Showing 11927 items
matching seive
-
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph
A sepia photograph of a group of unidentified tennis players at The Hill. See also #176.Handwritten on back: TENNIS AT THE HILL / ERIC BOARDMANsports, tennis, boardman, eric, the hill, sunbury asylum, george evans collection -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumPostcard
A POSTCARD / SEE IMAGE ON WORKSHEET NEW YEAR THOUGHTS FROM ACROSS THE SEADEAR MISS PERRY THIS CARD IS TO WISH YOU A HAPPY NEW YEAR. M WILL WRITE SOON . WITH LOVE FROM DOROTHEAlocal history, document, cards, greeting card -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumLeisure object - SILVER MATCH HOLDER
MATCH HOLDER DONATED BY MRS. PEG JAMES.1 METAL MATCHHOLDER - THE CONTAINER HAS A LID - SEE DRAWING .2 MATCHES. local history, metalcraft, silverware, smoking accessories -
 Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer Museum
Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer MuseumLice Comb
Xylophite double comb. Used for removable of lice. See photo of comb in the foreground. -
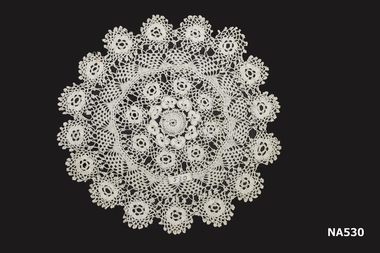 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Decorative object - Doyley
White crochet doyley. This is part of a set of three. See Na 500 and 550.handcrafts, needlework -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Decorative object - Doyley
White Lace doyley. This is part of a set of three. See Na 530 and 500.handcrafts, needlework -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Robin Boyd, 1968
Colour slide in a mount. House interior, probably Australia (see also S0876)Made in Australia / 20 / SEP 68M7slide, robin boyd -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Colour prints, Energy Education Centre, c. 1990
4 laminated photographs used for display purposes. See B11.0329, B11.0331, B11.0332.displays, burnley, energy education centre -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Digitised, Joanne Morris, Insect Collection, 1971-1973
Insects had to be collected, killed and mounted in hand made wooden boxes. Donated by Joanne Morris (1973) in June 2014.A student's Insect Collection, part of Entomology course. Digitised only: see Artefacts.students, insect collection, entomology course, joanne morris -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryTorches
Glass blower's torches. For age, see Gall Cat.No 1020 for "Oxygen" type. -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryRare Earthy Hydroxides Ce(Oh)4
Chemical specimens. Extraction of rare earths - by J.S.Anderson see also CH 195 -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Digital image, Wal Jack, 29/06/1955 12:00:00 AM
Yields information the appearance of the SEC tramcar No. 30 and the Mt Pleasant tram terminus during the reconstruction of the bridge over Canadian Creek.Digital image from the Wal Jack Ballarat Album of No. 30 at the Barkly St terminus, Mt Pleasant, 29-6-1955. Wal has the album notes of "standby car". Was provided to enable the service in Barkly St during the reconstruction of the Canadian Creek bridge during June-July 1955, see Reg Item 5157 as well and 5301, 5302 and 5305. See image i2 for rear of photograph. See image i3 for hi res scan of print. See image i4 for hi res scan of negativeon rear of photo in ink, "SEC Ballarat, No. 30 at Barkly St terminus (out of use). Mt Pleasant 29-6-55" In the top right hand corner is the W.Jack stamp but no negative number.trams, tramways, mt pleasant, barkly st, canadian creek, tram 30 -
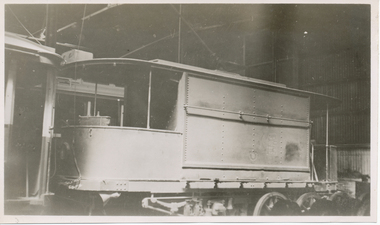 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Black & White Photograph/s, Wal Jack, 7/03/1954 12:00:00 AM
Black and White print contained within the Wal Jack Bendigo and Geelong Album, see Reg Item 5003 for more details. Photo of the first or old Bendigo Water tram or scrubber inside the depot, 7-3-1954, Photo by Wal Jack. Wal's album notes say that the vehicle is "now out of use". See Reg Item 7880 for another photograph from the other side. See image i2 for rear of photograph. See image i3 for hi res scan of negative On the rear in blue ink "SEC old "Brush" scrubber inside depot 7-3-54" with Wal Jack copyright stamp in the top right hand corner and the number "T73PC" written in.trams, tramways, bendigo, depot, scrubber tram, sprinkler tram, scrubber, sprinkler -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Boer War Veteran Alfred G. Johnston
Alfred G Johnston was a former Ballarat School of Mines student who was killed in action at Rhenosterkop, Middleburg district, Transvaal, South Africa, on 7 May 1901, aged 29 years. A letter of condolence was sent to his parents (see S.M.B. Council Meeting 31-5-1901).An image from the original black and white photograph showing the torso of a man in military uniform - Alfred G Johnston who served in the 5th Regiment of the Victorian Mounted Rifles. The uniform (the forerunner of the uniform of the Australian Light Horse) includes a slouch hat. Also see: Photograph of Alfred G. Johnston as S.M.B. student, 1899. Catalogue number 00414. A photograph of the memorial that Ballarat School of Mines put up in his honour is Catalogue number 00531.Verso: AUTHENTICATION REQUESTED Photographic portrait of LIEUTENANT ALFRED GRESHAM JOHNSTON (with handwritten note - or Gersham) 5th Regiment V.M.R. (late student of S.M.B.) Killed in action at Rhenoster Kop. South Africa, May 7, 1901 S.M.B. Council Meeting (31-5-1901) - - - letter of condolence to parents. Please return to W.T. Ryan, c/- School of Mines, Ballarat. 3350boer, boer war, south african war, south africa, volunteer regiments, alfred johnston, a g johnston, johnston, ballarat school of mines, victorian mounted rifles -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Postcard - Alice McGregor Postcard Collection, 1900 - 1920
Alice McGREGOR Born: 1908; unknown parents. Possibly adopted by the Salter family? Electoral Roll 1936: Highland Terrace Kangaroo Flat. Alice Mary Salter and William Robert Salter living together; presumed to be sister and brother. William Robert Salter was killed in a MVA in Bendigo in 1937 aged 26. In Victoria in 1938, Alice Mary Salter married James Thomas McGregor (born Victoria 1917, died Victoria 1983, buried Fawkner Cemetery) Lived: 1968; 22 Wade Street Golden Square Alice McGregor Died: 1999 aged 91 at Anne Caudle Centre, Bendigo Buried: Kangaroo Flat Cemetery See additional research. Postcard Album of Alice McGregor contained 86 post cards.Postcard Album of Alice McGregor containing 86 postcards. See 1400 Coloured photo of Cheapside, London. View looking down a busy street with horse drawn carriages, motor vehicles. Many pedestrians on footpath and street. Statue on a plinth facing down the street. Rear is blank except for the date in pencil at top left. Jan 12th, 1918 postcard, collector, alice mcgregor -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Postcard - Alice McGregor Postcard Collection, 1900 - 1920
Alice McGREGOR Born: 1908; unknown parents. Possibly adopted by the Salter family? Electoral Roll 1936: Highland Terrace Kangaroo Flat. Alice Mary Salter and William Robert Salter living together; presumed to be sister and brother. William Robert Salter was killed in a MVA in Bendigo in 1937 aged 26. In Victoria in 1938, Alice Mary Salter married James Thomas McGregor (born Victoria 1917, died Victoria 1983, buried Fawkner Cemetery) Lived: 1968; 22 Wade Street Golden Square Alice McGregor Died: 1999 aged 91 at Anne Caudle Centre, Bendigo Buried: Kangaroo Flat Cemetery See additional research. Postcard Album of Alice McGregor contained 86 post cards.Postcard Album of Alice McGregor containing 86 postcards. See 1400 B&W photo of the London & North Western Hotel, Lime Street Station, Liverpool. A multi-story building overlooking a statue atop a column. Horse drawn vehicles and pedestrians in the street. Addressee - Miss Kelly, Norwood, Wills St, Bendigo, Australia Sender - M.I. Grendell (?) Dated 25 5.06, Liverpool postcard, collector, alice mcgregor -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Postcard - Alice McGregor Postcard Collection, 1900 - 1920
Alice McGREGOR Born: 1908; unknown parents. Possibly adopted by the Salter family? Electoral Roll 1936: Highland Terrace Kangaroo Flat. Alice Mary Salter and William Robert Salter living together; presumed to be sister and brother. William Robert Salter was killed in a MVA in Bendigo in 1937 aged 26. In Victoria in 1938, Alice Mary Salter married James Thomas McGregor (born Victoria 1917, died Victoria 1983, buried Fawkner Cemetery) Lived: 1968; 22 Wade Street Golden Square Alice McGregor Died: 1999 aged 91 at Anne Caudle Centre, Bendigo Buried: Kangaroo Flat Cemetery See additional research. Postcard Album of Alice McGregor contained 86 post cards.Postcard Album of Alice McGregor containing 86 postcards. See 1400 B & W photo of the Rue St. Ferreol, Marseille, France Showing a tram down the middle of the street and a car and motorcycle. 5-storied shop buildings on either side Pedestrians on pavements No addressee, sender or date Rear is blank postcard, collector, alice mcgregor -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPhotograph - Digital Image, Oscar Reginald Turner Conductor retirement, 1953
Digital Image of a photograph of Oscar Turner standing in front of W2 636 - see also Reg Item 1925. See htd1930i for Certificate of Service - gives retirement date of 8/8/1953, i2 - tiff filetrams, tramways, retirements, conductors, mmtb, camberwell depot, tram 636 -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Eastern Spinebill, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Eastern Spinebill is found along the eastern coast of Australia, from Queensland to South Australia. It lives in wooded areas. It is an insectivore and also eats nectar, which is why its beak is a long slender shape. Females and males have slight aesthetic differences; the males have more distinct markings on the head. The female birds build nests and incubate eggs, but both parent birds will feed the young. The Eastern Spinebill has a bright rust coloured belly and throat, with black wings, crown and tail. Its back is light brown. There is a white stripe on its chest which stretches up underneath its eyes. The eyes are red. This taxidermy specimen is not a good representation of the live bird because it is considerably faded and their feathers are very ruffled. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.There are two birds on a wooden stand. One has its beak in the air and the catalogue tag attached to its foot (main bird). It has some minor pest damage around its eye. The opposite bird looks straight ahead. The birds are placed next to each other, facing opposite directions. They are faded and have some ruffled feathers. 60a/ Spine Bill / See catalogue, page 18taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, eastern spinebill -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Australian Hobby, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Australian Hobby is a medium-sized falcon of the Falconidae family, similar in look to the larger sized Peregrine Falcon. This species is widespread and can be found across most of mainland Australia and Tasmania, preferring lightly wooded areas such as timbered wetlands, open wooded farmland, and some urban areas. Their diet consists of small birds, bats, and flying insects, which are caught mid-air. They sometimes hunt cooperatively to catch their prey. This specimen is an accurate depiction of an Australian Hobby. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Australian Hobby has a dark brown cap and cream-coloured half-collar. The back feathers of the bird are also a dark brown colour, while the neck is a cream with lighter brown streaks. The flank is a dappled dark brown, rufous-brown and cream, which transitions back into cream with brown streaks near the legs. The underwing feathers appear to be a banded dark brown and cream. The tip of the hooked beak is black which recedes to light blue-grey and then to yellowish near the head join. The legs are also yellow. The specimen is perched on a wooden perch mount with a swing tag tied around its left leg.23. / Australian Hobby / See catalogue, page, 6 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian hobby, australian birds, little falcon -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Tawny Frogmouth, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Tawny Frogmouth, although often mistaken for an owl, is a nocturnal Australian bird of the Podargidae family that is more closely related to the nightjars. They are widespread in terms of distribution and can be found all across mainland Australia and Tasmania in a diverse variety of habitats from woodlands, forests and urban areas. Masters of camouflage, the Tawny Frogmouth sleeps during the day on tree branches in a stiff upward facing position (as with this specimen) to mimic broken tree branches, their feathers assist in this deception as the mottled grey and brown colours blend into the environment seamlessly. This specimen differs in colours from the usual appearance of a Tawny Frogmouth, as the beak is usually a olive-grey to blackish tone and the plumage is generally more dominantly grey all over the bird. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Tawny Frogmouth has a broad head and a creamy beige coloured wide triangular beak with a hooked tip. The plumage on the head and back of the bird is a combination of darker and rufous browns, mottled with streaks of cream and grey. The underside of the bird from the bottom of the beak to the tail tip is a lighter cream colour with streaks of rufous-brown. The feet are an orange-brown colour. This specimen is adopting the skyward looking pose associated with the species, mimicking dead tree branches.1a. / More-Park / See Catalogue, page 7 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, tawny frogmouth, frogmouth -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Barking Owl (Male), Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Barking Owl is a nocturnal, medium sized (390-440 mm) bird of prey native to Australia, parts of Papua New Guinea, and the Moluccas. Males are generally slightly larger by weight than females and they are only one of small number of owl species that do not exhibit marked sexual dimorphism. Barking Owls have characteristic vocalisations, ranging from 'a 'woof woof' barking dog sounds to shrill, human-like scream sounds, which reportedly alarmed early European settlers. The Barking Owl's shrill and explosive vocalisation is sometimes associated with Bunyip mythology or referred to as 'the screaming woman call'. The male call is slightly lower in pitch than the female, and males and females often duet, contrasting low and high pitches. The owls are brown-grey in colour with white spots on the wings and vertically streaked chest. Their eyes are large and yellow. Barking Owls may be vulnerable in some parts of Australia due to woodland habitat loss. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century. This male Barking Owl is average sized with brown, grey and white spots and vertical chest streaks. The face and breast are lighter in colour than the wings and dorsal plumage. The eyes are large and dark and the legs and feet are yellowish. The eyes are large and yellow irises and the legs and feet are yellowish. The specimen stands on a wooden perch pedestal with identification tags attached to its leg. 17. / Bookook Owl / See catalogue page, 4 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, owls, barking owls, screaming woman call, yowing, woodland birds, birds of prey, australian owls, endangered, loss of habitat, woodland habitat, bunyip, australian early settler mythology -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Masked Owl, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Masked Owls are an Australian barn owl species ranging across most of mainland Australia and Tasmania, generally within 300 km of coastline. Masked Owls are a medium sized bird averaging 390-500mm in length with wing spans up to 1250mm. There are several subspecies across Australia and the Tasmanian Masked Owl is the largest. Female Masked Owls are markedly larger than males. Masked Owls prefer forested, woodland, or timbered waterway habitats to open country, and nest in tall trees with suitable hollows and adjacent areas for foraging. They are territorial and hunt small mammals, rodents, rabbits, reptiles and small marsupials. Population numbers are in decline on the mainland and in Victoria the species is considered threatened. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century. This Masked Owl specimen is medium sized with a large head and distinctive heart-shaped facial markings. The plumage is mostly brown, patterned with flecks and patches of white, chestnut and light grey. The tail is short and largely concealed by long wing feathers. The face, feathered tarsi and underparts are much paler in contrast to the dorsal plumage, and the facial mask is edged by a distinct dark brown line. The eyes are large and yellow. This specimen stands on a wooden perch pedestal with identification tags attached to its leg. 12. / Delicate Owl / See Catalogue, page, 3 /taxidermy, taxidermy mount, masked owl, burke museum, australian museum, owls, birds of prey, heart-shaped faced owl, nocturnal birds, predator birds, barn owl, carnivore, tyto novaehollandiae, australian masked owl, tytonidae, tyto, territorial owl, threatened species, animalia, australian owls, tasmanian masked owl -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Grey Crow, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This specimen is named the Grey Crow on the swing tag but is more likely a Grey Currawong. There are six subspecies of Grey Currawongs and they can sometimes interbreed with other species of Currawong leading to a divergent series of appearances amongst the species. The species can be found in the south western to south eastern parts of Australia, including in Tasmania. It is an endangered species in the Northern Territory although the reasons why are not yet known. They prefer a wide range of habitats including coastal to arid and can also be occasionally found in suburban areas. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Grey Crow (or alternatively Grey Currawong) has mainly grey plumage with a white tail tip and darker undercarriage. It has yellow irises, made of glass, and brown claws. The bill is dark in colour. This specimen has been placed upon a wooden mount in a downwards facing position. It has a paper tag attached to its right leg.16a / Grey Cro [torn] / See Cat / [torn] /axidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, grey crow, grey currawong, currawong -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Morepork, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Morepork is a small brown and white spotted owl found in New Zealand, Tasmania and Norfolk Island. It is known by around twenty different names which are all onomatopoeic which emulate the birds distinctive two-pitched call. They are mostly nocturnal and carnivorous (eating insects and small vertebrates). They reside in habitats with trees, they sleep in roosts and hunt mainly in the evenings and early morning. Females are slightly bigger than males. This species attains full plumage in its third or fourth year. They can turn their heads 270 degrees." In Māori tradition the morepork was seen as a watchful guardian. It belonged to the spirit world as it is a bird of the night. Although the more-pork or ruru call was thought to be a good sign, the high pitched, piercing, ‘yelp’ call was thought to be an ominous forewarning of bad news or events." (NZ Department of Conservation). This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Morepork (also known as a Masked Owl) is covered in brown and white plumage on its head and body. The white feathers delineate its round yellow eyes. Its belly and back are brown and white with the white feathering appearing spotted. He sits on a wooden perch with his head turned to the left. A swing tag is attached to its leg.11 / Masked Owl / See Catalogue, page 3 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, ruru, spotted owl, tasmanian spotted owl, morepork, mopoke, new zealand owls, new zealand birds, tasmanian owls, tasmanian birds, norfolk island owls, norfolk island birds -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Brown Falcon, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Brown Falcon is a small to medium bird of prey which can be found all throughout Australia. These birds are raptors and typically feed on mammals, birds, snakes, insects and rabbits. The Brown Falcon are located in all but the densest forests. They typically prefer to reside in locations of open grassland and agricultural areas which have scattered trees or telephone poles which the bird can perch on. When frequenting towns located in the Australian Outback, these birds are reportedly quite tame and can be approached by humans. They may stay in the same location throughout the year or chose to move around locally in response to any changes in weather conditions. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th centuryThis specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Brown Falcon specimen has plumage which is mostly brown and intermixed with white. This provides the appearance of having spotted colouring on the birds back. The head is also mostly brown with white under the beak area and a characteristic brown streak under the eye area. The eye is made from dark coloured glass.3 / Brown Hawk / See Catalogue, page 2 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, brown falcon, falconidae -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Crimson Rosella
The Crimson Rosella is native to Australia and located in Queensland and South Australia. Australia has a diverse range of rosellas, but the crimson rosella is easily recognised by the red body and blue cheeks. These birds are friendly to humans and consume seeds, insects and some blossoms. They nest in high trees, preferably eucalyptus. Typically, a crimson rosella should have far brighter colours than the specimen collected. This specimen has also been documented as having a light blue or black beak. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Crimson Rosella has a red feathered chest and cape across the head and blue cheeks besides the bill. The tail and wing feathers are mostly black with blue around the edges. The head is angled slightly to the specimen's left. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.78a. / Rennauts Parakeet / See Catalogue, page 22 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, bird, california, australian native bird, crimson rosella, rosella, reynell eveleigh johns, platycercus elegans -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Musk Duck, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This particular Musk Duck is a male specimen. This is ascertained through the inclusion of a large bulbous lobe of skin hanging under the bill. The name Musk Duck comes from the strong musk odour produced from a gland on the rump of the bird. These ducks are found only in Australia, in south-western and south-eastern mainland and in Tasmania. They prefer to reside in locations which have deep water and plenty of aquatic vegetation. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.A male Musk Duck with a wide, heavy body covered in dark grey-brown plumage. This specimen has a broad and triangular shaped bill with a large lobe hanging from beneath the bill which helps identify this particular duck as male. The duck has glass eyes which are a dark brown colour. The legs on the Musk Duck are positioned towards the far back of the stocky body and the feet are webbed. This enables the duck to swim but provides a clumsy gait."8a Musk Duck. See Catalogue, page, 39."taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, duck, musk duck, aquatic, biziura lobata -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Dusky Moorhen, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Dusky Moorhens are a medium sized, dark coloured water bird. They are located in the wetlands of eastern and south-western Australia. They can also be found in India, New Guinea, Borneo and Indonesia. These birds have a bright face shield located above the bill; however, the bright colour of this feature grows duller in females and young males during autumn and winter. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum and the National Museum of Victoria, as well as individuals such amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.A Dusky Moorhen standing on a wooden platform with a paper tag attached to its left leg. The specimen has a sooty-black plumage with a yellow bill and black/yellow legs/toes. It has remnants of what would have been a reddish-yellow shield on its forehead. "18c Australian Coot. See Catalogue, Page, 35"taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, dusky moorhen, waterbird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Australiasian Shovelor, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Australasian Shoveler is a species of duck that can be commonly found in heavily vegetated swamps in southwestern and southeastern Australia, Tasmania and New Zealand. The species, Australasian Shoveler, is aptly named after their large shovel-shaped bill. These birds use these large bills which are equipped with fine hair-like components which strain the water and mud for food including tiny creatures including insects, crustaceans and seeds while it swims. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Australasian Shoveler is a species of low-floating duck with a dark head and brown plumage. The rear of this specimen is a dark brown, with mixed white and brown colouring on the upper torso. The underparts of this bird are brown and orange. The specimen has glass eyes made in an amber colour. The Shoveler is standing on a wooden platform which is labelled number 136. Amongst the feathers on the wings, this bird has a green coloured feather. The legs of the Shoveler would have once been a bright orange; however, the legs of this specimen have darkened in colour throughout the taxidermy process. This bird has a large bill shaped like a shovel from which the name "Shoveler" has been derived.5a. / Australian Shoveller / See Catalogue, page 38. /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, heron, duck, australaisian shovelor, shovelor
