Showing 3700 items
matching loose-pulley
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - NOMAD N22 OPTION DATA. OPTION R624. CO-PILOT ATTITUDE INDICATOR. AIM 500DCF(28)8, AEROSACE TECHNOLOGIES OF AUSTRALIA - ASTA
AEROSPACE TECHNOLOGIES OF AUSTRALIA - ASTA -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumNOMAD N22 OPTION DATA. OPTION R490 - R1065. MAINTENANCE MANUAL R490-R1065, AEROSPACE TECHNOLOGIES OF AUSTRALIA - ASTA
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual - NOMAD DESIGN MANUAL. N2 - 8004
nomad design manual -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Vickers Viscount 832 Airframe Engineers Lecture Notes
-
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratPhotograph of delegates to the Intercolonial Trades and Labour Congress - 7th Congress, Ballarat, 1891, April 1891
Ballarat Trades Hall was part of the Intercolonial Trades Hall Congresses created for the purposes of collective organising within labour organisations. There were eight Congresses held within Australia. See 0019-0026. There were eight Intercolonial Trades Hall Congresses in Australia: 1. Sydney 1879 2. Melbourne 1884 3. Sydney 1885 4. Adelaide 1886 5. Brisbane 1888 6. Hobart 1889 7. Ballarat 1891 8. Adelaide 1898 The photograph forms part of the history of the 7th Intercolonial Trades Hall Congress, showing delegates in attendance. It features the only known picture of David Temple of the Shearers' Union. The item is not currently available for loan or viewing. It is due for restoration.Cameo portraits - loose. ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, btlc, unions, delegates, photographs, organising, 7th intercolonial trades hall congress -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Vickers Viscount 720 Electrical Services Course Notes
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Vickers Viscount 720 Trans Australia Airlines TAA Electrical Instrument Training Manual
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Barber Coleman Test Report Quailification by Similarity for BYLB 51232 2 inch valve CAC
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Dunlop 700 Series Viscount, Dunlop 700 Series Viscount Part 3 Parts List Copy No. 30103
Handwritten title on outside -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Dunlop 700 Series Viscount, Dunlop Aviation Equipment fitted to The Viscount 700 Series
-
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaText, RVIB Garfield Auxiliary papers, 1956-7
The Garfiled RVIB Auxiliary formed on August 2, 1955. This small collection contains correspondence to and from RVIB head office ranging between 1956 -1957. Various loose papers royal victorian institute for the blind -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - De Havilland Heron Servicing School Engineers Airfram Pocket Manual
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual - Gipsy aero engines, Gipsy I Aero-Engine
Technical overview of Gipsy I aircraft engine circa 1931Includes loose amendmentsnon-fictionTechnical overview of Gipsy I aircraft engine circa 1931gipsy aero engine -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - (SP) AAP 721-94 Vol 1 Sabre Mk 31-32 General and Technical Information
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - (SP) AAP 721-94 Vol 3 RAAF Sabre Mk 31-32 Schedule of Spare Parts
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Fusee Clock Mechanism, early 20th Century
The origin of the fusee is not known. Many sources credit clockmaker Jacob Zech of Prague with inventing it around 1525. The earliest dated fusee clock was made by Zech in 1525, but the fusee appeared earlier, with the first spring-driven clocks in the 15th century. The idea probably did not originate with clockmakers, since the earliest known example is in a crossbow windlass shown in a 1405 military manuscript. Drawings from the 15th century by Filippo Brunelleschi and Leonardo da Vinci also show fusee mechanisms. The earliest existing clock with a fusee, also the earliest spring-powered clock, is the Burgunderuhr (Burgundy clock), a chamber clock whose iconography suggests that it was made for Phillipe the Good, Duke of Burgundy about 1430. Springs were first employed to power clocks in the 15th century, to make them smaller and portable.[1][5] These early spring-driven clocks were much less accurate than weight-driven clocks. Unlike a weight on a cord, which exerts a constant force to turn the clock's wheels, the force a spring exerts diminishes as the spring unwinds. The primitive verge and foliot timekeeping mechanism, used in all early clocks, was sensitive to changes in drive force. So early spring-driven clocks slowed down over their running period as the mainspring unwound. This problem is called lack of isochronism. Two solutions to this problem appeared with the first spring-driven clocks; the stack freed and the fusee. The stack freed, a crude cam compensator, added a lot of friction and was abandoned after less than a century. The fusee was a much more lasting idea. As the movement ran, the tapering shape of the fusee pulley continuously changed the mechanical advantage of the pull from the mainspring, compensating for the diminishing spring force. Clockmakers empirically discovered the correct shape for the fusee, which is not a simple cone but a hyperboloid. The first fusees were long and slender, but later ones have a squatter compact shape. Fusees became the standard method of getting constant force from a mainspring, used in most spring-wound clocks, and watches when they appeared in the 17th century. Around 1726 John Harrison added the maintaining power spring to the fusee to keep marine chronometers running during winding, and this was generally adopted. The fusee was a good mainspring compensator, but it was also expensive, difficult to adjust, and had other disadvantages: It was bulky and tall and made pocket watches unfashionably thick. If the mainspring broke and had to be replaced, a frequent occurrence with early mainsprings, the fusee had to be readjusted to the new spring. If the fusee chain broke, the force of the mainspring sent the end whipping about the inside of the clock, causing damage. The invention of the pendulum and the balance spring in the mid-17th century made clocks and watches much more isochronous, by making the timekeeping element a harmonic oscillator, with a natural "beat" resistant to change. The pendulum clock with an anchor escapement, invented in 1670, was sufficiently independent of drive force so that only a few had fusees. In pocketwatches, the verge escapement, which required a fusee, was gradually replaced by escapements which were less sensitive to changes in mainspring force: the cylinder and later the lever escapement. In 1760, Jean-Antoine Lépine dispensed with the fusee, inventing a going barrel to power the watch gear train directly. This contained a very long mainspring, of which only a few turns were used to power the watch. Accordingly, only a part of the mainspring's 'torque curve' was used, where the torque was approximately constant. In the 1780s, pursuing thinner watches, French watchmakers adopted the going barrel with the cylinder escapement. By 1850, the Swiss and American watchmaking industries employed the going barrel exclusively, aided by new methods of adjusting the balance spring so that it was isochronous. England continued to make the bulkier full plate fusee watches until about 1900. They were inexpensive models sold to the lower classes and were derisively called "turnips". After this, the only remaining use for the fusee was in marine chronometers, where the highest precision was needed, and bulk was less of a disadvantage until they became obsolete in the 1970s. Item is an example of clock mechanisms used until 1910 for many different styles of clocks and went out of fashion in the 1970s due to improvements in clock and watch making.Brass fusse clock movement, It has very heavy brass plates and wheels, high-count machined pinions, and a fusee. The mounting of the pendulum is missing and It has a recoil escapement. A fusee is a conical pulley driven through a chain by the spring barrel. As the spring runs down, the chain acts at a larger and larger radius on the conical pulley, equalising the driving torque. This keeps the rate of the clock more even over the whole run. It has motion work to drive an hour hand as well as a minute hand and the centre arbor is extended behind the back plate to drive some other mechanism.Inscription scratched on back"AM 40" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, clock mechanism, fusee mechanism, horology -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumMemorabilia - DIORAMA, KOKODA, Post WW2
Diorama inspired by image from State Library of Victoria image No H98 104 / 2102.Diorama mounted on black base. 1/35 scale model of 25 pounder field gun with 5 man crew maneuvering a gun into position around a tree with a pulley system. In black print on gold name plate attached to front of black base:: “25 Pounder Field Gun 14th Australian Field Regiment, Kokoda, September 1942”military history-army, arms-ordnance, handcrafts, kokoda -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Flower Pot Mould
Mould for making flower pots (terra cotta). Made of steel framing with a 'pedal' operated moulding shaft for forming pots of various sizes. The 'pedal' operates a chain and pulley system.ceramics, terracotta -
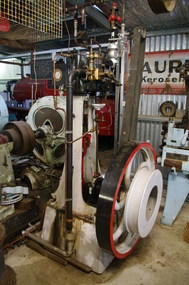 Maldon Vintage Machinery Museum Inc
Maldon Vintage Machinery Museum IncSteam Engine
Vertical cylinder steam engine painted black, red and grey. In working order. Large flywheel and pulley on RHS and mounted on a raised concrete base. Belt drive overhead governor.No. "8532" is cast on the LHS of the frame.engines, steam, vertical -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Administrative record - Work Book
The item is a hard cover book recording weekly work of T.J. Connolly, Ironmongers, Sandhurst. A list of names is written inside the front cover. An alphabet index at the front of the book, lists types of goods and equipment. The index is followed by handwritten pages recording each week's work including goods, fittings and equipment types, client surname or business name and a numbering system. The work records have also been checked off with ticks or crosses separately. The hard cardboard cover is green with red marbling, which is worn and torn. The leather binding has peeled away from the pages and front cover but is attached to the back cover. The pages are fragile with many loose pages due to the state of the binding. The book is full and includes the date range of 29 May 1886 to 12 October 1888. This item is part of the Margaret Roberts Collection.Business stamp on torn loose page inside front cover. margaret roberts collection, ironmongers, forest street, bendigo businesses -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Plays
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1945 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. SIGNIFICANCE The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, and to reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. As with many Mechanics' Institutes in Australia, the one which operated in Warrnambool was established and overseen for many years by key individuals associated with the development of the city itself. The WMI publication collection is historically significant because of its association with local people, places and the key historical themes in the development of Warrnambool of rural development, industry, farming, education, and community. The collection documents and illustrates the changing interests, focus and tastes of Victorians, especially those in regional cities. Generally the individual items in the collection are not particularly rare, as examples of all probably exist in other public collections in Victoria. It is primarily because there are so very few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections in Victoria, which lends this overall collection its significance. Many items in the WMI Collection have the potential to support further research, both as individual objects and through the collection in its entirety. This material is significant for its ability to assist in the interpretation of the history of the area and adds to the general understanding of the development of the township. Many components of the WMI publication collection complement and reinforce the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Collection, the Warrnambool Art Gallery Collection, and that in the Warrnambool Historical Society, and also contribute to a clearer understanding of the original Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute collections. This will greatly enhance the appreciation of the few surviving Mechanics' Institute collections across Victoria, and also in New South Wales. The similarities and differences between the small number of collections that have survived can provide further insights into how the people of Victoria in general, and Warrnambool in particular, constructed a civic culture of adult learning to foster an informed citizenry. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute publication collection is of both local and state significance. Plays The following is on an inside loose endpaper. "Christopher Marlowe, son of a shoemaker, born at Canterbury in 1564. Educated at Cambridge. Attached himself to the Earl of Nottingham's theatrical company, and subsequently associated with the leading men of letters. Killed in a brawl at Deptford in 1593 while a warrant for his arrest on a charge of blasphemy had been issued." Author: Christopher Marlowe Publisher: J M Dent & Sons Date: 1947Label on spine cover with typed text PAT 822 MAR Front loose endpaper has a stamp from Warrnambool Public Library covered by a sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Service Front loose endpaper has a stamp from Corangamite Regional Library Servicewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, pattison collection, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, ralph eric pattison, corangamite regional library service, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, great ocean road, plays, christopher marlowe -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncMemorabilia - Memorial Card, In Memory of Sarah Ann Shillinglaw, 1878
Sarah Ann Shillinglaw was the first child of Phillip Shillinglaw and Sarah Ann (nee Kidd). She was born February 14, 1873 at Bundoora and died June 3, 1878 at Bundoora and was buried in McLeans Cemetery at Preston. In Memory of Sarah Ann Shillinglaw Who died 3rd June 1878 Aged 5 years and 4 months Interred at McLean's Cemetery Also written in brown ink above main inscription in document held by the bird "I'm going to Heaven to see little Janie" Janie was Sarah's younger sister, Phillp and Sarah's second child born January 14, 1875 at Bundoora who died May 4, 1876 Memorial card manufactured in delicate embossed paper lace, printed in black and completed in (faded) brown ink; loosely placed on a black painted wooden mount inside a wooden frame 19 x 15 x 2 cm fitted with glass pane. Inserted loosely behind this lace card is a second half size embossed paper lace which states Sarah was interred at Melbourne Cemetery on 5th June 1878. G.W. Apps, Undertaker, 165 Fitzroy Street, Fitzroymarg ball collection, memorial card, sarah ann shillinglaw (1873-1878), jane shillinglaw (1875-1876), mcleans cemetery preston -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Minutes - CTS, Minutes of Council of School Activities. Collingwood Technical School. 1942-1950, 1942-1950
The Council of School Activities dealt with matters pertaining to student welfare, including extra curricular activities such as the brass band. This volume contains a revised (1944) constitution for the council.Details the activities within the school, including those teachers who were involved.Black exercise book with brown paper spine binding. Front cover is loose. Some loose documents are interleaved.Hand written on brown paper spine: "Annual Satff Meetings". Most entries are handwritten.collingwood technical school, cts, council of school activities, school council, council minutes, nmit, -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Equipment - Artefact, Lamson's Rapid Wire Cash Carrier, Youngers, C Early 20th century
Lamson was established in Australia in 1898 with the idea for a store security money handling system being patented in the latter part of the 19th century.The practise of taking money from the counter and customer to the cashier was time consuming and cumbersome.Some bright ideas were employed including tying the money and dockets in a hankerchief and throwing it to the cashier. The first attempt to improve this was the ball system where a ball containing the cash was rolled to the cashier on an elevated track. The rapid wire system superseded this in the early 1900's and for the next 50 years it became a popular part of money handling in stores around Australia. This particular Lamson's cash carrier was installed in Youngers department store which was situated in Liebig Street. The success of Youngers store was partly responsible for the shift to Liebig St as the main commercial district. The Warrnambool Standard reported in 1901 that Younger and Co would operate on a wholly cash basis replacing incidental trades of goods such as potatoes and other farm produce.This item has strong social and historical significance. Apart from having strong links to one of Warrnambool's largest and longest running businesses, the object itself is of considerable interest with thousands of the original ball systems and Rapid Wire cash carriers being in use around the world. Cylindrical brass top with central circular part with section either side which have two small pulleys. A wooden cylindrical section slots in below with a wire clip attached at the bottom.Lamson is cast into the brass on either side of therim of the top circular section. . AUS is on the side of this same section. warrnambool,, youngers, youngers warrnambool, lamson, lamson rapid wire cash carrier, wire cash carrier -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumAward - MEDAL, Post 1940
Dunkirk Medal with loose ribbon.Dunkerque 1940medals, military, british, passchendaele barracks trust -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Avro Lincoln Mk XXX Schedule of Spare Parts
All pages seem to be carbon copies of typed pages. No indication of organisationHandwritten on outside -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Vickers Viscount 800 Series Handling Operations
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Viscount Aircraft Electrical/Instrument Training Manual Trans-Australia Airlines V816
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumViscount 700 Series Instruments Type 701 Instruction Manual
Copy no. 68, Type 701 -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Trans Australia Airlines Airframe Training Manual Viscount Aircraft Copy 295
Previous owner P Broad
