Showing 7829 items matching "white pages"
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - White-Throated Treecreeper, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The White-throated Treecreeper is a commonly small bird of the Climacteridae family, that has a loud, piping, whistle-like call. Living in permanent territories and rarely seen on the ground, this species is found in forested areas of south-east and southern mainland Australia. The name tree-creeper comes from their foraging patterns, in which they spiral up the trunk of trees (usually eucalypts for their preferrable rough bark) head-first, probing for ants or nectar with their long, curved beak.The females are distinct from males through orange marks on the sides of their face. The colour of these specimens differ from white-throated tree-creepers, whose plummage on the head and back is usually a dark gray-brown. The beaks of these specimens are also an orange-brown colour whereas these birds usually have a black beak. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This mount includes two White-throated treecreepers secured on a stick, one above the other. The top specimen is female, distinguished by a distinctive orange mark on the sides of its face underneath the eyes. Both specimens have white throat, chest and streaks on the flank. The top of the head and back are both a brown to dark-brown colour, with streaks of those colours on the flank as well. The stick and specimens are mounted on a wooden platform and a swing tag is secured around a part of the stick.Swing tag: 67a. / White-throated treecreeper / See catalogue, page 20 / Wooden Mount: 85taxidermy mount, taxidermy, burke museum, beechworth, bird, treecreeper, australian birds, white-throated, white-throated treecreeper, reynell eveleigh johns -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Green Woodpecker, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This fairly large woodpecker of the Picadae family is widely distributed across most parts of Europe and the UK, with some occurrence in Western Asia. Preferring semi-open habitats such as woodlands, heathlands and gardens, the species is unique amongst woodpeckers as it prefers to hunt and feed on the ground for its ant prey. This species has a distinctive bright red crown, black moustasche-like stripes, mostly green back plumage and a paler green to yellow breast. This is a female of the species as the male has a red centre to the moustache stripe at the side of the beak. This specimen is a fairly accurate depiction of a Green Woodpecker. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Green Woodpecker has a distinctive red crown on its head that appears patchy. It has a black face, a black moustache-like stripe on each side of the beak, pale eyes and long light yellow-orange beak. The back of the bird is green, and its flank and breast is a pale cream-yellow colour. It has slightly visible distinct white-dotted brown feathers folded into its wings. The specimen is mounted on a wooden perch, with a metal tag tied around its right leg and a paper tag around each leg.Swing tag: 1e. / Green Woodpecker / Catalogue page 66 / Metal tag: 4308 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, woodpecker, green woodpecker, eurasian green woodpecker -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Satin Bowerbird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Satin Bowerbird is a medium-sized common bird found from Queensland to Victoria in rainforests and wet sclerophyll forest. During the summer, the diet consists mostly of fruit, with insects as a supplement. They're famous for their courtship behaviour and for decorating stick-structured nests with blue sparkling objects. With it's stunning glossy blue-black feathers, which evolve from green-brown in appearance, this Satin Bowerbird is more than seven years old, and therefore not any younger as they are often mistaken for females, which are supposed to look like the green catbird. The eyes of this mature male are violet-blue, and the bill is pale bluish white. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.Satin Bowerbirds are medium-sized birds. The adult male has striking glossy blue-black plumage, a pale bluish white bill and a violet-blue iris.47a / Satin Bower-bird / See Catalogue, page 16 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, satin bowerbird, bowerbird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Nankeen Kestrel, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Nankeen Kestrel, a small type of falcon, can be found all over Australia, usually in grassland or farmland areas. This falcon is carnivorous and hunts all manner of small prey including mice, lizards, insects, and other birds. When hunting, Nankeen Kestrels can be seen hovering in the air searching for prey. Nankeen Kestrels are generally monogamous, staying with the same breeding partner for multiple seasons. The Nankeen Kestrel is known for its reddish-brown feathers, spotted with a distinctive black pattern on its back, and have black-tipped wings and tail band, a stark contrast to its white chest. Females tend to be larger, and males will have a grey head and neck area. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Nankeen Kestrel is relatively small and slender. It is mostly reddish-brown, streaked with darker coloured areas. The tips of the wings and tail feathers are tipped in black. The chest is white with streaks of reddish-brown. The areas around its eyes, beak, and feet are a bright yellow. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing-tag: 19. / Unnamed / Catalogue page, 5 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, nankeen kestrel, falcon -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Magpie-Lark, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Magpie-Lark, also commonly known as a Mudlark, is a carnivorous bird found in many regions of Australia, Indonesia, Timor, and Southern New Guinea. They are a non-migratory species and are extremely adaptable to a variety of environments. These environments include dry forest, savannah, grassland, and even urban areas. Magpie-Larks are typically monogamous and are often found in pairs. They are black and white, with a white underbelly, long legs, and a long, thin beak. The females of this species have a white throat, while the males have a white eyebrow and a black throat. While juveniles have dark eyes, mature adults have light irises. This information helps identify this specimen as an adult male. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Magpie-Lark is a small to medium-sized bird which has distinctive black and white colouring. The bill is long and thin and is a whitish colour which differentiates it to other Magpie species. When mature, like this particular specimen, the Magpie-Lark have distinctive light irises. The glass eyes provided for this specimen are accurate in colour. This male specimen has a white 'eyebrow' marking and a black chest or bib. This Magpie-Lark stands on a wooden mount with a swing tag attached to its leg.Swing-tag: 20a. / Reed Grallina / See catalogue page 10 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, mudlark, magpie-lark -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Red Headed Woodpecker, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Red Headed Woodpeckers can be found in Southern Canada and a large portion of the United States of America, generally migrating to the south if they originated in the northern regions. Their habitat is open forests or savannahs. They are classed as omnivores, finding food from pecking at wood or in flight. The Red Headed Woodpecker is threatened in Canada and some areas of the United States due to deforestation, lack of deadwood for nesting, competition with other birds, and a lack of food. They are an important part of the ecosystem, controlling insect populations and pollinating flora. Red Headed Woodpeckers typically have a beautiful, vibrant red neck and head, a stark white chest, black back, and black wings with white secondary remiges. They have a large chisel-like beak, suitable for foraging for their food. Their heads are rounded and they have short tails. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Red Headed Woodpecker is a small to medium-sized bird found in North America. This specimen is tricoloured: it has a red head and neck, a white chest, a black back, and black wings with white secondary remiges. It has a large chisel-like beak. This specimen has pest or humidity damage on the neck and head area. This specimen is standing on a wooden mount with a swing tag attached to it's leg.Swing-tag: 151a. Unnamed / Catalogue page, 60 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, red headed woodpecker -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Barking Owl (Female), Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Barking Owls are a nocturnal, medium sized bird of prey native to Australia, parts of Papua New Guinea, and the Moluccas. Average size ranges between 390-440mm in length. Females are generally slightly smaller than males and they are only one of a small number of owl species that do not exhibit marked sexual dimorphism. Barking Owls have characteristic vocalisations, ranging from a 'woof woof' barking dog sound, to shrill, human-like screams, which reportedly alarmed early European settlers to Australia. The Barking Owl's shrill and explosive vocalisation is sometimes associated with Bunyip mythology or referred to as 'the screaming woman call'. The female call is slightly higher in pitch than the male, and males and females often duet, contrasting low and high pitches. Barking Owls may be vulnerable in some parts of Australia due to woodland habitat loss. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Barking Owl is of an average size. It has brown, grey and white spots and vertical streaks. The face and breast are lighter in colour than the wings and the dorsal plumage. The glass eyes are large and dark in colour while the tarsi and toes are yellowish. This specimen stands on a wooden perch with identification tags attached to its leg. [torn] / 16. / Winking Owl / See catalogue Page, 4 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, owls, barking owls, screaming woman call, yowing, woodland birds, birds of prey, australian owls, endangered, loss of habitat, woodland habitat, bunyip, australian early settler mythology -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Barking Owl (Male), Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Barking Owl is a nocturnal, medium sized (390-440 mm) bird of prey native to Australia, parts of Papua New Guinea, and the Moluccas. Males are generally slightly larger by weight than females and they are only one of small number of owl species that do not exhibit marked sexual dimorphism. Barking Owls have characteristic vocalisations, ranging from 'a 'woof woof' barking dog sounds to shrill, human-like scream sounds, which reportedly alarmed early European settlers. The Barking Owl's shrill and explosive vocalisation is sometimes associated with Bunyip mythology or referred to as 'the screaming woman call'. The male call is slightly lower in pitch than the female, and males and females often duet, contrasting low and high pitches. The owls are brown-grey in colour with white spots on the wings and vertically streaked chest. Their eyes are large and yellow. Barking Owls may be vulnerable in some parts of Australia due to woodland habitat loss. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century. This male Barking Owl is average sized with brown, grey and white spots and vertical chest streaks. The face and breast are lighter in colour than the wings and dorsal plumage. The eyes are large and dark and the legs and feet are yellowish. The eyes are large and yellow irises and the legs and feet are yellowish. The specimen stands on a wooden perch pedestal with identification tags attached to its leg. 17. / Bookook Owl / See catalogue page, 4 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, owls, barking owls, screaming woman call, yowing, woodland birds, birds of prey, australian owls, endangered, loss of habitat, woodland habitat, bunyip, australian early settler mythology -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Noisy Friarbird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Noisy Friarbird are conspicuous and active Honey-eaters mainly seen in small groups and often active in flowering plants, especially eucalyptus trees. Noisy Friarbirds are found along the east coast of Australia, from north-eastern Queensland to north-eastern Victoria. They often feed in noisy flocks, alongside other Honey-eaters such as the Red Wattlebird. This specimen has been mounted in an accurate, yet stylised fashion. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Noisy Friarbird has a characteristically black head which lacks plumage and has a prominent casque (bump) on the base of its strong bill. The specimen has an off-white underbody and neck, a light brown back and tail with a white tip at the end of the tail. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.59a / Friarbird / See Catalogue Page 18 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, bird, noisy friarbird, friarbird, australian birds, oz animals, wattlebird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Bassian Thrush, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Bassian Thrush is a secretive bird, often difficult to see, as it is an unobtrusive species that forages among dense vegetation. When disturbed, it sometimes crouches on the ground and freezes, relying on its scalloped plumage to conceal its presence. The Bassian Thrush feeds on the ground, scratching under the leaf-litter for small invertebrates. This specimen has been mounted in an accurate and yet stylised fashion. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century. This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The plumage of this Bassian Thrush specimen is a mottled brown to olive-brown colour, heavily scalloped with black crescent-shaped bars on the back, rump and head. The paler underparts all have brown-black scalloping. It has a white eye-ring which surrounds glass eyes which have been included by the taxidermist to replace the originals. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing Tag: 44a / mountain Thrush / See Catalogue Page 15 taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, bird, australian birds, bassian thrush, thrush, zoothera lunulata -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Grey Shrike-Thrush, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Grey Shrike-thrush is considered to be one of the best songsters in Australia, with hundreds, if not thousands, of different songs. The song has been described as glorious, pleasing and melodious, with sweet, mellow, rich and liquid notes. Whilst pleasant to humans, the song are less harmonious for nest birds, often hunted by the grey shrike-thrush. It has a varied diet consisting of insects, spiders, small mammals, frogs and lizards, and birds' eggs and young. Grey Shrike-thrushes most of Australia (with the exception of arid areas) and southern New Guinea. This specimen has been mounted in an accurate fashion. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Grey Shrike-thrush specimen is a mostly grey coloured bird, with the plumage around the shoulders a little browner. The underside and neck is paler, off-white with a white ring around the eye. The eyes are made of glass which is a brown colour and replace the original which do not survive the taxidermy process. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.27a / Harmonious Shrike-Thrush / See Catalogue Page 12 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, bird, australian birds, thrush, grey shrike-thrush, harmonious thrush, colluricincla harmonica -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Bassian Thrush, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The habitat of the Bassian Thrush includes leaf littered and canopied gullies and dense forests. It forages for food on the ground eating small invertebrates and nests in tree stumps and tree forks. Primarily found in Tasmania, South Australia and Queensland, there are three sub-species of thrush, Zoothera lunulata cuneate (Queensland), Zoothera lunulata halmaturina (South Australian and Western Bassian Thrushes) and Zoothera lunulata lunulata/Zoothera lunulata macrorhyncha (South East Australia, Queensland, Victoria and Tasmania). Because this bird is a ground foraging species, the main threat to the Bassian Thrush is the ground clearing of its habitat, and unfortunately, the South Australian Zoothera lunulata halmaturina sub-species is considered vulnerable because of the bush fires that have eliminated much of its habitat, especially on Kangaroo Island. While the overall structure of this particular representation of a Bassian Thrush is relatively accurate, some of the smaller details are lacking. The eyes within this particular specimen are not accurate. Instead of solid black eyes, this specimen has golden/yellow eyes with black pupils. Another inaccuracy is some inappropriate intrusions coming from the beak (most noticeable in the left and right close up images). From the photographs, it is unclear if this is a representative/presentation choice or a condition problem caused overtime. Unfortunately, several aging problems have also occurred over time, with the bird’s feathers fading (Bassian Thrushes have distinct dark brown and black and white scalloped plumage) and the beak which was probably once dark grey has faded to the under colour, a yellowy cream. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Bassian Thrush has white and black scalloped plumage on its underbelly with caramel, soft brown and black tipped scalloped plumage on its back. This soft brown continues onto the bird’s head and neck. The thrush has a white rim around the glass black eyes. When seen in flight, there is also a noticeable wide band across the underside of the wings which is not visible on this specimen due to its particular stance.Swing tag appears to read: ‘46a [the a is superscripted] / Mountain Thrush. / See Catalogue, Page 16. / The number in the top centre of the wooden perch reads '63'taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, bassian thrush, zoothera lunulata, white's thrush, ground thrush, scaly thrush -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Morepork, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Morepork is a small brown and white spotted owl found in New Zealand, Tasmania and Norfolk Island. It is known by around twenty different names which are all onomatopoeic which emulate the birds distinctive two-pitched call. They are mostly nocturnal and carnivorous (eating insects and small vertebrates). They reside in habitats with trees, they sleep in roosts and hunt mainly in the evenings and early morning. Females are slightly bigger than males. This species attains full plumage in its third or fourth year. They can turn their heads 270 degrees." In Māori tradition the morepork was seen as a watchful guardian. It belonged to the spirit world as it is a bird of the night. Although the more-pork or ruru call was thought to be a good sign, the high pitched, piercing, ‘yelp’ call was thought to be an ominous forewarning of bad news or events." (NZ Department of Conservation). This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Morepork (also known as the Masked Owl) is covered in brown and white plumage on its head and body. The white feathers delineate its round yellow eyes. Its belly and back are brown and white with the white feathering appearing spotted. This Morepork specimen sits on a wooden perch with his head turned to the left. A swing tag is attached to its left leg.Swing tag: 10 / Masked Owl / See Catalogue, page 3 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, ruru, spotted owl, tasmanian spotted owl, morepork, mopoke, new zealand owls, new zealand birds, tasmanian owls, tasmanian birds, norfolk island owls, norfolk island birds -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Black Shouldered Kite, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Black Shouldered Kite is commonly found throughout mainland Australia in grasslands and other open habitats. It is a raptor (bird of prey) that will eat mice and other small rodents. The species is monogamous and will find a mate by the male giving food to the female while both are in flight. It is sometimes confused with the letter-winged kite though there undercarriages when in flight are very different with the letter-winged showing the letter W or M and the black shouldered kite showing black wing tips with white towards its belly area. The feathers of this species when alive and in the wild are more white than this specimen. The iris is usually red in mature birds so this specimen may not have been a mature bird as its eyes are brown. However, this is difficult to ascertain because it is also possible that the taxidermist who replaced the original eyes with the current glass ones provided a colour which was not accurate to the age/species of the bird. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Black Shouldered Kite has a white face and front of body with a grey posterior from the top of its head to its tail. It has black on its wings/shoulders. Its face is white with its eyes delineated by small black apostrophe like shapes from the inner eye to the top of the eye. The specimen stands on a wooden perch and has a swing tag tied around its right leg. Its eye colour is brown rather than red, indicating it is not a mature specimen.9. / Black Shouldered Kite / See Catalogue, page 3 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, black shouldered kite -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Morepork, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Morepork is a small brown and white spotted owl found in New Zealand, Tasmania and Norfolk Island. It is known by around twenty different names which are all onomatopoeic which emulate the birds distinctive two-pitched call. They are mostly nocturnal and carnivorous (eating insects and small vertebrates). They reside in habitats with trees, they sleep in roosts and hunt mainly in the evenings and early morning. Females are slightly bigger than males. This species attains full plumage in its third or fourth year. They can turn their heads 270 degrees." In Māori tradition the morepork was seen as a watchful guardian. It belonged to the spirit world as it is a bird of the night. Although the more-pork or ruru call was thought to be a good sign, the high pitched, piercing, ‘yelp’ call was thought to be an ominous forewarning of bad news or events." (NZ Department of Conservation). This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Morepork (also known as a Masked Owl) is covered in brown and white plumage on its head and body. The white feathers delineate its round yellow eyes. Its belly and back are brown and white with the white feathering appearing spotted. He sits on a wooden perch with his head turned to the left. A swing tag is attached to its leg.11 / Masked Owl / See Catalogue, page 3 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, ruru, spotted owl, tasmanian spotted owl, morepork, mopoke, new zealand owls, new zealand birds, tasmanian owls, tasmanian birds, norfolk island owls, norfolk island birds -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Brown Falcon, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Brown Falcon is a small to medium bird of prey which can be found all throughout Australia. These birds are raptors and typically feed on mammals, birds, snakes, insects and rabbits. The Brown Falcon are located in all but the densest forests. They typically prefer to reside in locations of open grassland and agricultural areas which have scattered trees or telephone poles which the bird can perch on. When frequenting towns located in the Australian Outback, these birds are reportedly quite tame and can be approached by humans. They may stay in the same location throughout the year or chose to move around locally in response to any changes in weather conditions. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th centuryThis specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Brown Falcon specimen has plumage which is mostly brown and intermixed with white. This provides the appearance of having spotted colouring on the birds back. The head is also mostly brown with white under the beak area and a characteristic brown streak under the eye area. The eye is made from dark coloured glass.3 / Brown Hawk / See Catalogue, page 2 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, brown falcon, falconidae -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Merlin
This Merlin specimen is large for the falco columbarius species. It is brown and white in colouring which suggests that this particular specimen is female. This is because male Merlin's are usually blue, black, silver or grey. This species is predominantly found in the Northern Hemisphere. They are small, fast and highly skilled in hunting. The Merlin is generally a solitary bird outside of the mating season when it will socialise with other Merlins. The Merlin will consume smaller birds, mammals and bugs. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Merlin has a medium brown back with light brown and white speckled chest. The edges of her wings are dark brown and underneath her tail is white but also patterned in spots of light brown. It's bright yellow eyes are framed by tan coloured feathers and elaborate spotted patterns throughout it's body. Her small hooked beck ranges from orange to dark brown and feet are a faded yellow.Swing tag: 28 / Merlin / Catalogue, page 6 / Other swing tag: 56 / Falco / Cesalon Metal tag: 4033 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, bird, northern hemisphere, falcon, falco columberius, merlin, pigeon hawk -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Diurnal Owl / Ural Owl
Little owls (also known as the owl of Athena or owl of Minerva) usually prefer the warmer parts of Europe, North Africa and Asia, enjoying open country and agricultural land with high trees to swoop down upon their prey from. Their diet includes amphibians, small mammals, reptiles and insects that they also hunt from small holes in the ground. Little owls are monogamous and while they're usually solitary creatures, pairs who breed together will often stay together past breeding season. An Athene Noctua would usually be slightly smaller than this specimen. The colouring of browns and whites speckling the feathers is an accurate representation however the posture of a typical little owl would be more crouched, not so thin and tall. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Athene Nuctua (The Little Owl) is dark to medium brown with white specks all over the feathers. Large white spots are located on their wings/back. This specimen has some inconsistencies with how it has been styalised by the taxidermist. The tail curls in under itself where it should be straight and flat. There are several feathers which appear disheveled on the chest, shoulder and wing. The specimen is mounted on a wooden stand with paper and metal tags attached to the legs. Swing tag: 41. / Allied to / Diurnal Owl / Catalogue page 53 / Other tag: 31 / Strix Noctua / Holland Metal tag: 4061 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, bird, owl, little owl, athene noctua -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Pink-Eared Duck, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Pink-eared Duck can be found throughout Australia, commonly in locations that are timbered and near water. This species of Duck prefers to reside in areas which are shallow, temporary waters and on occasion may venture into open wetlands if with a large flock; however, this species is highly dispersive and often nomadic. The special bill of this Duck is designed to enable the bird to catch their food. The bill is fringed with grooves which filter out microscopic plants and animals from the water which makes up the birds diet. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Pink-Eared Duck is named for the small pink spot of feathers which feature on the sides of the drake's head. Another name for this bird is Zebra Duck because of the striking bold black and white striped plumage which decorates the duck's neck, breast and stomach. The bill is spoon shaped and the eyes are made of dark coloured glass and surrounded by brown colouring. The bird has brown wings and light coloured legs with webbed toes. This particular specimen stands on a wooden square platform. There are signs of damage on the platform and a wooden identification tag is tied to the upper right leg of the bird.6a./ Pink-eyed Duck / See Catalogue, page 39 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, duck, pink-eyed duck, pink-eared duck -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Superb Lyrebird, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Superb Lyrebird is a large ground-dwelling bird with powerful legs and long tail. Found in rainforest habitats in southeastern Australia, it forages in leaf litter for food. It has a very powerful song and is known for mimicking other species. The males have spectacular long tail comprising a variety of feather types, where juveniles and females lack the longer tail feathers. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Superb Lyrebird is primarily grey/brown. It has shorter tail feathers than the male, which are dark and light brown, and vary in size. The bird's wings, chest and belly are a lighter grey/brown, and there are hints of yellow-white in the edges of the feathers and through the bird's chest. The bird has strong legs and a small beak. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform.37a. / Lyrebird / See Catalogue, page [illegible] /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, superb lyrebird -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Snowy Owl, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860- 1880
The Snowy owl is a large and powerful bird. It is one of the largest species of owl, and in North America, it is on average the heaviest owl species. The adult male is virtually pure white, but females and young birds have some dark spots; the young are heavily barred, and dark spotting may even predominate. Thick plumage, heavily feathered taloned feet, and coloration render the Snowy owl well-adapted for life north of the Arctic Circle. This Snowy Owl example is slightly discoloured and in real life the Snowy Owl displays much more brilliant white feathers. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Snowy Owl adult male is virtually pure white with brown spot markings and a pale brownish wash. It has thick plumage and heavily feathered taloned feet. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing tag: [torn] snowy owl / See catalogue, page 54 / Metal tag: 4054 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, owl, snowy owl, arctic circle -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Common Buzzard, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860- 1880
The Common buzzard, a medium-sized raptor, is found across Europe and Asia, and in Africa in the winter months. It is the UK’s commonest bird of prey, found in nearly every county. Due to their large size and their brown color, they are often confused with other species, especially the Red kite and the Golden eagle. They may look the same from a distance, but the Common buzzard has a very distinctive call, like a cat’s mew, and a distinctive flying shape. When soaring and gliding, the tail is fanned and its wings are often held in a shallow 'V'. The colour of individuals varies from dark brown to much lighter, though they all have a finely barred tail and dark wingtips. This species occurs across Europe and Russia, and parts of Northern Africa and Asia in the cooler winter months. It lives in a range of habitats, especially woodland, moorland, pasture, scrub, arable land, marsh bog, villages, and sometimes towns and cities. This particular specimen has been mounted in a correct stylised fashion. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Common Buzzard is brown in colour with lighter markings on the chest. It has a white patch of feathers on the back of its head and it has darker wingtips and yellow feet. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing tag: 30 / Buzzard / Catalogue page 52. / Metal tag: 4043 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, common buzzard, bird of prey -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Little Pied Cormorant, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Little Pied Cormorant is commonly seen in Australia's wetlands. These birds reside amongst large flocks in locations where fish is plentiful. On the occasion that this bird is seen on inland streams and dams they will be solitary. This particular species willingly mixes with similar sized birds including the Little Black Cormorant. They feed on aquatic animals ranging from insects and yabbies and are labelled as benthic feeders because they find their prey on the seafloor. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Little Pied Cormorant specimen is a small bird with white and black colouring. The back of the head, neck, wings and tail are black while the undersides are a creamy white. The feet are webbed and are also dark in colouring. The bird has pale glass eyes and a medium sized bill and a long tail. This specimen is styled to look over it's left wing with its long neck bent to look in that direction. It stands on a wooden mount with a paper identification tag attached to the bird's right foot. The mount has the number 152 written on the wood.Swing tag: 21a. / Pied Cormorant / Catalogue page 41 / Mount: 152 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, cormorant, little piet cormorant, waterbird -
 Camperdown & District Historical Society
Camperdown & District Historical SocietyBook - "Australian Aborigines" by James Dawson, Australian Aborigines, 1881
First edition copy of James Dawson's book, "Australian Aborigines" (1881). Dawson's book draws on his daughter Isabella's ability to speak the local languages and attempts a balanced description of a culture he considered ill-used and under-appreciated by white settlers. This work remains one of the more valuable insights into the life of First Nations people at the point of first European contact.Title page of James Dawson's book "Australian Aborigines""AUSTRALIAN ABORIGINES" BY JAMES DAWSON THE LANGUAGES AND CUSTOMS OF SEVERAL TRIBES OF ABORIGINES IN THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF VICTORIA, AUSTRALIA BY JAMES DAWSON GEORGE ROBERTSON MELBOURNE, SYDNEY AND ADELAIDE MDCCCXXXIcdhs, cdhsfirstnations, djargurd wurrung, djargurdwurrung, isabella dawson -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societysouvenir programs, 1950 ; 1970
Orbost Aero Club began in 1969 with Basil Dowie as Chair, David Nixon as Secretary/Treasurer. The group went into recess from 1977-1991 closing in 1997. The mid 1960s were boom years in flying training in Australia and the number of Aero Clubs grew rapidly. The Club played a significant role in the establishment of the small airport at Marlo and in the ongoing operation and development of the airport over the years particularly for patient transfer by aerial ambulance. The Orbost Aero Club Club played a significant role in the establishment of the small airport at Marlo and in the ongoing operation and development of the airport over the years.Two souvenir programs and one advertising flyer. 2406.27 is a souvenir program for the Orbost Captain Cook Bi-Centenary Air Show 1970. It is purple print on a white background. It has seven folded glossy pages and cost 20c. On the cover is a photograph of a small plane. 2406.28 is a flyer for the Captain Cook Bi-Centenary Air Show, Sunday, April 19th 1970. It is black print on a pink background, 2406.29 is a souvenir program for Morwell Aero Pageant, Monday, January 30, 1950. Cost 3/-. No 4216. It is a grey/brown coloured card folder with black print.2406.28 - on back - Bruce Ham......(?) Yarram Tiger Moth orbost-aero-club captain-cook-bicentenary -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Victorian Railways Public Relations and Betterment Board ; Tourist Development Authority, Gippsland and its Lakes and Caves Victoria Australia, November 1954
Chairman of the Victorian Railways, Harold Clapp, established The Victorian Railways Public Relations and Betterment Board as part of a campaign to launch the Spirit of Progress – the first new train constructed during the Depression era. Clapp was an aggressive Chairman of Railway Commissioners who was determined to keep Victorian Railways prospering. This book was a promotion book for "The Gippslander". The Gippslander name has been used for trains in the Bairnsdale corridor since 1954This book is a useful research tool.A 28 pp paper back book, titled Gippsland and its Lakes and Caves Victoria Australia. The front cover has orange and black print with yellow, green and blue motifs on a white and yellow background. The book has a stapled spine. It contains a short description of each of Gippsland's towns, a centre, double page maap of the region and many b/w photographs.railway-transport gippsland clapp-harold -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical SocietyMagazine, The Australian Women's weekly, Sept, 1945, September 1 1945
The magazine was started in 1933 by Frank Packer as a weekly publication. The first editor was George Warnecke and the initial dummy was laid out by WEP (William Edwin Pidgeon) who went on to do many famous covers over the next 25 years. It is the most widely read magazine in the history of Australian publishing. During wartime despite printing restrictions, and it began publishing coloured photographic covers.This is an example of anAustralian women's magazine published during WW11.It gives practical advice on needlework / knitting and evidences the widespread interest in contemporary fashion. In doing so it shows what were the fashionable, but broadly affordable, women's and children's clothing styles of their day. These magazines also reflect women's interests.A 32 pp magazine, titled The Australian Women's Weekly. On the front cover is a coloured drawing of a man and a woman sitting under a tree. The woman is pouring tea from a billy into the tin cup held by the man. A tethered horse is grazing to their right and a small brown and white dog is in the foreground. This illustration is signed WEP (William Edwin Pidgeon). The magazine contains advertisements, stories and recipes.The special 4 page peace supplement is missing from the centre.In handrwitten pencil on the front cover - Gibbs.australian-women's-weekly magazine-ww11 -
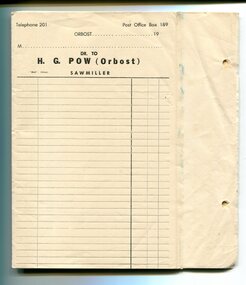 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyinvoice forms, Snowy River Mail as "Mail" Print, 19th century
These invoice forms were to be used by Hector G. Pow's Sawmiller Company in Newmerella ( Henty's & Pow). Pow's had a mill at Cabbage Tree as well. The mill is currently owned by Mectec.Orbost has historically been based on the timber industry, but that industry has declined considerably over the last 20 years. The number of locals involved in the timber industry has declined and many of the mills have closed. This item reflects a time when that industry was a significant contributor to the economy of the district.Unused invoice forms for H.G.Pow Orbost Sawmillers. They are white paper with black print and lines. On the right hand side are two small holes for filing. The page is perforated with carbon underneath to provide two copies - one for filing and one for the customer. At the top of each page is "Telephone 201 Post Office 189 Orbost" and a line for the date. Below this is a line for the customer's name and "Dr to H.G. Pow (Orbost) Sawmiller". There are columns for item descriptions and costs.h.g.pow sawmills timber-orbost -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societypamphlet, Snowy River Mail, Happy Holidays
This pamphlet was probably produced for use in the Slab Hut (Orbost Visitor Information Centre)These pamphlets are useful reference tools and reflect the tourism history of the local area.Two single page tourist brochures, printed on both sides and folded in the middle. They are white with pink and blue print. and have a map of East Gippsland and descriptions of places to visit.tourism-orbost -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societycertificate, July 3, 1858
This is a certificate of indenture, a legal agreement, between George Beattie of Forest Creek, near Castlemaine in the colony of Victoria, and Peter Christian Smith of the same place. Both were miners. Beattie was the vendor and Smith paid twenty-five pounds for a land parcel. The contract was witnessed by John Hedderwick, a law clerk in Castlemaine. There is a record in the Mount Alexander Mail, dated Wed. 22 April 1857, of George Beattie purchasing land for three pounds, sixteen and sixpence in Castlemaine and that it was withdrawn. Records also show that a Peter and Thomas Smith farmed in Sandon near Castlemaine.This item is a useful research tool as it a hand-written record of part of the history of the gold fields region of Victoria.A white paper certificate of conveyance with black print and hand-written details from George Beattie to Peter Smith. There is a wax seal on the second page.beattie-george smith-peter-christian castlemaine-certificate-conveyance
