Showing 162 items
matching form guide
-
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Booklet - Warrnambool Tourist Booklet, Warrnambool Progress Association, Warrnambool On the Sea, Victoria, Australia, Tourist Guide, 1932
Warrnambool Tourist GuideThis is a booklet with a cream cover featuring a sketch of a woman waterskiing and blue printing. The pages contain black and white photographs, advertisements, two maps and printed text. There is one fold-out page. The booklet is stapled and bound with glue.non-fictionWarrnambool Tourist Guidewarrnambool tourism, warrnambool progress association -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncNewsletter, Newsletter, No. 30 May 1983
Contents: • Next meeting; Discussion evening led by Russell Yeoman; Our local heritage – places to visit • Annual General Meeting • Subscriptions • Falkiner Cottage – Ely Street • Literary Guide to Australia • Kyneton trip by Bettina Woodburn The Shire of Eltham Historical Society was formed in October 1967. The first newsletter of the Society was issued May 1978 and has been published continuously ever since on a bi-monthly basis. With the cessation of the Shire of Eltham in late 1994, the Society's name was revised to Eltham District Historical Society and this name first appeared with issue No. 103, July 1995. The collection of the Society's newsletters provides a valuable resource on the history of the Society's activities, office bearers and committee members, guest speakers and subjects of historical interest pertinent to the former Shire of Eltham and the Eltham District.A4 photocopied newsletter distributed to membersnewsletter, eltham district historical society, shire of eltham historical society -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual - CASA VFR flight guides, Civil Aviation Authority Australia VFR Flight Guide
Overview of CASA flight regulations circa 2001Spiral bound book form . non-fictionOverview of CASA flight regulations circa 2001 -
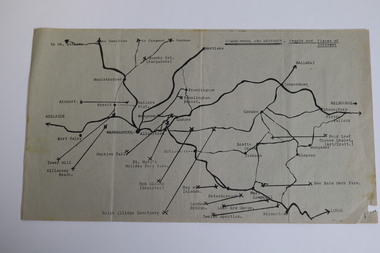 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Map - Tourist Map Collection: Warrnambool & District Tourist Maps, Philprint, Warrnambool
This is a diverse collection of Tourist Maps for the Warrnambool & District area. [.1] From information on this guide it dates from the mid 1970's. It appears to not have been commercially printed and includes details of attractions no longer operating in Warrnambool such as Warrnambool Aquarium and the Oasis Reptile Park and Zoo. [.2] Commercially printed Warrnambool tourist map (c mid 1980's) surrounded by advertisements for local businesses. [.3] Commercial printed December 1991 tourist map of Warrnambool and District includes a competition entry form [.4] Commercially printed tourist map aimed at children [.5] Walking map of Warrnambool and District [.6] Commercially printed Warrnambool tourist map (c mid 1980's) surrounded by advertisements for local businesses. This collection of maps from the mid 1970's to early 1990's gives an insight into what was available to assist tourists find their way around Warrnambool and District. They include advertisements for business operating during this period and include lists of available accommodation, eateries, and tourist attractions.[.1] Tourist Attractions In and Around Warrnambool two foolscap pages with two sides of type written information of local and district attractions. There is a Warrnambool City map with points of interest marked and a hand drawn district map; [.2]Commercially printed grid map of Warrnambool City surrounded by advertisements from local businesses. Reverse side has a district map and a map of the Warrnambool CBD surrounded by advertising. [.3] Brochure including small grid maps of Warrnambool and district listing accommodation providers and places of interest. Stylised blue & bright green design of Norfolk pines and sea. [.4] Children's treasure hunt map to Warrnambool There are two examples, one with blue edging (Jan 1986) and one with red edging (Aug 1993) Both have a circular logo with a stylised whale and lighthouse [.5] Walking maps of Warrnambool blue printed photo of four tourists walking coastline on the front cover. [.6] Commercially printed grid map of Warrnambool with a bright yellow inset of Warrnambool CBD main shopping centre. The map is surrounded by advertising for local businesses.warrnambool, tourist maps, warrnambool businesses, warrnambool accommodation -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual - Visual flight guides, Commonwealth of Australia Visual Flight Guide
Overview of flight preparation/procedures & general information circa 1972Manual in book form Overview of flight preparation/procedures & general information circa 1972flight preparation, flight procedures, general informatio -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual - Visual flight guides, Commonwealth of Australia Visual Flight Guide
Overview of flight preparation/procedures & general information circa 1969Manual in book form Overview of flight preparation/procedures & general information circa 1969flight preparation, flight procedures, general informatio -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPamphlet, Australian Electric Traction Association (AETA), "AETA 50th Anniversary Convention", 1993
Set of three pamphlets issued by the AETA in 1993 regarding events. .1 - Printed pamphlet advertising up to a 40 day tour of Australia including the AETA's 50th Anniversary convention. Printed in blue on gloss paper with black and white photographs. .2 - Booking form and program for the "AETA 50th Anniversary Convention", to be held in Melbourne April 1993. Also gives details of Austrasia 93 and changes to the program. .3 - 16 page, photocopied, stapled in top left hand corner, detailed program and tours notes for the "AETA 50th Anniversary Convention".trams, tramways, aeta, tours, tour guide, melbourne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Chronometer or Marine Clock
This chronometer was made around 1936 and has been on display at Flagstaff Hill for over 40 years as part of the exhibit of the ‘Reginald M’, an Australian-built, 19ss, coastal trader vessel. A chronometer is an accurate mechanical instrument used for measuring time. It is constructed carefully to remain stable even under the changing conditions of seafaring life such as temperature, humidity and air pressure. The Master or Navigator of a ship could use the chronometer and the positions of celestial bodies to calculate the ship’s latitude at sea. In 1905 the business Chronometerwerke GmbH was formed in Frankfurt, Germany, to supply the country with high-quality mechanical chronometers and ship clocks for their maritime trade, making the country independent of other international suppliers such as those in England. In 1938 the firm was renamed Wempe Chronometerwerke. The business continues today. Its products now include its well-known chronometers, battery-powered ship clocks, ship’s bell clocks, barometers, barographs, thermometers, hygrometers, comfort meters to measure temperature and humidity, and wristwatches. The company also performs chronometer testing facilities for the State’s Weights and Measures office. The article written by Givi in July 2022 “The Basics of Marine Meteorology – a Guide for Seafarers” refers to the weather’s signs and patterns being repeated over and over, and the recording of these observations helps forecasters predict changes in the weather. The chronometer is an example of a mechanical navigational marine instrument in use in the early to the mid-20th century. The maker is significant as part of a German government initiative to be self-sufficient in the production of good quality marine technology. This chronometer is significant as part of the exhibit, the Australian-built vessel, 1922 coastal trader ‘Reginald M’, listed on the Australian Register of Historic Vessels and on display for over 40 years.Marine chronometer or marine clock, brass case, glass cover, Roman numerals, 24-hour numbers beside them. Two black hands, a keyhole for winding and ventilation holes in the side. The base has a collar with four machined mounting holes. Inscriptions are on the clock’s face."Made in Germany" and "WEMPE / CHRONOMETERWERKE / HAMBURG"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, marine meteorology, horology, chronometer, marine technology, latitude, marine navigation, mechanical instrument, scientific instrument, ship clock, chromometerwerke gmbh, wempe chronometerwerke, marine clock -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaPainting - Artwork, Portrait of Bruce Small, 2002
Framed portrait of Bruce Small who was President of the Association for the Blind 1955-1964. It is part of a series of paintings commissioned by the VAF Board to commemorate the work of past presidents of the organisation. Mr Small stands in his Gold Coast mayoral robes, which consist of a dark blue velvet with ermine trim and a white ruffled shirt.. He wears a mayoral chain of office around his neck and glasses, with his hands clasped in front of him. Sir Bruce Small joined the Vision Australia’s General committee in 1944 and became President of the organisation in 1955. He developed an efficient team with Sir Hubert Opperman (for many years the world’s number one cyclist), whom he brought in as Vice President and Mr. Pat Lightfoot, himself president for many years. Sir Bruce had to leave school at an early age after the death of his father in order to support his family. The lessons he learned from this episode in his life created a man of quick wit, with a razor sharp mind and the skills of a gambler - attributes that enabled him to achieve his goal of “aiming for the stars”. This was put into effect when he proposed a plan for 3 new Vision Australia nursing homes in 5 years at Ballarat, Bendigo and Brighton at a cost, which at that time seemed impossible but which was finally achieved between 1957 and 1959, through astute financial management. Sir Bruce also supported the concept of organisational decentralization and made amendments to the constitution, which enabled the associated branches of the Vision Australia (then the Association for the Advancement of the Blind) to form local committees. This was in order to generate local interest in the blind people in the community and engage them in fund raising and running of the nursing homes. Although he resigned in 1964 when he moved to Queensland he still retained an interest in Vision Australia. Sir Bruce had always pushed for a symbol for Vision Australia which would be recognized by the public and serve a useful purpose. This took the form of a beacon which was erected at Brighton, overlooking the sea, having a twofold purpose – a reference point and guiding light for small craft, and symbolically for blind people a guiding light to direct them to a safe harbour. Sir Bruce switched on the guiding light at in 1969 having already donated the cost of $3000. Prior to joining Vision Australia, Sir Bruce had operated the Malvern Star bicycle business in Glenferrie Rd. He promoted and expanded the business making Malvern Star the industry leader in Australia. This was aided by his friendship with Sir Hubert Oppermen, who promoted Malvern Star bikes through his role as world’s number one cyclist. In 1967 he became Mayor of the Gold Coast and, in 1972 he was elected to the Queensland Parliament representing the seat of Surfers Paradise. 1 art original in gold frameThe plaque at the base of the painting reads 'Mr Bruce Small / President 1955 - 1964 / Association for the Blind'.association for the blind, bruce small -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionManual, Post Master General's Department, Telegram Delivery Instructions, 1967
Electrical telegraphs were point to point text messaging systems primarily used from the 1840's until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and were sent by an operator or telegrapher using Morse code. Social telegrams were also encouraged and special pictorial forms and envelopes were designed such as the special purple form and envelope which was used when conveying condolence details during World War 2.(fn. Powerhouse https://collection.powerhouse.com.au/object/163103). There was a brief resurgence in telegraphy during World War I but the decline continued as the world entered the Great Depression years of the 1930s. Although telegraph lines continued to play an important part in distributing news feeds from news agencies post World War 2, the rise of the internet in the 1990s and the widespread installation of the telephones in homes saw the need for telegrams to greatly decline. When the Commonwealth Post and Telegraph Act was passed in June 1902, and a national Postmaster General's Department (the PMG) was established the responsibility for the nation's mail and telephone services fell on Post Offices. The Bendigo Post Office, built in 1887 and situated on Pall Mall was the central distribution centre for receiving and delivering telegrams and continued to deliver communication and postal services until 1997. Now a Visitor Centre, dedicated volunteers at the Post Office continued to demonstrate and educate the public about telegraphic services and the development of this unique form of communication up until 2019 when Covid 19 disrupted every day life, coupled with the death Ted Rankins (the last Post Master and a long term telegraph volunteer at the Post Office). This book was issued to Junior Postal Workers in Bendigo to guide them in the delivery of telegrams and designed to fit into their delivery satchels and carried while on the job. In the early years telegrams were delivered by bicycle and this manual is part of the postal collection donated by the Rankins family in memory of Ted. Small, blue, vinyl covered manual. Contains thirty printed pages covering all aspects of how to correctly deliver telegrams. Topics include 'Loss of telegram', 'Undelivered Telegram', 'special Delivery' and 'Beware of Dogs'. Bound with two ring metal clip. Front cover; Australian Post Office / Telecommunications Division / Telegram / Delivery / Instructions / Headquarters / 1962 Various annotations and updates throughout. ted rankins collection, bendigo post office, bendigo tourism, city of greater bendigo tourism, post office collection -
 Merri-bek City Council
Merri-bek City CouncilWork on paper - Charcoal and pages from Aboriginal Words and Place Names, Jenna Lee, Without us, 2022
Jenna Lee dissects and reconstructs colonial 'Indigenous dictionaries' and embeds the works with new cultural meaning. Long obsessed with the duality of the destructive and healing properties that fire can yield, this element has been applied to the paper in the forms of burning and mark-making. In Without Us, Lee uses charcoal to conceal the text on the page, viewing this process as a ritualistic act of reclaiming and honouring Indigenous heritage while challenging the oppressive legacies of colonialism. Lee explains in Art Guide (2022), ‘These books in particular [used to create the proposed works] are Aboriginal language dictionaries—but there’s no such thing as “Aboriginal language”. There are hundreds of languages. The dictionary just presents words, with no reference to where they came from. It was specifically published by collating compendiums from the 1920s, 30s and 40s, with the purpose to give [non-Indigenous] people pleasant sounding Aboriginal words to name children, houses and boats. And yet the first things that were taken from us was our language, children, land and water. And the reason our words were so widely written down was because [white Australians] were trying to eradicate us. They thought we were going extinct. The deeper you get into it, the darker it gets. But the purpose of my work is to take those horrible things and cast them as something beautiful.’Framed artwork -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Hook, Mid-20th century
A cast iron hook was made for lifting heavy loads in a marine or warehouse environment. The hook would be attached to the end of a chain or rope around a heavy load such as a pallet or container. The other end may have been joined to a pulley or crane for lifting and moving it around. The inscription on the hook shows the SWL or Safe Working Load as 3 Ton. The SWL was used in the industry for many years to rate safe loads but it is no longer used to identify the maximum capacity of equipment. In 2002 the Australian Standard AS 1418 for Cranes, Hoists and Winches changed, and the term Safe Work Load was changed to Rated Capacity, which was defined differently.The hook represents the equipment needed on a ship or at a port, railyard, transport depot or warehouse in the 19th and 20th centuries to move cargo and loads. The inscription of SWL on the hook is significant for its use as a guide for many years to work out the weight of the load the hook could safely hold. However, time and experience have led to a change in Australian Standards and the load is now measured by another formula that gives the load's Rated Capacity.Hook; large iron hook with a ring formed in the top. Inscription stamped into the metal and indicates that the Safe Working Load (SWL) for the hook to lift is 3 Ton.Marked "ani" "SWL 3TON"warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, lifting hook, maritime equipment, lifting equipment, warehousing, cargo, loads, rigging, marine technology, swl, safe working load, 3 ton, rated capacity, load limit
