Showing 7184 items
matching marine
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNail
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).25½" of round solid copper nail. Recovered from "Falls of Halladale". Ship's nail.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, nail, copper nail, falls of halladale, ship's nail -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Paper, circa 1908
This roll or reel of paper was part of a consignment carried as cargo of the Falls of Halladale. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The roll of paper is an example of cargo brought to Australia in the early 20th century. It is also significant for its association with the Falls of Halladale shipwreck, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Roll of paper. Paper was part of a large consignment of paper listed as part of the cargo manifesto. It was recovered from the wreck of the ship Falls of Halladale. A section of the paper has been cut away after it was recovered.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co., paper, reel, roll, paper reel, paper roll, cargo, consignment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Paper, circa 1908
These sheets of paper were from a roll or reel of paper that was part of a consignment carried as cargo of the Falls of Halladale. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four-masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The roll of paper from which the sheets were cut is an example of cargo brought to Australia in the early 20th century. It is also significant for its association with the Falls of Halladale shipwreck, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Wad of paper sheets that was cut from a roll of paper. Three sides of the sheets are straight and the other side is rough due to exposure to sea water for many years. The roll was part of a large consignment of paper listed on the cargo manifesto of the wreck of the ship Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co., paper, paper reel, paper roll, cargo, consignment, paper sheets, wad of paper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessel - Sailing Ship, Foyle Photographic Studio, 1908
The photograph is of the sailing ship Falls of Halladale. The ship is in shallow water at Peterborough where it sank on November 14th 1908. The inscription on the photograph reads "Nov 4th 1908". The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The photograph shows the ship Falls of Halladale in full sail, demonstrating the sails used for power at sea.A sepia landscape photograph; image of a sailing ship in shallow water in full sail. The vessel is the"Falls of Halladale" aground off Peterborough 1908. A figure is in the foreground. Photographed in 1908 by Foyle of Warrnambool. A pencil inscription on the back is underlined. A white sticker is attached.In pencil on reverse "The Falls of Halladale / Wrecked at Peterborough / Nov 4th 1908" [Note: the ship was wrecked on Nov 14th 1908] On white sticker "131"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, photograph, falls of halladale, sailing ship, vessel, shipwreck, foyle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Photograph of the Falls of Halladale, at Peterborough 1908On back Foyle, Liebig St, Warrnambool flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, peterborough, photograph, foyle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole Frame, Russell & Co, ca. 1886
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Porthole frame, from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale, porthole and glass missing, brass with screw dog (part broken) and one hinge, eight retaining bolt holes. flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, porthole frame, ship’s fitting, brass porthole, reconditioned porthole, falls of halladale, russell & co., porthole -
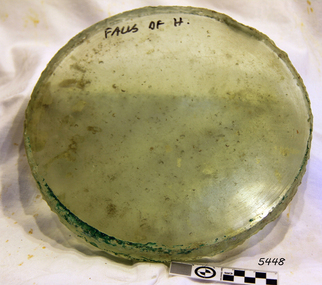 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole Glass
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Porthole Glass, from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale, little encrustation. "Falls of H" written in black texta penporthole glass, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSheave
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Wooden sheave from a block, from the wreck of The Falls of Halladale SW 13/1.74flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, block -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCap Liner
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Zinc Cap Porcelain liner, placed inside the zinc cap to stop the contents of the jar reacting with the zinc. Recovered from wreck of the "The Falls of Halladale". Artefact Rego No FoH 16.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, 1908 shipwreck -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageChair piece
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today in the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Chair piece, varnished wooden backstop from the chair with floral and leaf motif, from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, chair -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Crucible, The Patent Plumbago Crucible Company, circa 1878
This crucible was raised from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It is one of six similar relics, in a range of sizes, now in the Flagstaff Hill collection. All bear markings to indicate their manufacture by the Morgan brothers of Battersea, trading as the Patent Plumbago Crucible Co. A crucible is a container used for purifying and melting metals so that they can be cast in a mould to a predetermined shape and use. They must withstand extremely high temperatures, and abrupt cooling, and shed their contents with minimal adherence. The addition of graphite to the traditional firing clays greatly enhanced the durability of industrial crucibles in mid-Victorian Britain, a significant technological advance at a time of great activity in foundries and expansion of demand for refined metals. The Morgans first noticed the advantages of graphite crucibles at the Great Exhibition held in London in 1851. Initially, they contracted to be sole selling agents for the American-made products of Joseph Dixon and Co. from New Jersey, but in 1856 they obtained that firm’s manufacturing rights and began producing their own graphite crucibles from the South London site. The Morgans imported crystalline graphite in 4-5 cwt casks from the British colony of Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) and mixed it with conventional English (Stourbridge) clays to be fired in kilns. Their products were purchased by the Royal Mints in London and India, and exported to official mints in France and Germany. They were successful exhibitors of their crucibles and furnaces at the London Exhibition held in 1861 (Class 1, Mining, quarrying, metallurgy and mineral products, Exhibit 265, Patent Plumbago Crucible Co). The range of sizes represented by the six crucibles retrieved from the LOCH ARD, suggests they may have been part of a sample shipment intended for similar promotion in the Australian colonies ― at Melbourne’s International Exhibition to be held in 1880. The summary of the LOCH ARD cargo manifest, by Don Charlwood in ‘Wrecks and Reputations’, does not mention any crucibles, implying that they were not a large consignment of uniform items. A newspaper account of an 1864 tour of the Morgan brothers’ ‘Black Potteries’ at Battersea indicates: “All the pots were numbered according to their contents, each number standing for one kilogram, or a little over two pounds; a No. 2 crucible contains two kilogrammes; a No. 3, three kilogrammes, and so on.” These numbers are obscured by marine sediment on three of the crucibles in the Flagstaff Hill collection, but those legible on the remaining three are 5, 6, and 8. None of the six is of the same size from a visual appraisal. A brief history of the Loch Ard (1873-1878): - The sailing ship Loch Ard was one of the famous Loch Line of ships that sailed the long voyage from England to Australia. Barclay, Curdle and Co. built the three-masted iron vessel in Glasgow in 1873. It had sailed three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of recently married, 29-year-old Captain Gibbs. It was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, and a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. Other cargo included items intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The Loch Ard had been sailing for three months and was close to its destination on June 1, 1878. Captain Gibbs had expected to see land at about 3 am but the Loch Ard ran into a fog that greatly reduced visibility and there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. The fog lifted at 4 am and the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast were much closer to them than Captain Gibbs expected. He tried to manage the vessel but failed and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck loosened from the hull, and the masts and rigging crashed down, knocking passengers and crew overboard. The lifeboat was launched by Tom Pearce but crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. He clung onto its overturned hull and sheltered under it. He drifted out to sea and the tide brought him back to what is now called Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore and found a cave for shelter. A passenger, Eva Carmichael, had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening and was confronted by towering cliffs above the ship. She was soon swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He swam out and dragged her to the shelter of the cave. He revived her with a bottle of brandy from a case that had washed up on the beach. Tom scaled a cliff in search of help and followed some horse hoof prints. He came from two men from Glenample Station, three and a half miles away. He told the men of the tragedy and then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. They reached Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome and was presented with a medal and some money. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Register S417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best-known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.A Morgan’s Patent graphite crucible No.8 (i.e. 8kgs capacity), one of a set. It was recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It is in its original grey colouring with minimal sediment accretion on the top rim. It rises in a slight curve from a flat circular base to a wider rim with a pouring lip. Maker’s marks on the side of the container clearly identify the manufacturer. The maker's details are stamped into the base around and within a circle. A white sticker is attached. Made by the Patent Plumbago Crucible Company at the Battersea Works in London. Number “8”. Letters “MORGAN’S PATENT”. Details on the base "MORGAN'S PATENT" "THE PATENT PLUMBAGO CRUCIBLE COMPANY" Symbol [8] above "BATTERSEA WORKS LONDON" Handwritten on a white sticker in black pen "LA/89"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, graphite crucible, plumbago crucible, morgans crucible company, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, fluxing pots, crucible, morgan’s patent, morgan brothers, patent plumbago crucible co, battersea works, london, port campbell -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Crucible, The Patent Plumbago Crucible Company, circa 1878
This crucible was raised from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It is one of six similar relics, in a range of sizes, now in the Flagstaff Hill collection. All bear markings to indicate their manufacture by the Morgan brothers of Battersea, trading as the Patent Plumbago Crucible Co. A crucible is a container used for purifying and melting metals so that they can be cast in a mould to a predetermined shape and use. They must withstand extremely high temperatures, and abrupt cooling, and shed their contents with minimal adherence. The addition of graphite to the traditional firing clays greatly enhanced the durability of industrial crucibles in mid-Victorian Britain, a significant technological advance at a time of great activity in foundries and expansion of demand for refined metals. The Morgans first noticed the advantages of graphite crucibles at the Great Exhibition held in London in 1851. Initially, they contracted to be sole selling agents for the American-made products of Joseph Dixon and Co. from New Jersey, but in 1856 they obtained that firm’s manufacturing rights and began producing their own graphite crucibles from the South London site. The Morgans imported crystalline graphite in 4-5 cwt casks from the British colony of Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) and mixed it with conventional English (Stourbridge) clays to be fired in kilns. Their products were purchased by the Royal Mints in London and India, and exported to official mints in France and Germany. They were successful exhibitors of their crucibles and furnaces at the London Exhibition held in 1861 (Class 1, Mining, quarrying, metallurgy and mineral products, Exhibit 265, Patent Plumbago Crucible Co). The range of sizes represented by the six crucibles retrieved from the LOCH ARD, suggests they may have been part of a sample shipment intended for similar promotion in the Australian colonies ― at Melbourne’s International Exhibition to be held in 1880. The summary of the LOCH ARD cargo manifest, by Don Charlwood in ‘Wrecks and Reputations’, does not mention any crucibles, implying that they were not a large consignment of uniform items. A newspaper account of an 1864 tour of the Morgan brothers’ ‘Black Potteries’ at Battersea indicates: “All the pots were numbered according to their contents, each number standing for one kilogram, or a little over two pounds; a No. 2 crucible contains two kilogrammes; a No. 3, three kilogrammes, and so on.” These numbers are obscured by marine sediment on three of the crucibles in the Flagstaff Hill collection, but those legible on the remaining three are 5, 6, and 8. None of the six is of the same size from a visual appraisal. A brief history of the Loch Ard (1873-1878): - The sailing ship Loch Ard was one of the famous Loch Line of ships that sailed the long voyage from England to Australia. Barclay, Curdle and Co. built the three-masted iron vessel in Glasgow in 1873. It had sailed three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of recently married, 29-year-old Captain Gibbs. It was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, and a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. Other cargo included items intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The Loch Ard had been sailing for three months and was close to its destination on June 1, 1878. Captain Gibbs had expected to see land at about 3 am but the Loch Ard ran into a fog that greatly reduced visibility and there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. The fog lifted at 4 am and the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast were much closer to them than Captain Gibbs expected. He tried to manage the vessel but failed and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck loosened from the hull, and the masts and rigging crashed down, knocking passengers and crew overboard. The lifeboat was launched by Tom Pearce but crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. He clung onto its overturned hull and sheltered under it. He drifted out to sea and the tide brought him back to what is now called Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore and found a cave for shelter. A passenger, Eva Carmichael, had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening and was confronted by towering cliffs above the ship. She was soon swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He swam out and dragged her to the shelter of the cave. He revived her with a bottle of brandy from a case that had washed up on the beach. Tom scaled a cliff in search of help and followed some horse hoof prints. He came from two men from Glenample Station, three and a half miles away. He told the men of the tragedy and then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. They reached Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome and was presented with a medal and some money. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Register S417 Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best-known ahipwrecks in Victoria’s history.A Morgan’s Patent graphite crucible No.4 (i.e. 4kgs capacity), one of a set of three. It was recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It is in its original grey colouring with minimal sediment accretion on the top rim. It rises in a slight curve from a flat circular base to a wider rim with a pouring lip. Maker’s marks on the side of the container clearly identify the manufacturer. The maker's details are stamped into the base around and within a circle. A white sticker is attached. Made by the Patent Plumbago Crucible Company at the Battersea Works in London.Number or. Letters “MORGAN’S PATENT”. Details on the base "MORGAN'S PATENT" "THE PATENT PLUMBAGO CRUCIBLE COMPANY" Symbol [4] above "BATTERSEA WORKS LONDON" Handwritten on a white sticker in black pen "L89"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, graphite crucible, plumbago crucible, morgan's crucible company, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, fluxing pots, crucible, morgan’s patent, morgan brothers, patent plumbago crucible co, battersea works, london, port campbell -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, C. 1915 - 09/07/1917
This black and white photograph of the tugboat NYORA towing the steam ship INVERNESS-SHIRE was taken between 1915, when the INVERNESS-SHIRE was dis-masted, and 9the July 1917, when NYORA tragically sank. The sailing ship INVERNESS-SHIRE was a four masted steel barque built in 1894 by Robert Duncan & Co. Limited, Glasgow, U.K. (The supervising engineer during the building was William Cumming. He accompanied every ship he’d built on their maiden voyages from UK to Melbourne.) In 1916 she was purchased by A/S Christiansand (Sven O. Stray), Kristiansand, Norway and renamed SVARTSKOG. In October 1920 she disappeared at sea, carrying a cargo of coal, and all hands were lost. The steam powered NYORA was a powerful tugboat and a salvage vessel built by J.P. Rennoldson & Sons Ltd, South Shields, Tyne and Wear, UK. She was originally launched with the name NEPEAN in May 1909, then as NYORA in August 1909 and registered in Melbourne in November 1909 by owners Huddart Parker Pty Ltd. She was made of steel, had triple-compounded steam engines, and her dimensions were 306 ton, 135.0 x 25.1 x 13.6ft. The Melbourne tug NYORA was known as “one of the best known tugs in Victoria, and carried the latest appliances for firefighting and salvage purposes.” She serviced the Port of Melbourne for most of her career. In July 1917 NYORA was towing the American schooner ASTORIA from Port Pirie to Sydney, because ASTORIA’s engines had broken down; she had been delivering a large cargo of timber. On July 9th the vessels were two days out from Port Pirie. At 10:30am NYORA foundered after casting off at Cape Jaffa, 50 miles south of Kingston, South Australia, and sank. Only 2 of the 16 crew survived; NYORA’s Master, Captain W.M. McBain (William Murray) and helmsman, able seaman Gordon Lansley. They were rescued by the two Cape Jaffa light keepers, Jamieson & Clark, who launched the rescue from the Cape Jaffa lighthouse on Margaret Brock Reef. Both men were brought to the lighthouse keeper’s cottage where they recuperated after their long exposure to the rough. (The Queenscliff Sentinal of 14th July 1917 noted that both saved men originated from the same district; Gordon Lansley was from Queenscliff and Captain McBain formerly from Point Lonsdale.) The ASTORIA was “in a very dangerous position ten miles west of the Margaret Brock reef near the Cape Jaffa lighthouse, setting towards the land.” Captain Solly from Beachport later said “Owing to the position … the ship was very fortunate in making Guichen Bay in safety, as she did” (Guichen Bay is south of Robe). Captain Bull, manager of Huddart Packer Pty Ltd, NYORA’s owner, was unable to see any reason for the foundering, as the NYORA was well known for its seaworthiness. At a hearing later on, the Marine Board could blame on no-one either, but found that the ship had been swamped by heavy seas, and had listed to one side when a load of 40 tons of coal in sacks on her deck shifted. The tow line to the ASTORIA was cut to try and save the tug but a huge wave swamped her, crashed open the engine room door and flooded the compartment. It was impossible to launch the lifeboats due to the listing of the sea and NYORA sank within 15 minutes. There was some criticism of the length of time it took Captain Solly and the lifeboat crew to get from Beachport to Cape Jaffa to help with the rescue. However, they had great difficulty in the very strong seas, taking 9 hours just to reach Robe, which was only 32 miles away. There they filled the tanks with ample benzene for the task ahead (impossible to do at sea at the time), took in food and brought on board the Robe Harbour Master, Mr Sneath. The Harbour Master was then able to safely pilot the lifeboat to Cape Jaffa in the smoother coastal waters, saving very much time, but by the time they arrived at Cape Jaffa the 2 survivors had already been taken to the lighthouse on the mainland. There was also a question as to the chances of the ship ASTORIA lowering a lifeboat to help with the disaster. Captain Solly explained that it would have been impossible without sacrificing the lives of the lifeboat crew , due to the great height of the ship out of the water and the roughness of the sea. Captain Svenson, of the ASTORIA, said himself “We are ourselves in a helpless position” and “"Cannot see anything of lifeboats”. One of the 14 lost crew of the NYORA was Hugh Edwards, whose body was not recovered. The descendants of Captain William McBain have continued the seafaring heritage. His son was also a tugboat captain (Captain Norman Clive McBain), working mostly from Reid Street Pier, Williamstown, who would often take his own grandson out to sea to spend time with him on his tugboat. Now that grandson has built a tugboat in memory of his heritage and spends time in it with his own grandson. The Cape Jaffa original lighthouse has been dismantled and moved to Kingston and is now a Lighthouse Museum. The attached photographs of Margaret Brock Reef, and the Cape Jaffa Lighthourse keeper's cottage (now in ruins) is courtesy of Capt. William McBain's great grandson, who visited the area in 2015. There is a model of the NYORA in Museum Victoria, donated by Huddart Packer & Co Ltd. in 1937. This photograph is significant for its association with the tugboat NYORA, that is part of the seafaring history of the Port of Melbourne and associated Victorian ports. Black and White photograph of the tugboat NYORA and steam ship INVERNESS-SHIRE. C. 1915-1917.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, historic maritime photograph, lighthouses, shipwrecks, steamships, j.p. rennoldson & sons ltd, huddart parker pty ltd, nepean, nyora, inverness-shire, astoria, captain w.m. mcbain, william cummings supervising engineer, cape jaffa lighthouse, beachport lifeboat, captain solly, captain svenson, margaret brock reef -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCribbage Board
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Cribbage board, with inscription "Falls of Halladale Wrecked Peterborough Nov. 1908" Falls of Halladale Wrecked Peterborough Nov. 1908flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, cribbage board, falls of halladale, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLids
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Round glass lids (2) from Falls of Halladale wreck. Lids are semi-opaque due to sand abrasion. Artefact Reg No FoH/16.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lids, lid, falls of halladale, round glass lids, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCap Liner
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Round glass lid, from Falls of Halladale wreck. Artefact Reg No FoH/16.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, cap liner, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBulls Eye
Brought ashore by L Presse, Cadet Deck Officer on the "Falls of Halladale" after the wreck, The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today in the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Carved wooden Bulls Eye, varnished, from the Falls of Halladale wreck. Peterborough, 1908. Brought ashore by L. Piesse. Cadet Deck Officer from the Falls of Halladaleflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, l presse, falls of halladale, bulls eye, peterborough, 1908 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Diamond ring, about 1855
In 1975, 120 years after the sailing ship Schomberg was wrecked, Flagstaff Hill divers (Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden) found an ornate communion set amongst the wreckage. The set comprised a jug, ciborium, lid, chalice and plate. The items, apart from the lid, were then displayed at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The lid had etchings that did not match the chalice and sat in storage for several years. Then in 1978, while the marine concretion inside the lid was being examined, a surface layer came loose and revealed a glint of gold that was assumed to be a piece of brass. The layers of concretion were carefully removed and a ring-like band emerged. Further treatment exposed a 'large faceted stone in an intricate gold setting. Weeks later a detailed examination estimated the value of the ring, known as the Schomberg Diamond, to be $7000. When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen at a cost of £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, an oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. Land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signaled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in 825 meters of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. The actual lid in which the ring was found has not yet been completely identified and could belong to a coffee pot, sugar bowl or maybe a jug or something similar. Although all survived the wreck no-one came forward to claim the valuable diamond. The Schomberg Diamond is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village along with the rest of the communion set. Other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. One of the Schomberg bells is in the Warrnambool Library.The Schomberg Diamond is particularly significant in that it played a crucial part in having the legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter control over the salvaging of items from wreck sites. This ring is registered as Artefact S/105 in the Schomberg collection, the Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significant because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes. A mid-Victorian gentleman's solitaire diamond dress ring with a Brazilian cut diamond (cushion cut), one and one-third carat set within an 18 carat yellow gold ring consisting of four claws within an open scroll setting and a divided scroll shank. Colour is classified as 'J', clarity SII. The setting is handmade. warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, schomberg, shipwrecked-artefact, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, ciborium, ring, schomberg-diamond, schomberg-ring, gentleman's ring, dress ring -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Photograph of the Falls of Halladale at Peterborough with sails unfurled. Black and white with cardboard backing. Cardboard torn, photo is fading.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, photograph, 1908 shipwreck -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole Frame, Russell & Co, ca. 1886
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Porthole rim with the hinge and two flanged extensions. The ship's fitting was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladaleflagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, porthole, porthole frame, porthole rim, ship’s fitting, brass porthole, reconditioned porthole, falls of halladale, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWood Sample
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today in the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).A sample piece of rectangular wood from the Falls of Halladale. Date 2/2/17 Jean Howley. Heart with an arrow through it on back.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, wood sample -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHinge
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Hinge, brass. Artefact Reg No FoH/10, recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co., hinge -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCap Liner
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Glass Lid, some encrustation. Artefact Reg No FoH/16, recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, cap liner, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFabric
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Small piece of fabric that has been coated with unknown substance, very fragile. From the wreck of the Falls of Halladale.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, fabric, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Chart Case
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Chart Case, copper with screw-plug at one. Holed, heavily corroded and etched away. Artefact Reg No FoH/8, recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co., chart case -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePacking Strip
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Wooden Packing Strip from the slate stacks, Artefact Reg No FoH/16, recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co., packing strip -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Paper, circa 1908
This wad of paper is a section from a bale of paper that was recovered from the Falls of Halladale. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The section of paper has significance through its association with the Falls of Halladale. The shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Paper wad; a section of a bale of many sheets. The paper has several layers and shows the effects of being in the sea for many years. It was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, falls of halladale, shipwreck peterborough, 1908 shipwreck, great clipper ships, russell & co., paper, bale of paper, ream of paper, wad of paper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGeological specimen - Slate, c. 1908
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roof tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roof tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Californian, American, rectangular blue roof slate tile, recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale., slate, roof slate, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGeological specimen - Slate
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roof tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roof tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. SIGNIFICANCE The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976). Californian, American, blue roof slate tile, rectangular shape, recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, slate, roof slate, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGeological specimen - Slate, c. 1908
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roof tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roof tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Californian, American, rectangular blue roof slate, recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, slate, roof slate, russell & co.
