Showing 225 items
matching housing -- australia
-
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, c 1978
On 4th August 1978 the construction of the Goonawarra Estate commenced. The estate was formerly known as the Goonawarra Farm and overlooked the Sunbury Township and the Jacksons Creek Valley. Plans for the development included a golf course, houses and community and recreational facilities. The golf course opened in 1980 and the housing construction continued throughout the last two decades of the twentieth century and into the twenty first century.A coloured photograph of the reflecting pool at the entrance of the Goonawarra Golf Club. The surrounding area has been landscaped and a display home is in the distance.goonawarra golf club, goonawarra farm, goonawarra housing estate, housing developments, sharkey, robert b., kilkenny homes, australian ideas homes pty.ltd., glamor homes, craftsmen homes., villa bella homes, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, c 1978
On 4th August 1978 the construction of the Goonawarra Estate commenced. The estate was formerly known as the Goonawarra Farm and overlooked the Sunbury Township and the Jacksons Creek Valley. Plans for the development included a golf course, houses and community and recreational facilities. The golf course opened in 1980 and the housing construction continued throughout the last two decades of the twentieth century and into the twenty first century.A coloured photograph of the clubhouse at the Goonawarra Golf Course taken from the 10th fairway. Parked cars are visible on the RHS of the photograpg and there is a row of gum trees behind the clubhouse.goonawarra golf club, goonawarra farm, goonawarra housing estate, housing developments, sharkey, robert b., kilkenny homes, australian ideas homes pty.ltd., glamor homes, craftsmen homes., villa bella homes, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, c 1978
On 4th August 1978 the construction of the Goonawarra Estate commenced. The estate was formerly known as the Goonawarra Farm and overlooked the Sunbury Township and the Jacksons Creek Valley. Plans for the development included a golf course, houses and community and recreational facilities. The golf course opened in 1980 and the housing construction continued throughout the last two decades of the twentieth century and into the twenty first century.A coloured photograph of the clubhouse at Goonawarra Golf Course as seen from the 10th green. A small white van is parked ouitside the building. There is a line of trees behind the clubhouse.goonawarra golf club, goonawarra farm, goonawarra housing estate, housing developments, sharkey, robert b., kilkenny homes, australian ideas homes pty.ltd., glamor homes, craftsmen homes., villa bella homes, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, 1/10/1978
On 4th August 1978 the construction of the Goonawarra Housing Estate commenced. The estate was formerly known as the Goonawarra Farm and overloked the Sunbury town area and Jacksons Creek valley. Plans for the new development included a gold course, housing, community and recreational facilities. The construction continued througout the last two decades of the twentieth century and into the twenty first century.A coloured photograph of the clubhouse taken from the south west at the Goonawarra Golf Club. The surrounding garden has been planted out with trees and has been mulched. A green car is on the LHS of the photograph.goonawarra farm, goonawarra golf club, goonawarra housing estate, sharkey, robert b., kilkenny homes, australian ideas homes pty.ltd., craftsmen homes., glamor homes, villa bella homes, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, 1/11/1980
On 4th August 1978 the construction of the Goonawarra Housing Estate commenced. The estate was formerly known as the Goonawarra Farm and overloked the Sunbury town area and Jacksons Creek valley. Plans for the new development included a gold course, housing, community and recreational facilities. The construction continued througout the last two decades of the twentieth century and into the twenty first century.A coloured photograph of Francis Boulevard at the Goonawarra Estate showing the entrances and landscaping and looking south to Sunbury Road and Jacksons Hill (Sheoak Hill).goonawarra farm, goonawarra golf club, goonawarra housing estate, kilkenny homes, craftsmen homes., australian ideas homes pty.ltd., villa bella homes, glamor homes, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, 1/08/1980
On 4th August 1978 the construction of the Goonawarra Estate commenced. The estate was formerly known as the Goonawarra Farm and overlooked the Sunbury farm and the Jacksons Creek valley. Plans for the new development included a golf course, houses, community and recreational facilities. The golf course opened in 1980 and the housing construction continued throughout the last two decades of the twentieth century and into the twenty first century.A coloured photograph of a barbecue and picnic area at Goonawarra. The photograph shows the Stage 3 development of the area.goona warra golf club, goonawarra farm, goonawarra housing estate, sharkey, robert b., kilkenny homes, craftsmen homes., australian ideas homes pty.ltd., glamor homes, villa bella homes, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, 1/08/1980
On 4th August 1978 the construction of the Goonawarra Estate commenced. The estate was formerly known as the Goonawarra Farm and overlooked the Sunbury town and the Jacksons Creek valley. Plans for the development included a golf course, houses, community and recreational facilities..The golf course opened in 1980 and the housing construction continued throughout the last two decadesd of the twentieth century and into the twenty firsat century.A coloured photograph showing the signpost indicating the entrance to the Goonawarra Estate from Sunbury Road. Trees are growing on either side of the road and Mt. Holden can be seen across the skyline.goona warra golf club, goonawarra farm, goonawarra housing estate, sharkey, robert b., kilkenny homes, australian ideas homes pty.ltd., craftsmen homes., glamor homes, villa bella homes, mt. holden, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, 1/08/1978
On 4th of August 1978 work began on the construction of the Goonawarra Estate on land that was the former Goonawarra Farm which overlooked the town of Sunbury abnd the Jacksons Creek valley. Plans for the new development included a golf course, houses, community and recreational facilities.The golf course openrd in 1980 and housing construction continued throughout the last two decades of the twentieth century and into the twentieth first century.A coloured photograph of the first sod being turned at the Goonawarra Estate. Four large pieces of earth-moving machinery and a large semi-trailer are in picture. A man is standing in the foreground.goona warra golf club, goonawarra farm, goonawarra housing estate, housing developments, sharkey, robert b., killkenny homes, australian ideas homes pty.ltd., craftsmen homes., glamor homes, villa bella homes, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, c 1968
The Melbourne Airport at Tullamarine was constructed during the latter half of the 1960s and was officially opened in 1970.An aerial view of the recently completed airport at Tullamarine showing the Astrojet Centre and the motel under construction in the foreground. The terminal building is in the background.goonawarra farm, goonawarra golf club, goonawarra housing estate, sharkey, robert b., kilkenny homes, villa bella homes, australian ideas homes pty.ltd., glamor homes, craftsmen homes., george evans collection -
 Wangaratta Art Gallery
Wangaratta Art GalleryPainting, Mollie Hill, Borough Offices, 1962
Mollie Hill was a famous Welsh-born Australian watercolourist who studied at the Melbourne National Gallery Art School and is known for her 'eye for colour'. Her work features many landscapes of northern Victoria as she lived for some time in Shepparton and Wandiligong. She was also a well-known journalist. Depicted in this painting is the old council borough offices which were demolished in 1962. Rural City of Wangaratta Collection. Gift of Wangaratta Co-operative Housing Society No. 3 Ltd.A watercolour landscape of the old Wangaratta borough offices painted using shades of green, red, blue, and brown.Obverse: Mollie Hill/ (bottom right corner) PRESENTED/ TO THE BOROUGH OF WANGARATTA/ BY WANG. CO-OP. HOUSING SOCIETY/ NO. 3. LTD. IN APPRECIATION OF THE/ GENEROUS ASSISTANCE RECEIVED./ (in mounting board)wangaratta art gallery, mollie hill, watercolour, painting, landscape, borough offices -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilReinis ZUSTERS (b.1918 Ukraine, arr.1950 Aus - d.1999 NSW Aus), Sunday Morning Montsalvat, 1979
Reinis Zusters OAM was born 15 October 1918 in Odessa, Ukraine, of Latvian parents. Zusters’ father died before he was two years old and he was raised in an orphanage from an early age. He had one sister. He studied Art at the Riga Technical College, Latvia, from 1935 to 1940. He married Aldija Kapteinis, and they had a daughter, Rudite (born 1942 in Riga). After World War II the Zusters family were refugees. They reached Western Australia in 1950, where they stayed for 6 months before moving to Canberra, ACT. In 1952, Zusters moved from Canberra to Pennant Hills in Sydney with his second wife, Arija Biks. Their daughter Laura was born in Sydney in 1956. In 1966, Zusters met his future third wife, Venita Salnajs. In 1969, Zusters bought a house in Greenwich, Sydney. He married Venita on September 17, 1976, and they moved to Wentworth Falls in the Blue Mountains. Zusters died on 8 October, 1999 at Wentworth Falls, and was cremated at Rookwood Crematorium, Sydney. His ashes are buried in the Latvian section of Rookwood Cemetery. Zusters studied at the Technical College of Riga (Latvia), and at East Sydney Technical College, Australia. He was influenced by his Latvian cultural heritage, and admired the artist Voldemars Tone (1892-1958). Shortly after arrival in Australia, Zusters became a draughtsman with the Department of Works and Housing in Canberra. Later he was appointed chief designer with the Australian-American architectural firm Austin-Anderson, at St. Leonards, Sydney. Zusters practised as a full-time professional artist from 1968. Zusters was a prolific painter, predominantly in oils. He produced many large landscapes, including triptychs of the Blue Mountains. His landscapes were mountain scenes prepared in the manner of Jackson Pollock and completed with washes and pale glazes of colour. His cityscapes featured a rich paint surface and sharp-edged thickness of paint applied with a palette knife, layer upon layer. He painted urban scenes of Sydney, inland Australian scenes, and several major portraits including Sir Winston Churchill’s gardener (purchased by Art Gallery of NSW). He made many small informal portrait-drawings of friends. His usual signature was “Zusters”. His work is represented in numerous public and private collections in Australia and abroad. He won numerous prestigious awards in Australia, Japan and USA and was honoured with the Order of Australia Medal in 1994. -
 Slovenian Association Melbourne
Slovenian Association MelbourneVideo and DVD, Footage of Slovenian migrants in 1956 in Australia, 1956
- Migrant ships arriving into Port Melbourne in 1956. Migrants boarding the train to Bonegilla camp and resettling in Victoria. - Section on Olympic Games in Melbourne was filmed by Father Basil Valentin OFM who was the Chaplain of the American Olympic team. -Also showed extracts of Moomba festival in 1957. - Slovenian settling on Australian farms and weddings of members of the Slovenian community This video shows the magnitude of migrants who arrived in Australia in 1956 by ships mainly from Italian ports from Genoa, Trieste and Naples. It shows the settling of migrants into camps and depicts their everyday life including education and recreation and assimilation into Australia. 120 minute video cassette in colour depicting migrant ships arriving to Port Melbourne in 1956 and short clips of the Melbourne Olympic Games. Also includes footage of train journey to Bonegilla camp and camp housing facility.0002migration, resettlement, bonegilla, slovenians, ships, olympics 1956 -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBooklet, Kelly, Howard (Victorian SEMP Race and Ethnic Relations team) et al, Black Conditions, 1978
... -- Social conditions. | Aboriginal Australians -- Housing. | A study ...A study of Aboriginal communities and the living conditions of Aborigines. A social justice booklet.28 p.; ill.; 28 cm.A study of Aboriginal communities and the living conditions of Aborigines. A social justice booklet.aboriginal australians -- social conditions. | aboriginal australians -- housing. | -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Broom, Leonard, A blanket a year, 1973
Land rights, perhaps the best known of Aboriginal grievances, is bitterly expressed in 'All they give us now for our land is a blanket once a year'. Yet, as Broom and Jones show in this book, the Aborigines are disadvantaged in every way. No one knows who are Aborigines, how many there are, what jobs they hold, what education they have received. Yet, until this extraordinary ignorance is rectified, there is no basis for planning vital improvements. The authors stress the urgent need for public authorities to gather information on Aboriginal health, housing, employment, and education. Without this information no attempt to overcome the gross inequalities can hope to succeed. A Blanket a Year offers constructive professional help. It is vital reading for politicians, administrators, social workers, educationists, and for all fair-minded Australians.98 p. ; notes; tables; references; 23 cm.Land rights, perhaps the best known of Aboriginal grievances, is bitterly expressed in 'All they give us now for our land is a blanket once a year'. Yet, as Broom and Jones show in this book, the Aborigines are disadvantaged in every way. No one knows who are Aborigines, how many there are, what jobs they hold, what education they have received. Yet, until this extraordinary ignorance is rectified, there is no basis for planning vital improvements. The authors stress the urgent need for public authorities to gather information on Aboriginal health, housing, employment, and education. Without this information no attempt to overcome the gross inequalities can hope to succeed. A Blanket a Year offers constructive professional help. It is vital reading for politicians, administrators, social workers, educationists, and for all fair-minded Australians.aborigines. social planning. information requirements. australia. surveys | aboriginal australians -- social conditions. | australia -- social policy. | -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustDocument - Report, Brown, Jill W. (Roisin Hirschfeld and Diane Smith; under the supervision of Professor Edna Chamberlain), Aboriginals and Islanders in Brisbane, 1974
Demographic data on race, age, sex, marital status and mobility; education levels; housing and problems in finding accommodation; occupations and income; medical, legal, welfare and other services; hostels.ix, 119 p. ; 25 cm.Demographic data on race, age, sex, marital status and mobility; education levels; housing and problems in finding accommodation; occupations and income; medical, legal, welfare and other services; hostels.australian aborigines. social conditions. brisbane | torres strait islanders. social conditions. brisbane | aboriginal australians -- queensland -- brisbane -- social conditions. | torres strait islanders -- queensland -- brisbane -- social conditions. -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article - Newspaper Clipppings, Worker's paradise factory at Blackburn, 1951 & 1988
'The Belgians in Australia' gives a brief history of Roger, 1950 - 1975.Belgian, Roger de Stoop, plans a spinning and weaving factory at Blackburn. He plans many innovative amenities to keep his staff happy. Also another article - 'The Belgians in Australia' gives a brief history of Roger, 1950 - 1975. 'The Belgians in Australia' gives a brief history of Roger, 1950 - 1975.textiles, de stoop textile factory, de stoop, roger -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
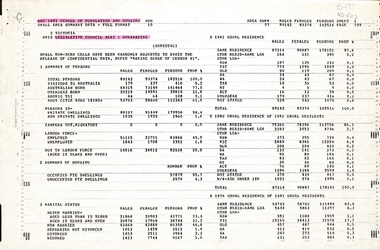
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Document, 1981 Census of population and housing, 1981
Copy of Australian Bureau of Statistics census of population and housing, 1981, Legislative Council Seat of Nunawading.Copy of Australian Bureau of Statistics census of population and housing, 1981, Legislative Council Seat of Nunawading.non-fictionCopy of Australian Bureau of Statistics census of population and housing, 1981, Legislative Council Seat of Nunawading.australia. census, 1981, victoria. parliament. nunawading seat, population -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, Housing 'Monster' surprise, 2015
Whitehorse Council voted to approve a 118-dwelling development by Australia Hua Cheng Pty Ltd, Blackburn.Whitehorse Council voted to approve a 118-dwelling development by Australia Hua Cheng Pty Ltd, Blackburn, on the corner of Middleborough Road made up of two five-storey buildings and 15 double-storey buildings on the 7421 sm site.Whitehorse Council voted to approve a 118-dwelling development by Australia Hua Cheng Pty Ltd, Blackburn. city of whitehorse, massoud, denise, australia hua cheng pty ltd -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Document, Landscape Submission, c 1976
A landscape submission written for the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) for Blackburn Lake and the Bell Bird Streets.A landscape submission written for the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) for Blackburn Lake and the Bell Bird Streets. Definitions given of boundaries of the Lake area, ownership, housing and gardens. Photographs and map.A landscape submission written for the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) for Blackburn Lake and the Bell Bird Streets.blackburn lake sanctuary, waratah crescent, blackburn, jeffery street, hill street, boongarry avenue, linum street, laurel grove, acacia avenue, city of nunawading, melbourne and metropolitan board of works, furness park, camberwell grammar school -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Pamphlet, Smithfield Walk, Vermont, n.d
Advertisement for housing development: 'Homestead Rise' at Smithfield Walk, Vermont. Land originally owned by L.L. Smith; purchased in 1924 by David Hastie Harvie. Developer: Residential Developments Australia Pty Ltd.auctions, smithfield walk, vermont, harvie, david hastie, residential developments australia pty ltd, homestead rise estate, vermont -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph -Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Interior of the Melbourne Exhibition Building, 2019, 31/03/2019
A competition was announced to design a suitable building for the proposed Melbourne International Exhibition in December 1877. Eighteen entries were received. The winner of 300 pounds was Joseph Reed of the architectual firm Reed and Barnes. The foundation stone was laid by Governor Sir George Bowen on 19 February 1879. Prominent Melbounre builder David Mitchell, father of Dame Nellie Melba, won the tender to construct the main building. Exhibitors were able to move in by May 1880. On 01 October 1880 the Melbourne International Exhibition opened, when over 6000 people entered the main hall to see the Governor, the Marquess of Normanby open the show. Thirty three nations participated and ofver 32,000 exhibits were displayed. At the close of the exhibition on 30 April 1881 over 1.3 million people had visited the exhibition. In 1881 Victoria's population was just over 250,000. The management of the Exhibition Building and eight hectares of the Carlton Gardens was handed to the Exhibition Trustees by the Melbourne International Exhibition Commissioners on 01 OCtober 1881. The Trustees maintained the building for 'future public exhibitions and ... general public instruction and recreation' until 1996 when management of the building was transferred to Museum Victoria. In 1901 when the Australian colonies federated there was no capital and no federal parliament building. The Federal Parliament moved into the Victorian State Parliament building, and the State Parliament moved into the Western Annexe of the Exhibition Building for 26 years. After World War One, on 04 February 1919, the exhibition Building was turned into a hospital to treat Melbournians struck down with the Spanis 'Flu'. Initially housing 500 beds, the hospital grew to accomodate 2000 patients. Femals were located between the concert platform in the western nave and the done; male patients occupied the spaces beyond. The basement was used a a morgue. With the departure of the State Parliament in 1927 the western annexe became home to the Country Roads Board. In 1932 it was joined by the MOtor Registration Branch, and the Transport Regulation Board in 1934. They co-existedin cramped offices until the 1960s. In 1949 the oval at the rear of the ExhibitionBuilding was leased to the Commonealth Government for the establishment of the Migrant Reception Centre. When it closed in 1961-62, the centre comrised 29 bungalows over 1.4 hectare. The centre provided temporary accomodation for thousands of new arrivals from Britain. On 01 July 2004 the Royal Exhibition Building and Carlton Gardens were inscribed on the World Heritage List. It is the only 19th century Great Hall to survive largely intact, still in its original landscape setting, and still used as a palace of industry. The Melbourne International Flower and Garden Show is a flower show held annually since 1995 in early April each year, in Melbourne, Australia. It is located in the World Heritage Site of Carlton Gardens and the Royal Exhibition Building.[1] It is the largest horticultural event in the southern hemisphere, attracting over 100,000 visitors. It is rated among the top five flower and garden shows in the world. (Wikipedia)Colour photograph of the interior of the Melbourne Exhibition Buildings during the 2019 Melbourne Flower and Garden Show.melbourne international flower and garden show, carlton gardens, melbourne exhibition building, royal exhibition buildings -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph -Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Interior of the Melbourne Exhibition Building, 2019, 31/03/2019
A competition was announced to design a suitable building for the proposed Melbourne International Exhibition in December 1877. Eighteen entries were received. The winner of 300 pounds was Joseph Reed of the architectual firm Reed and Barnes. The foundation stone was laid by Governor Sir George Bowen on 19 February 1879. Prominent Melbounre builder David Mitchell, father of Dame Nellie Melba, won the tender to construct the main building. Exhibitors were able to move in by May 1880. On 01 October 1880 the Melbourne International Exhibition opened, when over 6000 people entered the main hall to see the Governor, the Marquess of Normanby open the show. Thirty three nations participated and ofver 32,000 exhibits were displayed. At the close of the exhibition on 30 April 1881 over 1.3 million people had visited the exhibition. In 1881 Victoria's population was just over 250,000. The management of the Exhibition Building and eight hectares of the Carlton Gardens was handed to the Exhibition Trustees by the Melbourne International Exhibition Commissioners on 01 OCtober 1881. The Trustees maintained the building for 'future public exhibitions and ... general public instruction and recreation' until 1996 when management of the building was transferred to Museum Victoria. In 1901 when the Australian colonies federated there was no capital and no federal parliament building. The Federal Parliament moved into the Victorian State Parliament building, and the State Parliament moved into the Western Annexe of the Exhibition Building for 26 years. After World War One, on 04 February 1919, the exhibition Building was turned into a hospital to treat Melbournians struck down with the Spanis 'Flu'. Initially housing 500 beds, the hospital grew to accomodate 2000 patients. Femals were located between the concert platform in the western nave and the done; male patients occupied the spaces beyond. The basement was used a a morgue. With the departure of the State Parliament in 1927 the western annexe became home to the Country Roads Board. In 1932 it was joined by the MOtor Registration Branch, and the Transport Regulation Board in 1934. They co-existedin cramped offices until the 1960s. In 1949 the oval at the rear of the ExhibitionBuilding was leased to the Commonealth Government for the establishment of the Migrant Reception Centre. When it closed in 1961-62, the centre comrised 29 bungalows over 1.4 hectare. The centre provided temporary accomodation for thousands of new arrivals from Britain. On 01 July 2004 the Royal Exhibition Building and Carlton Gardens were inscribed on the World Heritage List. It is the only 19th century Great Hall to survive largely intact, still in its original landscape setting, and still used as a palace of industry. The Melbourne International Flower and Garden Show is a flower show held annually since 1995 in early April each year, in Melbourne, Australia. It is located in the World Heritage Site of Carlton Gardens and the Royal Exhibition Building.[1] It is the largest horticultural event in the southern hemisphere, attracting over 100,000 visitors. It is rated among the top five flower and garden shows in the world. (Wikipedia)Colour photograph of the interior of the Melbourne Exhibition Buildings during the 2019 Melbourne Flower and Garden Show. Four mottoes are painted under teh windows of the dome: Dei Grecia (By the grace of God), Carpe diem (Make the most of the day), Aude sapere (Dare to be wise) and Benigno numine (With benighn power)melbourne international flower and garden show, carlton gardens, melbourne exhibition building, royal exhibition buildings -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph -Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Interior of the Melbourne Exhibition Building, 2019, 31/03/2019
A competition was announced to design a suitable building for the proposed Melbourne International Exhibition in December 1877. Eighteen entries were received. The winner of 300 pounds was Joseph Reed of the architectual firm Reed and Barnes. The foundation stone was laid by Governor Sir George Bowen on 19 February 1879. Prominent Melbounre builder David Mitchell, father of Dame Nellie Melba, won the tender to construct the main building. Exhibitors were able to move in by May 1880. On 01 October 1880 the Melbourne International Exhibition opened, when over 6000 people entered the main hall to see the Governor, the Marquess of Normanby open the show. Thirty three nations participated and ofver 32,000 exhibits were displayed. At the close of the exhibition on 30 April 1881 over 1.3 million people had visited the exhibition. In 1881 Victoria's population was just over 250,000. The management of the Exhibition Building and eight hectares of the Carlton Gardens was handed to the Exhibition Trustees by the Melbourne International Exhibition Commissioners on 01 OCtober 1881. The Trustees maintained the building for 'future public exhibitions and ... general public instruction and recreation' until 1996 when management of the building was transferred to Museum Victoria. In 1901 when the Australian colonies federated there was no capital and no federal parliament building. The Federal Parliament moved into the Victorian State Parliament building, and the State Parliament moved into the Western Annexe of the Exhibition Building for 26 years. After World War One, on 04 February 1919, the exhibition Building was turned into a hospital to treat Melbournians struck down with the Spanis 'Flu'. Initially housing 500 beds, the hospital grew to accomodate 2000 patients. Femals were located between the concert platform in the western nave and the done; male patients occupied the spaces beyond. The basement was used a a morgue. With the departure of the State Parliament in 1927 the western annexe became home to the Country Roads Board. In 1932 it was joined by the MOtor Registration Branch, and the Transport Regulation Board in 1934. They co-existedin cramped offices until the 1960s. In 1949 the oval at the rear of the ExhibitionBuilding was leased to the Commonealth Government for the establishment of the Migrant Reception Centre. When it closed in 1961-62, the centre comrised 29 bungalows over 1.4 hectare. The centre provided temporary accomodation for thousands of new arrivals from Britain. On 01 July 2004 the Royal Exhibition Building and Carlton Gardens were inscribed on the World Heritage List. It is the only 19th century Great Hall to survive largely intact, still in its original landscape setting, and still used as a palace of industry. The Melbourne International Flower and Garden Show is a flower show held annually since 1995 in early April each year, in Melbourne, Australia. It is located in the World Heritage Site of Carlton Gardens and the Royal Exhibition Building.[1] It is the largest horticultural event in the southern hemisphere, attracting over 100,000 visitors. It is rated among the top five flower and garden shows in the world. (Wikipedia)Colour photograph of the interior of the Melbourne Exhibition Buildings during the 2019 Melbourne Flower and Garden Show. Four mottoes are painted under teh windows of the dome: Dei Grecia (By the grace of God), Carpe diem (Make the most of the day), Aude sapere (Dare to be wise) and Benigno numine (With benighn power)melbourne international flower and garden show, carlton gardens, melbourne exhibition building, royal exhibition buildings -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Roger de Stoop, 1956
Roger de Stoop was born in 1912 in Flanders, Belguim. He migrated to Australia and set up a mattress ticking factory in Blackburn North in 1950.The company produced damask ticking. de Stoop sponsored Belgian migrants to work in his factory and built housing for them close to the factory. He sold the business in the 1960's to Smith and Nephew but continued to manage the manage the business until 1966Black and white photograph of Roger de Stoop showing the Prince and Princess of Luxembourg around his Blackburn North textile factory which was established in 1950. Bales of ticking in foreground. Staff standing, guests seated.de stoop, roger, de stoop textile factory, blackburn north, textiles, prince of luxembourg, princess of luxembourg -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Roger de Stoop and Belgian workers, C 1950
Roger de Stoop came to Australia during the Second World War when the de Stoop spinning & weaving factory in Belgium was closed during the German occupation. He had previously met Dick Best, an Australian who wanted to establish a textile factory in Australia and in 1950 they built a factory at Blackburn North importing the weaving looms and many of their skilled workers from Belgium. Housing for the workers was built near the factory.Black and white photograph of Belgian family groups in front of one of the houses erected for the de Stoop workers. Roger de Stoop is in the centre of the photograph in a dark suit and tie.de stoop, roger. de stoop aust pty ltd. de stoop and best textile factory. weaving mills. belgians in australia -
 International House, The University of Melbourne
International House, The University of MelbournePhotograph (item), Australian News and Information Bureau, Newly constructed Ian Clunies Ross building at International House Melbourne, 1957
This building was the first residential housing for the newly established International House in Melbourne, which had been in its planning stages since 1954. The building housed both domestic and international students.residential college, international house, architecture -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratJustice for Aboriginal Australians: Report of the World Council of CHurches team visit to the Aborigines June 15 to July 3, 1981 (David Spiers Collection), World Council of Churches
Report of the World Council of Churches team visit to Australia to assess the situation of Australian Aboriginals in 1981.Aboriginal affairs, rights and welfare.Book; 91 pagesbtlc, ballarat trades and labour council, unions ballarat, aboriginal affairs, world council of churches, australian council of churches, mining, land rights, health, housing, education, employment -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photograph, Lisa Gervasoni, Housing in Cotham Ward, Kew, 2017
Housing units in Cotham Road, Kewkew, housing, streetscape, archiecture -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photograph, Lisa Gervasoni, Playground at Sacred Heart Catholic School, Kew, 2017
Colour photograph of a playground at Playground at Sacred Heart Catholic School, Kew kew, housing, streetscape, sacred heart kew, playground -
 RMIT Design Archives
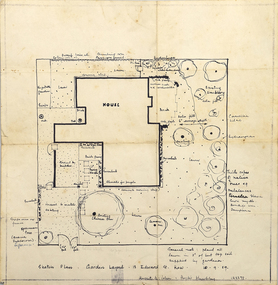
RMIT Design ArchivesDiazotypes, Sketch Plan: Garden Layout - 13 Edward St. Kew
John and Phyllis Murphy designed this house and garden in Kew for Sir Frank and Lady Macfarlane Burnet in 1959, the year before Burnet and Peter Medaware received the Nobel Prize for discovering acquired immunological tolerance. For the most highly honoured scientist to have worked in Australia, Burnet's house is modest - single storey with two bedrooms. Typical of post-war suburban housing thought, the garden is a generous, and the planting a mix of existing shrubs and trees, old favourites such as camelias, hydrangeas, lilacs, and a unusually 'a thick copse of native trees'. John Murphy (1920-2004) and Phyllis Murphy (nee Slater) (1924-) are alumni of RMIT. John commenced his architectural studies at Swinburne Technical College prior to WW2, and subsequently studied at Melbourne Technical College (now RMIT University) from 1944 to 1946. Phyllis studied architecture at Melbourne Technical College from 1942, before transferring to Melbourne University's Architectural Atelier in 1944 They both completed their Bachelor of Architecture in 1949, with Phyllis topping the fourth year, and John coming in second. They established their architectural practice in 1950. One early project was their design with Kevin Borland and Peter McIntyre for the Olympic Swimming Pool (1956). Ann Carew 2018dye, paper, garden design, kew
