Showing 1687 items
matching new people
-
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesPeriodical, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, Australian Aboriginal studies : journal of the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, 2010
'Whose Ethics?':Codifying and enacting ethics in research settings Bringing ethics up to date? A review of the AIATSIS ethical guidelines Michael Davis (Independent Academic) A revision of the AIATSIS Guidelines for Ethical Research in Indigenous Studies was carried out during 2009-10. The purpose of the revision was to bring the Guidelines up to date in light of a range of critical developments that have occurred in Indigenous rights, research and knowledge management since the previous version of the Guidelines was released in 2000. In this paper I present an outline of these developments, and briefly discuss the review process. I argue that the review, and the developments that it responded to, have highlighted that ethical research needs to be thought about more as a type of behaviour and practice between engaged participants, and less as an institutionalised, document-focused and prescriptive approach. The arrogance of ethnography: Managing anthropological research knowledge Sarah Holcombe (ANU) The ethnographic method is a core feature of anthropological practice. This locally intensive research enables insight into local praxis and culturally relative practices that would otherwise not be possible. Indeed, empathetic engagement is only possible in this close and intimate encounter. However, this paper argues that this method can also provide the practitioner with a false sense of his or her own knowing and expertise and, indeed, with arrogance. And the boundaries between the anthropologist as knowledge sink - cultural translator and interpreter - and the knowledge of the local knowledge owners can become opaque. Globalisation and the knowledge ?commons?, exemplified by Google, also highlight the increasing complexities in this area of the governance and ownership of knowledge. Our stronghold of working in remote areas and/or with marginalised groups places us at the forefront of negotiating the multiple new technological knowledge spaces that are opening up in the form of Indigenous websites and knowledge centres in these areas. Anthropology is not immune from the increasing awareness of the limitations and risks of the intellectual property regime for protecting or managing Indigenous knowledge. The relevance of the Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples in opening up a ?rights-based? discourse, especially in the area of knowledge ownership, brings these issues to the fore. For anthropology to remain relevant, we have to engage locally with these global discourses. This paper begins to traverse some of this ground. Protocols: Devices for translating moralities, controlling knowledge and defining actors in Indigenous research, and critical ethical reflection Margaret Raven (Institute for Sustainability and Technology Policy (ISTP), Murdoch University) Protocols are devices that act to assist with ethical research behaviour in Indigenous research contexts. Protocols also attempt to play a mediating role in the power and control inherent in research. While the development of bureaucratically derived protocols is on the increase, critiques and review of protocols have been undertaken in an ad hoc manner and in the absence of an overarching ethical framework or standard. Additionally, actors implicated in research networks are seldom theorised. This paper sketches out a typology of research characters and the different moral positioning that each of them plays in the research game. It argues that by understanding the ways actors enact research protocols we are better able to understand what protocols are, and how they seek to build ethical research practices. Ethics and research: Dilemmas raised in managing research collections of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander materials Grace Koch (AIATSIS) This paper examines some of the ethical dilemmas for the proper management of research collections of Indigenous cultural materials, concentrating upon the use of such material for Native Title purposes. It refers directly to a number of points in the draft of the revised AIATSIS Guidelines for Ethical Research in Indigenous Studies and draws upon both actual and hypothetical examples of issues that may arise when requests are made for Indigenous material. Specific concerns about ethical practices in collecting data and the subsequent control of access to both the data itself and to published works based upon it are raised within the context of several types of collections, including those held by AIATSIS and by Native Title Representative Bodies. Ethics or social justice? Heritage and the politics of recognition Laurajane Smith (ANU) Nancy Fraser?s model of the politics of recognition is used to examine how ethical practices are interconnected with wider struggles for recognition and social justice. This paper focuses on the concept of 'heritage' and the way it is often uncritically linked to 'identity' to illustrate how expert knowledge can become implicated in struggles for recognition. The consequences of this for ethical practice and for rethinking the role of expertise, professional discourses and disciplinary identity are discussed. The ethics of teaching from country Michael Christie (CDU), with the assistance of Yi?iya Guyula, Kathy Gotha and Dh�?gal Gurruwiwi The 'Teaching from Country' program provided the opportunity and the funding for Yol?u (north-east Arnhem Land Aboriginal) knowledge authorities to participate actively in the academic teaching of their languages and cultures from their remote homeland centres using new digital technologies. As two knowledge systems and their practices came to work together, so too did two divergent epistemologies and metaphysics, and challenges to our understandings of our ethical behaviour. This paper uses an examination of the philosophical and pedagogical work of the Yol?u Elders and their students to reflect upon ethical teaching and research in postcolonial knowledge practices. Closing the gaps in and through Indigenous health research: Guidelines, processes and practices Pat Dudgeon (UWA), Kerrie Kelly (Australian Indigenous Psychologists Association) and Roz Walker (UWA) Research in Aboriginal contexts remains a vexed issue given the ongoing inequities and injustices in Indigenous health. It is widely accepted that good research providing a sound evidence base is critical to closing the gap in Aboriginal health and wellbeing outcomes. However, key contemporary research issues still remain regarding how that research is prioritised, carried out, disseminated and translated so that Aboriginal people are the main beneficiaries of the research in every sense. It is widely acknowledged that, historically, research on Indigenous groups by non-Indigenous researchers has benefited the careers and reputations of researchers, often with little benefit and considerably more harm for Indigenous peoples in Australia and internationally. This paper argues that genuine collaborative and equal partnerships in Indigenous health research are critical to enable Aboriginal and Torres Islander people to determine the solutions to close the gap on many contemporary health issues. It suggests that greater recognition of research methodologies, such as community participatory action research, is necessary to ensure that Aboriginal people have control of, or significant input into, determining the Indigenous health research agenda at all levels. This can occur at a national level, such as through the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Road Map on Indigenous research priorities (RAWG 2002), and at a local level through the development of structural mechanisms and processes, including research ethics committees? research protocols to hold researchers accountable to the NHMRC ethical guidelines and values which recognise Indigenous culture in all aspects of research. Researching on Ngarrindjeri Ruwe/Ruwar: Methodologies for positive transformation Steve Hemming (Flinders University) , Daryle Rigney (Flinders University) and Shaun Berg (Berg Lawyers) Ngarrindjeri engagement with cultural and natural resource management over the past decade provides a useful case study for examining the relationship between research, colonialism and improved Indigenous wellbeing. The Ngarrindjeri nation is located in south-eastern Australia, a ?white? space framed by Aboriginalist myths of cultural extinction recycled through burgeoning heritage, Native Title, natural resource management ?industries?. Research is a central element of this network of intrusive interests and colonising practices. Government management regimes such as natural resource management draw upon the research and business sectors to form complex alliances to access funds to support their research, monitoring, policy development, management and on-ground works programs. We argue that understanding the political and ethical location of research in this contemporary management landscape is crucial to any assessment of the potential positive contribution of research to 'Bridging the Gap' or improving Indigenous wellbeing. Recognition that research conducted on Ngarrindjeri Ruwe/Ruwar (country/body/spirit) has impacts on Ngarrindjeri and that Ngarrindjeri have a right and responsibility to care for their lands and waters are important platforms for any just or ethical research. Ngarrindjeri have linked these rights and responsibilities to long-term community development focused on Ngarrindjeri capacity building and shifts in Ngarrindjeri power in programs designed to research and manage Ngarrindjeri Ruwe/Ruwar. Research agreements that protect Ngarrindjeri interests, including cultural knowledge and intellectual property, are crucial elements in these shifts in power. A preliminary review of ethics resources, with particular focus on those available online from Indigenous organisations in WA, NT and Qld Sarah Holcombe (ANU) and Natalia Gould (La Trobe University) In light of a growing interest in Indigenous knowledge, this preliminary review maps the forms and contents of some existing resources and processes currently available and under development in the Northern Territory, Queensland and Western Australia, along with those enacted through several cross-jurisdictional initiatives. A significant majority of ethics resources have been developed in response to a growing interest in the application of Indigenous knowledge in land and natural resource management. The aim of these resources is to ?manage? (i.e. protect and maintain) Indigenous knowledge by ensuring ethical engagement with the knowledge holders. Case studies are drawn on from each jurisdiction to illustrate both the diversity and commonality in the approach to managing this intercultural engagement. Such resources include protocols, guidelines, memorandums of understanding, research agreements and strategic plans. In conducting this review we encourage greater awareness of the range of approaches in practice and under development today, while emphasising that systematic, localised processes for establishing these mechanisms is of fundamental importance to ensuring equitable collaboration. Likewise, making available a range of ethics tools and resources also enables the sharing of the local and regional initiatives in this very dynamic area of Indigenous knowledge rights.b&w photographs, colour photographsngarrindjeri, ethics, ethnography, indigenous research, social justice, indigenous health -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Bruce Pascoe, Wathaurong : too bloody strong : stories and life journeys of people from Wauthaurong, 1997
Stolen children, stolen land, stolen freedom. Enough to break the strongest spirit but that?s what these people have got, they?re Too Bloody Strong to go under. The proud cry of survival is in all these stories and you can read the future in them to, From making baskets to building fences, from nursing to law, in education and art, the Wathaurong are preparing for the brand new day when the sun rises over a land of equality.maps, b&w illustrations, b&w photographswathaurong -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook with CD, Doreen Mellor et al, Many voices : reflections on experiences of Indigenous child separation, 2002
This book bring together voices of children who were separated from their families, people who cared for them, families who took them into their homes and Government officers who carried out official directions. Contents of CD: Track 1. Jim Hart, b.1927, Queensland, separated from family as a child. See ch. 5. Interviewer: David Woodgate (3m 02s) track 2. Clara Coulthard, b.1929, South Australia, separated from family as a child. See ch. 3. Interviewer: Sue Anderson (4m 06s) track 3. John Moriarty, AM, b.1938, New South Wales, South Australia, Northern Territory, separated from family as a child. See ch. 4. Interviewer: Frank Heimans (4m 12s) track 4. Sandra Hill, b.1951, Western Australia, separated from family as a child. See ch. 11. Interviewer: John Bannister (4m 11s) track 5. Trevor Deshong, b.1965, Queensland, separated from family as a child. See ch .6. Interviewer: Colleen Hattersley (4m 45s) track 6. Julie Wilson, b.1958, New South Wales, adopted as an infant. See ch. 6. Interviewer: Frank Heimans (4m 04s) track 7. Dorothy Pyatt, b.1918, South Australia, police officer in remote South Australia, 1950s and 1960s. See ch. 8. Interviewer: Karen George (4m 18s) track 8. Margaret Somerville, MBE, b.1912, New South Wales, Northern Territory, missionary and cottage mother. See ch. 7. Interviewer: Frank Heimans (3m 15s) track 9. Reg Worthy, OAM, b.1920, Queensland, Northern Territory, Victoria, welfare officer, senior administrator, Departmental Head. See ch. 8. Interviewer: Barbara Erskine (4m 55s)D?.b&w photographs, b&w illustrations, CDstolen generations, child welfare, bringing them home, oral histories -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesConference proceedings, Barbara Burnaby, Indigenous languages across the community, 2002
Language - Preservation and use. Language - Social function. [Maori: New Zealand Latin]. Language planning. [Language planning in a trans-national speech community]. [The way of the drum - when earth becomes heart] [The need for an ecological cultural community] Community language management. [Methods of madness: The Tuscarora Language Committee] [Daghida: Cold Lake First Nation works towards Dene language revitalization] [The Jicarilla Apache language summer day camp] [Report on the workshop "World of Inukitut"]. Arizona. New Mexico. Oklahoma. Adult education. Women's literacy. [Teaching reading with puppets] [Assessing Lakota language teaching issues on the Cheyenne River Reservation] [Incorporating traditional Nehiyaw/Plains Cree education in the university] [Collecting texts in Crao and Portuguese for teaching] [Early vocabularies and dictionary development: A cautionary note] [The process of spelling standardization of Innu-Aimun (Montagnais)] Pidgin. Creole. [Ojibway hockey CD-ROM in the making] [The use of multimedia and the arts in language revitalization, maintenance and development: The case of the Balsas Nahuas of Guerreo, Mexico] [The languages of Indigenous Peoples in Chukotka and the media] [Meeting of the Inukitut and Yupik family of languages on May 12, 2000]B&w photographs, diagrams,international language forum, community based practice, language research, conference papers, language policy, language and whole community development, literacy development, media, educational advances, canada, united states, new zealand, zimbabwe, mexico, russia, caribbean, inui, yupik -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesConference proceedings, Marleen Haboud, Endangered languages : voices and images, 2011
Linguistic and Sociolinguistic properties; sociolinguistics and endangered languages; Rights, identities and new technologies; New media cultures and endangered languages; Rebuilding peoples in Ecuador and revitalizing their languages Documentation - successful experience; Language rights of endangered languagesMaps, graphslanguage endangerment, worrorra, language technologies, documentation -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesDVD, Dylan McDonald, Buckskin, 2013
Jack Buckskin is a man whose mission is to sculpt a new urban Aboriginal language and culture, and through that bring hope back to his people. Broadcast on ABC1 Television on 13 October, 2013DVDkaurna, south australia, language activism -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Lenny and the big red kinan : an Awabakal Language Book, 2010
Awabakal is the language of the Aboriginal people from the Newcastle, Lake Macquarie and Lower Hunter region of New South Wales in Australia. As Lenny takes his walk and collects insects, we learn some words that relate to the bush, to the landscape and the little creatures that would be found there. This book has been printed with sound, which can be heard through an Audio Reader. If you have an Audio Reader, run it over the pages to hear the sound.word lists, colour illustrationsawabakal, newcastle, lake macquarie, hunter region, juvenile literature -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Robert Lane Greene, You are what you speak : grammar grouches, language laws &? the power of words, 2011
Why does language move some of us to anxiety or even rage? For centuries, sticklers have donned the cloak of authority to control how people use words. In this sensational new book, Robert Lane Greene strikes back to defend the fascinating, real-life diversity of this most basic human faculty. Chapters: 1 Babel and the Damage Done 2 A Brief History of Sticklers 3 Another Way to Love Language 4 More Equal than Others 5 Welcome to X. Now Speak Xish 6 Insubordinate Clauses 7 The Microsoft and Apple of Languages 8 Clouds, Not Boxes.sociolinguistics, linguistics -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Harold Koch, Aboriginal placenames : naming and re-naming the Australian landscape, 2009
"Aboriginal approaches to the naming of places across Australia differ radically from the official introduced Anglo-Australian system. However, many of these earlier names have been incorporated into contemporary nomenclature, with considerable reinterpretations of their function and form. Recently, state jurisdictions have encouraged the adoption of a greater number of Indigenous names, sometimes alongside the accepted Anglo-Australian terms, around Sydney Harbour, for example. In some cases, the use of an introduced name, such as Gove, has been contested by local Indigenous people." "The 19 studies brought together in this book present an overview of current issues involving Indigenous placenames across the whole of Australia, drawing on the disciplines of geography, linguistics, history, and anthropology. They include meticulous studies of historical records, and perspectives stemming from contemporary Indigenous communities. The book includes a wealth of documentary information on some 400 specific placenames, including those of Sydney Harbour, the Blue Mountains, Canberra, western Victoria, the Lake Eyre district, the Victoria River District, and southwestern Cape York Peninsula." -- Publisher description. Contents: Introduction: Old and new aspects of Indigenous place-naming /? Harold Koch and Luise Hercus NSW &? ACT: 1. Aboriginal placenames around Port Jackson and Botany Bay, New South Wales, Australia: sources and uncertainties /? Val Attenbrow 2. Reinstating Aboriginal placenames around Port Jackson and Botany Bay /? Jakelin Troy and Michael Walsh 3. The recognition of Aboriginal placenames in New South Wales /? Greg Windsor 4. New insights into Gundungurra place naming /? Jim Smith 5. The methodology of reconstructing Indigenous placenames: Australian Capital Territory and south-eastern New South Wales /? Harold Koch Victoria: 6. Toponymic books and the representation of Indigenous identities /? Laura Kostanski 7. Reviving old Indigenous names for new purposes /? Laura Kostanski and Ian D. Clark 8. Reconstruction of Aboriginal microtoponymy in western and central Victoria: case studies from Tower Hill, the Hopkins River, and Lake Boga /? Ian Clark South Australia &? Central Australia: 'Aboriginal names of places in southern South Australia': placenames in the Norman B.Tindale collection of papers /? Paul Monaghan 10. Why Mulligan is not just another Irish name: Lake Callabonna, South Australia /? J.C. McEntee 11. Murkarra, a landscape nearly forgotten: the Arabana country of the noxious insects, north and northwest of Lake Eyre /? Luise Hercus 12. Some area names in the far north-east of South Australia /? Luise Hercus 13. Placenames of central Australia: European records and recent experience /? Richard Kimber Northern Australia: 14. Naming Bardi places /? Claire Bowern 15. Dog-people: the meaning of a north Kimberley story /? Mark Clendon 16. 'Where the spear sticks up': the variety of locatives in placenames in the Victoria River District, Northern Territory /? Patrick McConvell 17. 'This place already has a name' /? Melanie Wilkinson, Dr R. Marika and Nancy M. Williams 18. Manankurra: what's in a name? placenames and emotional geographies /? John J. Bradley and Amanda Kearney 19. Kurtjar placenames /? Paul Black.Maps, b&w photographs, tables, word listsaustralian placenames, sociolinguistics, linguistics, anthropology, sydney harbour placenames, blue mountains placenames, canberra placenames, western victoria placenames, lake eyre placenames, victoria river district placenames, cape york peninsula placenames -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, ?Marja-Liisa Olthuis et al, Revitalising Indigenous languages : how to recreate a lost generation, 2013
The book tells the story of the Indigenous Aanaar Saami language (around 350 speakers) and cultural revitalisation in Finland. It offers a new language revitalisation method that can be used with Indigenous and minority languages, especially in cases where the native language has been lost among people of a working age. The book gives practical examples as well as a theoretical frame of reference for how to plan, organise and implement an intensive language programme for adults who already have a professional training. It is the first time that a process of revitalisation of a very small language has been systematically described from the beginning; it is a small-scale success story. The book finishes with self-reflection and cautious recommendations for Indigenous peoples and minorities who want to revive or revitalise their languages.Maps, colour photographsnative language studies, bilingual education, casle project, saami, language revival -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Te Taura Whiri I Te Reo Maori, Matariki : Aotearoa Pacific New Year : te whakarite kaupapa mo Matariki =? making plans for Matariki, 2005
Uses the Matariki, a celebration of culture, language, spirit and people, to promote language learning.Colour photographs, colour illustrationsmaori, matariki -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, D W A Baker, The civilised surveyor : Thomas Mitchell and the Australian Aborigines, 1997
Thomas Mitchell, surveyor in Sydney from 1827 at the time when Squatters were extending their runs with huge detriment to the Aboriginal population. Mitchell and his men were ambiguous in their treatment of the people. His conviction was in the superiority of the British civilisation.Maps, b&w illustrationsthomas mitchell, new south wales history, race relations, racism, colonisation -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Isabel Ellender et al, People of the Merri Merri : the Wurundjeri in colonial days, 2001
This book looks at the earliest years of contact between Aborigines and Europeans in the Melbourne area. The contact period saw the Wurundjerei-willam resisting, coping with and adapting to a new and alien culture. A degree of mutual respect seems to have existed, at least for a short time, of each other?s intentions. It appears that the settlement at Port Phillip did not encounter the degree of violence seen elsewhere.maps, b&w illustrations, colourwoiwurung, woi wurrung, wurundjeri, wurundjeri willam, merri merri, william thomas, -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Aboriginal Resource and Development Services, Cross cultural awareness education for Aboriginal people : a consultancy for the Office of Aboriginal Development, 1994
Includes - Section A: Legal & Economic Research Section B: Comments on the current siruation in the two selected communities Section C: Outline of the Education Model Section D: New Understanding - The Process Section E. Indicators for Assessment - Short and Long Section F: Recommendations for the program and its expansion.Maps, b&w illustrationsnorthern territory, arnhem land, multicultural education -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, St Philip's College Alice Springs - Principal Chris Tudor & Deputy Principal Chris Eldridge, 09/1986
In 1945 the Reverend Harry Griffiths, who worked for the Methodist Inland Mission in Alice Springs, saw the need for a boarding facility for children of families living in remote areas in Central Australia who needed access to schools. He and his wife established Griffiths House, on a site in the town centre, and for many years it became home for students from all over the Outback, including many young Aboriginal people. In the late 1950's the Rev Fred McKay, successor to the Rev John Flynn as Superintendent of the Australian Inland Mission, lobbied the United Church in the Northern Territory to build and expand on this important start. Together the Presbyterian, Methodist and Congregational churches embarked on a missionary venture to develop St Philip's College - a new, larger residential hostel which would one day become a full boarding school. An ideal site - 22 acres of bush at the junction of the Charles and Todd Rivers and backing on to the Telegraph Station National Park - was secured and after six years of planning, construction began in 1964. Fred McKay led the legendary work parties comprised of volunteers from all over Australia who travelled to Alice Springs, paying their own way and volunteering their expertise, time and labour, to turn a dream into a reality. This fantastic tradition continues today, with work parties arriving each mid-year holiday. On 13 February 1965 the first boarders moved in to St Philip's College. For the first 24 years, therefore, St Philip's College operated as a residential hostel only. The College’s ninth Headmaster, Mr Christopher Tudor, arrived in 1986. He and the Council Chairman, Mrs Jan Heaslip, judged that the time was right to complete the original plan to turn St Philip’s College into a fully fledged independent boarding/day school, serving not only “bush” families, but also the growing population of Alice Springs. The then College Council embraced the idea and three years of frantic, determined preparation and planning commenced, culminating in an extensive $2 million building program in 1988. To this day there continues to be further development with the new landscaping underway near The Minnamurra Hall, Reception and Rivergum Cafe, plus the recent completion of the Science & Food Technology building and the new Rivergum Cafe.Head & Shoulders of Chris Eldridgest. philip's college, tudor, chris, eldridge, chris -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, St Philip's College Alice Springs - Principal Chris Tudor & Deputy Principal Chris Eldridge, 09/1986
In 1945 the Reverend Harry Griffiths, who worked for the Methodist Inland Mission in Alice Springs, saw the need for a boarding facility for children of families living in remote areas in Central Australia who needed access to schools. He and his wife established Griffiths House, on a site in the town centre, and for many years it became home for students from all over the Outback, including many young Aboriginal people. In the late 1950's the Rev Fred McKay, successor to the Rev John Flynn as Superintendent of the Australian Inland Mission, lobbied the United Church in the Northern Territory to build and expand on this important start. Together the Presbyterian, Methodist and Congregational churches embarked on a missionary venture to develop St Philip's College - a new, larger residential hostel which would one day become a full boarding school. An ideal site - 22 acres of bush at the junction of the Charles and Todd Rivers and backing on to the Telegraph Station National Park - was secured and after six years of planning, construction began in 1964. Fred McKay led the legendary work parties comprised of volunteers from all over Australia who travelled to Alice Springs, paying their own way and volunteering their expertise, time and labour, to turn a dream into a reality. This fantastic tradition continues today, with work parties arriving each mid-year holiday. On 13 February 1965 the first boarders moved in to St Philip's College. For the first 24 years, therefore, St Philip's College operated as a residential hostel only. The College’s ninth Headmaster, Mr Christopher Tudor, arrived in 1986. He and the Council Chairman, Mrs Jan Heaslip, judged that the time was right to complete the original plan to turn St Philip’s College into a fully fledged independent boarding/day school, serving not only “bush” families, but also the growing population of Alice Springs. The then College Council embraced the idea and three years of frantic, determined preparation and planning commenced, culminating in an extensive $2 million building program in 1988. To this day there continues to be further development with the new landscaping underway near The Minnamurra Hall, Reception and Rivergum Cafe, plus the recent completion of the Science & Food Technology building and the new Rivergum Cafe.Head & Shoulders of Chris Tudor.st. philip's college, tudor, chris, eldridge, chris -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, St Philip's College Alice Springs - Principal Chris Tudor & Deputy Principal Chris Eldridge, 09/1986
In 1945 the Reverend Harry Griffiths, who worked for the Methodist Inland Mission in Alice Springs, saw the need for a boarding facility for children of families living in remote areas in Central Australia who needed access to schools. He and his wife established Griffiths House, on a site in the town centre, and for many years it became home for students from all over the Outback, including many young Aboriginal people. In the late 1950's the Rev Fred McKay, successor to the Rev John Flynn as Superintendent of the Australian Inland Mission, lobbied the United Church in the Northern Territory to build and expand on this important start. Together the Presbyterian, Methodist and Congregational churches embarked on a missionary venture to develop St Philip's College - a new, larger residential hostel which would one day become a full boarding school. An ideal site - 22 acres of bush at the junction of the Charles and Todd Rivers and backing on to the Telegraph Station National Park - was secured and after six years of planning, construction began in 1964. Fred McKay led the legendary work parties comprised of volunteers from all over Australia who travelled to Alice Springs, paying their own way and volunteering their expertise, time and labour, to turn a dream into a reality. This fantastic tradition continues today, with work parties arriving each mid-year holiday. On 13 February 1965 the first boarders moved in to St Philip's College. For the first 24 years, therefore, St Philip's College operated as a residential hostel only. The College’s ninth Headmaster, Mr Christopher Tudor, arrived in 1986. He and the Council Chairman, Mrs Jan Heaslip, judged that the time was right to complete the original plan to turn St Philip’s College into a fully fledged independent boarding/day school, serving not only “bush” families, but also the growing population of Alice Springs. The then College Council embraced the idea and three years of frantic, determined preparation and planning commenced, culminating in an extensive $2 million building program in 1988. To this day there continues to be further development with the new landscaping underway near The Minnamurra Hall, Reception and Rivergum Cafe, plus the recent completion of the Science & Food Technology building and the new Rivergum Cafe.Tudor and Eldridge in conversation with the College in the background.st. philip's college, tudor, chris, eldridge, chris -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Djiniyini Gondarra, 1986
Rev Dr Djiniyini Gondarra OAM, was born in Milingimbi, eastern Arnhemland in 1945. He was educated at Milingimbi Mission School and pursued his theological education as a youth leader and Sunday School teacher through the Methodist Church, before attending college in Brisbane. In 1969 he trained as a Minister in Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands under the Uniting Church, before returning to Arnhemland to minister his own people at the Galiwin’ku parish, firstly as a lay pastor (1971-1972) and then as a Minister from 1976-1982. In 1983-84, Rev Djiniyini worked as a Lecturer in Theology at Nungalinya College, Darwin. He was honoured with a Diploma of Theology (Honorary) from there in 1984, and in 1991 received a Cultural Doctorate in Literature (Honorary) from the World University, Roundtable, Arizona USA. Rev Djiniyini was awarded the Order of Australia Medal (OAM) in 1995. As well as being the Chairman of ALPA since 1993, Rev Djiniyini is currently the Director of Duduy’ngu Pty Ltd, which provides consultancy and cross-cultural services. He is also Director of Yirrkala Business Enterprises. Over the years, Rev Djiniyini has served on many committees and councils including: Member of the Steering Committee of the Australian Indigenous Cultural Network (1998-2001), CEO of Aboriginal Resource and Development Services Inc (1998-2001), CEO of the Northern Regional Council of the Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress (1998-2001), Director of Reconciliation Australia Limited (2000-2001), Member of Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation (1998-2000), Chairman of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress (1995-2000 & 1990-1993), Member of Central Committee of the World Council of Churches (1991-1994), Moderator of Northern Synod, Uniting Church in Australia (1985-1987), Secretary of newly formed Aboriginal Presbytery, Northern Synod, Uniting Church in Australia (1985), and Vice-President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress Uniting Church in Australia (1983-1987). Rev Dr Djiniyini Gondarra OAM has also been extensively published, and his works include: • Information Papers (co authored), Aboriginal Resource and Development Services: • Confusion Between Cultures (1998) • MHead & Shoulders of Djiniyini Gondarra facing right of picture."Rev. Djiniyini Gondarra 1986. Moderator Northern Synod and Vice President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Conference."gondarra, djiniyini, uaicc, northern synod uca -
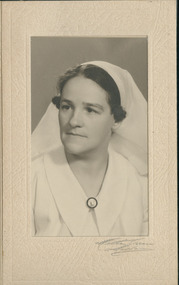 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, C1947
Hilda Charlotte Foster, 1902 - 1990, was a Double Certified Nurse when, at the age of 35, she successfully applied to the board of the Australian Inland Mission (AIM) to work at an outback field centre in South Australia. Born and raised in suburban Melbourne, she had been inspired by stories told to her by other missionaries about the fulfilment to be gained working amongst Aboriginal communities. Given her religious faith and nursing skills, she believed she could make a difference. She worked in Oodnadatta in South Australia for two years (1937-1939), followed by a stint in Innamincka in New South Wales in 1940 -1942. Before she became a nurse, Hilda Foster trained to be a Sunday School teacher and was a member of the Sunday School Council of Victoria. She completed first aid courses run through the Presbyterian Deaconesses Institute in Carlton, Victoria, and in 1930 successfully applied to become a trainee nurse at the Austin Hospital for Incurables, in Heidelberg. She commenced her training there in 1931, before moving to the Women's Hospital in 1933. In 1934 she had six months at the Fairfield Infectious Diseases Hospital, before returning to the Austin, where she was employed when she sat her final exams in November 1934. Her combined skills made her a most attractive option for the Australian Inland Mission. As well as being multi-skilled as a nurse, she provided religious instruction and spiritual ministry to members of the community. https://trove.nla.gov.au/people/762093?c=people Sister Foster nursed at Toora Bush Hospital prior to leaving for the Paton Memorial Hospital, Vila, New Hebrides in 1944. She left the New Hebrides in 1946.Matt, black and white, head and shoulders, studio portrait of Sister Hilda Charlotte Foster on card.australian inland mission, presbyterian deaconess, sister hilda charlotte foster, paton memorial hospital vila new hebrides -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Charles Harris, 07/1988
"School at Hall's Gap studies holistic Aboriginal theology" - article by Tim Angus - "Participants at a school of Aboriginal Theology were challenged to take up a new partnership in mission by the Rev. Charles Harris, president of the Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress… Charles Harris gave a quiet and determined witness to the power of the Gospel to free his people to become agents of their own destiny in spiritual, cultural and political terms."Head & shoulders, dressed casually."Rev. Charles Harris"harris, charles, aboriginal and islander christian congress -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Opening of Kilmany Orbost new units by politicians, 05/1986
Kilmany Family Care Community Residential Units - ordinary community houses that are adapted for accommodation for up to six people with intellectual disabilities - opened at Orbost. See article on p. 25 of C&N for May 14, 1986.Caroline Hogg, Community Affairs Minister & Barry Murphy MLC snipping ribbon at opening of new units.Identification of persons & place.kilmany family care, hogg, caroline, murphy, barry mlc -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Barry Baker - exit appointment, 1985
The class of '84 – Happily Settled. "Barry Baker has been mixing wheat farming with theological studies for several years. And now from his Rupanyup farm he's moving to Cavendish. He's 48, married with three children. His wife, Helen, married a farmer, and is working through her new role as a minister's wife. Barry is looking forward to going back to the country. He found the five years of study, the first three as a private student, a pretty long drag, although he's immensely enjoyed the privilege of theological study. He considers the ministry will be very much a pastoral one. "I've go to know my people before I can preach to them," he told me. He's interested in cricket and music."B & W head & shoulders photo of Rev. Barry Baker, wearing a skivvy and jumper.C&N identification.baker, barry, theological hall graduates 1984 -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph
Matthew Burnett (1839 - 1896). Wesleyan temperance evangelist. Born in Yorkshire, came to Australia in 1857 with his wife Sarah Gibson. He spent the years 1864 to 1867 on the goldfields evangelising against drink and securing temperance pledges. Sarah Burnett died in 1871 and Matthew returned to England in 1873, meeting leading temperance reformers. He returned to Australia in the mid-1870s. He went to South Australia, Western Australia, Tasmania and New Zealand as a temperance campaigner, and claimed to have received pledges from 140,000 people. He returned to England in 1890 and died at Scarborough in 1896.Sepia toned head and shoulders studio portrait of Matthew Burnett in three quarter profile."Yours faithfully Matthew Burnett"matthew burnett, sarah gibson, temperance, evangelist, wesleyan -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoriaphotograph, May 10th or 11th 1935
Kagawa, Toyohiko (1888-1960) Japanese evangelist and social movement leader Kagawa was born in Kobe to Kame and Junichi Kagawa. In lonely years following the death of his parents at age four, he met Harry W. Myers and Charles A. Logan, missionaries of the (Southern) Presbyterian Church, U.S., and was baptized by Myers on February 14, 1904, at the Tokushima church. He pursued theological study at Meiji Gakuin in Tokyo and Kobe Theological Seminary. During his student days in Kobe he moved into the Shinkawa slum to serve the physical and spiritual needs of some 7,500 people. Between August 1914 and May 1917 Kagawa studied in the United States at Princeton Theological Seminary and then became involved in labor and peasants movements in Japan and in organizing religious programs, with the Jesus Band of Kobe as the base of his work. In 1921 Kagawa organized the Friends of Jesus. This Franciscan-like band of young people strove for spiritual discipline, compassion for the poor, and an evangelical life of witness. When Tokyo suffered a massive earthquake in 1923, he shifted the main emphasis of his work to that city. He promoted economic cooperatives in Japan and peace and social reform programs before and after World War II. Kagawa was a prolific writer. Most of his writings are collected in the twenty-four volume Kagawa Toyohiko Zenshu (The work of Kagawa Toyohiko) (1964). His theological focus was on the redemptive love of God, manifest in the life of Jesus Christ, to whom people can commit themselves through a mystical experience of faith and intellectual creativity. Kagawa was known more as a Christian social reformer than as a religious leader both in and out of Japan, but he was fundamentally an evangelist throughout his life. Robert M. Fukada, “Kagawa, Toyohiko” in Biographical Dictionary of Christian Missions, ed. Gerald H. Anderson (New York: Macmillan Reference USA, 1998), 350. This article is reprinted from Biographical Dictionary of Christian Missions, Macmillan Reference USA, copyright © 1998 Gerald H. Anderson, by permission of Macmillan Reference USA, New York, NY. All rights reserved. B & W informal photograph of the Rev. H.C. Matthew and Toyohiko Kagawa standing in front of the door to Captain Cook's Cottage in the Fitzroy Gardens, Melbourne. "Melbourne May 19th or 11th 1935. H.C. Matthew & Toyohiko Kagawa standing by the cottage recently removed to Australia & re-erected in Melbourne Botanical Gardens in which Captain Cook was born."toyohiko kagawa, h.c. matthews, captain cook's cottage, friends of jesus, christian missions. -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, c Late 1970s
In the late 1970s an interstate tourist bus crashed on its side on Holden Bridge which spans the Deep Creek at Bulla. After this incident a newer and more substantial bridge was constructed over the Deep Creek.A black and white photograph of a bus crash which occurred on the Holden bridge at Bulla. The Stateliner Bus is on its side and a policeman and three other people are looking at the site of the accident.holden bridge, deep creek, stateliner buses, george evans collection -
 Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)
Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)Photograph, U Carpenter, 1950 c
Suspension bridge opened 22 November 1940 replaced by new prestressed reinforced concrete container bridge opened 1969Black and white photograph showing a car crossing the suspension bridge between San Remo and Newhaven Phillip Island Victoriasettlers, transport, people -
 Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)
Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)Photograph, 1990 c
Also a second photograph showing Peter Healy planting Nan Frasers new garden with Pope the dog helping at Rowe Street 05333.1 10 x 15 cmColour photograph showing Gwen Healy cutting cake and Nan Fraser seated both residents of units in Rowe Street Lakes Entrancechurches, people -
 Sunshine and District Historical Society Incorporated
Sunshine and District Historical Society IncorporatedHonour Board - PAST PRESIDENTS of the SUNSHINE and DISTRICT FRIENDLY SOCIETIES DISPENSARY
Friendly Societies originated in the industrial areas of the United Kingdom. The first society in Victoria was formed in 1839 and by 1913 more than half of the Victorian population was insured by Friendly Societies in some fashion. The societies were financed by Members' subscriptions and offered health benefits and other welfare services, before these services were provided by the government. Doctors were paid by the societies to treat members free of charge, and Dispensaries were established to provide members with subsidised quality medicines. The Sunshine and District Friendly Societies Dispensary was established on the 1st of March 1930 with a membership of 896, and it was located in Sun Crescent Sunshine. The membership grew to 1052 within 4.5 years, and the number of prescriptions dispensed in the 6 months prior to November 30,1935 totalled 10,535. The Dispenser was Mr. C. H. Semmens. Most Friendly Societies operated democratically with office bearers changed regularly to prevent power cliques. The Sunshine Dispensary appears to have operated in the same way as the societies that owned it. The Advocate of 10 July 1936 reports that the seven newly elected office bearers or delagates were from the Friendly Societies; A.N.A., M.U.I.O.O.F., P.A.F.S., and G.U.O.O.F. The names of all the seven people can be found on the Honour Board, indicating that they each have served at least one term as President of the Sunshine Dispensary. The health professions and the Labour Governments of the 1940's wanted to see the involvement of Friendly Societies in health care broken. The Commonwealth Free Medicine Plan appears to have been drawing customers away from Friendly Societies Dispensaries in general. The Sunshine Dispensary placed several advertisements in the Sunshine Advocate during late 1950 urging members to remain loyal to it. By the 1980's the increase in entrepreneurial clinics and the availability of take away medicine helped to vastly diminish the involvement of Friendly Societies in health care provision. The 1936 Sunshine Advocate refers to the Sunshine and District United Friendly Societies Dispensary, with the same office bearers as the Presidents on the Honour Board but on which the 'United' is missing from the name of the Dispensary. The 1950 advertisements were placed by Sunshine U.F.S. Dispensary of 23 Sun Crescent. It is thought that all three names refer to the same business, but the writer stands to be corrected. The above is a compilation of information sourced from Sunshine Advocates published in January and July 1936, and in September, October and November 1950. It also draws on an article written by Elizabeth Willis and published online by the the Department of History (University of Melbourne), and on an article written by Mr. Bill Kelly of the Australian Friendly Societies Pharmacies Association, and also on an article by Museum Victoria Australia. Corrections to what has been written are welcome from interested readers.The Honour Board provides a historical record of the Presidents that served 61 terms on the Board of the Sunshine and District Friendly Societies Dispensary. It also provides a reminder that when a government does not adequately look after the welfare needs of its citizens, the people can band together to find ways of helping each other. The Sunshine Dispensary no longer exists, and a more recently established Community Pharmacy which operated in Hampshire Road could not compete against the discount pharmacies that have taken over. These new pharmacies sell a wide range of profitable product lines, as well as dispensing traditional prescription medications.Brown stained wood particle board with picture frame type edging. The board has six straight sides however it is not typical hexagon shaped. The top is composed of three straight short edges to give an almost rounded edge to an otherwise oblong shaped bottom section. On the board in gold coloured lettering are the names of 'brothers' and 'sisters' who served a total of 61 terms as PRESIDENTS of the SUNSHINE AND DISTRICT FRIENDLY SOCIETIES DISPENSARY, which was established on the 1st of March 1930. Eight of the men served more than one term with BRO. I. MILLER serving four terms, and BRO. F. RICHER serving three. The three women SISTER. I. REWELL, SISTER. C. JOHNSON, and SISTER. M.S. ARMSTRONG served one term each. There is no indication of when each person served, but it is believed that the term length was around six months and that the list is in chronological order. This conclusion results from seeing that BRO. W. ROONEY is the 11th listed President, and that the Sunshine Advocate of 10 July 1936 states that he was elected as the new President.sunshine and district friendly societies dispensary, honour board, 1st march 1930, 1/3/1930, sunshine u.f.s. dispensary, semmens, rooney, miller, richer, armstrong, rewell, johnson -
 Sunshine and District Historical Society Incorporated
Sunshine and District Historical Society IncorporatedPrincess Mary 'Tin' - Bullet Pencil - War Service Medals, Circa 1914 -1918
A 'Sailors & Soldiers Christmas Fund' created by Princess Mary had overwhelming response and so it was decided to give every person 'wearing the King's uniform on Christmas Day 1914' the brass tin along with a Christmas card and a picture of the princess, and items such as pipe, lighter, tobacco, and 20 cigarettes. Non-smokers and boys received a bullet pencil and a packet of sweets. Indian troops often received sweets and spices, and nurses received chocolates. Many of the items were sent separately from the boxes because of lack of space. Not all the tins could be sent out by Christmas and so those sent in January 1915 contained a New Year card. Shortage of brass meant that many did not received their tins until summer 1916, however by January 1919 some still did not receive them. After using up the contents many service people then used the tins to store small items. The brass tin, bullet pencil, and medals belonged to Pte George Nutting of the 2nd London regiment, and regimental number 2080/230442. After World War 1 George Nutting sailed for Melbourne on June 1, 1922 aboard the S.S. Borda. He then lived at several addresses in the Sunshine/Albion area including Dawson St, 32 King Edward Ave, and 15 Kamarooka St. At one stage he was involved in a window cleaning and gardening business, and both he and his wife Janet were very good dancers. George Nutting was also involved in the loyal Sunshine Lodge and was presented with a Past Grand's Collar in 1943. He lived at 15 Kamarooka St until he passed away on March 20th 1979 at the age of 85. The above information was sourced from http://www.kinnethmont.co.uk/1914-1918_files/xmas-box-1914.htm (accessed 1/3/2014), and from http://museumvictoria.com.au/collections/items/1329146/tin-princess-mary-s-Christmas-gift-1914 (accessed 1/3/2014), and from research work done by Eva and Marie of S&DHS.The Tin and Medals provide a visible historical record of the Christmas gift, and the awards that the average WW1 British service person received about 100 years ago. The bullet pencil may indicate that Pte G. Nutting was probably a non-smoker, at least around circa 1914.Brass rectangular box with an embossed and hinged lid. The lid features the profile of Princess Mary with an 'M' on each side, and the names of Britain's allies in 1914. The pencil fits into the brass bullet casing to give the appearance of a bullet. The WW1 British medals are: 1. 1914 - 1915 Star, 2. British War Medal 1914 - 1918 (Silver), 3. Allied Victory Medal.TIN: Imperium Brittanicum, Christmas 1914, Belgium, France, Servia, Japan, Russia, Monte Negro. MEDALS: 2080 Pte G. Nutting 2 - Lond.R g. nutting, princess mary tin, christmas 1914, bullet pencil, british ww1 medals, 1914 - 1915 star, british war medal 1914 - 1918, allied victory medal -
 Chiltern Athenaeum Trust
Chiltern Athenaeum TrustPhotograph
Photo of Bluey Truscott. Squadron Leader Keith William (Bluey) Truscott was regarded as one of Australia’s most well known WW2 fighter pilot aces. He was born on the 17/5/1916 and died over Exmouth, Western Australia on 28/3/1943 in an Aircraft accident whilst on duty. He initially trained under the Commonwealth Empire Training Scheme In Canada at the beginning of WW2, and later on was posted to Number 452 Squadron England where he flew Spitfires over Europe. He was awarded the distinguished Flying Cross in 1941 for his Air action and bravery. In 1942 he was further awarded the DFC Bar for further outstanding Air action and bravery. He returned to Australia and commanded number 76 Squadron who undertook duties in Papua New Guinea, specifically Milne Bay. When with 76 Squadron they largely flew Kittyhawks. There is a club named after SQN LDR Truscott, called the Truscott Club, at Airforce Base Darwin. There is also a decommissioned WW2 Airfield in the Kimberley’s called after him ( Truscott Air Base). Truscott has more recently been called Mungalu-Truscott Air Base as it is now owned by the traditional people of the Wunambal Gaambera. The Airfield is now used for commercial and private flying and is heritage listed under the National Trust of Australia (W.A.) due to its historical significance relating to WW2 and the remaining artefacts that are still in place presently. Bluey Truscott was also a well known Australian Rules Football player prior to WW2 having played for Melbourne. Photograph of Keith William (Bluey) Truscott in uniform.ww2, bluey truscott, flying cross
