Showing 140 items
matching flanges
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Pattern, Briggs Brass Foundry, Early 20th century
The wooden pattern is part of a set that is stored in a strong wooden crate and may be part of another similar pattern. It was used at Briggs’ Brass Foundry for making sand casts. The traditional craft of sand casting is over 2000 years old. The handcrafted process produces brass and copper alloy goods that are well suited to marine use; bells, boat hooks, cowls, propellers, handles, lids, rowlocks, hooks, letters, bolts, rail holders, brackets, deck plates, flanges, rudder guides, portholes and covers. Briggs’ Bronze mixture is a copper-based alloy made from local ingots of copper, tin, zinc and lead in carefully measured quantities. The finished product is non-ferrous and can last indefinitely. The crate of patterns was donated by the Briggs family in the early years of Flagstaff Hill, along with other related items such as brassware, tools and machinery. The donated items were displayed in a simulated Brass Foundry in the Village along with other working crafts, trades and services found in a Maritime town. The items were on show from the completion of the building in 1986 until 1994 when the building was repurposed. The patterns represent the trades of foundering and metalwork, both supporting maritime industries such as shipwrights and boatbuilders. Farmers, manufacturers and other local industries also needed the castings made by foundries. The Brass Foundry included a historic Cornish chimney set up as a working model, to tell the story of smelted metal heated in furnaces then be poured into the sand moulds. This chimney was made from specially curved bricks and is now about two-thirds of its full height when originally located at the Grassmere Cheese factory. The craft of sand-casting from carved wooden patterns to create metal is an example of skills from the past that are still used today. The foundry pattern set is significant for its association with brass foundries locally and generally in coastal areas of Victoria. Marine industries such as ship and boat building rely on good quality castings for their machinery, equipment and fittings. Briggs Brass was especially formulated using non-ferrous metals to ensure their longevity. The patterns are associated with the long-running firm Briggs Brass Foundry that specialised in cast goods for the marine industry, ready to supply the needs for once-off or mass-produced items. Their products would have been fitted to sail and steam vessels along coastal Victoria including Warrnambool. Briggs Marine was also a bell-founder specialist and is also associated with the Schomberg Bell at Flagstaff Hill, having restored it to is former state as a fine example of the bell from a luxury migrant vessel from the mid-19th century. Pattern; unpainted, square wooden block with a semi-circle of dowel added to the centre of the side with rounded corners. Three short dowel pegs are inserted on one flat side; one below the semi-circle and one near the lower corners in an overall triangle configuration. The pattern is part of a set of foundry patterns from Briggs Brass Foundry.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, briggs' bronze, traditional method, trade, sand cast, cast, brass alloy, copper alloy, pattern, mould, foundry, brass foundry, metal foundry, casting, sand mould, sand casting, marine equipment, marine tools, marine fittings, copper tin zinc lead, non-ferrous, non-corrosive, brassware, metalware, foundering, metalwork, maritime, bell founders, ship chandlers, marine products, biggs, briggs family, herbert harrison briggs, h h briggs, george edward briggs, cyril falkiner mckinnon briggs, cyril briggs, briggs & son brass foundry, h h briggs & sons foundry, briggs marine, alliance casting & engineering solutions, grassmere cheese factory, cornish chimney, curved bricks, collingwood, moorabbin, collingwood foundry, moorabbin foundry, 1912 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Pattern, Briggs Brass Foundry, Early 20th century
The wooden patterns are part of a set that are stored in a strong wooden crate. It was used at Briggs’ Brass Foundry for making sand casts. It may fit together with one of the other patterns with a similar outline. The traditional craft of sand casting is over 2000 years old. The handcrafted process produces brass and copper alloy goods that are well suited to marine use; bells, boat hooks, cowls, propellers, handles, lids, rowlocks, hooks, letters, bolts, rail holders, brackets, deck plates, flanges, rudder guides, portholes and covers. Briggs’ Bronze mixture is a copper-based alloy made from local ingots of copper, tin, zinc and lead in carefully measured quantities. The finished product is non-ferrous and can last indefinitely. The crate of patterns was donated by the Briggs family in the early years of Flagstaff Hill, along with other related items such as brassware, tools and machinery. The donated items were displayed in a simulated Brass Foundry in the Village along with other working crafts, trades and services found in a Maritime town. The items were on show from the completion of the building in 1986 until 1994 when the building was repurposed. The patterns represent the trades of foundering and metalwork, both supporting maritime industries such as shipwrights and boatbuilders. Farmers, manufacturers and other local industries also needed the castings made by foundries. The Brass Foundry included a historic Cornish chimney set up as a working model, to tell the story of smelted metal heated in furnaces then be poured into the sand moulds. This chimney was made from specially curved bricks and is now about two-thirds of its full height when originally located at the Grassmere Cheese factory. The craft of sand-casting from carved wooden patterns to create metal is an example of skills from the past that are still used today. The foundry pattern set is significant for its association with brass foundries locally and generally in coastal areas of Victoria. Marine industries such as ship and boat building rely on good quality castings for their machinery, equipment and fittings. Briggs Brass was especially formulated using non-ferrous metals to ensure their longevity. The patterns are associated with the long-running firm Briggs Brass Foundry that specialised in cast goods for the marine industry, ready to supply the needs for once-off or mass-produced items. Their products would have been fitted to sail and steam vessels along coastal Victoria including Warrnambool. Briggs Marine was also a bell-founder specialist and is also associated with the Schomberg Bell at Flagstaff Hill, having restored it to is former state as a fine example of the bell from a luxury migrant vessel from the mid-19th century. Pattern; a pair of blocks that form a rectangle with a carved centre hole and disc shape inside. The block is made from laminated pieces of wood with cut corners. Both sides have four drilled holes in a square configuration but in different positions. The cut faces and the space carved into them are painted red; one piece has two dowel pins that fit into two drilled holes on the other. The pattern is part of a set of foundry patterns from Briggs Brass Foundry.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, briggs' bronze, traditional method, trade, sand cast, cast, brass alloy, copper alloy, pattern, mould, foundry, brass foundry, metal foundry, casting, sand mould, sand casting, marine equipment, marine tools, marine fittings, copper tin zinc lead, non-ferrous, non-corrosive, brassware, metalware, foundering, metalwork, maritime, bell founders, ship chandlers, marine products, biggs, briggs family, herbert harrison briggs, h h briggs, george edward briggs, cyril falkiner mckinnon briggs, cyril briggs, briggs & son brass foundry, h h briggs & sons foundry, briggs marine, alliance casting & engineering solutions, grassmere cheese factory, cornish chimney, curved bricks, collingwood, moorabbin, collingwood foundry, moorabbin foundry, 1912 -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryTool - Laryngoscope, Macintosh
A laryngoscope is an instrument used to view the larynx (voice box), which is the opening to the trachea and lungs. It consists of a “blade,” which goes into the patient’s mouth, and a handle. Prior to 1943 when Macintosh introduced his curved blade, most laryngoscope blades were long and straight. The straight blades were used to directly hold the epiglottis. Macintosh’s curved blade works differently: it indirectly opens the epiglottis by applying pressure to a space between the root of the tongue and epiglottis, called the vallecula. The flange running along the left lower edge of Macintosh’s blade was also a novel innovation. It was designed to move the tongue to the side, which improved the view of the larynx and made more room for a breathing tube. The Macintosh Laryngoscope remains one of the most popular blades worldwide. (Source: Wood Library Museum) This laryngoscope was previously owned by John Mainland, as evidenced by the name etched into the handle. Mainland graduated from the University of Melbourne in 1950 with a Bachelor of Science degree. After researching and completing his medical degree, Mainland entered into the field of anaesthetics, training at the Royal Women's and Royal Children's Hospitals, later Alfred Hospital, in 1959. He completed training in 1964 and remained at the Alfred Hospital. During his career, he also became the first anaesthetist appointed to the position of Professor in Victoria. His other achievements include manufacturing a respiratory monitoring module that accompanied astronauts on the United States moon landing and developing a stimulator to lessen the risk of deep vein thrombosis in surgical patients. Mainland became a Fellow of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists in 1992, retiring from the profession in 1997.Oblong shaped handle with textured grip. Attached is a laryngoscope blade in a cruved shaped with light tube running through one side.Etched into top of handle: J.F. MAINLAND •Stamped into top of handle: REGD TRADE MARK / PENLON / MADE IN ENGLAND •Stamped into base of handle: CLOSE [arrow] •Etched into base of blade: MAC / 4 •Stamped into side of blade: REGD TRADE MARK / PENLON / MADE IN ENGLAND •Stamped into side of blade: STAINLESSmacintosh, robert reynolds, new zealand, laryngoscope, mainland, john, alfred hospital, moon landing -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumMemorabilia - Display panel, The North Eastern Steel Co. Ltd. Middlesborough, Standard Section of Tramway Rails
Flanged Tramway Rails - sections from The North Eastern Steel Co. Ltd. Middlesborough - see https://www.gracesguide.co.uk/North_Eastern_Steel_Co 1 - Walthamstow & District Light Railways BS Section No. 3C - 106 lbs. per yard 1904 - Dick Kerr & Co. Contractors London. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tottenham_Outrage 2 - Bath & District Tramways 95 lbs per yard 1903 - George Hopkins & Sons Engineers London 3 - Burton on Trent Tramways 90 lbs per yard 1903 - Messrs Kincaid, Waller & Manville, Consulting Engineers 4 - Swindon Corporation Tramways BS Section No. 4 C, 111 lbs per yard, 1904 - Messrs J G White & Co. Ltd, Contractors London 5 - Wigan Corporation Tramways BS Section No. 5, 100 lbs per yard, 1903 - Messrs J G White & Co. Ltd, Contractors London 6 - Derby Corporation Tramways BS Section No. 6, 107 lbs per yard, 1904 - Messrs J G White & Co. Ltd, Contractors London 7 - Nottingham Corporation Tramways BS Section No. 1 , 90 lbs per yard, 1903, J. G. White Ltd, London, Contractors. 8 - Swindon Corporation Tramways, BS Section No. 4, 105 lbs per yard - Messrs J G White & Co. Ltd, Contractors London, Messrs Lacy & Sillars Consulting Engineer 9 - Kalgoorlie Electric Tramways BS Section ? 96 lbs per yard. 1904 - Messrs J G White & Co. Ltd, Contractors London 10 - Leicester Corporation Tramways & Track? 100 lbs per yard 1903, I George Maybey? MICE Engineer 11 - Ipswich Tramways 90 lbs per yard, 1902, Dick Kerr & Co. Contractors London Shows the type of tramway rail and cross section produced by The North Eastern Steel Co early 1900's, the relationship to the British Standard and who used them. Provenance of the item not fully known. Possibly given to the Electric Supply Co of Victoria at the time when they would have been ordering rails for use in Ballarat. May have been collected by other parties.Plywood sheet, covered in black cloth displaying 11 different British Standard Rail Sections made by The North Eastern Steel Co. Ltd. Middlesborough , early 1900's. Each section secured with two 20mm (¾”) long, 3mm dia (1/8”) machine screws, countersunk with a slotted head from the rear. All nickel plated on both sides, engraved as to the tramway used on, date of production on the head of the rail, Designing Engineers on the web and the manufacturer on the foot of the rail. Cloth secured with staples and drawing pins on the rear. On the rear is a chalked sign, the principal one being "No Thoroughfare"Engraved as listed.tramway rails, rails, tramways, north eastern steel co, middlesborough, walthamstow, bath, burton on trent, swindon, wigan, derby, nottingham, kalgoorlie, leichester, ipswich, j g white & co, dick kerr -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Letter - MCCOLL, RANKIN AND STANISTREET COLLECTION: QUOTE FROM MILLER AND CO. MACHINERY, 25th May 1931
Five-page letter and quote, 25th May 1931, from Miller & Co Machinery, 27 Queen Street, South Melbourne. Bendigo office phone 50. Quote for Central Nell Gwynne shaft: steam winch, straight line steam drive air compressor, air receiver, Cornish flue boiler, Worthington duplex steam pump. Price for foregoing 740 pounds. Delivery of boiler at Redan shaft, poppet legs standing at Buttrey's Reward Mine and the whole of the balance of the plant F.O.R. Melbourne Monument Hill Shaft: steam winch double cylinder, straight line single stage steam driven air compressor, air receiver crown flanged ends, Cornish flue boiler, steam pipes, air pipes, iron chimney stack 26'0' x 3'.6' diameter, black steel wire ropes 1000' length Price for foregoing 610 pounds. If preferred, self-contained boiler in lieu of Cornish type offered, the following is offered: return tube boiler, by Roberts and Sons Bendigo. This boiler is self-contained Deborah shaft: straight line steam driven air compressor, air receiver. Price 200 pounds.bendigo, gold mining, mccoll rankin and stanistreet, miller and co., machinery., central nell gwynne gold mine, monument hill gold mine -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Container - CHOCOLATE BOX COLLECTION: PASCALL BOX, 1920s
Object.Pascall 1920s Yellow Chocolate Box. Design Flanged Sexangular Box with Curved Sectional Top, Sepia Photograph with Subject's Hat and Dress tinted in Pale Yellow in Centre of Lid. Photograph Surrounded by Gold Border. Subject Young Woman & Her Pet Cat. Photograph has White Mark PC Parts in a circle and the number 524 underneath. Inside Lid Pascall 1 lb Net. Contained in Box Labels Packers No 493 and Checkers No 476. Packaging Brown Paper and Fine Paper Shavings in Pale & Dark Colours. Also Another Tag Buff Paper & Red Text In Top Left Hand Corner is the Pascall London Trademark Purity & Sweetness Seal & In The Top Right-hand Corner is A Floral Emblem & The Words Furzedown. The Title On This Tag Reads Co-operation Between The Manufacturer & Consumer. The Remaining Text Reads: - These chocolates were packed with the greatest care and left in our factory in perfect condition. Extremely hot weather or contact with steam pipes may turn these chocolates grey. This is not an indication of age but of the temperature to which they have been exposed. Goods are all packed full weight; the paper shavings used are for packing and protection only. If any complaint necessary please return this ticket with the goods. James Pascall, Ltd London England. Chocolates are also still contained within the box all these years later.domestic equipment, containers, decorative chocolate box -
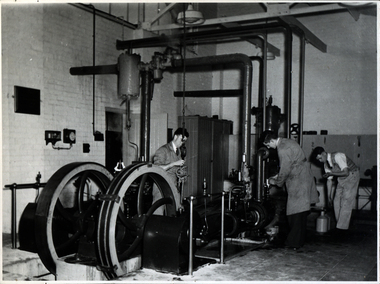 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Black and white photograph, Ballarat School of Mines Model Steam Engine
The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath. The 'substantial sum' was used to build an Engineering Laboratory. The Ballarat School of Mines Council minutes of 08 November 1901 record: - Plans for [the] proposed building were submitted ... and ... it was resolved that a temporary building for an Engineering Laboratory be put up.' This laboratory, as an existing building, is first mentioned in the Ballarat School of Mines President's Annual Report of 1901, presented on 28 February 1902, reporting 'the erection of a building 67ft long by 33 ft wide' This report also lists all the equipment that would be accommodated in the Engineering Laboratory, including the experimental steam engine and boiler. The experimental Davey-Paxman steam engine arrived in Ballarat towards the end of 1902. The Engineering Laboratory was opened on 14 August 1903 by His Excellency Sir Sydenham Clarke. This engineering laboratory remained in use till about 1945. By 1944 preparations were under way at the Ballarat School of Mines to expand existing facilities, to be ready for the influx of returned soldiers. A new Heat Engines laboratory was built, this time of brick construction, replacing the previous corrugated-iron shed. In the early stages the steam engine was used to drive an overhead transmission shaft for machinery in the adjacent workshop. Later the steam engine was moved to a space that became the Heat Thermodynamics Laboratory. At the end of 1969 the engine was relocated to the Thermodynamics Laboratory at the then Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE) Mt Helen Campus. It was donated to Sovereign Hill in 2006. According to the research of Rohan Lamb in 2001 around five experimental steam engines were made by Davey Paxman, and three of these had similar configuration to the Ballarat School of Mines Steam Engine, however, each of these was also unique with different valve arrangements. The list, which was on a scrap of paper in a folio held in the Essex Archives, confirmed that one was sent to India. The Ballarat steam engine can be dated to late 1901 to early 1902. Zig Plavina was responsible for moving the steam engine to Mount Helen, and worked on it as a technician for many years. He observed the following: * The condenser is driven by the low pressure engine. * The following arrangements are possible: i) the high pressure engine alone, exhausting to atmosphere. Condenser not used, crankshaft flanges not coupled. ii) crankshafts coupled, mains pressure (120 psi) steam supplied to high pressure engine, partially expanded steam delivered to low pressure engine (Tandem operation). Choice available re exhaust steam: either to the condenser or to atmosphere. iii) crankshafts not coupled, reduced pressure steam supplied to low pressure engine. Exhaust steam - either to the condenser or to atmosphere. * Valve arrangement - a choice of Pickering cut-off or throttle governor. On low pressure engine - throttle governor only.Black and white photograph of the Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine. On the brake is returned serviceman Norman WIlliam Ludbrook (Diploma Electrical Engineering, 1952). Far right is Roy E. Mawby (Diploma Electrical Engineering, 1950)steam engine, model steam engine, davey paxman, electrical engineering, laboratory, scientific instrument, norman ludbrook, norman william ludbrook, roay mawby, roy e. mawby -
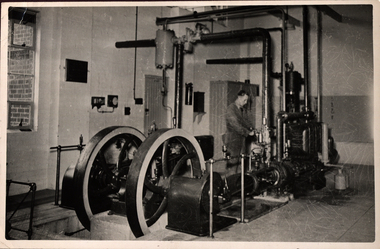 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Black and white, Ballarat School of Mines Model Steam Engine
The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath. The 'substantial sum' was used to build an Engineering Laboratory. The Ballarat School of Mines Council minutes of 08 November 1901 record: - Plans for [the] proposed building were submitted ... and ... it was resolved that a temporary building for an Engineering Laboratory be put up.' This laboratory, as an existing building, is first mentioned in the Ballarat School of Mines President's Annual Report of 1901, presented on 28 February 1902, reporting 'the erection of a building 67ft long by 33 ft wide' This report also lists all the equipment that would be accommodated in the Engineering Laboratory, including the experimental steam engine and boiler. The experimental Davey-Paxman steam engine arrived in Ballarat towards the end of 1902. The Engineering Laboratory was opened on 14 August 1903 by His Excellency Sir Sydenham Clarke. This engineering laboratory remained in use till about 1945. By 1944 preparations were under way at the Ballarat School of Mines to expand existing facilities, to be ready for the influx of returned soldiers. A new Heat Engines laboratory was built, this time of brick construction, replacing the previous corrugated-iron shed. In the early stages the steam engine was used to drive an overhead transmission shaft for machinery in the adjacent workshop. Later the steam engine was moved to a space that became the Heat Thermodynamics Laboratory. At the end of 1969 the engine was relocated to the Thermodynamics Laboratory at the then Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE) Mt Helen Campus. It was donated to Sovereign Hill in 2006. According to the research of Rohan Lamb in 2001 around five experimental steam engines were made by Davey Paxman, and three of these had similar configuration to the Ballarat School of Mines Steam Engine, however, each of these was also unique with different valve arrangements. The list, which was on a scrap of paper in a folio held in the Essex Archives, confirmed that one was sent to India. The Ballarat steam engine can be dated to late 1901 to early 1902. Zig Plavina was responsible for moving the steam engine to Mount Helen, and worked on it as a technician for many years. He observed the following: * The condenser is driven by the low pressure engine. * The following arrangements are possible: i) the high pressure engine alone, exhausting to atmosphere. Condenser not used, crankshaft flanges not coupled. ii) crankshafts coupled, mains pressure (120 psi) steam supplied to high pressure engine, partially expanded steam delivered to low pressure engine (Tandem operation). Choice available re exhaust steam: either to the condenser or to atmosphere. iii) crankshafts not coupled, reduced pressure steam supplied to low pressure engine. Exhaust steam - either to the condenser or to atmosphere. * Valve arrangement - a choice of Pickering cut-off or throttle governor. On low pressure engine - throttle governor only.Black and white photograph of the Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine installed at the Ballarat School of MInes. steam engine, model steam engine, davey paxman, thomas bath, experimental steam engine -
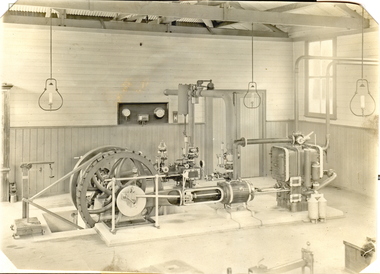 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Ballarat School of Mines Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine, c1902
The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath. The 'substantial sum' was used to build an Engineering Laboratory. The Ballarat School of Mines Council minutes of 08 November 1901 record: - Plans for [the] proposed building were submitted ... and ... it was resolved that a temporary building for an Engineering Laboratory be put up.' This laboratory, as an existing building, is first mentioned in the Ballarat School of Mines President's Annual Report of 1901, presented on 28 February 1902, reporting 'the erection of a building 67ft long by 33 ft wide' This report also lists all the equipment that would be accommodated in the Engineering Laboratory, including the experimental steam engine and boiler. The experimental Davey-Paxman steam engine arrived in Ballarat towards the end of 1902. The Engineering Laboratory was opened on 14 August 1903 by His Excellency Sir Sydenham Clarke. This engineering laboratory remained in use till about 1945. By 1944 preparations were under way at the Ballarat School of Mines to expand existing facilities, to be ready for the influx of returned soldiers. A new Heat Engines laboratory was built, this time of brick construction, replacing the previous corrugated-iron shed. In the early stages the steam engine was used to drive an overhead transmission shaft for machinery in the adjacent workshop. Later the steam engine was moved to a space that became the Heat Thermodynamics Laboratory. At the end of 1969 the engine was relocated to the Thermodynamics Laboratory at the then Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE) Mt Helen Campus. It was donated to Sovereign Hill in 2006. According to the research of Rohan Lamb in 2001 around five experimental steam engines were made by Davey Paxman, and three of these had similar configuration to the Ballarat School of Mines Steam Engine, however, each of these was also unique with different valve arrangements. The list, which was on a scrap of paper in a folio held in the Essex Archives, confirmed that one was sent to India. The Ballarat steam engine can be dated to late 1901 to early 1902. Zig Plavina was responsible for moving the steam engine to Mount Helen, and worked on it as a technician for many years. He observed the following: * The condenser is driven by the low pressure engine. * The following arrangements are possible: i) the high pressure engine alone, exhausting to atmosphere. Condenser not used, crankshaft flanges not coupled. ii) crankshafts coupled, mains pressure (120 psi) steam supplied to high pressure engine, partially expanded steam delivered to low pressure engine (Tandem operation). Choice available re exhaust steam: either to the condenser or to atmosphere. iii) crankshafts not coupled, reduced pressure steam supplied to low pressure engine. Exhaust steam - either to the condenser or to atmosphere. * Valve arrangement - a choice of Pickering cut-off or throttle governor. On low pressure engine - throttle governor only. Black and white photograph of an experimental steam engine which was produced for the Ballarat School of Mines. It was designed for experimental purposes, such as testing of efficiency, etc. The laboratory which housed the steam engine was lit with gas lighting. davey paxman experimental steam engine, model steam engine, davey paxman, steam, thomas bath, thermodynamics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Foundry Patterns set, Briggs Brass Foundry, Early 20th century
The wooden crate contains a set of patterns or moulds that were once used at Briggs’ Brass Foundry for making sand moulds. The traditional method of sand casting is over 2000 years old. It is part of a crafted process used to make brass and copper alloy goods suited to marine use; bells, boat hooks, cowls, propellers, handles, lids, rowlocks, hooks, letters, bolts, rail holders, brackets, deck plates, flanges, rudder guides, portholes and covers. Briggs’ Bronze is a copper-based alloy made from local ingots of copper, tin, zinc and lead in carefully measured quantities. The finished product is non-corrosive and can last indefinitely. The crate of patterns was donated by the Briggs family in the early years of Flagstaff Hill, along with other related items such as brassware, tools and machinery. The donated items were displayed in a simulated Brass Foundry in the Village. The items were on show from the completion of the building in 1986 until 1994 when the building was repurposed. The patterns represent the trades of foundering and metalwork, both supporting maritime industries such as shipwrights and boatbuilders. Farmers, manufacturers and other local industries also needed the castings made by foundries. The Brass Foundry display was one of the early ‘working craft’ shops at Flagstaff Hill. It included a historic Cornish chimney that was set up as a working model, telling the story of heat from furnaces to smelt metal, which would then be poured into the sand moulds. This chimney is made from specially curved bricks and is about two-thirds of its full height when originally located at the Grassmere Cheese factory. HISTORY of BRIGGS BRASS FOUNDRY: - The family business was founded in 1912 by Herbert Harrison Briggs (1963-1931) with his son George Edward Briggs, trading as Briggs & Son Foundry at 70 Wellington Street, Collingwood. Younger son Cyril Falkiner McKinnon Briggs joined the foundry in 1922, and it was renamed H H Briggs & Sons Foundry. Both sons ran the firm after Herbert’s death in 1931, making products mainly for marine purposes. They became Bell Founders in 1936 and were known for their specialty of high-quality ship bells. They produced miniature varieties of these and other decorative items such as small propellers. The firm became known as Briggs Marine Foundry. The great-granddaughter of Herbert Briggs inherited the Briggs Brass Bell, similar to the one at Flagstaff Hill. Cyril became the sole family member of the firm in 1965. The Briggs Marine was an exhibitor at the 1965 Boat Show, where he advertised as “non-ferrous founders” and “Bell Specialists”. The foundry relocated to Chesterville Rd, Moorabbin. Cyril passed away in 1967. It is thought that either Cyril or his business partner Frank Lee donated the objects from the Briggs’ Foundry around the time when the business moved to Moorabbin. However, Flagstaff Hill hadn’t been thought about until 1972. The donated items were registered in the Collection in 1986 but they could have been in storage from an earlier date. In October of that same year, Briggs Marine restored Schomberg Bell, a shipwreck artefact from the collection at Flagstaff Hill. Peter Oram, who had worked for the previous owners of Briggs Marine as a fitter and turner, took over the firm in 2014, reviving some of the old casts for current use. The business is now located at Seaford in Victoria and is part of Alliance Casting & Engineering Solutions (Alliance Casting Pty Ltd). In 2016 the original Collingwood Foundry building was repurposed as a thriving business hub named The Foundry. The crate and its patterns are significant for their association with brass foundries locally and generally in coastal areas of Victoria. Marine industries such as ship and boat building rely on good quality castings for their machinery, equipment and fittings. The patterns are associated with the long-running firm, Briggs Brass Foundry, that specialised in cast goods for the marine industry, ready to supply the needs for once-off or mass-produced items. Their products would have been fitted to sail and steam vessels along coastal Victoria including Warrnambool. Briggs Marine is also associated with the Schomberg Bell in Flagstaff Hill, restoring the bell to is former state to show an example of the bell from a luxury mid-19th century vessel. The craft of sand-casting from carved wooden patterns to create metal is an example of skills from the past that are still used today. Wooden rectangular crate with removable wooden lid. Inside is a set of wooden patterns of various shapes and sizes for making sand moulds in a metal foundry. The crate is made from thick wooden planks nailed together. The extended wooden struts on the long sides form a frame to hold the wooden lid. A pair of metal handles are at each short end of the crate, fixed with strong metal bolds. Between each pair of handles is an inscription stamped into the wood. The underside of the crate has red paint splashes. There are insect holes in the wood but no sign of current infestation. Stamped: "H.33 / II" (H may be N or a square B)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, pattern, mould, foundry, brass foundry, metal foundry, crate, box, wooden container, briggs, traditional method, trade, sand cast, cast, brass alloy, copper alloy, marine equipment, marine tools, marine fittings, briggs' bronze, copper tin zinc lead, non-corrosive, briggs family, brassware, metalware, foundering, metalwork, maritime, casting, cornish chimney, curved bricks, grassmere cheese factory, 1912, herbert harrison briggs, h h briggs, george edward briggs, briggs & son foundry, collingwood, cyril falkiner mckinnon briggs, cyril briggs, h h briggs & sons foundry, bell founders, schomberg bell, alliance casting & engineering solutions, collingwood foundry, ship chandlers, marine products, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, briggs & son brass foundry, briggs marine, moorabbin -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumFunctional object - Tramcar component, Boselli Italy, Luminator Texas, Set of six destination indicator equipment that was fitted to Z, Z3 and B class trams, c1975 - 1990's?
Set of six destination indicator equipment that was fitted to Z, Z3 and B class trams. .1 - dot matrix type destination sign fitted to the side of a B class tram - set at Preston Depot - serial number 232636 - Luminator type, back cover loose, 180H x 1300W x 100D. See images 3704i1a to e. .2 - dot matrix type route number fitted to the front of a tram, type fitted to B2 class tram, set at 86D, serial number 273644 - Luminator type, marked "163 No", 240H x 350W x 135D. See images 3704i2a to d. .3 - flipper type, side destination type, marked "ex 53" (Z class tram), made in Italy by Boselli has yellow label 37/702S, serial number 40A1603, set to St Kilda Beach and stamped 136 on one flange. 120H x 330W x 165D. See images 3704i3a to c .4 - flipper type, destination box, with markings "B'Wick Flaps", with labels "New" "Universal A flaps" made in Italy by Boselli, serial number 40A6623, set to St Kilda Junc". 210H x 1000W x 1900. See images 3704i4a to d. .5 - flap from an above type box, half of "Richmond" and "South Melb Depot", 970W x 80H. See images 3704i5a to b .6 - controller box, marked "No. 105" on rear, serial number 202311 Luminator, numeric pad, illuminated display and five control buttons made by gulton Luminator division fitted to a B2 tram. See images 3704i6a to b .7 - dot matrix destination sign fitted to the front of a B2 class tram, set to "Not in Service", Serial number 502626 Luminator, 220H x 1300W x 165D, See images 3704i7a to e. Source of items 3 and 4 name based on drawings held by the Museum for the destination signs fitted to Z class trams. Refer to drawing R11-982 as an example. Luminator made by Luminator Technology Group Texas - see https://www.ltgglobal.com/ access 12/7/2019. Imagetrams, tramways, destination indicators, z3 class, transport equipment, z class, b class -
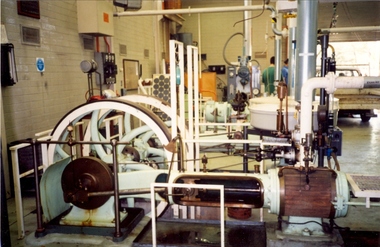 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour photograph, Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine in the Mount Helen Workshop, c1994
The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased by the Ballarat School of Mines as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath.The Davey Paxman Experimental Steam Engine was purchased as the result of a bequest from Thomas Bath. The 'substantial sum' was used to build an Engineering Laboratory. The Ballarat School of Mines Council minutes of 08 November 1901 record: - Plans for [the] proposed building were submitted ... and ... it was resolved that a temporary building for an Engineering Laboratory be put up.' This laboratory, as an existing building, is first mentioned in the Ballarat School of Mines President's Annual Report of 1901, presented on 28 February 1902, reporting 'the erection of a building 67ft long by 33 ft wide' This report also lists all the equipment that would be accommodated in the Engineering Laboratory, including the experimental steam engine and boiler. The experimental Davey-Paxman steam engine arrived in Ballarat towards the end of 1902. The Engineering Laboratory was opened on 14 August 1903 by His Excellency Sir Sydenham Clarke. This engineering laboratory remained in use till about 1945. By 1944 preparations were under way at the Ballarat School of Mines to expand existing facilities, to be ready for the influx of returned soldiers. A new Heat Engines laboratory was built, this time of brick construction, replacing the previous corrugated-iron shed. In the early stages the steam engine was used to drive an overhead transmission shaft for machinery in the adjacent workshop. Later the steam engine was moved to a space that became the Heat Thermodynamics Laboratory. At the end of 1969 the engine was relocated to the Thermodynamics Laboratory at the then Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE) Mt Helen Campus. It was donated to Sovereign Hill in 2006. According to the research of Rohan Lamb in 2001 around five experimental steam engines were made by Davey Paxman, and three of these had similar configuration to the Ballarat School of Mines Steam Engine, however, each of these was also unique with different valve arrangements. The list, which was on a scrap of paper in a folio held in the Essex Archives, confirmed that one was sent to India. The Ballarat steam engine can be dated to late 1901 to early 1902. Zig Plavina was responsible for moving the steam engine to Mount Helen, and worked on it as a technician for many years. He observed the following: * The condenser is driven by the low pressure engine. * The following arrangements are possible: i) the high pressure engine alone, exhausting to atmosphere. Condenser not used, crankshaft flanges not coupled. ii) crankshafts coupled, mains pressure (120 psi) steam supplied to high pressure engine, partially expanded steam delivered to low pressure engine (Tandem operation). Choice available re exhaust steam: either to the condenser or to atmosphere. iii) crankshafts not coupled, reduced pressure steam supplied to low pressure engine. Exhaust steam - either to the condenser or to atmosphere. * Valve arrangement - a choice of Pickering cut-off or throttle governor. On low pressure engine - throttle governor only.davey paxman experimental steam engine, model steam engine, steam, thermodynamics laboratory, thomas bath, bequest -
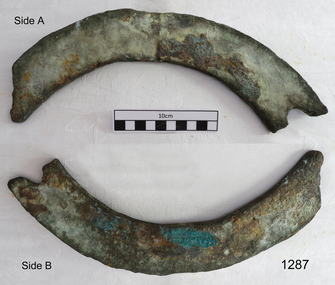 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Ship's Fitting, circa 1825
This attractively patinated artefact was raised from the wreck site of the CHILDREN (wrecked January 1839, recovered February 1974) and was quite reasonably catalogued as a portion of a ships porthole. This identification is unlikely however, because the CHILDREN was built at Liverpool in 1824, and round portholes were not in common use until the 1850s. The catalogue identification has since been changed to "Ship's Fitting" Prior to the appearance of round portholes in the middle of the nineteenth century, the function of introducing light to lower decks was performed by square half-glassed ‘ports’ in the side of the hull (known as a port-sash) , or ground-glass ‘bullseyes’ inserted in the deck (scuttles). In historical terms, ports were always square, cut into the timber originally to allow the firing of a ships guns, and were closed in weather by a tight fitting square hatch. Flagstaff Hill Shipwreck Museum has three portholes on display that illustrate the gradual development and adoption of circular brass portholes. First in sequence is a small 12.5cm diameter window (with a deep frame for thick wooden hulls) from the 1855 wreck of SCHOMBERG. The second and third are larger 25cm diameter windows (with a shallower frame for thinner iron hulls) from the 1892 wreck of the NEWFIELD and the 1908 wreck of the FALLS OF HALLADALE . Once the apparently obvious use of the brass object is discounted, an accurate and reliable alternative classification is difficult to specify. One artefact register notes it was ‘found in about the centre of the wreck site’. This would mitigate against the possibilities of (1) ‘horseshoe frame’ joining pieces of the keel and hull at the bow of the vessel, or (2) ‘deckseat’ for a binnacle at the stern. It may support the idea of a ‘head frame’ on a cooped companionway or a ‘deckseat’ for a mainmast pump. But this is only speculation. The actual identification is not known. The wreck of the CHILDREN is of State significance - Victorian Heritage Register S116Ship's fitting, of heavy gauge brass circle, previously classified as section of ship's fitting, which was raised from the wreck of the Children. One end is broken off at an original bolt hole and the other is severed or cut at an acute angle from the inner rim. The artefact is 6cm across and 1cm deep, indicating strength and function as a substantial and finished item of moulded metal. The upper face bears sedimentary accretion stained red/brown. The rear face has been gouged by hard or corrosive materials and bears brilliant blue/green oxidisation.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, the children, brass flange, brass rim, shop fitting -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Parts Catalog PC-203-2 Avco Lycoming O-320 B and D Series, High Compression Wide Cylinder Flange Model Aircraft Engines
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Parts Catalog PC 406-2 Avco Lycoming IO/LIO-360-C, -J, HIO, TIO, AEIO-360 Series Parts Catalog, Wide Cylinder Flange Models Aircraft Engines
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Parts Catalog Avco Lycoming O,LO,TO-360 Series Wide Cylindr Flange Models, Aircraft Engines PC-306-2
-
 Sunshine and District Historical Society Incorporated
Sunshine and District Historical Society IncorporatedPhotographs (1928), 'QUARTER MILE' BRIDGE Construction, 1928
One man lost his life during the building of this bridge. The bridge was constructed by the Victorian Railways between 1927 to 1929 to carry a new double track goods line. This enabled trains from all parts of the state except Gippsland to have direct access to the Tottenham marshalling and sorting yards. These yards were constructed in the 1920's to relieve congestion in the Melbourne Yard near Spencer Street station. The congestion was being caused by the construction of suburban passenger platforms associated with the electrification of the suburban railway network. Initially the bridge was for goods trains but during the Second World War it was also used by troop trains. When the standard gauge line was built in 1962 all trains to Albury and Sydney have used this route, thus avoiding travelling through Essendon and Pascoe Vale on the suburban tracks. The standard gauge track across the bridge took the place of one of the broad gauge tracks so broad gauge trains crossing the bridge in either direction have to now use the same track. The bridge is 1,257 feet (383.13 metres) long and 180 feet (54.86 metres) above the water level. It is just 63 feet (19.2 metres) short of a quarter mile in length between abutments. There is a similar bridge on the same railway line crossing the Moonee Ponds Creek between Gowenbrae and Glenroy, however it is smaller at 1060 feet (323.08 metres) length and 115 feet (35.05) height.The bridge is now Victorian Heritage Registered under Number: H1197, and Heritage Overlay Numbers HO5, and HO107. On the Heritage Register it is named RAIL BRIDGE (ALBION VIADUCT). According to the Heritage Report the bridge is scientifically and architecturally important because of its large size, and because of the cost effective design features such as two girders per span (one for each track), the K bracing in the towers, and the broad flange beams as columns. When it was being built it was the largest trestle bridge in Australia, and until the Sydney Harbour bridge was constructed it was the highest railway bridge.Five B&W yellowing photos showing stages of construction of the Maribyrnong River Viaduct known as the Trestle Bridge but mainly known locally as the QUARTER MILE BRIDGE. It is a railway only bridge which runs over the Maribyrnong River between Sunshine North and Keilor East. A sixth image, which is not part of this set of photos, is included to show what the completed bridge looks like. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumPlan - Drawings: 88732 (Proposed D/F Aerial, D/F Aerial Proposed Layouts, Aerials Arrangement, Aircraft Sealing, Cabinet Layout, Proposed Mounting, Proposed ‘Porters Installation), 89685 - Aerial Column Assembly, 89686 - Aerial Assembly, 89688 - Housing Top, 89689 - Housing Bottom, 89690 - Housing, 89691 - Screen, 89696 - Assembly Aerial Flange, 89699 - Flange, 8o702 - Stub Shaft, 89703 - Tube Inner, 89704 - Housing, 89705 - Bearing Upper, 89706 - Block Lamps, 89707 - Bracket, 89708 - Body, 89709 - Plate Illuminating, 89710 - Stop Plate, 89711 - Block Plug Mount, 89712 - Cap, 89713 - Scale, 89714 - Spacer, 89715 - Catch Pin, 89780 - Aerial Assembly, 89791 - Top Steady Anchorage Assembly, 90072 - Modifications Cessna, 90376 - Aerial Assembly Porter, 90391 - Modifications Porter, 90405 - Drilling Jig, o3031 - Experimental Auxiliary Aerial Project Thorough, Weapons Research Establishment
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDrawing - Item List for 89686D - Arial Assembly; Item List for 89744 Brake Sub-Assembly; Item List for 89791B - Top Steady Anchorage Assembly; Item List for 89696B - Arial, Flange Assembly, Weapons Research Establishment
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDrawing - Drawing Nos. 89692 - Gasket; 89693 - Plug Modified; 89694 - Element Outline; 89695 - Spacer; 89697 - Nut; 89698 - Washer; 89700 - Post; 89701 - Key; 89716 - Pin Threaded; 89717 - Connector Bracket; 89718 - Sliding Lock Retainer; 89719 - Block; 89720 - Straight Clamp; 89721 - Socket Modified; 89722 - Plate Mounting; 89723 - Plate Receptacle Mount; 89724 - Spring; 89u25 - Spring; 89726 - Spring; 89727 - Spring; 89728 - Bracket; 89729 - Clamp; 89730 - Pin Stop; 89731 - Button; 8o732 - Pin; 89733 - Nut; 89734 - Spring; 89735 - Cover Hinged; 89736 - Plate Hinge; 89737 - Washer; 89738 - Washer; 89739 - Washer; 89740 - Clamp Top; 89741 - Clamp Bottom; 89742 - Screw; 89743 - Mount; 89744 - Brake Sub Assembly; 89745 - Screw; 89746 - Sliding Lock Post; 89747 - Shaft; 89748 - Flange; 89749 - Brake; 89750 - Tappet; 89751 - Screw Top Plate; 89752 - Ring Retaining; 89753 - Locking Ring; 89754 - Knob; 89755 - Bearing Lower; 89756 - Plate; 89757 - Pin; 89758 - Hand Grip; 89759 - Pin Cam; 89760 - Insert; 80761 - Spacer; 89762 - Seal; 89763 - Bar Handle; 89764 - Key; 89765 - Ring Rotating; 89766 - Screw; 89767 - Support Ring; 89768 - Circlip; 89769 - Switch, Weapons Research Establishment
