, ellis, ferrier, futter, goldsbrough, graham, hartley, hodgson, illingworth, jessen, mathieson, mcinnes, padgett, patten, pattison, rogers, stansfield, waite, watmough, watson, wise, dickens birthday book, charles dickens, dickens quotes, skirrow -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionWork on paper - Vertical file, Cricket clubs
A vertical file containing the following information: 1. Notes on ‘Surrey Hills Cricket Club’ 17.9.1886-3.10.1930. (6 pages). 2. ‘Cricket in Surrey Hills’ from Alan Holt’s records (17 pages). 3. ‘Australian cricket team’ – 1935 Tour of England (1 page, typed). From Alan Holt records of Mr. L.T & Mrs. G. illiams of 9 Louise Avenue, Mont Albert, cricket enthusiasts. 4. ‘Canterbury to hit a century’, SHNN No. 22, June/July 1986. (1 page). 5. ‘Cricket at Canterbury A centenary history of the Canterbury Cricket Club 1887-1987’. 58 page book by Simon Gardiner. This copy given to P.M.I. – replaced by one from reference library where there were 2 copies. 6. Surrey Hills Cricket Club centenary celebrations. Typed notes by Alan Holt, in S.H.N.N. (no date) (1 page). 7. ‘Cricket centenary‘ re Canterbury. SHNN No. 33, April/May, 1988. (1 page). 8. Miscellaneous notes by Jocelyn Hall (no date) (2 pages). 9. ‘Canterbury Advertiser‘ notes typed by Jocelyn Hall (no date) (1 page). 10. ‘Surrey Hills cricket club centenary celebrations’. SHNN No. 40, June/July 1989. (1 page). 11. ‘Improvements at Canterbury’, S.H.N.N. No. 38, Feb. March 1989. (1 page). 12. ‘Cricket Club Centenary’ S.H.N.N. No. 42, Oct./Nov. 1989. (1 page). 13. ‘Surrey Hills Cricket Club hit a Century’, ‘Leader’, 28.2.1990. (1 page). 14. The Reverend John Barton and Wyclif Congregational Church 1896-1907 re cricket club, October, 2001. (1 page typed notes). 15. Committee of Management Canterbury Grounds Trust, Committee Meeting 11.5.1983. (1 page). 16. Committee of Management Canterbury Grounds Trust, Annual Meeting, 24.10.1984. (1 page). 17. Committee of Management Canterbury Grounds Trust, Committee Meeting, 2.7.1986. (1 page). 18. City of Camberwell letter of appreciation re long service on Committee of Management of Canterbury Sports Ground to Mrs. J.S. Green, 22.2.1982. (1 page), with a note from Stephen Gillespie re Jean Stevenson Green’s background. 19. ‘Run-out call on cricket club’, The Sun, 7.3.1983 re neighbour Ian Ward’s protest re cricket balls (1 page). -
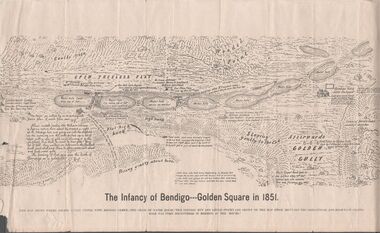 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - MAP - THE INFANCY OF BENDIGO - GOLDEN SQUARE IN 1851
Hand-drawn map of Bendigo - Golden Square in 1851. Map shows the chain of waterholes, Golden Gully, hill and bush areas and open treeless flat. Mentioned on the map are places where there were mia mias, stockyards, Gibson & Fenton's butchery & First Store.map, bendigo, goldfields, map the infancy of bendigo & golden square 1851, capt dane, william johnson, mrs kennedy, mrs farrell, ben hall, chris asquith, gibson & fenton's butchery & first store, p odonnell, walter r sandbach, william sandbach, mr frencham, john ross, thos myers, bendigo hut & little stockyard, commissioner horne, j jones, c cohen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDecorative object - Peacock, Minton Majolica life-size model, Paul Comolera, artist, Designed: c. 1873; Made: c. 1875
This majestic peacock embodies the technical achievement, skill and ingenuity of artisans during the 19th century. It is now known as the 'Loch Ard Peacock' and was designed and modelled in 1873 by Paul Comolera (1818-1897) and fired in one piece at the Minton factory at Stoke-on-Trent in the United Kingdom in 1875. The peacock has been portrayed in symbolic motifs and has figured heavily in folktales and fables since antiquity, and many cultures around the world see it as a symbol of beauty, rebirth and power. Wealthy Victorians loved majolica, and the large peacock would have been the ultimate home accessory as a conservatory ornament – combining their desire for nature, the exotic and vibrant colours. The peacock model was listed in catalogues by Minton & Co. for a retail price of 35 guineas or sold as a pair for 90 guineas. Minton & Co. was founded in 1793 by Thomas Minton (1765–1836) and became a famous pottery and porcelain manufacturer. Comolera was a French artist and sculptor, renowned for dramatic naturalistic forms and life-size renditions of birds and animals that won him admiration in public and artistic circles. He was employed by Minton & Co. from 1873 to 1880, and the life-sized peacock became his best-known work. Comolera kept a live peacock loaned from the nearby Duke of Sutherland's Trentham Hall Estate in his studio to create a life-size model of fine buff earthenware model, which was then hand painted in brilliantly coloured green and blue glazes to mimic the peafowl’s dazzling plumage. There are no surviving production records, but according to documents in the Minton Archive, nine peacocks were made by Comolera. However, today, some historians now believe that twelve were fired at the Minton factory; research is ongoing. These peacocks were so admired that Minton & Co. used them as exhibition showpieces at International Exhibitions in London, Paris, and the United States of America, ensuring the company had a worldwide reputation. So, when Melbourne hosted an International Exposition in 1880, Minton & Co. sent out ceramics and tiles, and in particular, this peacock was intended to be part of their exhibit in the British Court in the Exhibition Building, built in the Carlton Gardens. The early dispatch date (1878) indicates that the company may have intended to exhibit their wares, including the peacock, at the 1879 Sydney International Exhibition, but the company did not take up this option. The ship that Minton & Co. used to bring the peacock and their other wares to the Australian colonies was the ill-fated Loch Ard, which sunk after striking Mutton Bird Island near Port Campbell, Victoria, in calm foggy weather in June 1878 on the final leg of the ship's journey to Melbourne. The loss of 52 lives made it one of Victoria’s worst shipwrecks. Therefore, this peacock never made it to the grand exposition in Melbourne, as Minton & Co. had planned. Charles McGillivray dragged this peacock, still in its original packing case, onto the beach in the gorge just two days after the Loch Ard went down. The peacock was rescued unscathed apart from a chip on its beak (only repaired in 1988). After a disagreement with a Melbourne Customs Officer, Joseph Daish, McGillivray stopped his salvage operations, leaving the peacock on the beach. The second salvagers were James Miller and Thomas Keys. Miller was a member of the firm Howarth, Miller and Matthews, Geelong, who had brought the salvage rights to the Loch Ard wreck on 10 June. When Miller and Keys arrived at the wreck site, a storm had washed many of the salvaged goods, including this peacoc,k back into the sea. The two men found the peacock in its case ‘bobbing along in the water’ and pulled it back to the beach. To ensure the peacock wasn't washed out to sea again, Miller and Keys hauled the packing case containing the peacock up the gorge's cliff face to the top, ready to be transported. In an interview in 1928, Keys claimed that at the time of the rescue, the head had broken from the body. This account was proven to be true in 1988, following the birds' display in Brisbane. This peacock began its life in Australia, not in the grandeur of an International Exhibition as intended, but in the hallway of a simple domestic house in Geelong. It appears Minton & Co. did not attempt to buy this peacock back. Florence Miller, daughter of James Miller (Loch Ard salvage rights holder), later remarked that the only item of real value rescued from the wreck had been the peacock and that this had been kept by her father in the family home at Malvern for many years and became a treasured family possession. As such, this 'Loch Ard peacock' was almost forgotten and mistaken with other Minton peacocks around the world. Miss Florence Miller tried to sell the peacock due to financial difficulties in the 1930s but was unsuccessful. While attempting to sell her Loch Ard relic, it was displayed in the window of the old Argus newspaper office, which was at 76 Collins Street, Melbourne; the Argus had relocated to the corner of Elizabeth and La Trobe Streets in 1926. Between 1935 and 1939, the old Argus building was occupied by the Joshua N. McClelland Print Room, which sold not only paintings and prints but also antiques and authentic replicas, as well as hosting exhibitions. Miss Florence Miller loaned her peacock for display at the Victorian Historical Exhibition held in the National Gallery on 1st June 1935, the 57th anniversary of the Loch Ard wreck. As a result, the peacock attracted public attention in books, newspapers and magazine articles that told the story of its survival from a shipwreck. Miss Florence Miller was keen to sell the peacock, even writing overseas to Captain Blain on November 30th, 1938, about the possibility of a sale, but this became no longer possible due to the outbreak of war. Recent information points to the Loch Ard peacock being owned by John S R Heath before its sale to Frank Ridley-Lee in May 1941. Research is ongoing, but it seems likely that John Samuel Robert Heath, a leading Melbourne dentist with a practice in Collins Street, and his wife, a dental mechanic, had purchased Miss Miller’s Loch Ard peacock before its sale in 1941. They were lovers of fine arts, music, wine and food. The peacock in the window of the old Argus building could have attracted their attention as they had already purchased the old stone Presbyterian Church on Warrigal Road, Oakleigh, in 1933 and had converted its interior. The home, renamed The Studio, even included Melbourne’s first all-electric kitchen. The peacock was perfect for display in the Studio’s entrance. A magazine article published after the conversion was completed included photographs of the interior. The picture of the ‘portico’ had a caption below that stated, “Some of her [Mrs Heath’s] finest pottery was salvaged from the Loch Ard Wreck”. In 2025, Heath’s two remaining sons remember running around in the entrance with the peacock standing there, oblivious to its value. Heath was an accomplished artist, studying under Max Meldrum. He painted and exhibited his works at The Studio and in a public exhibition, and he was a finalist eight times in the coveted Archibald Prize portrait competition, including the submission of his self-portrait that is now part of his grandson’s collection. The next owner of the Loch Ard Peacock was Frank Ridley-Lee. He displayed it at his home in Ivanhoe after buying it at an auction in May 1941. The peacock remained in the hands of the Ridley-Lee family until it was offered for sale by auction in 1975 as part of an art collection belonging to Mrs Ridley-Lee's estate. The peacock was not sold at this time, as the reserve price of $4500 was not met. This news was passed on to the board of the newly created Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. Urgent efforts were made to collect the necessary money through fundraising by the Warrnambool City Council and public donations. The Fletcher Jones Company and the Victorian Government contributed half the cost. On 9 September 1975, the Loch Ard peacock was purchased by Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and it found a new home at the maritime museum. Since then, it has only left Warrnambool twice. Firstly, in 1980, at the centenary celebrations of the Royal Exhibition Building in Melbourne, and secondly, in 1988, the peacock was given pride of place at the entrance to the Victorian Pavilion at the Brisbane World Expo, acknowledging that this Minton Majolica peacock is the most significant shipwreck object in Australia. The Minton majolica peacock is considered of historical social and aesthetic significance to Victoria and is one of only a few 'objects' registered on the Victorian Heritage Register (H 2132), as it is a most notable and rare object associated with the Minton factory of the 1870s and works by the celebrated sculptor Paul Comolera along with the wreck of the Loch Ard on the Victorian coastline. This Minton peacock is historically significant for its rarity; it was one of only 9-12 known to exist. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is also of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register Ref (S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's early social and historical themes. The collection is historically significant is that it is associated, unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. The peacock, resplendent in polychrome glaze, stands perched on a rocky plinth decorated with vines, leaves, flowers, blackberries and wild mushrooms. The peacock’s breast is cobalt blue; the wings and legs are in naturalistic colours. The tail is a mass of feathers coloured in green, ochre blue and brown — a fantastic display of artistry and Minton expertise. Inscribed at the base :P Comolera, and a Minton & Co. design number: 2045.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, loch ard, loch ard gorge, peacock, paul comolera, victorian heritage register, minton peacock, minton & co., stoke upon trent, bird figures, mintons, ceramics, international expositions, majolica, naturalistic, staffordshire, john samuel robert heath, peacock statue, loch ard peacock, majorca peacock -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Fob Watch, ca 1878
The story behind this little gold watch is intriguing. The condition of the watch certainly shows the effects of time in the sea. Some inner workings can be seen through broken encrustations and missing sections of the watch’s case. The winding knob on the top is recognisable even though it is covered by sand and other adhesions from the sea. The manufacturer of this dainty watch may have made it for a female, and the value of the gold metal case shows that it would be marketed for a person with wealth. The watch was donated along with a letter, an envelope and a newspaper cutting, all neatly folded and tucked with the watch into a small, strong cardboard box with metal reinforcing on the corners and a fitted lid. The letter is dated March 6, 1905, and its sender writes about the ‘souvenir’ lady’s gold watch found in Loch Ard Gorge at Port Campbell, though the finder remains unnamed. The letter’s date is also uncertain, as there are only 27 years, not 28, between its date and the date the Loch Ard was wrecked (1905-1878 = 27). The signature on the letter appears to be ‘Wyon’, which is the name of a creek in NSW, and also the name of the renowned William Wyon, medallist and engraver of British coins, medals and stamps; and continued as Wyon and Sons, London. The envelope has a postmark for Florence (Firenze), Italy. It is stamped October 12th, 1911 (12.10.11). It is addressed to an illegible name, then Glencove, Portsea, Victoria, Australia: 'Glencove, Portsea' is referred to in newspapers between 1927 and 1949. The newspaper cutting puts the watch into its context, telling the story of the wreck of the Loch Ard, the survival of only two of the 54 people onboard, and a little of the survivors’ future events. It doesn’t single out the watch in any way. Any one of the 17 passengers sailing on the Loch Ard could have owned the watch, including Dr. Carmichael, his wife, Eva, their other three daughters, and two of their sons. Instead of belonging to anyone onboard, it may have been amongst the cargo, as the ship’s manifest includes ‘clocks and watches £25’. The donated watch was carefully packaged with related documents, showing respect for this small shipwreck artefact, which is nearing 150 years of age at the time of writing (2025). The watch’s connection to the sands of Loch Ard Gorge also connects it to the ship Loch Ard, contributing to our knowledge of personal items brought to Australia in 1878, whether as the belongings of a passenger or as cargo; a gold watch would be intended for a wealthy buyer. Although many people would have visited the shipwreck site, it was revealed over 25 years after the Loch Ard was wrecked; this length of time helps us understand the effects of the sea on shipwreck objects. The watch is significant for its connection to the infamous Loch Ard, where only two of the 54 people on board survived.Ladies' fob watch, thought to be gold. It is now covered in encrustation. A bump on the edge would be the winding mechanism for the watch. A small section of the back of the case has broken away, and an engraved surface can be seen. Face and hands are missing, revealing the spring workings inside. Donated with the watch were two documents and a newspaper cutting about the story of the shipwreck of the Loch Ard. They are all in a strong cardboard box with reinforced corners on the base and lid. Found at Loch Ard Gorge and said to have been from the Loch Ard. The three donated documents are: - 1. A rectangular envelope made of cream waxy paper lined with black and white diagonally striped paper. The top right corner, usually meant for a postage stamp, has been torn off, partly exposing text on a rectangular printed logo. A round black postmark stamp near the top centre shows the post office location and date. The address on the front is handwritten in black ink. The creases on the envelope suggest it has been folded three times. 2. A letter on cream rectangular paper features clear, handwritten script in black ink. The unevenly cut bottom edge has two short black vertical lines, possibly the tops of tall written letters. There are creases where the page has been folded three times. 3. A newspaper clipping featuring text, an illustration, and handwritten details of the newspaper’s source.1. Envelope: - Address: ”Australia (per Postage) / (illegible) / Glencove, (Portsea) / Victoria” Postmark: “FIRENZE” 12 10 11” “ - - - -PORTEN – (illegible)” Logo inside envelope: “BUSTA BRE--- / Earliera Lialia” [Italian; Busta = envelope, Earliera == earlier] 2. Letter: - “I am sending you a ‘souvenir’ from the wreck of the Loch Ard 28 years ago at Port Campbell. It is the remains of a lady’s gold watch found in the gorge where Miss Carmichael & Tom Pearce (the only two saved) were washed up. This souvenir was lying there ever since. I went down into the awful gorge & saw the cave where these two unfortunates (or fortunate perhaps, as they were saved) lived until rescued. I also saw the graves of those who were washed up from the wreck. One grave contains Dr and Mrs Carmichael & six of their children. Later on, when I can get some good views of that wild coast I will send them. [signed] Wyon. 6/3/05.” 3. Newspaper cutting: - History of the Lochard. Refer to the Sydney Morning Herald, Nov. 28th, 1971: “Loch Ard: the wreck that became a legend”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, ladies fob watch, gold watch, fob watch, pocket watch, horology, accessory, time keeping, scientific instrument, ladies' watch, ladies' pocket watch, diagonally striped envelope lining, glencove, portsea victoria, firenze, busta, earliera, souvenir watch, loch ard souvenir, lady's watch, port campbell, tom pearch, survivor, miss carmichael, mrs carmichael, dr carmichael, wyon, 1878, 1905, 1911, loch ard: the wreck that became a legend, florence, clocks and watches -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LONG GULLY HISTORY GROUP COLLECTION: BANKNOTES AND JAMES BEVERAGE
BHS CollectionTyped copy of what appears to be a speech. Mentioned is that after 1910 the Commonwealth took over the minting it's own money. Gold mining was chosen for the one pound note and a Bendigo scene was chosen. The scene chosen shows boring operations in the Victoria Quartz Mine. The picture was taken by Vincent Kelly of the five figures but for engraving only three were shown. They were Mr W Healy, Mr J Smith and Mr James Beverage. James Beverage was a member of Bendigo's first fire brigade. He went to Beechworth for a demonstration and on the way home stopped at Christie's Hotel in Swanston Street. There was a fire at the hotel and Mr Beverage rescued Mrs Christie, her baby and a servant. At a later date Mr Beverage saved a woman from a burning building in Moore Street in Bendigo. He received the Royal Humane Society's Medal which is now housed at the Bendigo Fire Station in Hargreaves Street. In the City's formative years the area that deposited its rain water into the Long Gully Creek was considered to be in Long Gully and for many years the Victoria Quartz Mine deposited many thousands of gallons of water into the Long Gully Creek. Mr Steve Gibbons unveiled the plaque.bendigo, history, long gully history group, the long gully history group - banknotes and james beverage, victoria quartz mine, vincent kelly, shepard's bush, mr rickards, mr abraham, mr w healy, mr j smith, mr james beverage, south iron bark mine, rae's hill, sandhurst no 1 fire brigade, christie's hotel, mrs christie, royal humane society's medal, bendigo fire station, long gully history group, mr steve gibbons, department of environment water heritage, arts commnmoration of historic events and famous persons -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - H.A. & S.R. WILKINSON COLLECTION: CONTRACT OF SALE
This business was owned by father and son, Henry Archibald Wilkinson and Samuel Ronald "Ron" Wilkinson. Henry (1882-1954) was born in Shepparton and died in Bendigo. He was married to Grace Hovendon in 1908. Samuel Ronald "Ron" (1914-1995), Henry's son, was married to Florence Jean McKerlie in 1937.Contract of sale of land dated 28th September, 1956 between G.A. Cox (seller) and Mr. R.L. & Mrs. E. Roche (buyer) for land being lot 1 on plan of subdivision No. 18242 part of Crown allotment 337 section E described in certificate of title volume 7132 folio 389 and situate no. 150 White Hills Road, Bendigo, together with 5-roomed brick dwelling and all sundry. Price 4,750 pounds.organization, business, h.a. & s.r wilkinson real estate -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Seat Squabs, mid-20th century
The term 'seat squabs' is no longer commonly used, but is sometimes referred to in the upholstery and motor vehicle industries. Squabs are padded cushions frequently added to wooden chairs or benches to add comfort to their hard forms. They have been made to an 18th-to-19th-century pattern using beautiful, richly coloured satin fabric and fancy cord tassels. The weighted flap at the rear of the squabs helps to keep them in place on the chair, and could be used on the top of the backrest instead of on the seat. These days, squabs are attached with fabric ties or hook-and-loop tabs. These seat squabs were once used in the St Nicholas Seamen's Church at 139 Nelson Place, Williamstown, Victoria, which was purchased and furnished around 1943. The furniture and furnishings are now part of the St. Nicholas Seamen's Church collection. DETAILED HISTORY of the Missions to Seamen: - The Missions to Seamen is an Anglican (Church of England) charity that has served the world’s seafarers since 1856. It was inspired by the work of Rev. John Ashley, who, 20 years earlier, had pioneered a ministry to seafarers in the Bristol Channel in Great Britain. When Ashley retired, others continued the work, founding the Missions to Seamen. It adopted a Flying Angel as its symbol, inspired by a verse from the Bible in Revelation 14. Today, over 200 world ports have Missions to Seamen centres and chaplains. A Missions to Seamen’s club warmly welcomes sailors of all colours, creeds and races and provides a wide range of facilities. The Missions to Seamen organisation changed its name to the Mission to Seafarers in 2000, continuing to include Missions to Seamen clubs in Victoria’s cities of Melbourne, Portland, Geelong and Hastings. Flagstaff Hill’s St Nicholas’ Seamen’s Church is named after its namesake from Williamstown, Victoria, which began in 1857. Bishop Perry opened the first Sailors’ Church, which was known as ‘Bethel’, on an old hulk floating in Hobson’s Bay, Port of Melbourne. In 1860, a Sailors’ Rest started operating from rented premises in Williamstown. In 1878, the Sailors’ Church moved into an old Wesleyan chapel in Ann Street. By the end of that year, they managed to purchase the building, which they had already refurbished. In 1883, they affiliated with the Victorian Seamen’s Mission. A few years later, in 1906, the building had to be demolished because it was no longer safe. While they raised funds for a new building, the Sailors’ Rest temporarily moved to premises in front of Customs House in Nelson Place. Around this time, in 1906, the Ladies Harbour Lights Guild was formed in Australia to support and raise funds for the Mission to Seamen organisation in Melbourne. Two of the most significant ladies of the Guild were founding members Ethel Godfrey and Alice Sibthorpe. During the Mission's time at Siddeley Street, Melbourne, the activities of the Guild raised funds for the Mission to Seamen's Chapel at their new, and still current, premises in Flinders Street, Melbourne, opened in 1917. The Guild continued its important work until the 1960s. In 1908, the Williamstown Mission had enough money to purchase the former Mascotte skating rink on Thompson Street, Williamstown. In August of that year, they were inaugurated into the Victorian Missions to Seamen. They continued at that venue for a few decades. In 1943, the former ES&A Bank building at 139 Nelson Place, Williamstown, was purchased for the new Mission to Seaman’s Club. The official opening was on May 6th, 1944. It was described as a ‘distinctive little building’. Funds had previously been raised for the building and furnishing of the chapel at the rear. The chapel was named St Nicholas’ Seamen’s Church, after St Nicholas, fourth-century bishop and patron saint of sailors. Services were held on Wednesdays and Sundays. The church was supported by the Williamstown Lightkeepers’ Auxiliary, newly founded by Mrs Ethel Margaret Musther in 1943, as well as the Harbour Lights Guild and the League of Soldiers’ and Sailors’ Friends. The Williamstown Mission to Seamen’s Church operated until 1966, when large international ships no longer used the Port of Williamstown. The Commonwealth Government then leased the premises. In the formative years of Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, the Advisory Board decided to include a Missions to Seamen Chapel and Recreation Room in its village. The Missions organisation was a significant feature of ports during the late 1800s and early 1900s, the period that the Village represents. They often erected Missions to house social and worshipful activities for seamen. Flagstaff Hill’s curator, Mr Ken Marshman, approached the Melbourne Board of Management of Missions to Seamen regarding the Williamstown branch. Consequently, the Board permitted the furnishings of the Williamstown chapel to be transferred to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. A provision of the transfer was that the Victoria Missions to Seamen be recognised, that the items would remain as a collection, and that the chapel would be called St Nicholas Seamen’s Church and conduct Divine services. The donation was approved on 21st May 1979. Flagstaff Hill's St. Nicholas Seamen's Church: - The idea behind Flagstaff Hill’s Missions to Seamen’s Church was partly driven by the offer of Stained Glass Memorial Windows that originated from the Warrnambool and District Base Hospital, which was undergoing multi-storey expansion in the late 1960s and early 1970s. The hospital’s Manager/Secretary was eager to see the historic window installed in a suitable place. The church, or chapel, was designed by a local architectural draftsman in collaboration with the Flagstaff Hill Planning Board and was constructed by Mr Leon Habel. The designers hoped the church would be used for formal worship, such as weddings, funerals, and multi-denominational special services like war commemorations. Its design was inspired by the ‘Missions to Seamen’ buildings in Portland and the Port of Melbourne. The furniture and furnishings were placed as accurately as possible according to photographs of the Williamstown St Nicholas Seamen’s Church and with assistance from local clergy. The Recreation Room was furnished and arranged on advice from experienced members of the Missions to Seamen organisation. A framed document in the building recognises the donor of the furnishings, Victoria Missions to Seamen, and includes the names of some original donors and their donated item/s. The building’s design incorporates local features such as Warrnambool sandstone, which was no longer commercially available but was procured from demolished buildings and uniformly cut to use as a veneer over the stronger Mt. Gambier stone. Also, traditional green American roofing slate was used, sourced from the 1908 local shipwreck “Falls of Halladale” by Flagstaff Hill volunteer divers. The bell tower includes a bell believed to be from a local shipwreck. Additional furnishings were acquired locally, and several items were donated by Warrnambool residents. Light fittings in both rooms were assembled to simulate 19th-century gas light fittings. The stained-glass window at the back of the church is a memorial to Dr Connell, a well-respected member of the Warrnambool community. It was originally installed in 1928 in the main building of Warrnambool Hospital. The St Nicholas’ Seamen’s Church at Flagstaff Hill was officially opened by His Worship the Mayor, Cr. John Lindsay, on Sunday, 11th October 1981. The event included a service of thanksgiving conducted by the Warrnambool Ministers Fraternal. Since then, the Chapel has been the historic venue for many weddings. This pair of seat squabs is historically significant for its origin in the St Nicholas Mission to Seamen's Church in Williamstown, established in 1857 to cater for seafarers’ physical, social, and spiritual needs. The organisation originated in Bristol, England, when a Seamen's Mission was formed in 1837. The squabs are also significant for their use in the St Nicholas Missions to Seamen's chapel, Williamstown, as the original building is now listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. Squabs or padded seat cushions, a pair of two. These 18th to 19th-century design squabs have crimson and cream satin fabric on top and underneath, and weighted tassels are attached to their rear corners. They can be used for comfort on hard seats and benches. The squabs were furnishings from the Missions to Seamen chapel in Williamstown, and they are now part of the St Nicholas Seamen's Church Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, st nicholas mission to seamen's church williamstown, mission to seamen williamstown, mission to seamen victoria, st nicholas mission to seamen, st nicholas seamen's church, religion, religious service, sailor's rest, ladies harbour light guild, squab, seat covers, cushions, squabs, religious furnishing, padded seats, seating, accessory
