Showing 7120 items matching "ice-cream"
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionLetter, London County Council letter, 26th Nov. 1935
cream paper with black typing smugging of ink folded twice brownedengraving of symbol Nation Scheme for disabled men stamped 74897london, county, council, frank wright -
 Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright Museum
Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright MuseumParasol
Pink and cream with black stripes. Cotton. Carved cane and wooden handleBurnt and painted floral design on handleparasol, sunshade, ladies accessories -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Plate, Alfred Meakin
The Process of Making Pottery Decorating, Firing, Glazing, Making, Technical There is a rhythm and flow to clay. It can’t be done all at once! Even the making process! It can take weeks to get everything done, especially if you can only work on your pottery once a week! Even though we have three hour classes, it’s often just not enough time! Here is an overview of some of the processes so you have a bit more grasp on some of the technical stuff! Step One – Design There are SO many ideas out there for making stuff in clay! From delicate porcelain jewellery, through to heavy sculptural work and everything in between. Deciding your direction is sometimes not that easy – when you first start, try everything, you will naturally gravitate to the style that you enjoy! The options and variations are endless and can get a wee bit overwhelming too! Check in with me before you start to ensure your ideas will work, what order you might do things, how you could achieve the look you are seeking and any other technical data required! Step Two – Making Clay is thixotropic. This means that as you work with it, the clay first gets sloppier and wetter, before is begins to dry in the atmosphere. For most things, you simply can’t do all parts of the project at once. An example of work order might look like: Get last weeks work out from the shelves Prepare clay for today’s work – roll your clay, prepare balls for throwing, make the first stage of a pinch pot) Clean up last week’s work and put it on the shelf for bisque firing Check that you have any glazing to do – and do enough of it that you will have time to finish your main project Do the next step of your next project – there might be a further step that can’t be complete immediately, in that case, wrap your work well and put onto the shelves. Letting your work rest for a while can really help keep your work clean and professional looking. Many things require bagging under plastic to keep it ready for work the next week – put your name on the outside of the bag so you can find your work easily. We have stickers and markers. Consider how you want to decorate your work – coloured slip can be applied at a fairly wet stage (remembering that it will make your work even wetter!). Trying to apply slip to dry clay won’t work! If you want to do sgraffito – you will need to keep the work leather hard (a state of dryness where you can still work the clay with a little effort and a little water and care). Step Three – Drying Most of the time your work can go into the rack uncovered to let it dry out for the following week. If you want to continue forming or shaping you will need to double bag your work – put your work on a suitable sized bat and put the bat in a bag so the base of the bag is under the bat, then put another bag over the top of the work and tuck the top of the bag under the bat. If you want to trim (or turn) your thrown work the following week, it should also be double bagged. If your work is large, delicate, or of uneven thicknesses, you should lightly cover your work for drying. When considering the drying process, bare in mind the weather, humidity and wind! The hotter and dryer, the faster things dry and work can dry unevenly in the shelves – this can lead to cracking – another time to lightly cover your work for drying. Step Four – Trimming and Cleaning Up Your work is dry! It is called greenware now and it is at it’s most fragile! Handle everything with two hands. I often refer to soft hands – keep everything gentle and with your fingers spread as much as possible. Try to not pick up things like plates too much, and always with both hands! Before your work can be bisque fired it should be “cleaned up”. You work won’t go into the kiln if it has sharp edges – when glazed, sharp edges turn into razor blades! Use a piece of fly wire to rub the work all over – this will scratch a little so be light handed. Use a knife or metal kidney to scrape any areas that require a bit more dynamic treatment than the fly wire offers! Finally, a very light wipe over with a slightly damp sponge can help soften and soothe all of your edges and dags! Trimming thrown work: If you are planning to trim (or turn) your thrown work (and you should be), make sure you bag it well – your work should be leather hard to almost dry for easiest trimming. Use this step to finish the work completely – use a metal kidney to polish the surface, or a slightly damp sponge to give a freshly thrown look. Wipe the sponge around the rim after trimming, and check the inside of the pot for dags! Trimming slip cast work: Usually I will trim the rims of your work on the wheel the following day to make that stage easier, however you will still need to check your work for lumps and bumps. Last but not least – check that your name is still clearly on the bottom of your work. Step Five – Bisque Firing When the work is completely dry it can go into the bisque kiln. The bisque kiln is fired to 1000°C. This process burns off the water in the clay as well as some of the chemically bound water. The structure of the clay is not altered that much at this temperature. Inside the bisque kiln, the work is stacked a little, small bowl inside a larger bowl and onto a heavy plate. Smaller items like decorations or drink coasters might get stacked several high. Consideration is paid to the weight of the stack and shape of the work. A bisque kiln can fire about one and a half times the amount of work that the glaze kiln can fire. The firing takes about 10 hours to complete the cycle and about two days to cool down. Once it has been emptied the work is placed in the glaze room ready for you to decorate! Step Six – Glazing Decorating your work with colour can be a lot of fun – and time consuming! There are three main options for surface treatment at this stage: Oxide Washes Underglazes Glazes Washes and underglazes do not “glaze” the work – It will still need a layer of glaze to fully seal the clay (washes don’t need glaze on surfaces not designed for food or liquid as they can gloss up a little on their own). Underglazes are stable colourants that turn out pretty much how they look in the jar. They can be mixed with each other to form other colours and can be used like water colours to paint onto your work. Mostly they should have a clear glaze on top to seal them. Oxides are a different species – the pink oxide (cobalt) wash turns out bright blue for instance. They don’t always need a glaze on top, and some glazes can change the colour of the wash! The glazes need no other “glaze” on top! Be careful of unknown glaze interactions – you can put any combination of glaze in a bowl or on a plate, but only a single glaze on the outside of any vertical surface! Glazes are a chemical reaction under heat. We don’t know the exact chemicals in the Mayco glazes we use. I can guess by the way they interact with each other, however, on the whole, you need to test every idea you have, and not run the test on a vertical surface! Simply put, glaze is a layer of glass like substance that bonds with the clay underneath. Clay is made of silica, alumina and water. Glaze is made of mostly silica. Silica has a melting point of 1700°C and we fire to 1240°C. The silica requires a “flux” to help it melt at the lower temperature. Fluxes can be all sorts of chemicals – a common one is calcium – calcium has a melting point of 2500°C, however, together they both melt at a much lower temperature! Colourants are metal oxides like cobalt (blue), chrome (green through black), copper (green, blue, even red!), manganese (black, purple and pink) iron (red brown), etc. Different chemicals in the glaze can have dramatic effects. for example, barium carbonate (which we don’t use) turns manganese bright pink! Other elements can turn manganese dioxide brown, blue, purple and reddish brown. Manganese dioxide is a flux in and of itself as well. So, glazes that get their black and purple colours, often interact with other glazes and RUN! Our mirror black is a good example – it mixes really well with many glazes because it fluxes them – causes them to melt faster. It will also bring out many beautiful colours in the glazes because it’s black colouring most definitely comes from manganese dioxide! Glaze chemistry is a whole subject on it’s own! We use commercial Mayco glazes on purpose – for their huge range of colour possibilities, stability, cool interactions, artistic freedom with the ability to easily brush the glazes on and ease of use. We currently have almost 50 glazes on hand! A major project is to test the interactions of all glazes with each other. That is 2,500 test tiles!!!! I’m going to make the wall behind the wheels the feature wall of pretty colours! Step Seven – Glaze (Gloss or sometimes called “Glost”) Firing Most of the time this is the final stage of making your creation (but not always!) The glaze kiln goes to 1240°C. This is called cone 6, or midrange. It is the low end of stoneware temperatures. Stoneware clays and glazes are typically fired at cone 8 – 10, that is 1260 – 1290°C. The energy requirement to go from 1240°C to 1280°C is almost a 30% more! Our clay is formulated to vitrify (mature, turn “glass-like”) at 1240°, as are our glazes. A glaze kiln take around 12 hours to reach temperature and two to three days to cool down. Sometimes a third firing process is required – this is for decoration that is added to work after the glaze firing. For example – adding precious metals and lustres. this firing temperature is usually around 600 – 800°C depending upon the techniques being used. There are many students interested in gold and silver trims – we will be doing this third type of firing soon! After firing your work will be in the student finished work shelves. Remember to pay for it before you head out the door! There is a small extra charge for using porcelain clay (it’s more than twice the price of regular clay), and for any third firing process! Once your work has been fired it can not turn back into clay for millennia – so don’t fire it if you don’t like it! Put it in the bucket for recycling. https://firebirdstudios.com.au/the-process-of-making-pottery/Ceramics have evolved over thousands of years.Earthenware dessert plate, cream colour. Made by Alfred Meakin, England. Backstamped ‘Alfred Meakin England’. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, alfred meakin, ceramics, earthenware, kitchenware -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDish
Pie Dish, ceramic, cream brown colour, has crazing of the glaze.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, pie dish, ceramic dish, ceramic pie dish -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Ballarat College of Advanced Education: 3rd Year Primary Education, 1984, 1984
Photograph mounted on cream card. Names of students printed under the photograph.. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Ballarat College of Advanced Education: 3rd Year Diploma of Teaching, 1982, 1982
Photograph mounted on cream card. Names of students printed under the photograph.. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Ballarat College of Advanced Education: 3rd Year Primary Education, 1985, 1985
Photograph mounted on cream card. Names of students printed under the photograph.. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Ballarat College of Advanced Education: 3rd Year Primary Education, 1986, 1986
Photograph mounted on cream card. Names of students printed under the photograph.. -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Haberdashery, Serviettes Linen with Crochet and needlework x2 c1910, c1910
The women of the early settler families made the clothes, haberdashery and napery as the market gardens and dairy farms were established c1900. The square of linen is edged with hand crochet and a flower in one corner is sewn with coloured silk The women of the early settler families in Moorabbin Shire c1910 were skilled dressmakers and craft workers. 2 cream linen serviettes with crocheted edge and a coloured needlework flower clothing,haberdashery, napery, serviettes, linen, crochet, brighton, moorabbin, pioneers, dressmaking, market gardeners, early settlers, craftwork , bentleigh, lacework, moorabbin shire, dairy farms, fruit orchards -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Domestic Object - POTTERY MIXING BOWL
Cream pottery mixing bowl with Greek key pattern around side.domestic equipment, food preparation, kitchen -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Accessory - PARASOL
Ladies silk parasol with bamboo handle, cream silk with grey stripes.costume accessories, female, parasol -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Container - MINIATURE POTTERY JUG
Miniature glazed pottery jug with handle, brown upper and cream bottom.domestic equipment, ornaments, pottery -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - W.D.MASON COLLECTION: REFERENCE, 25 Nov.1933
Cream Document, W.D.Mason Collection, a personal reference for Mr. A.G.Rowley.dated 25.11.1933business, retail, w d mason -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumCoffee tin
Cylindrical cream coloured coffee tin with pictures of flowers and ' coffee' on the side. -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumBottle, Betty Brown Pure Foods Co
Small glass bottle with blue and cream label with a picture of a woman and text.Imitation Essence of Lemon. Betty Brown Artificially coloured. Contents 1 fluid oz. Betty Brown Pure Foods Co. 18 Francis St. Melbourne. -
 Myrtleford and District Historical Society
Myrtleford and District Historical SocietyCigarette Dispenser
Such dispensers were sold in tobacconist and gift shops as everyday household novelty items.The dispenser links the role of a Myrtleford tobacconist and hairdresser to the local tobacco industry organization, the Tobacco Company of Victoria Ltd., who housed the item after closure of his business in 1976. Brown and cream coloured bakelite cigarette dispenser, incorporating shape of a kookabura. Upright shape of a kookabura at one end of the dispenser.cigarette dispenser. -
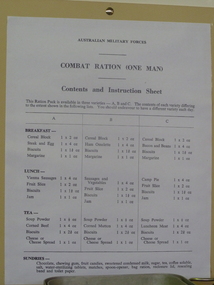 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Pamphlet, Combat Ration (one man)
printed list of contents and instruction sheet - rations mounted on cream cardList of rations and how to prepare themration sheet -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (item) - Civil Aviation Air Navigation Orders, Air Navigation Orders
-
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Clothing, Judo Pants
A pair of cream coloured cotton drill pants with draw string waistclothing, mcphail collection -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumProgramme - POSTER, ARTHUR J. GIDDINGS, 1919
Event to celebrate peace at the end of WW1, programme of boys and girls sports events, returned soldiers race.1 X PAGE RED AND BLUE PRINTING ON CREAM COLOURED BACKGROUNDJuly 19th, 1919 Clunes and District Peace Celebrations Sports Programmepeace celebrations 1919, giddings, sports programme 1919 -
 St Kilda Historical Society
St Kilda Historical SocietyEphemera - Invitation - mayoral ball, Borough of St Kilda, 1889
Samuel England Jeans, Mayor of St Kilda 1888-1889Cream card with brown printing and bearing logo of Borough of St Kilda1889 Borough of St Kilda. The Mayor of St Kilda (Councillor S. E. Jean)s and Mrs Jeans request the pleasure of Mr and Mrs Pugh's Company at a Ball in the Town Hall, St Kilda, on Tuesday Evening, 9th July, at 8.30 o'clock. The favour of an early reply (addressed to the Town Clerk, Town Hall, St. Kilda) is particularly requested.borough of st kilda, 1889, samuel england jeans, st kilda - history, 19th century, st kilda mayoral function -
 St Kilda Historical Society
St Kilda Historical SocietyEphemera - Flyer, Lecture and Concert, 1942
Promotion and program for a lecture and concert that was arranged by the City of St Kilda at St Kilda Town Hall on 19 June 1942. The lecture topic was 'The Empire's Air Forces at War', by British War Correspondent William Courtney, and the entertainment included musical performances and a film screening.Cream coloured paper (discoloured with age) printed in black on one sidewilliam courtney, margaret schofield, arnold matters, thea phillips, noel nickson, city of st kilda, arnold colman -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumDomestic object - EARTHENWARE SAUCER
A CREAM COLOURED EARTHENWARE SAUCER WITH 3 GOLD STRIPES ON THE RIM OF THE SAUCERearthenware, earthenware saucer, saucer -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumDomestic object - MILK JUG COVER
A CREAM COLOURED CROCHETED MILK JUG COVER WITH YELLOW GLASS BEADSmilk jug cover, jug cover, crochet jug cover -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchLetter, RS&SILA, 26/2/1941
Letter of sympathy to Mrs Seymour on the passing of her husband Gunner Barry SEYMOUR 19825Cream coloured paper letter with black type below letterhead and crest.The Returned Sailors and Soldiers' Imperial League of Australia dated 26/2/1941 and signed by State President G.W. Holland addressed to Mrs R. H. Seymour 29 Barnett Street, Kensington.rs&sila, barry seymour -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBread Box Cover
Made by Frida Steller (geb Orth 13-04-1900)cream coloured linen broderie anglais embroidered bread box cover.frida steller -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBook, The Rural Book, 1991
Written as information for rural areas with a view to informing them of availability of Government services. Foreword by Simon Crean, Minister for Primary Industry and Energy.Cream cover with etching showing rural activities guide to rural dwellers.country link program, books, reference, simon crean, government services, minister for primary industry and energy -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBooklet, We Remember, 2001
Discovered in Kingaroy, giving the history of wartime conditions in relation to shortage of labourers and presence of POW'sBlack lettering and cream covered. Illustrations of POW and representatives of the families they worked for.books, history, local -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBrochure, Custom is King, 1936
Dr. Leonhard Adam studied both anthropology and jurisdiction as a young manCream coloured paper cover. Black and red lettering. English textcustom is king, marett rr, adam l, adam murvitz mc, camp 2, tatura, ww2 camp 2, documents, pamphlets -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBelt, Macrame
Made by internee at Camp 13Cream coloured macrame belt with silver buckle, zig zag pattermbelt, macrame, baumann m, camp 13, tatura, ww2 camp 13, handcrafts
